Hydrogen Gas Mitigates Acute Hypoxia-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Brain Injuries in Medaka (Oryzias latipes)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Animals
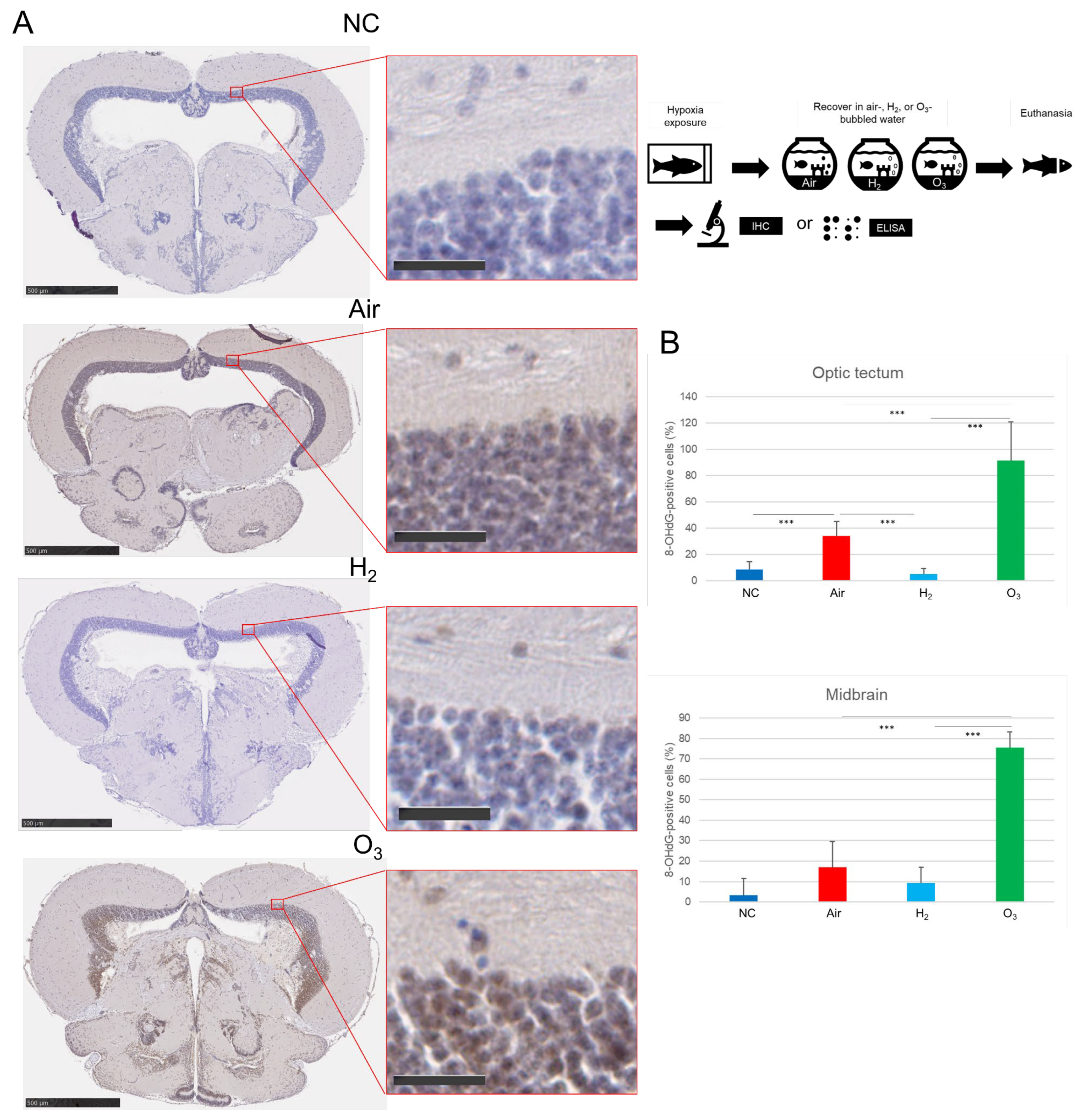
2.3. Hypoxia Exposure and Recovery
2.4. LOX-1 Signal Imaging
2.5. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.6. TUNEL Assay
2.7. ELISA
2.8. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity Assay
2.9. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Assay
2.10. Movement Tracking of Medaka
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
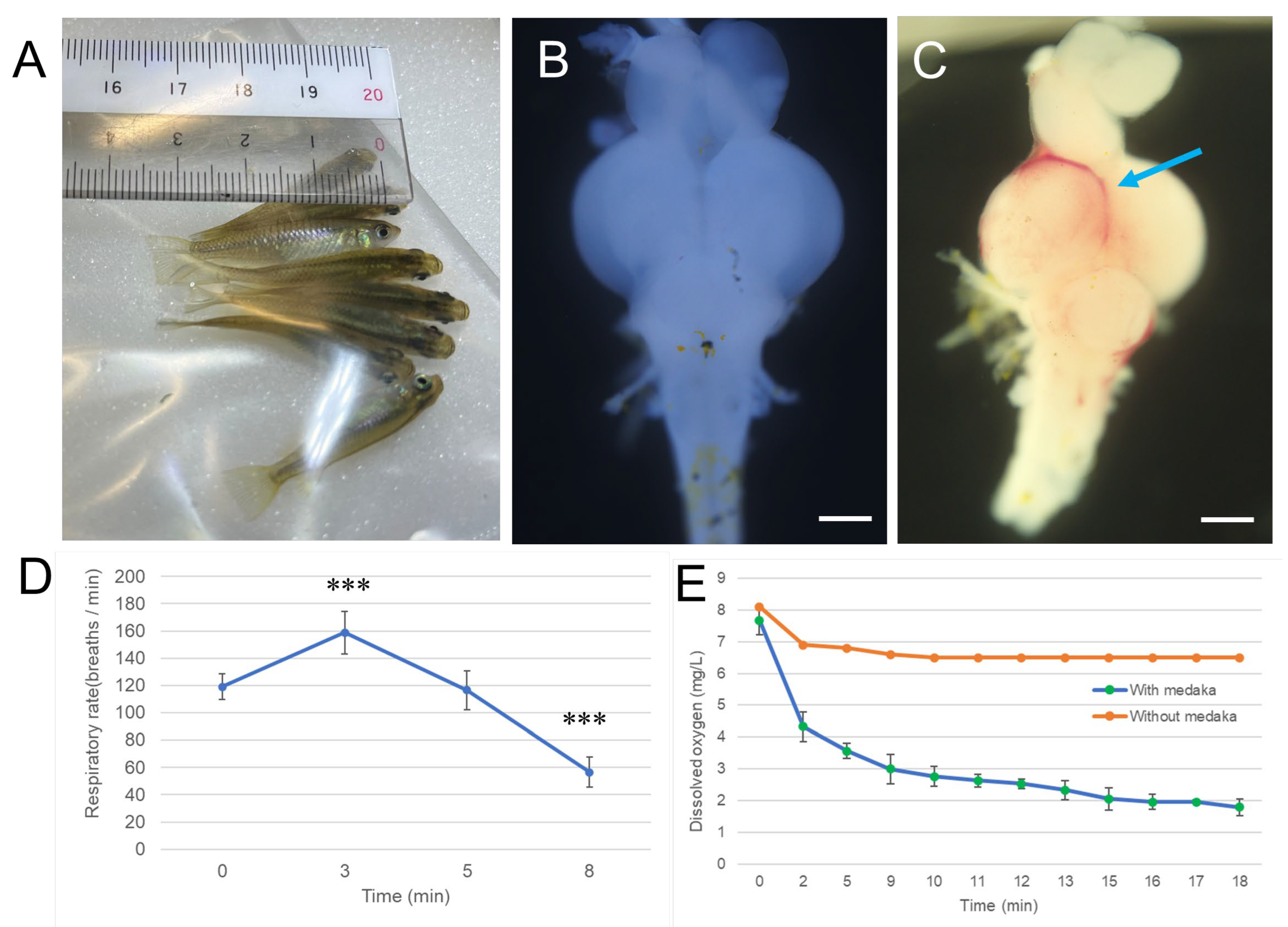
3.1. Exposure Duration of Hypoxia and Severity of Brain Damage in Medaka
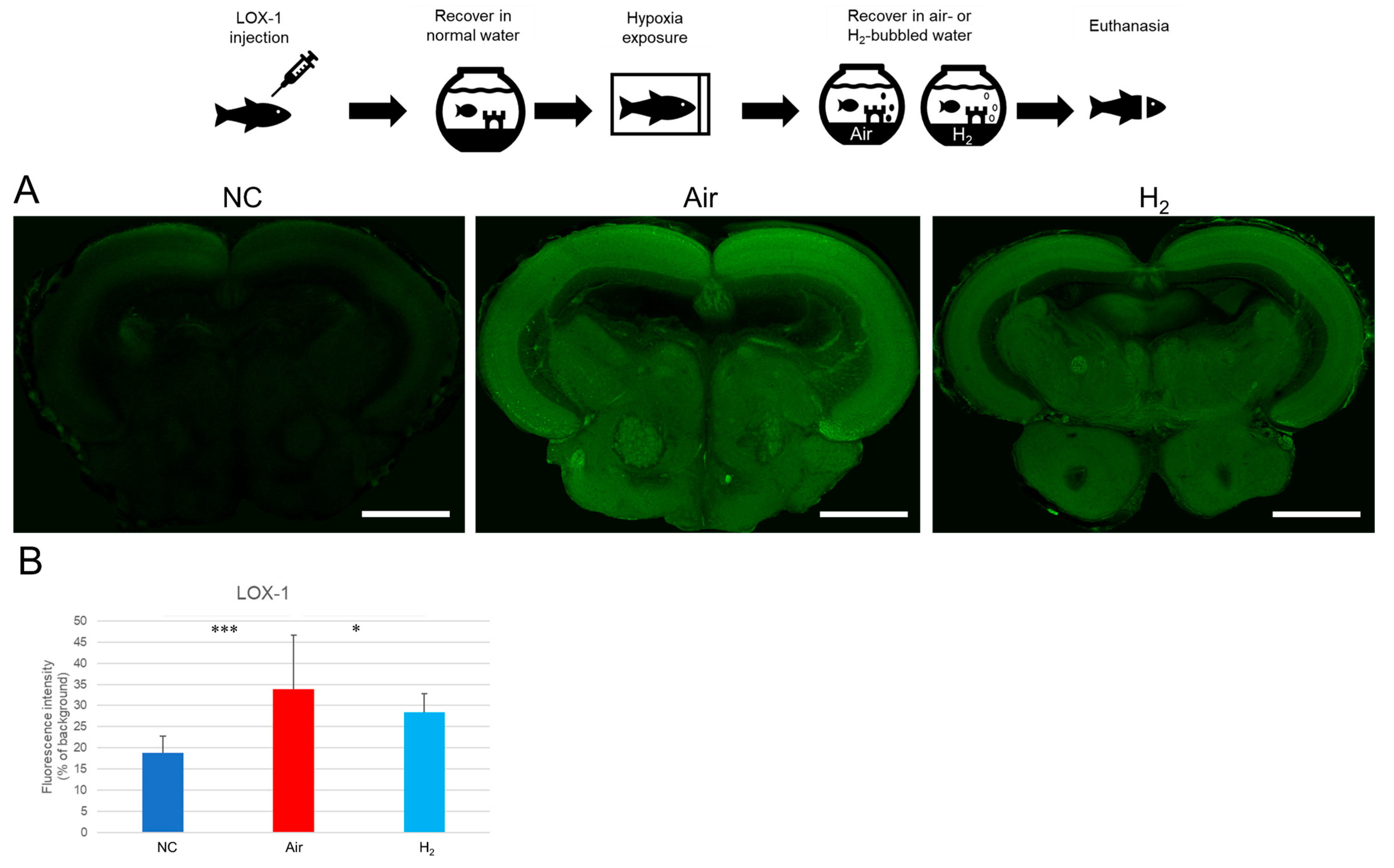
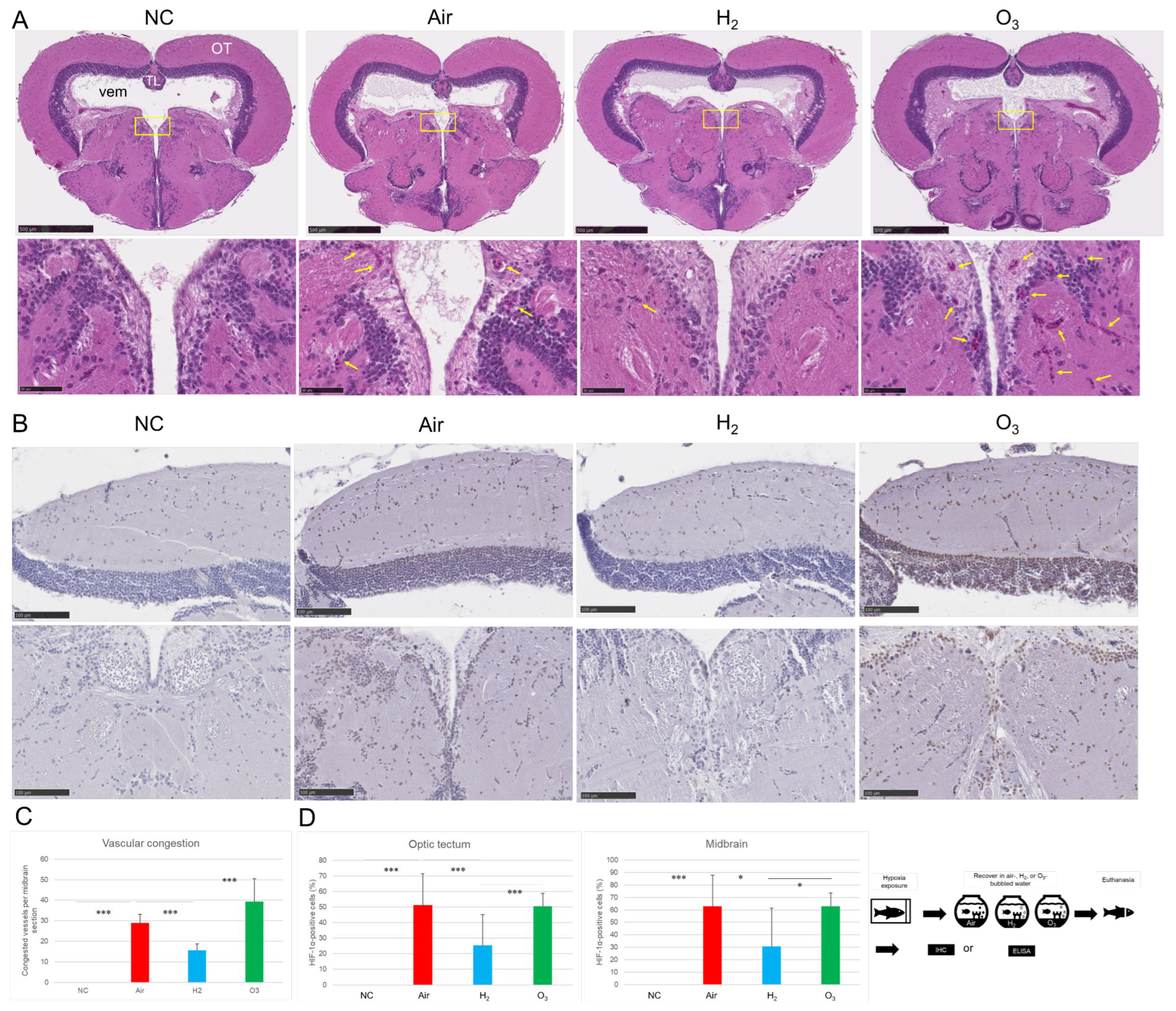
3.2. Hydrogen Gas Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced LOX-1 Signal and HIF-1α Expression and Alleviates Vascular Damage in the Medaka Brain
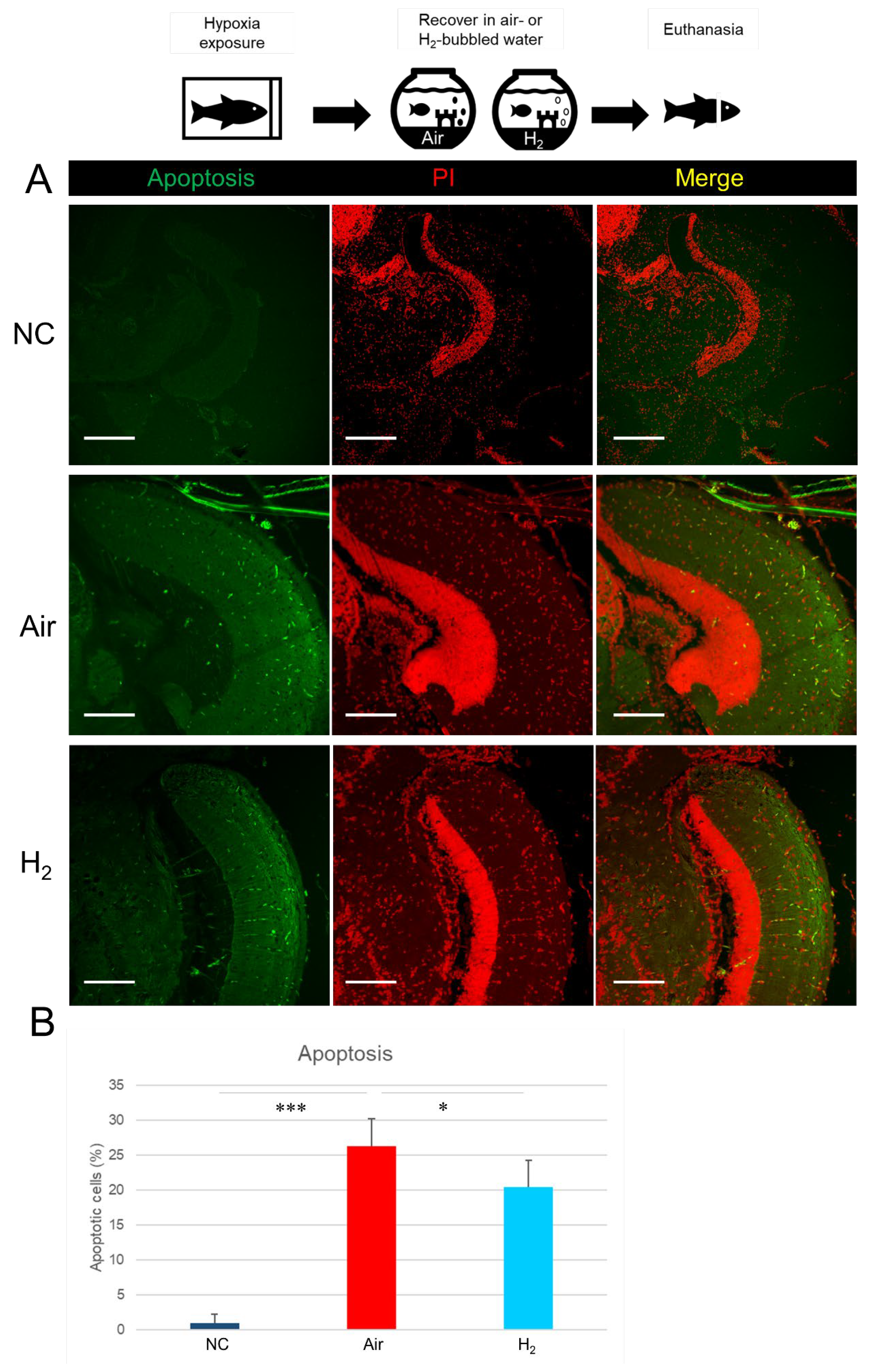
3.3. Hydrogen Gas Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death and Oxidative DNA Damage in the Medaka Brain Tissues
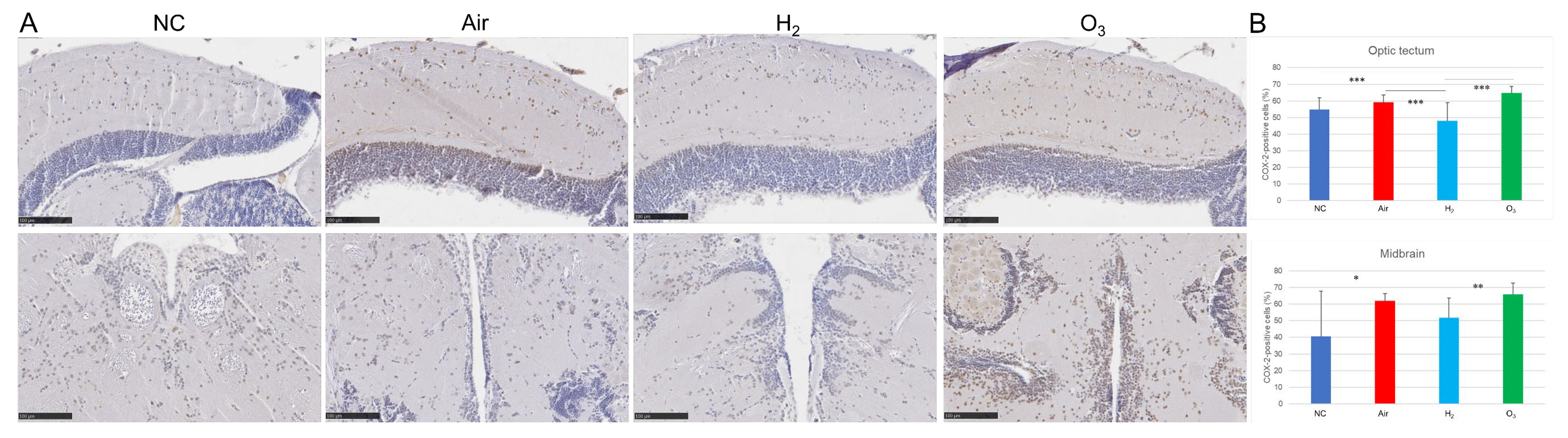
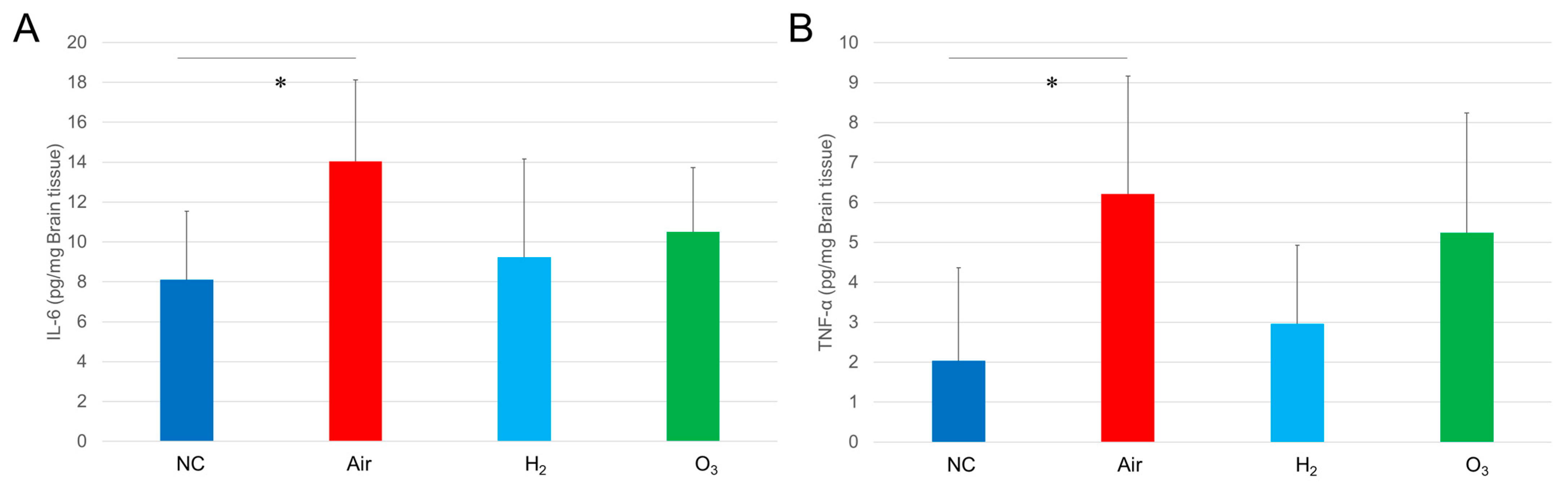
3.4. Hydrogen Gas Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Inflammatory Changes in Medaka Brain Tissues
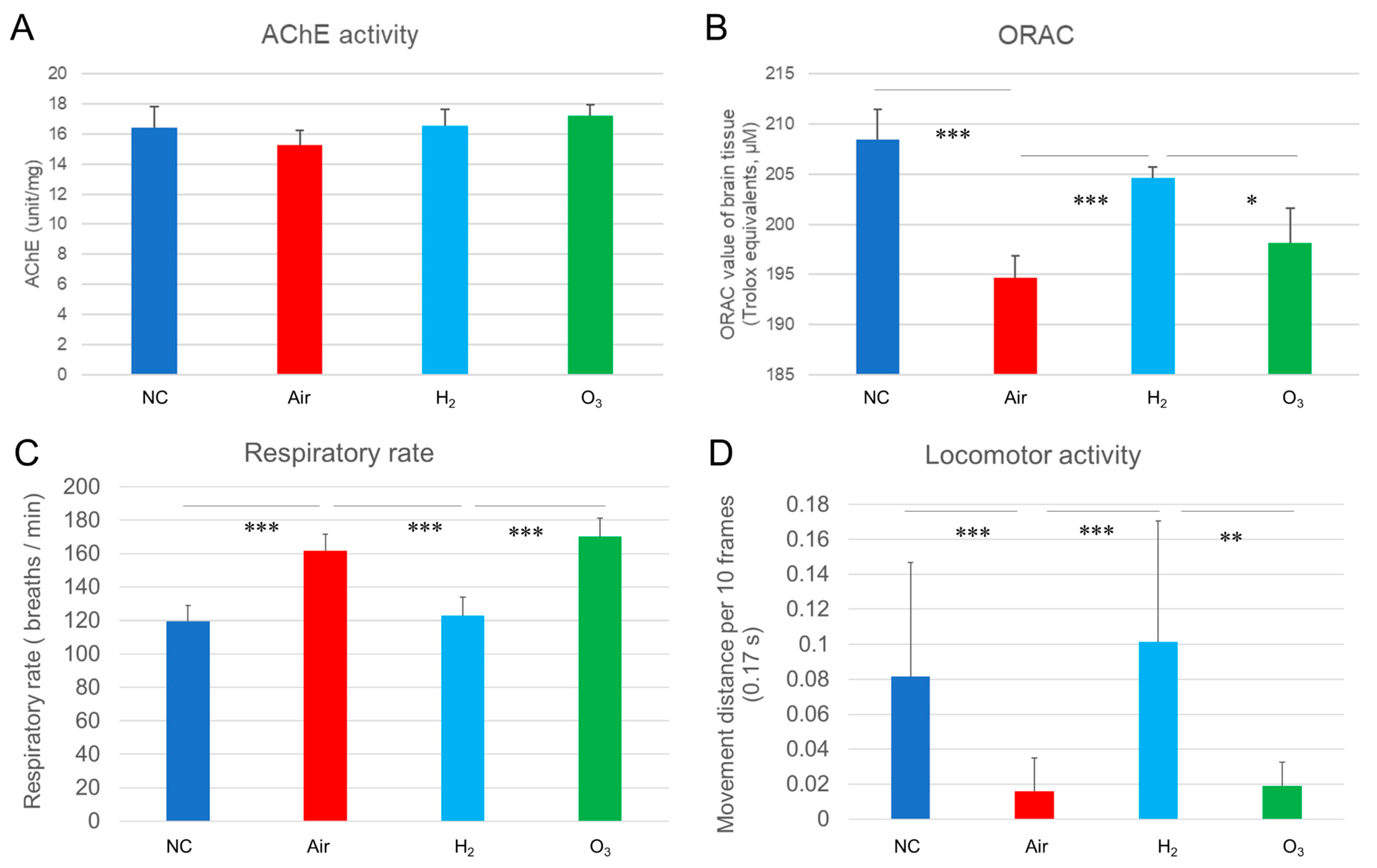
