Effect of Heterologous Vaccination Strategy on Humoral Response against COVID-19 with CoronaVac plus BNT162b2: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Vaccine Information
2.2.1. Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine by Sinovac (CoronaVacTM)
2.2.2. BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine by Pfizer & BioNTech (Comirnaty®)
2.2.3. Mixed Vaccine Administration
2.3. Immune Response Assessments
- -
- Cohort-I (CV/CV) included those who received only two doses of CoronaVac (n = 50);
- -
- Cohort-II (CV/CV/CV) included those who received three doses of CoronaVac (n = 17);
- -
- Cohort-III (CV/CV/BNT) included those who received two doses (prime) of CoronaVac followed by the third dose (booster) with BNT162b2 (n = 168).
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cyranoski, D. Did pangolins spread the China coronavirus to people? Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.H.; To, K.K.W.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Poon, R.W.S.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization Draft Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/a-future-for-children/novel-coronavirus_landscape_covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=4d8bd201_1 (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Shang, W.; Yang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Rao, X. The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia calls for viral vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soleimanpour, S.; Yaghoubi, A. COVID-19 vaccine: Where are we now and where should we go? Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for COVİD-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekin, A. Five things to know about: Mixing and Matching Coronavirus Vaccines. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research-and-innovation/en/horizon-magazine/five-things-know-about-mixing-and-matching-coronavirus-vaccines (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Oxford Vaccine Group COM-COV Comparing COVID-19 Vaccine Schedule Combinations. Available online: https://comcovstudy.org.uk/home (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Southampton University COV-BOOST Evaluating COVID-19 Vaccine Boosters. Available online: https://www.covboost.org.uk/home (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Chu, K.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, R.; Yin, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioNTech Product Monograph including Patient Medication Information Comirnaty(R) COVID-19 Vaccine. Available online: https://covid-vaccine.canada.ca/info/pdf/pfizer-biontech-covid-19-vaccine-pm1-en.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Diagnostic Snibe MAGLUMI 2019-nCoV IgM/IgG Immunoassay 2020. Available online: https://www.snibe.com/zh_en/en_newsView.aspx?id=576 (accessed on 24 April 2022).
