Biological Implications of Differential Expression of Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
Literature Search
3. Results
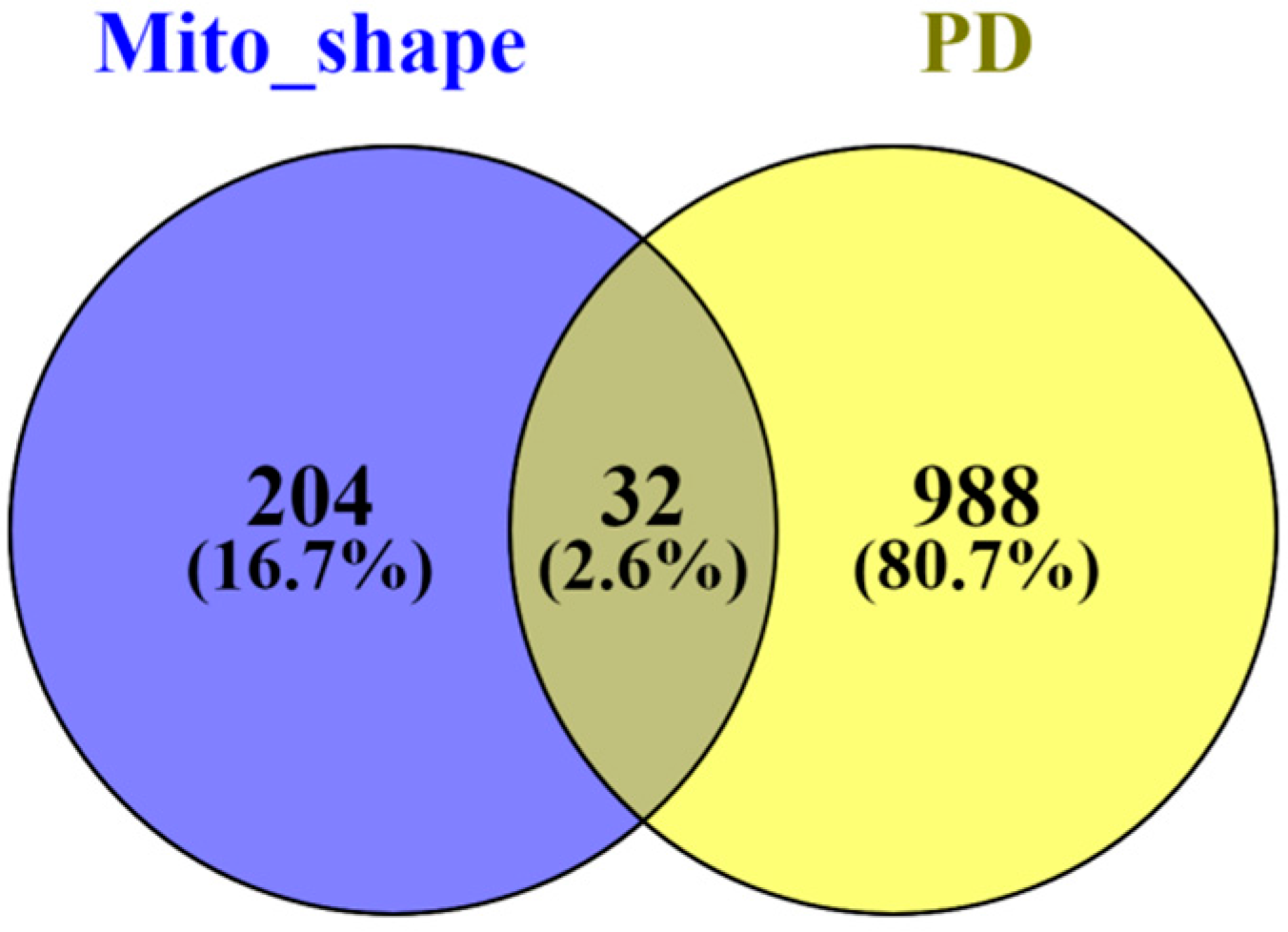
3.1. Differentially Expressed Mitochondrial Proteins Associated with Parkinson’s Disease
3.2. Binding Partners of Mitochondrial Proteins Differentially Expressed in Parkinson’s Disease
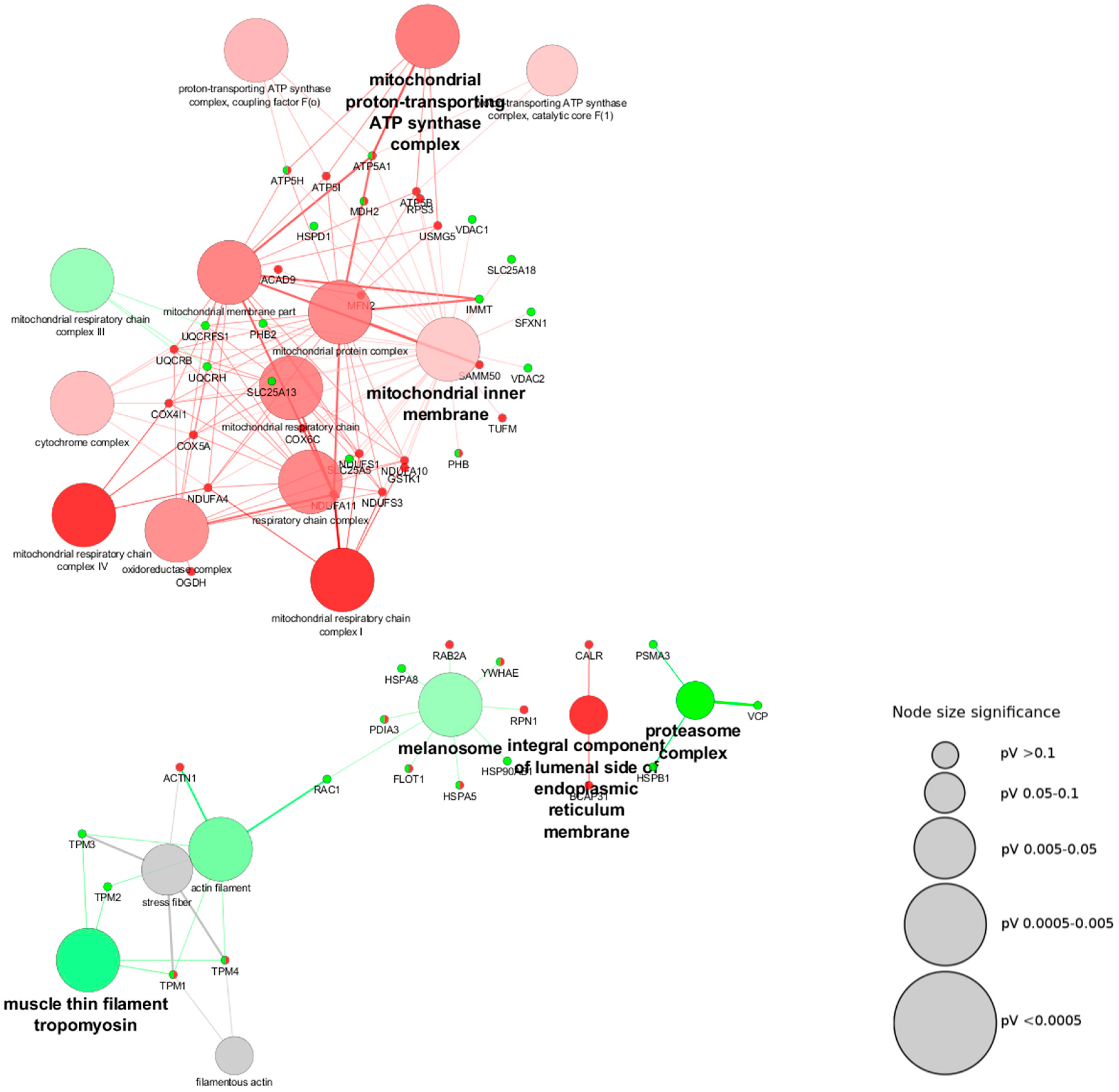
3.3. Biological Processes Associated with Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins Affected in Parkinson’s Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPL | actin-binding-like protein |
| ACAD9 | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 9 |
| ACP2 | acid phosphatase 2, lysosomal |
| ACTB | actin beta |
| ACTBL2 | actin, beta like 2 |
| ACTN1 | actinin alpha 1 |
| AD030 | ORF name for Mitochondrial Fission Factor |
| AD033 | ORF name for mitochondrial Fission Factor |
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| AHAS | acetolactate synthase-like protein |
| ALB | albumin |
| ALDA | aldolase, fructose-bisphosphate A |
| ALDH1B1 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member B1 |
| ALDH5 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 |
| ALDHX | Aldehyde dehydrogenase X |
| ALDOA | aldolase, fructose-bisphosphate A |
| ALS2CR3 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 chromosomal region candidate gene 3 protein |
| ANT2 | Adenine nucleotide translocator 2 |
| ANX2 | annexin 2 |
| ANX2L4 | annexin A2 |
| ANX2LG | annexin A2 ligand |
| ANXA2 | annexin A2 |
| APOA1 | apolipoprotein A1 |
| APOO | apolipoprotein O |
| APOOL | apolipoprotein O like |
| ARALAR1/AGC1 | aspartate-glutamate carrier 1 |
| ARALAR2/AGC2 | aspartate-glutamate carrier 2 |
| ARH12 | Aplysia ras-related homolog 12 |
| ARHA | Ras Homolog Gene Family, Member A |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| ATP5A | ATP synthase subunit alpha |
| ATP5A1 | ATP synthase subunit alpha subunit 1 |
| ATP5AL2 | ATP synthase subunit alpha |
| ATP5B | ATP synthase subunit beta |
| ATP5C1 | ATP synthase subunit gamma subunit 1 |
| ATP5D | ATP synthase subunit delta |
| ATP5E | ATP synthase subunit epsilon |
| ATP5F1 | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit B1 |
| ATP5G1 | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C1 |
| ATP5G2 | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2 |
| ATP5G3 | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C3 |
| ATP5H | ATP synthase subunit d |
| ATP5I | ATP synthase subunit e |
| ATP5J | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6 |
| ATP5J2 | ATP synthase subunit f |
| ATP5K | ATP synthase subunit e |
| ATP5L | ATP synthase subunit g |
| ATP5O | ATP synthase subunit O |
| ATPI | ATP synthase inhibitory factor |
| ATPIF1 | ATP synthase inhibitory factor subunit 1 |
| ATPM | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial |
| ATPMB | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial |
| ATPSB | ATP synthase subunit beta |
| BHAK | Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer |
| BAK | BCL2 antagonist killer 1 |
| BAP | B-cell receptor-associated protein |
| BAP31 | B cell receptor associated protein 31 |
| BAX | BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator |
| BCAP31 | B cell receptor associated protein 31 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2, apoptosis regulator |
| BCL2A1 | BCL2 related protein A1 |
| BCL2L11 | BCL2 like protein 11 |
| BCL2L3 | BCL2 like protein 3 |
| BCL2L4 | BCL2 like protein 4 |
| BCL2L5 | BCL2 like protein 5 |
| BCL2L7 | BCL2 like protein 7 |
| BCR | Breakpoint cluster region protein |
| BFL1 | Bcl-2-related gene expressed in fetal liver |
| BID | BH3 interacting domain death agonist |
| BIK | BCL2 interacting killer |
| BIM | Bcl-2 Interacting Mediator of cell death |
| C11orf83 | chromosome 11 open reading frame 83 |
| C14orf151 | chromosome 14 open reading frame 151 |
| C14orf173 | chromosome 14 open reading frame 73 |
| C15orf13 | chromosome 15 open reading frame 13 |
| C19orf70 | chromosome 19 open reading frame 70 |
| C1orf151 | chromosome 1 open reading frame 151 |
| C1orf166 | chromosome 1 open reading frame 166 |
| C1QBP | complement C1q binding protein |
| C20orf52 | chromosome 20 open reading frame 52 |
| C2orf33 | chromosome 2 open reading frame 33 |
| C9orf54 | chromosome 9 open reading frame 54 |
| CAL1H | Calpactin I heavy polypeptide Protein |
| LPC2D | Lipocortin II |
| CAL1L | Calpactin-1 light chain |
| CALR | calreticulin |
| CCDC56 | Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 3 homolog |
| CCT5 | Chaperonin Containing TCP1 Subunit 5 |
| CCTE | Chaperonin Containing TCP1, Subunit epsilon |
| CDM | Caldesmon |
| CDN1 | synonym for Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer |
| CGI-106 | comparative gene identification 106 |
| CGI-135 | comparative gene identification 135 |
| CGI-51 | comparative gene identification 51 |
| CGI-61 | comparative gene identification 61 |
| CHCHD3 | coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 3 |
| CLP11 | human gene encoding p11 |
| CMAR | Cell matrix adhesion regulator |
| COA3 | cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 3 |
| COX4 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1 |
| COX4I1 | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4I1 |
| COX4I2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 2 |
| COX5A | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5A |
| COX5B | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B |
| COX6A1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6A1 |
| COX6A2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6A2 |
| COX6B1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B1 |
| COX6B2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 |
| COX6C | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C |
| COX7A1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A1 |
| COX7A2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A2 |
| COX7B | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7B |
| COX7B2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7B2 |
| COX7C | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7C |
| COX8A | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 8A |
| COX8C | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 8C |
| CPRP1 | synonym of Mitofusin 2 |
| CRTC | Calreticulin |
| CXorf33 | Chromosome X open reading frame 33 |
| CYC1 | Ubiquinol-Cytochrome-C Reductase Complex Cytochrome C1 Subunit |
| CYPA | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A |
| DA | dopaminergic |
| DAPIT | Diabetes-associated protein in insulin-sensitive tissues |
| DDAH | dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase |
| DDAH1 | dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 |
| DDOST | dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase non-catalytic subunit |
| DHC1 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| DIC | Mitochondrial dicarboxylate carrier |
| DJ-1 | Protein/nucleic acid deglycase DJ-1 |
| DLP1 | dynamin like protein 1 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DNAJC19 | DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member C19 |
| DNCH1 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| DNCL | Dynein light chain 1 |
| DNECL | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| DNM1L | dynamin 1 like |
| DNM2 | dynamin 2 |
| DRP1 | dynamin related protein 1 |
| DXS1357E | p28 synonym |
| DYHC | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| DYN2 | dynamin 2 |
| DYNC1H1 | dynein cytoplasmic 1 heavy chain 1 |
| EC | Enzyme Commission number |
| EEF1A | eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 |
| EEF1A1 | eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1 |
| EEF1B | Elongation factor 1-beta |
| EEF1B2 | Elongation factor 1-beta |
| EF1A | Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 |
| EF1B | Elongation factor 1-beta |
| EFE2 | endomyocardial fibroelastosis |
| EIF5A | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERM | ezrin/moesin/radixin |
| ERP57 | Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 57 |
| ERP60 | Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60 |
| FAM121A | Family With Sequence Similarity 121A |
| FAM121B | Family With Sequence Similarity 121A |
| FAM73A | Family With Sequence Similarity 73A |
| FAM73B | Family With Sequence Similarity 73B |
| FIS1 | fission, mitochondrial 1 |
| FKBP4 | FK506 binding protein 4 |
| FKBP52 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP4 |
| FLN2 | filamin 2 |
| FLNC | filamin C |
| FLOT1 | flotillin 1 |
| FTSH1 | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease YME1L1 |
| FUBP1 | far upstream element binding protein 1 |
| FUNDC1 | FUN14 domain containing 1 |
| G4.5 | synonym of Tafazzin |
| GARS | glycyl-tRNA synthetase |
| GC1QBP | complement C1q binding protein |
| GC2 B415 | Glutamate carrier 2 |
| GDAP1 | ganglioside induced differentiation associated protein 1 |
| GIDE | Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase activator of NFKB 1 |
| GIG20 | growth-inhibiting gene 20 |
| GIG42 | growth-inhibiting gene 42 |
| GL004 | synonym of MFF |
| GRP58 | 58 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| GRP75 | 75 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| GRP78 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| GRS | Glasgow rearranged sequence |
| GSTK1 | glutathione S-transferase kappa 1 |
| GSTO1 | glutathione S-transferase omega 1 |
| GSTTLP28 | Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 |
| HABP1 | Hyaluronan Binding Protein 1 |
| HACBP | High Affinity Calcium-Binding Protein |
| HBEBP2 | HBEAG-binding protein 2 |
| HBPA1 | hematopoietic BCL2-related protein A1 |
| HC8 | human proteasome alpha-subunit C8 |
| HCVFTP2 | HCV F-Transactivated Protein 2 |
| HDCMD47P | synonym of Glutathione S-transferase Subunit 13 |
| hfzo1 | human fuzzy onions 1 |
| HIPPIE | Human Integrated Protein-Protein Interaction rEference web tool |
| HMP | synonym for inner membrane mitochondrial protein |
| HSC70 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein |
| HSP27 | Heat shock protein beta-1 |
| HSP28 | Heat shock protein beta-1 |
| HSP60 | heat shock protein family D (Hsp60) |
| HSP73 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein |
| HSP90AB1 | heat shock protein 90 alpha family class B member 1 |
| HSP90B | heat shock protein 90 alpha family class B |
| HSPA10 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein |
| HSPA1L | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 1 like |
| HSPA5 | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 5 |
| HSPA8 | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 8 |
| HSPA9 | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 9 |
| HSPA9B | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 9 |
| HSPB1 | heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 |
| HSPC009 | ORF name for Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 3 homolog |
| HSPC108 | ORF name for Stomatin-like protein 2 |
| HSPC2 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta |
| HSPC242 | ORF name for Mitochondrial fission process protein 1 |
| HSPC263 | ORF name for Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 |
| HSPCB | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta |
| HSPD1 | heat shock protein family D (Hsp60) member 1 |
| IF(1) | Inhibitor Of F(1)F(O)-ATPase |
| ILVBL | gene ilvB acetolactate synthase like |
| IMM | inner mitochondrial membrane |
| IMMT | inner membrane mitochondrial protein |
| IMS | intermembrane space |
| INF2 | protein inverted formin 2 |
| IPS1 | Interferon beta promoter stimulator protein 1 |
| KIAA0098 | synonym of CCT5 |
| KIAA0115 | synonym of DDOST |
| KIAA0214 | synonym of Mitofusin-2 |
| KIAA0313 | synonym of RAPGEF2 |
| KIAA0325 | synonym of DYNC1H1 |
| KIAA0348 | synonym of SYNJ2 |
| KIAA0491 | synonym of SH3GLB1 |
| KIAA0549 | synonym of TRAK2 |
| KIAA0567 | synonym of Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein |
| KIAA1042 | synonym of TRAK1 |
| KIAA1271 | synonym of MAVS |
| KIAA1848 | synonym of SH3GLB2 |
| LDHB | lactate dehydrogenase B |
| LEM6 | Ligand effect modulator 6 |
| LENG7 | Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 |
| LETM1 | leucine zipper and EF-hand containing transmembrane protein 1 |
| LGALS1 | Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 1 |
| LMN1 | Prelamin-A/C |
| LMNA | Lamin A |
| MADH2 | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 |
| MADR2 | Mad-related protein 2 Protein |
| MAP3K5 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5 |
| MAPL | Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase activator of NFKB 1 |
| MARCH5 | membrane associated ring-CH-type finger 5 |
| MAVS | mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein |
| MCL1 | Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 |
| MDH2 | malate dehydrogenase 2 |
| MFF | mitochondrial fission factor |
| MFN1 | mitofusin 1 |
| MFN2 | mitofusin 2 |
| MIC 27 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC27 |
| MIC10 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MI10 |
| MIC13 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC13 |
| MIC19 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC19 |
| MIC23 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC23 |
| MIC26 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC26 |
| MIC60 | synonym for MICOS complex subunit MIC60 |
| MICOS | mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system |
| MID49 | Mitochondrial dynamics protein MID49 |
| MID51 | Mitochondrial dynamics protein MID51 |
| MIEF1 | mitochondrial elongation factor 1 |
| MIEF2 | mitochondrial elongation factor 2 |
| MIG10 | Abnormal cell migration protein 10 |
