Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Extraction and Fractionation
2.3.2. Isolation of Compounds
2.3.3. In vitro Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibitory Assay
2.3.4. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.3.5. ONOO− Radical Scavenging Assay
2.3.6. ABTS•+ Radical Scavenging Assay
2.3.7. Kinetic Parameters of Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition
2.3.8. Mushroom Tyrosinase Molecular Docking Simulation
2.3.9. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
2.3.10. Melanin Content Assay
2.3.11. Cellular TYR Activity Assay
2.3.12. Determination of the Intracellular ROS Level
2.3.13. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inhibitory Activities of Compounds Isolated from E. stolonifera against Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.2. Radical Scavenging Activities of Compounds Isolated from E. stolonifera
3.3. Enzyme Kinetic Analysis of Compounds Isolated from E. stolonifera against Mushroom Tyrosinase
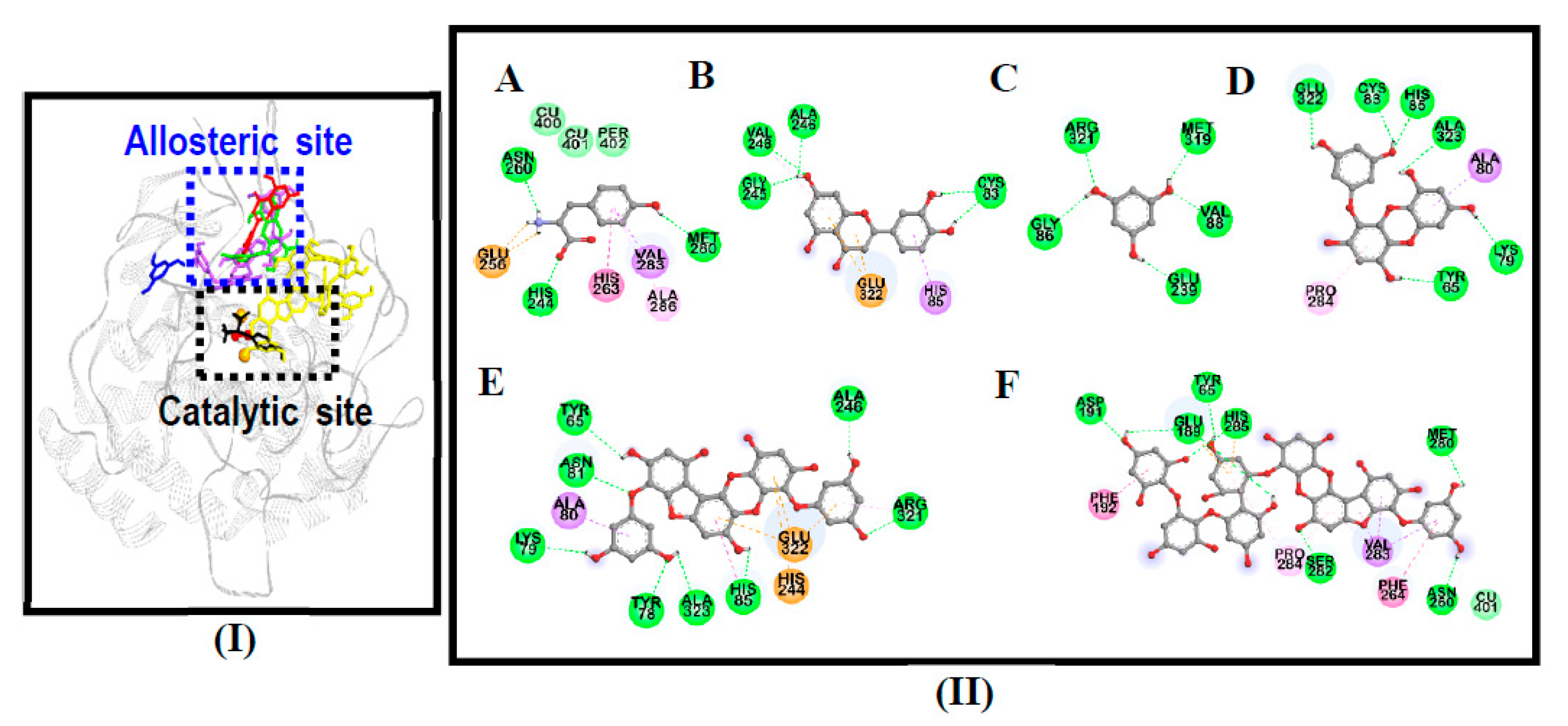
3.4. Molecular Docking Simulation on Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.5. Effect on Cell Viability
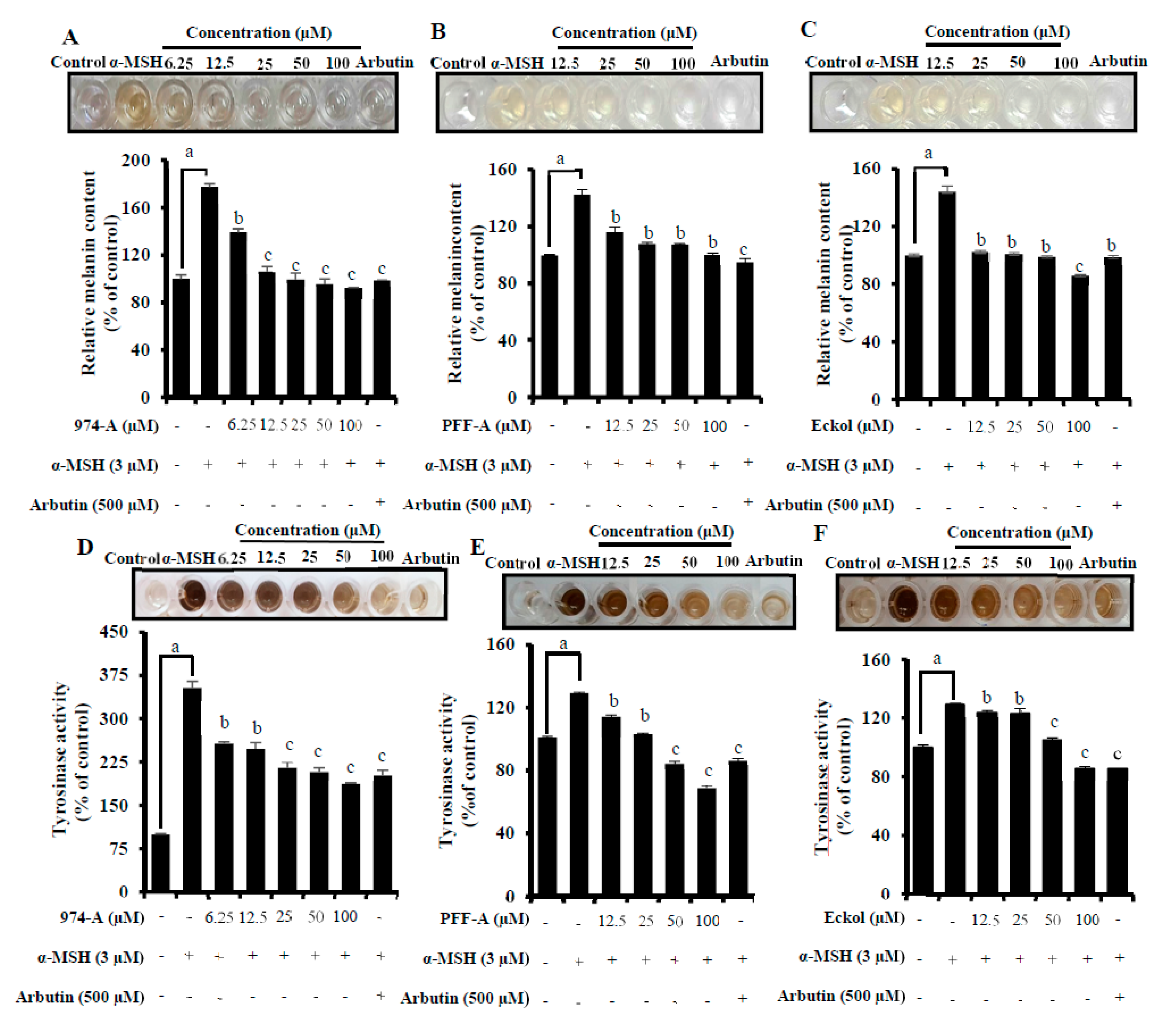
3.6. Effect on α-MSH-Induced Melanin Synthesis and Cellular TYR Activity
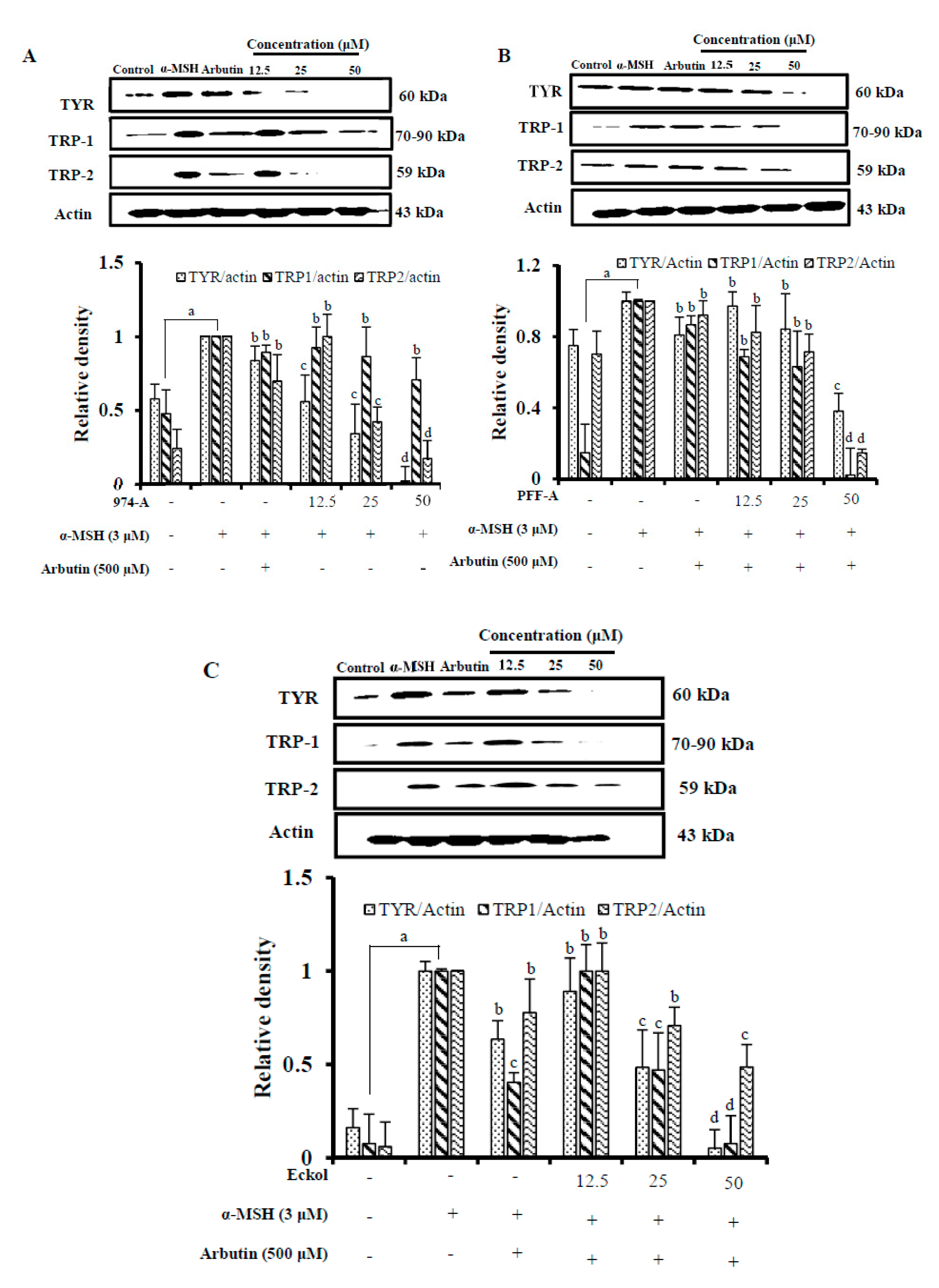
3.7. Effect on the Expression of Melanogenic Enzymes
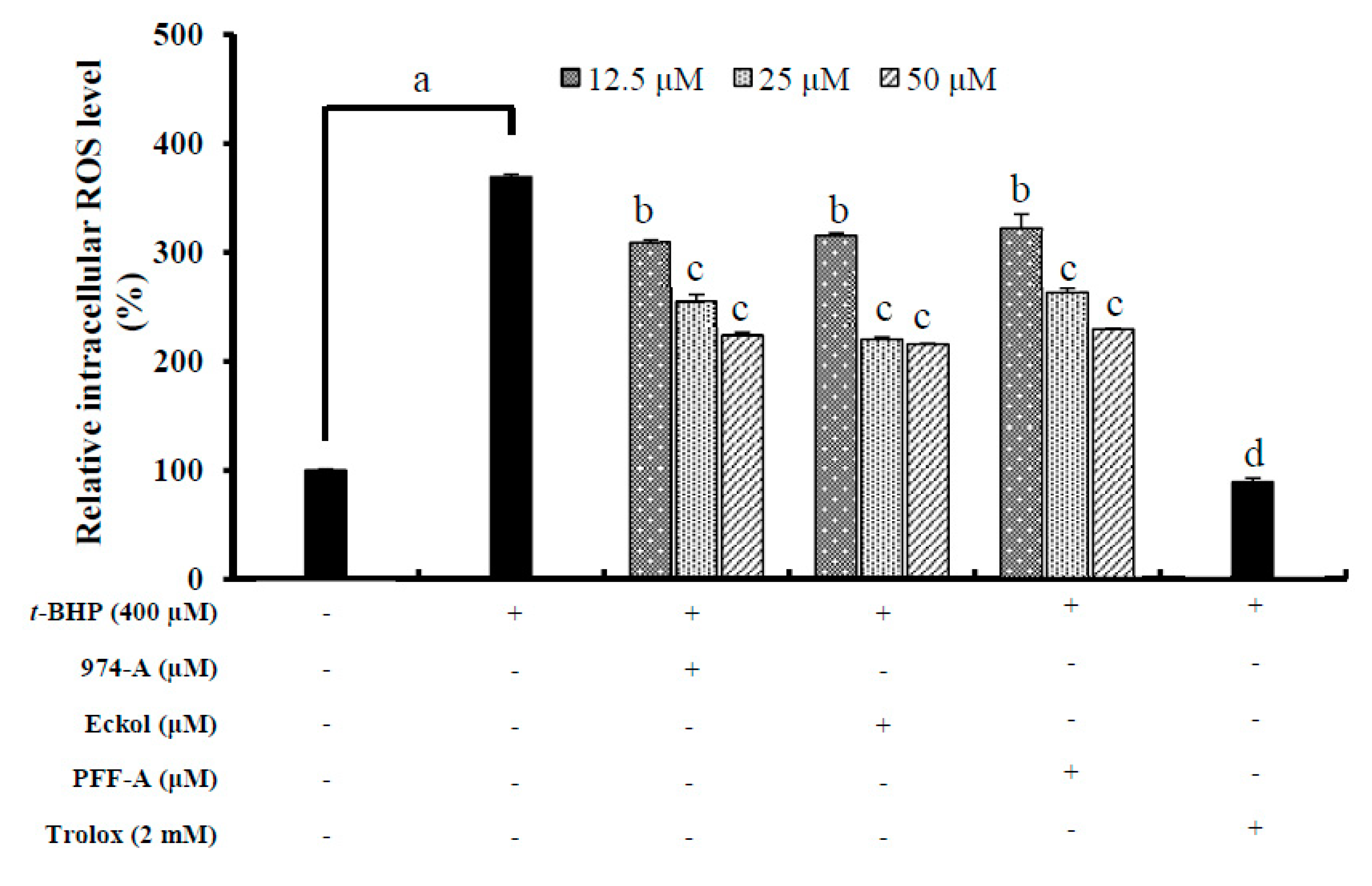
3.8. Effect on the Intracellular ROS Level
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyamura, Y.; Coelho, S.G.; Wolber, R.; Miller, S.A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Zmudzka, B.Z.; Ito, S.; Smuda, C.; Passeron, T.; Batzer, J. Regulation of human skin pigmentation and