3.5. Hydrogen Gas Restores Antioxidant Capacity and Normalizes Respiratory and Locomotor Activity Following Hypoxia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacerte, M.; Hays Shapshak, A.; Mesfin, F.B. Hypoxic Brain Injury. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537310/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, T.; Aschner, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Hypoxia causes mitochondrial dysfunction and brain memory disorder in a manner mediated by the reduction of Cirbp. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lai, U.H.; Zhu, L.; Singh, A.; Ahmed, M.; Forsyth, N.R. Reactive oxygen species formation in the brain at different oxygen levels: The role of hypoxia inducible factors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukandala, G.; Tynan, R.; Lanigan, S.; O’Connor, J.J. The effects of hypoxia and inflammation on synaptic signaling in the CNS. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Su, Z.Y.; Kong, A.N. The complexity of the Nrf2 pathway: Beyond the antioxidant response. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillam-Krakauer, M.; Shah, M.; Gowen, C.W., Jr. Birth Asphyxia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430782/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Burtscher, J.; Mallet, R.T.; Burtscher, M.; Millet, G.P. Hypoxia and brain aging: Neurodegeneration or neuroprotection? Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, B.; Shell, B.; Cunningham, J.T.; Cunningham, R.L. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces oxidative stress and inflammation in brain regions associated with early-stage neurodegeneration. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, S.; Singh, M.; Su, C.; Cunningham, R.L. Effects of oxidative stress and testosterone on pro-inflammatory signaling in a female rat dopaminergic neuronal cell line. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2824–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Heijnen, C.J.; van der Kooij, M.A.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F. The role and regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in brain development and neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 62, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.H.; Joo, H.; Bae, J.; Hyeon, S.J.; Her, S.; Ko, E.; Choi, H.G.; Ryu, H.; Hur, E.M.; Bu, Y.; et al. Brain injury induces HIF-1α-dependent transcriptional activation of LRRK2 that exacerbates brain damage. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K. Detrimental roles of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in severe hypoxic brain diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmedtje, J.F., Jr.; Ji, Y.S.; Liu, W.L.; DuBois, R.N.; Runge, M.S. Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-κB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.S.; Choi, H.R.