Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
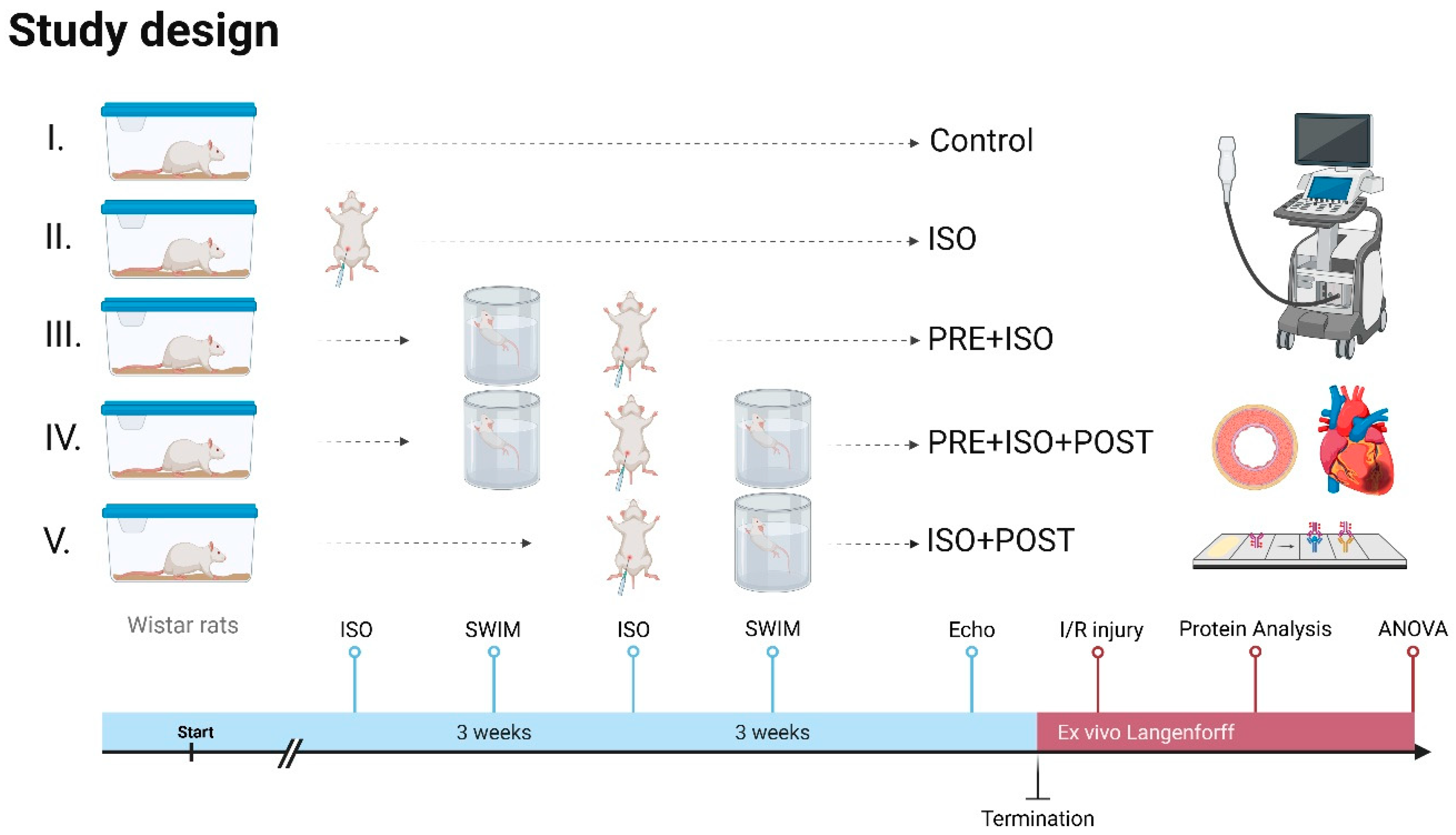
2.1. Animals and Exercise Training
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.2.1. Protein Analysis
2.2.2. Determination of Cardiac HO-1 Concentrations
2.2.3. Determination of Cardiac MPO Activity
2.2.4. Determination of Cardiac HO Activity
2.2.5. Echocardiography
2.2.6. Ischemia/Reperfusion Protocol
2.2.7. Measurement of Infarct Size
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
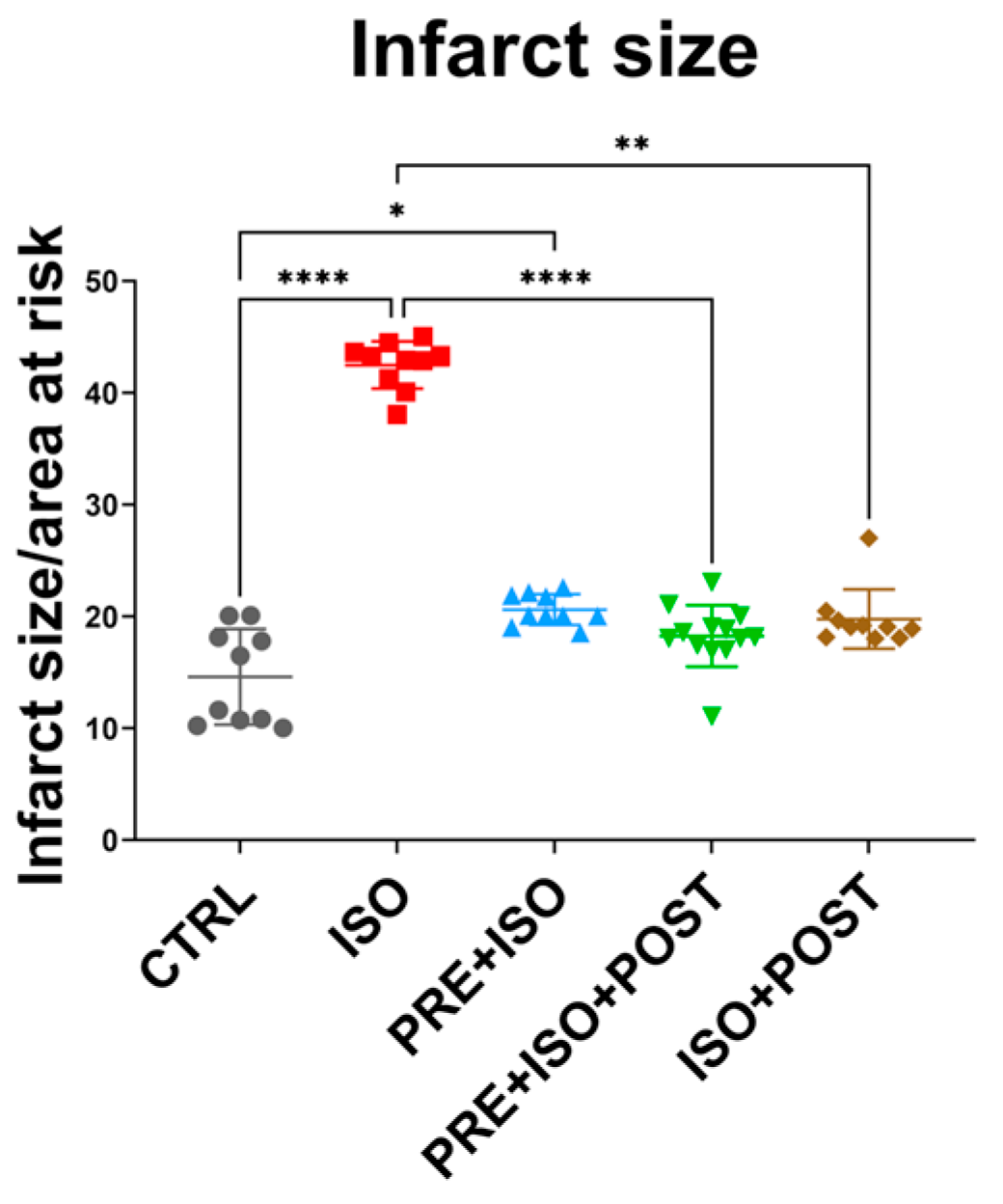
3.1. Infarct Size
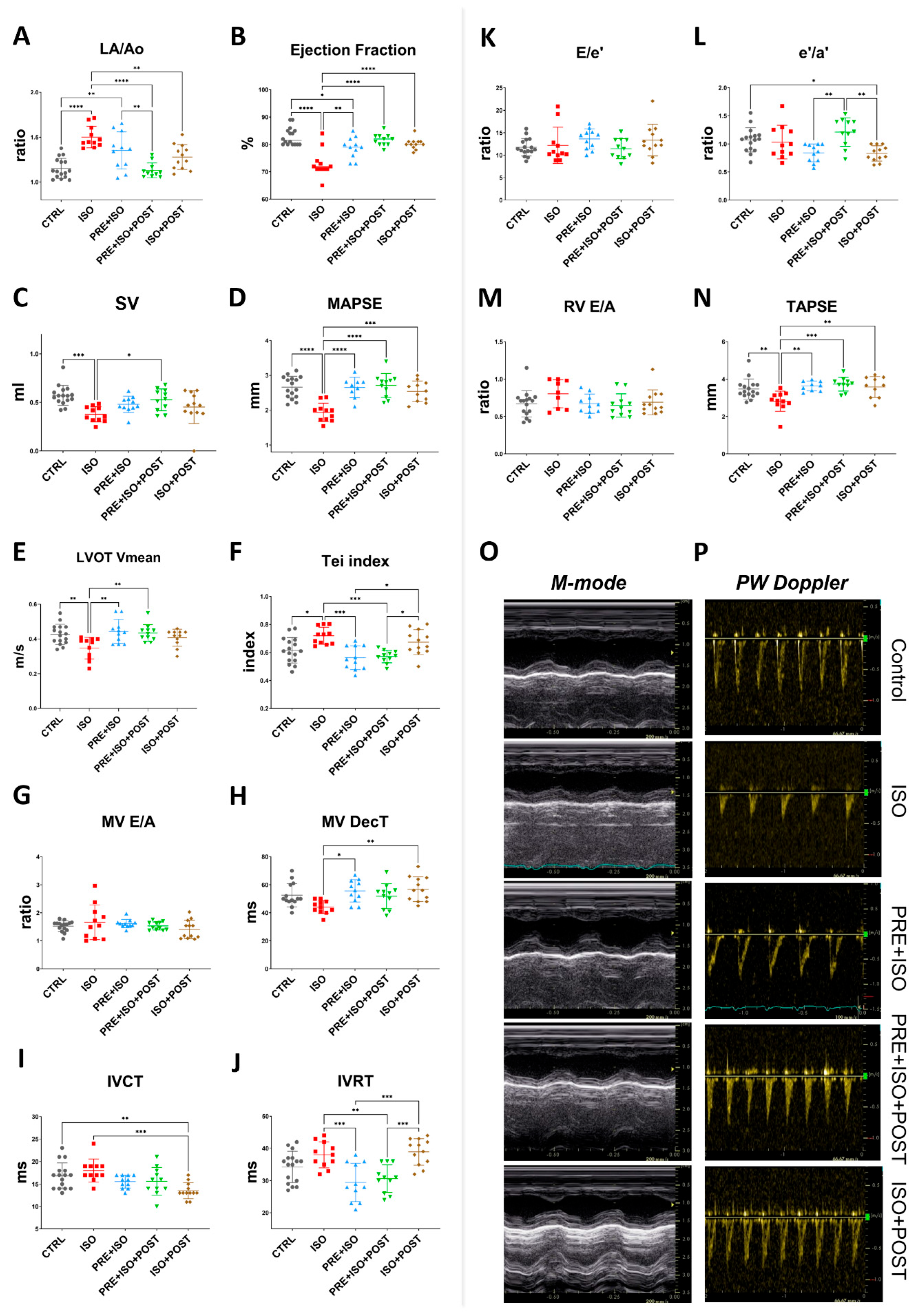
3.2. Echocardiography
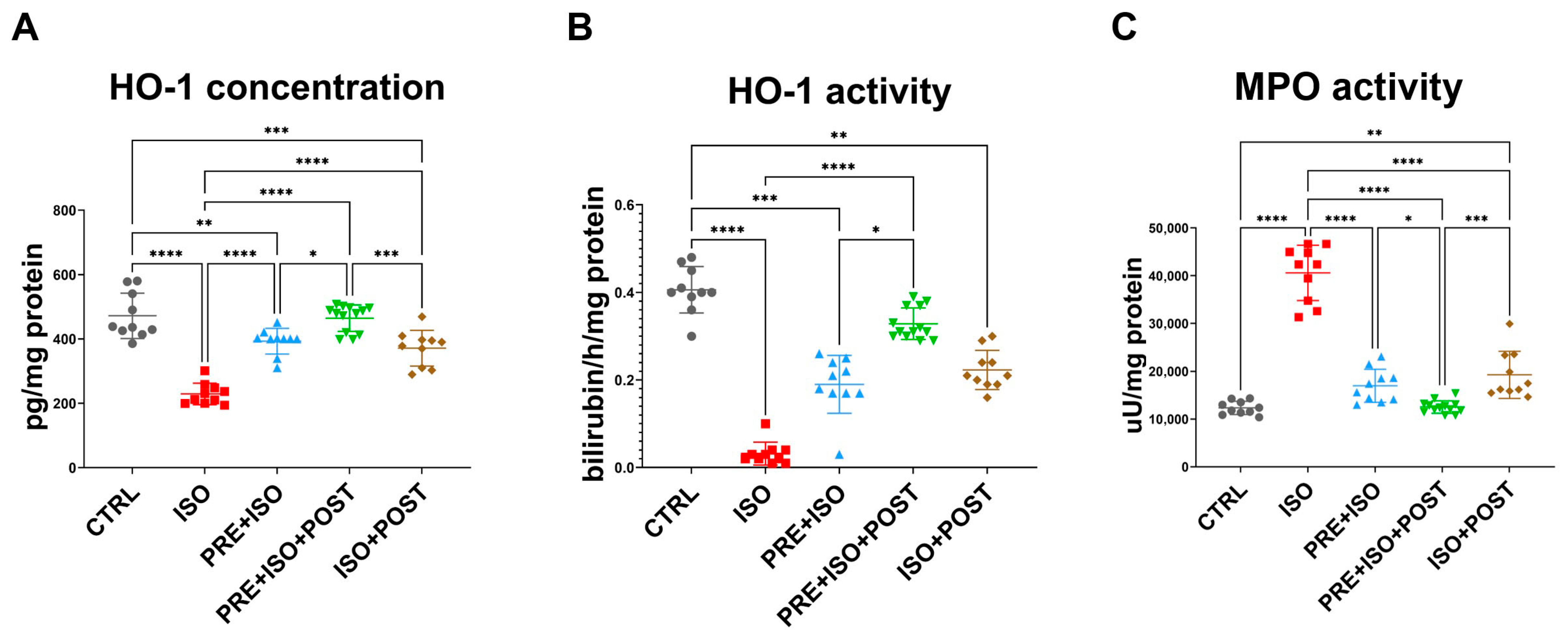
3.3. HO-1 Concentration
3.4. HO Activity
3.5. MPO Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendis, S.; Thygesen, K.; Kuulasmaa, K.; Giampaoli, S.; Mahonen, M.; Ngu Blackett, K.; Lisheng, L.; Writing Group on Behalf of the Participating Experts of the WHO Consultation for Revision of WHO Definition of Myocardial Infarction. World Health Organization Definition of Myocardial Infarction: 2008-09 Revision. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, C.; Francone, M.; Cundari, G.; Pisano, A.; d’Amati, G. Myocardial Fibrosis: Morphologic Patterns and Role of Imaging in Diagnosis and Prognostication. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 56, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-S.; Shen, J.; An, X.-B.; Zhang, C.-C.; Wu, J.-M.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; et al. IL-18 Cleavage Triggers Cardiac Inflammation and Fibrosis upon β-Adrenergic Insult. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusovits, D.; Murlasits, Z.; Kupai, K.; Baráth, Z.; Kang, H.L.; Osváth, P.; Szűcs, M.; Priksz, D.; Juhász, B.; Radák, Z.; et al. Paclitaxel Protects against Isoproterenol-Induced Damage in Rat Myocardium: Its Heme-Oxygenase Mediated Role in Cardiovascular Research. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, D.H.J.; Uthman, L.; Somani, Y.; Van Royen, N. Short-term Exercise-induced Protection of Cardiovascular Function and Health: Why and How Fast Does the Heart Benefit from Exercise? J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1339–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, M.A. Cardiac Remodeling and Physical Training Post Myocardial Infarction. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.S.; Joukar, S.; Rostamzadeh, F.; Najafipour, H.; Darvishzadeh-mahani, F.; Mortezaeizade, A. Exercise Training Attenuates Cardiac Vulnerability and Promotes Cardiac Resistance to Isoproterenol-Induced Injury Following Hookah Smoke Inhalation in Male Rats: Role of Klotho and Sirtuins. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2022, 22, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Majid, K.; Hamid, R.; Mojtaba, S. The Effect of Exercise Preconditioning with High-Intensity Interval Training on Cardiac Protection Following Induction of Myocardial Infarction through Mitochondrial Dynamic Changes in Cardiac Tissue in Male Rats. Arch. Sports Med. Physiother. 2023, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, G.; Gaze, D.; Oxborough, D.; O’Driscoll, J.; Shave, R. Reverse Left Ventricular Remodeling: Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Training in Myocardial Infarction Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 52, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, B.L.; Lock, M.J.; Davison, K.; Parfitt, G.; Buckley, J.P.; Eston, R.G. What Is the Effect of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Those Undergoing Cardiac Rehabilitation? A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.N.; McLaughlin, N.; Soo, S.; Luckey, S. Effects of Exercise Prior to and During Isoproterenol-Mediated Cardiac Disease. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 854.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavarnajand Bonab, H.; Tolouei Azar, J.; Soraya, H.; Nouri Habashi, A. Aerobic Interval Training Preconditioning Protocols Inhibit Isoproterenol-Induced Pathological Cardiac Remodeling in Rats: Implications on Oxidative Balance, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2024, 6, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Smuder, A.J.; Kavazis, A.N.; Quindry, J.C. Mechanisms of Exercise-Induced Cardioprotection. Physiology 2014, 29, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Niu, C.; Zhang, L.; Lai, H.; Liu, B.; Lv, D.; Zhuang, R.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Ma, L.; et al. The Impact of the Time Factors on the Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Outcomes of the Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochulska, A.; Bryndal, A.; Glowinski, S. The Impact of Early Rehabilitation Program on Exercise Tolerance in Post-Myocardial Infarction Patients: A 5-Week Intervention Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2025, 25, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemasi, A.; Cao, N.; An, X.; Wu, J.; Gu, H.; Yu, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; et al. Exercise Attenuates Acute β-Adrenergic Overactivation–Induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Modulating Cytokines. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2019, 12, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, S. ROS and Redox Signaling in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, G.A.; Rajagopal, R.; Vedantham, S.; Rajesh, M. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury and Remodeling: Revisited. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1656450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; DelCimmuto, N.R.; Flack, K.D.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Antioxidants as Immunomodulators in Exercise: Implications for Heme Oxygenase and Bilirubin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltobshy, S.A.G.; Hussein, A.M.; Elmileegy, A.A.; Askar, M.H.; Khater, Y.; Metias, E.F.; Helal, G.M. Effects of Heme Oxygenase-1 Upregulation on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Kashef, M.; Rajabi, H.; Salehpour, M. Effects of Exercise Preconditioning on NLRP3 and Mitochondrial Fission in Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarcted Rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 32, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E.; Quindry, J.C. Exercise and Cardioprotection against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury: A Review. Cond. Med. 2020, 3, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Quindry, J.; Hamilton, K. Exercise and Cardiac Preconditioning Against Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 9, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamian Jazi, A.; Abdi, H.; Haffezi Ahmadi, M.R.; Cheraghi, J. Effect of Endurance Exercise Training on Morphological Changes in Rat Heart Tissue Following Experimental Myocardial Infarction. J. Basic Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 4, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Batista, D.F.; Gonçalves, A.F.; Rafacho, B.P.; Santos, P.P.; Minicucci, M.F.; Azevedo, P.S.; Polegato, B.F.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Okoshi, K.; Paiva, S.A.R.; et al. Delayed Rather than Early Exercise Training Attenuates Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 170, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Szabó, R.; Börzsei, D.; Karácsonyi, Z.; Gesztelyi, R.; Nemes, K.; Berkó, A.M.; Veszelka, M.; Török, S.; Kupai, K.; Varga, C.; et al. Postconditioning-like Effect of Exercise: New Paradigm in Experimental Menopause. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H400–H407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, K.; Oroszi, T.; Van Der Zee, E.A.; Nyakas, C.; Schoemaker, R.G. The Effects of Exercise Training on Heart, Brain and Behavior, in the Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Infarct Model in Middle-Aged Female Rats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, K.; Oroszi, T.; Zee, E.A.; Nyakas, C.; Schoemaker, R.G. Exercise Training After Isoproterenol in Middle-Aged Female Rats Reversed Effects on the Heart, Without Affecting the Brain. Preprint 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo Filho, H.G.; Ferreira, N.L.; Sousa, R.B.D.; Carvalho, E.R.D.; Lobo, P.L.D.; Lobo Filho, J.G. Experimental Model of Myocardial Infarction Induced by Isoproterenol in Rats. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 26, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heather, L.C.; Catchpole, A.F.; Stuckey, D.J.; Cole, M.A.; Carr, C.A.; Clarke, K. Isoproterenol Induces In Vivo Functional and Metabolic Abnormalities: Similar to Those Found in the Infarcted Rat Heart. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, D.C.; Copp, S.W.; Colburn, T.D.; Craig, J.C.; Allen, D.L.; Sturek, M.; O’Leary, D.S.; Zucker, I.H.; Musch, T.I. Guidelines for Animal Exercise and Training Protocols for Cardiovascular Studies. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H1100–H1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Abraham, T.P.; Aurigemma, G.P.; Bax, J.J.; Beladan, C.; Browning, A.; Chamsi-Pasha, M.A.; Delgado, V.; Derumeaux, G.; Dolci, G.; et al. Interobserver Variability in Applying American Society of Echocardiography/European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging 2016 Guidelines for Estimation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e008122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhong, G.; Hou, Z.; Ye, Y.; Lin, J.; Luo, D. Hydromorphone Hydrochloride Preconditioning Combined with Postconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Improving Mitochondrial Function and Activating the PI3K /Akt Signaling Pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, e14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindry, J.C.; Hamilton, K.L.; French, J.P.; Lee, Y.; Murlasits, Z.; Tumer, N.; Powers, S.K. Exercise-Induced HSP-72 Elevation and Cardioprotection against Infarct and Apoptosis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, J.J.; McKay, L.E.; Hacker, T.A.; Diffee, G.M. The Effects of Short-Term Versus Long-Term Exercise on Reducing Infarct Size After Ischemia-Reperfusion in Male and Female Rat Hearts. FASEB J. 2018, 