Abstract
Host cell-free, axenic development of liver stages (LS) of the malaria parasite has been demonstrated. Here we explored axenic liver stages as a novel live whole parasite malaria vaccine platform, which is unaltered and not prone to human-error, compared to the immunization with live-attenuated sporozoites that must be done intravenously. We show that in contrast to live sporozoites, axenic LS are not infectious to the immunized host. Subcutaneous immunizations of mice with Plasmodium yoelii axenic LS, developed from wild-type (WT) sporozoites or WT sporozoites expressing enhanced-GFP, conferred sterile protection against P. yoelii infectious sporozoite challenge. Thus, axenic liver stages of P. falciparum and P. vivax might constitute an attractive alternative to live sporozoite immunization.
1. Introduction
While recent intervention strategies have led to the reduction in malaria burden, malaria remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality, especially in children under 5 years of age living in endemic areas. The global death estimate by malaria is about 405,000 peoples annually [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has reported that the rate of decline in malaria cases has slowed to 2% in the years 2015 to 2019, in comparison to 27% decline between 2000 to 2015 [2]. The predominant cause of this increase in malaria cases is the generation of drug resistance [3]. Therefore, an effective vaccine would be an important addition to the arsenal required to further reduce the number of malaria related deaths.
The malaria parasite pre-erythrocytic stage, which includes the mosquito-inoculated sporozoites and the liver stages (LS), is a clinically-asymptomatic life cycle stage of the malaria parasite, that precedes the pathogenic blood stage, which causes the malaria disease [4,5,6,7,8]. Therefore, the pre-erythrocyte stage is considered as a prime target for anti-infection malaria vaccine development [8,9,10]. Noteworthy, till now only live attenuated pre-erythrocytic stage vaccines have shown to provide sterilizing immunity against malaria [11,12,13]. Attenuation of live pre-erythrocytic stages has been achieved so far by gamma- or X-rays irradiation, by genetic deletion of LS essential genes. These methods can be prone to human errors in application, design or transfer, and are largely limited in their protective immunity to the attenuated strain used. Moreover, the injection of sporozoites that must be live and capable of invasion is a tremendous labor- and resource- intensive effort, given that they must be purified out of mosquitoes reared under aseptic conditions, and transferred in a frozen state. Importantly, the route of vaccination that is mandatory for this approach to show promise of efficacy is the intravenous route, which is not a practical route for mass-use in humans living in endemic areas.
In this study, we tried to address some of the above-mentioned challenges for whole-parasite live malaria vaccines by the generation of in-vitro developed LS from WT (wild-type) or WT-like Plasmodium yoelii sporozoites [14], and we used them as a foolproof and safe, live whole-parasite vaccine platform in subcutaneous immunizations that conferred sterile protection against infectious salivary gland sporozoites challenge.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Parasite
6–8-week-old female BALB/c mice were purchased from the animal service facility of Bezmialem Vakif University. The non-lethal P. yoelii 17X-NL WT and P. yoelii 17X-NL p230p(−) strains were stored as frozen stock at −150 °C. Pyp230p(−) is a eGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) expressing WT-like parasite strain, which was genetically modified to express eGFP in all life cycle stages, under the control of PyHSP70_1 constitutive promoter, as a knockout replacement of the dispensable gene Pyp230p. Targeted deletion of P230p did not show any phenotypic effect as described previously [15]. Freshly thawed parasites were injected into donor naive mice for mosquito feeding to get sporozoites as described earlier [16]. 4–8-day old female Anopheles stephensi mosquitos were allowed to blood-feed on anesthetized female BALB/c mice infected with both strains of parasites. Blood fed mosquito were maintained at 24 °C, 75% humidity. At day 15 post infection, mosquitoes were collected, rinsed with 70% ethanol for 10 s, and washed twice in sterile medium to reduce contamination before dissection.
2.2. Salivary Gland Sporozoite Collection and In-Vitro Transformation
On day 15 post infection, salivary glands were dissected in sterile culture media containing DMEM (Gibco, cat#11965092) supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco, cat#10082147), 500U/mL penicillin–streptomycin (Gibco, cat#15070063), and 1.50 µL/mL fungizone (Gibco, cat#15290018). The dissected glands were ground using a pestle and spun at 800 rpm for 3 min. Supernatant containing sporozoites were collected, and the number of sporozoites were determined using hemocytometer. For transformation 200,000 sporozoites per well in a 24-well culture plates were dispersed in 500 µL complete medium. The sporozoites were incubated at 37 °C temperature in 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. The transformation of sporozoites into early liver stage were observed by live fluorescence microscopy at different time intervals using eGFP expressing WT-like P. yoelii.
