The Hypoxia Tolerance of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Heart: The NOS/NO System and Beyond
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Isolated and Perfused In Vitro Working Heart Preparations
2.3. Experimental Protocols
2.3.1. Basal Conditions
2.3.2. Drug Application
2.3.3. Drugs and Chemicals
2.4. Western Blot and Densitometric Analysis
2.5. cGMP Determination
2.6. Biotin Switch Assay for Protein s-nitrosylation Assessment
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Isolated Heart Preparations
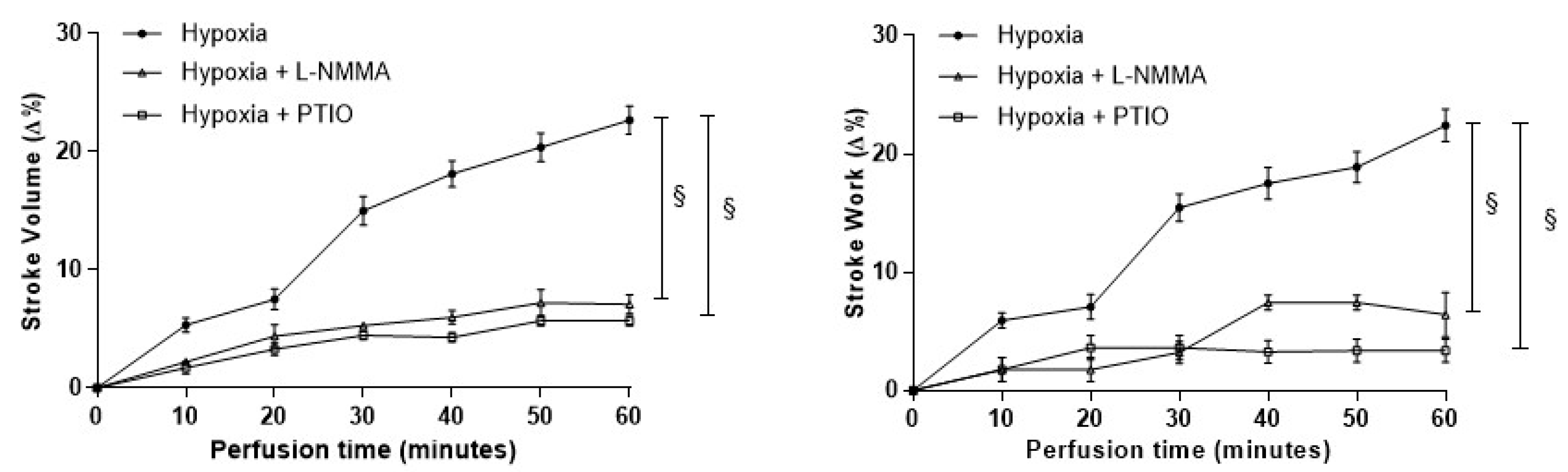
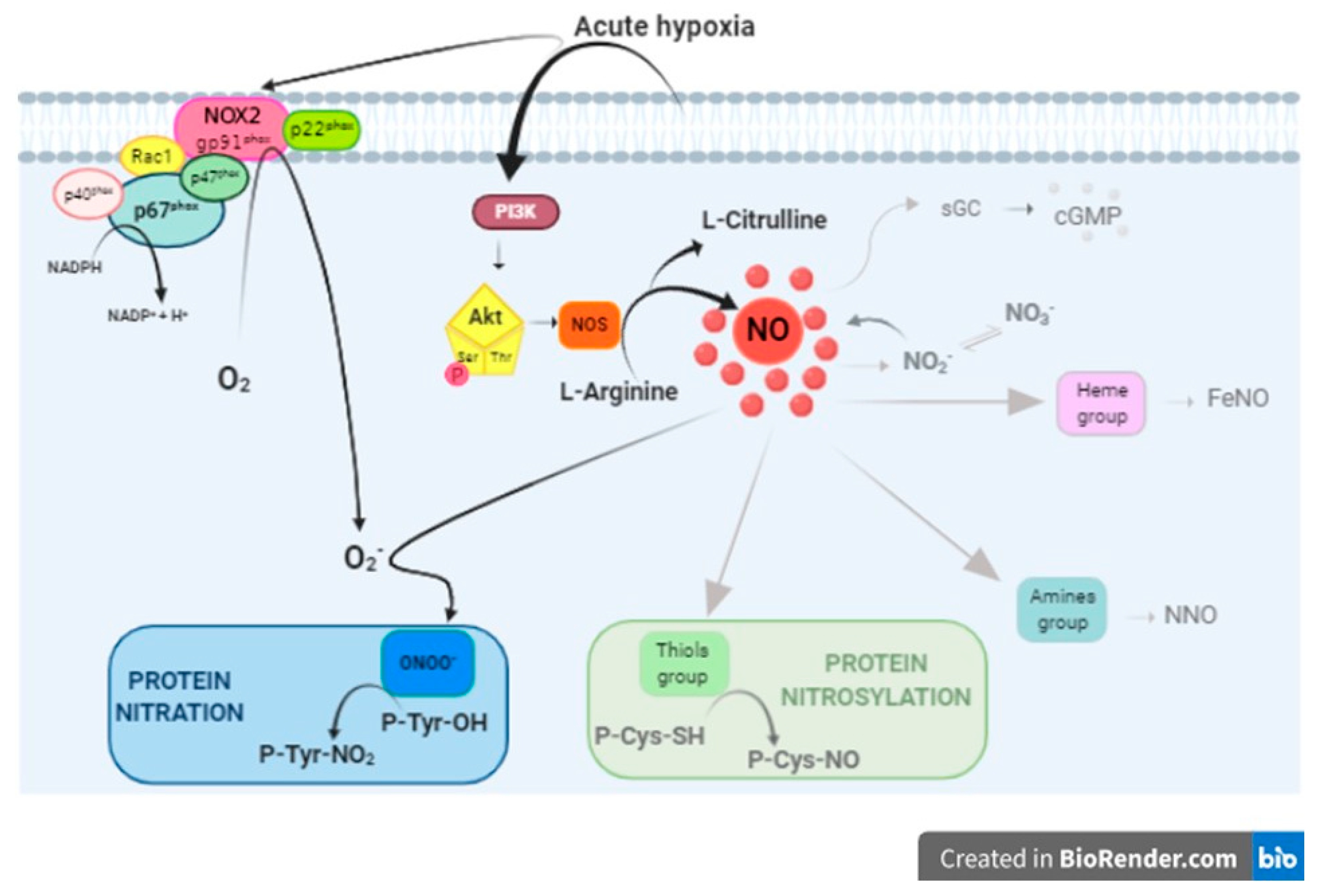
3.2. Role of the NOS/NO System in the Hypoxia-Induced Increase of Contractility
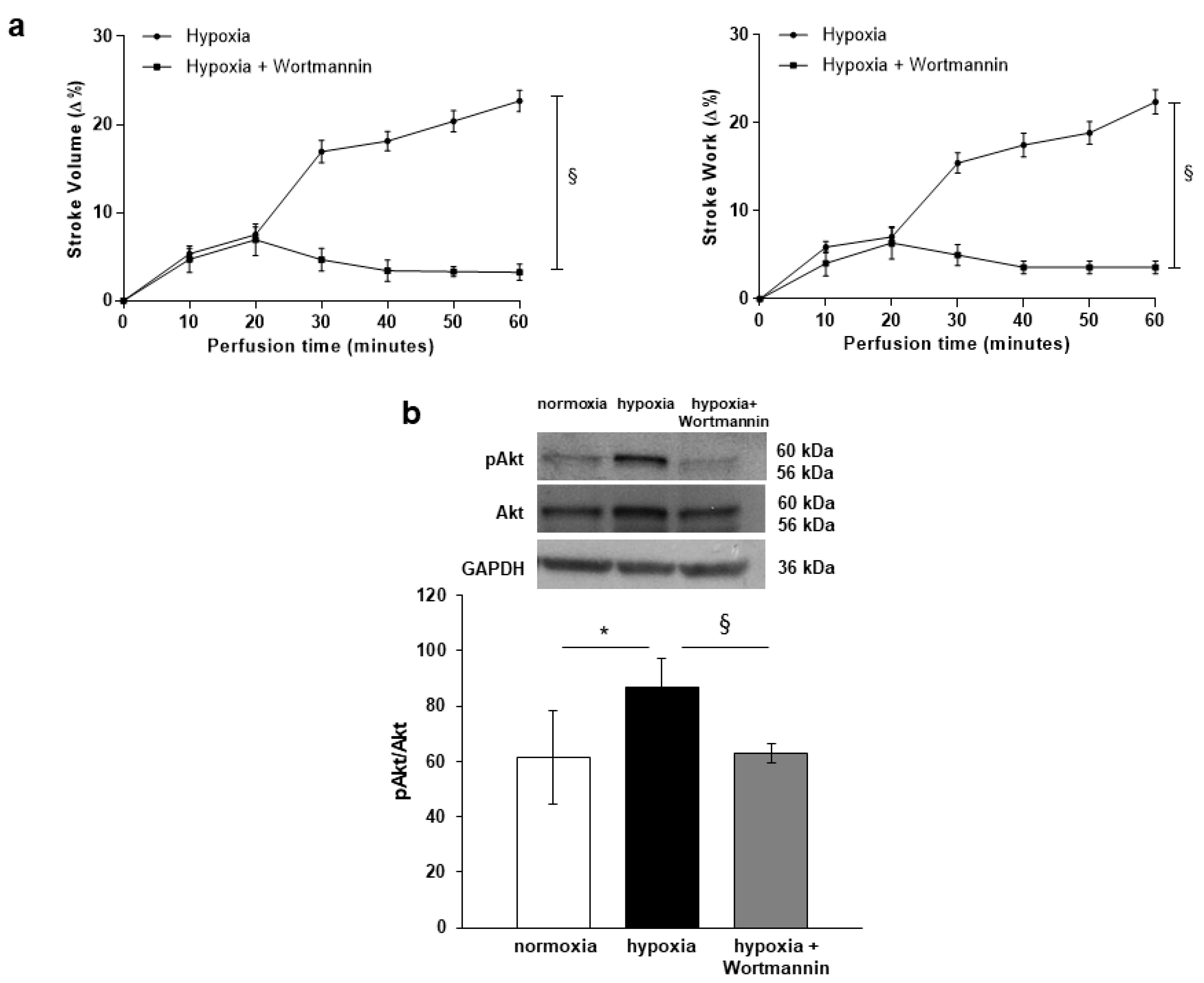
3.3. PI3-K/Akt-Dependent NOS Activation
3.4. NO Intracellular Signals
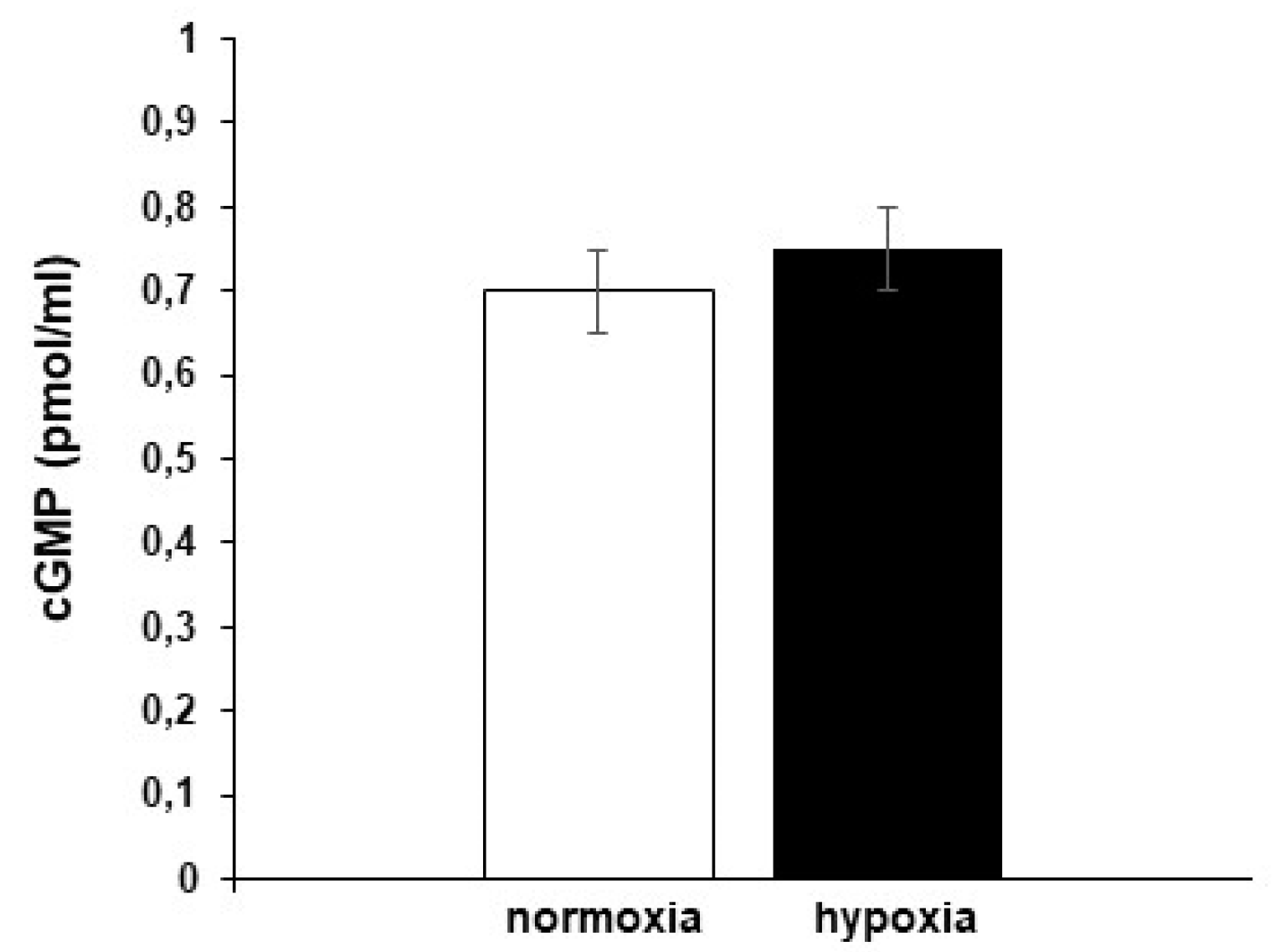
3.4.1. Role of cGMP
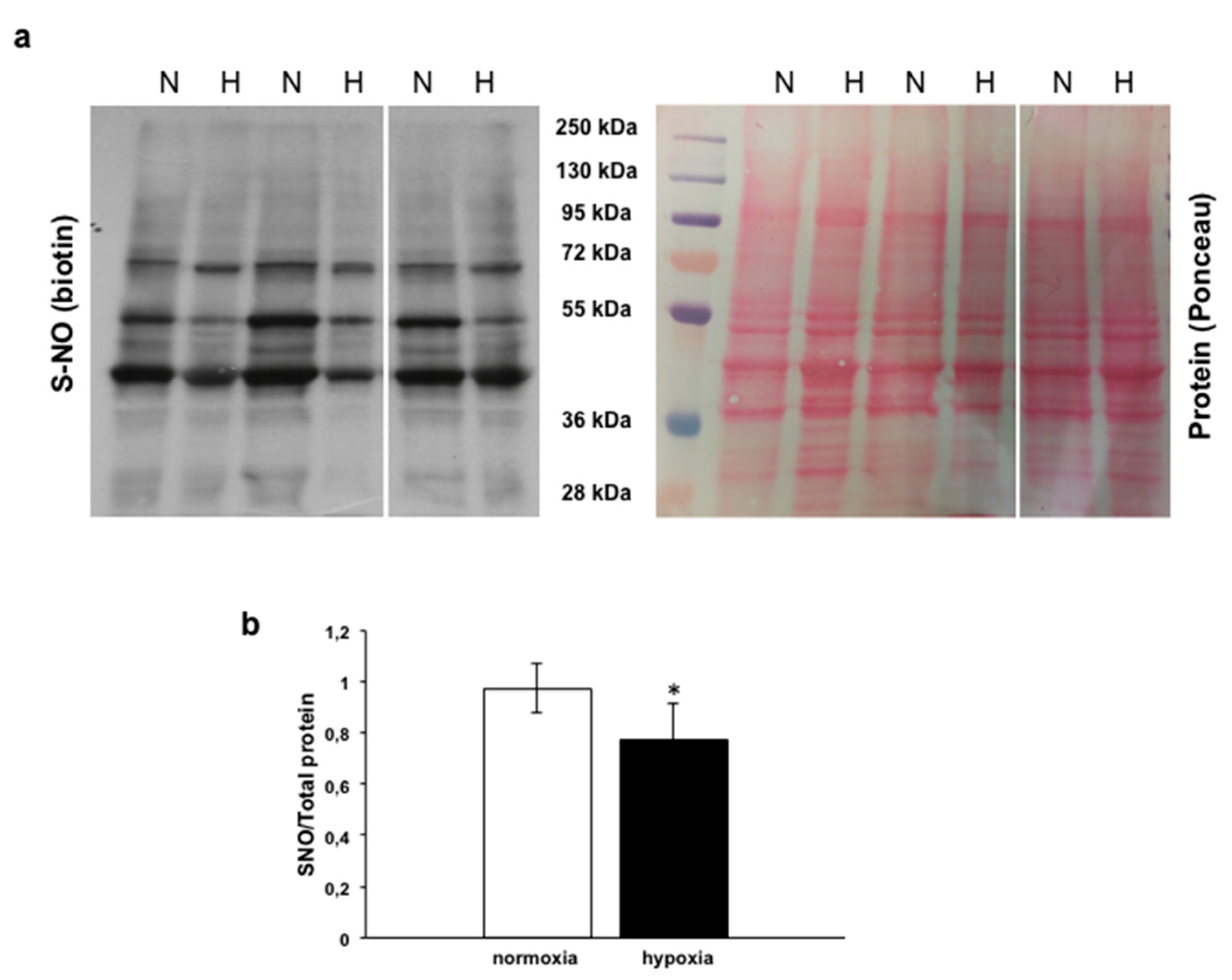
3.4.2. Analysis of s-nitrosylated Proteins
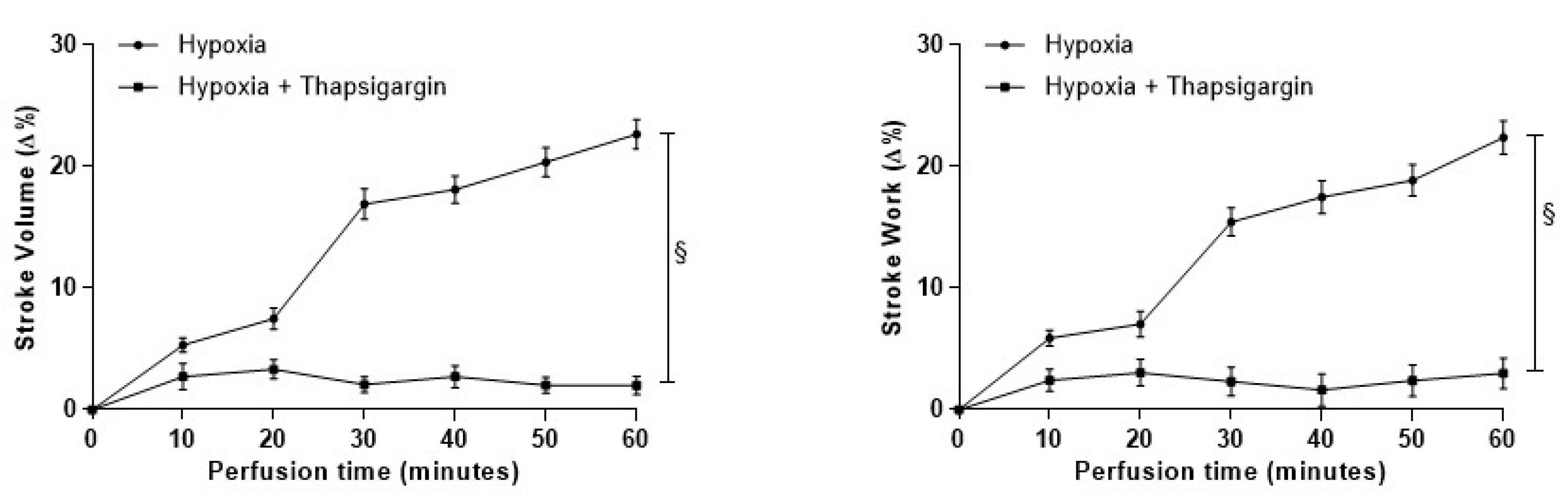
3.4.3. Role of SERCA2a Pumps
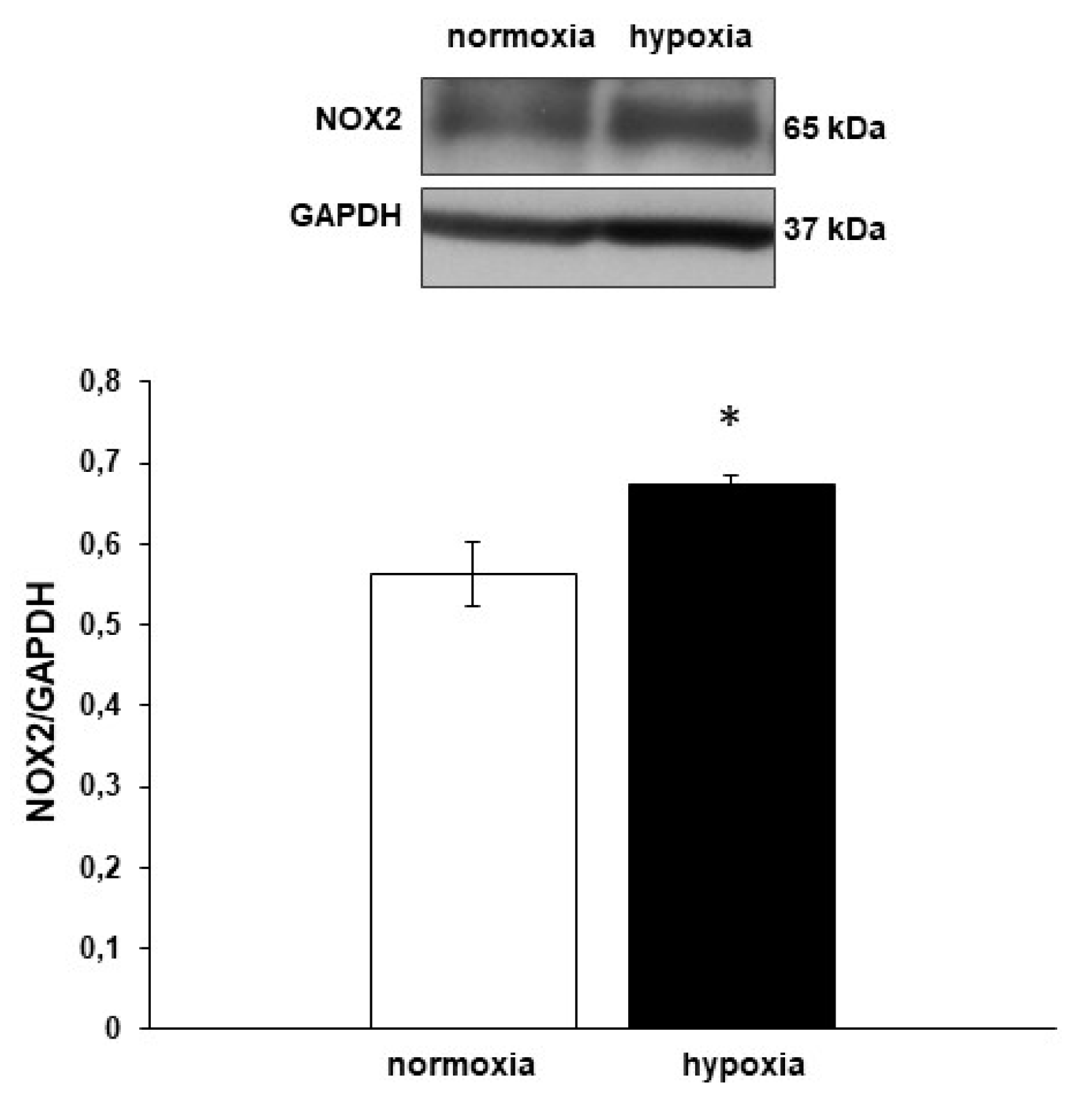
3.5. Nox2 Expression
4. Discussion
4.1. PI3-K/Akt/NOS/NO Pathway Activation
4.2. NO Downstream Effectors
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bograd, S.J.; Castro, C.G.; Lorenzo, E.D.; Palacios, D.M.; Bailey, H.; Gilly, W.; Chavez, F.P. oxygen declines and the shoaling of the hypoxic boundary in the california current. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, R.F.; Garcia, H.E. The change in oceanic O(2) inventory associated with recent global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7848–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitburg, D.; Levin, L.A.; Oschlies, A.; Gregoire, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Conley, D.J.; Garcon, V.; Gilbert, D.; Gutierrez, D.; Isensee, K.; et al. Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 2018, 359, eaam7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickler, P.E.; Buck, L.T. Hypoxia tolerance in reptiles, amphibians, and fishes: Life with variable oxygen availability. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedzic, W.R.; Gesser, H. Energy metabolism and contractility in ectothermic vertebrate hearts: Hypoxia, acidosis, and low temperature. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Aiello, D.; Filice, M.; Leo, S.; Mazza, R.; Cerra, M.C.; Napoli, A. MS-based proteomic analysis of cardiac response to hypoxia in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, S.; Gattuso, A.; Mazza, R.; Filice, M.; Cerra, M.C.; Imbrogno, S. Cardiac influence of the beta3-adrenoceptor in the goldfish (Carassius auratus): A protective role under hypoxia? J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecyk, J.A.; Stenslokken, K.O.; Farrell, A.P.; Nilsson, G.E. Maintained cardiac pumping in anoxic crucian carp. Science 2004, 306, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, A.; Garofalo, F.; Cerra, M.C.; Imbrogno, S. Hypoxia tolerance in teleosts: Implications of cardiac nitrosative signals. