Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Responses in 192 Adult Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 IFN-γ Release Assay
2.4. Lymphocyte Counts
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort
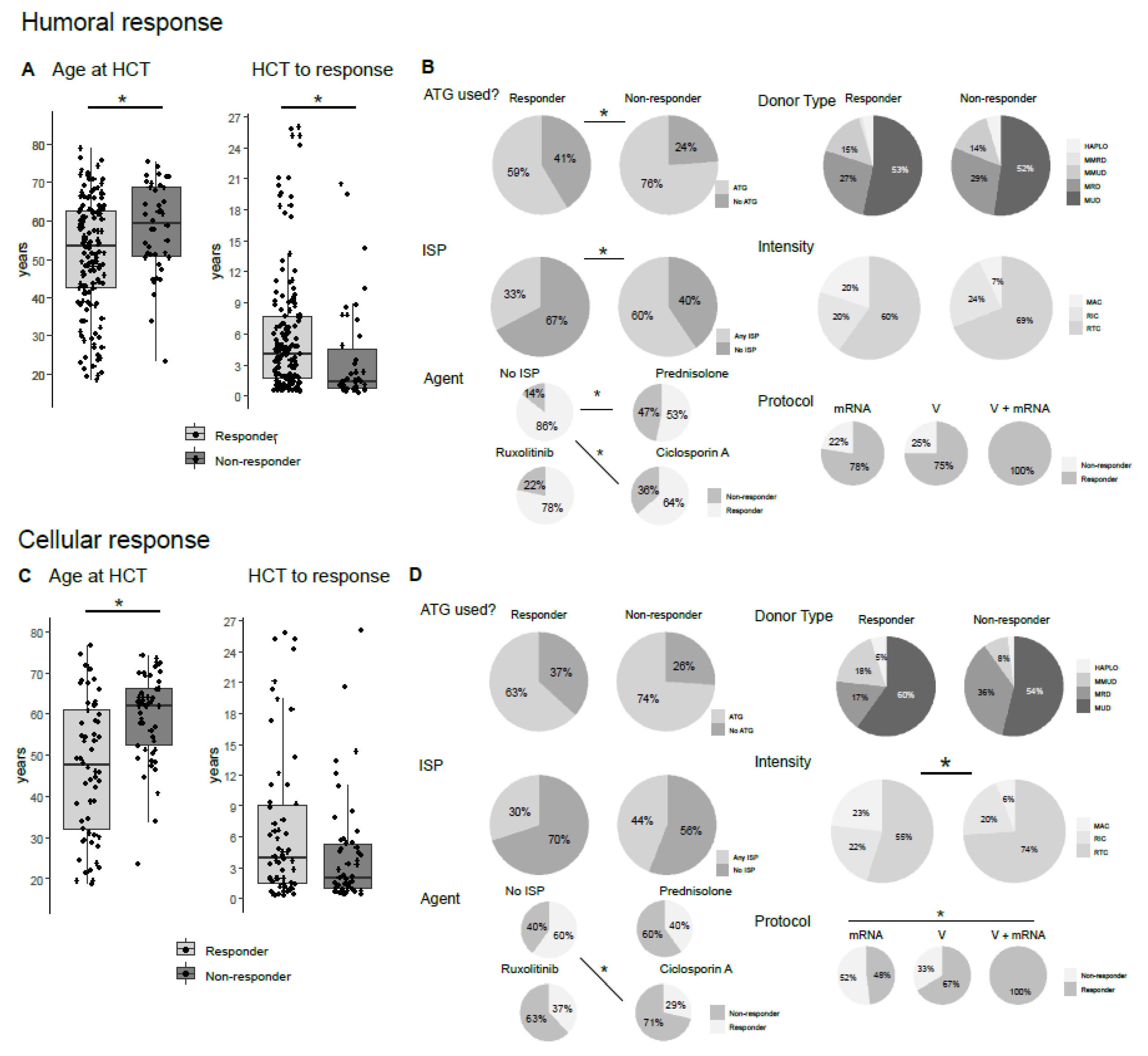
3.2. Humoral Vaccination Response Depends on Age, Time after Allo-HCT, Antithymocyte Globulin (ATG) Usage and Active Immunosuppression
3.3. Cellular Vaccination Response Depends on Age, Ciclosporin a Usage, Vaccination Scheme and cGvHD
3.4. Influence of Lymphocyte Subsets on Humoral and Cellular Vaccination Response
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ljungman, P.; de la Camara, R.; Mikulska, M.; Tridello, G.; Aguado, B.; Zahrani, M.A.; Apperley, J.; Berceanu, A.; Bofarull, R.M.; Calbacho, M.; et al. COVID-19 and Stem Cell Transplantation; Results from an EBMT and GETH Multicenter Prospective Survey. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2885–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Bhatt, N.S.; St Martin, A.; Abid, M.B.; Bloomquist, J.; Chemaly, R.F.; Dandoy, C.; Gauthier, J.; Gowda, L.; Perales, M.-A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Haematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e185–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffrath, J.; Brummer, C.; Wolff, D.; Holtick, U.; Kröger, N.; Bornhäuser, M.; Kraus, S.; Hilgendorf, I.; Blau, I.-W.; Penack, O.; et al. High Mortality of COVID-19 Early after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation—A Retrospective Multicenter Analysis on Behalf of the German Cooperative Transplant Study Group. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 337.e1–337.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, R.M.; Ashmawy, R.; Hamdy, N.A.; Elhadi, Y.A.M.; Reyad, O.A.; Elmalawany, D.; Almaghraby, A.; Shaaban, R.; Taha, S.H.N. Efficacy and Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, A.; Au, L.; Shepherd, S.T.C.; Byrne, F.; Cerrone, M.; Boos, L.A.; Rzeniewicz, K.; Gordon, W.; Shum, B.; Gerard, C.L.; et al. Functional Antibody and T Cell Immunity Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Including by Variants of Concern, in Patients with Cancer: The CAPTURE Study. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, M.; Le Bourgeois, A.; Coste-Burel, M.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; Rimbert, M.; Imbert, B.-M.; Le Gouill, S.; Moreau, P.; Mahe, B.; et al. B Cell Aplasia Is the Most Powerful Predictive Marker for Poor Humoral Response after BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 279.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerlage, A.; Leuzinger, K.; Valore, L.; Mathew, R.; Junker, T.; Drexler, B.; Passweg, J.R.; Hirsch, H.H.; Halter, J. Antibody Response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in 182 Patients after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2022, 24, e13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarucci, M.; Paolasini, S.; Isidori, A.; Guiducci, B.; Loscocco, F.; Capalbo, M.; Visani, G. Immunological Response Against SARS-COV-2 After BNT162b2 Vaccine Administration Is Impaired in Allogeneic but Not in Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Hagin, D.; Kikozashvilli, N.; Freund, T.; Amit, O.; Bar-On, Y.