| MIG5 | Abnormal cell migration protein 5 |
| MIGA1 | mitoguardin 1 |
| MIGA2 | mitoguardin 2 |
| MINOS1 | mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system 1 |
| MINOS2 | Mitochondrial Inner Membrane Organizing System 2 |
| MINOS3 | Mitochondrial Inner Membrane Organizing System 3 |
| Mito_shape | Mitochondrial shaping proteins |
| MITRAC12 | Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 3 homolog |
| MPP+ | 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium |
| MPRP1 | multidrug resistance protein 1 |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| MT-ATP6 | Mitochondrially Encoded ATP Synthase 6 |
| MT-ATP8 | Mitochondrially Encoded ATP Synthase 8 |
| MT-CO1 | Mitochondrially Encoded Cytochrome C Oxidase I |
| MT-CO2 | Mitochondrially Encoded Cytochrome C Oxidase II |
| MT-CO3 | Mitochondrially Encoded Cytochrome C Oxidase III |
| MT-CYB | Mitochondrially Encoded Cytochrome B |
| MTFP1 | mitochondrial fission process 1 |
| mt-HSP70 | mitochondrial heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) |
| MTP18 | Mitochondrial fission process protein 1 |
| MUL1 | mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 |
| MULAN | Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase activator of NFKB 1 |
| My022 | ORF name for Mitochondrial fission process protein 1 |
| My025 | ORF name for MICOS complex subunit MIC26 |
| My032 | ORF name for ATP synthase subunit d |
| MYL6 | myosin light chain 6 |
| NAD | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidized |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced |
| NBK | Bcl-2-interacting killer |
| NDUFA10 | NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A10 |
| NDUFA11 | NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A11 |
| NDUFA4 | NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) 1 Alpha Subcomplex, 4 |
| NDUFS1 | NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit S1 |
| NDUFS3 | NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit S3 |
| NEDD8 | neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8 |
| NFE2L2 | nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 |
| NFKB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NHERF | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 |
| NHERF1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 |
| NHERF-1 protein | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 |
| NIMA | never in mitosis gene a |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| Nox1 | NADPH oxidase 1 |
| NPM | nucleophosmin |
| NPM1 | nucleophosmin 1 |
| NRAPGEP | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
| NRF1 | nuclear respiratory factor 1 |
| NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| OAT | ornithine aminotransferase |
| OGDH | oxoglutarate dehydrogenase |
| OIP106 | O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase interacting protein 106 |
| OK/SW-cl.110 | ORF name for Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 |
| OK/SW-cl.56 | ORF name for Tubulin beta chain |
| OK/SW-cl.82 | ORF name for 40S ribosomal protein S15a |
| OMA1 | Overlapping Activity With M-AAA Protease |
| OMM | outer mitochondrial membrane |
| OPA1 | Optic Atrophy Protein 1 |
| OST48 OK/SW-cl.45 | synomym for Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase 48 kDa subunit |
| OTB1 | Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 |
| OTU1 | Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 |
| OTUB1 | OTU deubiquitinase, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 1 |
| OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| PARK2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin |
| PARL | presenilin associated rhomboid like |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PD04912 | ORF name for Up-regulated during skeletal muscle growth protein 5 |
| PDIA3 | protein disulfide isomerase family A member 3 |
| PDZGEF1 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
| PERC | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta |
| PGAM5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PGAM5 |
| PGC1 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| PGC1A | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| PGC1B | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta |
| PGK1 | phosphoglycerate kinase 1 |
| PGKA | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 |
| PGN | paraplegin |
| PHB | prohibitin |
| PHB2 | prohibitin 2 |
| PIG4 | ORF name for MICOS complex subunit MIC60 |
| PIG52 | ORF name for MICOS complex subunit MIC60 |
| PIN1 | peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 |
| PLD6 | phospholipase D family member 6 |
| PP578 | ORF name for Endophilin-B2 |
| PPARGC1 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| PPARGC1A | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| PPARGC1B | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta |
| PPIA | peptidylprolyl isomerase A |
| PRDX4 | peroxiredoxin 4 |
| PRELI | Protein Of Relevant Evolutionary And Lymphoid Interest |
| PRELID1 | PRELI domain-containing protein 1 |
| PRI | synonym for Ribonuclease inhibitor |
| PRKN | parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase |
| PRO0903 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| PRO1708 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| PRO2044 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| PRO2207 | ORF name for Presenilins-associated rhomboid-like protein |
| PRO2619 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| PRO2675 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| PSARL | Presenilins-associated rhomboid-like protein |
| PSC8 | Proteasome component C8 |
| PSEC0112 | ORF name for Mitoguardin 2 |
| PSMA3 | proteasome subunit alpha 3 |
| PTPN5 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 5 |
| QIL1 | synonym for Chromosome 19 Open Reading Frame 70 |
| RAB14 | Ras-related protein Rab-14 |
| RAB2 | Ras-related protein Rab2 |
| RAB2A | Ras-related protein Rab-2A |
| RAC1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| RAPGEF2 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
| REA | synonym for Prohibitin-2 |
| RHO12 | ras homolog family member |
| RHOA | ras homolog family member A |
| RING-type E3 | really interesting new gene type E3 |
| RNF153 | Ring Finger Protein 153 |
| RNF218 | Ring Finger Protein 218 |
| RNH | Ribonuclease inhibitor |
| RNH1 | ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor 1 |
| ROMO1 | reactive oxygen species modulator 1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RPN1 | Ribophorin I |
| RPN2 | ribophorin II |
| RPS15A | ribosomal protein S15a |
| RPS3, OK/SW-cl.26 | symbol and ORF name for 40S ribosomal protein S3 |
| S100A10 | S100 calcium binding protein A10 |
| SAM50 | Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog |
| SAMM50 | Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog |
| SBBI12 | ORF name for PRELI domain-containing protein 1 |
| SBP | selenium binding protein |
| SELENBP1 | selenium binding protein 1 |
| SF2P32 | nuclear splicing factor |
| SFXN1 | sideroflexin 1 |
| SH3 | SRC Homology 3 Domain |
| SH3GLB1 | SH3 domain containing GRB2 like, endophilin B1 |
| SH3GLB2 | SH3 domain containing GRB2 like, endophilin B2 |
| SIR2L | SIR2-like protein |
| SIR2L2 | SIR2-like protein 2 |
| SIRT2 | sirtuin 2 |
| SLC20A4 | solute carrier family 20 member 4 |
| Slc25A | solute carrier family 25 |
| SLC25A10 | solute carrier family 25 member 10 |
| SLC25A11 | solute carrier family 25 member 11 |
| SLC25A12 | solute carrier family 25 member 12 |
| SLC25A13 | solute carrier family 25 member 13 |
| SLC25A18 | solute carrier family 25 member 18 |
| SLC25A38 | solute carrier family 25 member 38 |
| SLC9A3R1 | solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 1 |
| SLP2 | Stomatin-like protein 2 |
| SMAD2 | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 |
| SMCR7 | Smith-Magenis Syndrome Chromosomal Region Candidate Gene 7 Protein |
| SMCR7L | Smith-Magenis Syndrome Chromosomal Region Candidate Gene 7 Protein-like |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| SPG7 | Paraplegin |
| SSBP | single stranded DNA binding protein |
| SSBP1 | single stranded DNA binding protein 1 |
| STOML2 | stomatin like 2 |
| SYNJ2 | synaptojanin 2 |
| TAZ | tafazzin |
| TC25 | Ras-Like Protein TC25 |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| TCF6 | Transcription factor |
| TCF6L2 | Transcription Factor 6-Like 2 |
| TCP-1-epsilon | T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon |
| TFAM | transcription factor A, mitochondrial |
| TIM14 | Mitochondrial Import Inner Membrane Translocase Subunit TIM14 |
| TIMM14 | Translocase Of Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 14 |
| TMSA | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain |
| TMSB | tropomyosin Beta |
| TPD52 | tumor protein D52 |
| TPM1 | tropomyosin 1 |
| TPM2 | tropomyosin 2 |
| TPM3 | tropomyosin 3 |
| TPM4 | tropomyosin 4 |
| TRAK1 | trafficking kinesin protein 1 |
| TRAK2 | trafficking kinesin protein 2 |
| TRG3 | transformation-related gene 3 |
| TTC11 | tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 11 |
| TUBA1A | tubulin alpha 1a |
| TUBA3 | tubulin alpha-3 chain |
| TUBB | tubulin beta class I |
| TUBB2C | Tubulin beta-4B chain |
| TUBB4B | tubulin beta 4B class IVb |
| TUBB5 | Tubulin beta chain |
| TUFM | Tu translation elongation factor, mitochondrial |
| UniProt | Universal Protein Resource |
| UNQ1866/PRO4302 | ORF name for MICOS complex subunit MIC26 |
| UNQ1868/PRO4304 | ORF name for ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease YME1L1 |
| UNQ655/PRO1286 | ORF name for Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase complex assembly factor 3 |
| UNQ696/PRO1341 | ORF name for Serum albumin |
| UNQ8193/PRO23204 | ORF for MICOS complex subunit MIC27 |
| UQBP | Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex 14 kDa protein |
| UQCC3 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex assembly factor 3 |
| UQCR10 | Ubiquinol-Cytochrome C Reductase, Complex III Subunit X |
| UQCR11 | Ubiquinol-Cytochrome C Reductase, Complex III Subunit XI |
| UQCRB | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase binding protein |
| UQCRC1 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 1 |
| UQCRC2 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 2 |
| UQCRFS1 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase, Rieske iron-sulfur polypeptide 1 |
| UQCRFS1 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase, Rieske iron-sulfur polypeptide 1 |
| UQCRFS1P1 | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase, Rieske iron-sulfur polypeptide 1 pseudogene 1 |
| UQCRFSL1 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Rieske iron-sulfur subunit pseudogene 1 |
| UQCRH | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase hinge protein |
| UQCRQ | ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex ubiquinone-binding protein QP-C |
| USMG5 | Up-regulated during skeletal muscle growth protein 5 |
| VAT1 | vesicle amine transport 1 |
| VCP | valosin containing protein |
| VDAC1 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 |
| VDAC2 | voltage dependent anion channel 2 |
| VDAC3 | voltage dependent anion channel 3 |
| VDAC | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel |
| VIM | vimentin |
| VISA | Virus-induced-signaling adapter |
| YME1L | YME1-like protein 1 |
| YME1L1 | YME1-like protein 1 |
| YWHAE | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein epsilon |
| YWHAZ | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein zeta |
References
- Kasahara, A.; Scorrano, L. Mitochondria: From cell death executioners to regulators of cell differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anesti, V.; Scorrano, L. The relationship between mitochondrial shape and function and the cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernas, L.; Scorrano, L. Mito-morphosis: Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and cristae remodeling as key mediators of cellular function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, F.; Su, B.; Wang, X. Abnormalities of mitochondrial dynamics in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangpaisan, W.; Mathews, A.; Hori, H.; Seidel, D. A systematic review of the worldwide prevalence and incidence of Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2011, 94, 749–755. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, P.M.; Diederich, N.J.; Kruger, R.; Balling, R. The hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5981–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Jenner, P.; Clark, J.B.; Marsden, C.D. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 1989, 1, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Clark, J.B.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haylett, W.; Swart, C.; van der Westhuizen, F.; van Dyk, H.; van der Merwe, L.; van der Merwe, C.; Loos, B.; Carr, J.; Kinnear, C.; Bardien, S. Altered mitochondrial respiration and other features of mitochondrial function in parkin-mutant fibroblasts from Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinson’s Dis. 2016, 2016, 1819209. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.Y.; Giasson, B.I.; Bonini, N.M. Dj-1 is critical for mitochondrial function and rescues pink1 loss of function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9747–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Aggarwal, K.; Pattnaik, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Sethi, T.; Tiwari, B.K.; Kumar, M.; Micheal, A.; Mabalirajan, U.; Ghosh, B.; et al. Computational classification of mitochondrial shapes reflects stress and redox state. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, D.; Nakamura, K. Understanding the susceptibility of dopamine neurons to mitochondrial stressors in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3702–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. Uniprot: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.R.; Mourier, A.; Yamada, J.; McCaffery, J.M.; Nunnari, J. MICOS coordinates with respiratory complexes and lipids to establish inner mitochondrial membrane architecture. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikon, N.; Ryan, R.O. Cardiolipin and mitochondrial cristae organization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1859, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, S.; Barrera, M.; Anand, R.; Reichert, A.S. The non-glycosylated isoform of MIC26 is a constituent of the mammalian MICOS complex and promotes formation of crista junctions. Biochimi. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkens, V.; Kohl, W.; Busch, K. Restricted diffusion of OXPHOS complexes in dynamic mitochondria delays their exchange between cristae and engenders a transitory mosaic distribution. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogliati, S.; Enriquez, J.A.; Scorrano, L. Mitochondrial cristae: Where beauty meets functionality. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Bliek, A.M.; Shen, Q.; Kawajiri, S. Mechanisms of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccenda, D.; Tan, C.H.; Seraphim, A.; Duchen, M.R.; Campanella, M. IF1 limits the apoptotic-signalling cascade by preventing mitochondrial remodelling. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Vargas, M.P.; Chipuk, J.E. Physiological and pharmacological control of BAK, BAX, and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello, S.; Scorrano, L. Mitochondrial shape changes: Orchestrating cell pathophysiology. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorrano, L. Opening the doors to cytochrome c: Changes in mitochondrial shape and apoptosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, J.G.; Cornut-Thibaut, A.; Juge, R.; Debaud, A.L.; Gimenez, D.; Gillet, G.; Bonnefoy-Berard, N.; Salgado, J.; Salles, G.; Aouacheria, A.; et al. Micro-calpain conversion of antiapoptotic Bfl-1 (BCL2A1) into a prodeath factor reveals two distinct alpha-helices inducing mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewski, M.; Scorrano, L. The changing shape of mitochondrial apoptosis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Lartigue, L.; Perkins, G.; Scott, R.T.; Dixit, A.; Kushnareva, Y.; Kuwana, T.; Ellisman, M.H.; Newmeyer, D.D. Opa1-mediated cristae opening is Bax/Bak and BH3 dependent, required for apoptosis, and independent of Bak oligomerization. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorrano, L.; Ashiya, M.; Buttle, K.; Weiler, S.; Oakes, S.A.; Mannella, C.A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. A distinct pathway remodels mitochondrial cristae and mobilizes cytochrome c during apoptosis. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, M.; Mathai, J.P.; McBride, H.M.; Shore, G.C. Endoplasmic reticulum Bik initiates DRP1-regulated remodelling of mitochondrial cristae during apoptosis. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.B.; Kalkhoran, S.B.; Hernandez-Resendiz, S.; Samangouei, P.; Ong, S.G.; Hausenloy, D.J. Mitochondrial-shaping proteins in cardiac health and disease—The long and the short of it! Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. Spons. Int. Soc. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2017, 31, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban-Ishihara, R.; Tomohiro-Takamiya, S.; Tani, M.; Baudier, J.; Ishihara, N.; Kuge, O. COX assembly factor ccdc56 regulates mitochondrial morphology by affecting mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3126–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter-Dennerlein, R.; Korwitz, A.; Haag, M.; Tatsuta, T.; Dargazanli, S.; Baker, M.; Decker, T.; Lamkemeyer, T.; Rugarli, E.I.; Langer, T. DNAJC19, a mitochondrial cochaperone associated with cardiomyopathy, forms a complex with prohibitins to regulate cardiolipin remodeling. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, K.M.; Parboosingh, J.S.; McLeod, D.R.; Chan, A.; Casey, R.; Ferreira, P.; Snyder, F.F.; Bridge, P.J.; Bernier, F.P. Mutation of DNAJC19, a human homologue of yeast inner mitochondrial membrane co-chaperones, causes DCMA syndrome, a novel autosomal recessive Barth syndrome-like condition. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Westrate, L.M.; Wu, H.; Page, C.; Voeltz, G.K. Multiple dynamin family members collaborate to drive mitochondrial division. Nature 2016, 540, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Chen, L.; Gao, R.; Liu, L.; et al. Mitophagy receptor FUNDC1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Autophagy 2016, 12, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Feng, D.; Chen, G.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Q.; Song, P.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wang, R.; Qi, W.; et al. Mitochondrial outer-membrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in mammalian cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, L.C.; Scorrano, L. Mitochondrial morphology in mitophagy and macroautophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, G.B.; Shang, Y.; Li, L.; Renken, C.; Mannella, C.A.; Selker, J.M.; Rangell, L.; Bennett, M.J.; Zha, J. The inner mitochondrial membrane protein mitofilin controls cristae morphology. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobova, F.; Ramabhadran, V.; Higgs, H.N. An actin-dependent step in mitochondrial fission mediated by the ER-associated formin INF2. Science 2013, 339, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmer, K.S.; Navoni, F.; Casarin, A.; Trevisson, E.; Endele, S.; Winterpacht, A.; Salviati, L.; Scorrano, L. LETM1, deleted in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome is required for normal mitochondrial morphology and cellular viability. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshiba, T. Mitochondrial-mediated antiviral immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perciavalle, R.M.; Stewart, D.P.; Koss, B.; Lynch, J.; Milasta, S.; Bathina, M.; Temirov, J.; Cleland, M.M.; Pelletier, S.; Schuetz, J.D.; et al. Anti-apoptotic MCL-1 localizes to the mitochondrial matrix and couples mitochondrial fusion to respiration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morciano, G.; Giorgi, C.; Balestra, D.; Marchi, S.; Perrone, D.; Pinotti, M.; Pinton, P. MCL-1 involvement in mitochondrial dynamics is associated with apoptotic cell death. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Detmer, S.A.; Ewald, A.J.; Griffin, E.E.; Fraser, S.E.; Chan, D.C. Mitofusins Mfn1 and Mfn2 coordinately regulate mitochondrial fusion and are essential for embryonic development. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Tian, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Duan, X.; Shang, W.; Fan, H.Y.; Tong, C. Mitoguardin regulates mitochondrial fusion through mitopld and is required for neuronal homeostasis. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, T.; Langer, T. Mitochondrial dynamics and metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Manczak, M.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondria-targeted molecules MitoQ and SS31 reduce mutant huntingtin-induced mitochondrial toxicity and synaptic damage in Huntington’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. The emerging role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereiter-Hahn, J.; Jendrach, M. Mitochondrial dynamics. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 284, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dabrowska, A.; Venero, J.L.; Iwasawa, R.; Hankir, M.K.; Rahman, S.; Boobis, A.; Hajji, N. PGC-1alpha controls mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics in lead-induced neurotoxicity. Aging 2015, 7, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, D.A.; Wong, J.; Khacho, M.; Soubannier, V.; Mailloux, R.J.; Pilon-Larose, K.; MacLaurin, J.G.; Park, D.S.; McBride, H.M.; Trinkle-Mulcahy, L.; et al. Opa1-dependent cristae modulation is essential for cellular adaptation to metabolic demand. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2676–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.R.; Burke, N.; Dongworth, R.K.; Hausenloy, D.J. Mitochondrial fusion and fission proteins: Novel therapeutic targets for combating cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1890–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, S.; Du, F.; Wang, X. The mitochondrial phosphatase PGAM5 functions at the convergence point of multiple necrotic death pathways. Cell 2012, 148, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkwirth, C.; Dargazanli, S.; Tatsuta, T.; Geimer, S.; Lower, B.; Wunderlich, F.T.; von Kleist-Retzow, J.C.; Waisman, A.; Westermann, B.; Langer, T. Prohibitins control cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating opa1-dependent cristae morphogenesis in mitochondria. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhlman, L.; Damiano, M.; Bertolin, G.; Ferrando-Miguel, R.; Lombes, A.; Brice, A.; Corti, O. Functional interplay between parkin and Drp1 in mitochondrial fission and clearance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2012–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBleu, V.S.; O’Connell, J.T.; Gonzalez Herrera, K.N.; Wikman, H.; Pantel, K.; Haigis, M.C.; de Carvalho, F.M.; Damascena, A.; Domingos Chinen, L.T.; Rocha, R.M.; et al. PGC-1alpha mediates mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Cui, Y.; Cui, A.; Qiao, A.; Kong, X.; Chen, Q.; Gupta, N.; et al. PGC-1 beta-regulated mitochondrial biogenesis and function in myotubes is mediated by Nrf-1 and ERR alpha. Mitochondrion 2010, 10, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesaki, H.; Dunn, C.D.; Iijima, M.; Shepard, K.A.; Yaffe, M.P.; Machamer, C.E.; Jensen, R.E. Ups1p, a conserved intermembrane space protein, regulates mitochondrial shape and alternative topogenesis of Mgm1p. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, B.; Wai, T.; Hu, H.; MacVicar, T.; Musante, L.; Fischer-Zirnsak, B.; Stenzel, W.; Graf, R.; van den Heuvel, L.; Ropers, H.H.; et al. Homozygous YME1L1 mutation causes mitochondriopathy with optic atrophy and mitochondrial network fragmentation. eLife 2016, 5, e16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, L.C.; Di Benedetto, G.; Scorrano, L. During autophagy mitochondria elongate, are spared from degradation and sustain cell viability. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaltouki, A.; Sivapatham, R.; Pei, Y.; Gerencser, A.A.; Momcilovic, O.; Rao, M.S.; Zeng, X. Mitochondrial alterations by PARKIN in dopaminergic neurons using PARK2 patient-specific and PARK2 knockout isogenic IPSC lines. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 4, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.; Ng, A.C.; Baird, S.; Dumoulin, A.; Shutt, T.; Mah, N.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; McBride, H.M.; Screaton, R.A. ROMO1 is an essential redox-dependent regulator of mitochondrial dynamics. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowski, M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Youle, R.J. Endophilin B1 is required for the maintenance of mitochondrial morphology. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, Q.; Chai, T.; Tang, T.S. Endophilin B2 promotes inner mitochondrial membrane degradation by forming heterodimers with endophilin B1 during mitophagy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, G.; Bu, G.; Fraser, P.E.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.W. Appoptosin interacts with mitochondrial outer-membrane fusion proteins and regulates mitochondrial morphology. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pan, C.C.; Shah, N.; Wheeler, S.E.; Hoyt, K.R.; Hempel, N.; Mythreye, K.; Lee, N.Y. Activation of mitofusin2 by smad2-RIN1 complex during mitochondrial fusion. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, Y.; De Camilli, P. Recruitment of an alternatively spliced form of synaptojanin 2 to mitochondria by the interaction with the PDZ domain of a outer mitochondrial membrane protein. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalvez, F.; D’Aurelio, M.; Boutant, M.; Moustapha, A.; Puech, J.P.; Landes, T.; Arnaune-Pelloquin, L.; Vial, G.; Taleux, N.; Slomianny, C.; et al. Barth syndrome: Cellular compensation of mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis inhibition due to changes in cardiolipin remodeling linked to tafazzin (TAZ) gene mutation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acehan, D.; Xu, Y.; Stokes, D.L.; Schlame, M. Comparison of lymphoblast mitochondria from normal subjects and patients with barth syndrome using electron microscopic tomography. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2007, 87, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmurs, M.; Foti, M.; Raemy, E.; Vaz, F.M.; Martinou, J.C.; Bairoch, A.; Lane, L. C11orf83, a mitochondrial cardiolipin-binding protein involved in bc1 complex assembly and supercomplex stabilization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eura, Y.; Ishihara, N.; Oka, T.; Mihara, K. Identification of a novel protein that regulates mitochondrial fusion by modulating mitofusin (Mfn) protein function. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 4913–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, J.C. Venny. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn’s Diagrams. Available online: http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 29 August 2017).
