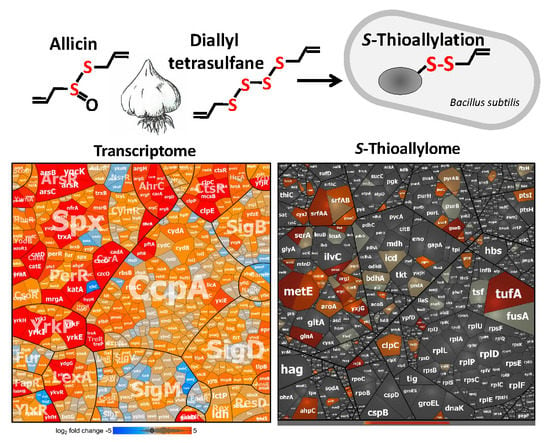
The Disulfide Stress Response and Protein S-thioallylation Caused by Allicin and Diallyl Polysulfanes in Bacillus subtilis as Revealed by Transcriptomics and Proteomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Identification of S-Thioallylated Proteins Using LTQ-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Microarray Transcriptome Analysis
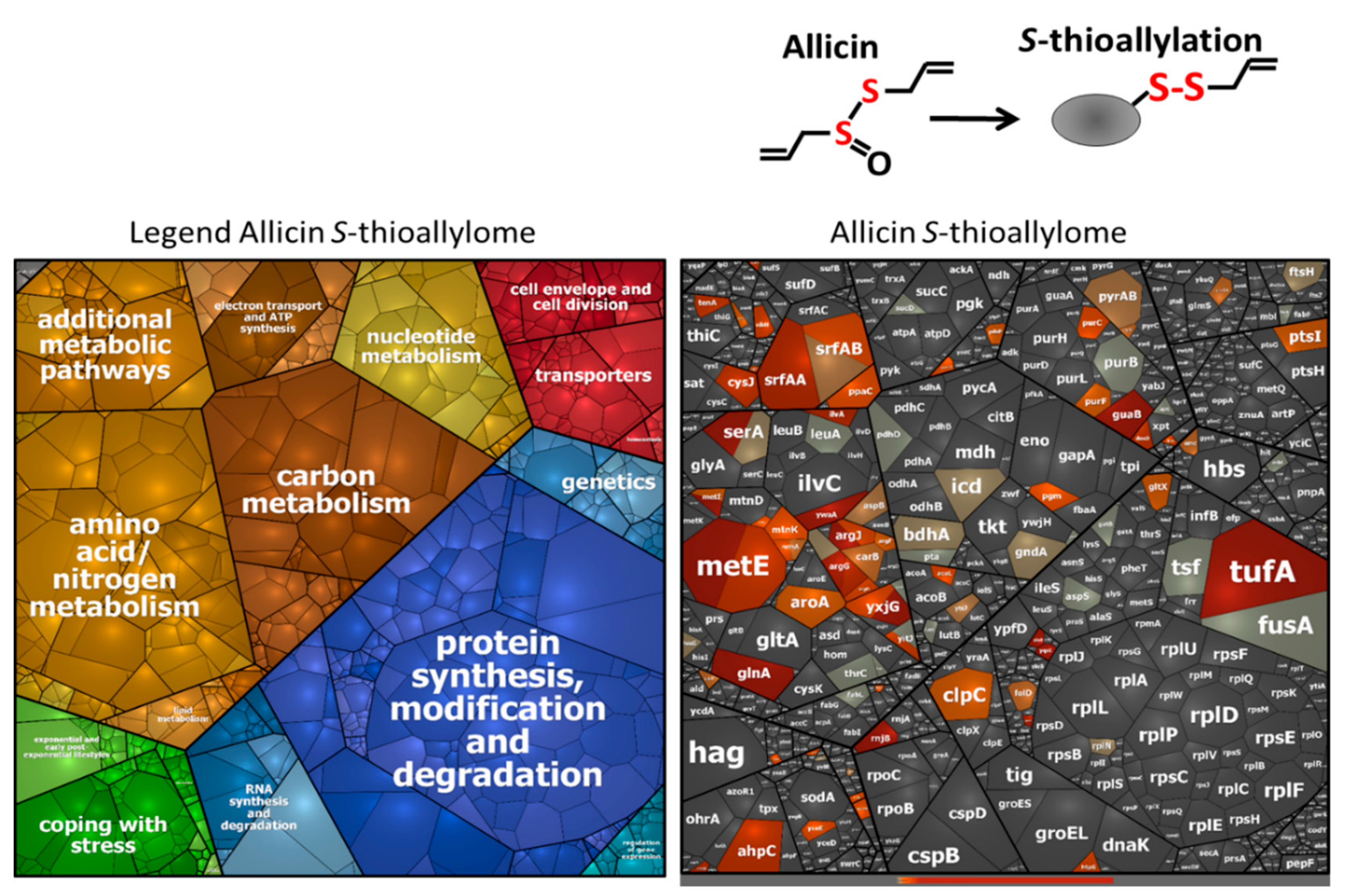
2.4. Construction of the Voronoi Transcriptome Treemap
2.5. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and Non-Reducing SDS-PAGE Analysis of OhrR-FLAG, HypR, YodB, and CatR Proteins
3. Results
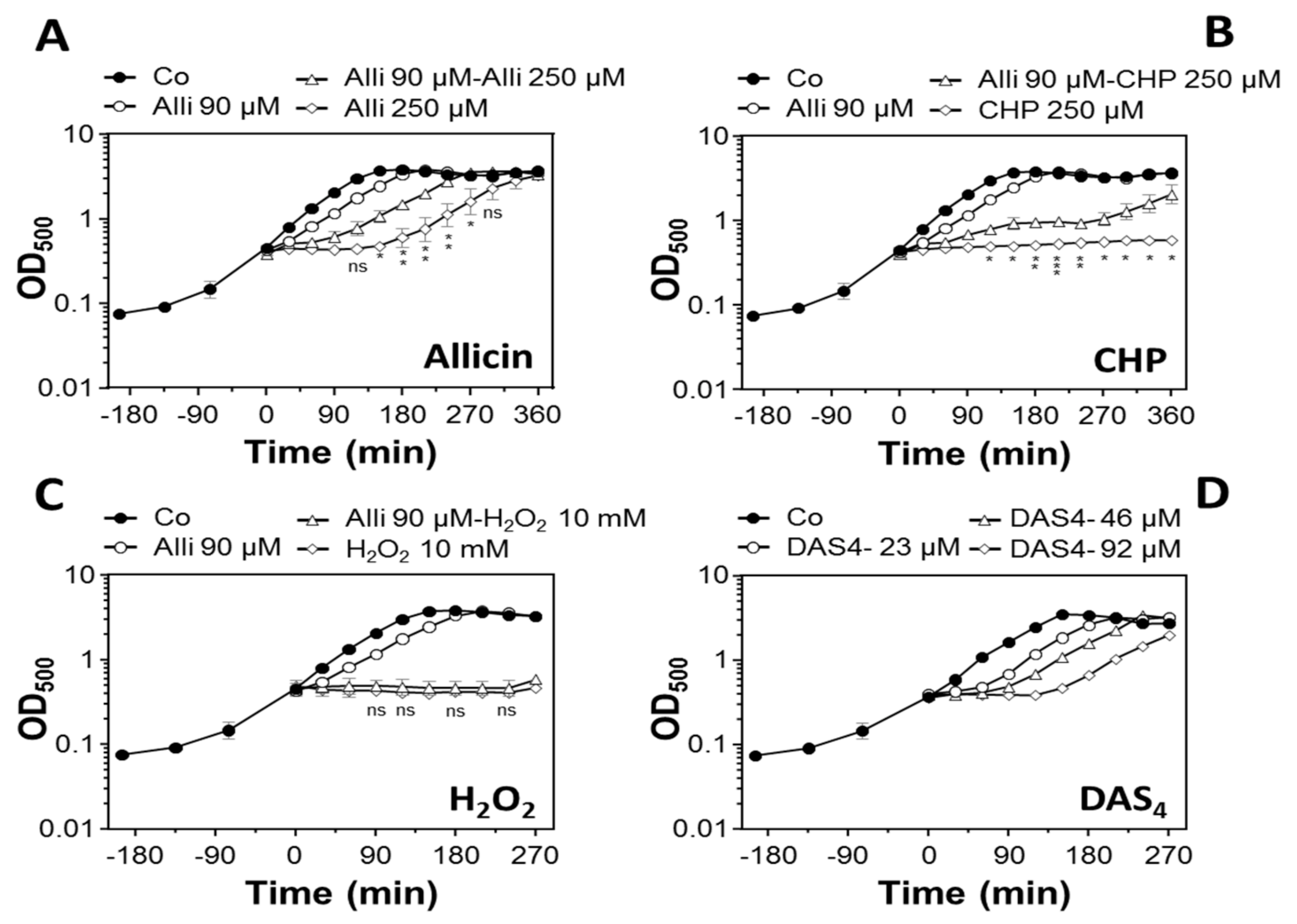
3.1. Determination of Sub-Lethal Allicin and DAS4 Concentrations and Allicin Priming Assays in B. subtilis
3.2. Allicin and DAS4 Cause a Strong Thiol-Specific Oxidative, Disulfide, and Sulfur Stress Response in the Transcriptome of B. subtilis
3.3. Allicin and DAS4 Lead to Widespread S-Thioallylation of Total 108 Proteins in B. subtilis
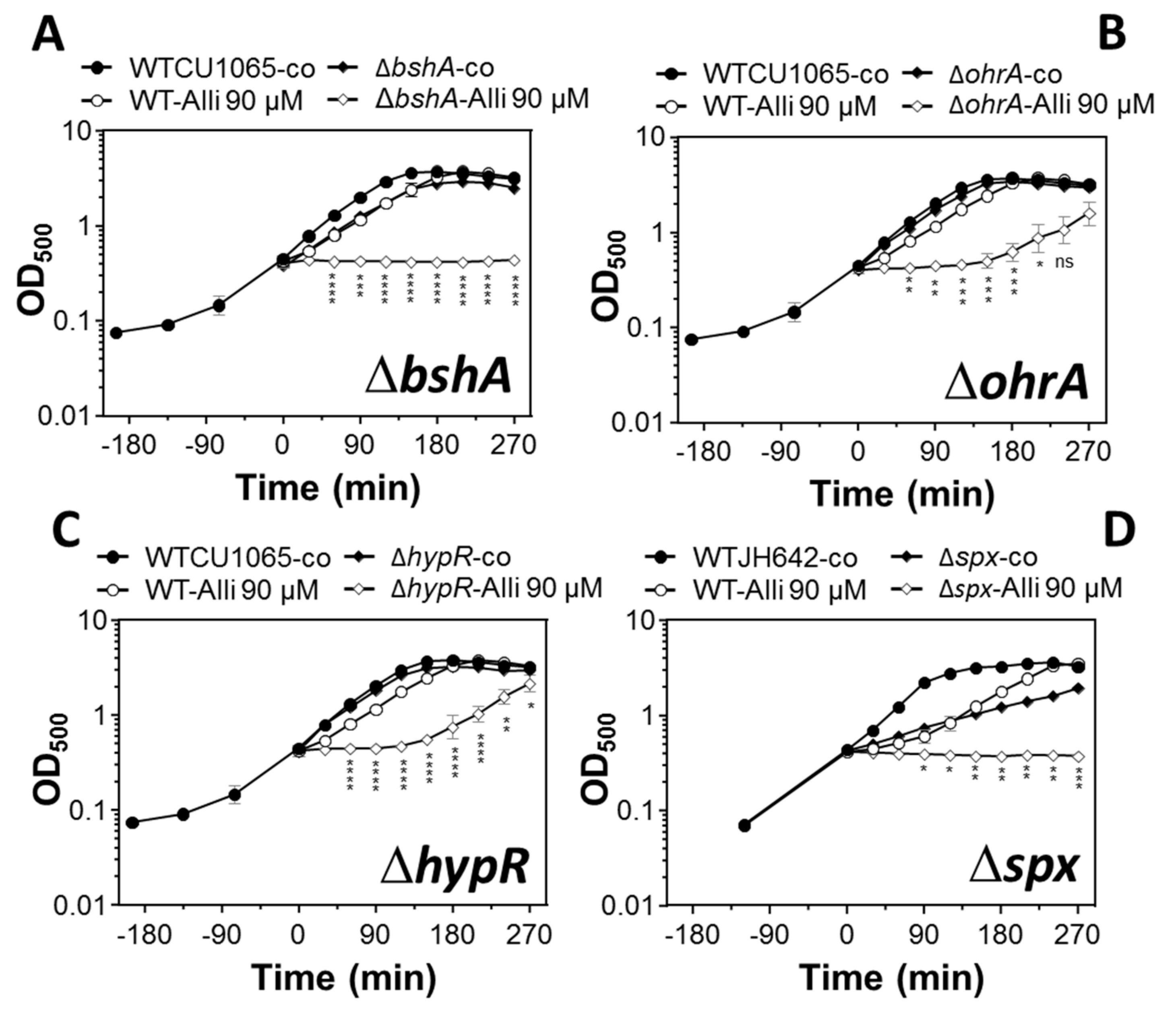
3.4. The LMW Thiol Bacillithiol and the Redox-Sensitive Regulators OhrR, HypR, and Spx Functions in the Defense of B. subtilis Against Allicin Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSH | bacillithiol |
| Brx | bacilliredoxin |
| CHP | cumene hydroperoxide |
| GSH | glutathione |
| DAS4 | diallyl tetrasulfane |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| HOCl | hypochloric acid |
| LMW thiol | low molecular weight thiol |
| OD500 | optical density at 500 nm |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RSS | reactive sulfur species |
References
- Rivlin, R.S. Historical perspective on the use of garlic. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 951S–954S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, R.S. Is garlic alternative medicine? J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 713S–715S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münchberg, U.; Anwar, A.; Mecklenburg, S.; Jacob, C. Polysulfides as biologically active ingredients of garlic. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocmo, R.; Wu, Y.; Liang, D.; Fogliano, V.; Huang, D. Boiling enriches the linear polysulfides and the hydrogen sulfide-releasing activity of garlic. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlinghaus, J.; Albrecht, F.; Gruhlke, M.C.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Slusarenko, A.J. Allicin: Chemistry and biological properties. Molecules 2014, 19, 12591–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, J.; Levina, N.; van der Linden, M.; Gruhlke, M.; Martin, C.; Slusarenko, A.J. Diallylthiosulfinate (Allicin), a volatile antimicrobial from garlic (Allium sativum), kills human lung pathogenic bacteria including MDR strains as a vapor. Molecules 2017, 22, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Eller, J.; Albrecht, F.; Prochnow, P.; Kuhlmann, K.; Bandow, J.E.