Guarana, Selenium, and L-Carnitine Supplementation Improves the Oxidative Profile but Fails to Reduce Tissue Damage in Rats with Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. GSC Supplement
2.3. Experimental Design and Induction of OA with Mia
2.4. Biochemical Analysis of Oxidative Parameters
2.4.1. Production of Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Species (TBARS)
2.4.2. Production of ROS
2.4.3. Catalase (CAT) Activity
2.4.4. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
2.4.5. Determination of Total Thiols (T-SH)
2.4.6. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
2.5. Histopathological Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. In Silico Analysis
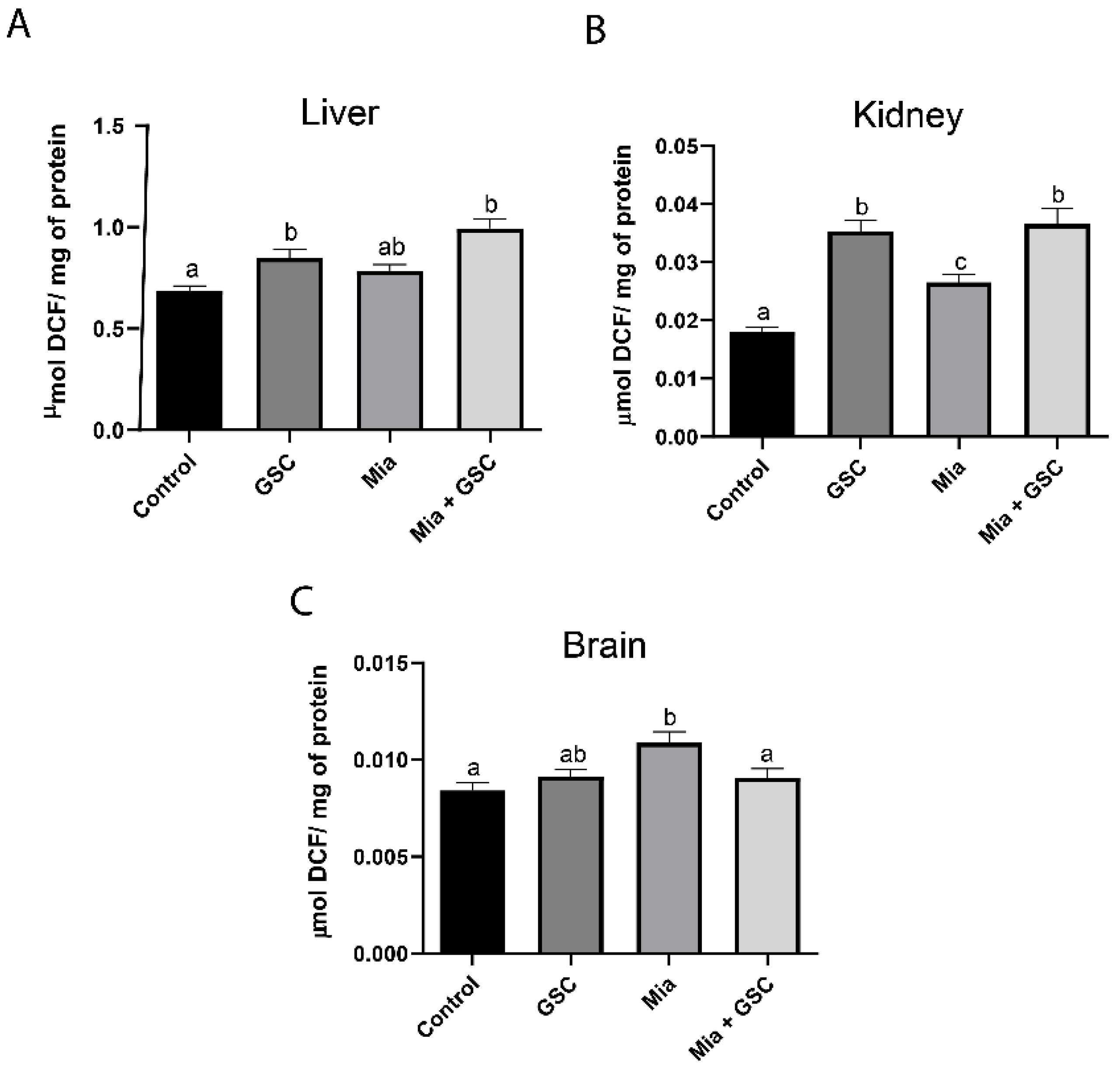