- Alanis-Lobato, G.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Schaefer, M.H. Hippie v2.0: Enhancing meaningfulness and reliability of protein-protein interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D408–D414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Bonekamp, N.A.; Galindo, M.F.; Jordan, J.; Schrader, M. 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induces Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation in SH-SY5Y cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, B. Mitochondrial morphogenesis, distribution, and Parkinson disease: Insights from pink1. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winklhofer, K.F.; Haass, C. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemerslage, L.; Ismael, S.; Lee, D. Early alterations of mitochondrial morphology in dopaminergic neurons from Parkinson’s disease-like pathology and time-dependent neuroprotection with D2 receptor activation. Mitochondrion 2016, 30, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laar, V.S.; Berman, S.B. Mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 218, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Khoshaghideh, F.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.J. Impairment of microtubule-dependent trafficking by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillardon, F. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 phosphorylates brain tubulin-beta isoforms and modulates microtubule stability—A point of convergence in Parkinsonian neurodegeneration? J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, A.K.; Exner, N.; Fett, M.E.; Schlehe, J.S.; Kloos, K.; Lammermann, K.; Brunner, B.; Kurz-Drexler, A.; Vogel, F.; Reichert, A.S.; et al. Loss of parkin or PINK1 function increases Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22938–22951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandebring, A.; Thomas, K.J.; Beilina, A.; van der Brug, M.; Cleland, M.M.; Ahmad, R.; Miller, D.W.; Zambrano, I.; Cowburn, R.F.; Behbahani, H.; et al. Mitochondrial alterations in PINK1 deficient cells are influenced by calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagda, R.K.; Gusdon, A.M.; Pien, I.; Strack, S.; Green, S.; Li, C.; Van Houten, B.; Cherra, S.J., 3rd; Chu, C.T. Mitochondrially localized PKA reverses mitochondrial pathology and dysfunction in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laar, V.S.; Arnold, B.; Cassady, S.J.; Chu, C.T.; Burton, E.A.; Berman, S.B. Bioenergetics of neurons inhibit the translocation response of parkin following rapid mitochondrial depolarization. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Csordas, G.; Jowdy, C.; Schneider, T.G.; Csordas, N.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Kohlhaas, M.; Meiser, M.; Bergem, S.; et al. Mitofusin 2-containing mitochondrial-reticular microdomains direct rapid cardiomyocyte bioenergetic responses via interorganelle Ca(2+) crosstalk. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuchner, S.; Mersiyanova, I.V.; Muglia, M.; Bissar-Tadmouri, N.; Rochelle, J.; Dadali, E.L.; Zappia, M.; Nelis, E.; Patitucci, A.; Senderek, J.; et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 cause charcot-marie-tooth neuropathy type 2A. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, J.G.; Cook, T.J.; Stewart, T.; Mattison, H.; Dreisbach, M.T.; Hoffer, Z.S.; Zhang, J. Astrocytic dynamin-like protein 1 regulates neuronal protection against excitotoxicity in Parkinson disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Hulette, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pan, C.; Wadhwa, R.; Zhang, J. Proteomic identification of a stress protein, mortalin/mthsp70/GRP75: Relevance to Parkinson disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobs, S.; Wurm, C.A. Super-resolution microscopy of mitochondria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, D.C.; Wurm, C.A.; Riedel, D.; Wenzel, D.; Stagge, F.; Deckers, M.; Rehling, P.; Jakobs, S. Sted super-resolution microscopy reveals an array of minos clusters along human mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8936–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfanner, N.; van der Laan, M.; Amati, P.; Capaldi, R.A.; Caudy, A.A.; Chacinska, A.; Darshi, M.; Deckers, M.; Hoppins, S.; Icho, T.; et al. Uniform nomenclature for the mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, C.; Ross, K.; Straub, S.; Thiede, B.; Gotz, M.; Goosmann, C.; Krischke, M.; Mueller, M.J.; Krohne, G.; Rudel, T.; et al. Sam50 functions in mitochondrial intermembrane space bridging and biogenesis of respiratory complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1173–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondera, D.; Grandemange, S.; Jourdain, A.; Karbowski, M.; Mattenberger, Y.; Herzig, S.; Da Cruz, S.; Clerc, P.; Raschke, I.; Merkwirth, C.; et al. SLP-2 is required for stress-induced mitochondrial hyperfusion. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steglich, G.; Neupert, W.; Langer, T. Prohibitins regulate membrane protein degradation by the m-AAA protease in mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3435–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijtmans, L.G.; de Jong, L.; Artal Sanz, M.; Coates, P.J.; Berden, J.A.; Back, J.W.; Muijsers, A.O.; van der Spek, H.; Grivell, L.A. Prohibitins act as a membrane-bound chaperone for the stabilization of mitochondrial proteins. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paumard, P.; Vaillier, J.; Coulary, B.; Schaeffer, J.; Soubannier, V.; Mueller, D.M.; Brethes, D.; di Rago, J.P.; Velours, J. The ATP synthase is involved in generating mitochondrial cristae morphology. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habersetzer, J.; Larrieu, I.; Priault, M.; Salin, B.; Rossignol, R.; Brethes, D.; Paumard, P. Human F1F0 ATP synthase, mitochondrial ultrastructure and OXPHOS impairment: A (super-) complex matter? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, M.; Hofhaus, G.; Schroder, R.R.; Kuhlbrandt, W. Dimer ribbons of ATP synthase shape the inner mitochondrial membrane. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereghetti, G.M.; Stangherlin, A.; Martins de Brito, O.; Chang, C.R.; Blackstone, C.; Bernardi, P.; Scorrano, L. Dephosphorylation by calcineurin regulates translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15803–15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.H.; Fontaine, J.F.; Vinayagam, A.; Porras, P.; Wanker, E.E.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Hippie: Integrating protein interaction networks with experiment based quality scores. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.H.; Lopes, T.J.; Mah, N.; Shoemaker, J.E.; Matsuoka, Y.; Fontaine, J.F.; Louis-Jeune, C.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Neumann, G.; Perez-Iratxeta, C.; et al. Adding protein context to the human protein-protein interaction network to reveal meaningful interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suratanee, A.; Schaefer, M.H.; Betts, M.J.; Soons, Z.; Mannsperger, H.; Harder, N.; Oswald, M.; Gipp, M.; Ramminger, E.; Marcus, G.; et al. Characterizing protein interactions employing a genome-wide sirna cellular phenotyping screen. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragoszewski, P.; Gornicka, A.; Sztolsztener, M.E.; Chacinska, A. The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates mitochondrial intermembrane space proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2136–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragoszewski, P.; Turek, M.; Chacinska, A. Control of mitochondrial biogenesis and function by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, C.; Petrucelli, L. A critical evaluation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, O. Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielson, S.R.; Andersen, J.K. Oxidative and nitrative protein modifications in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.R.; Lackner, L.L.; West, M.; DiBenedetto, J.R.; Nunnari, J.; Voeltz, G.K. ER tubules mark sites of mitochondrial division. Science 2011, 334, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartelli, D.; Casagrande, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Bucci, D.; Molinaro, G.; Traficante, A.; Passarella, D.; Giavini, E.; Pezzoli, G.; Battaglia, G.; et al. Microtubule alterations occur early in experimental Parkinsonism and the microtubule stabilizer epothilone D is neuroprotective. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.E. Control of mitochondrial shape. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleier, L.; Drose, S. Superoxide generation by complex III: From mechanistic rationales to functional consequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1827, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, F.L.; Liu, Y.; Van Remmen, H. Complex III releases superoxide to both sides of the inner mitochondrial membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49064–49073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartelli, D.; Goldwurm, S.; Casagrande, F.; Pezzoli, G.; Cappelletti, G. Microtubule destabilization is shared by genetic and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease patient fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passmore, J.B.; Pinho, S.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Schrader, M. The respiratory chain inhibitor rotenone affects peroxisomal dynamics via its microtubule-destabilising activity. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 148, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pages, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGo: A cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, K.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Przedborski, S. Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in Parkinson’s disease. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Chen, C.; Hou, J.; Xin, W.; Mori, A. Nitric oxide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in neuronal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1498, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, D.; Bryan, N.S. Nitric oxide availability as a marker of oxidative stress. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1208, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smeyne, M.; Smeyne, R.J. Glutathione metabolism and Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraibar, M.A.; Liu, L.; Ahmed, E.K.; Friguet, B. Protein oxidative damage at the crossroads of cellular senescence, aging, and age-related diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 919832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Zheng, J.; Bizzozero, O.A. Protein carbonylation and aggregation precede neuronal apoptosis induced by partial glutathione depletion. ASN Neuro 2012, 4, e00084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattenberger, Y.; James, D.I.; Martinou, J.C. Fusion of mitochondria in mammalian cells is dependent on the inner mitochondrial membrane potential and independent of microtubules or actin. FEBS Lett. 2003, 538, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackley, K.I.; Grantham, J. Activities of the chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT): Implications for cell cycle progression and cytoskeletal organisation. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Cristovao, A.C.; Guhathakurta, S.; Lee, J.; Joh, T.H.; Beal, M.F.; Kim, Y.S. NADPH oxidase 1-mediated oxidative stress leads to dopamine neuron death in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, A.; Gonzalez-Agosti, C.; Cordero, E.; Pinney, D.; Candia, C.; Solomon, F.; Gusella, J.; Ramesh, V. NHE-RF, a regulatory cofactor for Na(+)-H+ exchange, is a common interactor for merlin and ERM (MERM) proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Saminathan, H.; Kanthasamy, A.; Anantharam, V.; Jin, H.; Sondarva, G.; Harischandra, D.S.; Qian, Z.; Rana, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. The Peptidyl-prolyl Isomerase Pin1 Up-regulation and Proapoptotic Function in Dopaminergic Neurons: Relevance to the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21955–21971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braithwaite, A.W.; Del Sal, G.; Lu, X. Some p53-binding proteins that can function as arbiters of life and death. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, O.; Harbauer, A.B.; Rao, S.; Eyrich, B.; Zahedi, R.P.; Stojanovski, D.; Schonfisch, B.; Guiard, B.; Sickmann, A.; Pfanner, N.; et al. Regulation of mitochondrial protein import by cytosolic kinases. Cell 2011, 144, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, B.J.; Marshall, B.L.; Borra, M.T.; Denu, J.M.; Verdin, E. The human Sir2 ortholog, Sirt2, is an NAD+-dependent tubulin deacetylase. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, C. The tubulin code: Molecular components, readout mechanisms, and functions. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, D.A.; Camp, D.M.; Conant, S.B. Complement activation in the Parkinson’s disease substantia nigra: An immunocytochemical study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2006, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, P.J.; Nenutil, R.; McGregor, A.; Picksley, S.M.; Crouch, D.H.; Hall, P.A.; Wright, E.G. Mammalian prohibitin proteins respond to mitochondrial stress and decrease during cellular senescence. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 265, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros-Bernal, F.; Hunot, S.; Herrero, M.T.; Parnadeau, S.; Corvol, J.C.; Lu, L.