Preventive Gastroprotective Effect of a Functional Food Based on Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Ibuprofen-Induced Gastric Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation and Preparation of Quinoa Cookies
2.2. Determination of Total Phenolics, Flavonoids, and Antioxidant Capacity
2.3. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.4. Gastroprotective Activity
2.4.1. Animals and Experimental Diets
2.4.2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)-Induced Gastric Damage
2.5. Macroscopic and Microscopic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Gastrointestinal and Bioaccessibility of Total Phenolic Content (TPC), Total Flavonoid Content (TFC), and Antioxidant Capacity
3.2. Toxicity of Experimental Diets
3.3. Assessment of Gastric Damage After Treatment with the MQC and Q
3.4. Effect of Different Dietary Treatments on Histological Features
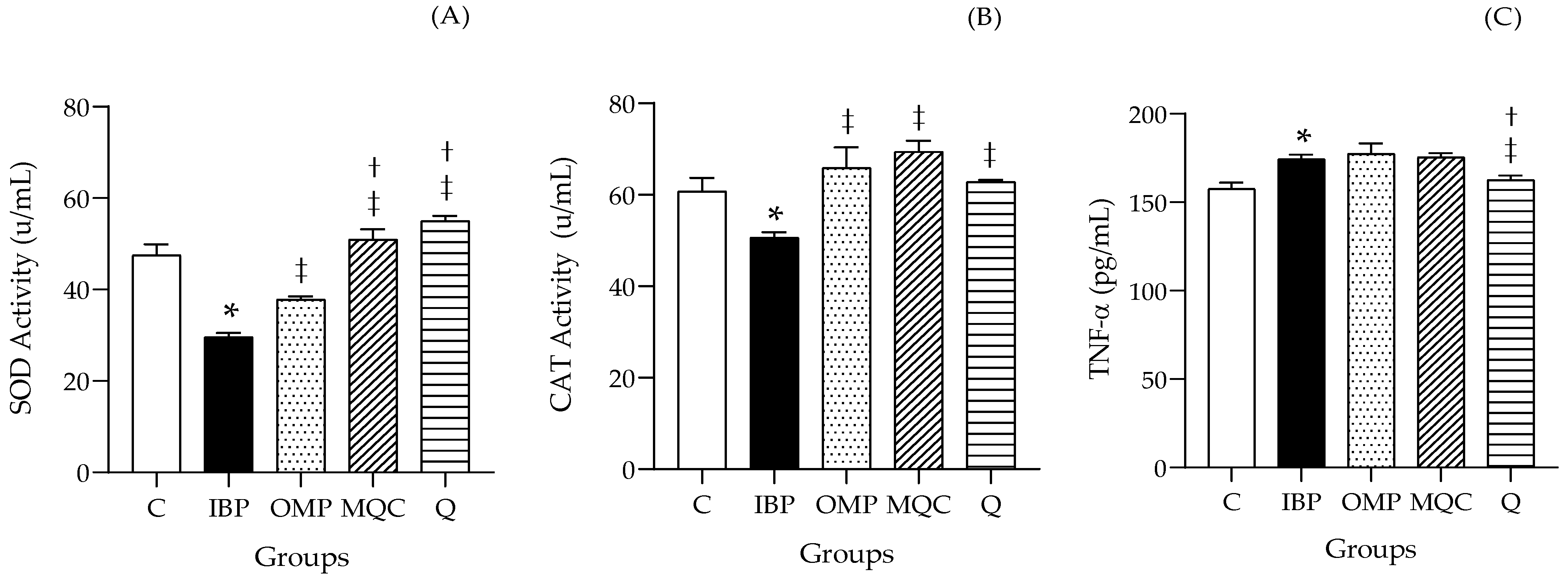
3.5. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Inflammatory Cytokine TNF-α
3.6. Effect of Experimental Diets on Antioxidant Activity in Blood Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| •OH | hydroxyl radical |
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxynonenal |
| BD | basal diet |
| C | control |
| CAT | catalase |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| GDI | gastric damage index |
| GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IBP | ibuprofen |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| MQC | microwave quinoa cookie |
| NSAIDs | nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| O2.- | superoxide radical |
| OMP | omeprazole |
| ORAC | oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
| PGE | prostaglandin |
| Q | quercetin |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SE | standard error |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Kolgazi, M.; Cilingir, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Gemici, M.; Yazar, H.; Ozer, S.; Elmas, M.; Arbak, S.; Suyen, G.G. Caffeic acid attenuates gastric mucosal damage induced by ethanol in rats via nitric oxide modulation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2021, 334, 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, D. The protective effect of quinoa on the gastric mucosal injury induced by absolute ethanol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado Montero, R.; Flores Cortez, D.; Villalobos Pacheco, E. Efecto del Capsicum annum L (pucunucho, ají mono) en úlcera gástrica experimental inducida en ratas. Rev. Gastroenterol. Perú 2015, 35, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oscanoa-Espinoza, T.; Lizaraso-Soto, F. Antiinflamatorios no esteroides: Seguridad gastrointestinal, cardiovascular y renal. Rev. Gastroenterol. Perú 2015, 35, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecien, S.; Jasnos, K.; Magierowski, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pajdo, R.; Brzozowski, B.; Mach, D.; Brzozowski, T. Lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species and antioxidative factors in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions and mechanism of protection against oxidative stress-induced gastric injury. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 65, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Travieso, J.C.F. Incidencia actual de la gastritis: Una breve revisión. Rev. CENIC. Cienc. Biológicas 2014, 45, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Evora Fumero, A.J. Revisión bibliográfica de los efectos secundarios del omeprazol. Rev. CENIC. CIenc. Biológicas 2017, 45, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz Casasola, L. Mucosa Gástrica: Mecanismos Protectores y Efectos Dañinos del Ácido Acetilsalicílico; Enfoques fisiológico y bioquímico; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sumbul, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Mohd, A.; Mohd, A. Role of phenolic compounds in peptic ulcer: An overview. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariod, A.A.; Salama, S.M. The Efficacy of Processing Strategies on the Gastroprotective Potentiality of Chenopodium quinoa Seeds. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 6326452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raish, M.; Shahid, M.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Ansari, M.A.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Ahad, A.; Abdelrahman, I.A.; Ahmad, A.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I. Gastroprotective effect of sinapic acid on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats: Involvement of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling and antiapoptotic role. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 622815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianavell, M.R.; Yuday, M.R.; Rodovaldo, G.S.; Rayza, H.D.; Margot, L.A. Efecto gastroprotector del extracto acuoso de caléndula y llantén en ratas con úlcera inducida. In CIBAMANZ-2023. 2023. Available online: https://cibamanz.sld.cu/index.php/cibamanz/2023/paper/view/454/229 (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Alves, N.M.; Nunes, P.H.M.; Mendes Garcez, A.; Lima de Freitas, M.C.; Oliveira, I.S.; Silva, F.V.D.; Fernandes, H.B.; de Sousa, D.P.; Oliveira, R.C.M.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; et al. Antioxidant mechanisms underlying the gastroprotective effect of menthofuran on experimentally induced gastric lesions in rodents. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2023, 2023, 9192494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Ferraretto, A.; De Noni, I.; Bottani, M.; Cattaneo, S.; Galli, S.; Brandolini, A. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties of pseudocereals-enriched water biscuits and their in vitro digestates. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, N.; Walia, S.; Kumar, R. Functional composition, physiological effect and agronomy of future food quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 118, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, A.C.; Sanlier, N. A new generation plant for the conventional cuisine: Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Hellström, J.K.; Pihlava, J.M.; Mattila, P.H. Flavonoids and other phenolic compounds in Andean indigenous grains: Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa), kañiwa (Chenopodium pallidicaule) and kiwicha (Amaranthus caudatus). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Lucas-Gonzales, R.; Ricci, A.; Fontecha, J.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chemical, fatty acid, polyphenolic profile, techno-functional and antioxidant properties of flours obtained from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eity, T.A.; Bhuia, M.S.; Chowdhury, R.; Ahmmed, S.; Sheikh, S.; Akter, R.; Islam, M.T. Therapeutic Efficacy of Quercetin and Its Nanoformulation Both the Mono-or Combination Therapies in the Management of Cancer: An Update with Molecular Mechanisms. J. Trop. Med. 2024, 2024, 5594462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lhamo, G.; Ma, M.