Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
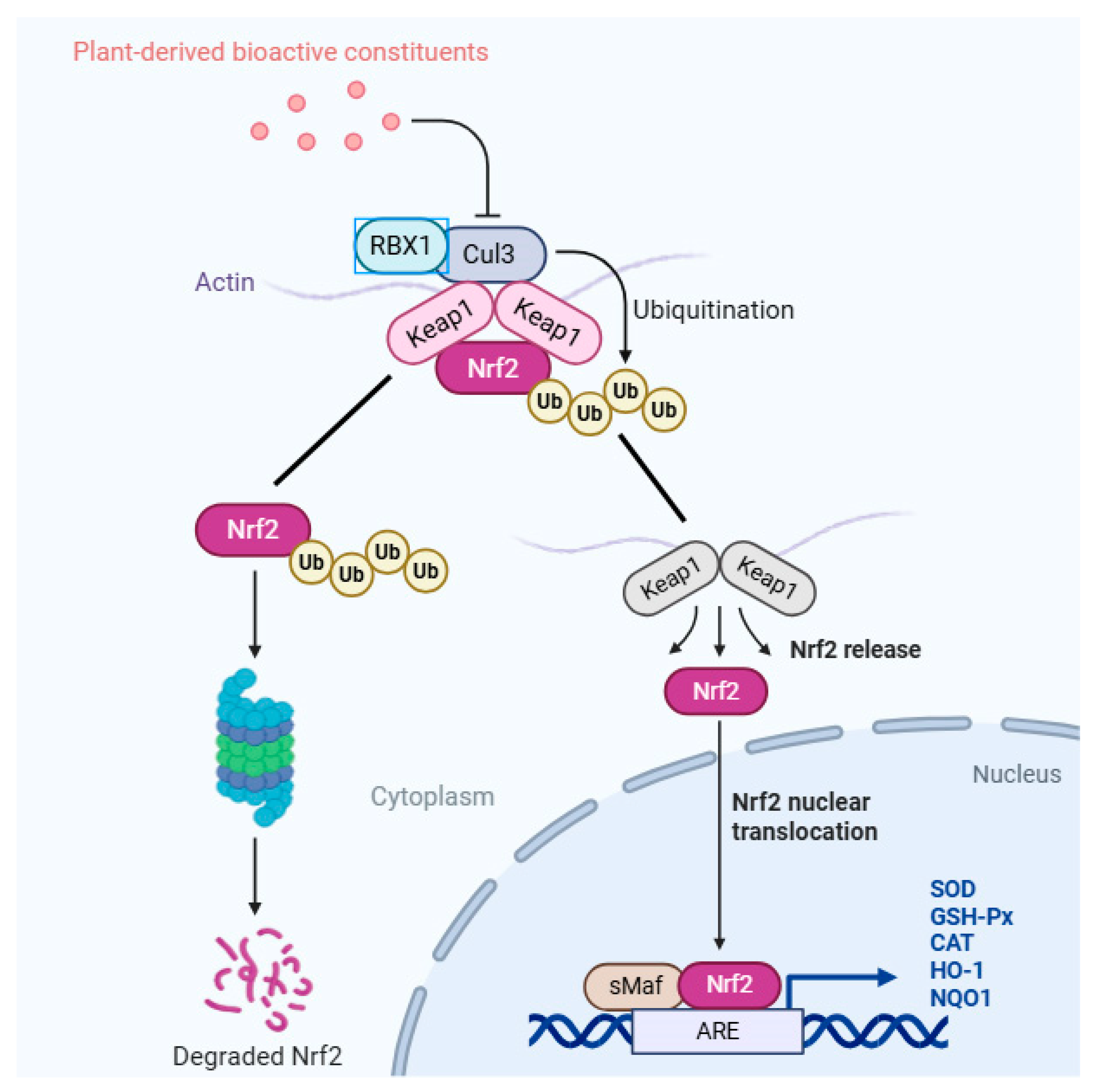
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. (WEAA)
2.2. Animals and Grouping
2.3. Raising and Management
2.4. Collection of Peripheral Blood and Preparation of Lymphocyte Suspension
2.5. Cell Culture and WEAA Treatment
2.6. Collection of Sheep Serum, Liver, and Spleen Samples
2.7. Cell Viability
2.8. Antioxidant Indices in Serum, Liver, and Spleen
2.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of WEAA on Antioxidant Indexes of Sheep
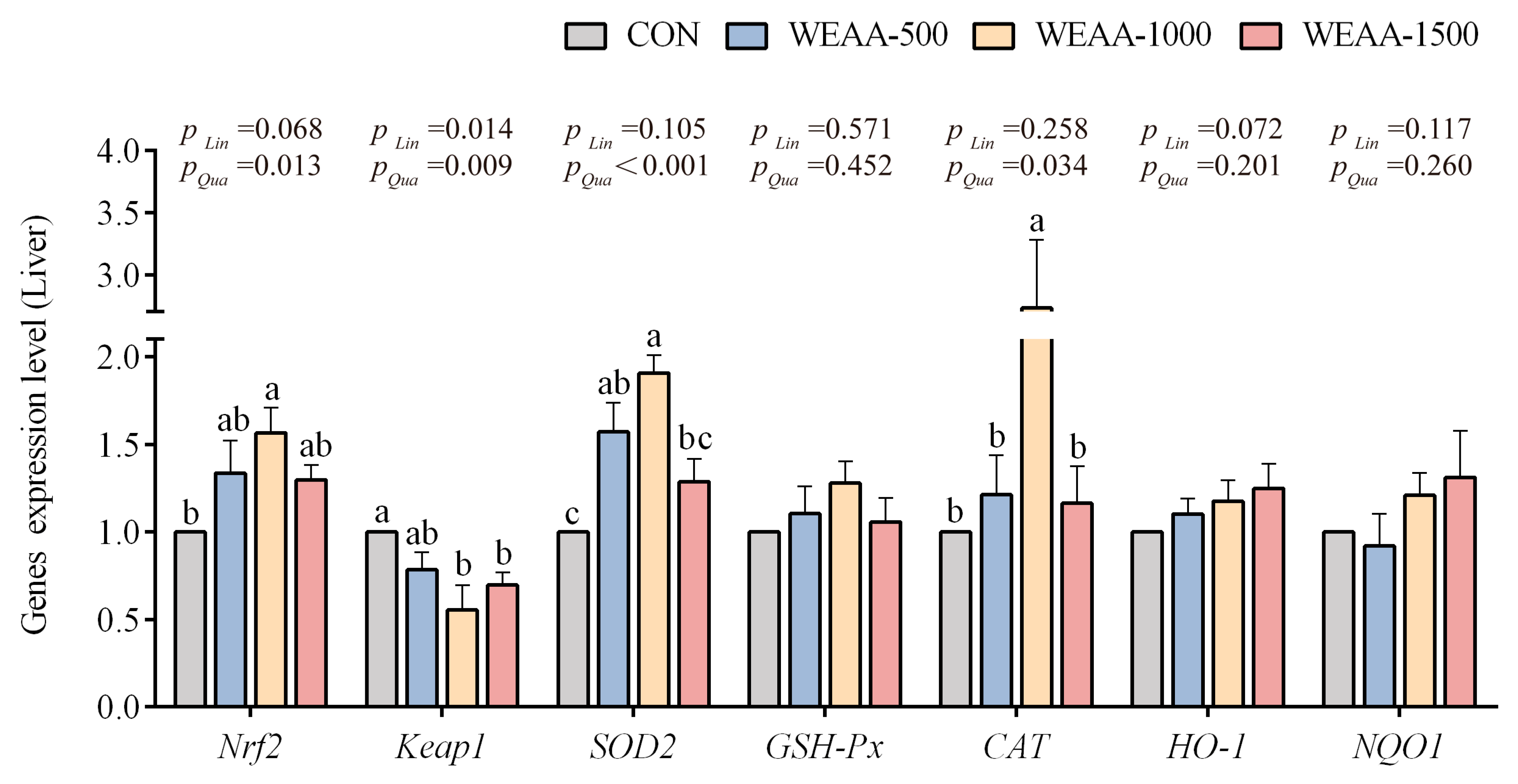
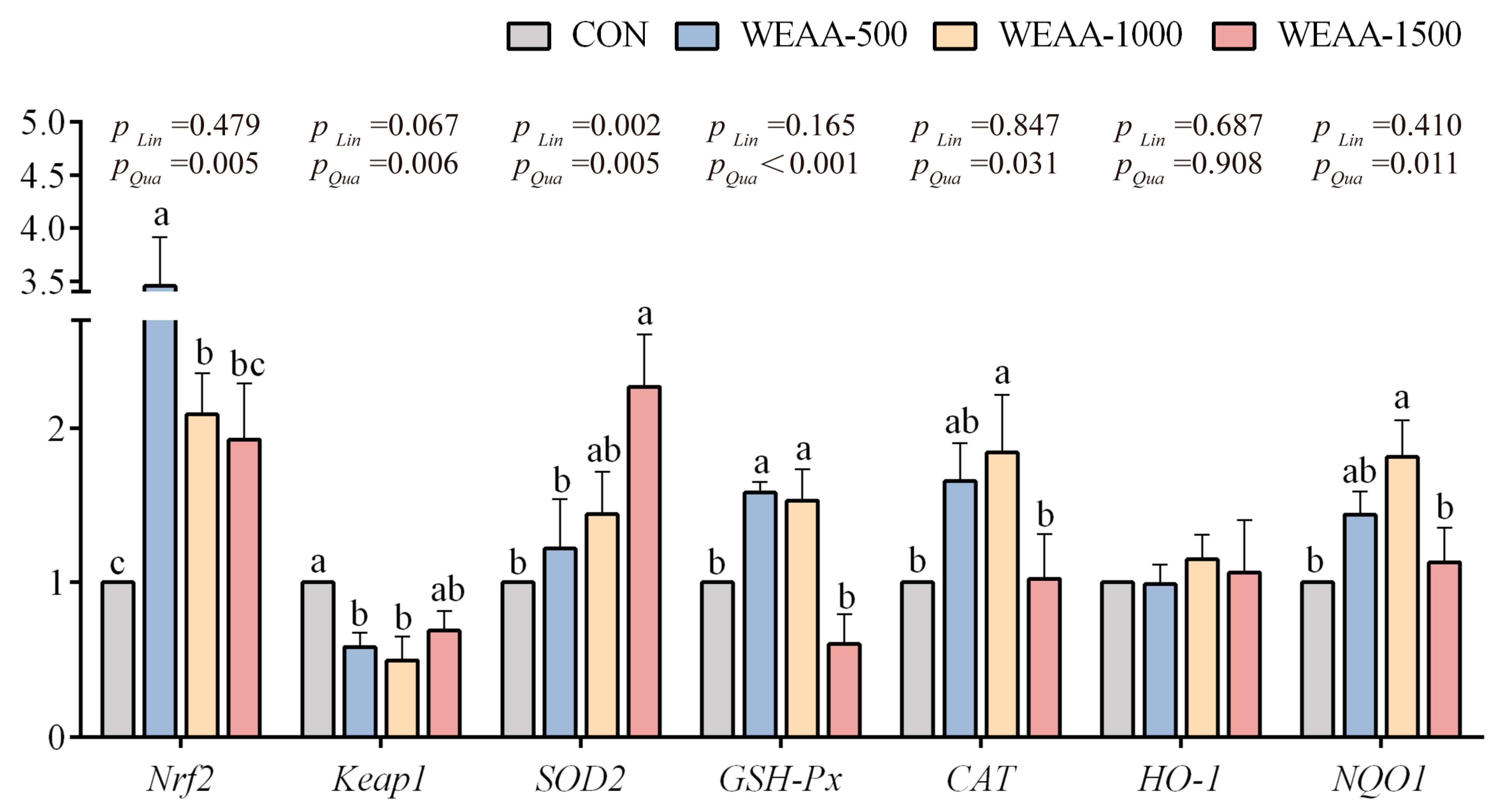
3.2. Effects of WEAA on the Expression of Antioxidant-Related Genes in the Liver and Spleen of Sheep
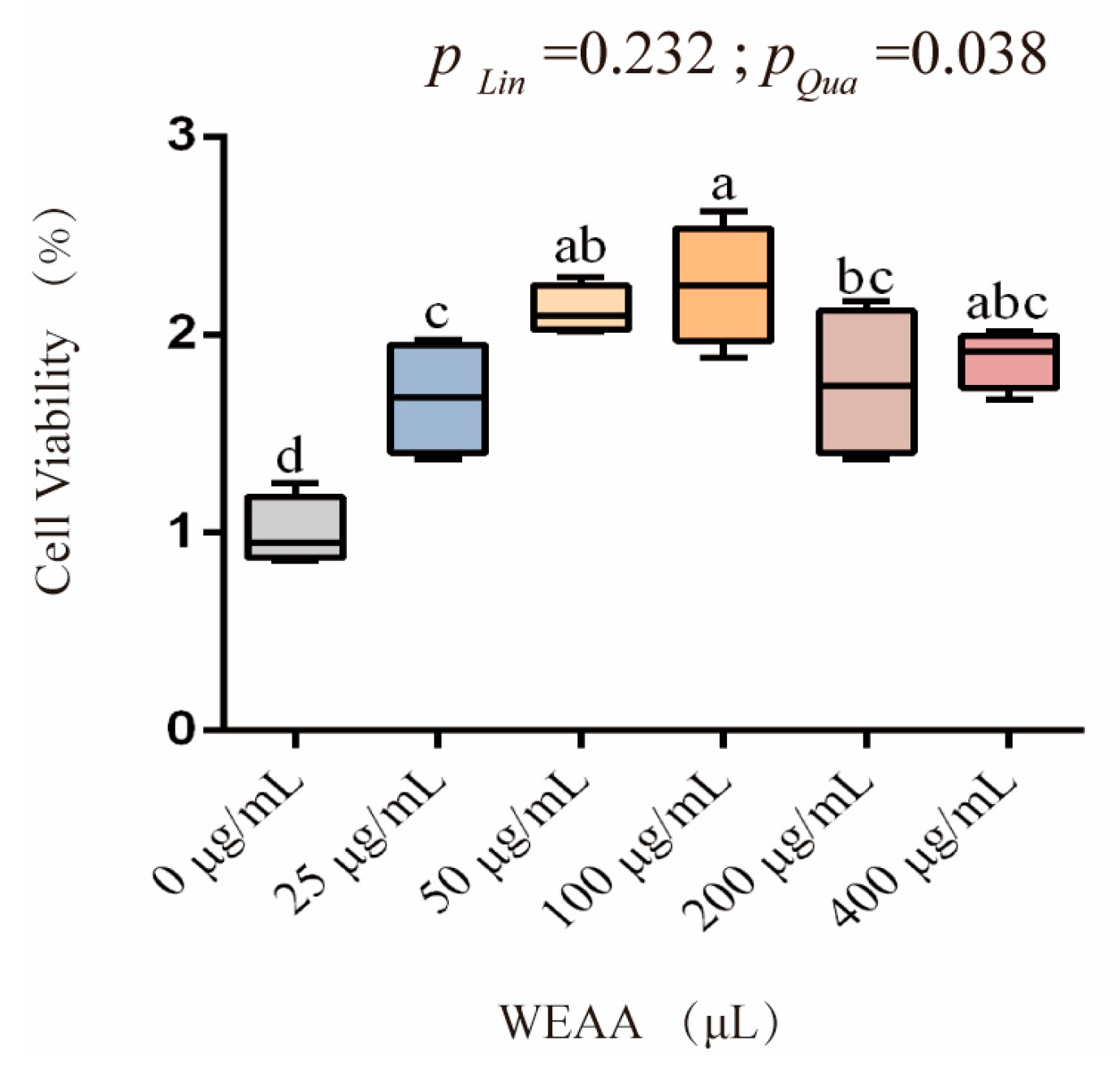
3.3. Effects of WEAA on the Cell Viability of PBLs
3.4. Effects of WEAA on Antioxidant Indexes in Culture Medium of PBLs
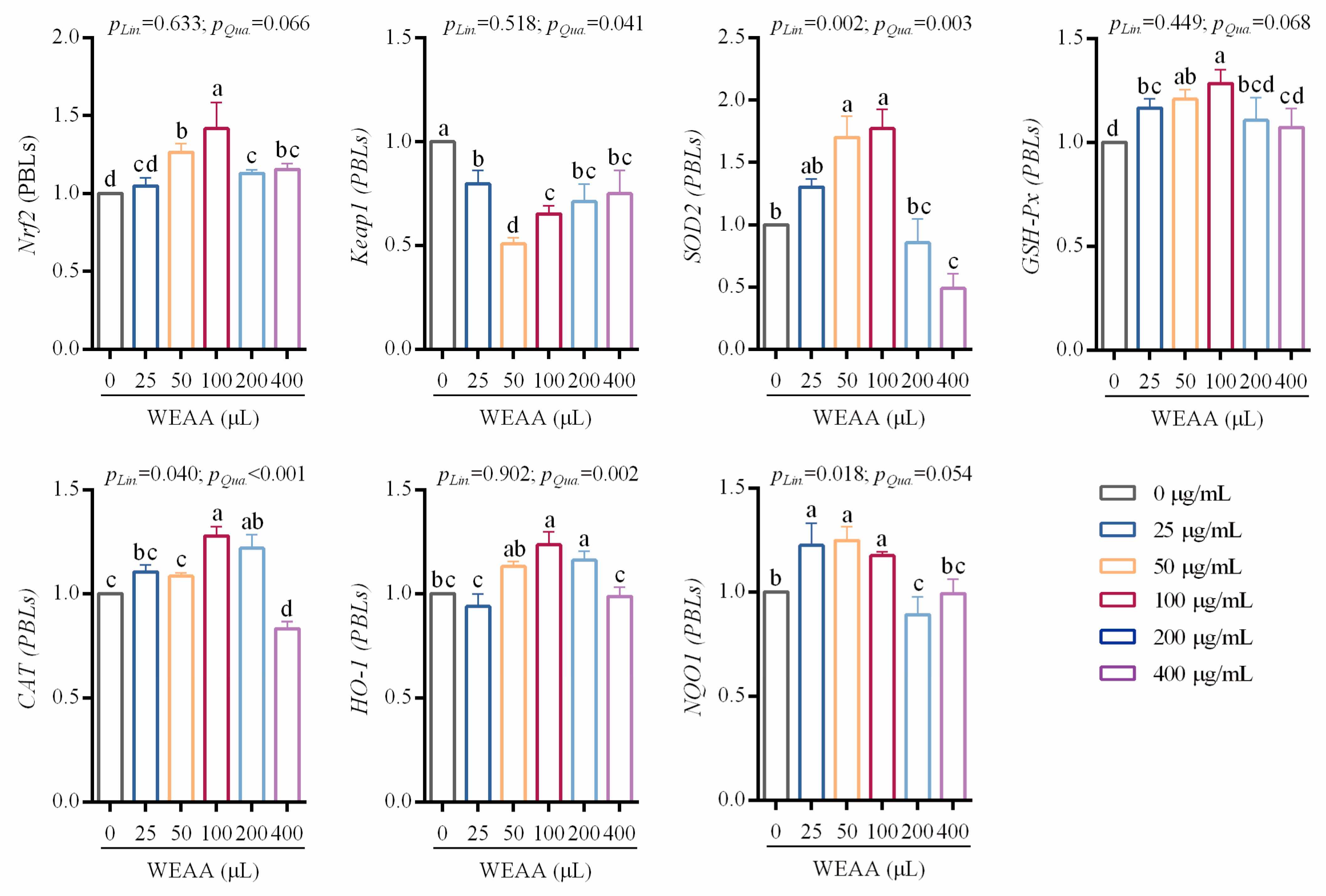
3.5. Effects of WEAA on the Expression of Antioxidant-Related Genes of PBLs
3.6. Effects of WEAA on Antioxidative Indexes in the Culture Medium of ML385-Blocked PBLs
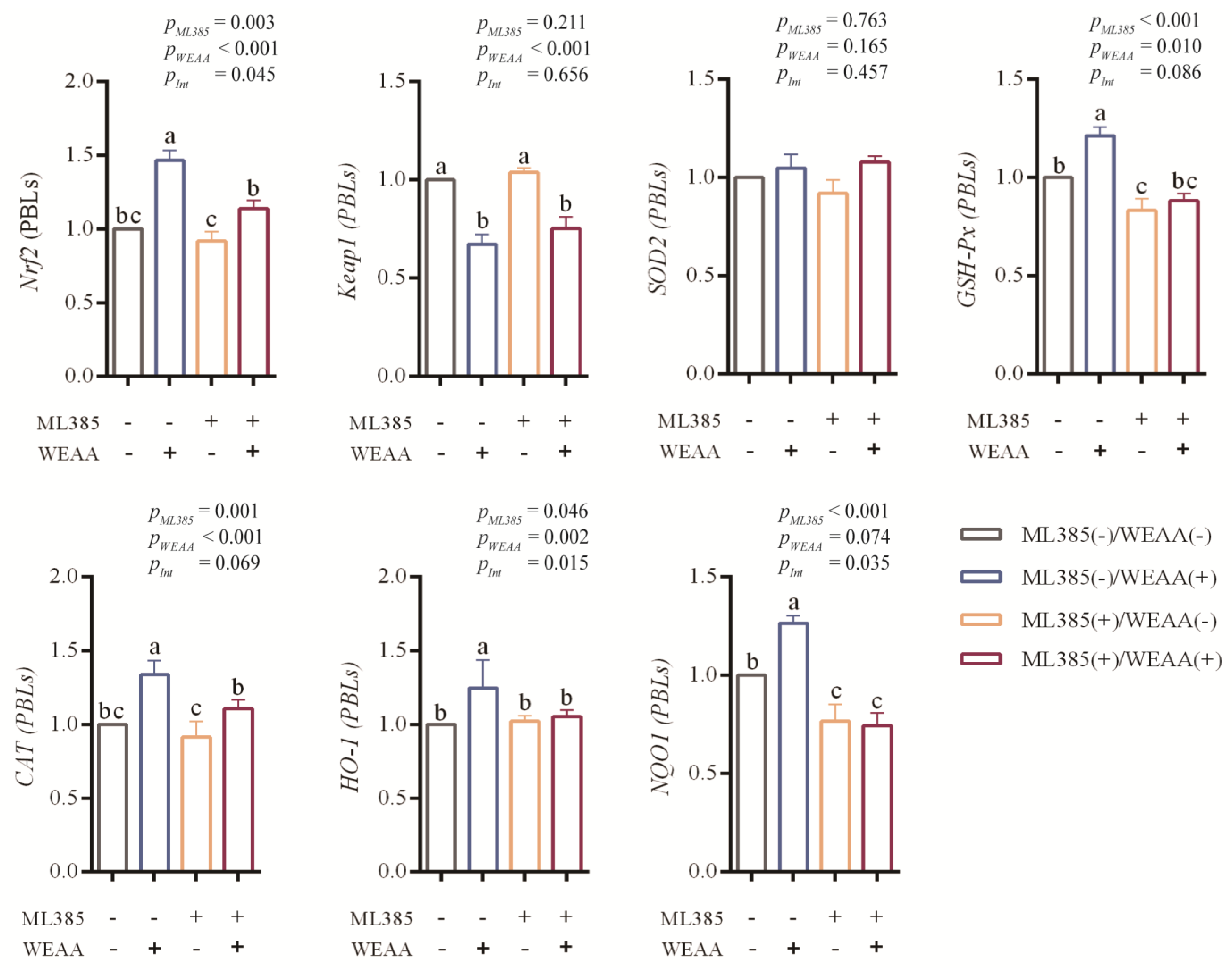
3.7. Effects of WEAA on Gene Expression of Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in ML385-Blocked PBLs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasapidou, E.; Basdagianni, Z.; Papadopoulos, V.; Karaiskou, C.; Kesidis, A.; Tsiotsias, A. Effects of intensive and semi-intensive production on sheep milk chemical composition, physicochemical characteristics, fatty acid profile, and nutritional indices. Animals 2021, 11, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrič, D.; Mravčáková, D.; Kucková, K.; Čobanová, K.; Kišidayová, S.; Cieslak, A.; Váradyová, Z. Effect of dry medicinal plants (wormwood, chamomile, fumitory and mallow) on in vitro ruminal antioxidant capacity and fermentation patterns of sheep. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Lu, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, P.; Li, A.; Jian, F.; Yu, G.; Huang, S. Meat of sheep: Insights into mutton evaluation, nutritive value, influential factors, and interventions. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, G.Q.; Yu, Q.; Yang, J. Identifications of immune-responsive genes for adaptative traits by comparative transcriptome analysis of spleen tissue from Kazakh and Suffolk sheep. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, N.; Hao, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, Y.; He, Z. Plant-derived polysaccharides regulated immune status, gut health and microbiota of broilers: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 791371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, M.; Che, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G.; Feng, T. Phytogenic feed additives as natural antibiotic alternatives in animal health and production: A review of the literature of the last decade. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Liao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, R.; Chen, M.; Huang, A.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y. Antioxidant and anti-inflammation effects of dietary phytochemicals: The Nrf2/NF-κB signalling pathway and upstream factors of Nrf2. Phytochemistry 2022, 204, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.K.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.H.; Guo, S.W.; Shi, L.L.; Jin, X.; Xu, Y.Q.; Yan, S.M.; Shi, B.L. Artemisia ordosica polysaccharides enhance antioxidant capacity of peripheral blood lymphocytes in poultry through Nrf2/Keap1 and TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Yang, W. Polysaccharide from alfalfa activates RAW 264.7 macrophages through MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.H.; Yang, F.X.; Bai, Y.C.; Zhao, J.Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Dou, T.F.; Jia, J.J. Research progress on the mechanisms underlying poultry immune regulation by plant polysaccharides. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1175848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, S.C.; Castilho, P.C. Artemisia annua L.: Essential oil and acetone extract composition and antioxidant capacity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Lalarizo Rakoto, M.; Marodon, C.; Bedoui, Y.; Nakab, J.; Simon, E.; Hoarau, L.; Savriama, S.; Strasberg, D.; Guiraud, P.; et al. Artemisia annua, a traditional plant brought to light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Chou, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, X. Artemisia annua water extract attenuates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis by restraining Th2 cell mediated inflammatory responses in BALB/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Sun, H.; Liao, R.