Weizmannia coagulans BC179 Alleviates Post-Alcohol Discomfort May via Taurine-Related Metabolism and Antioxidant Regulation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Object
2.1.1. Pilot Crossover Study
2.1.2. Main Randomized Controlled Trial
2.2. Hangover Symptom Questionnaire
2.3. Blood Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Serum Metabolomic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pre-Experiment Results
3.1.1. Baseline Characteristics
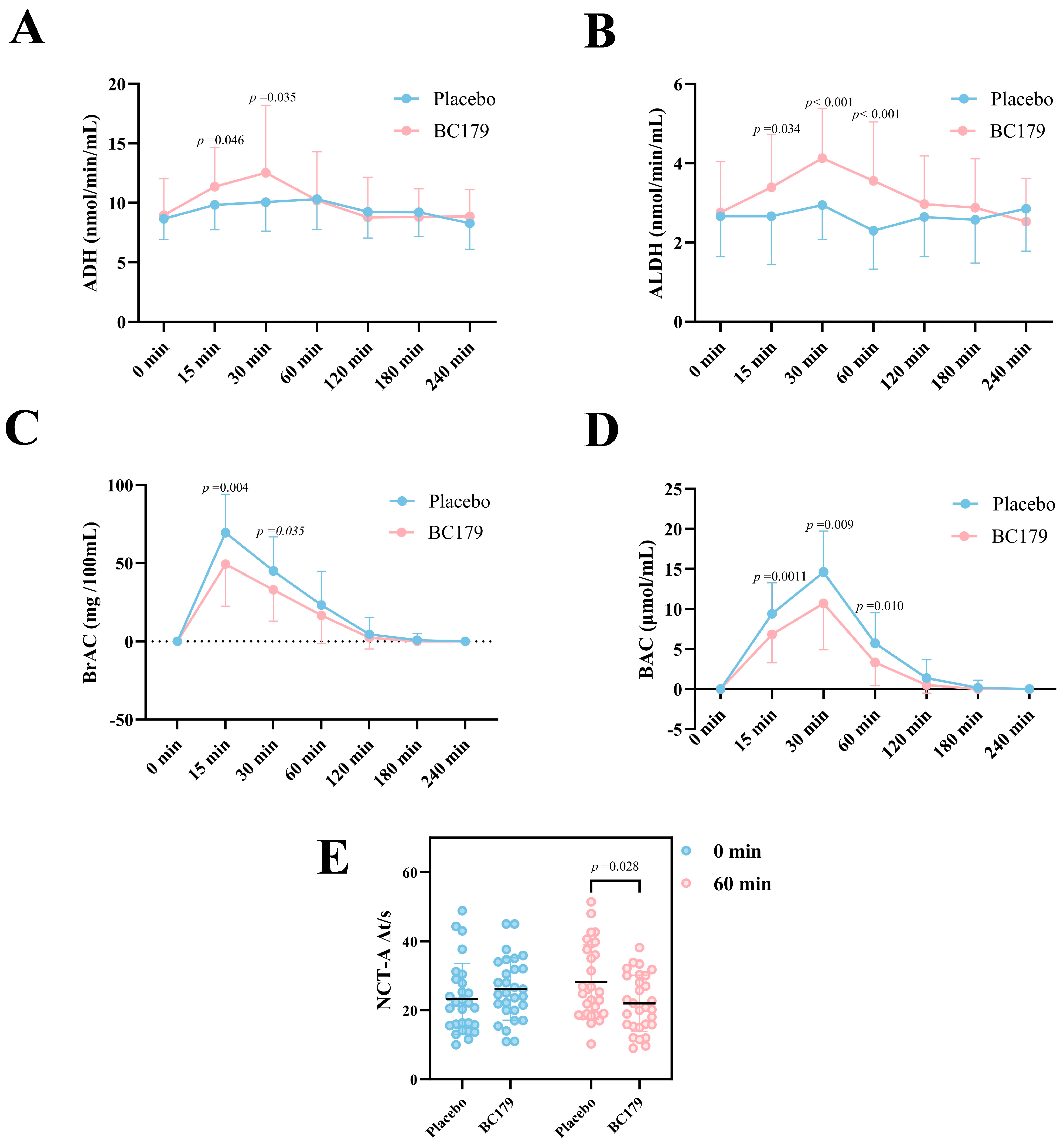
3.1.2. Serum ADH and ALDH Activity Within 4 h Post-Alcohol Intake
3.1.3. Changes in Alcohol Level Within 4 h After Drinking
3.1.4. Number Connection Test (NCT-A)
3.2. Formal Experimental Results
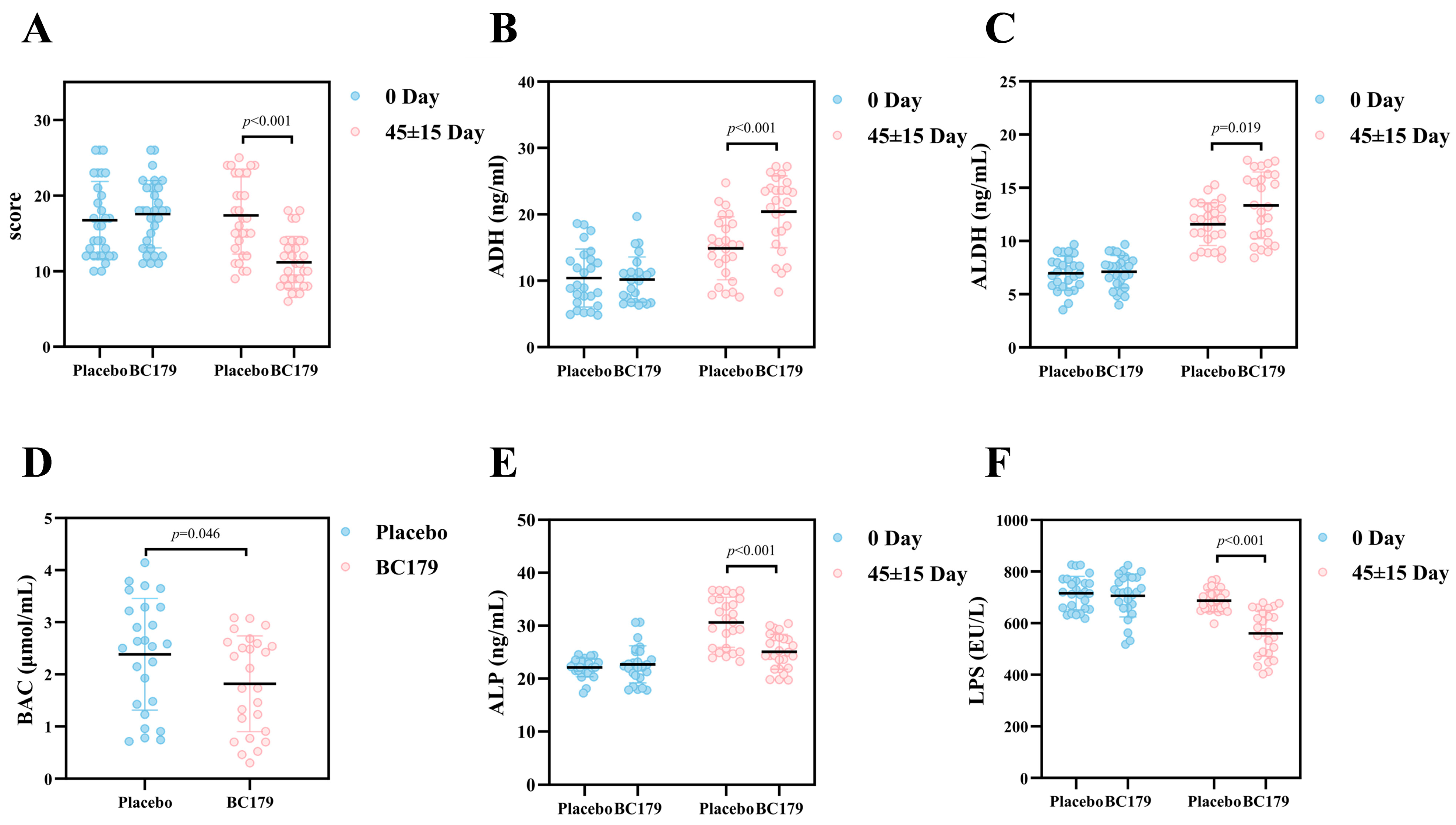
3.2.1. Hangover Questionnaire
3.2.2. Alcohol Metabolizing Enzymes and Blood Alcohol Concentration
3.2.3. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase and Intestinal Barrier
3.2.4. Inflammatory Factors
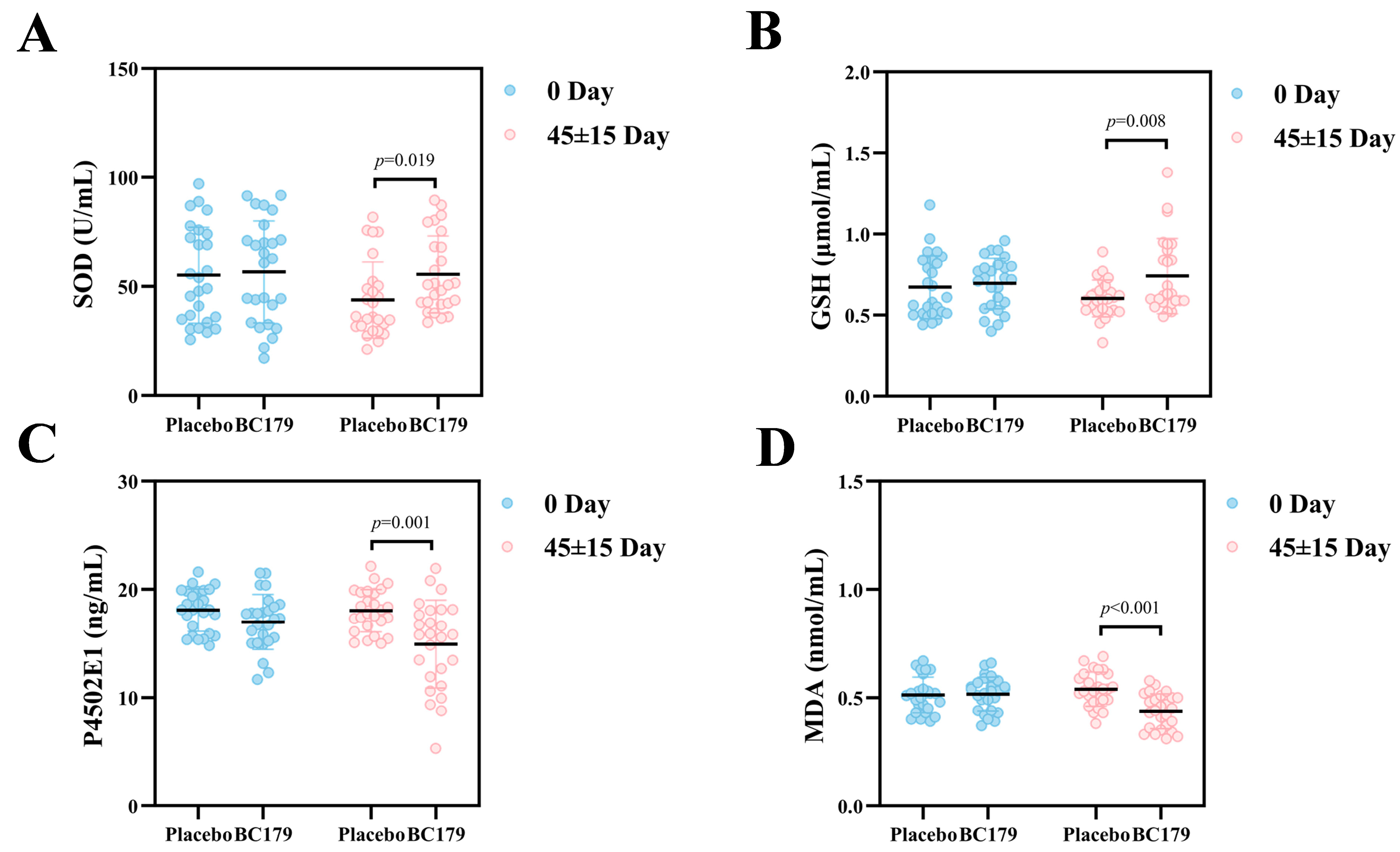
3.2.5. Oxidative Stress
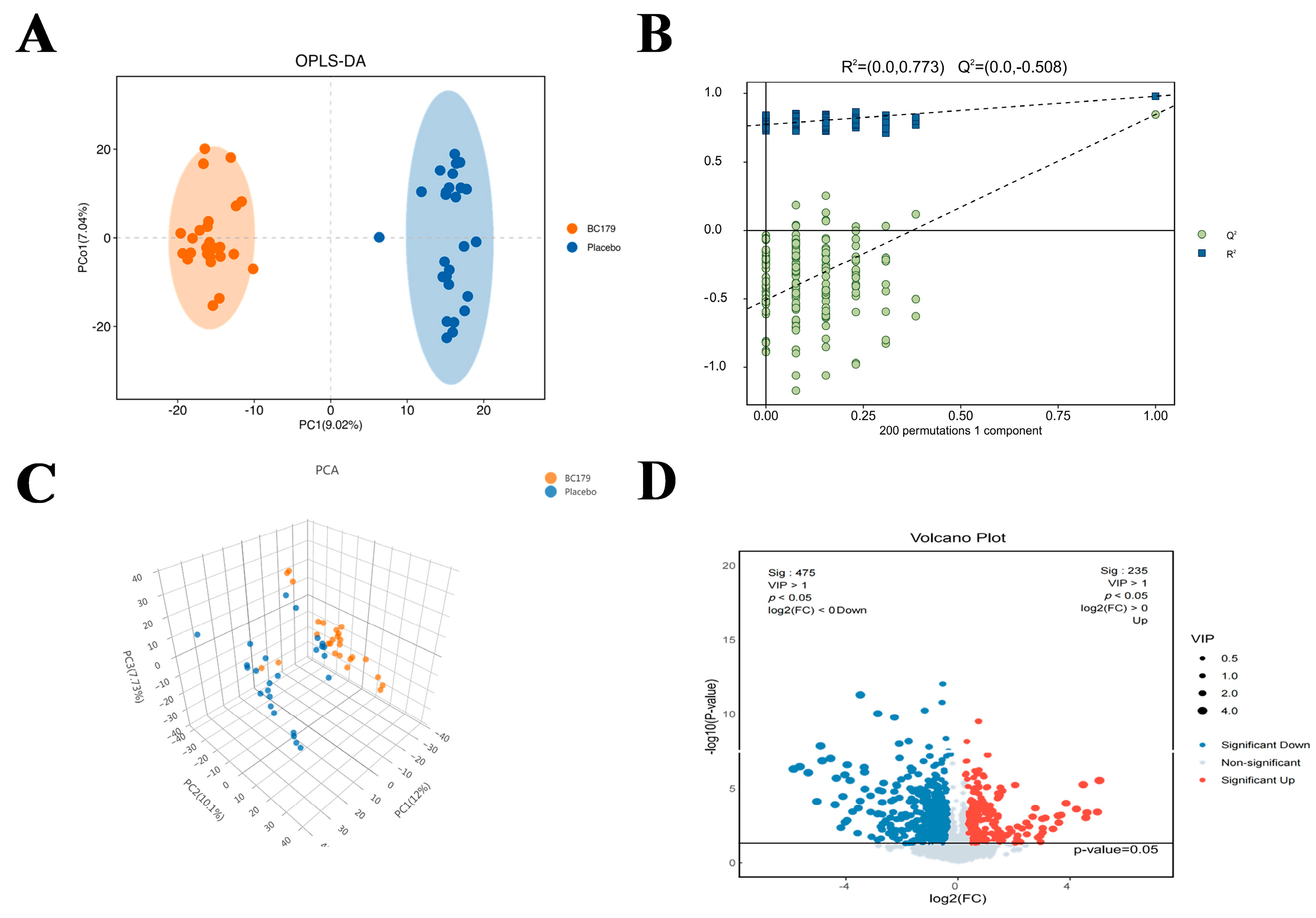
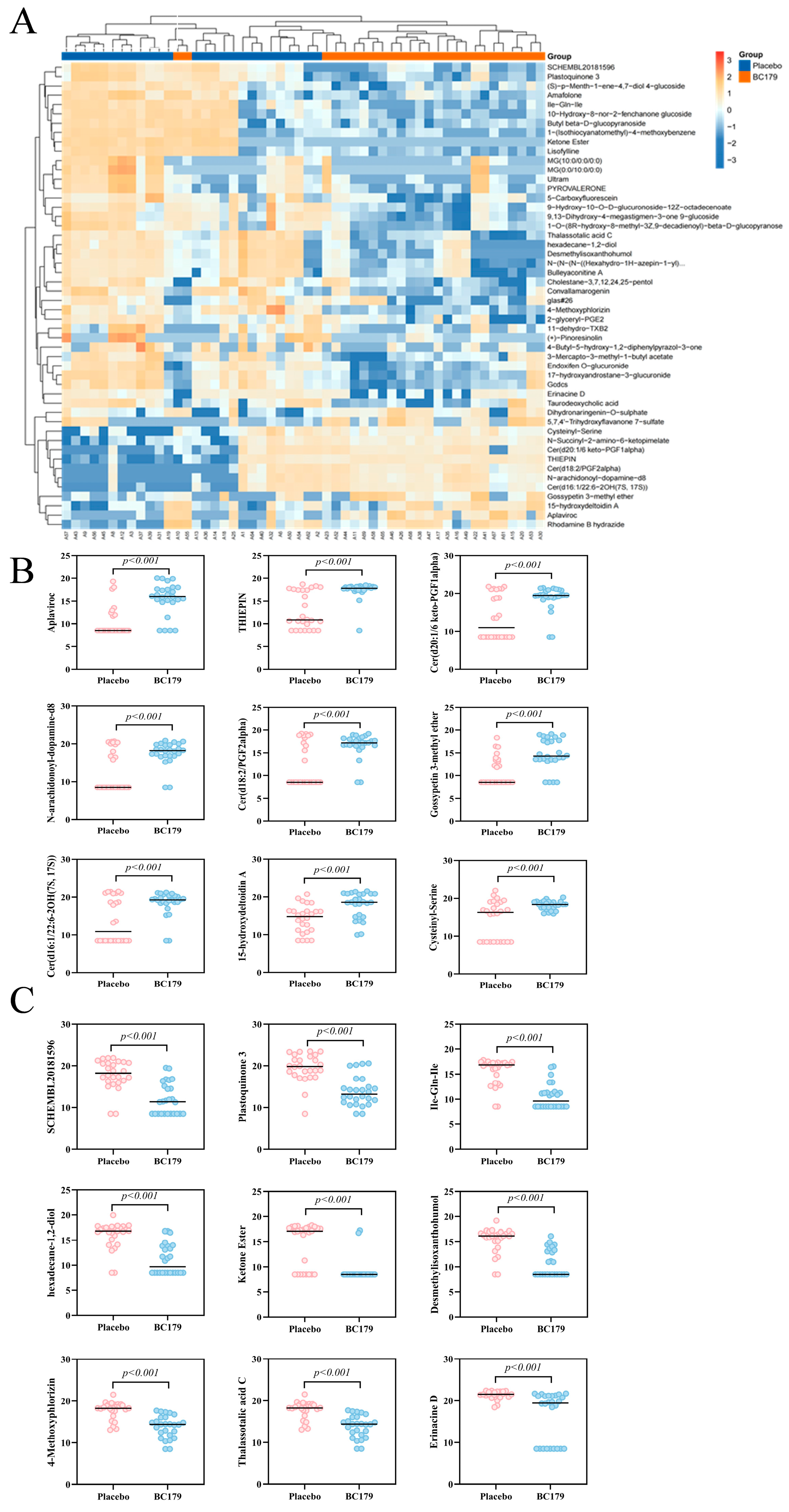
3.2.6. Serum Metabolomics
Differential Metabolites
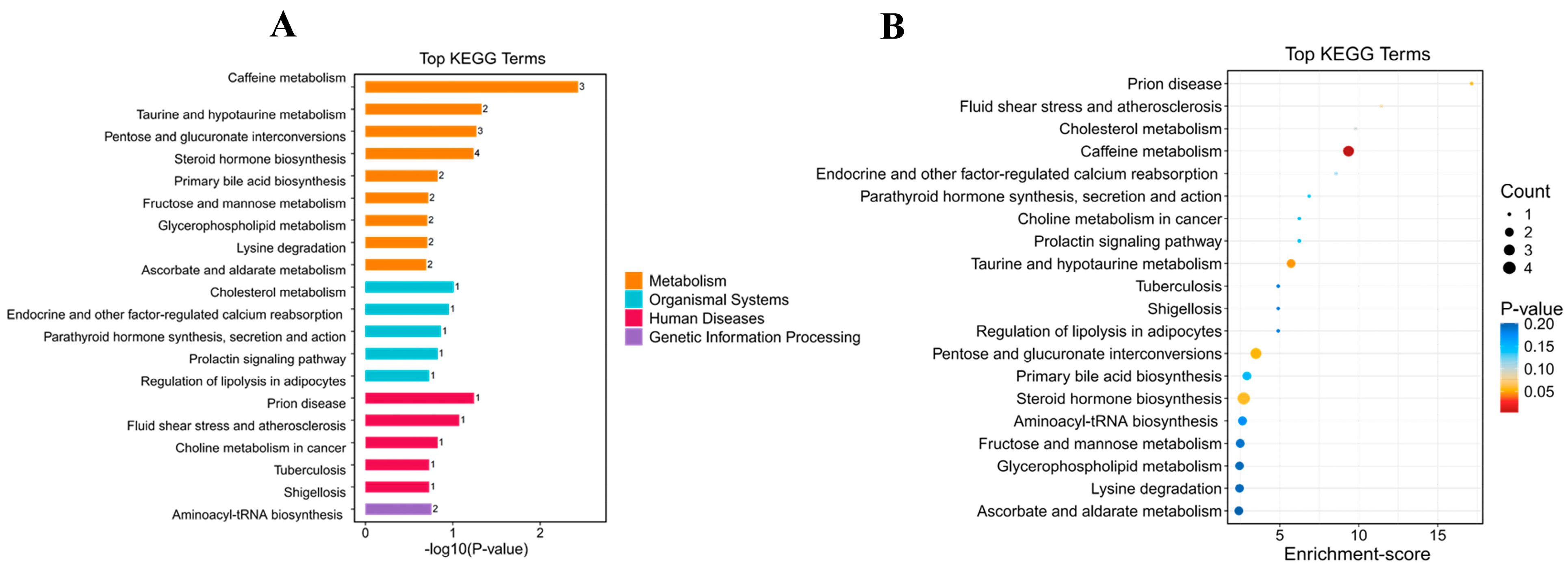
Effects of BC179 on Metabolic Pathways
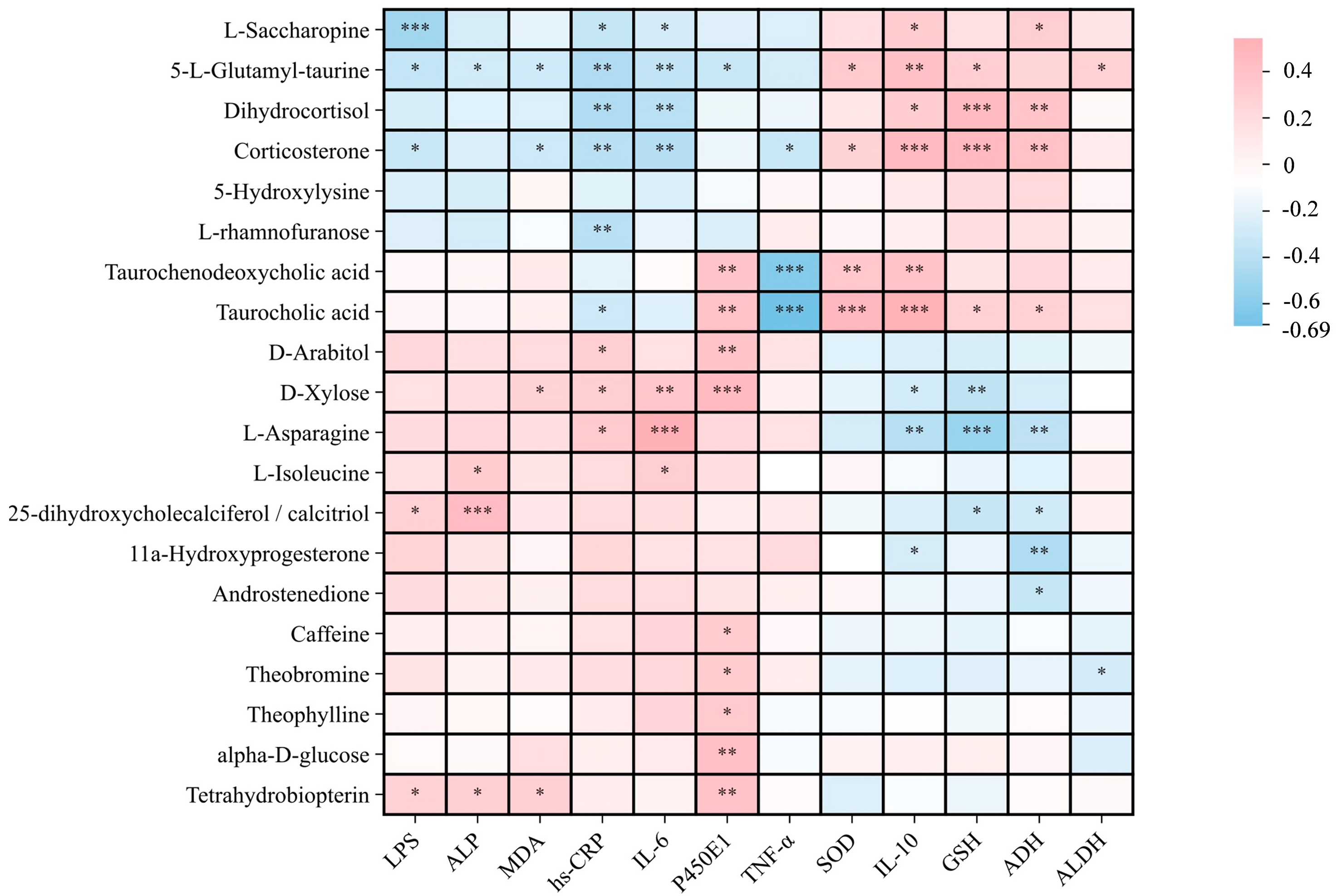
Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malnick, S.D.H.; Alin, P.; Somin, M.; Neuman, M.G. Fatty Liver Disease-Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic: Similar but Different. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursz, M.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Moreno, C.; Spahr, L.; Sterneck, M.; Cortez-Pinto, H. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 154–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Carr, R. Alcohol effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Mateos, R.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Albillos, A. Dysfunctional Immune Response in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: It Takes Two to Tango. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Jeong, J.-J.; Gupta, H.; Sharma, S.P.; Oh, K.K.; Won, S.-M.; Kwon, G.H.; et al. Microbiome-Based Metabolic Therapeutic Approaches in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.; Souza-Smith, F.M.; Molina, P.E. Alcohol-Associated Tissue Injury: Current Views on Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ciaula, A.D.; Bonfrate, L.; Krawczyk, M.; Frühbeck, G.; Portincasa, P. Synergistic and Detrimental Effects of Alcohol Intake on Progression of Liver Steatosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhai, S.; Duan, M.; Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gu, S. Weizmannia coagulans BC99 Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function by Modulating Butyrate Formation to Alleviate Acute Alcohol Intoxication in Rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Duan, M.; Qu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, S.; Gu, S. The Improvement Effects of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Liver Function and Gut Microbiota of Long-Term Alcohol Drinkers: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2000, 284, 3043–3045. [CrossRef]
- Neighbors, C.; Leasure, J.L.; Shank, F.; Ryan, P.; Najjar, L.Z.; Sze, C.; Henderson, C.E.; Young, C.M. Physical activity as a moderator of the association between alcohol consumption and hangovers. Addict. Behav. 2024, 159, 108145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumgay, H.; Shield, K.; Charvat, H.; Ferrari, P.; Sornpaisarn, B.; Obot, I.; Islami, F.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P.; Rehm, J.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of cancer in 2020 attributable to alcohol consumption: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-F.; Varady, K.A.; Wang, X.-D.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tayyem, R.; Latella, G.; Bergheim, I.; Valenzuela, R.; George, J.; et al. The role of dietary modification in the prevention and management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international multidisciplinary expert consensus. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A. Screening and Brief Behavioral Counseling Interventions to Reduce Unhealthy Alcohol Use in Adults 18 Years and Older, Including Pregnant Women. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackus, M.; Van De Loo, A.J.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Scholey, A.; Verster, J.C. The Role of Alcohol Metabolism in the Pathology of Alcohol Hangover. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Gao, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Ma, G.Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Nong, Q.N.; Wang, Y.B.; Tan, J. Structure characteristics of a novel pectic polysaccharide from Fructus Corni and its protective effect on alcoholic fatty liver. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 352, 123153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sangwung, P.; Kondo, R.; Jung, Y.; McConnell, M.J.; Jeong, J.; Utsumi, T.; Sessa, W.C.; Iwakiri, Y. Alcohol-induced Hsp90 acetylation is a novel driver of liver sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction and alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wei, M.; Hou, T. Preparation, Structural Identification, and Screening of Egg-Derived Peptides with Facilitating Alcohol Metabolism Activity. Foods 2024, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastre, A.; Bélanger, M.; Beauchesne, E.; Nguyen, B.N.; Desjardins, P.; Butterworth, R.F.; Bassaganya-Riera, J. Inflammatory cascades driven by tumor necrosis factor-alpha play a major role in the progression of acute liver failure and its neurological complications. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Sun, X.; Cheng, D.; Liu, S.; Pan, C.Q.; Xing, H. Intestinal microbiome-targeted therapies improve liver function in alcohol-related liver disease by restoring bifidobacteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1274261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Singh, P.; Molla, M.; Yimer, Y.S.; Dinda, S.C.; Chandra, P.; Singh, B.K.; Dagnew, S.B.; Assefa, A.N.; Ewunetie, A. Harnessing the potential of probiotics in the treatment of alcoholic liver disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1212742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Zhu, L.; Tang, F.