responses to ultraviolet radiation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2007, 20, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaban, R.; Patton, R.S.; Cheng, E.; Svedine, S.; Trombetta, E.S.; Wahl, M.L.; Ariyan, S.; Hebert, D.N. Abnormal acidification of melanoma cells induces tyrosinase retention in the early secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14821–14828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, I.F.D.S.; Moura, D.F.L.; Magina, S. Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Jackson, I.J.; Urabe, K.; Montague, P.M.; Hearing, V.J. A second tyrosinase-related protein, TRP-2, is a melanogenic enzyme termed DOPAchrome tautomerase. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Camarillo, C.; Arechaga Ocampo, E.; Lopez Casamichana, M.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, E.; Marchat, L.A. Protein kinases and transcription factors activation in response to UV-radiation of skin: Implications for carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 142–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, N.; Yoon, K.N.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, T.S. Consequence of the antioxidant activities and tyrosinase inhibitory effects of various extracts from the fruiting bodies of Pleurotus ferulae. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Son, B.W.; Choi, J.S. A new phlorotannin from the brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Hwang, E.K.; Lee, S.J.; Roh, K.W.; Sohn, C.H. Age and growth of Ecklonia stolonifera Okamura in Pusan bay, Korea. Korean J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1994, 27, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.R.; Shin, T.S.