2.3. Live Fluorescence Imaging
The conversion of salivary gland sporozoites into early liver stage was confirmed by live fluorescence imaging of cultured eGFP expressing sporozoites. Transformed parasites were harvested at 6 hrs (6 h), 12 hrs, 18 hrs and 24 hrs time intervals and images were captured using confocal laser scanning microscope Leica TCS SP8.
2.4. Infectivity of Sporozoites and Axenic LS in mice
6 to 8-week-old female BALB/c mice were used to check the infectivity of axenically developed early LS. Axenic LS from 500,000 and 1,000,000 cultured day-14 salivary gland sporozoites doses, and day 15 freshly-dissected salivary gland sporozoites doses were injected into groups of 3 BALB/c mice per group. After 24 hrs of incubation, transformed parasites were harvested, and collected by centrifugation at 7000 rpm for 1 min. The doses were prepared in 200 µL with incomplete sterile RPMI media for axenic LS and sporozoite doses (Gibco, cat#a1049101), and injected intravenously into mice. Blood stage infection was monitored from day 3 to day 15 post sporozoite injection by Giemsa-staining of thin blood smears from tail vein.
2.5. Vaccination
6–8-week-old female BALB/c mice were used to check the efficacy of axenically developed early LS vaccine candidate. 200,000 cultured sporozoites were used as a single axenic LS vaccine dose. After 24 hrs of incubation, transformed parasites were harvested, and collected by centrifugation at 7000 rpm for 1 min. The supernatant was removed and remaining 200 µL was resuspended to vaccinate mice. Subcutaneous (SC) (n = 10 mice per group for both PyWT and Pyp230p(−)) route was used to immunize mice. Four immunizations were performed at a three-week interval between prime (0 day), first boost (21 days), second boost (42 days) and third boost (63 day).
2.6. Parasite Challenge
The efficacy of immunization was checked by challenge with day 14/15 P. yoelii infectious salivary gland sporozoites. Mice were intravenously injected with P. yoelii 17X-NL salivary gland sporozoites resuspended in incomplete RPMI media. Sporozoites were prepared as described earlier [16]. Eight weeks after the final immunization, each mouse was injected via the tail vein with 200 µL of RPMI media containing 500 salivary gland sporozoites. Two groups of five naive mice each were also used as control groups in parasite challenge study. After parasite challenge, blood stage infection was monitored from day 3 to day 15 by Giemsa staining of tail vein thin blood smears. Protection was defined as the complete absence of erythrocytic stage parasitemia on day 15 post challenge
