The Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Prognosis in Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
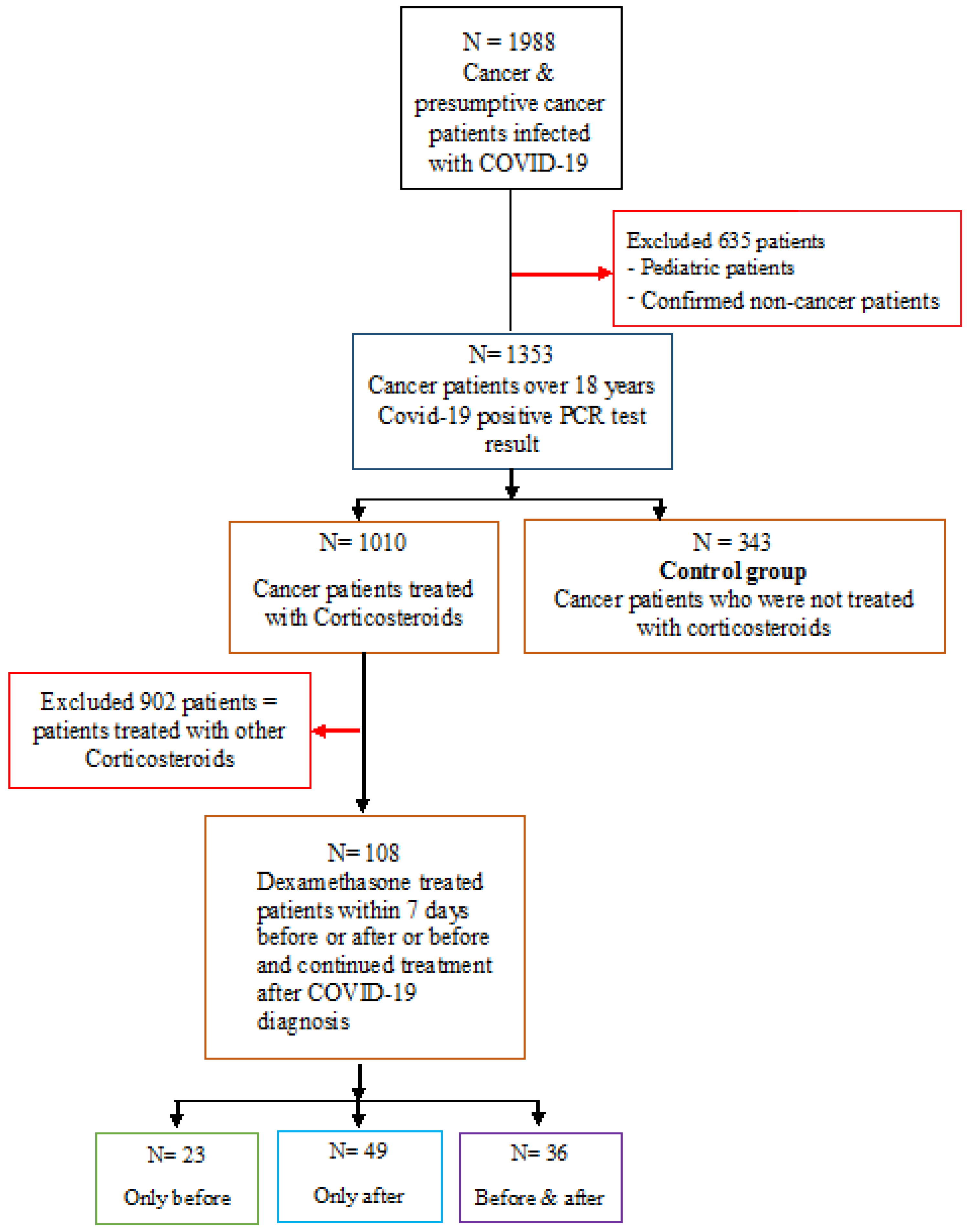
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Groups of Patients According to Their Dexamethasone Healthcare Treatment Plan and COVID-19 Infection Onset
2.3. COVID-19 Disease Severity Indicators
2.4. Effects of Dexamethasone Treatment on Laboratory Parameters in COVID-19-Infected Cancer Patients
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Disease Prognosis
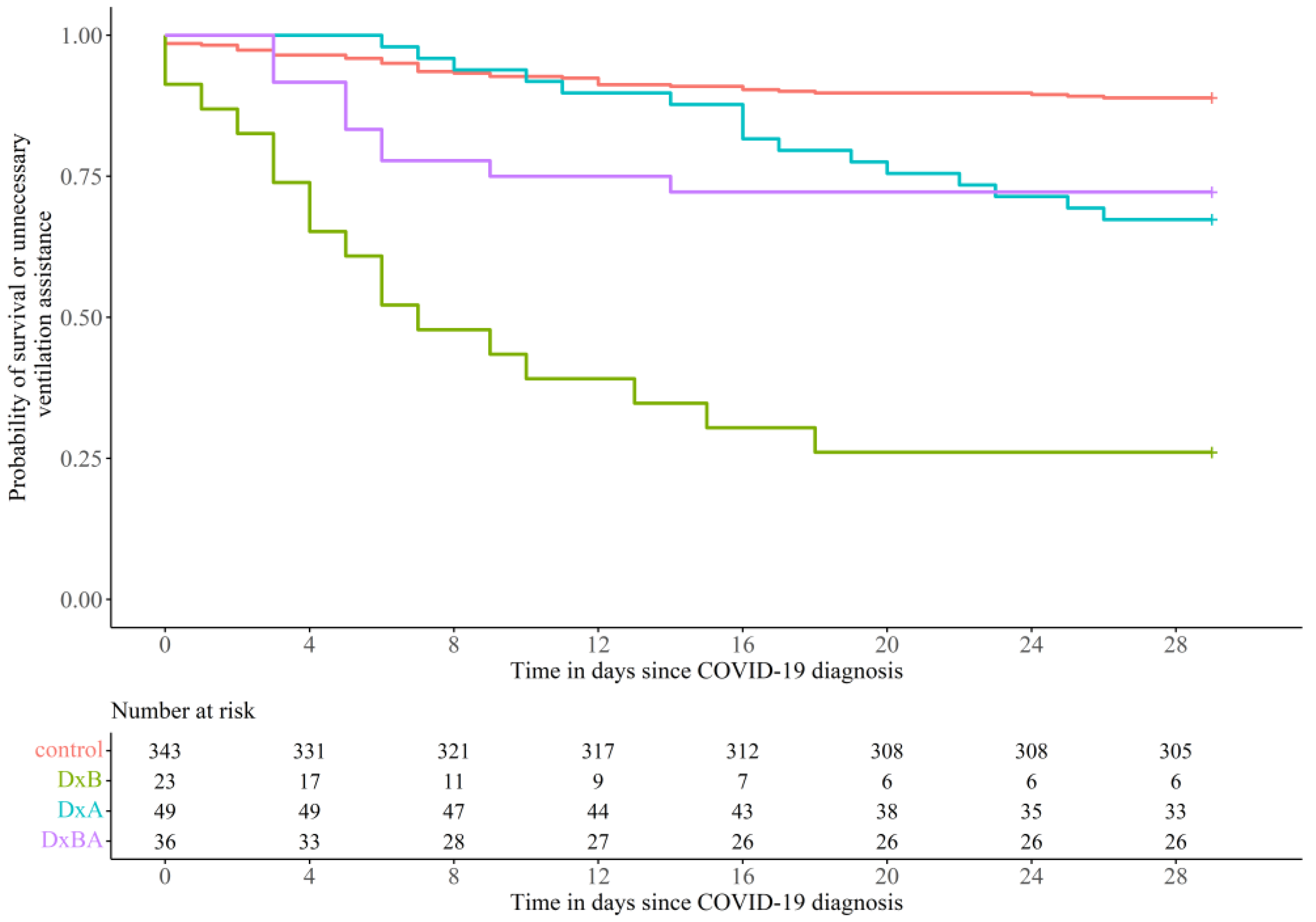
3.2. Comparison within the Three Subgroups of Dexamethasone
3.3. Outcome and Survival of Various Subgroups
3.4. Multivariable Cox Proportional Hazards Model
3.5. Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment Dose
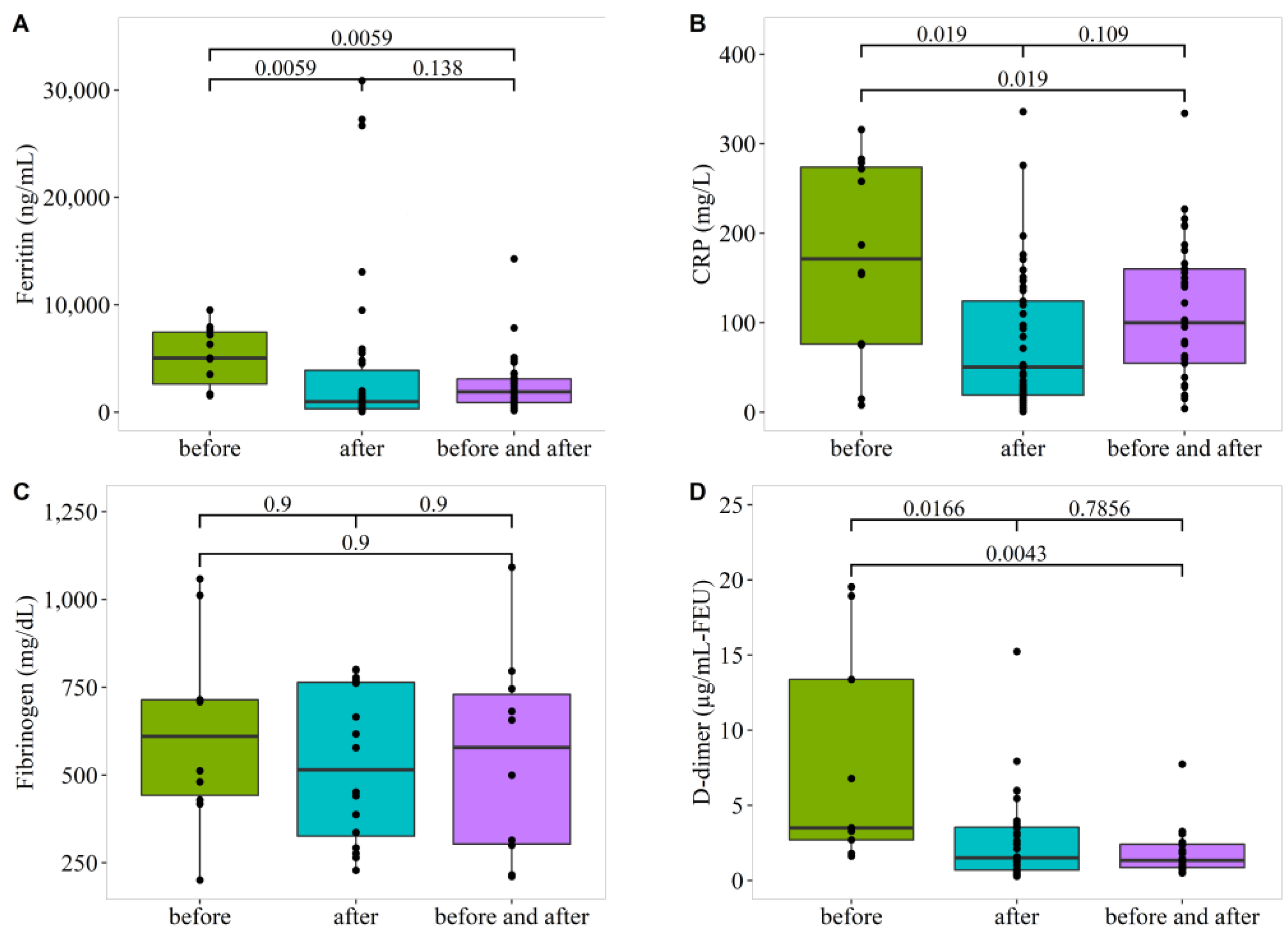
3.6. Effect of Dexamethasone Healthcare Treatment Plan on Laboratory Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Guo, Y.-R.; Cao, Q.-D.; Hong, Z.-S.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-D.; Jin, H.-J.; Tan, K.-S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yan, Y. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—An update on the status. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Ongoing COVID-19 global crisis and scientific challenges. J. Health Allied Sci. NU 2020, 10, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungroo, M.R.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Novel Coronavirus: Current Understanding of Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment Options. Pathogens 2020, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.J.; Nwagwu, C.; Anyim, O.; Ekweremadu, C.; Kim, S. COVID-19 and cancer: From basic mechanisms to vaccine development using nanotechnology. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kumar, B.K.; Deekshit, V.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Detection technologies and recent developments in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogado, J.; Obispo, B.; Pangua, C.; Serrano-Montero, G.; Marino, A.M.; Pérez-Pérez, M.; López-Alfonso, A.; Gullón, P.; Lara, M.Á. COVID-19 transmission, outcome and associated risk factors in cancer patients at the first month of the pandemic in a Spanish hospital in Madrid. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 2364–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, C.; Fallani, S.; Voller, F.; Silvestri, C. Treatment for COVID-19: An overview. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 889, 173644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Greco, M.; Zanella, A.; Albano, G.; Antonelli, M.; Bellani, G.; Bonanomi, E.; Cabrini, L.; Carlesso, E.; Castelli, G.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Mortality Among Patients with COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; RECOVERY Collaborative Group; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, L.; Li, S.; Pan, L.; Tefsen, B.; Li, Y.; French, N.; Chen, L.; Yang, G.; Villanueva, E.V. Corticosteroid treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Med. J. Aust. 2020, 212, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkin, R.M.; Gregory, S.A.; Mohrbacher, A.; Hussein, M.A. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, vincristine, and dexamethasone provide significant reduction in toxicity compared with doxorubicin, vincristine, and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: A Phase III multicenter randomized trial. Cancer 2006, 106, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, C.; Stewart, A.K. Mechanism of immunomodulatory drugs’ action in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.A.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Stock, W.; Heffner, L.T.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Pierce, S.; Lu, B.; et al. Phase 1 multicenter study of vincristine sulfate liposomes injection and dexamethasone in adults with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2009, 115, 5490–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, J.; Buijs, J.T.; van der Horst, G.; Cheung, H.; van der Mark, M.; van Bloois, L.; Rizzo, L.Y.; Lammers, T.; Pelger, R.C.; Storm, G.; et al. Liposomal delivery of dexamethasone attenuates prostate cancer bone metastatic tumor growth in vivo. Prostate 2015, 75, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Guan, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Li, C.; Ai, Q.; Lu, W.; Liang, H.; et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.-Y.; Liu, D.-B.; Liu, M.; Zhou, F.