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.E. Surviving anoxia with the brain turned on. News Physiol. Sci. 2001, 16, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbrogno, S.; Capria, C.; Tota, B.; Jensen, F.B. Nitric oxide improves the hemodynamic performance of the hypoxic goldfish (Carassius auratus) heart. Nitric Oxide 2014, 42, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.N.; Jensen, F.B. Nitric oxide metabolites in goldfish under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, E.A.; Huang, L.; Malkey, R.; Govoni, M.; Nihlen, C.; Olsson, A.; Stensdotter, M.; Petersson, J.; Holm, L.; Weitzberg, E.; et al. A mammalian functional nitrate reductase that regulates nitrite and nitric oxide homeostasis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.G.; Dranka, B.P.; Bailey, S.M.; Lancaster, J.R., Jr.; Darley-Usmar, V.M. What part of NO don’t you understand? Some answers to the cardinal questions in nitric oxide biology. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19699–19704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronson, R.S.; Nakamura, M.; Vinten-Johansen, J. The cardiovascular effects and implications of peroxynitrite. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 44, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, T.A.; Da Silva, R.S.; Miranda, K.M.; Switzer, C.H.; Wink, D.A.; Fukuto, J.M. Biological nitric oxide signalling: Chemistry and terminology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Nitric oxide, oxidants, and protein tyrosine nitration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4003–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.W.; Liu, L.; Zeng, M.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. A genetic analysis of nitrosative stress. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Garofalo, F.; Amelio, D.; Capria, C.; Cerra, M.C. Humoral control of cardiac remodeling in fish: Role of Angiotensin II. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 194, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filice, M.; Amelio, D.; Garofalo, F.; David, S.; Fucarino, A.; Jensen, F.B.; Imbrogno, S.; Cerra, M.C. Angiotensin II dependent cardiac remodeling in the eel Anguilla anguilla involves the NOS/NO system. Nitric Oxide 2017, 65, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, F.; Parisella, M.L.; Amelio, D.; Tota, B.; Imbrogno, S. Phospholamban s-nitrosylation modulates Starling response in fish heart. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 4043–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbrogno, S.; Cerra, M.C. Hormonal and Autacoid Control of Cardiac Function. In Fish Physiology: The Cardiovascular System Morphology, Control and Function; Gamperl, A.K., Gillis, T.E., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press Publication: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 36, pp. 265–315. [Google Scholar]
