Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Aims
2.2. Secondary Endpoints
- Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in adult AIIRD-RTX patients compared with immunocompetent controls.
- Development of a calculator to predict the probability of a seropositive immunogenic response to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination in AIIRD-RTX patients and its validation in an independent cohort of vaccinated AIIRD-RTX patients.
- Safety of the vaccination.
- Effect of the vaccination on disease activity in AIIRD-RTX patients stratified by positive and negative immunogenic response to vaccination.
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Vaccination Procedure
2.6. Vaccine Immunogenicity
2.7. Vaccine Safety
2.8. Assessment of AIIRD Activity
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
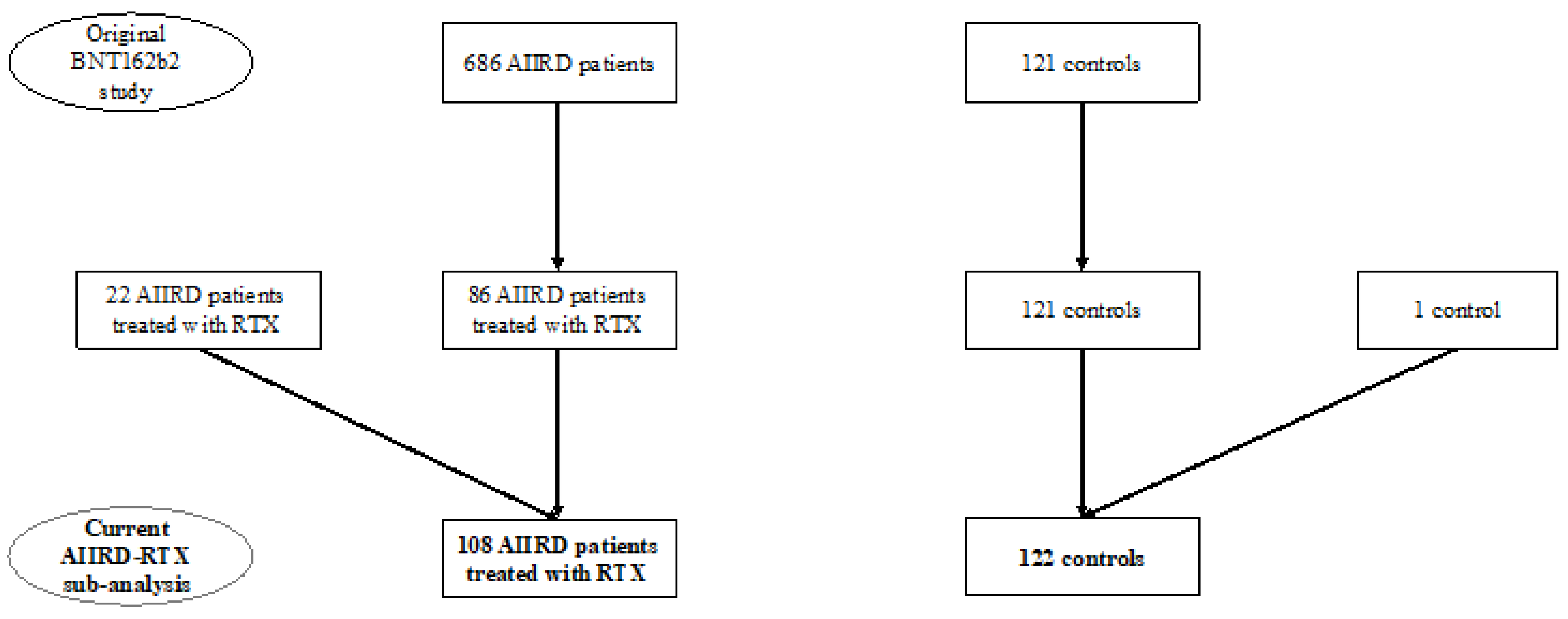
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 Vaccine
3.3. Development and Validation of the Predicting Calculator for a Seropositive Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in RTX-Treated Patients
3.4. BNT162b2 Vaccine Safety in Seropositive and Seronegative RTX-AIIRD Patients
3.5. BNT162b2 Vaccine Impact on Disease Activity in RTX-AIIRD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. C4591001 Clinical Trial Group Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. COVE Study Group Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.R.; Johnson, S.R.; Anthony, D.D.; Arasaratnam, R.J.; Baden, L.R.; Bass, A.R.; Calabrese, C.; Gravallese, E.M.; Harpaz, R.; Kroger, A.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Guidance for COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases: Version 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, e30–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, U.M.; Berner, D.K.; Tran, F.; Sümbül, M.; Vullriede, L.; Ciripoi, M.; Reid, H.M.; Schaffarzyk, A.; Longardt, A.C.; Franzenburg, J.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and immunosuppressive therapy in a monocentric cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberman, R.H.; Herati, R.; Simon, D.; Samanovic, M.; Blank, R.B.; Tuen, M.; Koralov, S.B.; Atreya, R.; Tascilar, K.; Allen, J.R.; et al. Methotrexate hampers immunogenicity to BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in immune-mediated inflammatory disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furer, V.; Eviatar, T.; Zisman, D.; Peleg, H.; Paran, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Zisapel, M.; Elalouf, O.; Kaufman, I.; Meidan, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: A multicentre study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, P.; Kim, W.; Paley, M.A.; Yang, M.; Carvidi, A.B.; Demissie, E.G.; El-Qunni, A.A.; Haile, A.; Huang, K.; Kinnett, B.; et al. Effect of Immunosuppression on the Immunogenicity of mRNA Vaccines to SARS-CoV-2: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendecki, M.; Clarke, C.; Edwards, H.; McIntyre, S.; Mortimer, P.; Gleeson, S.; Martin, P.; Thomson, T.; Randell, P.; Shah, A.; et al. Humoral and T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients receiving immunosuppression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Kaplan, M.; Braun, M.; Markovits, D.; Giryes, S.; Toledano, K.; Tavor, Y.; Dolnikov, K.