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.E.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jang, B.C.; Byun, D.S.; et al. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, N.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, J.E. Acetyl-and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of sterols and phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.E.; Islam, M.N.; Ahn, B.R.; Chowdhury, S.S.; Sohn, H.S.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and α-glucosidase inhibitory phlorotannins from edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.A.; Hyun, S.K.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, J.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme I inhibitory activity of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Shin, T.; Utsuki, T.; Choi, J.S.; Byun, D.S.; Kim, H.R. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties in tacrine-treated HepG2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5340–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, S.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.K. Antimicrobial effect of phlorotannins from marine brown algae. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3251–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, M.J.; Kim, S.N.; Choi, H.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Park, G.M.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, Y.K. The inhibitory effects of eckol and dieckol from Ecklonia stolonifera on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human dermal fibroblasts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, H.R.; Byun, D.S.; Son, B.W.; Nam, T.J.; Choi, J.S. Tyrosinase inhibitors isolated from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Kondo, S.; Segawa, S.; Lin, Y.C.; Toyohara, H.; Ito, H.; Konoki, K.; Cho, Y.; Uchida, T. Isolation and structural determination of two novel phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome Okamura, and their radical scavenging activities. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooy, N.W.; Royall, J.A.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Beckman, J.S. Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish-Bowden, A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem. J. 1974, 137, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, A.; Seong, S.H.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Identifying an isoflavone from the root of Pueraria lobata as a potent tyrosinase inhibitor. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Tzanakakis, G.; Kim, H.S.; Le, B.; Sifaki, M.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsukamoto, C.; Chung, G. Soyasaponin Ag inhibits α MSH induced melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells via the downregulation of TRP 2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Lim, S.J.; Lee, B.; Shin, T.; Kim, H.R. Ethanolic extract of Sargassum serratifolium inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by cell cycle arrest. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y. Slow-binding inhibition of tyrosinase by Ecklonia cava phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Sun, M.; Xing, J.; Luo, Q.; Corke, H. Structure–radical scavenging activity relationships of phenolic compounds from traditional Chinese medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2872–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoll, L.G.; Rodríguez-López, J.N.; Varón, R.; García-Ruiz, P.A.; García-Cánovas, F.; Tudela, J. Action mechanism of tyrosinase on meta-and para-hydroxylated monophenols. Biol. Chem. 2000, 381, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.; Todd, C.; Cresswell, J.E.; Thody, A.J. Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone and its analogue Nle4DPhe7 alpha-MSH affect morphology, tyrosinase activity and melanogenesis in cultured human melanocytes. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, S.M.; Sok, C.H.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Cellular activities and docking studies of eckol isolated from Ecklonia cava (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) as potential tyrosinase inhibitor. Algae 2015, 30, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, N.Y.; Eom, T.K.; Kim, M.M.; Kim, S.K. Inhibitory effect of phlorotannins isolated from Ecklonia cava on mushroom tyrosinase activity and melanin formation in mouse B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4124–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Ko, S.C.; Cha, S.H.; Kang, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Choi, Y.U.; Kim, D.; Jung, W.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Effect of phlorotannins isolated from Ecklonia cava on melanogenesis and their protective effect against photo-oxidative stress induced by UV-B radiation. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.M.; Dizdaroglu, M; Cooke, S.M. Oxidative DNA damage and disease: Induction, repair and significance. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2004, 567, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denat, L.; Kadekaro, L.A.; Marrot, L.; Leachman, A.S.; Abdel-Malek, A.Z. Melanocytes as instigators and victims of oxidative stress. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