- Amelio, D.; Garofalo, F.; Capria, C.; Tota, B.; Imbrogno, S. Effects of temperature on the nitric oxide-dependent modulation of the Frank-Starling mechanism: The fish heart as a case study. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Garofalo, F.; Cerra, M.C.; Mahata, S.K.; Tota, B. The catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin (chromogranin A344–363) modulates myocardial function in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tota, B.; Imbrogno, S.; Mannarino, C.; Mazza, R. Vasostatins and Negative Inotropy in Vertebrate Hearts. Curr. Med. Chem. Immunol. Endocr. Metab. Agents 2004, 4, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Mazza, R.; Pugliese, C.; Filice, M.; Angelone, T.; Loh, Y.P.; Tota, B.; Cerra, M.C. The Chromogranin A-derived sympathomimetic serpinin depresses myocardial performance in teleost and amphibian hearts. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 240, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Filice, M.; Cerra, M.C.; Gattuso, A. NO, CO and H2 S: What about gasotransmitters in fish and amphibian heart? Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2018, 223, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbrogno, S.; Filice, M.; Cerra, M.C. Exploring cardiac plasticity in teleost: The role of humoral modulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 283, 113236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvik, G.K.; Nilsson, G.E.; Jensen, F.B. Dramatic increase of nitrite levels in hearts of anoxia-exposed crucian carp supporting a role in cardioprotection. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R468–R477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hansen, M.N.; Lundberg, J.O.; Filice, M.; Fago, A.; Christensen, N.M.; Jensen, F.B. The roles of tissue nitrate reductase activity and myoglobin in securing nitric oxide availability in deeply hypoxic crucian carp. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, F.; Imbrogno, S.; Tota, B.; Amelio, D. Morpho-functional characterization of the goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) heart. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 163, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderman, S.L.; Harter, T.S.; Wilson, J.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Farrell, A.P.; Brauner, C.J. Evidence for a plasma-accessible carbonic anhydrase in the lumen of salmon heart that may enhance oxygen delivery to the myocardium. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadal, B. Hypoxia and the heart of poikilotherms. Curr. Res. Cardiol. 2014, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; Gattuso, A.; Filice, M.; Cantafio, P.; Cerra, M.C.; Angelone, T.; Imbrogno, S. Nesfatin-1 as a new positive inotrope in the goldfish (Carassius auratus) heart. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 224, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, J.X.; Wilson, I.; Cameron, J.S. Cardioprotective effects of K ATP channel activation during hypoxia in goldfish Carassius auratus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2765–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; Gattuso, A.; Imbrogno, S.; Boukhzar, L.; Leo, S.; Mallouki, B.Y.; Filice, M.; Rocca, C.; Angelone, T.; Anouar, Y.; et al. Selenoprotein T as a new positive inotrope in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb201202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelone, T.; Gattuso, A.; Imbrogno, S.; Mazza, R.; Tota, B. Nitrite is a positive modulator of the Frank-Starling response in the vertebrate heart. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R1271–R1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Imbrogno, S.; Angelone, T.; Adamo, C.; Pulera, E.; Tota, B.; Cerra, M.C. Beta3-adrenoceptor in the eel (Anguilla anguilla) heart: Negative inotropy and NO-cGMP-dependent mechanism. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 4966–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Angelone, T.; Corti, A.; Adamo, C.; Helle, K.B.; Tota, B. Influence of vasostatins, the chromogranin A-derived peptides, on the working heart of the eel (Anguilla anguilla): Negative inotropy and mechanism of action. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 139, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrogno, S.; Cerra, M.C.; Tota, B. Angiotensin II-induced inotropism requires an endocardial endothelium-nitric oxide mechanism in the in-vitro heart of Anguilla anguilla. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbrogno, S.; De Iuri, L.; Mazza, R.; Tota, B. Nitric oxide modulates cardiac performance in the heart of Anguilla anguilla. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossi-George, A.; Gow, A.J. Immunofluorescent detection of s-nitrosoproteins in cell culture. Methods 2013, 62, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei, B.; Sears, C.E. Nitric-oxide-mediated regulation of cardiac contractility and stretch responses. Prog. Biophys Mol. Biol. 2003, 82, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massion, P.B.; Pelat, M.; Belge, C.; Balligand, J.L. Regulation of the mammalian heart function by nitric oxide. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 142, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, C.E.; Bryant, S.M.; Ashley, E.A.; Lygate, C.A.; Rakovic, S.; Wallis, H.L.; Neubauer, S.; Terrar, D.A.; Casadei, B. Cardiac neuronal nitric oxide synthase isoform regulates myocardial contraction and calcium handling. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, e52–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, R.P.; Weissmann, N.; Schroder, K. NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 687–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fago, A.; Jensen, F.B. Hypoxia tolerance, nitric oxide, and nitrite: Lessons from extreme animals. Physiology (Beth.) 2015, 30, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota, B.; Angelone, T.; Mancardi, D.; Cerra, M.C. Hypoxia and anoxia tolerance of vertebrate hearts: An evolutionary perspective. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Gao, F.; Ma, X.L. Insulin says NO to cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, C.; Scavello, F.; Granieri, M.C.; Pasqua, T.; Amodio, N.; Imbrogno, S.; Gattuso, A.; Mazza, R.; Cerra, M.C.; Angelone, T. Phoenixin-14: Detection and novel physiological implications in cardiac modulation and cardioprotection. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Sepulveda, M.A.; Ceravolo, G.S.; Fortes, Z.B.; Carvalho, M.H.; Tostes, R.C.; Laurindo, F.R.; Webb, R.C.; Barreto-Chaves, M.L. Thyroid hormone stimulates NO production via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in vascular myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaanine, A.H.; Hajjar, R.J. AKT signalling in the failing heart. Eur. J. Heart Fail 2011, 13, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Li, L.; Del Monte, F.; Fukui, Y.; Franke, T.F.; Hajjar, R.J.; Rosenzweig, A. Adenoviral gene transfer of activated phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase and Akt inhibits apoptosis of hypoxic cardiomyocytes in vitro. Circulation 1999, 100, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; Angelone, T.; Pasqua, T.; Gattuso, A. Physiological evidence for beta3-adrenoceptor in frog (Rana esculenta) heart. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 169, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; Mannarino, C.; Imbrogno, S.; Barbieri, S.F.; Adamo, C.; Angelone, T.; Corti, A.; Tota, B. Crucial role of cytoskeleton reorganization in the negative inotropic effect of chromogranin A-derived peptides in eel and frog hearts. Regul. Pept. 2007, 138, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; Pasqua, T.; Cerra, M.C.; Angelone, T.; Gattuso, A. Akt/eNOS signaling and PLN S-sulfhydration are involved in H(2)S-dependent cardiac effects in frog and rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R443–R451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, C.; Boukhzar, L.; Granieri, M.C.; Alsharif, I.; Mazza, R.; Lefranc, B.; Tota, B.; Leprince, J.; Cerra, M.C.; Anouar, Y.; et al. A selenoprotein T-derived peptide protects the heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury through inhibition of apoptosis and oxidative stress. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2018, 223, e13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kim, S.O.; Marshall, H.E.; Stamler, J.S. Protein s-nitrosylation: Purview and parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerra, M.C.; Angelone, T.; Parisella, M.L.; Pellegrino, D.; Tota, B. Nitrite modulates contractility of teleost (Anguilla anguilla and Chionodraco hamatus, i.e. the Antarctic hemoglobinless icefish) and frog (Rana esculenta) hearts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1787, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rizza, S.; Giglio, P.; Faienza, F.; Filomeni, G. Therapeutic aspects of protein denitrosylation. In Therapeutic Application of Nitric Oxide in Cancer and Inflammatory Disorders; Morbidelli, L., Bonavida, B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 173–189. [Google Scholar]
- Durham, W.J.; Aracena-Parks, P.; Long, C.; Rossi, A.E.; Goonasekera, S.A.; Boncompagni, S.; Galvan, D.L.; Gilman, C.P.; Baker, M.R.; Shirokova, N.; et al. RyR1 S-nitrosylation underlies environmental heat stroke and sudden death in Y522S RyR1 knockin mice. Cell 2008, 133, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Yao, D.; Shi, Z.Q.; Gu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Masliah, E.; Nomura, Y.; Lipton, S.A. S-nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 441, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sips, P.Y.; Irie, T.; Zou, L.; Shinozaki, S.; Sakai, M.; Shimizu, N.; Nguyen, R.; Stamler, J.S.; Chao, W.; Kaneki, M.; et al. Reduction of cardiomyocyte s-nitrosylation by s-nitrosoglutathione reductase protects against sepsis-induced myocardial depression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H1134–H1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartesaghi, S.; Romero, N.; Radi, R. Nitric oxide and derived oxidants. In Principiles of Free Radical Biomedicine; Pantapoulos, K., Shipper, H.M., Eds.; Nova Science Publisher Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ischiropoulos, H. Biological selectivity and functional aspects of protein tyrosine nitration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, D.J. Nitrotyrosine-modified SERCA2: A cellular sensor of reactive nitrogen species. Pflugers Arch. 2009, 457, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batthyany, C.; Bartesaghi, S.; Mastrogiovanni, M.; Lima, A.; Demicheli, V.; Radi, R. Tyrosine-nitrated proteins: Proteomic and bioanalytical aspects. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, R. Protein tyrosine nitration: Biochemical mechanisms and structural basis of functional effects. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerra, M.C.; Imbrogno, S. Phospholamban and cardiac function: A comparative perspective in vertebrates. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2012, 205, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyshev, I.Y.; Aymasheva, N.P.; Malenyuk, E.B.; Manukhina, E.B.; Khaspekov, G.L.; Mikoyan, V.D.; Kubrina, L.N.; Vanin, A.F. Nitric oxide increases gene expression of Ca(2+)-ATPase in myocardial and skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: Physiological implications. Med. Sci. Monit. 