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Shefer, G.; Moshiashvili, M.M.; Karni, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients after Allogeneic HCT or CD19-Based CART Therapy-A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redjoul, R.; Le Bouter, A.; Beckerich, F.; Fourati, S.; Maury, S. Antibody Response after Second BNT162b2 Dose in Allogeneic HSCT Recipients. Lancet 2021, 398, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bourgeois, A.; Coste-Burel, M.; Guillaume, T.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; Béné, M.C.; Chevallier, P. Safety and Antibody Response After 1 and 2 Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2126344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñana, J.L.; López-Corral, L.; Martino, R.; Montoro, J.; Vazquez, L.; Pérez, A.; Martin-Martin, G.; Facal-Malvar, A.; Ferrer, E.; Pascual, M.-J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Reactive Antibody Detection after SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Prospective Survey from the Spanish Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cell Therapy Group. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneikis, K.; Šablauskas, K.; Ringelevičiūtė, U.; Vaitekėnaitė, V.; Čekauskienė, R.; Kryžauskaitė, L.; Naumovas, D.; Banys, V.; Pečeliūnas, V.; Beinortas, T.; et al. Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine and Early Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Haematological Malignancies in Lithuania: A National Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e583–e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Abedin, S.; Fenske, T.; Chhabra, S.; Ledeboer, N.; Hari, P.; Hamadani, M. Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood 2021, 138, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Ngo, D.; Aribi, A.; Arslan, S.; Dadwal, S.; Marcucci, G.; Nakamura, R.; Forman, S.J.; Chen, J.; Al Malki, M.M. Safety and Tolerability of SARS-CoV2 Emergency-Use Authorized Vaccines for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 938.e1–e938.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamez, A.-C.; Pradier, A.; Giannotti, F.; Petitpas, A.; Urdiola, M.F.; Vu, D.-L.; Masouridi-Levrat, S.; Morin, S.; Dantin, C.; Clerc-Renaud, D.; et al. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV2 Vaccination in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 3094–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easdale, S.; Shea, R.; Ellis, L.; Bazin, J.; Davis, K.; Dallas, F.; Thistlethwayte, E.; Ethell, M.; Potter, M.; Arias, C.; et al. Serologic Responses Following a Single Dose of SARS-Cov-2 Vaccination in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 880.e1–e880.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhardt, V.; Luxenburger, H.; Kemming, J.; Schulien, I.; Ciminski, K.; Giese, S.; Csernalabics, B.; Lang-Meli, J.; Janowska, I.; Staniek, J.; et al. Rapid and Stable Mobilization of CD8+ T Cells by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine. Nature 2021, 597, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Dowell, A.C.; Pearce, H.; Verma, K.; Long, H.M.; Begum, J.; Aiano, F.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Hoschler, K.; Brooks, T.; et al. Robust SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Immunity Is Maintained at 6 Months Following Primary Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clémenceau, B.; Guillaume, T.; Coste-Burel, M.