Current Insights into Glutathione Depletion in Adult Septic Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction and Background
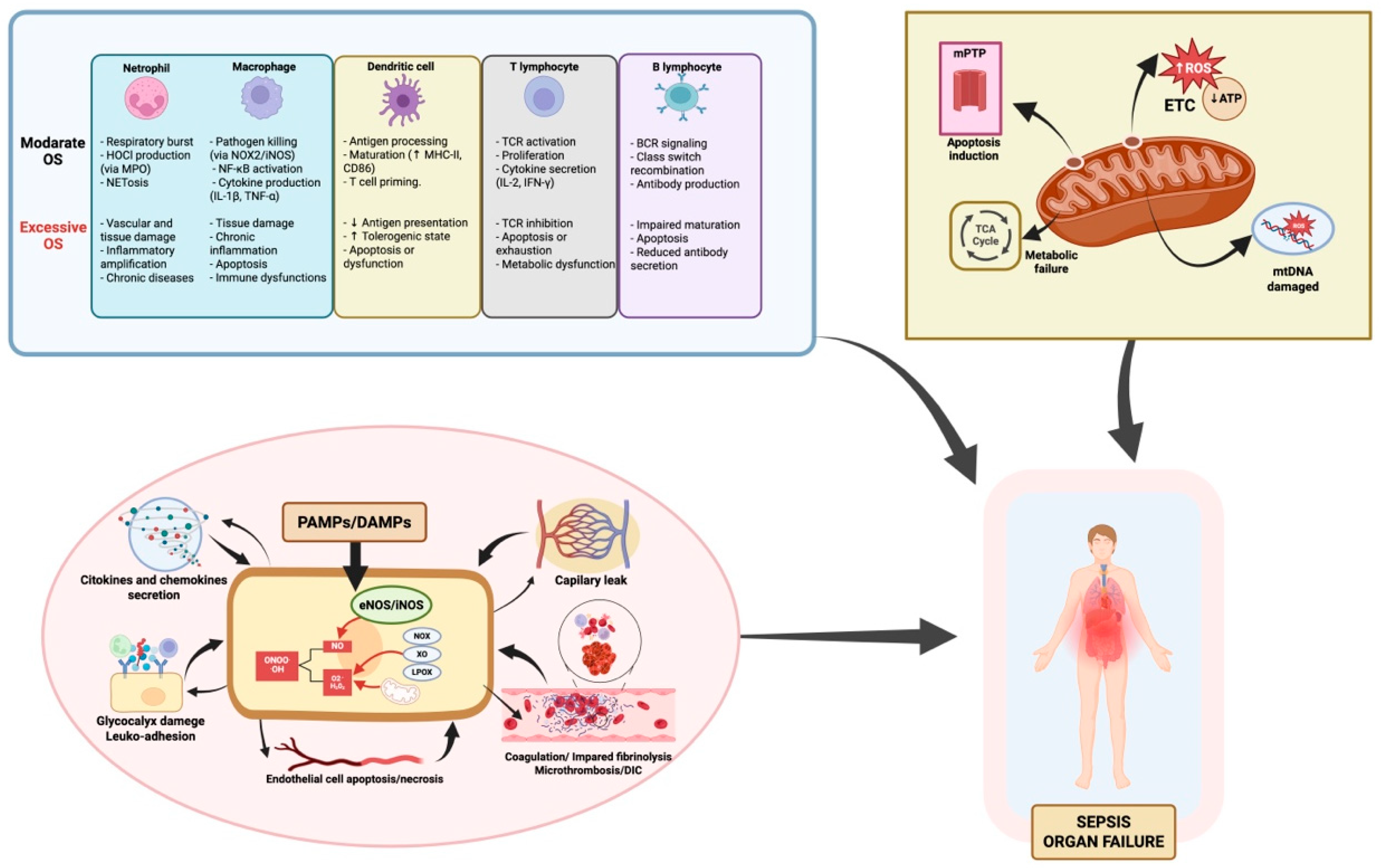
2. Oxidative Stress and Sepsis
3. Biology and Function of Glutathione
3.1. Intracellular Dynamics and Functional Roles of Glutathione
- Maintaining intracellular redox homeostasis as the primary non-enzymatic antioxidant, directly neutralizing ROS/RNS and preserving cellular integrity via GPx-mediated peroxide reduction and GR-mediated recycling [18].
- Regulating metabolic processes, amino acid transport, signal transduction, gene expression, mitochondrial integrity, and apoptosis prevention by inhibiting cytochrome c release and caspase activation.
- Serving as a cysteine reservoir and transporter via the γ-glutamyl cycle, protecting thiol groups from extracellular oxidation.
- Detoxifying xenobiotics through conjugation (via glutathione-S-transferase), followed by further processing and excretion as mercapturic acid derivatives [117].
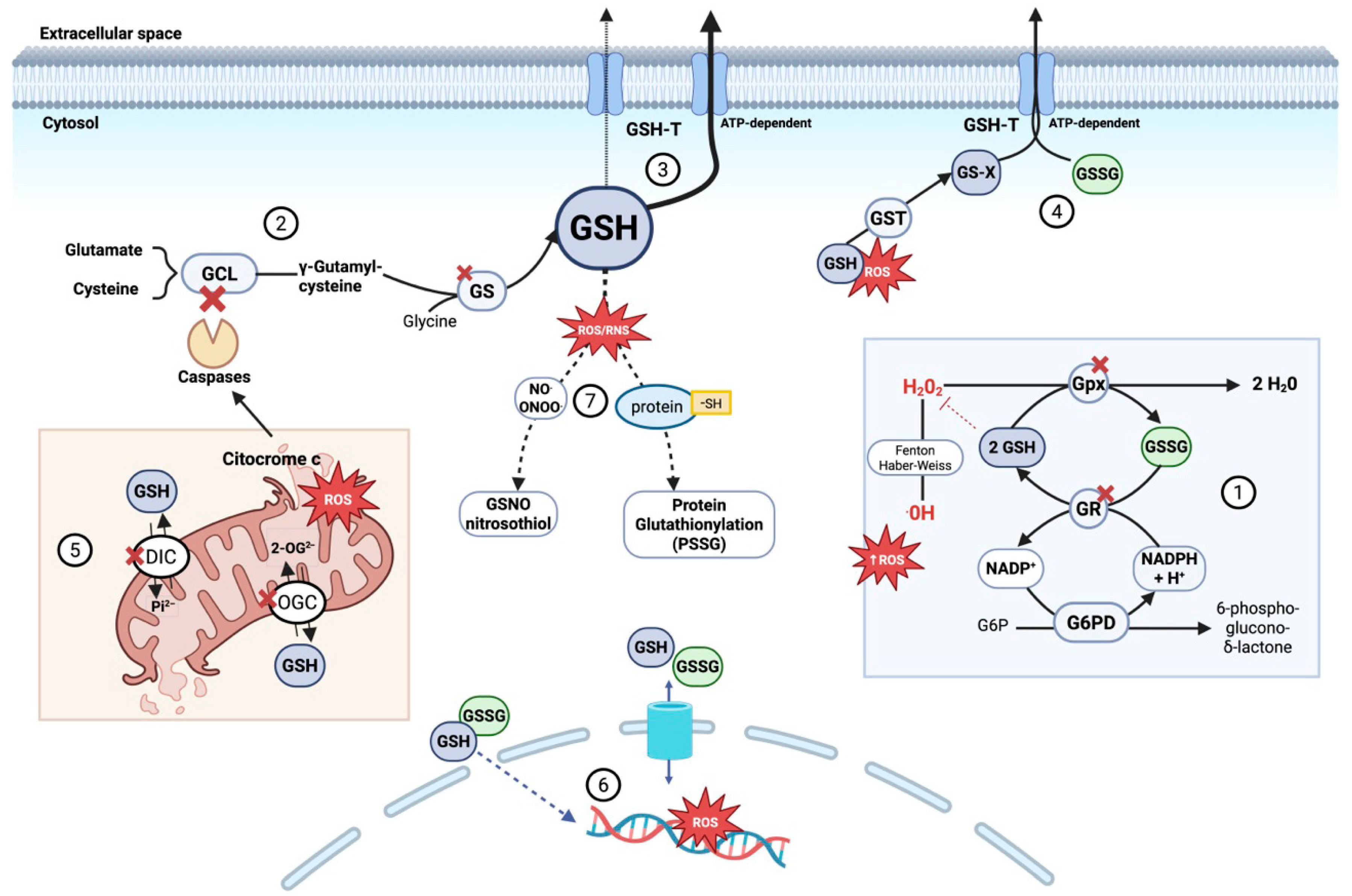
3.2. Mechanisms of Intracellular Glutathione Depletion in Sepsis
- Enhanced consumption of GSH via detoxification of peroxides is mediated by GPx, increasing GSSG levels. The regenerative system involving GR and NADPH is impaired by metabolic dysfunction, direct oxidative inhibition of GR, and NADPH depletion, resulting in GSH/GSSG imbalance and redox collapse.