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Carrillo-de Sauvage, M.A.; Saurini, F.; Coussieu, C.; et al. Microglial glucocorticoid receptors play a pivotal role in regulating dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6632–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.T.; Estrada, C.; Maatouk, L.; Vyas, S. Inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Role of glucocorticoids. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, E.H.; Kim, D.W.; Shin, M.J.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, H.R.; Woo, S.J.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; et al. PEP-1-ribosomal protein S3 protects dopaminergic neurons in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 55, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.; Colicos, M.A.; Goda, Y. Actin-dependent regulation of neurotransmitter release at central synapses. Neuron 2000, 27, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, Y.; Akiguchi, I.; Nakamura, S.; Honjyo, Y.; Shibasaki, H.; Budka, H. 14-3-3 proteins in lewy bodies in Parkinson disease and diffuse lewy body disease brains. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabelo, N.; Martin, V.; Santpere, G.; Marin, R.; Torrent, L.; Ferrer, I.; Diaz, M. Severe alterations in lipid composition of frontal cortex lipid rafts from Parkinson’s disease and incidental Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.; Hatano, T.; Hattori, N. Lipid rafts involvement in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Choi, Y.R.; Heo, C.H.; Kang, S.J.; Joe, E.H.; Jou, I.; Kim, H.M.; Park, S.M. Loss of parkin promotes lipid rafts-dependent endocytosis through accumulating caveolin-1: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B.R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Functions of S100 proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner-Schmidt, J.L.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhang, X.; Marshall, J.J.; Morozov, A.; Svenningsson, P.; Greengard, P. A role for p11 in the antidepressant action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvanpour, A.; Santamaria-Kisiel, L.; Shaw, G.S. The S100A10-annexin A2 complex provides a novel asymmetric platform for membrane repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40174–40183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieberich, E. Synthesis, processing, and function of N-glycans in N-glycoproteins. Adv. Neurobiol. 2014, 9, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.; Panin, V.M. The role of protein N-glycosylation in neural transmission. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picconi, B.; Piccoli, G.; Calabresi, P. Synaptic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 970, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mercado, G.; Valdes, P.; Hetz, C. An ercentric view of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broers, J.L.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Bonne, G.; Yaou, R.B.; Hutchison, C.J. Nuclear lamins: Laminopathies and their role in premature ageing. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 967–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Vosse, D.W.; Wan, Y.; Wozniak, R.W.; Aitchison, J.D. Role of the nuclear envelope in genome organization and gene expression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D.N.; Zastrow, M.S.; Wilson, K.L. Direct actin binding to A- and B-type lamin tails and actin filament bundling by the lamin A tail. Nucleus 2010, 1, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauseef, W.M.; McCormick, S.J.; Clark, R.A. Calreticulin functions as a molecular chaperone in the biosynthesis of myeloperoxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4741–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, O.B.; Pringle, M.A.; Schopp, I.M.; Braakman, I.; Bulleid, N.J. Erdj5 is the ER reductase that catalyzes the removal of non-native disulfides and correct folding of the LDL receptor. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, J.W.; Ballard, P.A., Jr. Parkinson’s disease in a chemist working with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gautier, C.A.; Corti, O.; Brice, A. Mitochondrial dysfunctions in Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 170, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroso, M.; Ferreira, R.; Freitas, A.; Vitorino, R.; Gomez-Lazaro, M. New insights on the mitochondrial proteome plasticity in Parkinson’s disease. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perier, C.; Tieu, K.; Guegan, C.; Caspersen, C.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Carelli, V.; Martinuzzi, A.; Hirano, M.; Przedborski, S.; Vila, M. Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterham, H.R.; Koster, J.; van Roermund, C.W.; Mooyer, P.A.; Wanders, R.J.; Leonard, J.V. A lethal defect of mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, M.; Przedborski, S. Genetic clues to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S58–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsoum, M.J.; Yuan, H.; Gerencser, A.A.; Liot, G.; Kushnareva, Y.; Graber, S.; Kovacs, I.; Lee, W.D.; Waggoner, J.; Cui, J.; et al. Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by dynamin-related GTPases in neurons. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3900–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.; Gaume, B.; Bergmann-Leitner, E.S.; Leitner, W.W.; Robert, E.G.; Catez, F.; Smith, C.L.; Youle, R.J. The role of dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in apoptosis. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, P.A.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Parks, J.K.; Keeney, P.; Bennett, J.P., Jr.; Miller, S.W.; Davis, R.E.; Parker, W.D., Jr. Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in sporadic Parpkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease cybrid cell lines. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 162, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilkerson, R.W.; Selker, J.M.; Capaldi, R.A. The cristal membrane of mitochondria is the principal site of oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2003, 546, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannella, C.A. Structure and dynamics of the inner mitochondrial membrane cristae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zick, M.; Rabl, R.; Reichert, A.S. Cristae formation-linking ultrastructure and function of mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perier, C.; Bove, J.; Vila, M. Mitochondria and programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease: Apoptosis and beyond. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, M.; Przedborski, S. Targeting programmed cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; Pinton, P. The endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria connection: One touch, multiple functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1837, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.H.; Xia, C.; Zhong, G.; Babcock, H.P.; Vaughan, J.C.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Bi, G.Q.; Zhuang, X. Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of organelles in live cells with photoswitchable membrane probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13978–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J.P.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Parker, W.D.; Miller, S.W.; Davis, R.E.; Tuttle, J.B. Altered calcium homeostasis in cells transformed by mitochondria from individuals with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1997, 68, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomello, M.; Drago, I.; Pizzo, P.; Pozzan, T. Mitochondrial Ca2+ as a key regulator of cell life and death. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedskog, L.; Pinho, C.M.; Filadi, R.; Ronnback, A.; Hertwig, L.; Wiehager, B.; Larssen, P.; Gellhaar, S.; Sandebring, A.; Westerlund, M.; et al. Modulation of the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interface in Alzheimer’s disease and related models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7916–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleichmann, M.; Mattson, M.P. Neuronal calcium homeostasis and dysregulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabadkai, G.; Bianchi, K.; Varnai, P.; De Stefani, D.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Cavagna, D.; Nagy, A.I.; Balla, T.; Rizzuto, R. Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial Ca2+ channels. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Su, T.P. Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca2+ signaling and cell survival. Cell 2007, 131, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, G.; Castillo, V.; Soto, P.; Sidhu, A. ER stress and Parkinson’s disease: Pathological inputs that converge into the secretory pathway. Brain Res. 2016, 1648, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasawa, R.; Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Datler, C.; Pazarentzos, E.; Grimm, S. Fis1 and Bap31 bridge the mitochondria-ER interface to establish a platform for apoptosis induction. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verfaillie, T.; Rubio, N.; Garg, A.D.; Bultynck, G.; Rizzuto, R.; Decuypere, J.P.; Piette, J.; Linehan, C.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A.; et al. Perk is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamasaki, M.; Furuta, N.; Matsuda, A.; Nezu, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Fujita, N.; Oomori, H.; Noda, T.; Haraguchi, T.; Hiraoka, Y.; et al. Autophagosomes form at ER-mitochondria contact sites. Nature 2013, 495, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, O.M.; Scorrano, L. Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature 2008, 456, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, D.J. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, regulation of exocytosis and their relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.R.; Sullivan, P.G.; Geddes, J.W. Synaptic mitochondria are more susceptible to Ca2+ overload than nonsynaptic mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11658–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbeck, P.J. The pattern and mechanism of mitochondrial transport in axons. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 1996, 1, d91–d102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Chylinski, T.M.; Pimenta, A.; Ortiz, D.; Shea, T.B. Neurofilament transport is dependent on actin and myosin. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9486–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. Mitochondria: The next (neurode) generation. Neuron 2011, 70, 1033–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim-Han, J.S.; Antenor-Dorsey, J.A.; O’Malley, K.L. The Parkinsonian mimetic, MPP+, specifically impairs mitochondrial transport in dopamine axons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7212–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, C.; Voelker, D.R.; Langer, T. Making heads or tails of phospholipids in mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Huang, P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Chan, D.C.; Schiller, J.; Frohman, M.A. A common lipid links mfn-mediated mitochondrial fusion and snare-regulated exocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montessuit, S.; Somasekharan, S.P.; Terrones, O.; Lucken-Ardjomande, S.; Herzig, S.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Manstein, D.J.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Basanez, G.; Meda, P.; et al. Membrane remodeling induced by the dynamin-related protein Drp1 stimulates Bax oligomerization. Cell 2010, 142, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, P.J.; Stepanyants, N.; Mehrotra, N.; Mears, J.A.; Qi, X.; Sesaki, H.; Ramachandran, R. A dimeric equilibrium intermediate nucleates Drp1 reassembly on mitochondrial membranes for fission. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiebish, M.A.; Han, X.; Cheng, H.; Lunceford, A.; Clarke, C.F.; Moon, H.; Chuang, J.H.; Seyfried, T.N. Lipidomic analysis and electron transport chain activities in c57bl/6j mouse brain mitochondria. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, G.P.; Peuchen, S.; Clark, J.B. Energy thresholds in brain mitochondria. Potential involvement in neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12753–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Menu, P.; Tschopp, J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011, 469, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbel, N.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V. Voltage-dependent anion channel 1-based peptides interact with Bcl-2 to prevent antiapoptotic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name (with Synonyms) | Protein Name | Function | Localization | Shaping Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOO, FAM121B, MIC23, MIC26, My025, UNQ1866/PRO4302 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC26 (Apolipoprotein O) (MICOS Complex subunit MIC23) (Protein FAM121B) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [14,15,16] |
| APOOL, CXorf33, FAM121A, MIC27, UNQ8193/PRO23204 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC27 (Apolipoprotein O-like) (Protein FAM121A) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [14,15,17,18] |
| ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5C1, ATP5D, ATP5E, ATP5F1, ATP5G1, ATP5G2, ATP5G3, ATP5H, ATP5I, ATP5J, ATP5J2, ATP5L, ATP5O, MT-ATP6, MT-ATP8 | ATP synthase | ATP production | IMM | Cristae shape | [3,15,19] |
| ATPIF1, ATPI | ATPase inhibitor, mitochondrial (Inhibitor of F(1)F(o)-ATPase) (IF(1)) (IF1) | ATP production regulation | Matrix | Cristae shape | [3,20] |