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, E.A.; Cho, S.W.; Yang, S.J. Hypoxia-induced S100A8 expression activates microglial inflammation and promotes neuronal apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Cai, Y.; Tang, E.H.; Yan, D.; Kosuru, R.; Li, H.; Irwin, M.G.; Ma, H.; Xia, Z. Cox-2 inhibition protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via Akt-dependent enhancement of iNOS expression. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3453059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Ma, Q. MicroRNAs in the blood-brain barrier in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zou, P.; Feng, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, F.; Liu, T.C.; Duan, R.; Yang, L. Molecular hydrogen: An emerging therapeutic medical gas for brain disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 1749–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, K.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates brain injury in mice with cecal ligation and puncture via inhibiting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis. Brain Res. 2014, 1589, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Molecular hydrogen mitigates traumatic brain injury-induced lung injury via NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. BMC Chem. 2025, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Suzuki, M.; Homma, K.; Sano, M.; HYBRID II Study Group. Efficacy of inhaled hydrogen on neurological outcome following brain ischaemia during post-cardiac arrest care (HYBRID II): A multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.H.; Chiu, J.M.; Wu, R.S. Hypoxia turns genotypic female medaka fish into phenotypic males. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lau, K.; Lai, K.P.; Zhang, J.W.; Tse, A.C.; Li, J.W.; Tong, Y.; Chan, T.F.; Wong, C.K.; Chiu, J.M.; et al. Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Tam, N.; Wang, S.Y.; Tse, W.K.F.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Au, D.W.T.; Wu, R.S.S.; et al. Proteomic response of the brain to hypoxic stress in marine medaka fish (Oryzias melastigma). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 618489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Sato, E.; Ide, R.; Shimamura, N.; Saiki, C.; Miwa, N. Comparative Analysis of Davidson and Glyoxal Fixatives on Autofluorescence and Immunolabeling in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Tissues. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkel, M.D.; Eames, S.C.; Philipson, L.H.; Prince, V.E. Intraperitoneal injection into adult zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 42, 2126. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Brioudes, E.; Labbé, J.-C.