- Increased GSH export via ATP-binding transporters (e.g., MRPs) supports precursor reuse and eliminates toxic xenobiotic conjugates; however, this accelerates intracellular GSH loss. In the extracellular milieu, GSH may become inactivated by reacting with RNS to form S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) or by protein glutathionylation (PSSG), further depleting functional GSH.
- GCL (the rate-limiting enzyme) may be genetically or epigenetically impaired under sepsis, exacerbated by inflammatory mediators and metabolic stress. Caspase-mediated degradation of GCL during apoptosis further reduces synthetic capacity.
- Cysteine availability declines due to accelerated catabolism, reduced absorption, and hepatic dysfunction, limiting GSH biosynthetic flux.
- Mitochondrial GSH import is hindered by ROS-mediated damage to transporters, impairing mitochondrial redox protection.
- Nuclear GSH diffusion may be altered by oxidative overload.
- Endoplasmic reticulum GSH transport remains incompletely characterized but likely vulnerable to oxidative conditions.
4. Consequences of Glutathione Depletion in Sepsis
4.1. Glutathione as a Key Redox Immunological Modulator in Sepsis: Biphasic Impact on Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses
4.2. Glutathione, Endothelium, and Mitochondria: Intertwined Mechanisms in the Progression of Septic Organ Dysfunction
4.3. Glutathione and Organ Failure in Sepsis: Clinical Evidence and Prognostic Implications
4.4. Glutathione as a Potential Therapeutic Option in Adult Patients
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farrah, K.; McIntyre, L.; Doig, C.J.; Talarico, R.; Taljaard, M.; Krahn, M.; Fergusson, D.; Forster, A.J.; Coyle, D.; Thavorn, K. Sepsis-associated mortality, resource use, and healthcare costs: A propensity-matched cohort study. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Sepsis. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sepsis (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Barrett, K.A.; Sheikh, F.; Chechulina, V.; Chung, H.; Dodek, P.; Rosella, L.; Thavorn, K.; Scales, D.C. High-cost users after sepsis: A population-based observational cohort study. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gaieski, D.F.; Edwards, J.M.; Kallan, M.J.; Carr, B.G. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 4, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, C.; Sakr, Y.; Vincent, J.L.; Le Gall, J.R.; Reinhart, K.; Ranieri, V.M.; Gerlach, H.; Fielden, J.; Groba, C.B.; Payen, D. An evaluation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome signs in the Sepsis Occurrence in Acutely ill Patients (SOAP) study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2006, 32, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goode, H.F.; Cowley, H.C.; Walker, B.E.; Howdle, P.D.; Webster, N.R. Decreased antioxidant status and increased lipid peroxidation in patients with septic shock and secondary organ dysfunction. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 23, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, H.C.; Bacon, P.J.; Goode, H.F.; Webster, N.R.; Jones, J.G.; Menon, D.K. Plasma antioxidant potential in severe sepsis: A comparison of survivors and nonsurvivors. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.C.; Shiesh, S.C.; Chi, C.H.; Tu, Y.F.; Hor, L.I.; Shieh, C.C.; Chen, M.F. Serum total antioxidant capacity reflects severity of illness in patients with severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Borrelli, E.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Grau, G.E.; Girardin, E.; Ricou, B.; Dayer, J.; Suter, P.M. Plasma concentrations of cytokines, their soluble receptors, and antioxidant vitamins can predict the development of multiple organ failure in patients at risk. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galley, H.F. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 107, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Introductory Remarks. In Oxidative Stress; Sies, H., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1985; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, A. Roles of neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in organ function impairment in sepsis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2022, 23, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Andrades, M.É.; Morina, A.; Spasić, S.; Spasojević, I. Bench-to-bedside review: Sepsis—From the redox point of view. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joffre, J.; Hellman, J. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in sepsis and acute inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, V.K.; Kaushik, S.; Saxena, J.; Jyoti, A. Free radicals, mitochondrial dysfunction and sepsis-induced organ dysfunction: A mechanistic insight. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 3, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzoin Vulcano, L.A.; Soraci, A.L.; Tapia, M.O. Glutathione homeostasis. Acta Bioquímica Clin. Latinoam. 2013, 47, 529–539. [Google Scholar]
- Labarrere, C.A.; Kassab, G.S. Glutathione: A Samsonian life-sustaining small molecule that protects against oxidative stress, ageing and damaging inflammation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1007816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Braunstein, I.; Motohashi, H.; Dallenga, T.; Schaible, U.E.; Benhar, M. Redox signaling in innate immunity and inflammation: Focus on macrophages and neutrophils. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 237, 427–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, N.; Madhoun, A.; Arefanian, H.; Wilson, A.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Shenouda, S.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R.; Sindhu, S. Oxidative stress induces expression of the Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4 in the human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Implications for metabolic inflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mu, S.; Yan, D.; Qin, H.; Zheng, Z. Comprehending toll-like receptors: Pivotal element in the pathogenesis of sepsis and its complications. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1591011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumar, V. Toll-like receptors in sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative regulators as future immunomodulatory targets. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, S.F.; Malik, A.B. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L622–L645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Type I interferon: Friend or foe? J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boxx, G.M.; Cheng, G. The roles of type I interferon in bacterial infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cicchinelli, S.; Pignataro, G.; Gemma, S.; Piccioni, A.; Picozzi, D.; Ojetti, V.; Franceschi, F.; Candelli, M. PAMPs and DAMPs in sepsis: A review of their molecular features and potential clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vringer, E.; Tait, S.W.G. Mitochondria and cell death-associated inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Coyne, C.B.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. PAMPs and DAMPs: Signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harrington, J.S.; Huh, J.W.; Schenck, E.J.; Nakahira, K.; Siempos, I.I.; Choi, A.M.K. Circulating mitochondrial DNA as predictor of mortality in critically ill patients. Chest 2019, 156, 1120–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brealey, D.; Brand, M.; Hargreaves, I.; Heales, S.; Land, J.; Smolenski, R.; Davies, N.A.; Cooper, C.E.; Singer, M. Association between mitochondrial dysfunction and severity and outcome of septic shock. Lancet 2002, 360, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Thimmulappa, R.; Kombairaju, P.; Biswal, S. NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species mediate amplified TLR4 signaling and sepsis-induced mortality in Nrf2-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, M.E.; Lee, J.S. Advances in the regulation of inflammatory mediators in nitric oxide synthase: Implications for disease modulation and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Radi, R. Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26464–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szabó, C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Radi, R. Peroxynitrite: Biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huang, S.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, H.C.; Cai, Q.L.; Gao, C.; Li, L.; Cao, J.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment options. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brady, J.; Horie, S.; Laffey, J.G. Role of the adaptive immune response in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2020, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Poll, T.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Wiersinga, W.J. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity 2021, 54, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, J.S.; To, K.; Chang, K.C.; Takasu, O.; Osborne, D.F.; Walton, A.H.; Bricker, T.L.; Jarman, S.D.; Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; et al. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. JAMA 2011, 306, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chang, K.; Svabek, C.; Vazquez-Guillamet, C.; Sato, B.; Rasche, D.; Wilson, S.; Robbins, P.; Ulbrandt, N.; Suzich, J.; Green, J.; et al. Targeting the programmed cell death 1: Programmed cell death ligand 1 pathway reverses T cell exhaustion in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care. 2014, 18, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, S.C.; Scicluna, B.P.; Arts, R.J.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Lachmandas, E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Kox, M.; Manjeri, G.R.; Wagenaars, J.A.; Cremer, O.L.; et al. Broad defects in the energy metabolism of leukocytes underlie immunoparalysis in sepsis. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.C.; Quintin, J.; Cramer, R.A.; Shepardson, K.M.; Saeed, S.; Kumar, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Martens, J.H.; Rao, N.A.; Aghajanirefah, A.; et al. mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science 2014, 345, 1250684, Erratum in Science 2014, 346, aaa1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, S.; Xie, M.; Kang, R.; Cao, L.; Tang, D. AMPK regulates immunometabolism in sepsis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 72, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Z. Metabolic reprogramming and its regulatory mechanism in sepsis-mediated inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clementi, E.; Brown, G.C.; Feelisch, M.; Moncada, S. Persistent inhibition of cell respiration by nitric oxide: Crucial role of S-nitrosylation of mitochondrial complex I and protective action of glutathione. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7631–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Chu, Y. Reactive oxygen species: The signal regulator of B cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 142, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; van Soest, D.M.K.; Polderman, P.E.; Burgering, B.M.T.; Dansen, T.B. DNA damage and oxidant stress activate p53 through differential upstream signaling pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Traganos, F.; Albino, A.P.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Oxidative stress induces cell cycle-dependent Mre11 recruitment, ATM and Chk2 activation and histone H2AX phosphorylation. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sherman, M.H.; Kuraishy, A.I.; Deshpande, C.; Hong, J.S.; Cacalano, N.A.; Gatti, R.A.; Manis, J.P.; Damore, M.A.; Pellegrini, M.; Teitell, M.A. AID-induced genotoxic stress promotes B cell differentiation in the germinal center via ATM and LKB1 signaling. Mol. Cell. 2010, 39, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qin, W.; Scicluna, B.P.; van der Poll, T. The role of host cell DNA methylation in the immune response to bacterial infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ciarlo, E.; Savva, A.; Roger, T. Epigenetics in sepsis: Targeting histone deacetylases. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42 (Suppl. 1), S8–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Venet, F.; Monneret, G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, M.L.; Rodrigues, B.P.; Menezes, T.N.; Ceschim, S.L.; Casarini, D.E.; Gava, A.L.; Pereira, T.M.; Vasquez, E.C.; Campagnaro, B.P.; Meyrelles, S.S. Reactive oxygen species contribute to dysfunction of bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells in aged C57BL/6 J mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mira, J.C.; Brakenridge, S.C.; Moldawer, L.L.; Moore, F.A. Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome (PICS). Crit. Care Clin. 2017, 33, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chadda, K.R.; Puthucheary, Z. Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome (PICS): A review of definitions, potential therapies, and research priorities. Br. J. Anaesth. 2024, 132, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aird, W.C. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 2003, 101, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Tong, X.; He, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Z. Sepsis-induced endothelial dysfunction: Permeability and regulated cell death. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 9953–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pflug. Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kataoka, H.; Ushiyama, A.; Akimoto, Y.; Matsubara, S.; Kawakami, H.; Iijima, T. Structural behavior of the endothelial glycocalyx is associated with pathophysiologic status in septic mice: An integrated approach to analyzing the behavior and function of the glycocalyx using both electron and fluorescence intravital microscopy. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psenakova, K.; Hexnerova, R.; Srb, P.; Obsilova, V.; Veverka, V.; Obsil, T. The redox-active site of thioredoxin is directly involved in apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 binding that is modulated by oxidative stress. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1626–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, J.; Toriumi, S.; Awano, K.; Ichijo, H.; Sasaki, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tamura, S. Regulation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 by protein phosphatase 2Cepsilon. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Tsantes, E.A.; Bonova, E.; Tsante, K.A.; Mantzios, P.G.; Vaiopoulus, A.G.; Tsalas, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Houhoula, D.; et al. Sepsis-induced coagulopathy: An update on pathophysiology, biomarkers, and current guidelines. Life 2023, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elbers, P.W.G.; Ince, C. Mechanisms of critical illness–classifying microcirculatory flow abnormalities in distributive shock. Crit. Care 2006, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shapiro, N.I.; Schuetz, P.; Yano, K.; Sorasaki, M.; Parikh, S.M.; Jones, A.E.; Trzeciak, S.; Ngo, L.; Aird, W.C. The association of endothelial cell signaling, severity of illness, and organ dysfunction in sepsis. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fink, M.P. Bench-to-bedside review: Cytopathic hypoxia. Crit. Care 2002, 6, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daga, M.K.; Khan, N.A.; Singh, H.; Chhoda, A.; Mattoo, S.; Gupta, B.K. Markers of oxidative stress and clinical outcome in critically ill septic patients: A preliminary study from North India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OC35–OC38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huet, O.; Cherreau, C.; Nicco, C.; Dupic, L.; Conti, M.; Borderie, D.; Pene, F.; Vicaut, E.; Benhamou, D.; Mira, J.P.; et al. Pivotal role of glutathione depletion in plasma-induced endothelial oxidative stress during sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, O.; Obata, R.; Aubron, C.; Spraul-Davit, A.; Charpentier, J.; Laplace, C.