32, lb336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, E.C.D.A.; Melo, B.L.D.; Vieira, S.D.S.; Simões, R.S.; Valenti, V.E.; Campos, M.F.; Vale, J.E.T.M.R.D.; Rica, R.L.; Soares-Júnior, J.M.; Baracat, E.C.; et al. Prior Exercise Training and Experimental Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinics 2020, 75, e1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, E.C.A.; Antonio, E.L.; Bocalini, D.S.; Murad, N.; Abreu, L.C.; Tucci, P.J.F.; Sato, M.A. Prior Exercise Training Does Not Prevent Acute Cardiac Alterations after Myocardial Infarction in Female Rats. Clinics 2011, 66, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yang, R.; Li, W.; Ogasawara, A.K.; Schwall, R.; Eberhard, D.A.; Zheng, Z.; Kahn, D.; Paoni, N.F. Early Treatment with Hepatocyte Growth Factor Improves Cardiac Function in Experimental Heart Failure Induced by Myocardial Infarction. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B. The Role of Exercise-Induced Myokines in Promoting Angiogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 981577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Berr, S.S.; Gilson, W.D.; Toufektsian, M.-C.; French, B.A. Simultaneous Evaluation of Infarct Size and Cardiac Function in Intact Mice by Contrast-Enhanced Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Contractile Dysfunction in Noninfarcted Regions Early After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2004, 109, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yang, L.; Tian, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J.; Lu, P.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Qi, Z. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition Abolishes Exercise-Mediated Protection against Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Female Mice. Cardiology 2015, 130, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.; Challa, A.K.; Devarajan, A.; Athmanathan, B.; Litovsky, S.H.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Davidson, C.J.; Rajasekaran, N.S. Exercise Mediated Nrf2 Signaling Protects the Myocardium from Isoproterenol-Induced Pathological Remodeling. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusifov, A.; Borders, M.O.; DeHoff, M.A.; Polson, S.M.; Schmitt, E.E.; Bruns, D.R. Juvenile Physical Activity Protects against Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction Later in Life. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 135, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Fu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, R.; Shen, J.; An, X.; Shen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Cardiac Fibrosis Alleviated by Exercise Training Is AMPK-Dependent. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Xu, X. Pharmacological Inhibition of ICOS Attenuates the Protective Effect of Exercise on Cardiac Fibrosis Induced by Isoproterenol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 965, 176327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M.K. Heme Oxygenase-1/Carbon Monoxide: From Basic Science to Therapeutic Applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.; Zhang, R.Y.K.; Bello, I.; Rye, K.-A.; Thomas, S.R. Myeloperoxidase as a Promising Therapeutic Target after Myocardial Infarction. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, C.L.; Frohlich, J.J.; Hill, J.S. Myeloperoxidase and C-Reactive Protein Have Combined Utility for Long-Term Prediction of Cardiovascular Mortality After Coronary Angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandamali, J.A.N.; Hewawasam, R.P.; Jayatilaka, K.A.P.W.; Mudduwa, L.K.B. Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Blume (Ceylon Cinnamon) Bark Extract Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhu, T.; Ni, J.; Zhang, R. The Expression of Myeloperoxidase in Thrombi Is Associated with Reduced Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction and Worse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Acute ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, A.R.; Abo-Aly, M.; Elsawalhy, E.; Campbell, C.; Ziada, K.M.; Abdel-Latif, A. Prognostic Role of Elevated Myeloperoxidase in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 2872607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiak, P.; Kowalski, T.; Rębiś, K.; Klusiewicz, A.; Sadowska, D.; Wilk, A.; Wiecha, S.; Barylski, M.; Poliwczak, A.R.; Wierzbiński, P.; et al. Oxygen Uptake Efficiency Plateau Is Unaffected by Fitness Level—The NOODLE Study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiak, P.; Kowalski, T.; Rębiś, K.; Klusiewicz, A.; Starczewski, M.; Ładyga, M.; Wiecha, S.; Barylski, M.; Poliwczak, A.R.; Wierzbiński, P.; et al. Below or All the Way to the Peak? Oxygen Uptake Efficiency Slope as the Index of Cardiorespiratory Response to Exercise—The NOODLE Study. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1348307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhalil, M.H.; Hussein, O.E.; Aladaileh, S.H.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Al-Amarat, W.; Saghir, S.A.