Abelmoschus esculentus Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− Mice via Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AE Preparation
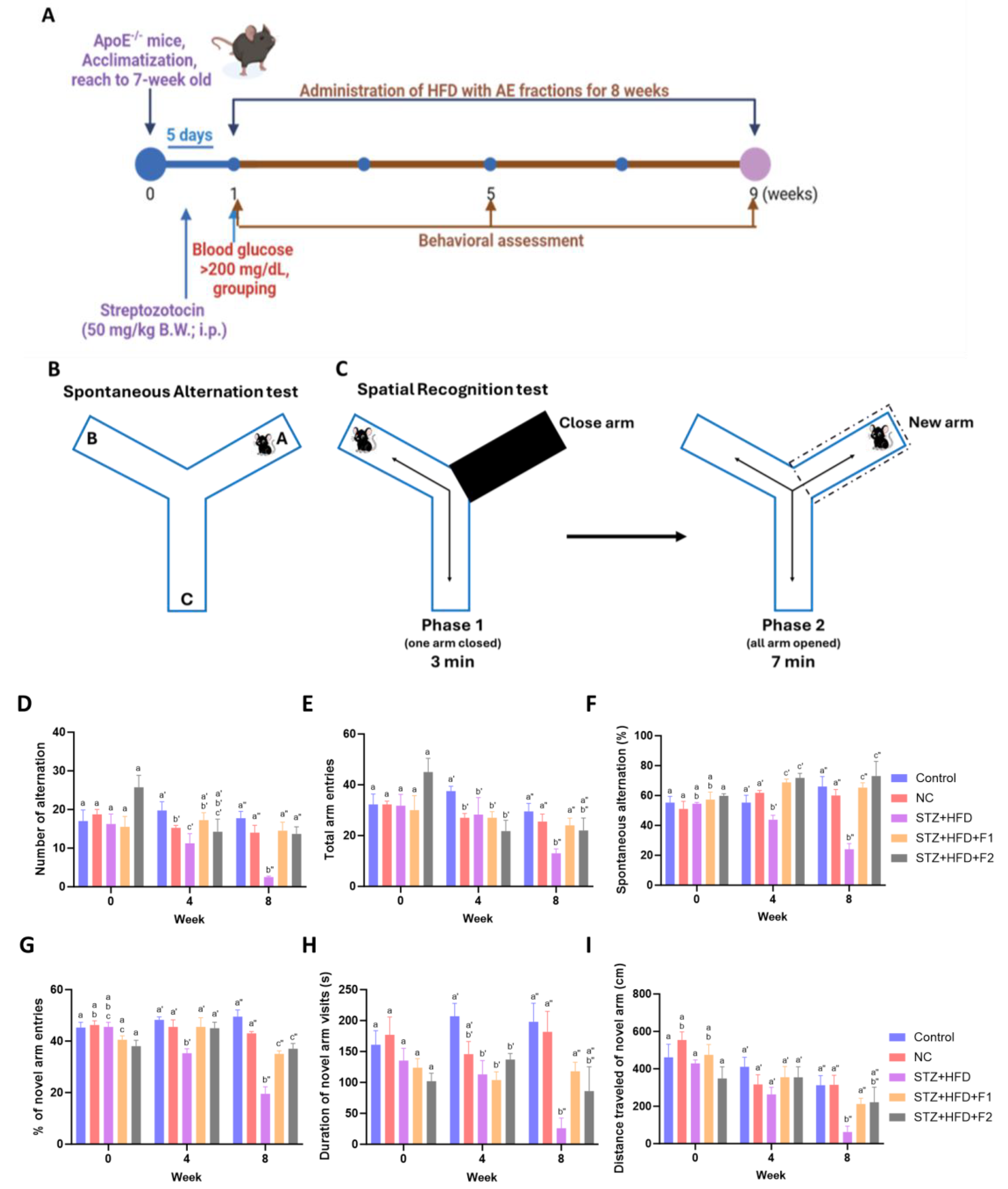
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Behavioral Experiments
2.4. Blood Biochemical Analysis
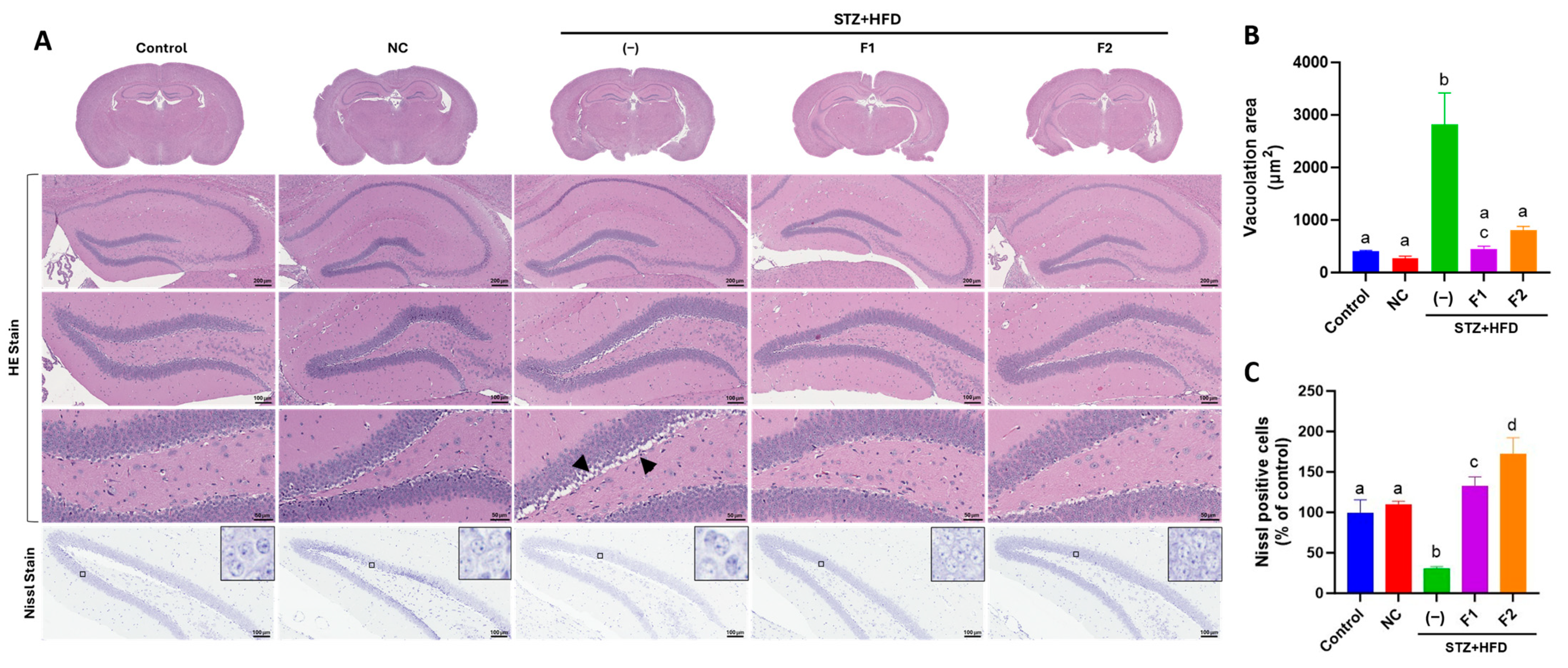
2.5. Histological Examination
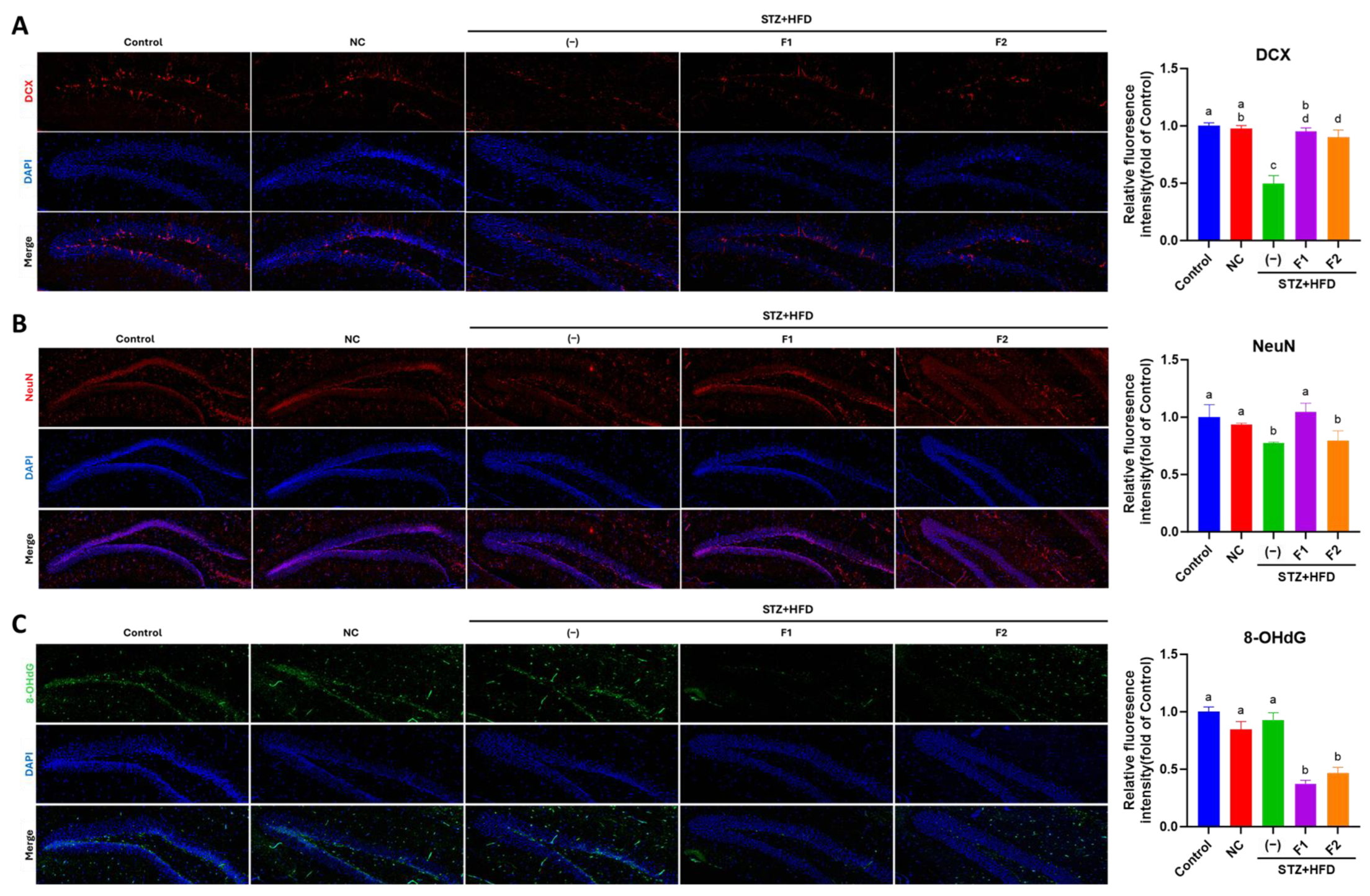
2.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Examination
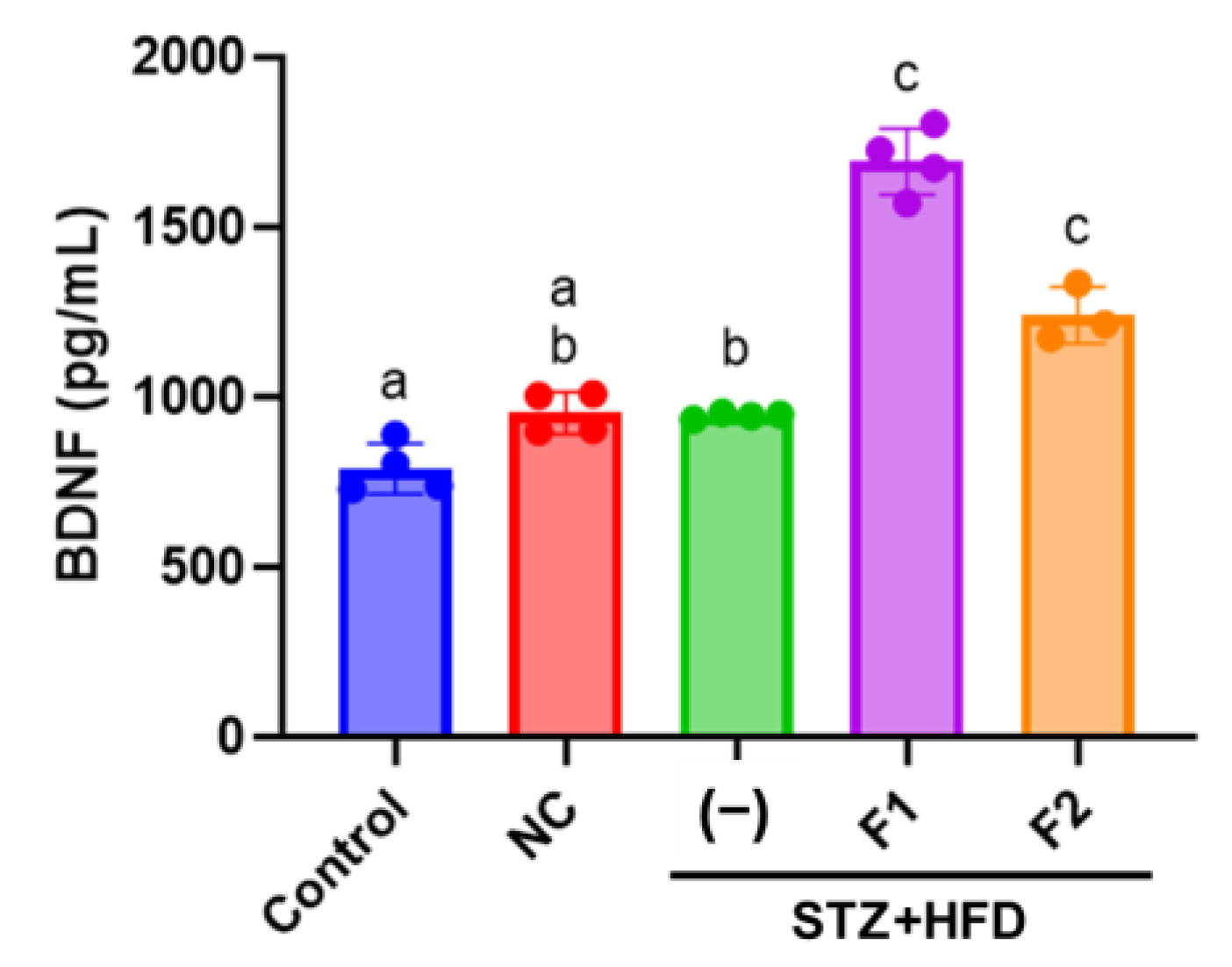
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Immunoblot
2.10. Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of AE Fractions on Blood Profiles
3.2. AE Fractions Enhance Cognitive Function in STZ + HFD-Treated ApoE−/− Mice
3.3. AE Fractions Mitigate Hippocampal Degeneration in STZ + HFD-Treated ApoE−/− Mice
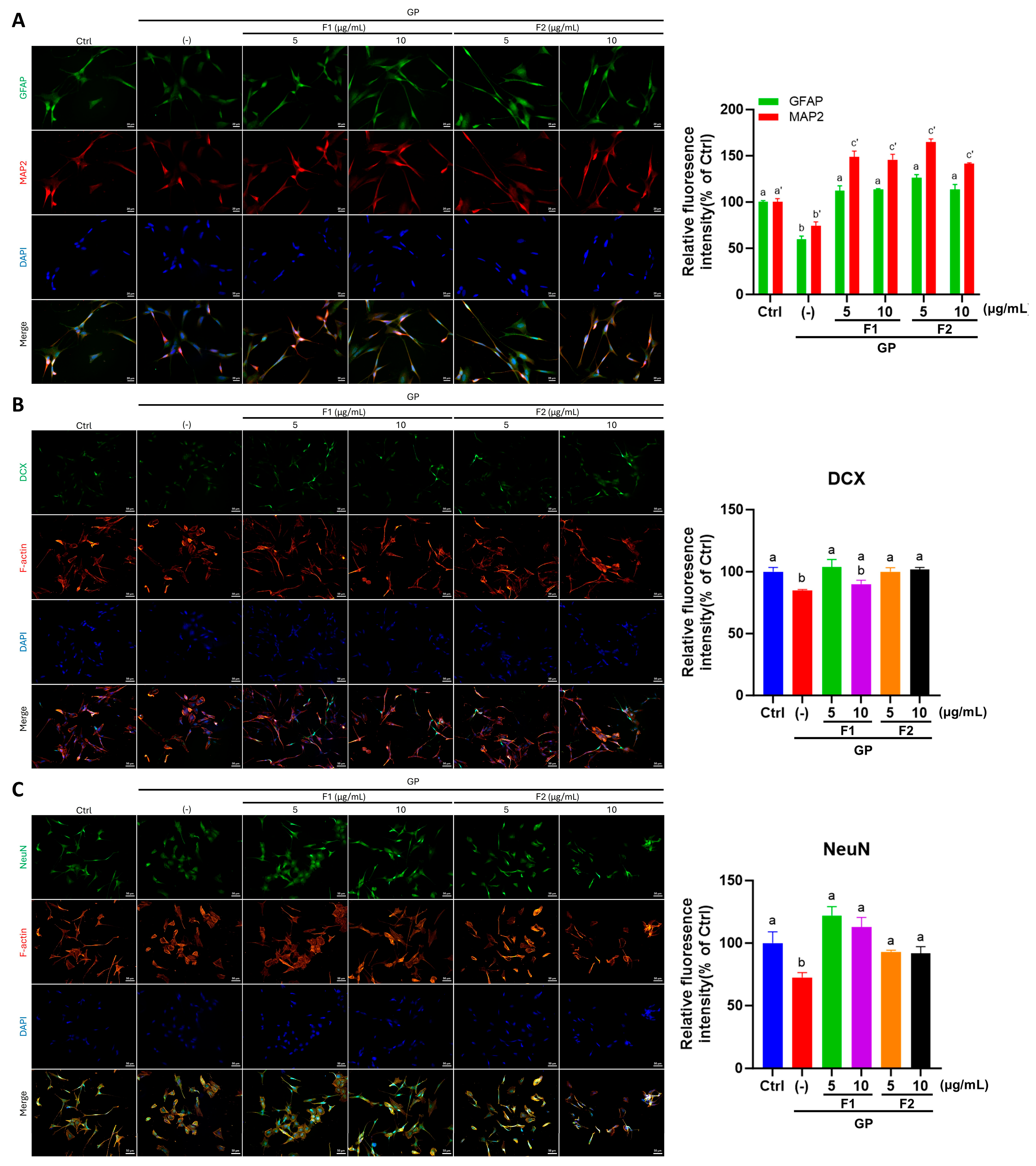
3.4. AE Fractions Promote Hippocampal Differentiation and Reduce Oxidative Stress
3.5. AE Fractions Increase Blood BDNF Levels
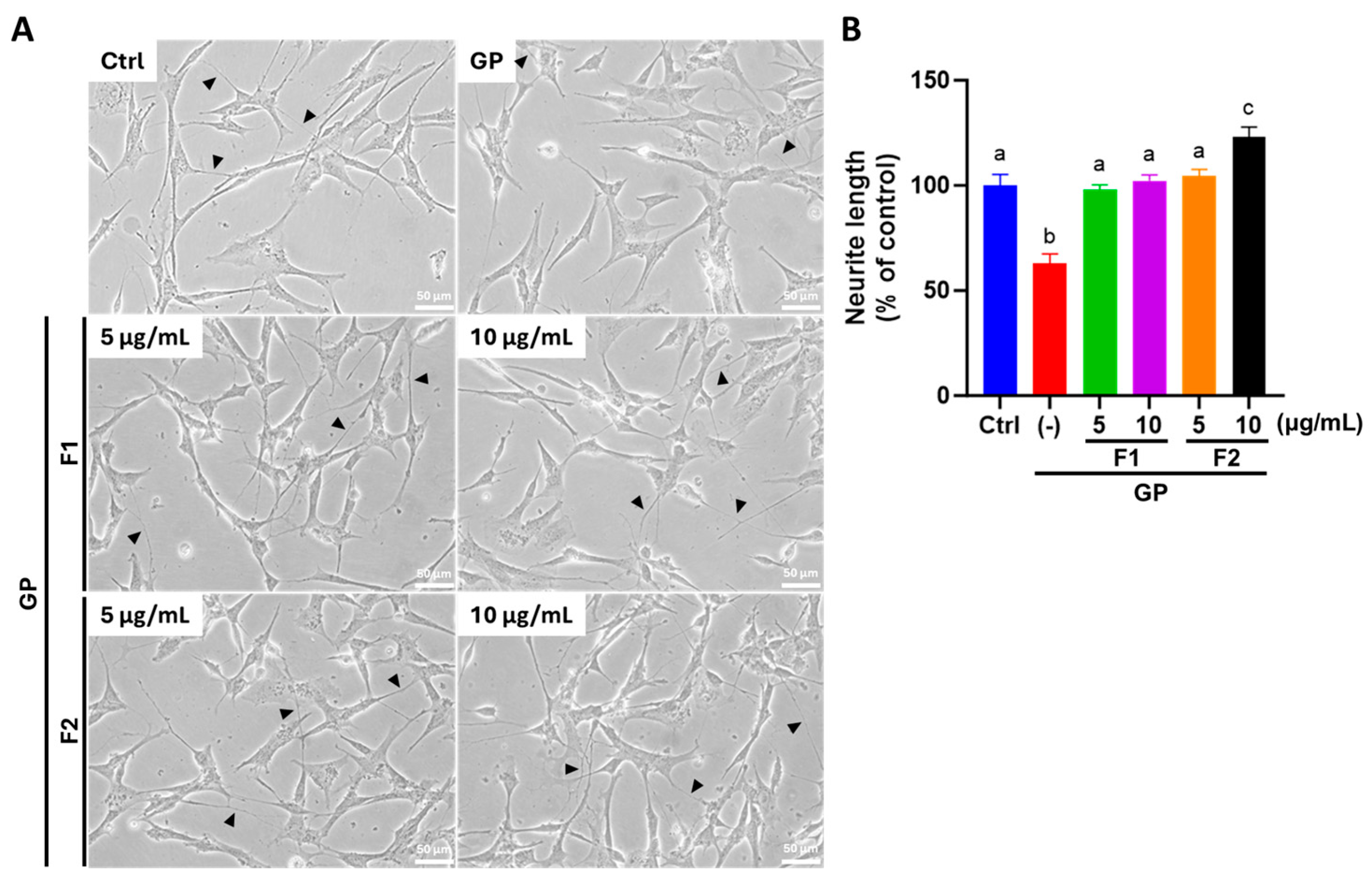
3.6. AE Fractions Promote Neurite Growth and Neuronal Differentiation in Differentiated SH-SY5Y Cells
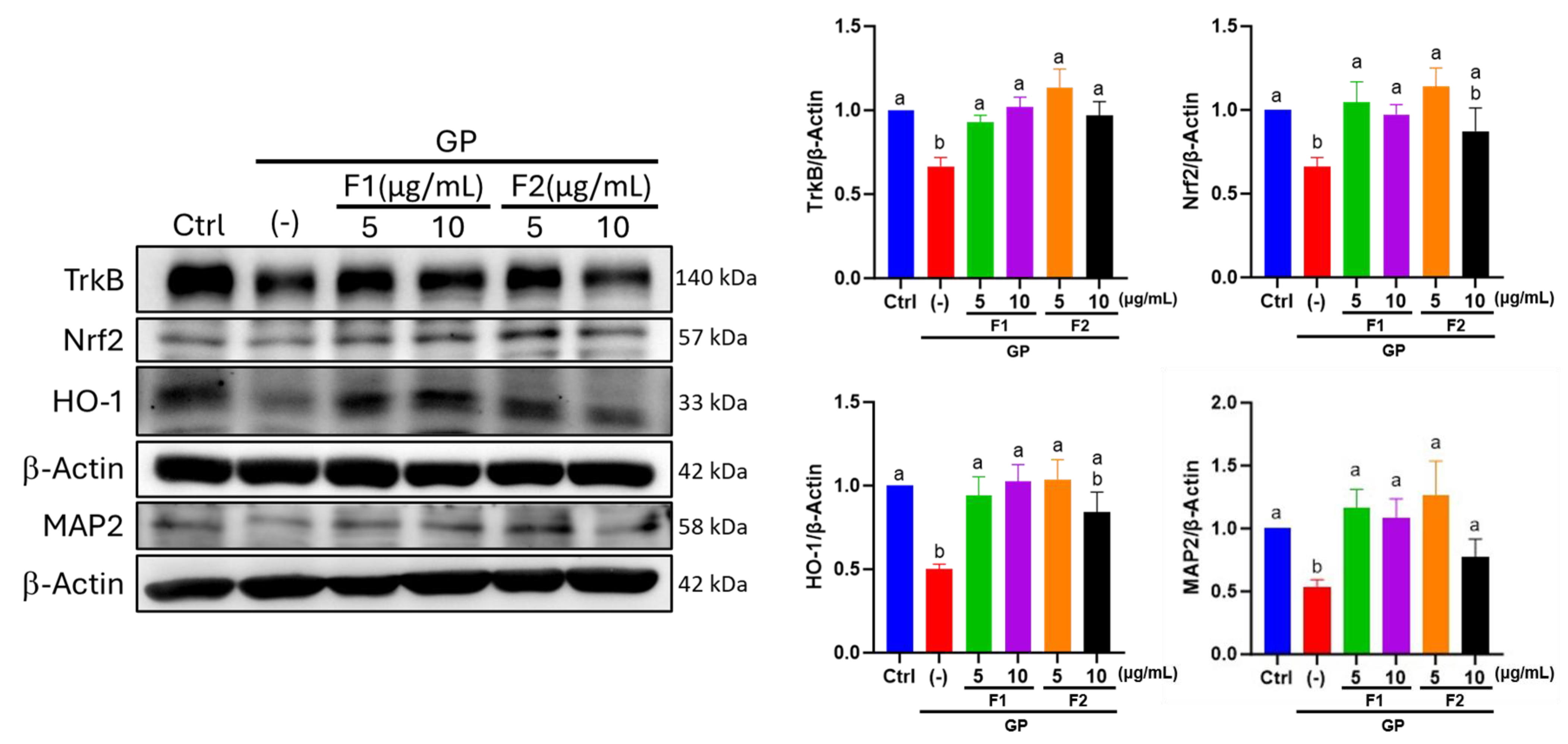
3.7. Effect of AE Fractions on Neuronal Oxidative Stress and BDNF Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, Y.-H.; Foxe, D.; Suh, G.-H.; Wang, H.; Dominguez, J.C.; Maukera, R.; Kounnavong, S.; Piguet, O. Post-diagnosis dementia care in the Western Pacific region: Assessment of needs and pathways to optimal care. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2024, 50, 101182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordestgaard, L.T.; Christoffersen, M.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Shared risk factors between dementia and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Lopez, O.; Cohen, A.; Reis, S.E. Cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease: The heart–brain axis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.B.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Lopez, O.; Jackson, S.; Lyketsos, C.; Jagust, W.; Ives, D.; DeKosky, S.T.; Kuller, L.H. Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease Incidence in Relationship to Cardiovascular Disease in the Cardiovascular Health Study Cohort. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, U.K.; Bennet, A.M.; Gatz, M.; Dickman, P.W.; Pedersen, N.L. Nonstroke cardiovascular disease and risk of Alzheimer disease and dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.Y.; Snyder, P.J.; Wu, W.