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Conti, M.; Vicaut, E.; Mira, J.P.; et al. Plasma-induced endothelial oxidative stress is related to the severity of septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekstegers, P.; Weidenhöfer, S.; Kapsner, T.; Werdan, K. Skeletal muscle partial pressure of oxygen in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 22, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, P.S.; Yoon, Y.; Robotham, J.L.; Anders, M.W.; Sheu, S.S. Calcium, ATP, and ROS: A mitochondrial love-hate triangle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 287, C817–C833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Raoof, M.; Chen, Y.; Sumi, Y.; Sursal, T.; Junger, W.; Brohi, K.; Itagaki, K.; Hauser, C.J. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature 2010, 464, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abais, J.M.; Xia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Boini, K.M.; Li, P.L. Redox regulation of NLRP3 inflammasomes: ROS as trigger or effector? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1111–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shimada, K.; Crother, T.R.; Karlin, J.; Dagvadorj, J.; Chiba, N.; Chen, S.; Ramanujan, V.K.; Wolf, A.J.; Vergnes, L.; Ojcius, D.M.; et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity 2012, 36, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gehrke, N.; Mertens, C.; Zillinger, T.; Wenzel, J.; Bald, T.; Zahn, S.; Tüting, T.; Hartmann, G.; Barchet, W. Oxidative damage of DNA confers resistance to cytosolic nuclease TREX1 degradation and potentiates STING-dependent immune sensing. Immunity 2013, 39, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopfner, K.P.; Hornung, V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 21, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez, P.A.; Castro, E.; Montalvo, M.; Aguayo, S.; Velarde, G.; Jara González, F.E.; Vélez, J.L. Role of apoptosis in sepsis. Horiz. Med. 2020, 20, e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Sheeja Prabhakaran, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Luo, G.; He, W.; Liou, Y.C. Mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ermak, G.; Davies, K.J.A. Calcium and oxidative stress: From cell signaling to cell death. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilokani, L.; Nagashima, S.; Paupe, V.; Prudent, J. Mitochondrial dynamics: Overview of molecular mechanisms. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouny, R.; Shutt, T.E. Reciprocal Regulation of Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, W.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Chiang, P.C.; Hsiao, H.W.; Chuang, S.M.; Lue, S.I.; Hsu, C. Suppression of autophagy in rat liver at late stage of polymicrobial sepsis. Shock 2011, 35, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Pai, P.Y.; Hsueh, H.W.; Yuan, S.S.; Hsieh, Y.C. Complete induction of autophagy is essential for cardioprotection in sepsis. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Lo, S.; Perng, D.S.; Wu, D.B.; Lee, P.H.; Chang, Y.F.; Kuo, P.L.; Yu, M.L.; Yuan, S.S.; Hsieh, Y.C. Complete activation of autophagic process attenuates liver injury and improves survival in septic mice. Shock 2014, 41, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Metabolic reprogramming consequences of sepsis: Adaptations and contradictions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Wei, W.; Huang, Y.; Fu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Metabolic reprogramming in septic acute kidney injury: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Metabolism 2024, 158, 155974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Swanson, P.E.; Freeman, B.D.; Tinsley, K.W.; Cobb, J.P.; Matuschak, G.M.; Buchman, T.G.; Karl, I.E. Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 1230–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; De Santis, V.; Vitale, D.; Jeffcoate, W. Multiorgan failure is an adaptive, endocrine-mediated, metabolic response to overwhelming systemic inflammation. Lancet 2004, 364, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meister, A. Glutathione; Metabolism and function via the γ-glutamyl cycle. Life Sci. 1974, 15, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.S.; Anderson, M.E.; Meister, A. Amino acid sequence and function of the light subunit of rat kidney gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20578–20583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelig, G.F.; Meister, A. Glutathione biosynthesis; gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase from rat kidney. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 113, pp. 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, C.C.; Backos, D.S.; Mohar, I.; White, C.C.; Forman, H.J.; Kavanagh, T.J. Structure, function, and post-translational regulation of the catalytic and modifier subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, S.C. Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meister, A. On the discovery of glutathione. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1988, 13, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballatori, N.; Krance, S.M.; Marchan, R.; Hammond, C.L. Plasma membrane glutathione transporters and their roles in cell physiology and pathophysiology. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meister, A.; Anderson, M.E. Glutathione. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1983, 52, 711–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolo, G.; Antonione, R.; De Cicco, M. Glutathione metabolism in sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, S591–S595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, M.J.; Reed, D.J. Status of the mitochondrial pool of glutathione in the isolated hepatocyte. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 3747–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballatori, N.; Krance, S.M.; Notenboom, S.; Shi, S.; Tieu, K.; Hammond, C.L. Glutathione dysregulation and the etiology and progression of human diseases. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marí, M.; de Gregorio, E.; de Dios, C.; Roca-Agujetas, V.; Cucarull, B.; Tutusaus, A.; Morales, A.; Colell, A. Mitochondrial glutathione: Recent insights and role in disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, D.P.; Carlson, J.L.; Mody, V.C.; Cai, J.; Lynn, M.J.; Sternberg, P. Redox state of glutathione in human plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompella, A.; Visvikis, A.; Paolicchi, A.; De Tata, V.; Casini, A.F. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvagno, F.; Vernone, A.; Pescarmona, G.P. The role of glutathione in protecting against the severe inflammatory response triggered by COVID-19. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, D.P.; Moldfus, P.; Stead, A.H.; Ormstad, K.; Jörnvall, H.; Orrenius, S. Metabolism of glutathione and a glutathione conjugate by isolated kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 2787–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Analytical methods to investigate glutathione and related compounds in biological and pathological processes. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2002, 781, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ruiz, C.; Colell, A.; Morales, A.; Kaplowitz, N.