Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by the Third Dose of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccines Using a Homologous or Heterologous Booster Vaccination Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
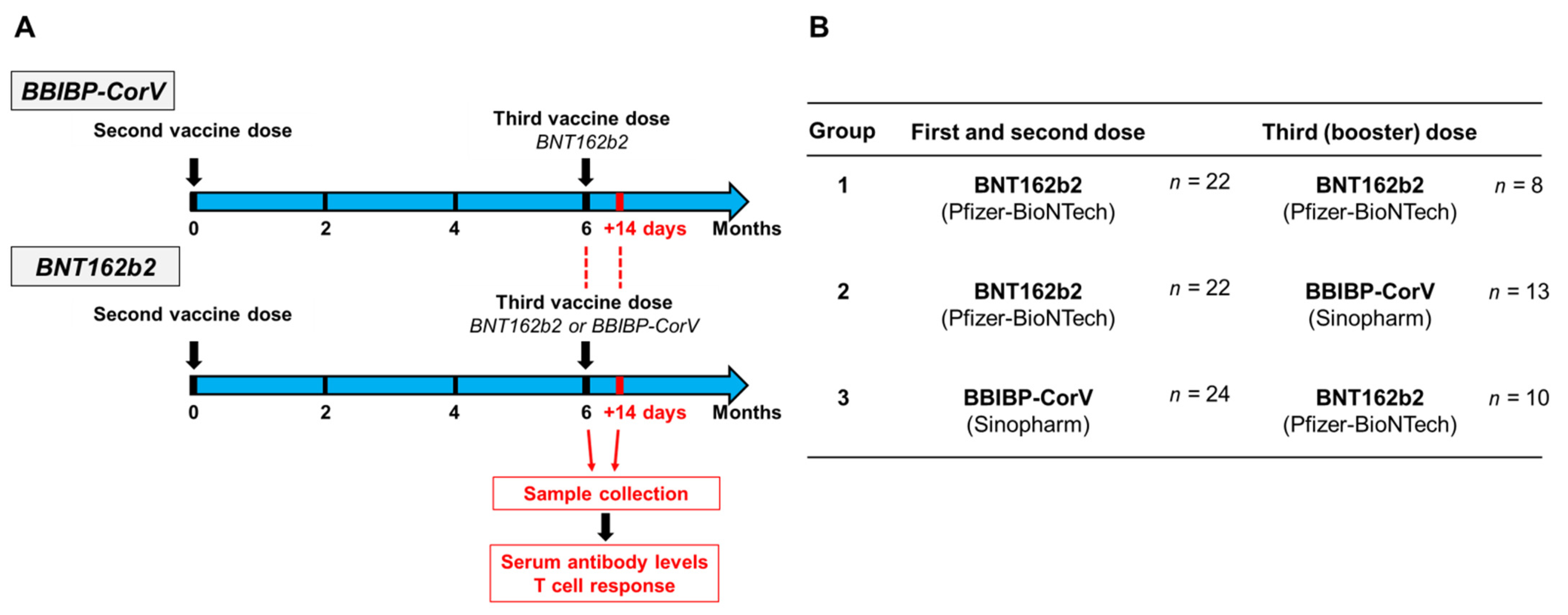
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Response
2.2. Determination of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody Response
2.3. SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody and T Cell Responses 6 Months after Two-Dose BBIBP-CorV or BNT162b2 Vaccine Regimen
2.4. SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody and T Cell Responses after Third BNT162b2 Vaccine following a Two-Dose BNT162b2 or BBIBP-CorV Vaccine Regimen, or after Third BBIBP-CorV Vaccine following a Two-Dose BNT162b2 Vaccine Regimen
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
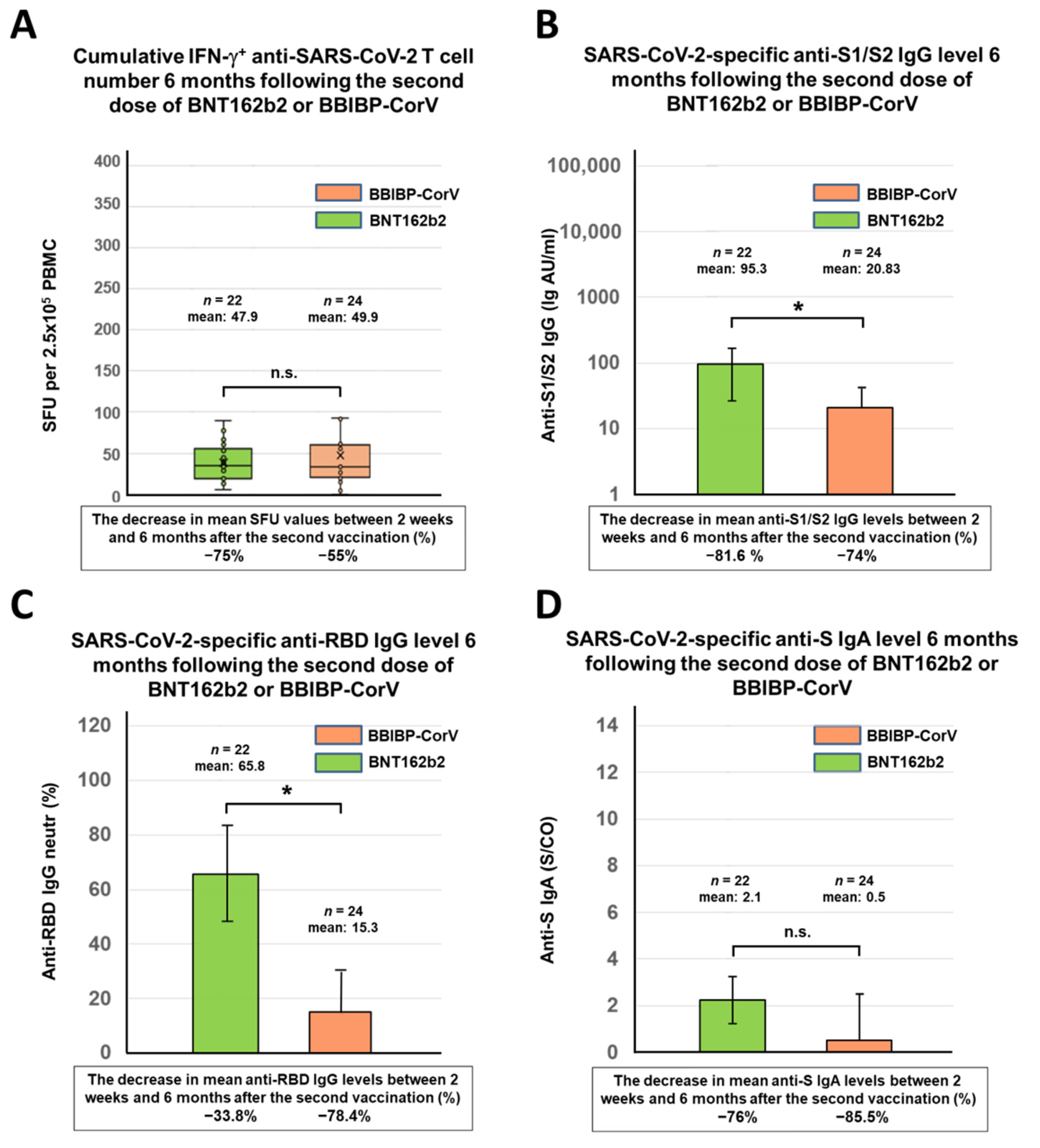
3.1. Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 6 Months after Immunization with Two-Dose BNT162b2 or BBIBP-CorV Vaccine
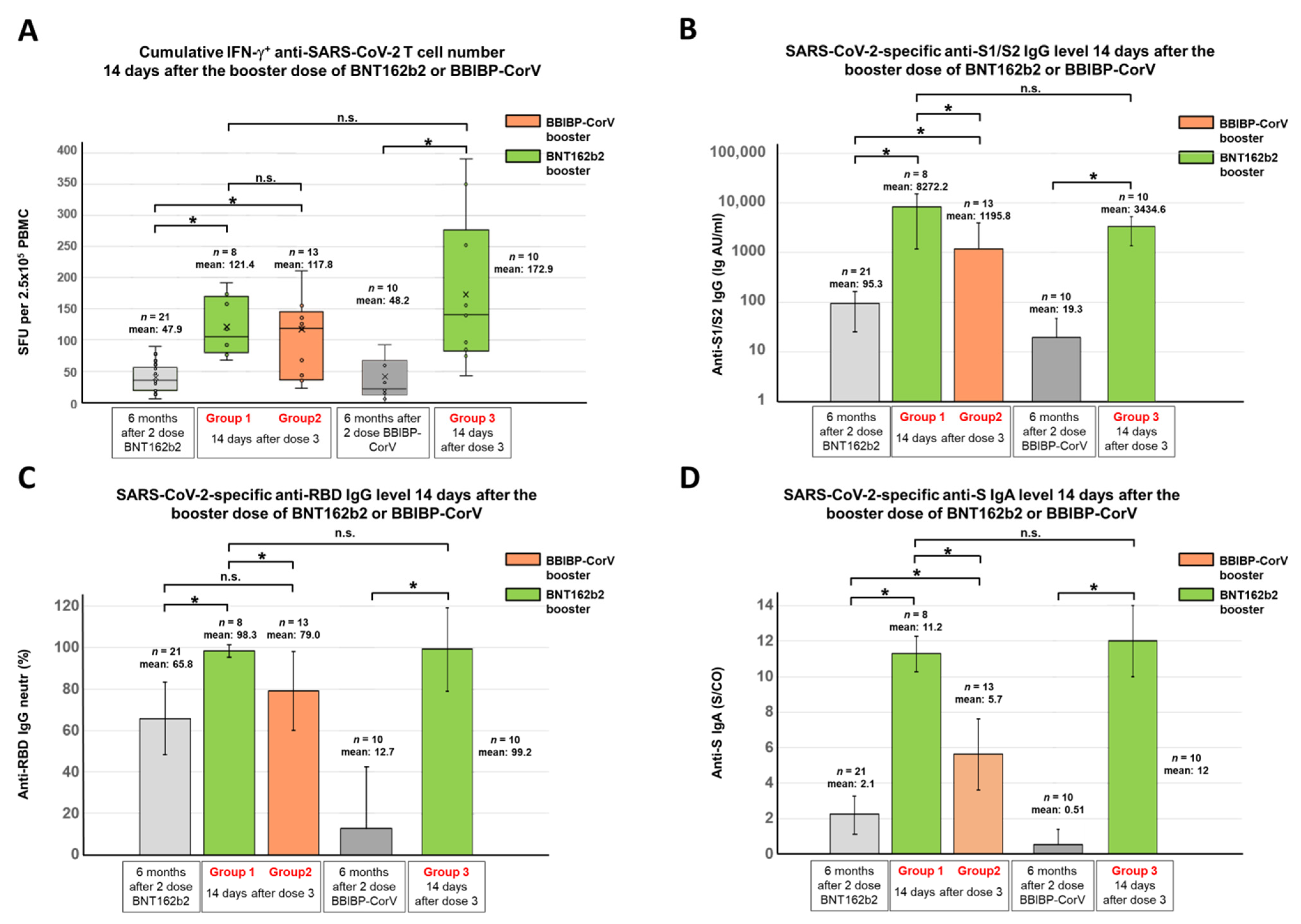
3.2. SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody and T Cell Responses after the Third (Booster) Dose of BNT162b2 or BBIBP-CorV Vaccines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallapaty, S. China’s COVID vaccines have been crucial—Now immunity is waning. Nature 2021, 598, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolgin, E. Omicron thwarts some of the world’s most-used COVID vaccines. Nature 2022, 601, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kaabi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, Y.; Al Qahtani, M.M.; Abdulrazzaq, N.; Al Nusair, M.; Hassany, M.; Jawad, J.S.; Abdalla, J.; et al. Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection in Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, R.; Patino, E.G.; de Oliveira Piorelli, R.; Conde, M.; Batista, A.P.; Zeng, G.; Xin, Q.; Kallas, E.G.; Flores, J.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; et al. Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of treating Healthcare Professionals with the Adsorbed COVID-19 (Inactivated) Vaccine Manufactured by Sinovac—PROFISCOV: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Mok, B.W.; Chen, L.L.; Chan, J.M.; Tsang, O.T.; Lam, B.H.; Chuang, V.W.; Chu, A.W.; Chan, W.M.; Ip, J.D.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by sera from BNT162b2 or Coronavac vaccine recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, ciab1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Xiao, L.; Xiang, Z.