| BAK1, BAK, BCL2L7, CDN1 | Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer (Apoptosis regulator BAK) | Promotes apoptosis | OMM | OMM permeabilization | [3,21] |
| BAX, BCL2L4 | Apoptosis regulator BAX | Accelerates apoptosis | OMM | OMM permeabilization | [3,19,21,22] |
| BCL2 | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | Promotes cell survival | OMM | OMM permeabilization | [3,22] |
| BCL2A1, BCL2L5, BFL1, GRS, HBPA1 | Bcl-2-related protein A1 (A1-A) (Hemopoietic-specific early response protein) (Protein BFL-1) | Promotes cell survival | OMM | Not clear function | [23,24] |
| BCL2L11, BIM | Bcl-2-like protein 11 (Bcl2-L-11) (Bcl2-interacting mediator of cell death) | Induces apoptosis and anoikis | IMM | Cristae remodeling | [25,26] |
| BID | BH3-interacting domain death agonist | The major proteolytic product p15 BID allows the release of cytochrome c | IMM | Cristae remodeling | [25,27] |
| BIK, NBK | Bcl-2-interacting killer (Apoptosis inducer NBK) (BIP1) (BP4) | Promotes apoptosis | IMM | Cristae remodeling | [25,28] |
| CHCHD3, MIC19, MINOS3 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC19 (Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 3) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [14,16,18] |
| COA3, CCDC56, MITRAC12, HSPC009 | Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 3 homolog, mitochondrial (Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 56) (Mitochondrial translation regulation assembly intermediate of cytochrome c oxidase protein of 12 kDa) | Core component of the MITRAC (mitochondrial translation regulation assembly intermediate of cytochrome c oxidase) Complex, which regulates cytochrome c oxidase assembly. | IMM | Cytochrome c oxidase | [29,30] |
| COX4I1, COX4I2, COX5A, COX5B, COX6A1, COX6A2, COX6B1, COX6B2, COX6C, COX7A1, COX7A2, COX7B, COX7B2, COX7C, COX8A, COX8C, MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3 | Mitochondrial Complex IV: cytochrome c oxidase subunits | ATP production | IMM | Cristae shape | [18] |
| CYC1, MT-CYB, UQCR10, UQCR11, UQCRB, UQCRC1, UQCRC2, UQCRFS1, UQCRH, UQCRQ | Mitochondrial Complex III: ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Complex subunits (UQCR) | ATP production | IMM | Cristae shape | [18] |
| DNAJC19, TIM14, TIMM14 | Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM14 (DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 19) | Probable component of the PAM Complex, a Complex required for the translocation of transit peptide-containing proteins from the inner membrane into the mitochondrial matrix in an ATP-dependent manner | IMM | Crista shape | [15,31,32] |
| DNM1L, DLP1, DRP1 | Dynamin-1-like protein (EC 3.6.5.5) (Dnm1p/Vps1p-like protein) (DVLP) (Dynamin family member proline-rich carboxyl-terminal domain less) (Dymple) (Dynamin-like protein) (Dynamin-like protein 4) (Dynamin-like protein IV) (HdynIV) (Dynamin-related protein 1) | Mitochondrial and peroxisome division | OMM and cytosol | Fission | [3,18,22] |
| DNM2, DYN2 | Dynamin-2 (EC 3.6.5.5) | Microtubule-associated force-producing protein involved in producing microtubule bundles and able to bind and hydrolyze GTP | Cytosol | Fission | [4,33] |
| FIS1, TTC11, CGI-135 | Mitochondrial fission 1 protein (FIS1 homolog) (hFis1) (Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 11) (TPR repeat protein 11) | Mitochondrial fragmentation | OMM | Fission | [3,19,22] |
| FUNDC1 | FUN14 domain-containing protein 1FUN14 domain-containing protein 1 | Mitophagy | OMM | Fission | [29,34,35,36] |
| GDAP1 | Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1 | Mitochondrial fission | OMM | Fission | [1,19,22] |
| hfzo1 | Mitochondrial transmembrane GTPase Fzo-1 | FUNDC1 mediates highly selective mitochondrial clearance under hypoxic conditions without impacting general autophagy | OMM | Fusion | [19] |
| IMMT, HMP, MIC60, MINOS2, PIG4, PIG52 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC60(Cell proliferation-inducing gene 4/52 protein) (Inner mitochondrial membrane protein) (Mitofilin) (p87/89) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [15,16,18,19,37] |
| INF2, C14orf151, C14orf173 | Inverted formin-2 (HBEBP2-binding protein C) | Severs actin filaments and accelerates their polymerization and depolymerization | Cytosol | Mitochondrial constriction | [29,38] |
| LETM1 | Mitochondrial proton/calcium exchanger protein (Leucine zipper-EF-hand-containing transmembrane protein 1) | Mitochondrial proton/calcium antiporter that mediates proton-dependent calcium efflux from mitochondria | IMM | Fission | [1,22,39] |
| MARCH5, RNF153 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MARCH5 (EC 2.3.2.27) (Membrane-associated RING finger protein 5) (Membrane-associated RING-CH protein V) (MARCH-V) (Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase) (MITOL) (RING finger protein 153) (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase MARCH5) | Membrane-bound E3 ligase for mitochondrial morphology control | OMM | Fission | [1,19] |
| MAVS, IPS1, KIAA1271, VISA | Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) (CARD adapter inducing interferon beta) (Cardif) (Interferon beta promoter stimulator protein 1) (IPS-1) (Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 031N) (Virus-induced-signaling adapter) (VISA) | Required for innate immune response against viruses | OMM | Fusion | [22,40] |
| MCL1, BCL2L3 | Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 (Bcl-2-like protein 3) (Bcl2-L-3) (Bcl-2-related protein EAT/mcl1) (mcl1/EAT) | Regulation of apoptosis | IMM and OMM | Cristae shape (IMM isoform) | [18,29,41,42] |
| MFF, C2orf33, AD030, AD033, GL004 | Mitochondrial Fission Factor | Mitochondrial and peroxisome division | OMM | Fission | [3,19] |
| MFN1 | Mitofusin-1 (EC 3.6.5.-) (Fzo homolog) (Transmembrane GTPase MFN1) | Mitochondrial fusion | OMM | Fusion | [18,22,43] |
| MFN2, CPRP1, KIAA0214 | Mitofusin-2 (EC 3.6.5.-) (Transmembrane GTPase MFN2) | Regulates mitochondrial clustering and fusion | OMM | Fusion | [18,22,43] |
| MIC13, C19orf70, QIL1 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC13 (Protein P117) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [15,18] |
| MIEF1, MID51, SMCR7L | Mid51/Mief, mitochondrial dynamics proteins of 51 | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | OMM | Fission | [3,19] |
| MIEF2, MID49, SMCR7 | Mitochondrial dynamics protein MID49 (Mitochondrial dynamics protein of 49 kDa) (Mitochondrial elongation factor 2) (Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosomal region candidate gene 7 protein) | Component of the MICOS Complex, a large protein Complex of the inner mitochondrial membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | OMM | Fission | [3,19] |
| MIGA1, FAM73A | Mitoguardin 1 (Protein FAM73A) | Regulator of mitochondrial fusion | OMM | Fusion | [4,44] |
| MIGA2, C9orf54, FAM73B, PSEC0112 | Mitoguardin 2 (Protein FAM73B) | Regulator of mitochondrial fusion | OMM | Fusion | [4,44] |
| MINOS1, C1orf151, MIC10 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC10 (Inner mitochondrial membrane organizing system protein 1) | Maintenance of cristae junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [15,18] |
| MTFP1, MTP18, HSPC242, My022 | Mitochondrial fission process protein 1(Mitochondrial 18 kDa protein) (MTP18) | Involved in the mitochondrial division probably by regulating membrane fission | IMM | Fission | [1,22,45] |
| MUL1, C1orf166, GIDE, MAPL, MULAN, RNF218 | Mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase activator of NFKB 1 (EC 2.3.2.27) (E3 SUMO-protein ligase MUL1) (E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MUL1) (Growth inhibition and death E3 ligase) (Mitochondrial-anchored protein ligase) (MAPL) (Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 266) (RING finger protein 218) (RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase NFKB 1) | Ubiquitin ligase activity | OMM | Fusion | [19,29] |
| NFE2L2, NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) (NFE2-related factor 2) (HEBP1) (Nuclear factor, erythroid derived 2, like 2) | Transcription activator that binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements in the promoter regions of target genes | Cytosol | Fusion | [29,46,47] |
| NRF1 | Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1) (Alpha palindromic-binding protein) (Alpha-pal) | Transcription factor implicated in the control of nuclear genes required for respiration, heme biosynthesis, and mitochondrial DNA transcription and replication | Cytosol | Fission | [29,46,48,49] |
| OMA1, MPRP1 | Metalloendopeptidase OMA1, mitochondrial (EC 3.4.24.-) (Metalloprotease-related protein 1) (MPRP-1) (Overlapping with the m-AAA protease 1 homolog) | Metalloprotease that is part of the quality control system in the inner membrane of mitochondria | IMM | Fusion | [1,19] |
| OPA1, KIAA0567 | Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial (EC 3.6.5.5) (Optic atrophy protein 1) (Cleaved into: Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, form S1) | Opa1 mediates dynamics changes in cristae morphology that correlate with the metabolic state of the organelle | IMM | Cristae shape, fusion | [1,3,15,18,22,50] |
| PARL, PSARL, PRO2207 | Presenilins-associated rhomboid-like protein, mitochondrial (EC 3.4.21.105) (Mitochondrial intramembrane cleaving protease PARL) (Cleaved into: P-beta (Pbeta)) | Required for the control of apoptosis | IMM | Mitochondrial morphology | [1,51] |
| PGAM5 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PGAM5, mitochondrial (EC 3.1.3.16) (Bcl-XL-binding protein v68) (Phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5) | Displays phosphatase activity for serine/threonine residues, as well as dephosphorylates and activates MAP3K5 kinase | OMM | Fission | [1,29,52] |
| PHB | Prohibitin | Prohibitin inhibits DNA synthesis; it has a role in regulating proliferation | IMM | Cristae shape | [1,15,18,31,53] |
| PHB2, BAP, REA | Prohibitin-2 (B-cell receptor-associated protein BAP37) (D-prohibitin) (Repressor of estrogen receptor activity) | Acts as a mediator of transcriptional repression by nuclear hormone receptors via the recruitment of histone deacetylases (by similarity); functions as an estrogen receptor (ER)-selective coregulator that potentiates the inhibitory activities of antiestrogens and represses the activity of estrogens | IMM | Cristae shape | [1,15,18] |
| PINK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1, mitochondrial (EC 2.7.11.1) (BRPK) (PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1) | Protects against mitochondrial dysfunction during cellular stress by phosphorylating mitochondrial proteins | OMM | Fission | [1,54] |
| PLD6 | Mitochondrial cardiolipin hydrolase (EC 3.1.-.-) (Choline phosphatase 6) (Mitochondrial phospholipase) (MitoPLD) (Phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D6) (Phospholipase D6) (PLD 6) (Protein zucchini homolog) | Proposed to act as a cardiolipin hydrolase to generate phosphatidic acid at the mitochondrial surface | OMM | Fusion | [4,19,22,45] |
| PPARGC1A, LEM6, PGC1, PGC1A, PPARGC1 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1-alpha) (PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha) (PPARGC-1-alpha) (Ligand effect modulator 6) | Transcriptional coactivator for steroid receptors and nuclear receptors | Cytoplasm and nucleus | Fusion | [29,49,55] |
| PPARGC1B, PERC, PGC1, PGC1B, PPARGC1 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta (PGC-1-beta) (PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-beta) (PPARGC-1-beta) (PGC-1-related estrogen receptor alpha coactivator) | Plays the role of stimulator of transcription factors and nuclear receptors activities | Nucleus | Fusion | [29,55,56] |
| PRELID1, PRELI, CGI-106, SBBI12 | PRELI domain-containing protein 1, mitochondrial (25 kDa protein of relevant evolutionary and lymphoid interest) (Px19-like protein) | Involved in the modulation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by ensuring the accumulation of cardiolipin (CL) in mitochondrial membranes | Intermembrane space | Fission | [57,58] |
| PRKN, PARK2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin (Parkin) (EC 2.3.2.-) (Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase) (Parkinson juvenile disease protein 2) (Parkinson disease protein 2) | Functions within a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase Complex, catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins | Cytosol and mitochondria | Fission | [1,54,59,60] |
| ROMO1, C20orf52 | Reactive oxygen species modulator 1(ROS modulator 1) (Epididymis tissue protein Li 175) (Glyrichin) (Mitochondrial targeting GxxxG motif protein) (MTGM) (Protein MGR2 homolog) | Induces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are necessary for cell proliferation | IMM | Fusion | [29,61] |
| SAMM50, SAM50, CGI-51, TRG3 | Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog (Transformation-related gene 3 protein) (TRG-3) | Plays a crucial role in the maintenance of the structure of mitochondrial cristae and the proper assembly of the mitochondrial respiratory chain Complexes | OMM | Cristae shape | [18] |
| SH3GLB1, KIAA0491, CGI-61 | Endophilin-B1 (Bax-interacting factor 1) (Bif-1) (SH3 domain-containing GRB2-like protein B1) | Outer mitochondrial dynamics | OMM | OMM permeability | [1,22,62] |
| SH3GLB2, KIAA1848, PP578 | Endophilin-B2 (SH3 domain-containing GRB2-like protein B2) | Mitophagy | Cytosol | Fission | [63] |
| SLC25A10, DIC | Mitochondrial dicarboxylate carrier (Solute carrier family 25 member 10) | Involved in the translocation of malonate, malate, and succinate in exchange for phosphate, sulfate, sulfite, or thiosulfate across the inner mitochondrial membrane | IMM | Cristae shape | [18,50] |