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, L. Quercetin as a therapeutic agent for acute pancreatitis: A comprehensive review of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1587314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, S.A.; Barbosa, I.S.; de Almeida, C.L.; de Medeiros, J.W.; Silva Neto, J.C.; Rolim, L.A.; da Silvaa, T.G.; Ximenes, R.M.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Caldas, G.F.R.; et al. Evaluation of gastroprotective and ulcer healing activities of yellow mombin juice from Spondias mombin L. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201561. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201561. [Google Scholar]
- Brend, Y.; Galili, L.; Badani, H.; Hovav, R.; Galili, S. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of red and yellow quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds as affected by baking and cooking conditions. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, I.; Tenore, G.C.; Dini, A. Antioxidant compound contents and antioxidant activity before and after cooking in sweet and bitter Chenopodium quinoa seeds. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.; Spanier, L.P.; Botelho, F.T.; Gularte, M.A.; Helbig, E. Effect of different types of processing on the total phenolic compound content, antioxidant capacity, and saponin content of Chenopodium quinoa Willd grains. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-González, M.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Ledesma-Osuna, A.I.; Astiazarán-García, H.; Salazar-López, N.J.; Vidal-Quintanar, R.L.; Robles-Sánchez, M. Bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, and consumer acceptability of heat-treated quinoa cookies. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e43421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Nutritive value of pseudocereals and their increasing use as functional gluten-free ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, A.; Salas-González, M.; Lorenzo-Mora, A.M.; Bermejo, L.M. Beneficios nutricionales y sanitarios de los cereales de grano completo. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Peñas, E.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Pseudocereal grains: Nutritional value, health benefits and current applications for the development of gluten-free foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chu, G.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y. Benefits of Monascus anka solid-state fermentation for quinoa polyphenol bioaccessibility and the anti-obesity effect linked with gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tsao, R. Phytochemicals in quinoa and amaranth grains and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential health beneficial effects: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lietz, G.; Seal, C.J. Effects of quinoa intake on markers of cardiovascular risk: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshahidi, L.K.; Caballero, E.; Osses, A.; Hyland, B.W.; Ternan, N.G.; Gill, C.I. Modest improvement in CVD risk markers in older adults following quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) consumption: A randomized-controlled crossover study with a novel food product. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Perez, D.; Radcliffe, J.; Tierney, A.; Jois, M. Quinoa seed lowers serum triglycerides in overweight and obese subjects: A dose-response randomized controlled clinical trial. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 1, e001321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela González, M.; Cárdenas López, J.L.; Burgos Hernández, A.; Salazar López, N.J.; Viuda Martos, M.; Ruiz Hernández, A.A.; Robles Sánchez, R.M. Quinoa treated by an optimized method of microwave heating and their effect on antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. CyTA-J. Food 2023, 21, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Cereal Chemists—AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar Lopez, N.J.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Campos-Vega, R.; Gaytán Martínez, M.; Morales Sánchez, E.; Esquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A.; Robles Sánchez, M. The extrusion process as an alternative for improving the biological potential of sorghum bran: Phenolic compounds and antiradical and anti-inflammatory capacity. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 8387975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Hernández, A.A.; Rouzaud Sández, O.; Frías, J.; Ayala Zavala, F.; Astiazarán García, H.; Robles Sánchez, M. Optimization of the duration and intensity of UV-A radiation to obtain the highest free phenol content and antioxidant activity in sprouted sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-López, N.J.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Robles-Sánchez, M. Bioaccessibility of hydroxycinnamic acids and antioxidant capacity from sorghum bran thermally processed during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotocina, S.G.; Sorge, R.E.; Zaloum, A.; Tuttle, A.H.; Martin, L.J.; Wieskopf, J.S.; Mapplebeck, J.C.S.; Wei, P.; Zhan, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Rat Grimace Scale: A partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions. Mol. Pain 2011, 7, 1744–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: Final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Ippoushi, K.; Terao, J. Evaluation of tolerable levels of dietary quercetin for exerting its antioxidative effect in high cholesterol-fed rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramini-Costa, D.B.; Monteiro, K.M.; Iwamoto, L.H.; Jorge, M.P.; Tinti, S.V.; Pilli, R.A.; de Carvalho, J.E. Gastroprotective effects of goniothalamin against ethanol and indomethacin-induced gastric lesions in rats: Role of prostaglandins, nitric oxide and sulfhydryl compounds. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, B.; Lv, L.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Gastroprotective effect of aucubin against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Life Sci. 2017, 189, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancino-Espinoza, E.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Quispe, I. Organic quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa L.) production in Peru: Environmental hotspots and food security considerations using Life Cycle Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kataria, A.; Singh, B. Effect of thermal processing on the bioactive compounds, antioxidative, antinutritional and functional characteristics of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). LWT 2022, 160, 113256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Cao, H.; Guan, X. Microwaving released more polyphenols from black quinoa grains with hypoglycemic effects compared with traditional cooking methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5948–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Feng, J.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Hu, F.; Prasad, C.; Wei, Z.J. Morin como ingrediente alimentario funcional inminente: Actualización sobre su eficacia mejorada en el tratamiento y la prevención de síndromes metabólicos. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8424–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Hurtado, P.A.; Garduño-Siciliano, L.; Dominguez-Verano, P.; Martinez-Galero, E.; Canales-Martinez, M.M.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A. Evaluation of the gastroprotective effects of Chihuahua propolis on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in mouse. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M. Toxicidad de los antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE) ácido acetilsalicílico, paracetamol, diclofenaco, ibuprofeno y naproxeno en invertebrados de agua dulce: Una revisión. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrassi, G.; Pergolizzi, J.V.; Dowling, P.; Paladini, A. Ibuprofen safety at the golden anniversary: Are all NSAIDs the same? A narrative review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Rafi, S.; Hayllar, J.; Sigthorsson, G.; Jacob, M.; Price, A.B.; Macpherson, A.; Mahmod, T.; Scott, D.; Wrigglesworth, J.M.; et al. Mitochondrial damage: A possible mechanism of the “topical” phase of NSAID induced injury to the rat intestine. Gut 1997, 41, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso-Roca, E.C.; Arroyo-Acevedo, J.L.; Común-Ventura, P.W.; Tinco-Jayo, J.A.; Aguilar-Felices, E.J.; Ramos-Meneses, M.B.; Carrera-Palao, R.E.; Herrera-Calderon, O. The Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant and Gastroprotective Effects of Three Varieties of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Sprouts Cultivated in Peru. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, A.; Challa, R.R.; Vallamkonda, B.; Viswanadh, M.K.; Muthu, M.S. Implicaciones clínicas de los inhibidores de la bomba de protones y los sistemas de micro/nanoadministración de fármacos de vonoprazán para los trastornos relacionados con la acidez gástrica y la imagenología. Nanotheranostics 2024, 8, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldum, H.L.; Hauso, Ø.; Fossmark, R. The regulation of gastric acid secretion–clinical perspectives. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumba, C.; Pritchard, D.M.; Pirmohamed, M. cellular and molecular mechanisms of NSAID-induced peptic ulcers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashmawy, N.E.; Khedr, E.G.; El-Bahrawy, H.A.; Selim, H.M. Gastroprotective effect of garlic in indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats. Nutrition 2016, 32, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyagi, A.; Ogawa, K.; Kakino, M.; Hara, H. Protective effects of a gastrointestinal agent containing Korean red ginseng on gastric ulcer models in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katary, M.A.; Salahuddin, A. Gastroprotective effect of vanillin on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats: Protective pathways and anti-Secretory mechanism. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 7, 1000232. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Raheem, I.T. Gastroprotective effect of rutin against indomethacin-induced ulcers in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 107, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, K.; Mota, D.L.; Eduardo, G.; Dias, N.; Emili, M.; Pinto, F.; Luiz-ferreira, Â.; Souza-brito, A.R.M.; Akiko, C.; Lima, H.; et al. Flavonoids with Gastroprotective Activity. Molecules 2009, 14, 979–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgerini, M.; Mieli, S.; Mastroianni, P.D.C. Safety assessment of omeprazole use: A review. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2018, 136, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