- Snibe Diagnostic Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers-MAGLUMI 2019-nCoV IgM/IgG 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142231/download (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Food and Drug Administration (U.S.A). EUA Authorized Serology Test Performance, in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Emergency Use Authorizations for Medical Devices; Food and Drug Administration (U.S.A): Silver Spring, ML, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/eua-authorized-serology-test-performance (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Shaw, R.H.; Stuart, A.; Greenland, M.; Liu, X.; Van-Tam, J.S.N.; Snape, M.D. Heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccination: Initial reactogenicity data. Lancet 2021, 397, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail Samsonov (R-Pharm) Study in Adults of AZD1222 and rAd26-S Administered as Heterologous Prime-Boost Regimen for the Prevention of COVID-19. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04684446?term=NCT04684446&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Borobia, A.M.; Carcas, A.J.; Pérez Olmeda, M.T.; Castaño, L.; Jesús Bertrán, M.; García-Pérez, J.; Campins, M.; Portolés, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, M.; García Morales, M.T.; et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of BNT162b2 booster in ChAdOx1-S-primed participants (CombiVacS): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillus, D.; Schwarz, T.; Tober-Lau, P.; Hastor, H.; Thibeault, C.; Kasper, S.; Helbig, E.T.; Lippert, L.J.; Tscheak, P.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of homologous and heterologous prime-boost immunisation with ChAdOx1-nCoV19 and BNT162b2: A prospective cohort study. medRxiv 2021, 9, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, G. Mixing COVID-19 Vaccines Appears to Boost İmmune Responses. Available online: https://www.science.org/content/article/mixing-covid-19-vaccines-appears-boost-immune-responses (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Pérez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Vaccine Cohorts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or Mean ± Standard Deviation (Min-Max) | |||
| Characteristics | Cohort-I | Cohort-II | Cohort-III |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 24 (24.5) | 7 (7.1) | 67 (68.4) |
| Female | 26 (19.0) | 10 (7.3) | 101 (73.7) |
| Chronic disease present | |||
| Yes | 11 (18.0) | 4 (6.6) | 46 (75.4) |
| No | 38 (22.0) | 13 (7.5) | 122 (70.5) |
| History of COVID-19 infection | |||
| Never | 42 (22.0) | 12 (6.3) | 137 (71.7) |
| Before the 1st dose | 6 (16.2) | 5 (13.5) | 26 (70.3) |
| After the 2nd dose | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0) | 7 (71.4) |
| Age | 35.66 ± 8.13 | 39.29 ± 8.18 | 40.67 ± 10.94 |
| Interval between | 148.35 ± 15.32 | 142.85 ± 10.48 | |
| 2nd and 3rd doses (days) | (136–180) | (136–186) | |
| Interval between | 39.52 ± 10.50 | 45.92 ± 12.47 | |
| 2nd dose and blood sampling (days) | (18–50) | (18–71) | |
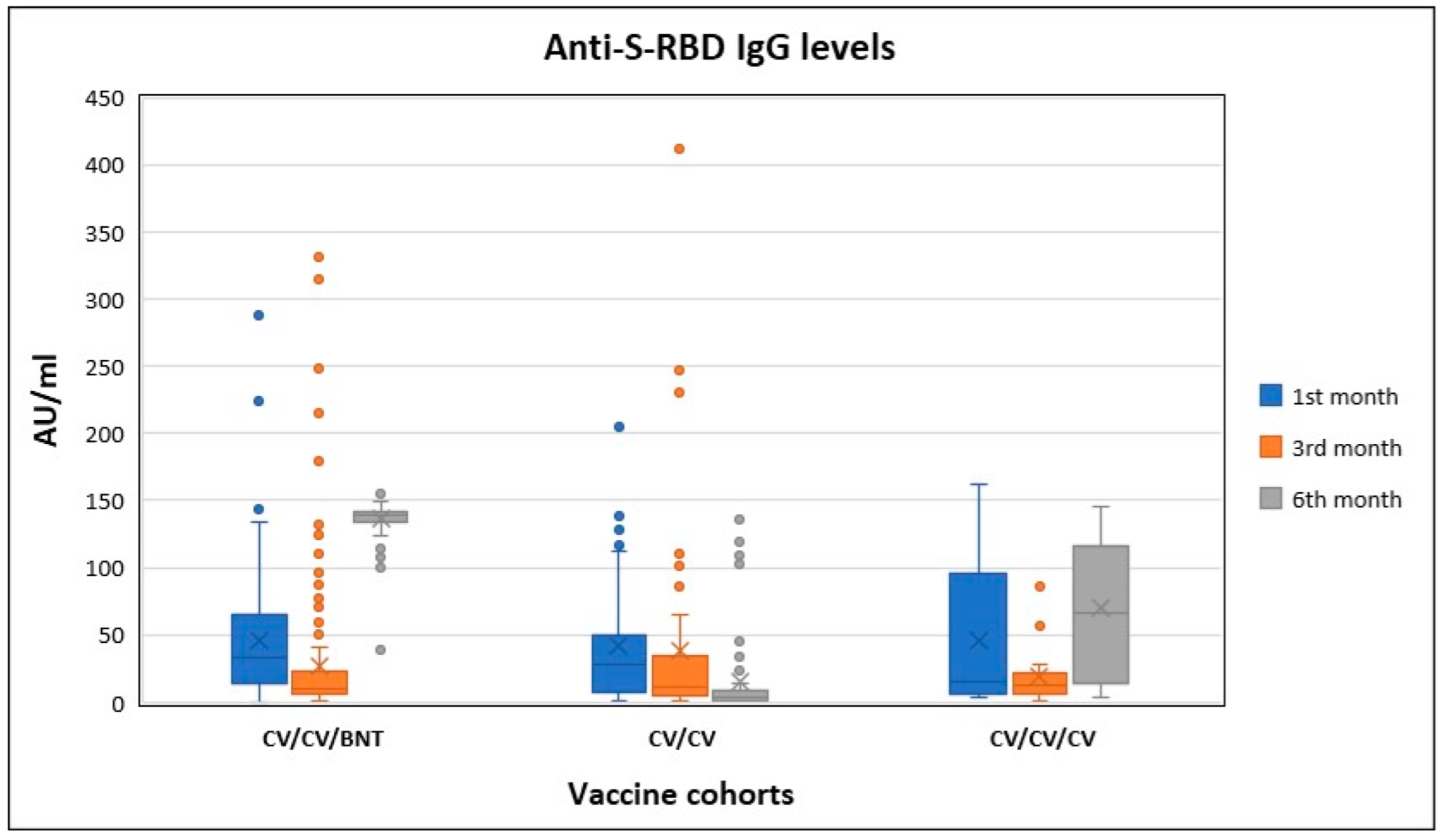
| Anti-S-RBD IgG (AU/mL) | Antibody Proportions | Humoral Immune Response | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Cohorts | 1st Month | 3rd Month | 6th Month | p | 6th/1st a | 6th/3rd b | N/R (%) c | |