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; Le Bourgeois, A.; Jullien, M.; Ollier, J.; Grain, A.; Béné, M.C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 T-Cell Responses in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recipients Following Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, P.; Doores, K.J.; Saha, C.; Saunders, J.; Child, F.; Dillon, R.; Saglam, S.; Raj, K.; McLornan, D.; Avenoso, D.; et al. Repeated Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 Elicits Robust Polyfunctional T Cell Response in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, M.; Klisanin, V.; Thümmler, L.; Fisenkci, N.; Tsachakis-Mück, N.; Ditschkowski, M.; Schwarzkopf, S.; Klump, H.; Reinhardt, H.C.; Horn, P.A.; et al. Humoral and Cellular Vaccination Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huzly, D.; Panning, M.; Smely, F.; Enders, M.; Komp, J.; Falcone, V.; Steinmann, D. Accuracy and Real Life Performance of a Novel Interferon-γ Release Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV2 Specific T Cell Response. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 148, 105098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canti, L.; Humblet-Baron, S.; Desombere, I.; Neumann, J.; Pannus, P.; Heyndrickx, L.; Henry, A.; Servais, S.; Willems, E.; Ehx, G.; et al. Predictors of Neutralizing Antibody Response to BNT162b2 Vaccination in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shem-Tov, N.; Yerushalmi, R.; Danylesko, I.; Litachevsky, V.; Levy, I.; Olmer, L.; Lusitg, Y.; Avigdor, A.; Nagler, A.; Shimoni, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamari, R.; Politikos, I.; Knorr, D.A.; Vardhana, S.A.; Young, J.C.; Marcello, L.T.; Doddi, S.; Devlin, S.M.; Ramanathan, L.V.; Pessin, M.S.; et al. Predictors of Humoral Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano Mortari, E.; Russo, C.; Vinci, M.R.; Terreri, S.; Fernandez Salinas, A.; Piccioni, L.; Alteri, C.; Colagrossi, L.; Coltella, L.; Ranno, S.; et al. Highly Specific Memory B Cells Generation after the 2nd Dose of BNT162b2 Vaccine Compensate for the Decline of Serum Antibodies and Absence of Mucosal IgA. Cells 2021, 10, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeton, R.; Tincho, M.B.; Ngomti, A.; Baguma, R.; Benede, N.; Suzuki, A.; Khan, K.; Cele, S.; Bernstein, M.; Karim, F.; et al. T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Cross-Recognize Omicron. Nature 2022, 603, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Cicin-Sain, C.; Pasin, C.; Epp, S.; Audigé, A.; Müller, N.J.; Nilsson, J.; Bankova, A.; Wolfensberger, N.; Vilinovszki, O.; et al. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 214.e1–e214.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuapio, A.; Boulouis, C.; Filipovic, I.; Wullimann, D.; Kammann, T.; Parrot, T.; Chen, P.; Akber, M.; Gao, Y.; Hammer, Q.; et al. NK Cell Frequencies, Function and Correlates to Vaccine Outcome in BNT162b2 mRNA Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinated Healthy and Immunocompromised Individuals. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Sainz, T.; Lee, S.A.; Hunt, P.W.; Sinclair, E.; Shacklett, B.L.; Ferre, A.L.; Hayes, T.L.; Somsouk, M.; Hsue, P.Y.; et al. HIV-Infected Individuals with Low CD4/CD8 Ratio despite Effective Antiretroviral Therapy Exhibit Altered T Cell Subsets, Heightened CD8+ T Cell Activation, and Increased Risk of Non-AIDS Morbidity and Mortality. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikby, A.; Ferguson, F.; Forsey, R.; Thompson, J.; Strindhall, J.; Löfgren, S.; Nilsson, B.-O.; Ernerudh, J.; Pawelec, G.; Johansson, B. An Immune Risk Phenotype, Cognitive Impairment, and Survival in Very Late Life: Impact of Allostatic Load in Swedish Octogenarian and Nonagenarian Humans. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Innate Immune Response to Adenoviral Vectors Is Mediated by Both Toll-like Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Farber, D.L. COVID-19 Vaccines: Modes of Immune Activation and Future Challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Entire Cohort (n = 192) |