-X.; Li, G.-L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.-A.; You, H.; Wu, M.; Zheng, Q.-C.; et al. Patients with Cancer Appear More Vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: A Multicenter Study during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, J.; Foote, M.B.; Lumish, M.; Stonestrom, A.J.; Wills, B.; Narendra, V.; Avutu, V.; Murciano-Goroff, Y.R.; Chan, J.E.; Derkach, A.; et al. Chemotherapy and COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients with Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.; Stonestrom, A.J.; Devlin, S.; Nguyentran, T.; Wills, B.; Narendra, V.; Foote, M.B.; Lumish, M.; Vardhana, S.A.; Pastores, S.M.; et al. Oncologic immunomodulatory agents in patients with cancer and COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchié, A.; Batticciotto, A.; Tangianu, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Pennella, B.; Abenante, A.; Corso, R.; Grazioli, S.; Mumoli, N.; Para, O.; et al. High-dose dexamethasone treatment for COVID-19 severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cesaro, S.; Ljungman, P.; Mikulska, M.; Hirsch, H.H.; von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Cordonnier, C.; Meylan, S.; Mehra, V.; Styczynski, J.; Marchesi, F.; et al. Recommendations for the management of COVID-19 in patients with haematological malignancies or haematopoietic cell transplantation, from the 2021 European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia (ECIL 9). Leukemia 2022, 36, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sulaiman, K.; Korayem, G.B.; Eljaaly, K.; Altebainawi, A.F.; Al Harbi, O.; Badreldin, H.A.; Al Harthi, A.; Al Yousif, G.; Vishwakarma, R.; Albelwi, S.; et al. Early dexamethasone use as a protective measure in non-mechanically ventilated critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedero, P.; Gea, A.; Castro, P.; Candela-Toha, A.M.; Hernández-Sanz, M.L.; Arruti, E.; Villar, J.; Ferrando, C. Early corticosteroids are associated with lower mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A cohort study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Paassen, J.; Vos, J.S.; Hoekstra, E.M.; Neumann, K.M.I.; Boot, P.C.; Arbous, S.M. Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, E.