| Cohort-I n = 42 | Mean | 44.38 | 23.47 | 11.14 | ||||
| S.D. | 49.84 | 40.51 | 24.97 | <0.001 | 0.64 | 0.40 | 16.7/83.3 | |
| Median | 27.57 | 7.53 | 2.66 | |||||
| Range | 203.73 | 229.62 | 119.14 | |||||
| Cohort-II n = 12 | Mean | 46.61 | 15.02 | 76.18 | ||||
| S.D. | 55.53 | 15.65 | 53.28 | 0.003 | 3.53 | 5.13 | 0/100.0 | |
| Median | 13.99 | 8.61 | 85.99 | |||||
| Range | 158.16 | 55.46 | 139.06 | |||||
| Cohort-III n = 137 | Mean | 42.34 | 17.59 | 136.82 | ||||
| S.D. | 37.73 | 27.17 | 11.00 | <0.001 | 17.00 | 20.44 | 0/100.0 | |
| Median | 29.63 | 9.21 | 139.20 | |||||
| Range | 146.10 | 214.71 | 116.40 | |||||
| Total Anti-Spike/Anti-Nucleocapsid IgG | Antibody Proportions | Humoral Immune Response | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Cohort | 1st Month | 3rd Month | 6th Month | p | 6th/1st a | 6th/3rd b | N/R (%) c | |
| Cohort-I n = 42 | Mean | 30.26 | 22.72 | 1.91 | ||||
| S.D. | 38.68 | 45.32 | 3.77 | <0.001 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 71.4/28.6 | |
| Median | 11.98 | 3.39 | 0.054 | |||||
| Range | 143.02 | 251.08 | 15.80 | |||||
| Cohort-II n = 12 | Mean | 12.81 | 9.92 | 22.01 | ||||
| S.D. | 11.36 | 12.82 | 28.64 | 0.035 | 4.15 | 3.58 | 16.7/83.3 | |
| Median | 10.60 | 2.85 | 9.42 | |||||
| Range | 35.05 | 36.69 | 89.43 | |||||
| Cohort-III n = 137 | Mean | 27.74 | 19.01 | 1.82 | ||||
| S.D. | 44.08 | 49.10 | 5.64 | <0.001 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 75.2/24.8 | |
| Median | 10.88 | 3.82 | 0.062 | |||||
| Range | 367.68 | 407.32 | 40.72 | |||||
| Anti-S-RBD IgG Levels | Antibody Proportions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Cohorts | COVID-19 History | 1st Month | 3rd Month | 6th Month | p | 6th/1st a | 6th/3rd b | |
| Cohort-I | No (n = 42) | Mean | 44.38 | 23.47 | 11.14 | |||
| S.D. | 49.84 | 40.51 | 24.97 | <0.001 | 0.47 e | 0.39 f | ||
| Median | 27.57 | 7.53 | 2.66 | |||||
| Range | 203.73 | 229.62 | 119.14 | |||||
| Yes, before the 1st dose | Mean | 31.71 | 42.23 | 13 | ||||
| (n = 6) | S.D. | 14.44 | 34.36 | 10.56 | 0.135 | 0.49 | 0.47 | |
| 90.0 ± 46 (30–150) c | Median | 33.15 | 26.45 | 8.51 | ||||
| days before the 1st dose | Range | 30.51 | 85.11 | 28.17 | ||||
| Yes, after the 2nd dose | Mean | 33.03 | 329.7 | 118.9 | ||||
| (n = 2) d | S.D. | 24.52 | 116.81 | 23.75 | 0.135 | 4.6 | 0.37 | |
| 55.0 ± 21.21 (40–70) d | Median | 33.03 | 329.7 | 118.9 | ||||
| days after the 2nd dose | Range | 34.68 | 165.2 | 33.6 | ||||
| Cohort-II | No | Mean | 46.61 | 15.02 | 76.18 | |||
| (n = 12) | S.D. | 55.53 | 15.65 | 53.28 | 0.003 | 4.02 g | 6.44 h | |
| Median | 13.99 | 8.61 | 85.99 | |||||
| Range | 158.16 | 55.46 | 139.06 | |||||
| Yes, before the 1st dose | Mean | 42.03 | 28.95 | 49.83 | ||||
| (n = 5) | S.D. | 44.03 | 32.22 | 44.84 | 0.779 | 2.07 | 1.51 | |
| 98.60 ± 54.17 (43–180) c | Median | 14.68 | 19.4 | 45.12 | ||||
| days before the 1st dose | Range | 95.35 | 81.26 | 101.51 | ||||
| Cohort-III | No | Mean | 42.34 | 17.59 | 136.82 | |||