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S. Effects of herbal extracts (Foeniculum vulgare and Artemisia annua) on growth, liver antioxidant capacity, intestinal morphology and microorganism of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sawy, S.A.; Amin, Y.A.; El-Naggar, S.A.; Abdelsadik, A. Artemisia annua L. (Sweet wormwood) leaf extract attenuates high-fat diet-induced testicular dysfunctions and improves spermatogenesis in obese rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Said, K.S.; Haidyrah, A.S.; Mobasher, M.A.; Khayyat, A.I.A.; Shakoori, A.; Al-Sowayan, N.S.; Barnawi, I.O.; Mariah, R.A. Artemisia annua extract attenuate doxorubicin-induced hepatic injury via PI-3K/Akt/Nrf-2-mediated signaling pathway in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Dong, G. Dandelion extract alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress through the Nrf2 pathway in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.; Ko, Y. Influence of dietary addition of dried Wormwood (Artemisia sp.) on the performance and carcass characteristics of Hanwood steers and the nutrient digestibility of sheep. Agric. Food Sci. 2007, 6, 390–395. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjad, N.; Wani, A.; Sharma, A.; Ali, R.; Hassan, S.; Hamid, R.; Habib, H.; Ganai, B.A. Artemisia amygdalina upregulates Nrf2 and protects neurons Against oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 43562–2023; Code of Practice for Livestock and Poultry Slaughtering Operation—Sheep. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- NY/T 816–2021; Nutritional Requirements of Meat—type Sheep. Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Administration: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Ekiert, H.; Świątkowska, J.; Klin, P.; Rzepiela, A.; Szopa, A. Artemisia annua—Importance in traditional medicine and current state of knowledge on the chemistry, biological activity and possible applications. Planta Medica 2021, 87, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.D. The biosynthesis of artemisinin (Qing hao su) and the phytochemistry of Artemisia annua L. (Qing hao). Molecules 2010, 15, 