2000, 6, 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Viner, R.I.; Ferrington, D.A.; Williams, T.D.; Bigelow, D.J.; Schoneich, C. Protein modification during biological aging: Selective tyrosine nitration of the SERCA2a isoform of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in skeletal muscle. Biochem. J. 1999, 340, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Weisbrod, R.M.; Pimentel, D.R.; Ying, J.; Sharov, V.S.; Schoneich, C.; Cohen, R.A. S-Glutathiolation by peroxynitrite activates SERCA during arterial relaxation by nitric oxide. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misquitta, C.M.; Mack, D.P.; Grover, A.K. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ (SERCA)-pumps: Link to heart beats and calcium waves. Cell. Calcium. 1999, 25, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, M.; Huke, S. SERCA pump level is a critical determinant of Ca(2+)homeostasis and cardiac contractility. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periasamy, M.; Kalyanasundaram, A. SERCA pump isoforms: Their role in calcium transport and disease. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, K.; Kranias, E.G. Phospholamban and cardiac contractility. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.H.; Kranias, E.G. Phospholamban: A crucial regulator of cardiac contractility. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 4, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.L.; Hamstra, S.I.; Messner, H.N.; Fajardo, V.A. SERCA2a tyrosine nitration coincides with impairments in maximal SERCA activity in left ventricles from tafazzin-deficient mice. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viner, R.I.; Ferrington, D.A.; Huhmer, A.F.; Bigelow, D.J.; Schoneich, C. Accumulation of nitrotyrosine on the SERCA2a isoform of SR Ca-ATPase of rat skeletal muscle during aging: A peroxynitrite-mediated process? FEBS Lett. 1996, 379, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, E. Mitochondrial free radical production and cell signaling. Mol. Aspects Med. 2004, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, F.; Gonzalez, D.R.; Minhas, K.M.; Sun, Q.A.; Foster, M.W.; Khan, S.A.; Treuer, A.V.; Dulce, R.A.; Harrison, R.W.; Saraiva, R.M.; et al. Dynamic denitrosylation via S-nitrosoglutathione reductase regulates cardiovascular function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4314–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.Y.; Huso, D.