| (n = 137) | S.D. | 37.73 | 27.17 | 11 | <0.001 | 19.68 j | 23.19 k | |
| Median | 29.63 | 9.21 | 139.2 | |||||
| Range | 146.1 | 214.71 | 116.4 | |||||
| Yes, before the vaccinations | Mean | 66.28 | 42.41 | 137.7 | ||||
| (n = 26) | S.D. | 69.09 | 45.71 | 4.74 | <0.001 | 5.33 | 8.89 | |
| 130.2 ± 91.31 (30–330) c | Median | 38.48 | 22.02 | 137.75 | ||||
| days before the 1st dose | Range | 280.32 | 175.18 | 18.3 | ||||
| Yes, between the 2nd and 3rd dose | Mean | 39.91 | 188 | 134.22 | ||||
| (n = 5) | S.D. | 16.4 | 153.94 | 19.28 | 0.247 | 4.02 | 2.94 | |
| 88.0 ± 51.67 (60–180) d | Median | 33.41 | 248 | 142.7 | ||||
| days after the 2nd dose | Range | 38.95 | 319.73 | 45.7 | ||||
| Vaccine Cohorts | Age (Years) | Anti-S-RBD IgG Levels | Antibody Proportions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Month | 3rd Month | 6th Month | p | 6th/1st a | 6th/3rd b | |||
| Cohort-I | 20–29 (n = 12) | Mean | 42.91 | 16.11 | 4.82 | |||
| S.D. | 42.30 | 22.92 | 6.59 | <0.001 | 0.31 | 0.34 | ||
| Median | 35.61 | 8.08 | 2.15 | |||||
| Range | 129.93 | 84.31 | 24.01 | |||||
| 30–39 (n = 17) | Mean | 67.04 | 39.44 | 22.10 | ||||
| S.D. | 61.91 | 57.35 | 36.72 | <0.001 | 0.27 | 0.47 | ||
| Median | 48.64 | 25.63 | 6.26 | |||||
| Range | 202.24 | 229.62 | 119.14 | |||||
| 40–49 (n = 11) | Mean | 15.17 | 9.77 | 2.74 | ||||
| S.D. | 11.96 | 11.37 | 2.47 | <0.001 | 1.04 | 0.35 | ||
| Median | 9.97 | 4.67 | 1.91 | |||||
| Range | 34.04 | 38.40 | 8.21 | |||||
| 50 and older (n = 2) | Mean | 21.36 | 7.21 | 2.19 | ||||
| S.D. | 14.70 | 3.84 | 1.07 | 0.135 | 0.11 | 0.30 | ||
| Median | 21.36 | 7.21 | 2.19 | |||||
| Range | 20.80 | 5.44 | 1.52 | |||||
| Cohort-II | 20–29 (n = 2) | Mean | 98.43 | 32.31 | 94.41 | |||
| S.D. | 89.32 | 33.96 | 53.71 | 0.223 | 1.20 | 4.57 | ||
| Median | 98.43 | 32.31 | 94.41 | |||||
| Range | 126.33 | 48.04 | 75.97 | |||||
| 30–39 (n = 5) | Mean | 28.70 | 10.52 | 99.12 | ||||
| S.D. | 42.42 | 8.422 | 52.96 | 0.018 | 7.02 | 10.65 | ||
| Median | 12.89 | 9.99 | 105.30 | |||||
| Range | 99.98 | 20.39 | 135.69 | |||||
| 40–49 (n = 2) | Mean | 102.25 | 20.42 | 94.14 | ||||
| S.D. | 18.30 | 9.71 | 36.56 | 0.223 | 0.96 | 5.67 | ||
| Median | 102.25 | 20.42 | 94.14 | |||||
| Range | 25.89 | 13.74 | 51.71 | |||||
| 50 and older (n = 3) | Mean | 4.80 | 5.90 | 13.81 | ||||
| S.D. | 1.46 | 1.09 | 9.43 | 0.264 | 2.94 | 2.59 | ||
| Median | 4.62 | 5.86 | 10.56 | |||||
| Range | 2.92 | 2.18 | 18.00 | |||||
| Cohort-III | 20–29 (n = 26) | Mean | 49.34 | 22.95 | 138.94 | |||
| S.D. | 40.50 | 29.62 | 4.81 | <0.001 | 6.19 | 15.47 | ||
| Median | 34.14 | 10.39 | 139.60 | |||||
| Range | 140.81 | 121.32 | 17.00 | |||||
| 30–39 (n = 30) | Mean | 44.10 | 14.74 | 137.29 | ||||
| S.D. | 36.72 | 17.40 | 7.14 | <0.001 | 7.64 | 18.98 | ||
| Median | 29.95 | 9.08 | 138.10 | |||||
| Range | 130.97 | 85.35 | 34.90 | |||||
| 40–49 (n = 43) | Mean | 45.97 | 13.72 | 137.92 | ||||
| S.D. | 40.64 | 16.13 | 7.09 | <0.001 | 8.92 | 23.34 | ||
| Median | 25.56 | 9.07 | 139.90 | |||||
| Range | 127.45 | 96.56 | 40.90 | |||||
| 50 and older (n = 38) | Mean | 32.05 | 20.56 | 133.76 | ||||