-C.; Zhang, M.; Echeverria, A.; Alber, J. Pathophysiologic relationship between Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular disease, and cardiovascular risk: A review and synthesis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 7, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Nunez, J.; Toresco, D.L.; Wen, C.; Slotabec, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Rouhi, N.; Adenawoola, M.I.; Li, J. Alterations in the inflammatory homeostasis of aging-related cardiac dysfunction and Alzheimer’s diseases. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhong, Z. The SNPs rs429358 and rs7412 of APOE gene are association with cerebral infarction but not SNPs rs2306283 and rs4149056 of SLCO1B1 gene in southern Chinese Hakka population. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.L.; Talkington, G.M.; Ouvrier, B.; Ismael, S.; Solch-Ottaiano, R.J.; Bix, G. Reactive Oxygen Species, a Potential Therapeutic Target for Vascular Dementia. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez, E.C.; Peotta, V.A.; Gava, A.L.; Pereira, T.M.; Meyrelles, S.S. Cardiac and vascular phenotypes in the apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, S.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Gerard, R.D.; Hammer, R.E.; Herz, J. Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Plump, A.S.; Raines, E.W.; Breslow, J.L.; Ross, R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler. Thromb. A J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, J. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease a role in amyloid catabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliah, E.; Mallory, M.; Ge, N.; Alford, M.; Veinbergs, I.; Roses, A.D. Neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of apoE-deficient mice. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 136, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veinbergs, I.; Mante, M.; Jung, M.W.; Van Uden, E.; Masliah, E. Synaptotagmin and synaptic transmission alterations in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 23, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Progression of atherosclerosis in ApoE-knockout mice fed on a high-fat diet. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3863–3867. [Google Scholar]