|---|---|
| Age at data cut-off (year), median (range) | 61 (21–83) |
| Age at allo-HCT (year), median (range) | 54 (19–79) |
| Time from allo-HCT to best humoral response (years), median (range) | 3.3 (0.35–26.03) |
| Time from allo-HCT to best cellular response (years), median (range) | 3.4 (0.41–26.03) |
| Male, n (%) | 115 (60) |
| Female, n (%) | 77 (40) |
| Number of vaccinations documented, n (%) | |
| 1 | 192 (100) |
| 2 | 177 (92) |
| 3 | 4 (2) |
| Type of vaccination, n (%) | |
| mRNA | 129 (67) |
| Vector | 20 (10) |
| 1 mRNA + 1 Vector | 10 (5) |
| Unconventionally vaccinated | 2 (1) |
| Not documented | 31 (16) |
| Baseline disease, n (%) | |
| AML | 78 (41) |
| ALL | 10 (5) |
| MDS | 21 (11) |
| MDS/MPN | 6 (3) |
| Myeloma | 21 (11) |
| Other NHL | 20 (10) |
| Immunodeficiency | 5 (3) |
| Other | 7 (4) |
| Donor type, n (%) | |
| MUD | 102 (53) |
| MRD | 52 (27) |
| MMUD | 29 (15) |
| MMRD | 2 (1) |
| HAPLO | 7 (4) |
| Graft source, n (%) | |
| PBSC | 183 (95) |
| BM | 9 (5) |
| Conditioning intensity | |
| MAC | 33 (17) |
| RTC | 119 (62) |
| RIC | 40 (21) |
| CMV, n (%) | |
| −/− | 83 (43) |
| −/+ | 36 (19) |
| +/− | 23 (12) |
| +/+ | 50 (26) |
| GvHD, n (%) | |
| aGvHD | 122 (64) |
| aGvHD Grade II or more | 76 (40) |
| cGvHD | 111 (58) |
| cGvHD moderate or severe | 74 (39) |
| Active immunosuppression, n (%) | |
| None | 118 (61) |
| Ruxolitinib | 23 (12) |
| Ciclosporin A | 22 (11) |
| Prednisolone | 15 (8) |
| Prednisolone dose (mg), median (range) | 10 (2.50–50) |
| Everolimus | 6 (3) |
| Mycophenolic acid | 2 (1) |
| Other | 29 (15) |
| Combination of 2 agents | 11 (6) |
| Combination of 3 agents | 6 (3) |
| Time from vaccination to response (years) | |
| For humoral response n = 167 | |
| median (IQR) | 0.15 (0.07–0.28) |
| For cellular response n = 113 | |
| median (IQR) | 0.18 (0.10–0.28) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meyer, T.; Ihorst, G.; Bartsch, I.; Zeiser, R.; Wäsch, R.; Bertz, H.; Finke, J.; Huzly, D.; Wehr, C. Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Responses in 192 Adult Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111782
Meyer T, Ihorst G, Bartsch I, Zeiser R, Wäsch R, Bertz H, Finke J, Huzly D, Wehr C. Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Responses in 192 Adult Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Vaccines. 2022; 10(11):1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111782
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeyer, Thomas, Gabriele Ihorst, Ingrid Bartsch, Robert Zeiser, Ralph Wäsch, Hartmut Bertz, Jürgen Finke, Daniela Huzly, and Claudia Wehr. 2022. "Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Responses in 192 Adult Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation" Vaccines 10, no. 11: 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111782
APA StyleMeyer, T., Ihorst, G., Bartsch, I., Zeiser, R., Wäsch, R., Bertz, H., Finke, J., Huzly, D., & Wehr, C. (2022). Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Responses in 192 Adult Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Vaccines, 10(11), 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111782