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Cultured Sporozoites Transform into Early Liver Stages within 24 hrs of Incubation
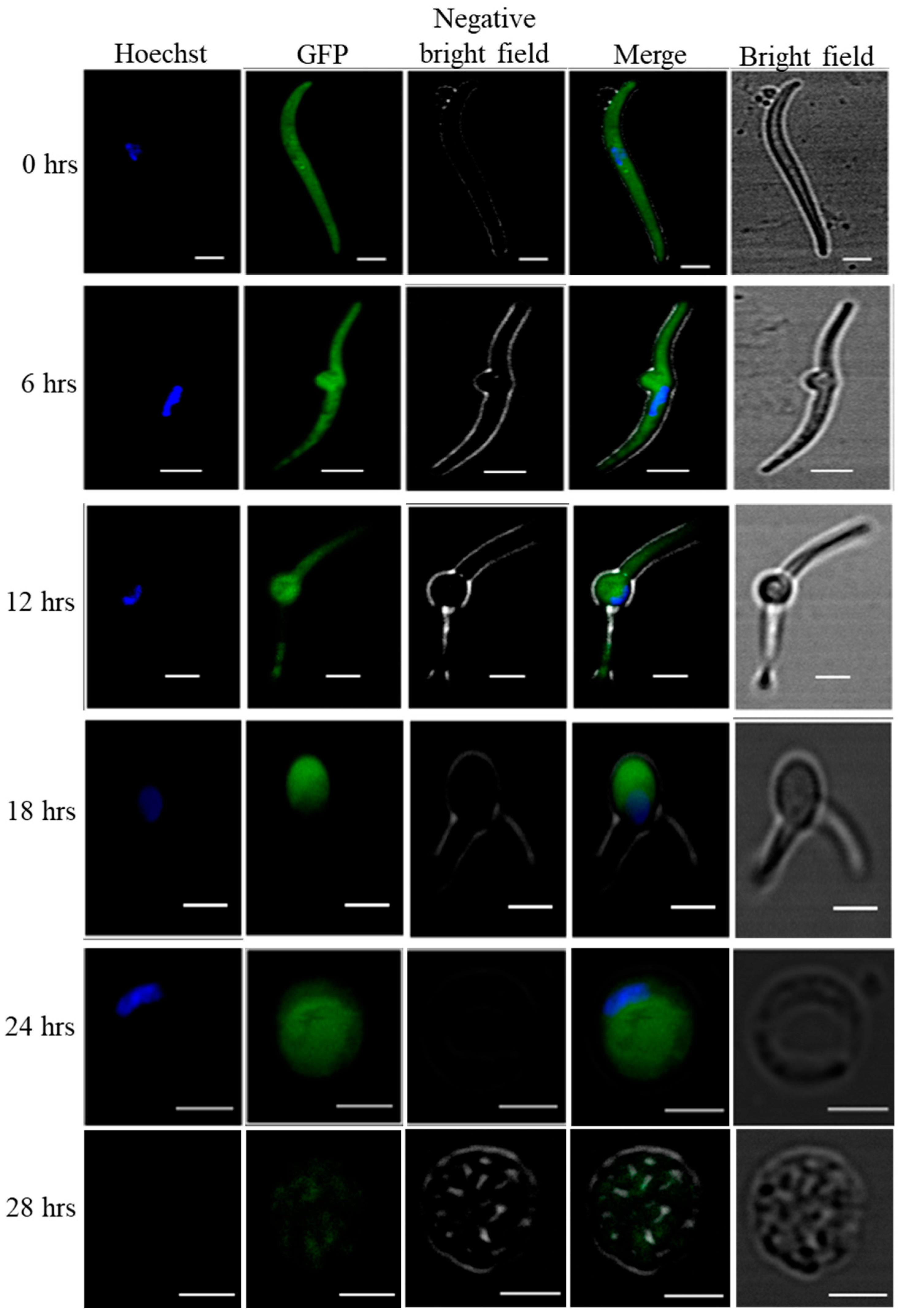
To check the transformation of salivary gland sporozoites into early exoerythrocytic forms, we used WT-like eGFP expressing P. yoelii strain Pyp230p(−) [15]. The live fluorescence microscopy clearly shows that the transformation started within the 6 hrs of incubation where cultured sporozoites developed into transformation bulbs, and at 24 hrs of incubation the cultured sporozoites completely developed into early LS. (Figure 1).
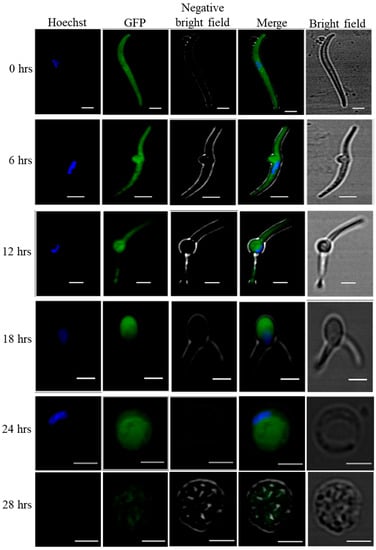
Figure 1.
Axenic transformation of eGFP expressing P. yoelii p230p(−) salivary gland sporozoites into LS. In-vitro host cell free cultured salivary gland sporozoites completely transform into early LS after 24 hrs of incubation. To follow the cell free transformation of salivary gland sporozoites into early exoerythrocytic forms, we used eGFP expressing Pyp230p(−) and followed the transformation by confocal microscopy of cultured sporozoites at 6 hrs intervals for 24 hrs. At 28th of Axenic LS culture we could not find any good GFP images. Scale bars 2 µm.
3.2. Immunization with Cell-Free Developed Early Liver Stages is Safe and Provides Sterile Protection
Safety of the vaccine is a major concern when developing attenuated whole organism malaria vaccine [17]. Therefore, the axenic LS transformation was followed by the infectivity test of in-vitro cell free developed early LS. 500,000 and 1,000,000 sporozoites were cultured per well and were harvested 24 hrs later and intravenously injected into 6-7 weeks old BALB/c mice. The infectivity was followed by Giemsa staining of tailed blood smearing from day 3 to day 15 post infection. We did not observe any blood stage parasite until day 15 post infection, in contrast to mice injected with WT or WT-like sporozoites that developed all parasitemia by day 4 post intravenous sporozoite injection. Hence, axenically developed early LS were considered as a safe whole organism vaccine candidate. The scheme of the infectivity test is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Infectivity and Immunizations with axenically developed P. yoelii LS.