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Disease activity and humoral response in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases after two doses of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, F.P.B.; Najm, A.; Alunno, A.; Schoones, J.W.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Machado, P.M.; Navarro-Compán, V. Risk and prognosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: A systematic literature review to inform EULAR recommendations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schietzel, S.; Anderegg, M.; Limacher, A.; Born, A.; Horn, M.P.; Maurer, B.; Hirzel, C.; Sidler, D.; Moor, M.B. Humoral and cellular immune responses on SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with anti-CD20 therapies: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 1342 patients. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondaan, C.; Furer, V.; Heijstek, M.W.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Bijl, M.; Breedveld, F.C.; D’Amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; van Laar, J.M.; et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases: A systematic literature review for the 2019 update of EULAR recommendations. RMD Open 2019, 5, e001035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulze-Koops, H.; Krueger, K.; Vallbracht, I.; Hasseli, R.; Skapenko, A. Increased risk for severe COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases treated with rituximab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strangfeld, A.; Schäfer, M.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; Liew, J.W.; Ljung, L.; Mateus, E.F.; Richez, C.; Santos, M.J.; Schmajuk, G.; et al. COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Consortium Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAI2R/SFR/SNFMI/SOFREMIP/CRI/IMIDIATE Consortium and Contributors. Severity of COVID-19 and survival in patients with rheumatic and inflammatory diseases: Data from the French RMD COVID-19 cohort of 694 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moor, M.B.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Horn, M.P.; Aeberli, D.; Amsler, J.; Möller, B.; Njue, L.M.; Medri, C.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Borradori, L.; et al. Humoral and cellular responses to mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with a history of CD20-B-cell depleting therapy. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrak, D.; Tobudic, S.; Koblischke, M.; Graninger, M.; Radner, H.; Sieghart, D.; Hofer, P.; Perkmann, T.; Haslacher, H.; Thalhammer, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in rituximab-treated patients: B cells promote humoral immune responses in the presence of T-cell-mediated immunity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekel, L.; Steenhuis, M.; Hooijberg, F.; Besten, Y.R.; van Kempen, Z.L.E.; Kummer, L.Y.; van Dam, K.P.J.; Stalman, E.W.; Vogelzang, E.H.; Cristianawati, O.; et al. Antibody development after COVID-19 vaccination in patients with autoimmune diseases in the Netherlands: A substudy of data from two prospective cohort studies. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e778–e788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammitzbøll, C.; Bartels, L.E.; Bøgh Andersen, J.; Risbøl Vils, S.; Elbaek Mistegård, C.; Dahl Johannsen, A.; From Hermansen, M.-L.; Kragh Thomsen, M.; Erikstrup, C.; Hauge, E.-M.; et al. Impaired antibody response to the bnt162b2 messenger RNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moor, M.B.