7603–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinyuy, L.M.; Loe, G.E.; Jansen, O.; Mamede, L.; Ledoux, A.; Noukimi, S.F.; Abenwie, S.N.; Ghogomu, S.M.; Souopgui, J.; Robert, A.; et al. Secondary metabolites isolated from Artemisia afra and Artemisia annua and Their anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties-pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: A review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Weng, X.G.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zidek, Z. Flavonoids casticin and chrysosplenol D from Artemisia annua L. inhibit inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Weathers, P.J. SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants are susceptible in vitro to Artemisia annua hot water extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 308, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghban-Kanani, P.; Hosseintabar-Ghasemabad, B.; Azimi-Youvalari, S.; Seidavi, A.; Ragni, M.; Laudadio, V.; Tufarelli, V. Effects of using Artemisia annua leaves, probiotic blend, and organic acids on performance, egg quality, blood biochemistry, and antioxidant status of laying hens. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 56, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Leng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of dietary Artemisia annua supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune function, and gut microbiota of geese. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Shi, B.; Ma, G.; Yan, S.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Artemisia ordosica crude polysaccharide on antioxidant and immunity response, nutrient digestibility, rumen fermentation, and microbiota in cashmere goats. Animals 2023, 13, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.L.; Niu, Y.; Zheng, X.C.; Huang, Q.; Su, W.P.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, T. Antioxidant capacities of Artemisia annua L. leaves and enzymatically treated Artemisia annua L. in vitro and in broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 221, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Yun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Effect of diet supplemented with enzymatically treated Artemisia annua L. on intestinal digestive function and immunity in weaned pigs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, J.S.; Ko, K.H.; Hong, S.P.; Kim, E.H.; Hahm, K.B. Nrf2-mediated mucoprotective and anti-inflammatory actions of Artemisia extracts led to attenuate stress-related mucosal damages. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 56, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, N.P.; He, M.T.; Lee, C.D.; Lee, Y.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, S. Artemisia extracts and phytochemicals inhibit glutamate-induced oxidative cell death and upregulate the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in HT22 neuronal cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 349, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.; Chen, S.; Chang, L. The role of HO-1 and its crosstalk with oxidative stress in cancer cell survival. Cells 2021, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Jin, X.; Xu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Yan, S.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, B. Effects of total flavonoids of Artemisia ordosica on growth performance, oxidative stress, and antioxidant status of lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, S.; Shi, L.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Yan, S.; Shi, B. Artemisia ordosica polysaccharide ameliorated LPS-induced growth inhibition and intestinal injury in broilers through enhancing immune-regulation and antioxidant capacity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 115, 109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xing, Y.; Shi, L.; Guo, S.; Jin, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, S.; Shi, B. The effects of dietary supplementation of Artemisia argyi polysaccharide on immune and antioxidative functions in broilers. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2022, 52, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, H.; Kim, M.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Liu, K.H.; Kim, J.-S. Protective Effect of Artemisia annua L. extract against galactose-induced oxidative stress in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101486. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Lai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, L.; Gu, Y.; et al. Inhibition of NRF2 enhances the acute myeloid leukemia cell death induced by Veneto lax via the ferroptosis pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldi, R.; Isacchi, B.; Predieri, S.; Marconi, G.; Vincieri, F.F.; Bilia, A.R. Distribution of artemisinin and bioactive flavonoids from Artemisia annua L. during plant growth. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisibe, E.A.; Umoren, U.E.; Brisibe, F.; Magalhäes, P.M.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Luthria, D. Nutritional characterisation and antioxidant capacity of different tissues of Artemisia annua L. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czechowski, T.; Rinaldi, M.A.; Famodimu, M.T.; Van Veelen, M.; Larson, T.R.; Winzer, T. Flavonoid versus artemisinin anti-malarial activity in Artemisia annua whole-leaf extracts. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item | Content |
|---|---|
| Ingredients | |
| Alfalfa | 16.25 |
| Corn straw grass | 14.00 |
| Oat grass | 24.75 |
| Corn | 23.25 |
| Soybean meal | 10.95 |
| Wheat bran | 4.25 |
| Corn germ meal | 1.95 |
| Soybean oil | 1.10 |
| Limestone | 1.10 |
| Calcium phosphate dibasic | 0.70 |
| Salt | 0.40 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.80 |
| Premix 1 | 0.50 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Nutrient levels 2 | |
| Digestible energy (MJ/kg) | 12.01 |
| Dry matter | 89.89 |
| Crude protein | 15.80 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 40.80 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 26.24 |
| Calcium | 1.08 |
| Phosphorus | 0.40 |
| Gene 1 | Sequence (5′- > 3′) 2 | GenBank No. | Length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F-ACAATGTGGCCGAGGACTTT | NM_001009784.3 | 278 |
| R-GCCGTGATGGCTGACCATTC | |||
| GAPDH | F-TTATGACCACTGTCCACGCC | NM_001190390.1 | 216 |
| R-TCAGATCCACAACGGACACG | |||
| Nrf2 | F-TGTGGAGGAGTTCAACGAGC | XM_004004557.1 | 88 |
| R-CGCCGCCATCTTGTTCTTG | |||
| Keap1 | F-TTCAACAGCGAAAGTCAGGC | XM_027969637.2 | 157 |
| R-TGCGTAGCCTCCGATACTCT | |||
| SOD2 | F-AAACCGTCAGCCTTACACC | NM_001280703.1 | 116 |
| R-ACAAGCCACGCTCAGAAAC | |||
| GSH-Px | F-TGGTCGTACTCGGCTTCCC | XM_004018462.1 | 163 |
| R-AGCGGATGCGCCTTCTCG | |||
| CAT | F-GAGCCCACCTGCAAAGTTCT | XM_004016396 | 148 |
| R-CTCCTACTGGATTACCGGCG | |||
| HO-1 | F-CGATGGGTCCTCACACTCAG | XM_027967703.2 | 74 |
| R-CACACTCGCATTCACATGGC | |||