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Role of oxidative stress generated from the mitochondrial electron transport chain and mitochondrial glutathione status in loss of mitochondrial function and activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B: Studies with isolated mitochondria and rat hepatocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.; Federici, G.; Bertini, E.; Piemonte, F. Analysis of glutathione: Implication in redox and detoxification. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2003, 333, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.J.; Sies, H. Subcellular glutathione contents in isolated hepatocytes treated with L-buthionine sulfoximine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 123, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ruiz, C.; Morales, A.; Ballesta, A.; Rodés, J.; Kaplowitz, N.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Effect of chronic ethanol feeding on glutathione and functional integrity of mitochondria in periportal and perivenous rat hepatocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Griffith, O.W.; Meister, A. Origin and turnover of mitochondrial glutathione. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4668–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, L.; Kaplowitz, N. Glutathione in liver diseases and hepatotoxicity. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marí, M.; Morales, A.; Colell, A.; García-Ruiz, C.; Kaplowitz, N.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial glutathione: Features, regulation and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaplowitz, N.; Aw, T.Y.; Ookhtens, M. The regulation of hepatic glutathione. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1985, 25, 715–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Graf, P. Hepatic thiol and glutathione efflux under the influence of vasopressin, phenylephrine and adrenaline. Biochem. J. 1985, 226, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garibotto, G.; Sofia, A.; Saffioti, S.; Russo, R.; Deferrari, G.; Rossi, D.; Verzola, D.; Gandolfo, M.T.; Sala, M.R. Interorgan exchange of aminothiols in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E757–E763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glutathione efflux and cell death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1694–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, B.H.; Lee, C.H. Mechanisms of action of vitamin D as supplemental therapy for Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sánchez-Vallejo, V.; Benlloch-Navarro, S.; López-Pedrajas, R.; Romero, F.J.; Miranda, M. Neuroprotective actions of progesterone in an in vivo model of retinitis pigmentosa. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Borg, H.M.; Rakoczy, S.G.; Uthus, E.O. Growth hormone alters components of the glutathione metabolic pathway in Ames dwarf mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1019, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Das, S.; Sarkar, P.K. Thyroid hormone promotes glutathione synthesis in astrocytes by up regulation of glutamate cysteine ligase through differential stimulation of its catalytic and modulator subunit mRNAs. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, J.; Pallardó, F.V.; Llopis, J.; Furukawa, T.; Viña, J.R.; Viña, J. Glutathione depletion by hyperphagia-induced obesity. Life Sci. 1989, 45, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolo, G.; Heer, M.; Narici, M.; Strollo, F. Microgravity as a model of ageing. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozden, M.; Maral, H.; Akaydin, D.; Cetinalp, P.; Kalender, B. Erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase activity, plasma malondialdehyde and erythrocyte glutathione levels in hemodialysis and CAPD patients. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sido, B.; Hack, V.; Hochlehnert, A.; Lipps, H.; Herfarth, C.; Dröge, W. Impairment of intestinal glutathione synthesis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1998, 42, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morris, D.; Khurasany, M.; Nguyen, T.; Kim, J.; Guilford, F.; Mehta, R.; Gray, D.; Saviola, B.; Venketaraman, V. Glutathione and infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3329–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, P. Role of glutathione in immunity and inflammation in the lung. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kwon, D.H.; Lee, H.; Park, C.; Hong, S.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Cha, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, H.J.; et al. Glutathione induced immune-stimulatory activity by romoting M1-Like macrophages polarization via potential ROS scavenging capacity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kozlov, E.M.; Ivanova, E.; Grechko, A.V.; Wu, W.K.; Starodubova, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Involvement of oxidative stress and the innate immune system in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diseases 2021, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, T.; Tsutsuki, H.; Islam, W.; Ono, K.; Takeda, K.; Akaike, T.; Sawa, T. ATP exposure stimulates glutathione efflux as a necessary switch for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Villa, P.; Saccani, A.; Sica, A.; Ghezzi, P. Glutathione protects mice from lethal sepsis by limiting inflammation and potentiating host defense. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Fernández-Fierro, A.; Covián, C.; Bueno, S.M.; Riedel, C.A.; Mackern-Oberti, J.P.; Kalergis, A.M. Naturally derived heme-oxygenase 1 inducers and their therapeutic application to immune-mediated diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cabrera-Pérez, J.; Condotta, S.A.; Badovinac, V.P.; Griffith, T.S. Impact of sepsis on CD4 T cell immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 96, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Blum, J.S.; Wearsch, P.A.; Cresswell, P. Pathways of antigen processing. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 443–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feige, M.J.; Hendershot, L.M. Disulfide bonds in ER protein folding and homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murata, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Hamuro, J. The polarization of Th1/Th2 balance is dependent on the intracellular thiol redox status of macrophages due to the distinctive cytokine production. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.D.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Vasquez, K.; Waltenbaugh, C. Glutathione levels in antigen-presenting cells modulate Th1 versus Th2 response patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khanfar, A.; Al Qaroot, B. Could glutathione depletion be the Trojan horse of COVID-19 mortality? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12500–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyer, J.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Bailis, W. Metabolic signaling in T cells. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 649–659, Erratum in Cell Res. 2020, 30, 1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00421-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dröge, W.; Breitkreutz, R. Glutathione and immune function. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japiassú, A.M.; Santiago, A.P.; d’Avila, J.C.; Garcia-Souza, L.F.; Galina, A.; Castro Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, F.A.; Oliveira, M.F. Bioenergetic failure of human peripheral blood monocytes in patients with septic shock is mediated by reduced F1Fo adenosine-5′-triphosphate synthase activity. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.K.; Yang, K.D.; Shaio, M.F. Lymphocyte proliferation modulated by glutamine: Involved in the endogenous redox reaction. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 117, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hadzic, T.; Li, L.; Cheng, N.; Walsh, S.A.; Spitz, D.R.; Knudson, C.M. The role of low molecular weight thiols in T lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2 secretion. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7965–7972, Erratum in J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilano, K.; Baldelli, S.; Ciriolo, M.R. Glutathione: New roles in redox signaling for an old antioxidant. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stojkov, D.; Amini, P.; Oberson, K.; Sokollik, C.; Duppenthaler, A.; Simon, H.U.; Yousefi, S. ROS and glutathionylation balance cytoskeletal dynamics in neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 4073–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Serfass, R.E.; Ganther, H.E. Defective microbicidal activity in glutathione peroxidase-deficient neutrophils of selenium-deficient rats. Nature 1975, 255, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyun, X.; Fan, Y.; Weiping, W.; Qing, Y.; Bingwei, S. Metabolomic analysis of spontaneous neutrophil apoptosis reveals the potential involvement of glutathione depletion. Innate Immun. 2021, 27, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, J.; Meng, X.; Wancket, L.M.; Lintner, K.; Nelin, L.D.; Chen, B.; Francis, K.P.; Smith, C.V.; Rogers, L.K.; Liu, Y. Glutathione reductase facilitates host defense by sustaining phagocytic oxidative burst and promoting the development of neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lorente, J.A.; García-Frade, L.J.; Landín, L.; de Pablo, R.; Torrado, C.; Renes, E.; García-Avello, A. Time course of hemostatic abnormalities in sepsis and its relation to outcome. Chest 1993, 103, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Kidokoro, A.; Yagi, Y. The role of the endothelium in changes in procoagulant activity in sepsis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998, 187, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.A.; Wang, T.Y.; Varadharaj, S.; Reyes, L.A.; Hemann, C.; Talukder, M.A.; Chen, Y.R.; Druhan, L.J.; Zweier, J.L. S-glutathionylation uncouples eNOS and regulates its cellular and vascular function. Nature 2010, 468, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Forgione, M.A.; Weiss, N.; Heydrick, S.; Cap, A.; Klings, E.S.; Bierl, C.; Eberhardt, R.T.; Farber, H.W.; Loscalzo, J. Cellular glutathione peroxidase deficiency and endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H1255–H1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgione, M.A.; Cap, A.; Liao, R.; Moldovan, N.I.; Eberhardt, R.T.; Lim, C.C.; Jones, J.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J.; Loscalzo, J. Heterozygous cellular glutathione peroxidase deficiency in the mouse: Abnormalities in vascular and cardiac function and structure. Circulation 2002, 106, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubos, E.; Kelly, N.J.; Oldebeken, S.R.; Leopold, J.A.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Glutathione peroxidase-1 deficiency augments proinflammatory cytokine-induced redox signaling and human endothelial cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35407–35417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Pan, S.; Berk, B.C. Glutaredoxin mediates Akt and eNOS activation by flow in a glutathione reductase-dependent manner. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M. Participation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/endothelial-nitric-oxide synthase signaling in the processes of angiogenesis and vascular remodeling. Nefrologia 2002, 22, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murata, H.; Ihara, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; Sumikawa, K.; Kondo, T. Glutaredoxin exerts an antiapoptotic effect by regulating the redox state of Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50226–50233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernansanz-Agustín, P.; Enríquez, J.A. Generation of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Venditti, P.; Di Stefano, L.; Di Meo, S. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, D.A.; Galley, H.F. Mitochondrial protection by the thioredoxin-2 and glutathione systems in an in vitro endothelial model of sepsis. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lash, L.H. Evidence for mitochondrial uptake of glutathione by dicarboxylate and 2-oxoglutarate carriers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Putt, D.A.; Lash, L.H. Enrichment and functional reconstitution of glutathione transport activity from rabbit kidney mitochondria: Further evidence for the role of the dicarboxylate and 2-oxoglutarate carriers in mitochondrial glutathione transport. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 373, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, H.M.; Brock, S.; Gray, J.J.; Linseman, D.A. Stable over-expression of the 2-oxoglutarate carrier enhances neuronal cell resistance to oxidative stress via Bcl-2-dependent mitochondrial GSH transport. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ha, S.D.; Park, S.; Han, C.Y.; Nguyen, M.L.; Kim, S.O. Cellular adaptation to anthrax lethal toxin-induced mitochondrial cholesterol enrichment, hyperpolarization, and reactive oxygen species generation through downregulating MLN64 in macrophages. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 4846–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Ferrington, D.A.; Kannan, R. Glutathione Metabolism and the Novel Role of Mitochondrial GSH in Retinal Degeneration. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Legault, J.; Carrier, C.; Petrov, P.; Renard, P.; Remacle, J.; Mirault, M.E. Mitochondrial GPx1 decreases induced but not basal oxidative damage to mtDNA in T47D cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 272, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Kwon, W.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Suh, G.J.; Jung, Y.S. Low serum NADPH and GSH levels were associated with the mortality of patients with septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kwon, W.Y.; Suh, G.J.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.E. Plasma glutathione reductase activity and prognosis of septic shock. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 200, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Cadenas, E. Mitochondrial thiols in the regulation of cell death pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Olafsdottir, K.; Reed, D.J. Retention of oxidized glutathione by isolated rat liver mitochondria during hydroperoxide treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 964, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, T.R.; Requejo, R.; Filipovska, A.; Brown, S.; Prime, T.A.; Robinson, A.J.; Fearnley, I.M.; Murphy, M.P. Complex I within oxidatively stressed bovine heart mitochondria is glutathionylated on Cys-531 and Cys-704 of the 75-kDa subunit: Potential role of CYS residues in decreasing oxidative damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24801–24815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beer, S.M.; Taylor, E.R.; Brown, S.E.; Dahm, C.C.; Costa, N.J.; Runswick, M.J.; Murphy, M.P. Glutaredoxin 2 catalyzes the reversible oxidation and glutathionylation of mitochondrial membrane thiol proteins: Implications for mitochondrial redox regulation and antioxidant defense. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47939–47951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Xuan, J.Y.; McBride, S.; Maharsy, W.; Thorn, S.; Holterman, C.E.; Kennedy, C.R.; Rippstein, P.; deKemp, R.; da Silva, J.; et al. Glutaredoxin-2 is required to control oxidative phosphorylation in cardiac muscle by mediating deglutathionylation reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14812–14828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernandes, R.S.; Cotter, T.G. Apoptosis or necrosis: Intracellular levels of glutathione influence mode of cell death. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, J.; Mari, M.; Colell, A.; Morales, A.; Basañez, G.