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Bredt, D.S.; Becker, L.C. Nitric oxide synthase in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balligand, J.L.; Kobzik, L.; Han, X.; Kaye, D.M.; Belhassen, L.; O’Hara, D.S.; Kelly, R.A.; Smith, T.W.; Michel, T. Nitric oxide-dependent parasympathetic signaling is due to activation of constitutive endothelial (type III) nitric oxide synthase in cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14582–14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbrogno, S.; Tota, B.; Gattuso, A. The evolutionary functions of cardiac NOS/NO in vertebrates tracked by fish and amphibian paradigms. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, D.; Garofalo, F.; Brunelli, E.; Loong, A.M.; Wong, W.P.; Ip, Y.K.; Tota, B.; Cerra, M.C. Differential NOS expression in freshwater and aestivating Protopterus dolloi (lungfish): Heart vs kidney readjustments. Nitric Oxide 2008, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, D.; Garofalo, F.; Pellegrino, D.; Giordano, F.; Tota, B.; Cerra, M.C. Cardiac expression and distribution of nitric oxide synthases in the ventricle of the cold-adapted Antarctic teleosts, the hemoglobinless Chionodraco hamatus and the red-blooded Trematomus bernacchii. Nitric Oxide 2006, 15, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakis, N.; D’Aniello, S.; Albalat, R.; Patti, F.P.; Garcia-Fernandez, J.; Procaccini, G.; Sordino, P.; Palumbo, A. Evolution of the nitric oxide synthase family in metazoans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cardiac Parameters | CO (mL min−1 kg−1) | SV (mL kg−1) | HR (Beats min−1) | SW (mJ g−1) | Preload (kPa) | Afterload (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normoxia | 13.531 ± 0.379 | 0.186 ± 0.016 | 76.333 ± 5.459 | 0.235 ± 0.020 | 0.073 ± 0.002 | 1.413 ± 0.018 |
| Hypoxia | 13.777 ± 0.479 | 0.194 ± 0.017 | 76.769 ± 6.299 | 0.288 ± 0.032 | 0.064 ± 0.006 | 1.434 ± 0.031 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filice, M.; Mazza, R.; Leo, S.; Gattuso, A.; Cerra, M.C.; Imbrogno, S. The Hypoxia Tolerance of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Heart: The NOS/NO System and Beyond. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060555
Filice M, Mazza R, Leo S, Gattuso A, Cerra MC, Imbrogno S. The Hypoxia Tolerance of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Heart: The NOS/NO System and Beyond. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(6):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060555
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilice, Mariacristina, Rosa Mazza, Serena Leo, Alfonsina Gattuso, Maria Carmela Cerra, and Sandra Imbrogno. 2020. "The Hypoxia Tolerance of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Heart: The NOS/NO System and Beyond" Antioxidants 9, no. 6: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060555
APA StyleFilice, M., Mazza, R., Leo, S., Gattuso, A., Cerra, M. C., & Imbrogno, S. (2020). The Hypoxia Tolerance of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Heart: The NOS/NO System and Beyond. Antioxidants, 9(6), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060555