- Takubo, M.; Watanabe, K.; Saito, H.; Kohno, G.; Ishihara, H. Therapy Combining Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist with Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Suppresses Atherosclerosis in Diabetic ApoE-Deficient Mice. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2024, 132, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, W.; Ouyang, X.; Lei, X.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Deng, W.; Liang, Z. The SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin has a therapeutic effect on atherosclerosis in diabetic ApoE−/− mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6305735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, D.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) on metabolic syndrome: A review. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-N.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Lin, H.-T.; Peng, C.-H. The nutraceutical benefits of subfractions of Abelmoschus esculentus in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, J. Potential role of quercetin glycosides as anti-atherosclerotic food-derived factors for human health. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Tanaka, A.; Nishihira, J.; Murayama, N. Effect of quercetin glycosides on cognitive functions and cerebral blood flow: A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 8700–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hamoud, G.A.; Al-Musayeib, N.M.; Amina, M.; Ibrahim, S.R. Abubidentin A, New Oleanane-type Triterpene Ester from Abutilon bidentatum and Its Antioxidant, Cholinesterase and Antimicrobial Activities. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R. Purification and antioxidant properties of triterpenic acids from blackened jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) by macroporous resins. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5070–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Szakiel, A.; Głowacka, A.; Rozpara, E.; Marszałek, K.; Skąpska, S. Triterpenoids of Three Apple Cultivars—Biosynthesis, Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties, and Fate during Processing. Molecules 2023, 28, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Huang, C.-N.; Lee, H.-J. Abelmoschus esculentus Improves Hippocampal Function Associated with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 in High Fat Diet-Fed db/db Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2024, 2024, 5554538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Nian, T.; Liao, Z.; Xiao, F.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; He, B.; Jia, Y. Antidepressant effects of a polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L) Moench) by anti-inflammation and rebalancing the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-N.