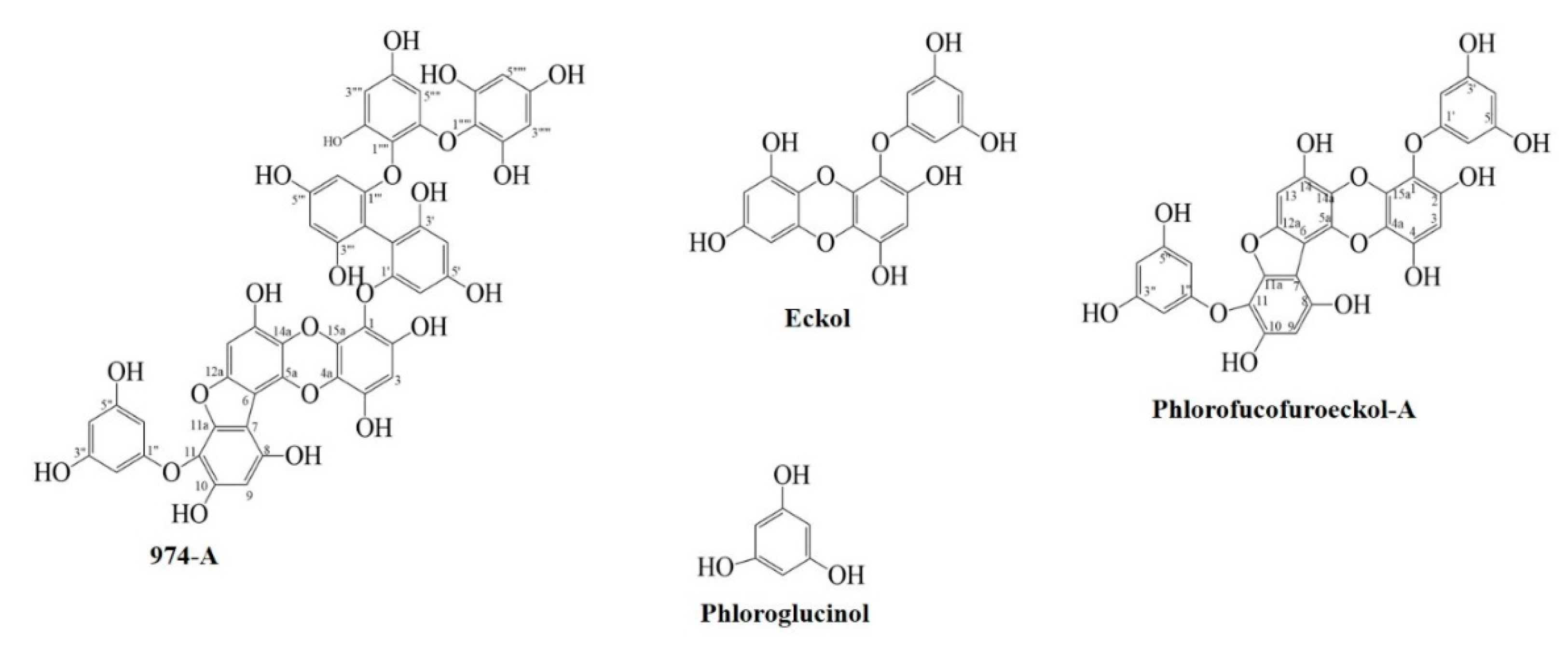
| Compounds | IC50 Value (µM, Mean ± SD) 1 | Type of inhibition 2, Ki Value 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition | Radical Scavenging Activity | ||||||
| l-Tyrosine | l-DOPA | ONOO− | DPPH | ABTS•+ | l-Tyrosine | l-DOPA | |
| 974-A | 1.57 ± 0.08 | 3.56 ± 0.22 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.11 | 6.29 ± 0.34 | Competitive, 0.69 | Competitive, 3.33 |
| Phlorofucofuroeckol-A | 3.42 ± 0.01 | 8.14 ± 0.29 | 0.85 ± 0.10 | 1.92 ± 0.09 | 12.87 ± 0.95 | Non-competitive, 2.70 | Non-competitive, 7.14 |
| Eckol | 9.12 ± 0.36 | 29.59 ± 0.48 | 0.73 ± 0.07 | 1.63 ± 0.65 | 5.01 ± 0.19 | Non-competitive, 8.60 | Non-competitive, 28.47 |
| Phloroglucinol | 251.00 ± 5.52 | >400 | 1.72 ± 0.59 | >100 | 31.48 ± 1.68 | - | - |
| Arbutin 4 | 172.82 ± 4.70 | >500 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kojic acid 4 | 7.82 ± 0.70 | 9.35 ± 0.70 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Penicillamine 4 | - | - | 1.07 ± 0.21 | - | - | - | - |
| Ascorbic acid 4 | - | - | - | 0.69 ± 0.04 | - | - | - |
| Trolox 4 | - | - | - | - | 18.40 ± 0.70 | - | - |
| Compounds | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | No. of H-Bonds | H-Bond Interaction Residues | Hydrophobic Interacting Residues | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 974-A | −3.92 | 8 | Asp191, Ser282, His285, Met280, Asn260, Glu189, Tyr65 | Pi-Sigma: Val283, Pi-Pi T-shaped: Phe192, Phe264, Pi-Alkyl: Pro284, Val283, Pro284 | Electrostatic bond: His285, Glu189, van der Waals: Cu401 |