| SLC25A11, SLC20A4 | Mitochondrial 2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier protein (OGCP) (Solute carrier family 25 member 11) | Catalyzes the transport of 2-oxoglutarate across the inner mitochondrial membrane in an electroneutral exchange for malate or other dicarboxylic acids, and plays an important role in several metabolic processes, including the malate-aspartate shuttle, the oxoglutarate/isocitrate shuttle, in gluconeogenesis from lactate, and in nitrogen metabolism | IMM | Cristae shape | [18,50] |
| SLC25A12, ARALAR1 | Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar1 (Mitochondrial aspartate glutamate carrier 1) (Solute carrier family 25 member 12) | Catalyzes the calcium-dependent exchange of cytoplasmic glutamate with mitochondrial aspartate across the inner mitochondrial membrane; may have a function in the urea cycle | IMM | Cristae shape | [18,50] |
| SLC25A13, ARALAR2 | Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar2 (Citrin) (Mitochondrial aspartate glutamate carrier 2) (Solute carrier family 25 member 13) | Catalyzes the calcium-dependent exchange of cytoplasmic glutamate with mitochondrial aspartate across the inner mitochondrial membrane; may have a function in the urea cycle | IMM | Cristae shape | [18,50] |
| SLC25A38 | Solute carrier family 25 member 38, Appoptosin | Mitochondrial import machinery | IMM | Fusion | [29,64] |
| SMAD2, MADH2, MADR2 | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 (MAD homolog 2) (Mothers against DPP homolog 2) (JV18-1) (Mad-related protein 2) (hMAD-2) (SMAD family member 2) (SMAD 2) (Smad2) (hSMAD2) | Receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that is an intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinases | Cytosol | Fusion | [29,65] |
| SPG7, CAR, CMAR, PGN | Paraplegin (EC 3.4.24.-) (Cell matrix adhesion regulator) (Spastic paraplegia 7 protein) | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease | IMM | Cristae shape | [18] |
| SPG7, CAR, CMAR, PGN | Paraplegin (EC 3.4.24.-) (Cell matrix adhesion regulator) (Spastic paraplegia 7 protein) | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease | IMM | Fusion | [1,22,51] |
| STOML2, SLP2, HSPC108 | Stomatin-like protein 2, mitochondrial(SLP-2) (EPB72-like protein 2) (Paraprotein target 7) (Paratarg-7) | Mitochondrial protein that probably regulates the biogenesis and the activity of mitochondria; stimulates cardiolipin biosynthesis, binds cardiolipin-enriched membranes where it recruits and stabilizes some proteins including prohibitin, and may therefore act in the organization of functional microdomains in mitochondrial membranes | IMM | Cristae shape/Stabilize IM structure | [15,18] |
| SYNJ2, KIAA0348 | Synaptojanin-2(EC 3.1.3.36) (Synaptic inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 2) | Membrane trafficking and signaling transduction | Cytosol | Mitochondrial aggregation | [66] |
| TAZ, EFE2, G4.5 | Tafazzin (Protein G4.5) | Some isoforms may be involved in cardiolipin (CL) metabolism | OMM | Cristae shape | [15,16,67,68] |
| TFAM, TCF6, TCF6L2 | Transcription factor A, mitochondrial (mtTFA) (Mitochondrial transcription factor 1) (MtTF1) (Transcription factor 6) (TCF-6) (Transcription factor 6-like 2) | Binds to the mitochondrial light strand promoter and functions in mitochondrial transcription regulation | Matrix | Mitochondrial biogenesis | [29,46] |
| TRAK1, KIAA1042, OIP106 | Trafficking kinesin-binding protein 1 (106 kDa O-GlcNAc transferase-interacting protein) | Organelle trafficking | OMM and cytosol | Fusion | [1,4,19] |
| TRAK2, ALS2CR3, KIAA0549 | Trafficking kinesin-binding protein 2 (Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 chromosomal region candidate gene 3 protein) | Organelle trafficking | OMM and cytosol | Fusion | [1,4,19] |
| UQCC3, C11orf83, UNQ655/PRO1286 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase Complex assembly factor 3 | Required for the assembly of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Complex (mitochondrial respiratory chain Complex III or cytochrome b-c1 Complex), mediating cytochrome b recruitment and probably stabilization within the Complex | IMM | Cristae shape | [18,69] |
| VAT1 | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog (EC 1.-.-.-) (Mitofusin-binding protein) (Protein MIB) | Negatively regulates mitochondrial fusion | OMM | Fusion | [1,19,22,70] |
| YME1L1, FTSH1, YME1L, UNQ1868/PRO4304 | ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease YME1L1 (EC 3.4.24.-) (ATP-dependent metalloprotease FtsH1) (Meg-4) (Presenilin-associated metalloprotease) (PAMP) (YME1-like protein 1) | Putative ATP-dependent protease; plays a role in mitochondrial organization and mitochondrial protein metabolism, including the degradation of PRELID1 and OPA1 | IMM | Cristae shape | [19,58] |
| Gene Symbol (bioDBnet) | Name | Mito_Shaping |
|---|---|---|
| APOO, FAM121B, MIC23, MIC26, My025, UNQ1866/PRO4302 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC26 (Apolipoprotein O) (MICOS Complex subunit MIC23) (Protein FAM121B) | Cristae shape |
| ATP5A1, ATP5A, ATP5AL2, ATPM | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial | Cristae shape |
| ATP5B, ATPMB, ATPSB | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | Cristae shape |
| ATP5H | ATP synthase subunit d | Cristae shape |
| ATP5I | ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial | Cristae shape |
| SAMM50, SAM50, CGI-51, TRG3 | Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog (Transformation-related gene 3 protein) (TRG-3) | Cristae shape |
| COX4I1, COX4 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1, mitochondrial (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV) (Cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV isoform 1) (COX IV-1) | Cristae shape |
| COX5A | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5A, mitochondrial (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide Va) | Cristae shape |
| COX6C | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide VIc) | Cristae shape |
| COX7C | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7C, mitochondrial (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide VIIc) | Cristae shape |
| MFN2, CPRP1, KIAA0214 | Mitofusin-2 (EC 3.6.5.-) (Transmembrane GTPase MFN2) | Fusion |
| DNM1L | Dynamin-like protein | Fission |
| IMMT | Mitofilin | Cristae shape |
| MT-CO1 | Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide I | Cristae shape |
| PHB | Prohibitin | Cristae shape |
| PHB2 | Prohibitin-2 | Cristae shape |
| SH3GLB2 | SH3-containing protein SH3GLB2 | Fission |
| SLC25A13 | Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar2 | Cristae shape |
| UQCRB, UQBP | Cytochrome b-c1 Complex subunit 7 (Complex III subunit 7) (Complex III subunit VII) (QP-C) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Complex 14 kDa protein) | Cristae shape |
| UQCRFS1 | Ubiquinol cytochrome c reductase iron–sulfur subunit | Cristae shape |
| UQCRH | Cytochrome b-c1 Complex subunit 6, mitochondrial | Cristae shape |
| VAT1 | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog | Fusion |
| Gene Names | Protein Names |
|---|---|
| ACAD9 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 9, mitochondrial (ACAD-9) (EC 1.3.99.-) |
| ACP2 | Lysosomal acid phosphatase (LAP) (EC 3.1.3.2) |
| ACTB | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 (Beta-actin) (Cleaved into: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed) |
| ACTBL2 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 (Kappa-actin) |
| ACTN1 | Alpha-actinin-1 (Alpha-actinin cytoskeletal isoform) (F-actin cross-linking protein) (Non-muscle alpha-actinin-1) |
| ALB, GIG20, GIG42, PRO0903, PRO1708, PRO2044, PRO2619, PRO2675, UNQ696/PRO1341 | Serum albumin |
| ALDH1B1, ALDH5, ALDHX | Aldehyde dehydrogenase X, mitochondrial (EC 1.2.1.3) (Aldehyde dehydrogenase 5) (Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member B1) |
| ALDOA, ALDA | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A (EC 4.1.2.13) (Lung cancer antigen NY-LU-1) (Muscle-type aldolase) |
| ANXA2, ANX2, ANX2L4, CAL1H LPC2D | Annexin A2 (Annexin II) (Annexin-2) (Calpactin I heavy chain) (Calpactin-1 heavy chain) (Chromobindin-8) (Lipocortin II) (Placental anticoagulant protein IV) (PAP-IV) (Protein I) (p36) |
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I (Apo-AI) (ApoA-I) (Apolipoprotein A1) (Cleaved into: Proapolipoprotein A-I (Proapo A-I); Truncated apolipoprotein A-I (Apolipoprotein A-I(1-242))) |
| ATP5A1, ATP5A, ATP5AL2, ATPM | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial |
| ATP5B, ATPMB, ATPSB, | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial (EC 3.6.3.14) |
| ATP5H, My032 | ATP synthase subunit d, mitochondrial (ATPase subunit d) |
| ATP5I, ATP5K | ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial (ATPase subunit e) (Cleaved into: ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial, N-terminally processed) |
| BCAP31, BAP31, DXS1357E | B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 (BCR-associated protein 31) (Bap31) (6C6-AG tumor-associated antigen) (Protein CDM) (p28) |
| C1QBP, GC1QBP, HABP1, SF2P32 | Complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein, mitochondrial (ASF/SF2-associated protein p32) (Glycoprotein gC1qBP) (C1qBP) (Hyaluronan-binding protein 1) (Mitochondrial matrix protein p32) (gC1q-R protein) (p33) |
| CALR, CRTC | Calreticulin (CRP55) (Calregulin) (Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60) (ERp60) (HACBP) (grp60) |
| CCT5, CCTE, KIAA0098 | T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon (TCP-1-epsilon) (CCT-epsilon) |
| COX4I1, COX4 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1, mitochondrial (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide IV) (Cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV isoform 1) (COX IV-1) |
| COX5A | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5A, mitochondrial (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide Va) |
| COX6C | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C (Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide VIc) |
| DDAH1, DDAH | N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 (DDAH-1) (Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1) (EC 3.5.3.18) (DDAHI) (Dimethylargininase-1) |
| DDOST, KIAA0115, OST48 OK/SW-cl.45 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase 48 kDa subunit (DDOST 48 kDa subunit) (Oligosaccharyl transferase 48 kDa subunit) |
| DNM1L, DLP1, DRP1 | Dynamin-1-like protein (EC 3.6.5.5) (Dnm1p/Vps1p-like protein) (DVLP) (Dynamin family member proline-rich carboxyl-terminal domain less) (Dymple) (Dynamin-like protein) (Dynamin-like protein 4) (Dynamin-like protein IV) (HdynIV) (Dynamin-related protein 1) |
| DYNC1H1, DHC1, DNCH1, DNCL, DNECL, DYHC, KIAA0325 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 (Cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain 1) (Dynein heavy chain, cytosolic) |
| EEF1A1, EEF1A, EF1A, LENG7 | Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (EF-1-alpha-1) (Elongation factor Tu) (EF-Tu) (Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 A-1) (eEF1A-1) (Leukocyte receptor cluster member 7) |
| EEF1B2, EEF1B, EF1B | Elongation factor 1-beta (EF-1-beta) |
| EIF5A | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 (eIF-5A-1) (eIF-5A1) (Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A isoform 1) (eIF-5A) (Rev-binding factor) (eIF-4D) |
| FKBP4, FKBP52 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP4 (PPIase FKBP4) (EC 5.2.1.8) (51 kDa FK506-binding protein) (FKBP51) (52 kDa FK506-binding protein) (52 kDa FKBP) (FKBP-52) (59 kDa immunophilin) (p59) (FK506-binding protein 4) (FKBP-4) (FKBP59) (HSP-binding immunophilin) (HBI) (Immunophilin FKBP52) (Rotamase) (Cleaved into: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP4, N-terminally processed) |
| FLNC, ABPL, FLN2 | Filamin-C (FLN-C) (FLNc) (ABP-280-like protein) (ABP-L) (Actin-binding-like protein) (Filamin-2) (Gamma-filamin) |
| FLOT1 | Flotillin-1 |
| FUBP1 | Far upstream element-binding protein 1 (FBP) (FUSE-binding protein 1) (DNA helicase V) (hDH V) |
| GARS | Glycine-tRNA ligase (EC 3.6.1.17) (EC 6.1.1.14) (Diadenosine tetraphosphate synthetase) (AP-4-A synthetase) (Glycyl-tRNA synthetase) (GlyRS) |
| GSTK1, HDCMD47P | Glutathione S-transferase kappa 1 (EC 2.5.1.18) (GST 13-13) (GST class-kappa) (GSTK1-1) (hGSTK1) (Glutathione S-transferase subunit 13) |
| GSTO1, GSTTLP28 | Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 (GSTO-1) (EC 2.5.1.18) (Glutathione S-transferase omega 1-1) (GSTO 1-1) (Glutathione-dependent dehydroascorbate reductase) (EC 1.8.5.1) (Monomethylarsonic acid reductase) (MMA(V) reductase) (EC 1.20.4.2) (S-(Phenacyl)glutathione reductase) (SPG-R) |
| HSP90AB1, HSP90B HSPC2, HSPCB | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta (HSP 90) (Heat shock 84 kDa) (HSP 84) (HSP84) |
| HSPA1L | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1-like (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1L) (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1-Hom) (HSP70-Hom) |
| HSPA5, GRP78 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP-78) (Endoplasmic reticulum lumenal Ca(2+)-binding protein grp78) (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 5) (Immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein) (BiP) |
| HSPA8, HSC70, HSP73, HSPA10 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8) (Lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 1) (LAP-1) (LPS-associated protein 1) |
| HSPA9, GRP75, HSPA9B, mt-HSP70 | Stress-70 protein, mitochondrial (75 kDa glucose-regulated protein) (GRP-75) (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 9) (Mortalin) (MOT) (Peptide-binding protein 74) (PBP74) |