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Yen, A.-T.; Li, H.-H.; Peng, C.-H. Abelmoschus esculentus subfractions attenuate beta amyloid-induced neuron apoptosis by regulating DPP-4 with improving insulin resistance signals. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-N.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Li, H.-H.; Yen, A.-T.; Peng, C.-H. Abelmoschus esculentus subfractions attenuate Aβ and tau by regulating DPP-4 and insulin resistance signals. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-N.; Lin, C.-L.; Li, H.-H.; Tsou, S.-H.; Peng, C.-H. Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) prevents insulin resistance and restores neuron autophagy by regulating dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and thus improving hippocampal function. J. Med. Food 2023, 26, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zuo, X.; Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Tai, H.; Du, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y. Combined use of bFGF/EGF and all-trans-retinoic acid cooperatively promotes neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth in neural stem cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 690, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Sun, X.; Zhou, C.; Yan, J.; Cheng, C. Neuroblasts migration under control of reactive astrocyte-derived BDNF: A promising therapy in late neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Chyau, C.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Lin, H.-T.; Huang, C.-N.; Ker, Y.-B. Abelmoschus esculentus fractions potently inhibited the pathogenic targets associated with diabetic renal epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S.J.; Kim, J.; Goo, N.; Jeong, Y.; Cho, K.; Cai, M.; Jung, S.Y.; Kwon, K.J. Green tea extract containing enhanced levels of epimerized catechins attenuates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lin, C.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, M.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Hsu, L.S. Nelumbo nucifera leaves extract ameliorated scopolamine-induced cognition impairment via enhanced adult hippocampus neurogenesis. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.W.; Shih, H.