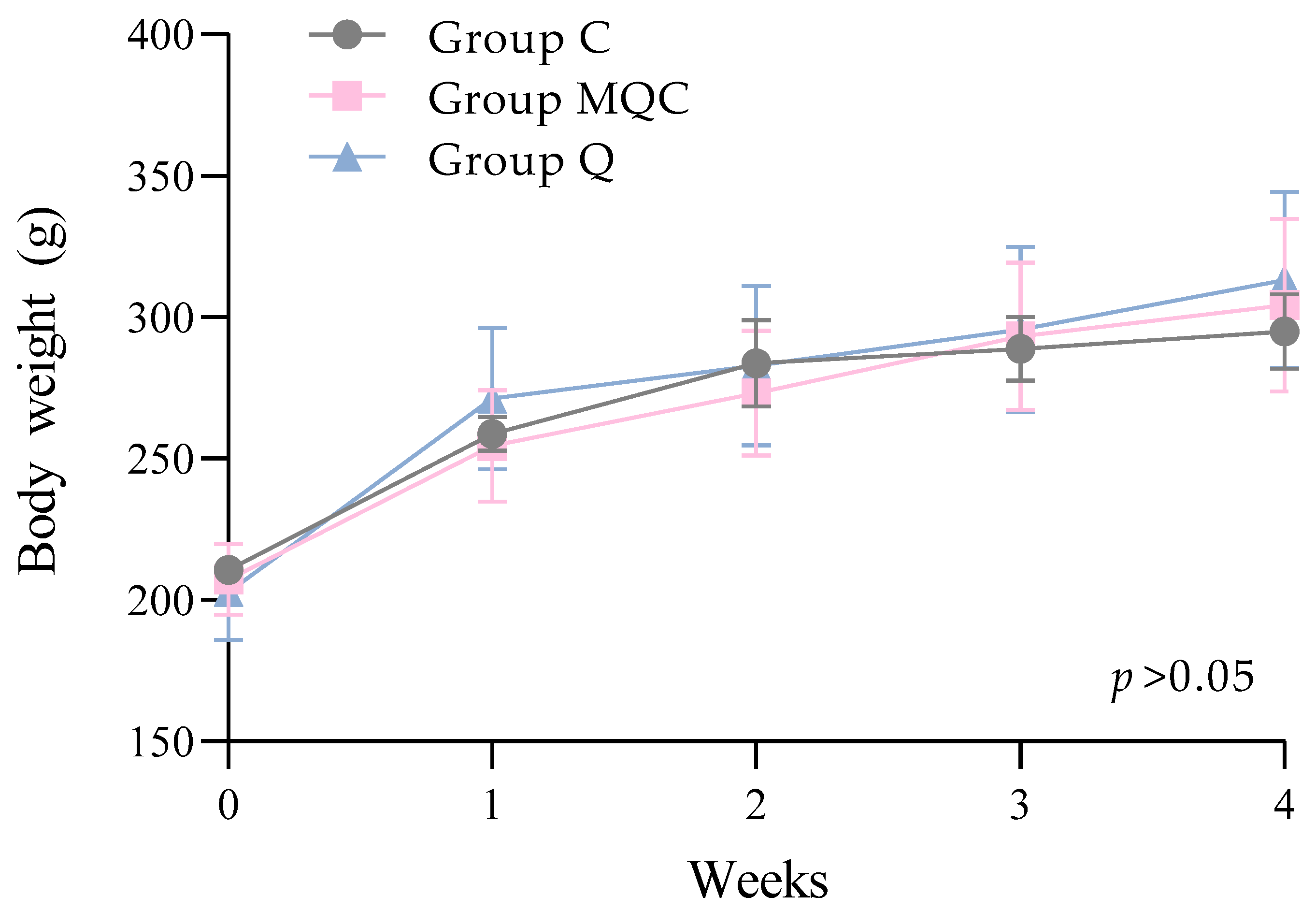


| Ingredients | Group 1 C | Group 2 IBP 1 | Group 3 OMP 2 | Group 4 MQC | Group 5 Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg/d | |||||
| Casein | 17.90 | 17.90 | 17.90 | 17.90 | 17.90 |
| Starch | 36.28 | 36.28 | 36.28 | 21.53 | 36.13 |
| Sucrose | 7.14 | 7.14 | 7.14 | 7.14 | 7.14 |
| Soybean Oil | 3.57 | 3.57 | 3.57 | 3.57 | 3.57 |
| Cellulose | 5.71 | 5.71 | 5.71 | 5.71 | 5.71 |
| Vitamin Mix | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Mineral Mix | 2.48 | 2.48 | 2.48 | 2.48 | 2.48 |
| Microwaved Quinoa Cookie (MQC) | -- | -- | -- | 14.75 | -- |
| Quercetin (Q) | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.14 |
| TOTAL (daily intake) | 73.79 | 73.79 | 73.79 | 73.79 | 73.79 |
| Parameter | Points |
|---|---|
| Loss of normal morphology | 1 point |
| Mucosal discoloration | 1 point |
| Mucosal edema | 1 point |
| Hemorrhages | 1 point |
| Petechial points (up to 9) | 2 points |
| Petechial points (>10) | 3 points |
| Ulcers up to 1 mm | n × 2 points |
| Ulcers (>1 mm) | n × 3 points |
| Perforated ulcers | n × 4 points |
| Groups | ORAC |
|---|---|
| C | 7.21 ± 0.37 a |
| IBP | 5.71 ± 0.30 b |
| OMP | 5.36 ± 0.27 bc |
| MQC | 4.70 ± 0.16 c |
| Q | 7.40 ± 0.23 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela-González, M.; Cárdenas-López, J.L.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Salazar-López, N.J.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Villegas-Ochoa, M.A.; Martínez-Coronilla, G.; Domínguez-Avila, J.A.; Gorinstein, S.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; et al. Preventive Gastroprotective Effect of a Functional Food Based on Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Ibuprofen-Induced Gastric Damage. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070893
Valenzuela-González M, Cárdenas-López JL, Burgos-Hernández A, Salazar-López NJ, Viuda-Martos M, Villegas-Ochoa MA, Martínez-Coronilla G, Domínguez-Avila JA, Gorinstein S, González-Aguilar GA, et al. Preventive Gastroprotective Effect of a Functional Food Based on Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Ibuprofen-Induced Gastric Damage. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(7):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070893
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela-González, Maribel, José Luis Cárdenas-López, Armando Burgos-Hernández, Norma Julieta Salazar-López, Manuel Viuda-Martos, Mónica A. Villegas-Ochoa, Gustavo Martínez-Coronilla, J. Abraham Domínguez-Avila, Shela Gorinstein, Gustavo A. González-Aguilar, and et al. 2025. "Preventive Gastroprotective Effect of a Functional Food Based on Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Ibuprofen-Induced Gastric Damage" Antioxidants 14, no. 7: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070893
APA StyleValenzuela-González, M., Cárdenas-López, J. L., Burgos-Hernández, A., Salazar-López, N. J., Viuda-Martos, M., Villegas-Ochoa, M. A., Martínez-Coronilla, G., Domínguez-Avila, J. A., Gorinstein, S., González-Aguilar, G. A., & Robles-Sánchez, R. M. (2025). Preventive Gastroprotective Effect of a Functional Food Based on Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Quercetin in a Murine Model of Ibuprofen-Induced Gastric Damage. Antioxidants, 14(7), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070893