| HSPB1, HSP27, HSP28 | Heat shock protein beta-1 (HspB1) (28 kDa heat shock protein) (Estrogen-regulated 24 kDa protein) (Heat shock 27 kDa protein) (HSP 27) (Stress-responsive protein 27) (SRP27) |
| HSPD1, HSP60 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial (EC 3.6.4.9) (60 kDa chaperonin) (Chaperonin 60) (CPN60) (Heat shock protein 60) (HSP-60) (Hsp60) (HuCHA60) (Mitochondrial matrix protein P1) (P60 lymphocyte protein) |
| ILVBL, AHAS | Acetolactate synthase-like protein (EC 2.2.1.-) (IlvB-like protein) |
| IMMT, HMP, MIC60, MINOS2, PIG4, PIG52 | MICOS Complex subunit MIC60 (Cell proliferation-inducing gene 4/52 protein) (Inner mitochondrial membrane protein) (Mitofilin) (p87/89) |
| LDHB | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain (LDH-B) (EC 1.1.1.27) (LDH heart subunit) (LDH-H) (Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-46) |
| LGALS1 | Galectin-1 (Gal-1) (14 kDa laminin-binding protein) (HLBP14) (14 kDa lectin) (Beta-galactoside-binding lectin L-14-I) (Galaptin) (HBL) (HPL) (Lactose-binding lectin 1) (Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 1) (Putative MAPK-activating protein PM12) (S-Lac lectin 1) |
| LMNA, LMN1 | Prelamin-A/C (Cleaved into: Lamin-A/C (70 kDa lamin) (Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-32)) |
| MDH2 | Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial (EC 1.1.1.37) |
| MFN2, CPRP1, KIAA0214 | Mitofusin-2 (EC 3.6.5.-) (Transmembrane GTPase MFN2) |
| MYL6 | Myosin light polypeptide 6 (17 kDa myosin light chain) (LC17) (Myosin light chain 3) (MLC-3) (Myosin light chain alkali 3) (Myosin light chain A3) (Smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin light chain alkali 6) |
| NDUFA10 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10, mitochondrial (Complex I-42kD) (CI-42kD) (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 42 kDa subunit) |
| NDUFA11 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 11 (Complex I-B14.7) (CI-B14.7) (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit B14.7) |
| NDUFA4 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit NDUFA4 (Complex I-MLRQ) (CI-MLRQ) (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase MLRQ subunit) |
| NDUFS1 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial (EC 1.6.5.3) (EC 1.6.99.3) (Complex I-75kD) (CI-75kD) |
| NDUFS3 | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) iron-sulfur protein 3, mitochondrial (EC 1.6.5.3) (EC 1.6.99.3) (Complex I-30kD) (CI-30kD) (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 30 kDa subunit) |
| NEDD8 | NEDD8 (Neddylin) (Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated protein 8) (NEDD-8) (Ubiquitin-like protein Nedd8) |
| NPM1, NPM | Nucleophosmin (NPM) (Nucleolar phosphoprotein B23) (Nucleolar protein NO38) (Numatrin) |
| OAT | Ornithine aminotransferase, mitochondrial (EC 2.6.1.13) (Ornithine delta-aminotransferase) (Ornithine—oxo-acid aminotransferase) (Cleaved into: Ornithine aminotransferase, hepatic form; Ornithine aminotransferase, renal form) |
| OGDH | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial (EC 1.2.4.2) (2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex component E1) (OGDC-E1) (Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) |
| OTUB1, OTB1, OTU1, HSPC263 | Ubiquitin thioesterase OTUB1 (EC 3.4.19.12) (Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1) (OTU domain-containing ubiquitin aldehyde-binding protein 1) (Otubain-1) (hOTU1) (Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease OTUB1) |
| PDIA3, ERP57, ERP60, GRP58 | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 (EC 5.3.4.1) (58 kDa glucose-regulated protein) (58 kDa microsomal protein) (p58) (Disulfide isomerase ER-60) (Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 57) (ER protein 57) (ERp57) (Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60) (ER protein 60) (ERp60) |
| PGK1, PGKA, MIG10, OK/SW-cl.110 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (EC 2.7.2.3) (Cell migration-inducing gene 10 protein) (Primer recognition protein 2) (PRP 2) |
| PHB | Prohibitin |
| PHB2, BAP, REA | Prohibitin-2 (B-cell receptor-associated protein BAP37) (D-prohibitin) (Repressor of estrogen receptor activity) |
| PIN1 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (EC 5.2.1.8) (Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1) (PPIase Pin1) (Rotamase Pin1) |
| PPIA, CYPA | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A (PPIase A) (EC 5.2.1.8) (Cyclophilin A) (Cyclosporin A-binding protein) (Rotamase A) (Cleaved into: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A, N-terminally processed) |
| PRDX4 | Peroxiredoxin-4 (EC 1.11.1.15) (Antioxidant enzyme AOE372) (AOE37-2) (Peroxiredoxin IV) (Prx-IV) (Thioredoxin peroxidase AO372) (Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase A0372) |
| PSMA3, HC8, PSC8 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-3 (EC 3.4.25.1) (Macropain subunit C8) (Multi-catalytic endopeptidase complex subunit C8) (Proteasome component C8) |
| PTPN5 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 5 (EC 3.1.3.48) (Neural-specific protein-tyrosine phosphatase) (Striatum-enriched protein-tyrosine phosphatase) (STEP) |
| RAB14 | Ras-related protein Rab-14 |
| RAB2A, RAB2 | Ras-related protein Rab-2A |
| RAC1, TC25, MIG5 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Cell migration-inducing gene 5 protein) (Ras-like protein TC25) (p21-Rac1) |
| RAPGEF2, KIAA0313, NRAPGEP, PDZGEF1 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 (Cyclic nucleotide ras GEF) (CNrasGEF) (Neural RAP guanine nucleotide exchange protein) (nRap GEP) (PDZ domain-containing guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1) (PDZ-GEF1) (RA-GEF-1) (Ras/Rap1-associating GEF-1) |
| RHOA, ARH12, ARHA, RHO12 | Transforming protein RhoA (Rho cDNA clone 12) (h12) |
| RNH1, PRI, RNH | Ribonuclease inhibitor (Placental ribonuclease inhibitor) (Placental RNase inhibitor) (Ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor 1) (RAI) |
| RPN1 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase subunit 1 (Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase 67 kDa subunit) (Ribophorin I) (RPN-I) (Ribophorin-1) |
| RPN2 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase subunit 2 (Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase 63 kDa subunit) (RIBIIR) (Ribophorin II) (RPN-II) (Ribophorin-2) |
| RPS15A, OK/SW-cl.82 | 40S ribosomal protein S15a (Small ribosomal subunit protein uS8) |
| RPS3, OK/SW-cl.26 | 40S ribosomal protein S3 (EC 4.2.99.18) (Small ribosomal subunit protein uS3) |
| S100A10, ANX2LG CAL1L CLP11 | Protein S100-A10 (Calpactin I light chain) (Calpactin-1 light chain) (Cellular ligand of annexin II) (S100 calcium-binding protein A10) (p10 protein) (p11) |
| SAMM50, SAM50 CGI-51 TRG3 | Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog (Transformation-related gene 3 protein) (TRG-3) |
| SELENBP1, SBP | Selenium-binding protein 1 (56 kDa selenium-binding protein) (SBP56) (SP56) |
| SFXN1 | Sideroflexin-1 (Tricarboxylate carrier protein) (TCC) |
| SH3GLB2, KIAA1848, PP578 | Endophilin-B2 (SH3 domain-containing GRB2-like protein B2) |
| SIRT2, SIR2L, SIR2L2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 (EC 3.5.1.-) (Regulatory protein SIR2 homolog 2) (SIR2-like protein 2) |
| SLC25A13, ARALAR2 | Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar2 (Citrin) (Mitochondrial aspartate glutamate carrier 2) (Solute carrier family 25 member 13) |
| SLC25A18, GC2 | Mitochondrial glutamate carrier 2 (GC-2) (Glutamate/H(+) symporter 2) (Solute carrier family 25 member 18) |
| SLC25A5, ANT2 | ADP/ATP translocase 2 (ADP, ATP carrier protein 2) (ADP, ATP carrier protein, fibroblast isoform) (Adenine nucleotide translocator 2) (ANT 2) (Solute carrier family 25 member 5) (Cleaved into: ADP/ATP translocase 2, N-terminally processed) |
| SLC9A3R1, NHERF, NHERF1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 (NHERF-1) (Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50) (EBP50) (Regulatory cofactor of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger) (Sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor 1) (Solute carrier family 9 isoform A3 regulatory factor 1) |
| SSBP1, SSBP | Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, mitochondrial (Mt-SSB) (MtSSB) (PWP1-interacting protein 17) |
| TPD52 | Tumor protein D52 (Protein N8) |
| TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain (Alpha-tropomyosin) (Tropomyosin-1) |
| TPM2, TMSB | Tropomyosin beta chain (Beta-tropomyosin) (Tropomyosin-2) |
| TPM3 | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain (Gamma-tropomyosin) (Tropomyosin-3) (Tropomyosin-5) (hTM5) |
| TPM4 | Tropomyosin alpha-4 chain (TM30p1) (Tropomyosin-4) |
| TUBA1A, TUBA3 | Tubulin alpha-1A chain (Alpha-tubulin 3) (Tubulin B-alpha-1) (Tubulin alpha-3 chain) (Cleaved into: Detyrosinated tubulin alpha-1A chain) |
| TUBB, TUBB5, OK/SW-cl.56 | Tubulin beta chain (Tubulin beta-5 chain) |
| TUBB4B, TUBB2C | Tubulin beta-4B chain (Tubulin beta-2 chain) (Tubulin beta-2C chain) |
| TUFM | Elongation factor Tu, mitochondrial (EF-Tu) (P43) |
| UQCRB, UQBP | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 7 (Complex III subunit 7) (Complex III subunit VII) (QP-C) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex 14 kDa protein) |
| UQCRFS1 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske, mitochondrial (EC 1.10.2.2) (Complex III subunit 5) (Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 5) (Rieske iron-sulfur protein) (RISP) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase iron-sulfur subunit) (Cleaved into: Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 11 (Complex III subunit IX) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase 8 kDa protein)) |
| UQCRFS1P1, UQCRFSL1 | Putative cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske-like protein 1 (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Rieske iron-sulfur subunit pseudogene 1) |
| UQCRH | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 6, mitochondrial (Complex III subunit 6) (Complex III subunit VIII) (Cytochrome c1 non-heme 11 kDa protein) (Mitochondrial hinge protein) (Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex 11 kDa protein) |
| USMG5, DAPIT, HCVFTP2, PD04912 | Upregulated during skeletal muscle growth protein 5 (Diabetes-associated protein in insulin-sensitive tissues) (HCV F-transactivated protein 2) |
| VCP | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase (TER ATPase) (EC 3.6.4.6) (15S Mg(2+)-ATPase p97 subunit) (Valosin-containing protein) (VCP) |
| VDAC1, VDAC | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 (VDAC-1) (hVDAC1) (Outer mitochondrial membrane protein porin 1) (Plasmalemmal porin) (Porin 31HL) (Porin 31HM) |
| VDAC2 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 (VDAC-2) (hVDAC2) (Outer mitochondrial membrane protein porin 2) |
| VDAC3 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 3 (VDAC-3) (hVDAC3) (Outer mitochondrial membrane protein porin 3) |
| VIM | Vimentin |
| YWHAE | 14-3-3 protein epsilon (14-3-3E) |
| YWHAZ | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta (Factor activating exoenzyme S) (FAS) (Protein kinase C inhibitor protein 1) (KCIP-1) |
| Upregulated | Downregulated |
|---|---|
| ATP biosynthetic process | ATP metabolic process |
| Positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process | Membrane raft assembly |
| Response to unfolded protein | Positive regulation of stress fiber assembly |
| Auditory receptor cell morphogenesis | Gluthatione derivative biosynthetic process |
| Binding of sperm to zona pellucida | Protein N-linked glycosylation via asparagine |
| Regulation of protein dephosphorylation | Glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway |
| Mitochondrial electron transport ubiquinol to cytochrome c | ER-nucleus signaling pathway |
| Regulation of exit from mitosis | Substantia nigra development |
| NAD metabolic process | Positive regulation of NFkB signaling |
| Muscle filament sliding | Mitochondrial transmembrane transport |
| Regulation of complement activation | Mitochondrial electron transport cytochrome c to oxygen |
| Midbrain development and positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis | Respiratory electron transport chain |
| Oxidative phosphorylation | |
| Mitochondrial respiratory chain Complex I assembly | |
| Mitochondrial electron transport NADH to ubiquinone | |
| Mitochondria respiratory chain complex assembly | |
| Mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled to electron transport | |
| Cellular respiration and proton transport |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha, S.; Freitas, A.; Guimaraes, S.C.; Vitorino, R.; Aroso, M.; Gomez-Lazaro, M. Biological Implications of Differential Expression of Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010001
Rocha S, Freitas A, Guimaraes SC, Vitorino R, Aroso M, Gomez-Lazaro M. Biological Implications of Differential Expression of Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha, Sara, Ana Freitas, Sofia C. Guimaraes, Rui Vitorino, Miguel Aroso, and Maria Gomez-Lazaro. 2018. "Biological Implications of Differential Expression of Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease" Antioxidants 7, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010001
APA StyleRocha, S., Freitas, A., Guimaraes, S. C., Vitorino, R., Aroso, M., & Gomez-Lazaro, M. (2018). Biological Implications of Differential Expression of Mitochondrial-Shaping Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxidants, 7(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010001