-S. Elafibranor: A promising treatment for alcoholic liver disease, metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, and cholestatic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuqwider, J.; Altamimi, M.; Mauriello, G. Limosilactobacillus reuteri in Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-García, L.; Portillo, M.P.; Martínez, J.A.; Milton-Laskibar, I. Usefulness of Probiotics in the Management of NAFLD: Evidence and Involved Mechanisms of Action from Preclinical and Human Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Han, S.; Xia, H.; Chen, H.; Li, L. Lactobacillus reuteri Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.; Ridker, P. High sensitivity C-reactive protein for predicting cardiovascular disease: An inflammatory hypothesis. Eur. Hear. J. 2001, 22, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.A.; Jeong, J.-J.; Han, S.H.; Kwon, G.H.; Lee, K.J.; Gupta, H.; Sharma, S.P.; Won, S.-M.; Oh, K.-K.; Yoon, S.J.; et al. Gut-microbiota prompt activation of natural killer cell on alcoholic liver disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2281014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Du, A.; Qiu, M.; Shu, H.; Li, L.; Kong, X.; Sun, W. ROS inhibition increases KDM6A-mediated NOX2 transcription and promotes macrophages oxidative stress and M1 polarization. Cell Stress Chaperones 2023, 28, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Cao, M.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X. Hierarchy-Assembled Dual Probiotics System Ameliorates Cholestatic Drug-Induced Liver Injury via Gut-Liver Axis Modulation. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2200986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, T.; Chu, M.; et al. The Hepatoprotective Effect of the Probiotic Clostridium butyricum against Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Acute Liver Damage in Mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4042–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gong, L.; Ni, J.; Li, W. Probiotic Bacillus Alleviates Oxidative Stress-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Gut-Liver Axis in a Rat Model. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.J.; Guo, J.-T.; Lin, M.-K.; Lee, M.-S.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, W.-H. Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum against chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in the murine model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8597–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, V.; Lubau, N.S.A.; Mukerjee, N.; Kumarasamy, V. Alcohol-induced liver injury in signalling pathways and curcumin’s therapeutic potential. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 11, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Kim, H.W. Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xie, Z.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, F. The role of taurine through endoplasmic reticulum in physiology and pathology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 226, 116386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliou, S.; Adamaki, M.; Ioannou, P.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Spandidos, D.A.; Christodoulou, I.; Kyriakopoulos, A.M.; Zoumpourlis, V. Protective role of taurine against oxidative stress (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- András, G.; Arturo, A.-L.; Marc, P.; Kalina, D. The distinct mechanism regulating taurine homeostasis in mice: Nutrient availability affects taurine levels in the liver and energy restriction influences it in the intestine. Life Sci. 2024, 359, 123213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadi, I.A.; Al Ansari, A.M.; AlSaleh, A.F.F.; Alabbasi, A.M.A. Systematic review of the effect of caffeine therapy effect on cardiometabolic markers in rat models of the metabolic syndrome. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Cao, F.; Zhuge, H.; Lai, S.; Cao, W.; Wei, H.; Guo, R.; Qiu, J.; Song, Q.; Pei, L.; et al. Hepatic NMNAT1 is required to defend against alcohol-associated fatty liver disease. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadt6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lee, J.; He, L.; Vatsalya, V.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Z.; et al. Probiotic-derived nanoparticles inhibit ALD through intestinal miR194 suppression and subsequent FXR activation. Hepatology 2022, 77, 1164–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodella, P.; Boreski, D.; Luz, M.A.M.; Gabriel, E.A.; Takase, L.F.; Chin, C.M. Taurine Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis Effect in Chronic Ethanol-Induced Rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Projects | BC179 Group (n = 15) | Placebo Group (n = 15) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p-Value | |