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Horn, M.P.; Aeberli, D.; Amsler, J.; Möller, B.; Njue, L.M.; Medri, C.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Borradori, L.; et al. Humoral and cellular responses to mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with a history of CD20 B-cell-depleting therapy (RituxiVac): An investigator-initiated, single-centre, open-label study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e789–e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitoun, S.; Henry, J.; Desjardins, D.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Dib, N.; Belkhir, R.; Mouna, L.; Joly, C.; Bitu, M.; Ly, B.; et al. Rituximab Impairs B Cell Response But Not T Cell Response to COVID-19 Vaccine in Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landewé, R.B.; Machado, P.M.; Kroon, F.; Bijlsma, H.W.; Burmester, G.R.; Carmona, L.; Combe, B.; Galli, M.; Gossec, L.; Iagnocco, A.; et al. EULAR provisional recommendations for the management of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in the context of SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.-M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Andrassy, K.; Bacon, P.A.; Churg, J.; Gross, W.L.; Hagen, E.C.; Hoffman, G.S.; Hunder, G.G.; Kallenberg, C.G. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; de Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. International Myositis Classification Criteria Project consortium, The Euromyositis register and The Juvenile Dermatomyositis Cohort Biomarker Study and Repository (JDRG) (UK and Ireland) 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, E.; Diotti, R.A.; Strollo, M.; Rolla, S.; Ambrosi, A.; Locatelli, M.; Burioni, R.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Clementi, N. Weak correlation between antibody titers and neutralizing activity in sera from SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Shin, S.; Nam, M.; Hong, Y.J.; Roh, E.Y.; Park, K.U.; Song, E.Y. Performance evaluation of three automated quantitative immunoassays and their correlation with a surrogate virus neutralization test in coronavirus disease 19 patients and pre-pandemic controls. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkmann, T.; Perkmann-Nagele, N.; Koller, T.; Mucher, P.; Radakovics, A.; Marculescu, R.; Wolzt, M.; Wagner, O.F.; Binder, C.J.; Haslacher, H. Anti-Spike Protein Assays to Determine SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Five Quantitative Assays. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0024721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyahi, E.; Bakhdiyarli, G.; Oztas, M.; Kuskucu, M.A.; Tok, Y.; Sut, N.; Ozcifci, G.; Ozcaglayan, A.; Balkan, I.I.; Saltoglu, N.; et al. Antibody response to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine (CoronaVac) in immune-mediated diseases: A controlled study among hospital workers and elderly. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, C.M.; Koenig, D.; Ravi, S.N.; Azar, A.; Kant, S.; Dalal, M.; Duchen, J.; Seo, P.; Antiochos, B.; Paik, J.J.; et al. Correspondence on “SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in rituximab-treated patients: Evidence for impaired humoral but inducible cellular immune response” by Bonelli et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiera, R.; Jinich, S.; Jannat-Khah, D. Rituximab, but not other antirheumatic therapies, is associated with impaired serological response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benucci, M.; Damiani, A.; Infantino, M.; Manfredi, M.; Grossi, V.; Lari, B.; Li Gobbi, F.; Sarzi Puttini, P. Correspondence on “SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in rituximab-treated patients: Evidence for impaired humoral but inducible cellular immune response” by Bonelli et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, J.; Rizzi, M.; Engesser, M.; Dufner, A.