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Leichert, L.I. Allicin induces thiol stress in bacteria through S-allylmercapto modification of protein cysteines. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11477–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinkov, A.; Miron, T.; Konstantinovski, L.; Wilchek, M.; Mirelman, D.; Weiner, L. The mode of action of allicin: Trapping of radicals and interaction with thiol containing proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1379, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbach, M.; Santana, T.M.; Moxham, H.; Tinson, R.; Anwar, A.; Groom, M.; Hamilton, C.J. Antimicrobial garlic-derived diallyl polysulfanes: Interactions with biological thiols in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinkov, A.; Zhu, X.Z.; Grafi, G.; Galili, G.; Mirelman, D. Alliin lyase (Alliinase) from garlic (Allium sativum). Biochemical characterization and cDNA cloning. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1994, 48, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.; Seebeck, E. The specificity of the alliinase from Allium sativum. C. R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1951, 232, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hile, A.G.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; Block, E. Aversion of European starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) to garlic oil treated granules: Garlic oil as an avian repellent. Garlic oil analysis by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2192–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Gould, E.; Tinson, R.; Iqbal, J.; Hamilton, C. Redox modulation at work: Natural phytoprotective polysulfanes from alliums based on redox-active sulfur. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyal, P.; Craft, J.D.; Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. The chemical compositions of the volatile oils of garlic (Allium sativum) and wild garlic (Allium vineale). Foods 2017, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, S.M.; Yin, M.C. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of four diallyl sulphides occurring naturally in garlic and Chinese leek oils. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, S.M.; Hsu, C.C.; Yin, M.C. Garlic extract and two diallyl sulphides inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in BALB/cA mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.M.; Liu, W.H.; Yin, M.C. Two diallyl sulphides derived from garlic inhibit meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in diabetic mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gara, E.A.; Hill, D.J.; Maslin, D.J. Activities of garlic oil, garlic powder, and their diallyl constituents against Helicobacter pylori. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2269–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, V.V.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Busche, T.; Tung, Q.N.; Gruhlke, M.C.H.; Kalinowski, J.; Bernhardt, J.