-C.; Shyu, B.C. The P2X7 Hypothesis of Central Post-Stroke Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famurewa, A.C.; Nwankwo, O.E.; Folawiyo, A.M.; Igwe, E.C.; Epete, M.A.; Ufebe, O.G. Repeatedly heated palm kernel oil induces hyperlipidemia, atherogenic indices and hepatorenal toxicity in rats: Beneficial role of virgin coconut oil supplementation. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2017, 16, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, D.S.E.; Fouad, M.A.; Elmeshad, A.N.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Elhabal, S.F. Anti-Obesity Effect of Combining White Kidney Bean Extract, Propolis Ethanolic Extract and CrPi3 on Sprague-Dawley Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongjaroenbuangam, W.; Ruksee, N.; Chantiratikul, P.; Pakdeenarong, N.; Kongbuntad, W.; Govitrapong, P. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin, rutin and okra (Abelmoschus esculentus Linn.) in dexamethasone-treated mice. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, H.T.; Mokhtar, F.A.; Elmaidomy, A.H.; Aly, H.F.; Younis, E.A.; Alzubaidi, M.A.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.A.; Majrashi, M.A.A.; Alsenani, F.; et al. Abelmoschus eculentus Seed Extract Exhibits In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Alzheimer’s Potential Supported by Metabolomic and Computational Investigation. Plants 2023, 12, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mairuae, N.; Connor, J.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Cheepsunthorn, P.; Tongjaroenbuangam, W. The effects of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus Linn.) on the cellular events associated with Alzheimer’s disease in a stably expressed HFE neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 603, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalabone, T.T.; Dlamini, S.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Modjadji, P.; Lebelo, S.L. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L.(okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruwita Arachchige, S.; Uluwaduge, D.I.; Premakumara, S.; Wijayabandara, J. Cardio protective activity of Abelmoschus esculentus (Okra). Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr 2018, 3, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhu, R.K.; Puri, V. Phytochemical, nutritional and pharmacological evidences for Abelmoschus esculentus (L.). J. Phytopharm. 2016, 5, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Xie, W.; Zheng, F. Association between age at diagnosis of hyperlipidemia and subsequent risk of dementia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2024, 25, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Torres, L.D.; Rezende, F.; Peschke, E.; Will, O.; Hövener, J.