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Cholesterol and peroxidized cardiolipin in mitochondrial membrane properties, permeabilization and cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marí, M.; Colell, A.; Morales, A.; Caballero, F.; Moles, A.; Fernández, A.; Terrones, O.; Basañez, G.; Antonsson, B.; García-Ruiz, C.; et al. Mechanism of Mitochondrial Glutathione-Dependent Hepatocellular Susceptibility to TNF Despite NF-κB Activation. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, H.; Kong, L. The emerging role of ferroptosis in sepsis, opportunity or challenge? Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 5551–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, L.; Lin, D.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Lenahan, C.; Pan, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Shao, A.; Zhang, J. Ferroptosis in acute central nervous system injuries: The future direction? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berg, R.M.G.; Møller, K.; Bailey, D.M. Neuro-oxidative-nitrosative stress in sepsis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bharat, A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Scott Budinger, G.R.; Kreisel, D.; DeWet, C.J.; Gelman, A.E.; Waites, K.; Crabb, D.; Xiao, L.; Bhorade, S.; et al. Disseminated Ureaplasma infection as a cause of fatal hyperammonemia in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 284re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Shao, L.; Li, X. Irisin protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/GPX4 signal axis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 171–184, Erratum in Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 193, 676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.11.024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Luo, L.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Li, S.; et al. miR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bayır, H.; Dixon, S.J.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Kellum, J.A.; Kagan, V.E. Ferroptotic mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, H.M.; Korge, P.; Weiss, J.N. Mitochondria and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1047, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, P. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and rapid depletion of mitochondrial glutathione by β-phenethyl isothiocyanate: Mechanisms for anti-leukemia activity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Romero, F.J.; Romá, J. Careful consideration of the effects induced by glutathione depletion in rat liver and heart. The involvement of cytosolic and mitochondrial glutathione pools. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1989, 70, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparetto, A.; Corbucci, G.G.; Candiani, A.; Gohil, K.; Edwards, R.H. Effect of tissue hypoxia and septic shock on human skeletal muscle mitochondria. Lancet 1983, 2, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekstegers, P.; Weidenhöfer, S.; Pilz, G.; Werdan, K. Peripheral oxygen availability within skeletal muscle in sepsis and septic shock: Comparison to limited infection and cardiogenic shock. Infection 1991, 19, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer-Graiwer, J.E.; Firestein, B.L.; Bredt, D.S. Nitric oxide mediated induction of cytochrome c oxidase mRNA and protein in a mouse macrophage cell line. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 288, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, K.Y.; Askanazi, J.; Michelson, C.B.; Kantrowitz, L.R.; Fürst, P.; Kinney, J.M. Effect of injury and sepsis on high-energy phosphates in muscle and red cells. J. Trauma 1980, 20, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M. Critical illness and flat batteries. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Navarrete, M.L.; Cerdeño, M.C.; Serra, M.; Conejero, R. Mitochondrial and microcirculatory distress syndrome in the critical patient. Therapeutic implications. Med. Intensiva 2013, 37, 476–484, Erratum in Med. Intensiva. 2014, 38, 63. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrabou, G.; Morén, C.; López, S.; Tobías, E.; Cardellach, F.; Miró, O.; Casademont, J. The effects of sepsis on mitochondria. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, M.; Astiz, M.E.; Barua, R.S.; Osman, M. Impaired mitochondrial function induced by serum from septic shock patients is attenuated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase and poly(ADP-ribose) synthase. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmezat, T.; Breuillé, D.; Capitan, P.; Mirand, P.P.; Obled, C. Glutathione turnover is increased during the acute phase of sepsis in rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
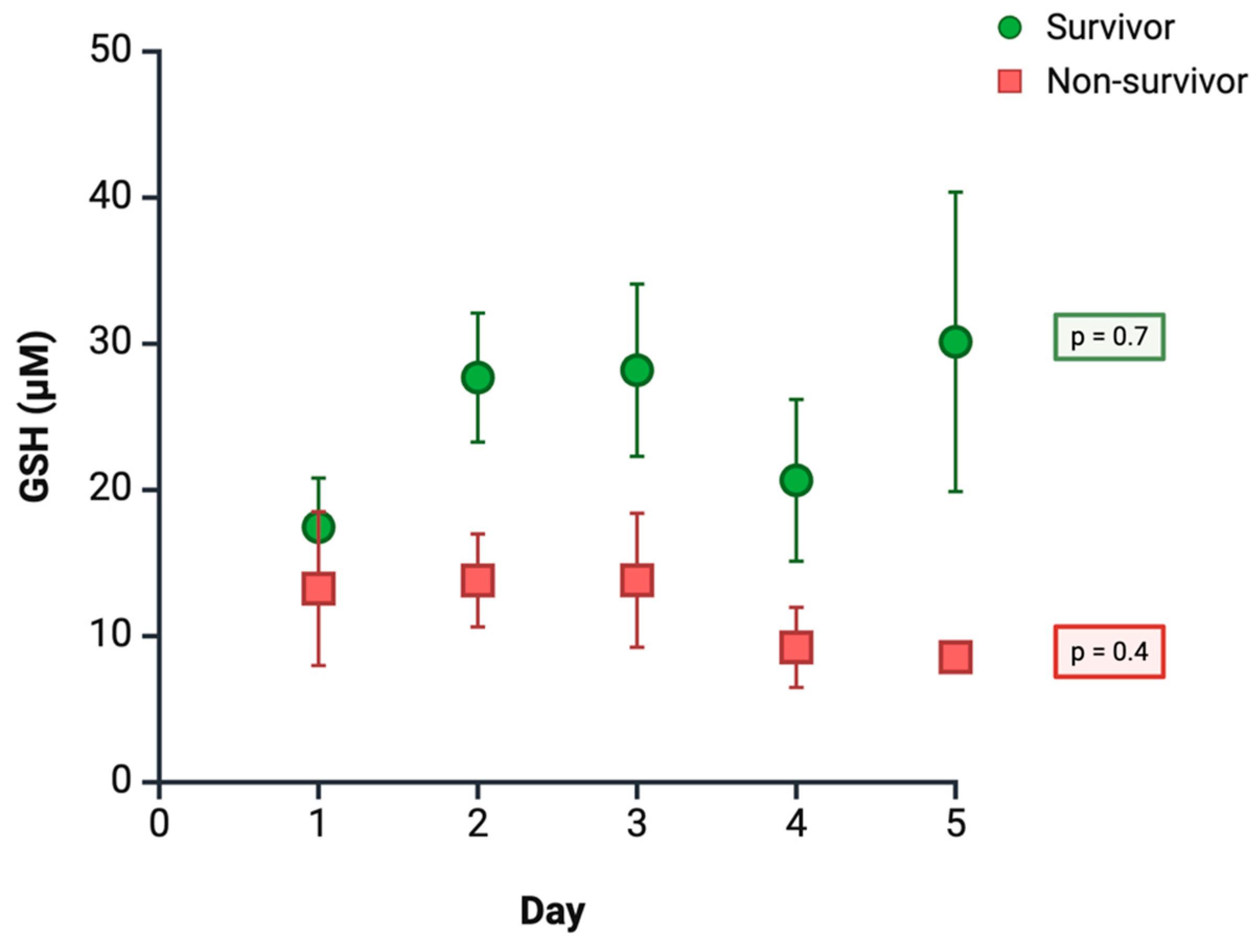
- Fläring, U.B.; Rooyackers, O.E.; Hebert, C.; Bratel, T.; Hammarqvist, F.; Wernerman, J. Temporal changes in whole-blood and plasma glutathione in ICU patients with multiple organ failure. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, M.; Regueira, T.; Bruhn, A.; Perez, D.; Strobel, P.; Dougnac, A.; Marshall, G.; Leighton, F. Lipoperoxidation and protein oxidative damage exhibit different kinetics during septic shock. Mediat. Inflamm. 2008, 2008, 168652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsai, K.; Hsu, T.; Kong, C.; Lin, K.; Lu, F. Is the endogenous peroxyl-radical scavenging capacity of plasma protective in systemic inflammatory disorders in humans? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, K.L.; Molnar, Z.; Lowe, D.; Watson, I.D.; Shearer, E. Measures of total free radical activity in critically ill patients. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 32, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetsa, M.; Pitsika, M.; Goutzourelas, N.; Stagos, D.; Tousia Becker, A.; Zakynthinos, E. Oxidative status in ICU patients with septic shock. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, A.C.; Groeneveld, A.B.; Straub, J.P.; Thijs, L.G. Plasma lipid peroxides and antioxidants in human septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1991, 17, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, S.Y.; Kung, C.T.; Su, C.M.; Lai, Y.R.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, N.W.; Wang, H.C.; Cheng, B.C.; Su, Y.J.; Lin, W.C.; et al. Impact of oxidative stress on treatment outcomes in adult patients with sepsis: A prospective study. Medicine 2020, 99, e20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semedi, B.P.; Rehatta, N.M.; Nugraha, J.; Soetjipto. Antioxidant role in critically ill patients with vasodilatory shock: Does glutathione peroxidase correlate to severity of tissue hypoxia and organ failure. Open Access Emerg. Med. 2023, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lorente, L.; Martín, M.M.; Almeida, T.; Abreu-González, P.; Ferreres, J.; Solé-Violán, J.; Labarta, L.; Díaz, C.; Jiménez, A. Association between serum total antioxidant capacity and mortality in severe septic patients. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, e7–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, L.; Martín, M.M.; Pérez-Cejas, A.; Abreu-González, P.; López, R.O.; Ferreres, J.; Solé-Violán, J.; Labarta, L.; Díaz, C.; Palmero, S.; et al. Serum total antioxidant capacity during the first week of sepsis and mortality. J. Crit. Care 2018, 47, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Malhotra, D.; Levy, H.; Marcadis, D.; Blackwell, W.; Johnston, D. Decreased total antioxidant capacity but normal lipid hydroperoxide concentrations in sera of critically ill patients. Life Sci. 1997, 60, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissi, E.; Salim-Hanna, M.; Pascual, C.; del Castillo, M.D. Evaluation of total antioxidant potential (TRAP) and total antioxidant reactivity from luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence measurements. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; De Backer, D.; Antonelli, M.; Beale, R.; Bakker, J.; Hofer, C.; Jaeschke, R.; Mebazaa, A.; Pinsky, M.R.; Teboul, J.L.; et al. Consensus on circulatory shock and hemodynamic monitoring. Task force of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1795–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rinaldi, S.; Landucci, F.; De Gaudio, A.R. Antioxidant therapy in critically septic patients. Curr. Drug Targets 2009, 10, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V. Oxidative stress and role of antioxidant supplementation in critical illness. Clin. Lab. 2007, 53, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szakmany, T.; Hauser, B.; Radermacher, P. N-acetylcysteine for sepsis and systemic inflammatory response in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD006616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Smith, R.A.J.; Murphy, M.P. Animal and human studies with the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1201, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R. How to increase cellular glutathione. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Design and Sample | Objetive | Biomarkers | Sample/Method | Measurement Time | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ogilvie et al., 1991 [208] | Prospective observational; adults with septic shock (n = 12) | Assess oxidative stress and antioxidants in septic shock | MDA, fluorescent lipid peroxidation products, α-tocopherol, selenium, GPx, conjugated dienes | Plasma; spectrophotometry/HPLC | UCI admission, first 6 h | ↑ MDA, ↓ antioxidants; oxidative imbalance associated with worse prognosis |
| Goode et al., 1995 [8] | Prospective observational; adults with septic shock (n = 16) | Assess antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in patients with septic shock and their relationship with organ dysfunction. | Retinol, α-tocoferol, β-caroteno, lycopeno, TBARS, nitrites | Plasma; colorimetry/HPLC | ≤24 h frome diagnosis | ↓ Antioxidant vitamins, ↑ TBARS and nitrites; correlation between lipid peroxidation and antioxidant deficiency; association with organ dysfunction |
| Cowley et al., 1996 [9] | Prospective cohort; adults with severe sepsis and organ dysfunction (n = 15) | Determine plasma antioxidant potential and its relationship with prognosis | Plasma antioxidant potential | Plasma; UV spectrophotometry | ≤16 h from onset of organ dysfunction; days 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15 | ↓ Initial antioxidant potential. Normalization or increase to supranormal values in survivors, persistence of low values in non-survivors, correlating with worse prognosis |
| Fläring et al., 2005 [203] | Prospective descriptive study; adults with multiple organ failure and ICU stay ≥ 6 days (n = 11). Reference groups: n = 21 COPD, n = 10 healthy controls | Evaluate temporal changes in total and reduced glutathione | Total and reduced glutathione | Whole blood and plasma; HPLC | Every 72 h for 6–15 days | ↓ Glutathione in whole blood; ↑ plasma glutathione in patients with multiple organ failure compared with reference groups |
| Chuang et al., 2006 [10] | Prospective observational study; severe sepsis (n = 73) and controls (n = 76) | Relate TAC to severity (APACHE II) | TAC; uric acid; bilirubin; albumin | Serum; TRAP | Day 1 of sepsis diagnosis | ↑ TAC in severe sepsis; correlated with APACHE II and mortality |
| Huet et al., 2008 [70] | Prospective study; adults with septic shock (n = 15). Healthy controls (n = 10) | Evaluate endothelial oxidative stress and GSH depletion | GSH, ROS, RNS, catalase and SOD activity, cell death | Plasma and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC); spectrofluorimetry, YOPRO staining, and MTT assay | First 24 h of septic shock | ↓ Intracellular GSH in HUVEC; ↑ ROS and cell death; ROS and cell death reduced with N-acetylcysteine or GSH pretreatment; no changes in RNS |
| Andresen et al., 2008 [204] | Prospective study; adults with septic shock (n = 21) | Evaluate oxidative damage and its relationship with disease severity | BARS, protein carbonyls, methionine sulfoxide, FRAP, TRAP, vitamin C, vitamin E, bilirubin, uric acid, red blood cell glutathione | Plasma and red blood cells; spectrophotometry, HPLC | ICU admission, 24 h, 72 h, day 7, and 3 months | ↑ TBARS and red blood cell glutathione; ↓ vitamin C and reduced glutathione; ↑ bilirubin and uric acid; correlation between ↑ TBARS and sepsis severity |
| Karapetsa et al., 2013 [207] | Prospective pilot study; adults with septic shock (n = 17) | Evaluate variability of oxidative stress during sepsis progression | TBARS, TAC, protein carbonyls, reduced and oxidized glutathione, catalase activity | Erythrocytes/plasma; HPLC/spectrophotometry | Days 1, 3, 5, and 8 after sepsis onset | ↑ TBARS and protein carbonyls, ↓ reduced GSH, ↓ TAC, and ↓ catalase activity in non-survivors |
| Lorente et al., 2015 [211] | Prospective multicenter study; adults with severe sepsis (n = 213) | Relationship between TAC and 30-day mortality in severe sepsis | TAC, MDA | Serum; TRAP and TBARS methods | Day 1 of ICU admission | ↑ TAC and MDA in non-survivors; TAC levels associated with higher 30-day mortality |
| Kim et al., 2016 [174] | Prospective study; adults with septic shock (n = 60) | Evaluate the relationship between plasma GR activity and mortality in septic shock | Glutathione reductase (GR) activity | Plasma and red blood cells; spectrophotometry | 0 h and 24 h post-admission | ↓ GR in non-survivors; 24 h decrease associated with ↑ 28-day mortality; positive correlations between plasma and erythrocyte GR, inverse correlation with GSH/GSSG |
| Lorente et al., 2018 [212] | Prospective multicenter study; adults with severe sepsis (n = 319) | Evaluate the relationship between TAC during the first week of sepsis and 30-day mortality | TAC and MDA | Serum; TRAP and TBARS methods | Days 1, 4, and 8 of ICU admission | TAC during the first week associated with lipid peroxidation, sepsis severity, and 30-day mortality |
| Hsiao et al., 2020 [209] | Prospective study; adults with sepsis (n = 100) | Evaluate the evolution of oxidative stress and antioxidants with clinical outcomes | TBARS; total GSH; GPx activity | Whole blood/erythrocytes; TBARS by spectrophotometry, GSH and GPx by HPLC | Days 1, 4, and 7 | ↑ Oxidative stress and ↓ GPx in non-survivors; TBARS predicts mortality and is associated with hospital length of stay |
| Semedi et al., 2023 [210] | Prospective single-center study; adults with vasodilatory shock (including sepsis) (n = 34) | Evaluate whether GPx activity is associated with shock severity and clinical outcomes | GPx activity | Serum; ELISA | At admission and 24 h | GPx activity does not predict mortality, but is inversely associated with lactate and SOFA score, reflecting vasodilatory shock severity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomar, S.; Bou, R.; Puertas, F.J.; Miranda, M.; Romero, F.J.; Romero, B. Current Insights into Glutathione Depletion in Adult Septic Patients. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091033
Gomar S, Bou R, Puertas FJ, Miranda M, Romero FJ, Romero B. Current Insights into Glutathione Depletion in Adult Septic Patients. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(9):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091033
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomar, Sonia, Ricardo Bou, Francisco Javier Puertas, María Miranda, Francisco Javier Romero, and Belén Romero. 2025. "Current Insights into Glutathione Depletion in Adult Septic Patients" Antioxidants 14, no. 9: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091033
APA StyleGomar, S., Bou, R., Puertas, F. J., Miranda, M., Romero, F. J., & Romero, B. (2025). Current Insights into Glutathione Depletion in Adult Septic Patients. Antioxidants, 14(9), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14091033