-K.; Troilo, A.; Lorenzetti, R.; Voll, R.E.; Venhoff, N. B cell repopulation kinetics after rituximab treatment in ANCA-associated vasculitides compared to rheumatoid arthritis, and connective tissue diseases: A longitudinal observational study on 120 patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salviani, C.; Jeannin, G.; Cancarini, G.; Gregorini, G. 346. factors influencing b cell repopulation after remission induction with rituximab in newly diagnosed, treatment–naïve patients with anca-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, kez063-070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergwerk, M.; Gonen, T.; Lustig, Y.; Amit, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, C.; Mandelboim, M.; Levin, E.G.; Rubin, C.; Indenbaum, V.; et al. COVID-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Age, Years, Median (Range) | 65.5 (23–88) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 83 (76.85) |
| Seasonal influenza vaccine uptake, n/total (%) | 90/107 (84.11) |
| AIIRD diagnosis, n (%) | |
| RA | 49 (45.37) |
| SLE | 11 (10.19) |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis | 23 (21.3) |
| Other systemic vasculitis | 6 (5.56) |
| IIM | 18 (16.67) |
| Concomitant lymphoma, n/total (%) | 5/88 (5.68) |
| AIIRD duration, years, median (range) | 10.5 (0.75–45) |
| Rituximab-relevant details, (mg), median (range) | |
| Serum IgG level prior last RTX course (mg/dL) (n = 105) | 911 (357–3405) |
| Hypogammaglobulinemia < 500 mg/dL (prior to last RTX course), n/total (%) | 6/106 (5.66) |
| RTX cumulative dose | 6000 (1000–30,000) |
| RTX dose of last course prior to vaccination | 2000 (500–3210) |
| Total number of RTX courses | 4 (1–15) |
| Interval between last RTX course and BNT162b2 vaccination, days | 162.5 (2–2794) |
| Concomitant immunosuppressive medications, n (%) | |
| csDMARDs | 34 (31.48) |
| Methotrexate | 16 (14.81) |
| Methotrexate dose, mg/week, mean ± SD | 13.1 ± 5.32 |
| Prednisone | 54 (50) |
| Prednisone dose, mg/d, mean ± SD | 5.9 ± 3.44 |
| Other immunosuppressants, n (%) | |
| Leflunomide | 2 (1.85) |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 5 (4.63) |
| IVIG | 9 (8.33) |
| Vaccine Responders, n = 45 | Vaccine Non-Responders, n = 63 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median (range) | 64 (29–88) | 67 (23–87) | 0.075 |
| Sex, female, n (%) | 37 (82.22) | 46 (73.02) | 0.356 |
| Seasonal influenza vaccine uptake, n/total (%) | 35/44 (79.55) | 55/63 (87.3) | 0.296 |
| Disease duration, years, median (range) | 13 (0.75–45) | 9 (1–42) | 0.146 |
| AIIRD diagnosis, n (%) * | |||
| RA | 23 (51.11) | 26 (41.27) | 0.333 |
| SLE | 9 (20) | 2 (3.17) | 0.007 |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis | 6 (13.33) | 17 (26.98) | 0.101 |
| Other systemic vasculitis | 2 (4.44) | 4 (6.35) | 1 |
| IIM, n (%) | 4 (8.89) | 14 (22.22) | 0.074 |
| History of lymphoma, n/total (%) | 4/39 (10.26) | 1/49 (2.04) | 0.166 |