-B.; Spiecker, F.; Özorhan, Ü.; Lampe, J.; Stölting, I.; Aherrahrou, Z. Incidence of microvascular dysfunction is increased in hyperlipidemic mice, reducing cerebral blood flow and impairing remote memory. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1338458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Mardani, H.; Nezhad, B.P.; Alaghi, A.; Sahebkar, A. Beneficial Effects of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) Consumption on Anthropometric Measures, Blood Pressure, Glycemic Control, Lipid Profile, and Liver Function Tests in Randomized Controlled Trials: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2025, 133, 637–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, H.; Shahraki Jazinaki, M.; Rahnama, I.; Aghakhani, L.; Amini, M.R.; Malekahmadi, M. The cardiometabolic benefits of okra-based treatment in prediabetes and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1454286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Holt, K.; Lebrun, S.; Stinn, W.; Conroy, L.; Wallerath, T.; Schleef, R. Progression of atherosclerosis in the Apo E−/− model: 12-month exposure to cigarette mainstream smoke combined with high-cholesterol/fat diet. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Breslow, J. The emergence of mouse models of atherosclerosis and their relevance to clinical research. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, A.; Rateri, D.L. Development of experimental designs for atherosclerosis studies in mice. Methods 2005, 36, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.X. Rethinking oxidized low-density lipoprotein, its role in atherogenesis and the immune responses associated with it. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2004, 52, 225–239. [Google Scholar]
- Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalaboni, K. Comprehensive overview of the effects of Amaranthus and Abelmoschus esculentus on markers of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Life 2023, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Liao, Z.; Wu, B.; He, B.; Jia, Y. The flavonoids of okra insulates against oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and restores BDNF levels in Aβ1–42 induced mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 147, 111263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iu, E.C.Y.; Chan, C.B. Is brain-derived neurotrophic factor a metabolic hormone in peripheral tissues? Biology 2022, 11, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.