| NQO1 | F-CTCTGGCCAATTCAGAGTGG | XM_004015102.5 | 296 |
| R-TCCATTGGGATGGACTTGCC |
| Item 1 | WEAA Supplemental Level, mg/kg | SEM | p-Value 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | Linear | Quadratic | ||
| Day 0 | |||||||
| T-AOC, mM | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.256 | 0.398 |
| T-SOD, U/mL | 83.76 | 82.48 | 84.75 | 82.71 | 1.57 | 0.952 | 0.991 |
| GSH-Px, U/mL | 81.31 | 81.48 | 81.22 | 81.57 | 3.18 | 0.936 | 0.995 |
| CAT, U/mL | 1.50 | 1.74 | 1.65 | 1.48 | 0.15 | 0.912 | 0.747 |
| MDA, nmol/mL | 2.13 | 2.13 | 2.16 | 2.06 | 0.10 | 0.838 | 0.951 |
| Day 30 | |||||||
| T-AOC, mM | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0.617 | 0.837 |
| T-SOD, U/mL | 81.88 | 82.33 | 82.72 | 82.46 | 1.12 | 0.837 | 0.968 |
| GSH-Px, U/mL | 89.42 ab | 104.93 a | 80.18 ab | 64.58 b | 5.92 | 0.060 | 0.068 |
| CAT, U/mL | 1.42 b | 3.05 a | 3.15 a | 3.03 a | 0.20 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| MDA, nmol/mL | 2.12 a | 1.93 ab | 1.71 b | 1.85 ab | 0.06 | 0.076 | 0.084 |
| Day 60 | |||||||
| T-AOC, mM | 0.62 b | 0.64 ab | 0.68 a | 0.67 a | 0.01 | 0.014 | 0.029 |
| T-SOD, U/mL | 89.64 | 90.22 | 91.31 | 89.32 | 0.86 | 0.987 | 0.77 |
| GSH-Px, U/mL | 93.69 b | 117.04 ab | 145.98 a | 129.77 ab | 6.60 | 0.017 | 0.016 |
| CAT, U/mL | 2.35 c | 3.77 b | 6.07 a | 4.10 b | 0.26 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| MDA, nmol/mL | 1.82 a | 1.63 ab | 1.50 b | 1.82 a | 0.05 | 0.762 | 0.020 |
| Item | WEAA Supplemental Level, mg/kg 1 | SEM | p-Value 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | Linear | Quadratic | ||
| Liver | |||||||
| T-AOC, μmol/mg protein | 0.0277 | 0.0278 | 0.0308 | 0.0230 | 0.00 | 0.259 | 0.106 |
| T-SOD, U/mg protein | 1066.79 | 1070.69 | 1165.97 | 1075.04 | 19.04 | 0.490 | 0.371 |
| GSH-Px, U/mg protein | 114.81 | 124.79 | 121.88 | 112.65 | 2.75 | 0.709 | 0.207 |
| CAT, U/mg protein | 68.52 b | 75.75 a | 76.52 a | 70.36 ab | 1.25 | 0.581 | 0.018 |
| MDA, nmol/mg protein | 3.55 a | 2.88 b | 2.97 ab | 3.27 ab | 0.10 | 0.427 | 0.043 |
| Spleen | |||||||
| T-AOC, μmol/mg protein | 0.0185 c | 0.0240 b | 0.0295 a | 0.0218 bc | 0.00 | 0.101 | 0.001 |
| T-SOD, U/mg protein | 542.55 b | 667.18 ab | 682.75 a | 653.96 ab | 23.19 | 0.092 | 0.056 |
| GSH-Px, U/mg protein | 157.00 b | 157.00 b | 209.23 a | 160.34 b | 4.95 | 0.163 | 0.013 |