| Phlorofucofuroeckol-A | −8.79 | 8 | Tyr78, Asn81, Arg321, Ala246, His85, Lys79, Ala323, Tyr65 | Pi-Sigma: Ala80, Pi-Pi T-shaped: His85, Pi-Alkyl: Arg321 | Electrostatic bond: His244, Glu322 |
| Eckol | −6.29 | 6 | His85, Cys83, Glu322, Tyr65, Ala323, Lys79 | Pi-Sigma: Ala80, Pi-Alkyl: Pro284 | - |
| Phloroglucinol | −4.87 | 5 | Arg321, Gly86, Glu239, Val88, Met319 | - | - |
| l-Tyrosine 1 | −6.31 | 5 | His244, Asn260, Met280, Glu256 (Salt-bridge) | Pi-Alkyl: Ala286, Pi-Sigma: Val283, Pi-Pi Stacked: His263 | van der Waals: Cu401, Cu400, Per402 |
| Luteolin 1 | −6.19 | 4 | Cys83, Gly245, Ala246, Val248 | Pi-Alkyl: Val248, Pi-Sigma: His85 | Electrostatic bond: Glu322 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manandhar, B.; Wagle, A.; Seong, S.H.; Paudel, P.; Kim, H.-R.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080240
Manandhar B, Wagle A, Seong SH, Paudel P, Kim H-R, Jung HA, Choi JS. Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(8):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080240
Chicago/Turabian StyleManandhar, Bandana, Aditi Wagle, Su Hui Seong, Pradeep Paudel, Hyeung-Rak Kim, Hyun Ah Jung, and Jae Sue Choi. 2019. "Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera" Antioxidants 8, no. 8: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080240
APA StyleManandhar, B., Wagle, A., Seong, S. H., Paudel, P., Kim, H.-R., Jung, H. A., & Choi, J. S. (2019). Phlorotannins with Potential Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Activity Isolated from the Marine Seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera. Antioxidants, 8(8), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8080240