-M.; Sulaiman, G.-M.; Mohammed, H.-A.; Albukhaty, S.; Albuhadily, A.-K.; Al-Gareeb, A.-I.; Klionsky, D.-J.; Abomughaid, M.-M. The compelling role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in multiple sclerosis: Role of BDNF activators. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e70167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Wang, C.-J.; Huang, C.-N. Abelmoschus esculentus subfractions improved nephropathy with regulating dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and type 1 glucagon-like peptide receptor in type 2 diabetic rats. Front. Nutr. 2019, 27, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Stewart, D.; Touchard, C.; Boinapally, S.; Choi, A.M.; Cook, J.L. Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26071–26078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, W.M. Quercetin Alleviates Red Bull Energy Drink-Induced Cerebral Cortex Neurotoxicity via Modulation of Nrf2 and HO-1. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9482529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczyova, K.; Kalocayova, B.; Bartekova, M. Potential implications of quercetin and its derivatives in cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlowska, A.; Szostak-Wegierek, D. Flavonoids–Food Sources, Health Benefits, and Mechanisms Involved. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillonn, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.A.; Perez-Jimenez, J.; Neveu, V.; Medina-Remon, A.; M’hiri, N.; García-Lobato, P.; Manach, C.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. Phenol-Explorer 3.0: A major update of the Phenol-Explorer database to incorporate data on the effects of food processing on polyphenol content. Database 2013, 2013, bat070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambali, A.; Jusril, N.A.; Md Hashim, N.F.; Abd Manan, N.; Adam, S.K.; Mehat, M.Z.; Adenan, M.I.; Stanslas, J.; Abdul Hamid, H. The standardized extract of Centella asiatica and its fractions exert antioxidative and anti-neuroinflammatory effects on microglial cells and regulate the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 99, S119–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, D.; Yang, X. Effect of okra fruit powder supplementation on metabolic syndrome and gut microbiota diversity in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control | NC | STZ + HFD | STZ + HFD + F1 | STZ + HFD + F2 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 26.45 ± 0.25 a | 28.53 ± 1.08 a | 23.53 ± 1.09 b | 24.13 ± 0.38 b | 25.83 ± 1.58 a |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.03 ± 0.10 a | 3.93 ± 0.10 a | 7.00 ± 0.36 b | 4.95 ± 0.88 a | 5.00 ± 0.35 a |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 287.75 ± 58.39 a | 202.50 ± 24.14 ab | 454.50 ± 54.88 ac | 220.75 ± 40.14 ab | 193.67 ± 62.22 ab |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 105.75 ± 4.03 a | 807.25 ± 77.68 b | 1545.50 ± 87.58 c | 1415.00 ± 51.68 c | 1398.67 ± 45.83 d |
| TG (mg/dL) | 65.75 ± 6.95 a | 92.25 ± 7.76 a | 163.25 ± 25.10 b | 88.00 ± 18.24 a | 85.67 ± 11.06 a |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 59.75 ± 6.13 a | 100.50 ± 12.66 b | 135.25 ± 30.61 c | 100.75 ± 15.31 b | 109.33 ± 13.61 bc |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 10.00 ± 1.63 a | 109.75 ± 10.53 b | 244.75 ± 35.49 c | 132.75 ± 24.58 b | 146.00 ± 29.72 b |
| LDL/HDL Ratio | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 1.10 ± 0.15 b | 1.89 ± 0.56 c | 1.32 ± 0.20 bc | 1.33 ± 0.14 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.-H.; Liang, H.-W.; Wang, C.-J.; Huang, C.-N.; Lee, H.-J. Abelmoschus esculentus Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− Mice via Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Differentiation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080955
Peng C-H, Liang H-W, Wang C-J, Huang C-N, Lee H-J. Abelmoschus esculentus Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− Mice via Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Differentiation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(8):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080955
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chiung-Huei, Hsin-Wen Liang, Chau-Jong Wang, Chien-Ning Huang, and Huei-Jane Lee. 2025. "Abelmoschus esculentus Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− Mice via Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Differentiation" Antioxidants 14, no. 8: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080955
APA StylePeng, C.-H., Liang, H.-W., Wang, C.-J., Huang, C.-N., & Lee, H.-J. (2025). Abelmoschus esculentus Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− Mice via Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Differentiation. Antioxidants, 14(8), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080955