| CAT, U/mg protein | 2.08 c | 2.73 b | 3.19 a | 2.81 ab | 0.10 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| MDA, nmol/mg protein | 2.40 a | 1.45 c | 1.60 bc | 2.26 ab | 0.14 | 0.993 | 0.009 |
| Item | WEAA Supplemental Level, µg/mL 1 | SEM | p-Value 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | Linear | Quadratic | ||
| T-AOC, mM | 0.43 b | 0.42 b | 0.48 ab | 0.51 a | 0.53 a | 0.48 ab | 0.01 | 0.085 | 0.002 |
| T-SOD, U/mL | 38.8 cd | 40.78 c | 36.68 d | 48.45 a | 44.75 b | 39.00 cd | 1.00 | 0.837 | 0.001 |
| GSH-Px, U/mL | 42.53 b | 44.62 b | 55.95 a | 60.13 a | 58.74 a | 34.51 c | 2.53 | 0.118 | <0.001 |
| CAT, U/mL | 0.60 cd | 0.78 bc | 0.82 b | 1.09 a | 0.63 bcd | 0.53 d | 0.05 | 0.078 | 0.030 |
| MDA, nmol/mL | 2.75 a | 2.32 ab | 2.01 b | 2.15 b | 2.22 b | 2.25 b | 0.08 | 0.435 | 0.101 |
| Item | ML385(−) 1 | ML385(+) | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WEAA(−) | WEAA(+) | WEAA(−) | WEAA(+) | ML385 | WEAA | WEAA × ML385 | ||
| T-AOC, mM | 0.40 ab | 0.42 a | 0.39 ab | 0.41 b | 0.02 | 0.184 | 0.023 | 0.799 |
| T-SOD, U/mL | 30.56 b | 37.08 a | 25.46 c | 28.19 bc | 1.15 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.239 |
| GSH-Px, U/mL | 74.83 b | 95.98 a | 58.70 c | 59.38 c | 3.82 | <0.001 | 0.031 | 0.03 |
| CAT, U/mL | 0.72 b | 1.29 a | 0.70 b | 0.68 b | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.058 | 0.04 |
| MDA, nmol/mL | 0.90 ab | 0.70 b | 1.05 a | 0.94 ab | 0.05 | 0.022 | 0.064 | 0.592 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gang, G.; Gao, R.; Li, R.; Jin, X.; Xing, Y.; Yan, S.; Xu, Y.; Shi, B. Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070885
Gang G, Gao R, Li R, Jin X, Xing Y, Yan S, Xu Y, Shi B. Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(7):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070885
Chicago/Turabian StyleGang, Gen, Ruiheng Gao, Ruizhen Li, Xiao Jin, Yuanyuan Xing, Sumei Yan, Yuanqing Xu, and Binlin Shi. 2025. "Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway" Antioxidants 14, no. 7: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070885
APA StyleGang, G., Gao, R., Li, R., Jin, X., Xing, Y., Yan, S., Xu, Y., & Shi, B. (2025). Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants, 14(7), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070885