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Wu, P.; Lin, S.; Peng, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, F.; et al. Cancer history is an independent risk factor for mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups Demographic | Control N (%) | Dexamethasone N (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N = 451) | 343 (60.5%) | 108 (19.1%) | |
| Age | |||
| Median (years) | 58.0 | 58.5 | 0.438 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 151 (44%) | 58 (54%) | 0.0992 |
| Female | 192 (56%) | 50 (46%) | |
| Cancer type | |||
| Solid | 318 (93%) | 91 (87%) | 0.0846 |
| Hematological | 25 (7%) | 14 (13%) |
| Indicator Variables | Control | Dexamethasone | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | ||
| Total (n = 451) | 343 (60.5%) | 108 (19.1%) | |
| Ventilation assistance | <0.05 | ||
| Yes | 7 (2%) | 14 (13%) | |
| No | 336 (98%) | 94 (87%) | |
| Admitted to hospital | |||
| Yes | 59 (17%) | 68 (63%) | <0.05 |
| No | 284 (83%) | 40 (37%) | |
| Admitted to ICU | |||
| Yes | 2 (1%) | 14 (13%) | <0.05 |
| No | 341 (99%) | 94 (87%) | |
| Mortality within 28 days of COVID-19 | <0.05 | ||
| Yes | 36 (10%) | 39 (36%) | |
| No | 307 (90%) | 69 (64%) |
| Groups | Control | Dexamethasone Treatment before COVID-19 Infection or within 7 Days from Testing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator variables | N (%) | N (%) | p-value |
| Total (n = 451) | 343 (76.1%) | 23 (5.1%) | |
| Ventilation assistance | 7 (2%) | 6 (26%) | <0.05 |
| Yes | |||
| No | 336 (98%) | 17 (74%) | |
| Admitted to hospital | |||
| Yes | 59 (17%) | 11 (48%) | <0.05 |
| No | 284 (83%) | 12 (52%) | |
| Admitted to ICU | |||
| Yes | 2 (1%) | 6 (26%) | <0.05 |
| No | 341 (99%) | 17 (74%) | |
| Mortality within 28 days of COVID-19 | |||
| Yes | 36 (10%) | 17 (74%) | <0.05 |
| No | 307 (90%) | 6 (26%) | |
| Groups | Dexamethasone Treatment before vs. after COVID-19 Infection | Dexamethasone Treatment before vs. before and after COVID-19 Infection | Dexamethasone Treatment after vs. before and after COVID-19 Infection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators variables | DxB vs. DxA | p-value | DxB vs. DxBA | p-value | DxA vs. DxBA | p-value |
| Ventilation assistance | 26% vs. 4% | <0.05 | 26% vs. 17% | 0.586 | 4% vs. 17% | 0.112 |