| S.D. | 32.12 | 39.18 | 17.82 | <0.001 | 50.61 | 30.49 | ||
| Median | 17.88 | 7.93 | 138.15 | |||||
| Range | 143.20 | 214.71 | 109.80 | |||||
| Adverse Events | Vaccine Administered as the Third Dose [n(line %)] | |
|---|---|---|
| Inactivated Vaccine (n:17) | mRNA Vaccine (n:168) | |
| Total | 3 (2.5) | 116 (97.5) |
| Rash at the injection site | 0 (0.0) | 13 (100.0) |
| Pain at the injection site | 1 (0.9) | 113 (99.1) |
| Swelling at the injection site | 1 (5.0) | 19 (95.0) |
| Itching at the injection site | - | 9 (100.0) |
| Hypoesthesia at the injection site | - | 2 (100.0) |
| Induration at the injection site | - | 15 (100.0) |
| Numbness in the vaccinated arm | - | 18 (100.0) |
| Weakness | 2 (3.5) | 55 (96.5) |
| Fatigue | - | 48 (100.0) |
| Fever | - | 19 (100.0) |
| Shake | - | 8 (100.0) |
| Chest pain | - | 5 (100.0) |
| Diarrhoea | - | 2 (100.0) |
| Nausea | - | 7 (100.0) |
| Vomiting | - | 2 (100.0) |
| Headache | 1 (3.4) | 28 (96.6) |
| Dizziness | 1 (3.7) | 26 (96.3) |
| Vertigo | - | 10 (100.0) |
| Muscle pain | - | 30 (100.0) |
| Back pain | - | 21 (100.0) |
| Joint pain | - | 23 (100.0) |
| Cough | - | 2 (100.0) |
| Sore throat | - | 2 (100.0) |
| Dyspnea | - | 3 (100.0) |
| Papule | - | - |
| Abdominal pain | - | 1 (100.0) |
| Loss of appetite | - | 6 (100.0) |
| Palpitation | - | 6 (100.0) |
| Anosmia | - | 1 (100.0) |
| Loss of taste | - | - |
| Rash in the skin/mucosa | - | - |
| Numbness in the tongue | - | - |
| Syncope | - | - |
| Increased blood pressure | - | 1 (100.0) |
| Decreased blood pressure | - | - |
| Allergic reaction/urticaria | - | - |
| Anaphylaxis/anaphylactoid reaction | - | - |
| Neurological complications | - | - |
| Lymphadenopathy | - | 3 (100.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demirhindi, H.; Mete, B.; Tanir, F.; Kara, E.; Kibar, F.; Cetiner, S.; Candevir, A.; Akti, S.E. Effect of Heterologous Vaccination Strategy on Humoral Response against COVID-19 with CoronaVac plus BNT162b2: A Prospective Cohort Study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050687
Demirhindi H, Mete B, Tanir F, Kara E, Kibar F, Cetiner S, Candevir A, Akti SE. Effect of Heterologous Vaccination Strategy on Humoral Response against COVID-19 with CoronaVac plus BNT162b2: A Prospective Cohort Study. Vaccines. 2022; 10(5):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050687
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemirhindi, Hakan, Burak Mete, Ferdi Tanir, Ertan Kara, Filiz Kibar, Salih Cetiner, Aslihan Candevir, and Sukriye Ece Akti. 2022. "Effect of Heterologous Vaccination Strategy on Humoral Response against COVID-19 with CoronaVac plus BNT162b2: A Prospective Cohort Study" Vaccines 10, no. 5: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050687
APA StyleDemirhindi, H., Mete, B., Tanir, F., Kara, E., Kibar, F., Cetiner, S., Candevir, A., & Akti, S. E. (2022). Effect of Heterologous Vaccination Strategy on Humoral Response against COVID-19 with CoronaVac plus BNT162b2: A Prospective Cohort Study. Vaccines, 10(5), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10050687