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Antelmann, H. Staphylococcus aureus responds to allicin by global S-thioallylation—Role of the Brx/BSH/YpdA pathway and the disulfide reductase MerA to overcome allicin stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, T.; Listowsky, I.; Wilchek, M. Reaction mechanisms of allicin and allyl-mixed disulfides with proteins and small thiol molecules. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrangsu, P.; Loi, V.V.; Antelmann, H.; Helmann, J.D. The role of bacillithiol in Gram-positive Firmicutes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, G.L.; Rawat, M.; La Clair, J.J.; Jothivasan, V.K.; Budiarto, T.; Hamilton, C.J.; Claiborne, A.; Helmann, J.D.; Fahey, R.C. Bacillithiol is an antioxidant thiol produced in Bacilli. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, V.R.; Newton, G.L.; Pogliano, K. Bacillithiol: A key protective thiol in Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 1089–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruhlke, M.C.; Portz, D.; Stitz, M.; Anwar, A.; Schneider, T.; Jacob, C.; Schlaich, N.L.; Slusarenko, A.J. Allicin disrupts the cell’s electrochemical potential and induces apoptosis in yeast. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, T.; Bettray, W.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Gruhlke, M.C.H. S-allylmercaptoglutathione is a substrate for glutathione reductase (E.C. 1.8.1.7) from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruhlke, M.C.H.; Antelmann, H.; Bernhardt, J.; Kloubert, V.; Rink, L.; Slusarenko, A.J. The human allicin-proteome: S-thioallylation of proteins by the garlic defence substance allicin and its biological effects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.K.; Gronau, K.; Mäder, U.; Hessling, B.; Becher, D.; Antelmann, H. S-bacillithiolation protects against hypochlorite stress in Bacillus subtilis as revealed by transcriptomics and redox proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, 009506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballa, A.; Newton, G.L.; Antelmann, H.; Parsonage, D.; Upton, H.; Rawat, M.; Claiborne, A.; Fahey, R.C.; Helmann, J.D. Biosynthesis and functions of bacillithiol, a major low-molecular-weight thiol in Bacilli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6482–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Soonsanga, S.; Helmann, J.D. A complex thiolate switch regulates the Bacillus subtilis organic peroxide sensor OhrR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8743–8748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.K.; Roberts, A.A.; Huyen, T.T.; Bäsell, K.; Becher, D.; Albrecht, D.; Hamilton, C.J.; Antelmann, H. S-bacillithiolation protects conserved and essential proteins against hypochlorite stress in Firmicutes bacteria. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1273–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imber, M.; Pietrzyk-Brzezinska, A.J.; Antelmann, H. Redox regulation by reversible protein S-thiolation in Gram-positive bacteria. Redox Biol. 2018, 20, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, G.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Protein S-glutathionylation: A regulatory device from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Giustarini, D.; Colombo, R.; Milzani, A. S-glutathionylation in protein redox regulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, P. Regulation of protein function by glutathionylation. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, V.V.; Rossius, M.; Antelmann, H. Redox regulation by reversible protein S-thiolation in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuangthong, M.; Atichartpongkul, S.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Helmann, J.D. OhrR is a repressor of ohrA, a key organic hydroperoxide resistance determinant in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4134–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulke, J.; Hanschke, R.; Hecker, M. Temporal activation of beta-glucanase synthesis in Bacillus subtilis is mediated by the GTP pool. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1993, 139, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.M.; Hajarizadeh, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zuber, P. Loss-of-function mutations in yjbD result in ClpX- and ClpP-independent competence development of Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, G.J.; Khanh Chi, B.; Waack, P.; Gronau, K.; Becher, D.; Albrecht, D.; Hinrichs, W.; Read, R.J.; Antelmann, H. Structural insights into the redox-switch mechanism of the MarR/DUF24-type regulator HypR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4178–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaino, J.A.; Csordas, A.; Del-Toro, N.; Dianes, J.A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Csordas, A.; Sun, Z.; Jarnuczak, A.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Ternent, T.; Campbell, D.S.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Okuda, S.; Kawano, S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium in 2017: Supporting the cultural change in proteomics public data deposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1100–D1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, D.; Avissar, Y.J.; Wyche, J.H. Simultaneous and rapid isolation of bacterial and eukaryotic DNA and RNA: A new approach for isolating DNA. Biotechniques 1991, 11, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charbonnier, Y.; Gettler, B.; Francois, P.; Bento, M.; Renzoni, A.; Vaudaux, P.; Schlegel, W.; Schrenzel, J. A generic approach for the design of whole-genome oligoarrays, validated for genomotyping, deletion mapping and gene expression analysis on Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlan, H.; Schmidt, F.; Weiss, S.; Schuler, J.; Fuchs, S.; Riedel, K.; Bernhardt, J. Data visualization in environmental proteomics. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2805–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, B.K.; Kobayashi, K.; Albrecht, D.; Hecker, M.; Antelmann, H. The paralogous MarR/DUF24-family repressors YodB and CatR control expression of the catechol dioxygenase CatE in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Eiamphungporn, W.; Mäder, U.; Liebeke, M.; Lalk, M.; Hecker, M.; Helmann, J.D.; Antelmann, H. Genome-wide responses to carbonyl electrophiles in Bacillus subtilis: Control of the thiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase AdhA and cysteine proteinase YraA by the MerR-family regulator YraB (AdhR). Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichert, L.I.; Scharf, C.; Hecker, M. Global characterization of disulfide stress in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelmann, H.; Helmann, J.D. Thiol-based redox switches and gene regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkolsuk, S.; Helmann, J.D. Regulation of inducible peroxide stress responses. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, P. Spx-RNA polymerase interaction and global transcriptional control during oxidative stress. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Küster-Schock, E.; Grossman, A.D.; Zuber, P. Spx-dependent global transcriptional control is induced by thiol-specific oxidative stress in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13603–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaballa, A.; Chi, B.K.; Roberts, A.A.; Becher, D.; Hamilton, C.J.; Antelmann, H.; Helmann, J.D. Redox regulation in Bacillus subtilis: The bacilliredoxins BrxA(YphP) and BrxB(YqiW) function in de-bacillithiolation of S-bacillithiolated OhrR and MetE. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheyeva, I.V.; Thomas, J.M.; Kolar, S.L.; Corvaglia, A.R.; Gaiotaa, N.; Leo, S.; Francois, P.; Liu, G.Y.; Rawat, M.; Cheung, A.L. YpdA, a putative bacillithiol disulfide reductase, contributes to cellular redox homeostasis and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antelmann, H.; Hecker, M.; Zuber, P. Proteomic signatures uncover thiol-specific electrophile resistance mechanisms in Bacillus subtilis. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2008, 5, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelakriangsak, M.; Huyen, N.T.; Töwe, S.; van Duy, N.; Becher, D.; Hecker, M.; Antelmann, H.; Zuber, P. Regulation of quinone detoxification by the thiol stress sensing DUF24/MarR-like repressor, YodB in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 1108–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, B.K.; Albrecht, D.; Gronau, K.; Becher, D.; Hecker, M.; Antelmann, H. The redox-sensing regulator YodB senses quinones and diamide via a thiol-disulfide switch in Bacillus subtilis. Proteomics 2010, 10, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurimoto, H.; Hirai, R.; Matsuno, N.; Yasueda, H.; Kato, N.; Sakai, Y. HxlR, a member of the DUF24 protein family, is a DNA-binding protein that acts as a positive regulator of the formaldehyde-inducible hxlAB operon in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, V.V.; Busche, T.; Tedin, K.; Bernhardt, J.