| Rituximab-relevant details, (mg), median (range) | |||
| Serum IgG level prior last RTX (mg/dL) ** | 1189.78 ± 576.28 | 884.33 ± 302.31 | 0.002 |
| Hypogammaglobulinemia < 500 mg/dL (prior to last RTX course), n/total (%) | 1/44 (2.27) | 5/62 (8.06) | 0.397 |
| RTX cumulative dose | 4000 (2000–20,000) | 8000 (1000–30,000) | 0.033 |
| RTX dose of last course prior to vaccination | 2000 (500–3210) | 2000 (500–2000) | 0.168 |
| Total number of RTX courses | 3 (1–10) | 5 (1–15) | 0.007 |
| Time interval between last RTX course and BNT162b2 vaccination, days | 255 (6–2794) | 130 (2–1163) | 0.0009 |
| Up to 180 days, n (%) | 14 (31.11) | 49 (77.78) | <0.0001 |
| 181–365 days, n (%) | 13 (28.89) | 11 (17.46) | |
| Over 365 days, n (%) | 18 (40) | 3 (4.76) | |
| Concomitant immunosuppressive medication, n (%) | |||
| csDMARDs | 18 (40) | 16 (25.4) | 0.142 |
| Methotrexate | 6 (13.33) | 10 (15.87) | 0.789 |
| Methotrexate dose, mg/week, mean ± SD | 10.63 ± 4.27 | 14.17 ± 5.59 | 0.287 |
| Prednisone | 18 (40) | 36 (57.14) | 0.118 |
| Prednisone dose, mg/d, mean ± SD *** | 5.47 ± 3.23 | 6.16 ± 3.56 | 0.505 |
| Other immunosuppressants, n (%) | |||
| Leflunomide | 1 (2.22) | 1 (1.59) | 1 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 1 (2.22) | 4 (6.35) | 0.399 |
| IVIG | 3 (6.67) | 6 (9.52) | 0.732 |
| Predictors | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RA | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| AIIRD diagnosis | |||
| SLE | 4.225 | 0.543–32.89 | 0.169 |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis | 0.209 | 0.046–0.96 | 0.044 |
| Other systemic vasculitis | 0.478 | 0.044–5.244 | 0.546 |
| IIM | 0.189 | 0.036–0.987 | 0.048 |
| Rituximab-relevant details | |||
| Serum IgG level (50 mg/dL increments, prior to last RTX course) | 1.104 | 1.019–1.196 | 0.016 |
| Total number of RTX courses | 0.874 | 0.75–1.018 | 0.084 |
| Time interval between last RTX course and BNT162b2 vaccine (weeks) | 1.048 | 1.018–1.079 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furer, V.; Eviatar, T.; Zisman, D.; Peleg, H.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Paran, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Zisapel, M.; Elalouf, O.; et al. Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab. Vaccines 2022, 10, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060901
Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, Peleg H, Braun-Moscovici Y, Balbir-Gurman A, Paran D, Levartovsky D, Zisapel M, Elalouf O, et al. Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab. Vaccines. 2022; 10(6):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060901
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurer, Victoria, Tali Eviatar, Devy Zisman, Hagit Peleg, Yolanda Braun-Moscovici, Alexandra Balbir-Gurman, Daphna Paran, David Levartovsky, Michael Zisapel, Ofir Elalouf, and et al. 2022. "Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab" Vaccines 10, no. 6: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060901
APA StyleFurer, V., Eviatar, T., Zisman, D., Peleg, H., Braun-Moscovici, Y., Balbir-Gurman, A., Paran, D., Levartovsky, D., Zisapel, M., Elalouf, O., Kaufman, I., Broyde, A., Polachek, A., Feld, J., Haddad, A., Gazitt, T., Elias, M., Higazi, N., Kharouf, F., ... Elkayam, O. (2022). Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab. Vaccines, 10(6), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060901