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Loss of human Greatwall results in G2 arrest and multiple mitotic defects due to deregulation of the cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12564–12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liao, F.; Ide, R.; Horie, T.; Fan, Y.; Saiki, C.; Miwa, N. Enzyme-digested Colla Corii Asini (E’jiao) prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death and accelerates amyloid beta clearance in neuronal-like PC12 cells. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 2270–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen-rich water achieves cytoprotection from oxidative stress injury in human gingival fibroblasts in culture or 3D-tissue equivalents, and wound-healing promotion, together with ROS-scavenging and relief from glutathione diminishment. Hum. Cell 2017, 30, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.I.; Sakagami, H.; Miwa, N. A new method for testing filtration efficiency of mask materials under sneeze-like pressure. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.V. Zebrafish as an alternative model for hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.S.; Dixon, C.E. Alterations in cholinergic pathways and therapeutic strategies targeting cholinergic system after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghzadeh, J.; Hosseini, L.; Mobed, A.; Zangbar, H.S.; Jafarzadeh, J.; Pasban, J.; Shahabi, P. The impact of cerebral ischemia on antioxidant enzymes activity and neuronal damage in the hippocampus. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 3915–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, N.; Eide, S.; Sun, H.S.; Feng, Z.P. Animal models for neonatal brain injury induced by hypoxic ischemic conditions in rodents. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Sun, Z.M.; Luo, L.F.; Zhao, Y.S.; Yang, S.C.; Yu, F.Y.; Wang, N.; Ji, E.S. Hydrogen gas alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury through reducing iron overload. Molecules 2019, 24, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: Overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 555, 289–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, M.; Kim, C.S.; Shon, W.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, E.Y.; Shin, D.M. Hydrogen-rich water reduces inflammatory responses and prevents apoptosis of peripheral blood cells in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen nano-bubble water suppresses ROS generation, adipogenesis, and interleukin-6 secretion in hydrogen-peroxide- or PMA-stimulated adipocytes and three-dimensional subcutaneous adipose equivalents. Cells 2021, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, S.; Chen, L.; Li, S. Hydrogen-rich medium protects human skin fibroblasts from high glucose or mannitol induced oxidative damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Long, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J. Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.S.; Kawamura, T.; Peng, X.; Tochigi, N.; Shigemura, N.; Billiar, T.R.; Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y. Hydrogen inhalation reduced epithelial apoptosis in ventilator-induced lung injury via a mechanism involving nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, E.; Shimamura, N.; Saiki, C.; Sunada, K.; Miwa, N.; Xiao, L. Hydrogen Gas Mitigates Acute Hypoxia-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Brain Injuries in Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091130
Sato E, Shimamura N, Saiki C, Sunada K, Miwa N, Xiao L. Hydrogen Gas Mitigates Acute Hypoxia-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Brain Injuries in Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Antioxidants. 2025; 14(9):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091130
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Eriko, Naohiro Shimamura, Chikako Saiki, Katsuhisa Sunada, Nobuhiko Miwa, and Li Xiao. 2025. "Hydrogen Gas Mitigates Acute Hypoxia-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Brain Injuries in Medaka (Oryzias latipes)" Antioxidants 14, no. 9: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091130
APA StyleSato, E., Shimamura, N., Saiki, C., Sunada, K., Miwa, N., & Xiao, L. (2025). Hydrogen Gas Mitigates Acute Hypoxia-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Brain Injuries in Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Antioxidants, 14(9), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091130