| Admitted to hospital | 48% vs. 67% | 0.185 | 48% vs. 67% | 0.244 | 67% vs. 67% | 1 |
| Admitted to ICU | 26% vs. 10% | 0.163 | 26% vs. 8% | 0.139 | 10% vs. 8% | 1 |
| Mortality within 28 days of COVID-19 | 74% vs. 31% | <0.05 | 74% vs. 19% | <0.05 | 31% vs. 19% | 0.362 |
| Variable | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| age | 1.03 (1.01–1.05) | 3.435 | <0.005 |
| diabetes | 1.8 (0.99–3.1) | 1.943 | 0.0521 |
| heart failure | 1.2 (0.37–4.0) | 0.335 | 0.738 |
| history of stroke | NA | NA | NA |
| myocardial infarction | 0.4 (0.04–3.6) | −0.814 | 0.416 |
| Obstructive lung disease | 2.0 (0.42–9.14) | 0.852 | 0.394 |
| acute kidney injury | NA | NA | NA |
| Hypertension | 0.6 (0.3–1.1) | −1.61 | 0.107 |
| Gender | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | −0.745 | 0.456 |
| admission to ICU | 3.4 (1.6–7.4) | 3.069 | <0.005 |
| admission to hospital | 7.3 (4.2–13.0) | 6.875 | <0.005 |
| Type of cancer (hematological vs. solid) | 1.8 (0.9–3.6) | 1.592 | 0.111 |
| Dexamethasone before vs. control | 5.8 (2.8–12.0) | 4.682 | <0.005 |
| Dexamethasone after vs. control | 0.9 (0.5–1.7) | −0.411 | 0.681 |
| Dexamethasone before and after vs. control | 0.8 (0.3–1.7) | −0.669 | 0.504 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souan, L.; Al-Khairy, Z.; Al-Binni, M.A.; Battah, A.; Sughayer, M.A. The Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Prognosis in Cancer Patients. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111798
Souan L, Al-Khairy Z, Al-Binni MA, Battah A, Sughayer MA. The Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Prognosis in Cancer Patients. Vaccines. 2022; 10(11):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111798
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouan, Lina, Zienab Al-Khairy, Maysaa’ Adnan Al-Binni, Abdelkader Battah, and Maher A. Sughayer. 2022. "The Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Prognosis in Cancer Patients" Vaccines 10, no. 11: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111798
APA StyleSouan, L., Al-Khairy, Z., Al-Binni, M. A., Battah, A., & Sughayer, M. A. (2022). The Effect of Dexamethasone Treatment on COVID-19 Prognosis in Cancer Patients. Vaccines, 10(11), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111798