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant to convalescent and CoronaVac vaccine plasma. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, S.; Jackson, L.; Khoury, D.S.; Khan, K.; Moyo-Gwete, T.; Tegally, H.; San, J.E.; Cromer, D.; Scheepers, C.; Amoako, D.G.; et al. Omicron extensively but incompletely escapes Pfizer BNT162b2 neutralization. Nature 2021, 602, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Fu, Z.; et al. Omicron variant showed lower neutralizing sensitivity than other SARS-CoV-2 variants to immune sera elicited by vaccines after boost. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wei, D.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Qu, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, E. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant to antibody neutralization elicited by booster vaccination. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, M.; Cheng, S.; Mok, C.K.P.; Leung, Y.; Ng, S.; Chan, K.; Ko, F.; Yiu, K.; Lam, B.; Lau, E.; et al. Neutralizing antibody titres to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and wild-type virus in those with past infection or vaccinated or boosted with mRNA BNT162b2 or inactivated CoronaVac vaccines. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Clemens, S.A.; Weckx, L.; Clemens, R.; Almeida Mendes, A.V.; Ramos Souza, A.; Silveira, M.B.V.; da Guarda, S.N.F.; de Nobrega, M.M.; de Moraes Pinto, M.I.; Gonzalez, I.G.S.; et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine in Brazil (RHH-001): A phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomised study. Lancet 2022, 399, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, A.U.; Bolukcu, S.; Ciragil, P.; Topkaya, A.E. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses after third CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccine following two-dose CoronaVac vaccine regimen. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyi-Nagy, I.; Matula, Z.; Gonczi, M.; Tasnady, S.; Beko, G.; Reti, M.; Ajzner, E.; Uher, F. Comparison of antibody and T cell responses elicited by BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in healthy adult humans. GeroScience 2021, 43, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, R.L.; Lyke, K.E.; Deming, M.E.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Rostad, C.A.; Martin, J.M.; Johnston, C.; Rupp, R.E.; et al. Heterologous SARS-CoV-2 Booster Vaccinations—Preliminary Report. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, R.L.; Lyke, K.E.; Deming, M.E.; Jackson, L.A.; Branche, A.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Rostad, C.A.; Martin, J.M.; Johnston, C.; Rupp, R.E.; et al. Homologous and Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Vaccinations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven COVID-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): A blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, P.; Ulmer, H.; Mutschlechner, B.; Benda, M.; Severgnini, L.; Volgger, A.; Lang, T.; Atzl, M.; Huynh, M.; Gasser, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of heterologous booster vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in haemato-oncological patients with no antibody response. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Heinzel, A.; Mayrdorfer, M.; Jabbour, R.; Hofbauer, T.M.; Merrelaar, A.; Eder, M.; Regele, F.; Doberer, K.; Spechtl, P.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response 4 Weeks After Homologous vs. Heterologous Third Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglayan, D.; Suner, A.F.; Siyve, N.; Guzel, I.; Irmak, C.; Isik, E.; Appak, O.; Celik, M.; Ozturk, G.; Alp Cavus, S.; et al. An analysis of antibody response following the second dose of CoronaVac and humoral response after booster dose with BNT162b2 or CoronaVac among healthcare workers in Turkey. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghnieh, R.; Mekdashi, R.; El-Hassan, S.; Abdallah, D.; Jisr, T.; Bader, M.; Jizi, I.; Sayegh, M.H.; Rahman Bizri, A. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of BNT162b2 booster in BBIBP-CorV—Vaccinated individuals compared with homologous BNT162b2 vaccination: Results of a pilot prospective cohort study from Lebanon. Vaccine 2021, 39, 6713–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorsaeng, R.; Suntronwong, N.; Phowatthanasathian, H.; Assawakosri, S.; Kanokudom, S.; Thongmee, T.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Auphimai, C.; Wongsrisang, L.; Srimuan, D.; et al. Immunogenicity of a third dose viral-vectored COVID-19 vaccine after receiving two-dose inactivated vaccines in healthy adults. Vaccine 2022, 40, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P. The T cell immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.Y.; Jeong, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, E.C. T cell-oriented strategies for controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the total CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell reactivity in infected or vaccinated individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Quadeer, A.A.; McKay, M.R. SARS-CoV-2 T Cell Responses Elicited by COVID-19 Vaccines or Infection Are Expected to Remain Robust against Omicron. Viruses 2022, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, D.; Shamier, M.C.; Bogers, S.; den Hartog, G.; Gommers, L.; Nieuwkoop, N.N.; Schmitz, K.S.; Rijsbergen, L.C.; van Osch, J.A.T.; Dijkhuizen, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern partially escape humoral but not T-cell responses in COVID-19 convalescent donors and vaccinees. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabj1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranbhai, V.; Nathan, A.; Kaseke, C.; Berrios, C.; Khatri, A.; Choi, S.; Getz, M.A.; Tano-Menka, R.; Ofoman, O.; Gayton, A.; et al. T cell reactivity to the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is preserved in most but not all prior infected and vaccinated individuals. Cell 2022, 185, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Sellers, D.; Barrett, J.; Lifton, M.; McMahan, K.; Sciacca, M.; VanWyk, H.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; et al. Vaccines Elicit Highly Cross-Reactive Cellular Immunity to the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. MedRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, H. ‘Killer’ immune cells still recognize Omicron variant. Nature 2022, 601, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, D.; Leung, K.Y.; Fan, Y.; Lu, L.; Chan, P.C.; To, K.K.; Chen, H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Chan, K.H.; et al. Immunogenicity of a Heterologous Prime-Boost COVID-19 Vaccination with mRNA and Inactivated Virus Vaccines Compared with Homologous Vaccination Strategy against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barda, N.; Dagan, N.; Cohen, C.; Hernan, M.A.; Lipsitch, M.; Kohane, I.S.; Reis, B.Y.; Balicer, R.D. Effectiveness of a third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for preventing severe outcomes in Israel: An observational study. Lancet 2021, 398, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim-Raz, N.; Leibovici-Weisman, Y.; Stemmer, A.; Ness, A.; Awwad, M.; Ghantous, N.; Stemmer, S.M. Antibody Titers Before and After a Third Dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 Vaccine in Adults Aged ≥60 Years. JAMA 2021, 326, 2203–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchett, W.E.; Joag, V.; Stolley, J.M.; Shepherd, F.K.; Quarnstrom, C.F.; Mickelson, C.K.; Wijeyesinghe, S.; Soerens, A.G.; Becker, S.; Thiede, J.M.; et al. Nucleocapsid vaccine elicits spike-independent SARS-CoV-2 protective immunity. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thura, M.; Sng, J.X.E.; Ang, K.H.; Li, J.; Gupta, A.; Hong, J.M.; Hong, C.W.; Zeng, Q. Targeting intra-viral conserved nucleocapsid (N) proteins as novel vaccines against SARS-CoVs. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, A.; Cauda, R. Multicomponent vaccines to fight SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Vaccine 2021, 39, 6969–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B. The need for broadly protective COVID-19 vaccines: Beyond S-only approaches. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4239–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matula, Z.; Gönczi, M.; Bekő, G.; Kádár, B.; Ajzner, É.; Uher, F.; Vályi-Nagy, I. Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by the Third Dose of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccines Using a Homologous or Heterologous Booster Vaccination Strategy. Vaccines 2022, 10, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040539
Matula Z, Gönczi M, Bekő G, Kádár B, Ajzner É, Uher F, Vályi-Nagy I. Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by the Third Dose of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccines Using a Homologous or Heterologous Booster Vaccination Strategy. Vaccines. 2022; 10(4):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040539
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatula, Zsolt, Márton Gönczi, Gabriella Bekő, Béla Kádár, Éva Ajzner, Ferenc Uher, and István Vályi-Nagy. 2022. "Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by the Third Dose of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccines Using a Homologous or Heterologous Booster Vaccination Strategy" Vaccines 10, no. 4: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040539
APA StyleMatula, Z., Gönczi, M., Bekő, G., Kádár, B., Ajzner, É., Uher, F., & Vályi-Nagy, I. (2022). Antibody and T Cell Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by the Third Dose of BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccines Using a Homologous or Heterologous Booster Vaccination Strategy. Vaccines, 10(4), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10040539