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Weise, C.; Kalinowski, J.; Wahl, M.C.; Fulde, M.; et al. Redox-sensing under hypochlorite stress and infection conditions by the Rrf2-family repressor HypR in Staphylococcus aureus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Gaballa, A.; Hui, M.; Ye, R.W.; Helmann, J.D. Genetic and physiological responses of Bacillus subtilis to metal ion stress. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Helmann, J.D. Metal ion homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaldone, G.T.; Helmann, J.D. CsoR regulates the copper efflux operon copZA in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 2007, 153, 4123–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Wu, H.; Wong, M.W.; Huang, D. Diallyl Trisulfide Is a Fast H2S Donor, but Diallyl Disulfide Is a Slow One: The Reaction Pathways and Intermediates of Glutathione with Polysulfides. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4196–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackray, P.D.; Moir, A. SigM, an extracytoplasmic function sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis, is activated in response to cell wall antibiotics, ethanol, heat, acid, and superoxide stress. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3491–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Palmer, L.D.; Kehl-Fie, T.E.; Skaar, E.P.; Trinidad, J.C.; Giedroc, D.P. Hydrogen sulfide and reactive sulfur species impact proteome S-sulfhydration and global virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebke, J.L.; Arnold, R.J.; Giedroc, D.P. Selenite and tellurite form mixed seleno- and tellurotrisulfides with CstR from Staphylococcus aureus. Metallomics 2013, 5, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebke, J.L.; Shen, J.; Bruce, K.E.; Kehl-Fie, T.E.; Peng, H.; Skaar, E.P.; Giedroc, D.P. The CsoR-like sulfurtransferase repressor (CstR) is a persulfide sensor in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 94, 1343–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, J.; Edmonds, K.A.; Luebke, J.L.; Hickey, A.K.; Palmer, L.D.; Chang, F.J.; Bruce, K.A.; Kehl-Fie, T.E.; Skaar, E.P.; et al. Sulfide homeostasis and nitroxyl intersect via formation of reactive sulfur species in Staphylococcus aureus. mSphere 2017, 2, e00082-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, K.A.; Peng, H.; Luebke, J.L.; Chang, F.M.; Giedroc, D.P. Conformational analysis and chemical reactivity of the multidomain sulfurtransferase, Staphylococcus aureus CstA. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 2385–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Keithly, M.E.; Armstrong, R.N.; Higgins, K.A.; Edmonds, K.A.; Giedroc, D.P. Staphylococcus aureus CstB is a novel multidomain persulfide dioxygenase-sulfurtransferase involved in hydrogen sulfide detoxification. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4542–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imber, M.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Pietrzyk-Brzezinska, A.J.; Loi, V.V.; Hillion, M.; Bernhardt, J.; Thärichen, L.; Kolsek, K.; Saleh, M.; Hamilton, C.J.; et al. Protein S-bacillithiolation functions in thiol protection and redox regulation of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gap in Staphylococcus aureus under hypochlorite stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 410–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imber, M.; Loi, V.V.; Reznikov, S.; Fritsch, V.N.; Pietrzyk-Brzezinska, A.J.; Prehn, J.; Hamilton, C.; Wahl, M.C.; Bronowska, A.K.; Antelmann, H. The aldehyde dehydrogenase AldA contributes to the hypochlorite defense and is redox-controlled by protein S-bacillithiolation in Staphylococcus aureus. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillion, M.; Antelmann, H. Thiol-based redox switches in prokaryotes. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, B.K.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Loi, V.V.; Gruhlke, M.C.H.; Schaffer, M.; Mäder, U.; Maaß, S.; Becher, D.; Bernhardt, J.; Arbach, M.; et al. The Disulfide Stress Response and Protein S-thioallylation Caused by Allicin and Diallyl Polysulfanes in Bacillus subtilis as Revealed by Transcriptomics and Proteomics. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120605
Chi BK, Huyen NTT, Loi VV, Gruhlke MCH, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Maaß S, Becher D, Bernhardt J, Arbach M, et al. The Disulfide Stress Response and Protein S-thioallylation Caused by Allicin and Diallyl Polysulfanes in Bacillus subtilis as Revealed by Transcriptomics and Proteomics. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(12):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120605
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Bui Khanh, Nguyen Thi Thu Huyen, Vu Van Loi, Martin Clemens Horst Gruhlke, Marc Schaffer, Ulrike Mäder, Sandra Maaß, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Miriam Arbach, and et al. 2019. "The Disulfide Stress Response and Protein S-thioallylation Caused by Allicin and Diallyl Polysulfanes in Bacillus subtilis as Revealed by Transcriptomics and Proteomics" Antioxidants 8, no. 12: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120605
APA StyleChi, B. K., Huyen, N. T. T., Loi, V. V., Gruhlke, M. C. H., Schaffer, M., Mäder, U., Maaß, S., Becher, D., Bernhardt, J., Arbach, M., Hamilton, C. J., Slusarenko, A. J., & Antelmann, H. (2019). The Disulfide Stress Response and Protein S-thioallylation Caused by Allicin and Diallyl Polysulfanes in Bacillus subtilis as Revealed by Transcriptomics and Proteomics. Antioxidants, 8(12), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8120605