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Algefare, A.I.; Alanazi, K.M.; Al-Swailmi, F.K.; et al. Visnagin Prevents Isoproterenol-induced Myocardial Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation and Upregulating Nrf2 Signaling in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althunibat, O.Y.; Abduh, M.S.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Aladaileh, S.H.; Hanieh, H.; Mahmoud, A.M. Umbelliferone Prevents Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Injury by Upregulating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling, and Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Death in Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, C.; Alloatti, G.; Crisafulli, A. Mechanisms Involved in Cardioprotection Induced by Physical Exercise. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 1115–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Meng, X.; Li, G.; Gokulnath, P.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J. Exercise Training after Myocardial Infarction Attenuates Dysfunctional Ventricular Remodeling and Promotes Cardiac Recovery. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marocolo, M.; Souza, H.L.R.; Surke, P.; Ferrauti, A. Potential Short- and Long-Term Physiological Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning as an Ergogenic Aid: Revisiting Foundational Mechanisms and Applications. Sports Med. 2025, 55, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kupai, K.; Murlasits, Z.; Kang, H.L.; Regős, E.; Várkonyi, Á.; Lengyel, C.; Pávó, I.; Radák, Z.; Juhász, B.; Priksz, D.; et al. Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model. Antioxidants 2026, 15, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020152
Kupai K, Murlasits Z, Kang HL, Regős E, Várkonyi Á, Lengyel C, Pávó I, Radák Z, Juhász B, Priksz D, et al. Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model. Antioxidants. 2026; 15(2):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020152
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupai, Krisztina, Zsolt Murlasits, Hsu Lin Kang, Eszter Regős, Ákos Várkonyi, Csaba Lengyel, Imre Pávó, Zsolt Radák, Béla Juhász, Dániel Priksz, and et al. 2026. "Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model" Antioxidants 15, no. 2: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020152
APA StyleKupai, K., Murlasits, Z., Kang, H. L., Regős, E., Várkonyi, Á., Lengyel, C., Pávó, I., Radák, Z., Juhász, B., Priksz, D., & Pósa, A. (2026). Temporal Exercise Conditioning Confers Dual-Phase Cardioprotection Against Isoproterenol-Induced Injury in a Rat Model. Antioxidants, 15(2), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox15020152