| Age | 30.400 | 13.16 | 31.93 | 12.578 | 0.747 |
| BMI | 23.67 | 2.83 | 22.81 | 2.54 | 0.386 |
| Sex (M/F) | 10/5 | 12/3 | 0.408 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Azeem, S.; Dong, Y.; Gai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Fang, S.; Gu, S. Weizmannia coagulans BC179 Alleviates Post-Alcohol Discomfort May via Taurine-Related Metabolism and Antioxidant Regulation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091038
Duan M, Wu Y, Zhang J, Azeem S, Dong Y, Gai Z, Zhu J, Fang S, Gu S. Weizmannia coagulans BC179 Alleviates Post-Alcohol Discomfort May via Taurine-Related Metabolism and Antioxidant Regulation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(9):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091038
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Mengyao, Ying Wu, Jie Zhang, Saman Azeem, Yao Dong, Zhonghui Gai, Jianguo Zhu, Shuguang Fang, and Shaobin Gu. 2025. "Weizmannia coagulans BC179 Alleviates Post-Alcohol Discomfort May via Taurine-Related Metabolism and Antioxidant Regulation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Antioxidants 14, no. 9: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091038
APA StyleDuan, M., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Azeem, S., Dong, Y., Gai, Z., Zhu, J., Fang, S., & Gu, S. (2025). Weizmannia coagulans BC179 Alleviates Post-Alcohol Discomfort May via Taurine-Related Metabolism and Antioxidant Regulation: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Antioxidants, 14(9), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091038