Subsequently, Immunization was performed using axenic LS which demonstrated strong protection against salivary gland infectious sporozoites infection. Mice were immunized with the harvested axenic LS using subcutaneous route of immunization (n = 10 mice per group for both P. yoelii WT and P. yoelii p230p(−)). The vaccinated mice were intravenously challenged with 500 P. yoelii 17X-NL salivary gland sporozoites eight weeks after the final immunization to check the effectiveness of vaccine candidate. A 100% sterile protection was confirmed with no blood stage infection observed until day 15 post sporozoite challenge. The immunization scheme is summarized in Table 1.
4. Discussion
Immunization using whole attenuated sporozoites is the only vaccination strategy which provides complete long-lasting protection in human subjects [18]. Different approaches have been applied to develop whole parasite vaccine (WPV) using sporozoites, including radiation [19], genetically-attenuated [20] and infectious sporozoites concurrent with antimalarial drug treatment cover [21,22]. However, all these methods have their own limitations and are prone to human error in attenuation method, attenuation design, transfer of attenuated parasites or application of drug cover, and are therefore not entirely foolproof [23]. Importantly, it has been shown so far that the protective immunity developed following immunization with whole parasite vaccine are largely strain specific. Since these attenuation methods are extremely labor- and resource-intensive and need to be applied intravenously in order to be effective, therefore it is not foreseeable that these attenuation methods can be applied systematically to target geographically-distinct malaria parasite strains.
Therefore, herein we report a more practical and foolproof method of attenuation that does not involve alteration of the parasite or treatment of the host. The axenically-developed LS vaccine candidate is completely safe and highly efficacious with a widely accepted subcutaneous (SC) route of immunization and shows sterile protection against infectious sporozoite challenge in the immunized mice. Though, studies show WSV elicit primarily CD8+ T cell mediated protection, [24,25,26], it will be an important goal for future studies to identify the type of protective immunity induced by axenically developed LS as a WPV, as the subcutaneous inoculation might possibly induce humoral immunity.
5. Conclusions
Herein, we are showing that axenically developed early LS parasites are safe and provide sterile protection against salivary gland sporozoites challenge in immunized mice. Our data also supports future work toward testing our malaria vaccine in other animal models of malaria infection such as nonhuman primate models. This future work will be critical to support future human clinical trials using vaccines targeting clinically asymptomatic stage and achieving the World Health Organization’s goal of malaria eradication by 2030.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.S.I.A. and S.H.I.K.; Experimental design: A.S.I.A.; Methodology: M.K., G.D., U.Y.K. and A.S.I.A.; Data analysis: M.K. and A.S.I.A.; Supervision and Funding acquisition: A.S.I.A.; Writing and editing of the manuscript: M.K. and A.S.I.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by TUBITAK 1001 grant (Project No:119Z409) to A.S.I.A. from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal care and handling procedures were approved by the animal ethical committee of Bezmialem Vakif University, Istanbul Turkey (No-2019/244). All efforts were made to minimize the suffering in the animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Elif Kurt for her help in animal care and insectary maintenance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaslow, D.C. Malaria vaccine research & innovation: The intersection of IA2030 and zero malaria. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015791 (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Blasco, B.; Leroy, D.; Fidock, D.A. Antimalarial drug resistance: Linking Plasmodium falciparum parasite biology to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, P.E.; Patrick Gorres, J. Malaria vaccines since 2000: Progress, priorities, products. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Pan, H.; Gu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Ran, N.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F. Prospects for malaria vaccines: Pre-erythrocytic stages, blood stages, and transmission-blocking stages. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9751471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.S.I.; Vaughan, A.M.; Kappe, S.H.I. Malaria Parasite development in the mosquito and infection of the mammalian host. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, A.M.; Aly, A.S.; Kappe, S.H. Malaria Parasite Pre-Erythrocytic Stage Infection: Gliding and Hiding. Available online: ttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=18779047 (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Mikolajczak, S.A.; Aly, A.S.; Kappe, S.H. Preerythrocytic malaria vaccine development. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 20, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.M.; Reuschel, E.L.; Bah, M.A.; Yun, K.; Tursi, N.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Chu, J.; Zaidi, F.I.; Yilmaz, I.; Hart, R.J.; et al. Synthetic DNA vaccines adjuvanted with pIL-33 drive liver-localized t cells and provide protection from plasmodium challenge in a mouse model. Vaccines 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, P.J.F.; Kamil, M.; Yilmaz, I.; Atmaca, H.N.; Kalkan-Yazici, M.; Ziya Doymaz, M.; Kousoulas, K.G.; Aly, A.S.I. An attenuated HSV-1-derived malaria vaccine expressing liver-stage exported proteins induces sterilizing protection against infectious sporozoite challenge. Vaccines 2022, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, J.G.; Kurtovic, L.; Dobaño, C.; Opi, D.H.; Chan, J.A.; Feng, G.; Good, M.F.; Reiling, L.; Boyle, M.J. Challenges and strategies for developing efficacious and long-lasting malaria vaccines. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, P.E.; Sahu, T.; Akue, A.; Milman, N.; Anderson, C. Pre-erythrocytic malaria vaccines: Identifying the targets. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Franky, J.; Cuy-Chaparro, L.; Camargo, A.; Reyes, C.; Gómez, M.; Salamanca, D.R.; Patarroyo, M.A.; Patarroyo, M.E. Plasmodium falciparum pre-erythrocytic stage vaccine development. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Camargo, N.; Kappe, S.H.I. Transformation of sporozoites into early exoerythrocytic malaria parasites does not require host cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.J.; Lawres, L.; Fritzen, E.; Mamoun, C.B.; Aly, A.S.I. Plasmodium yoelii vitamin B5 pantothenate transporter candidate is essential for parasite transmission to the mosquito. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.S.I.; Deveci, G.; Yilmaz, I.; Abraham, A.; Golshan, A.; Hart, R.J. Phenotypic analysis of rodent malaria parasite asexual and sexual blood stages and mosquito stages. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 147, e55688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvie, O.; Semblat, J.P.; Franetich, J.F.; Hannoun, L.; Eling, W.; Mazier, D. Effects of irradiation on Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite hepatic development: Implications for the design of pre-erythrocytic malaria vaccines. Parasite Immunol. 2002, 24, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsara, L.S.; Zhou, Y.; Do, J.; Grieser, A.M.; Vaughan, A.M.; Ghosh, A.K. The Development of whole sporozoite vaccines for Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, S.L.; Goh, L.M.L.; Luke, T.C.; Schneider, I.; Le, T.P.; Doolan, D.L.; Sacci, J.; de la Vega, P.; Dowler, M.; Paul, C.; et al. Protection of humans against malaria by immunization with radiation-attenuated Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kublin, J.G.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; Sack, B.K.; Fishbaugher, M.E.; Seilie, A.; Shelton, L.; VonGoedert, T.; Firat, M.; Magee, S.; Fritzen, E.; et al. Complete attenuation of genetically engineered Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites in human subjects. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordmuller, B.; Surat, G.; Lagler, H.; Chakravarty, S.; Ishizuka, A.S.; Lalremruata, A.; Gmeiner, M.; Campo, J.J.; Esen, M.; Ruben, A.J.; et al. Sterile protection against human malaria by chemoattenuated PfSPZ vaccine. Nature 2017, 542, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.M.; Machado, M.; Gonçalves-Rosa, N.; Reuling, I.J.; Foquet, L.; Marques, C.; Salman, A.M.; Yang, A.S.P.; Moser, K.A.; Dwivedi, A.; et al. A Plasmodium berghei sporozoite-based vaccination platform against human malaria. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzfeld, O.; Muller, K.; Matuschewski, K. Engineering of genetically arrested parasites (GAPs) for a precision malaria vaccine. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, L.; Villaquiran, J.; Ferreira, A.; Schellekens, H.; Nussenzweig, R.; Nussenzweig, V. γ Interferon, CD8+ T cells and antibodies required for immunity to malaria sporozoites. Nature 1987, 330, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seder, R.A.; Chang, L.J.; Enama, M.E.; Zephir, K.L.; Sarwar, U.N.; Gordon, I.J.; Holman, L.A.; James, E.R.; Billingsley, P.F.; Gunasekera, A.; et al. Protection against malaria by intravenous immunization with a nonreplicating sporozoite vaccine. Science 2013, 341, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyke, K.E.; Ishizuka, A.S.; Berry, A.A.; Chakravarty, S.; DeZure, A.; Enama, M.E.; James, E.R.; Billingsley, P.F.; Gunasekera, A.; Manoj, A.; et al. Attenuated PfSPZ vaccine induces strain-transcending T cells and durable protection against heterologous controlled human malaria infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).