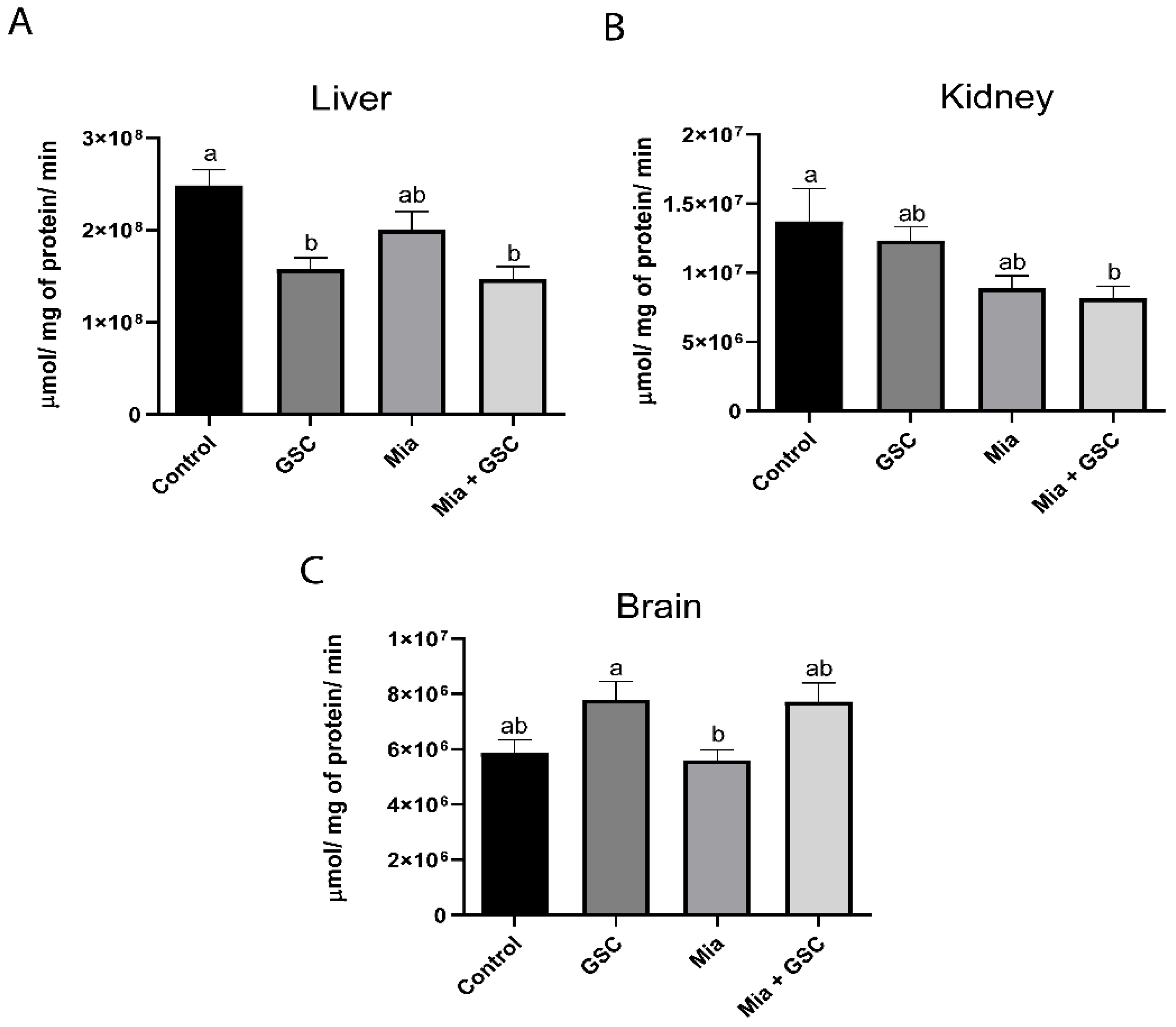
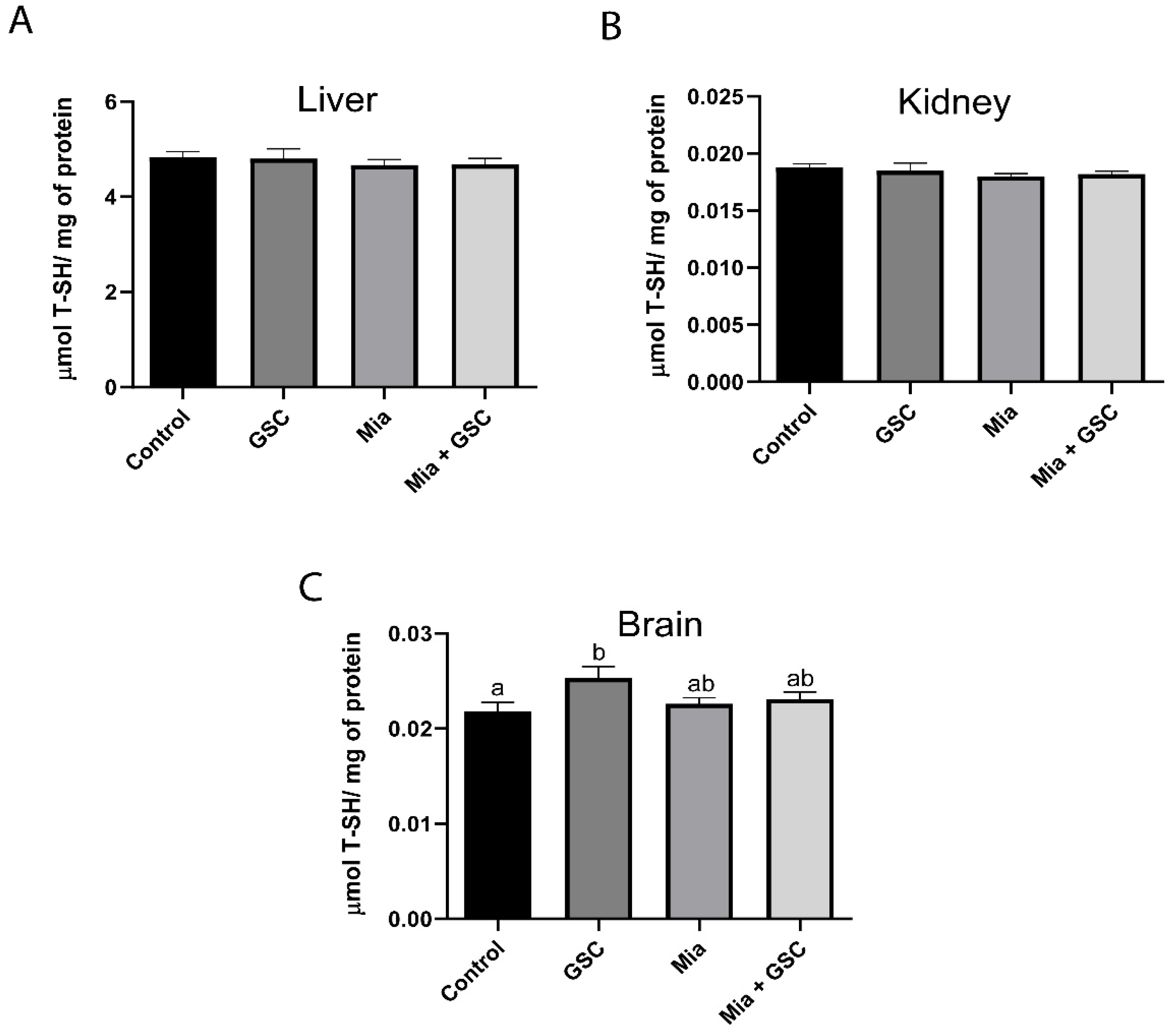
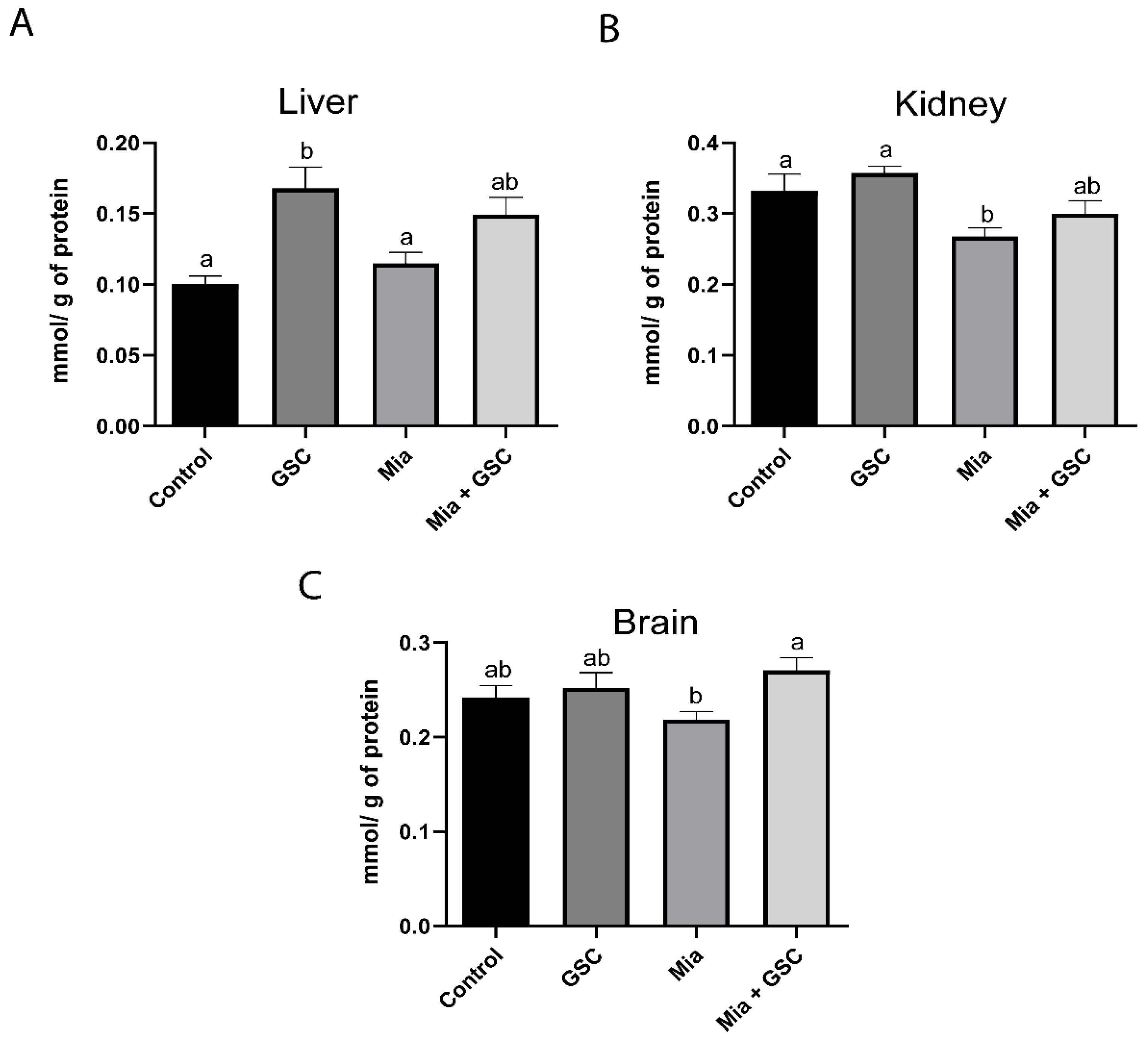
3. Results
3.1. Production of TBARS
3.2. ROS Production
3.3. CAT Activity
3.4. AChE Quantification
3.5. Determination of Total T-SH
3.6. Measure of TAC
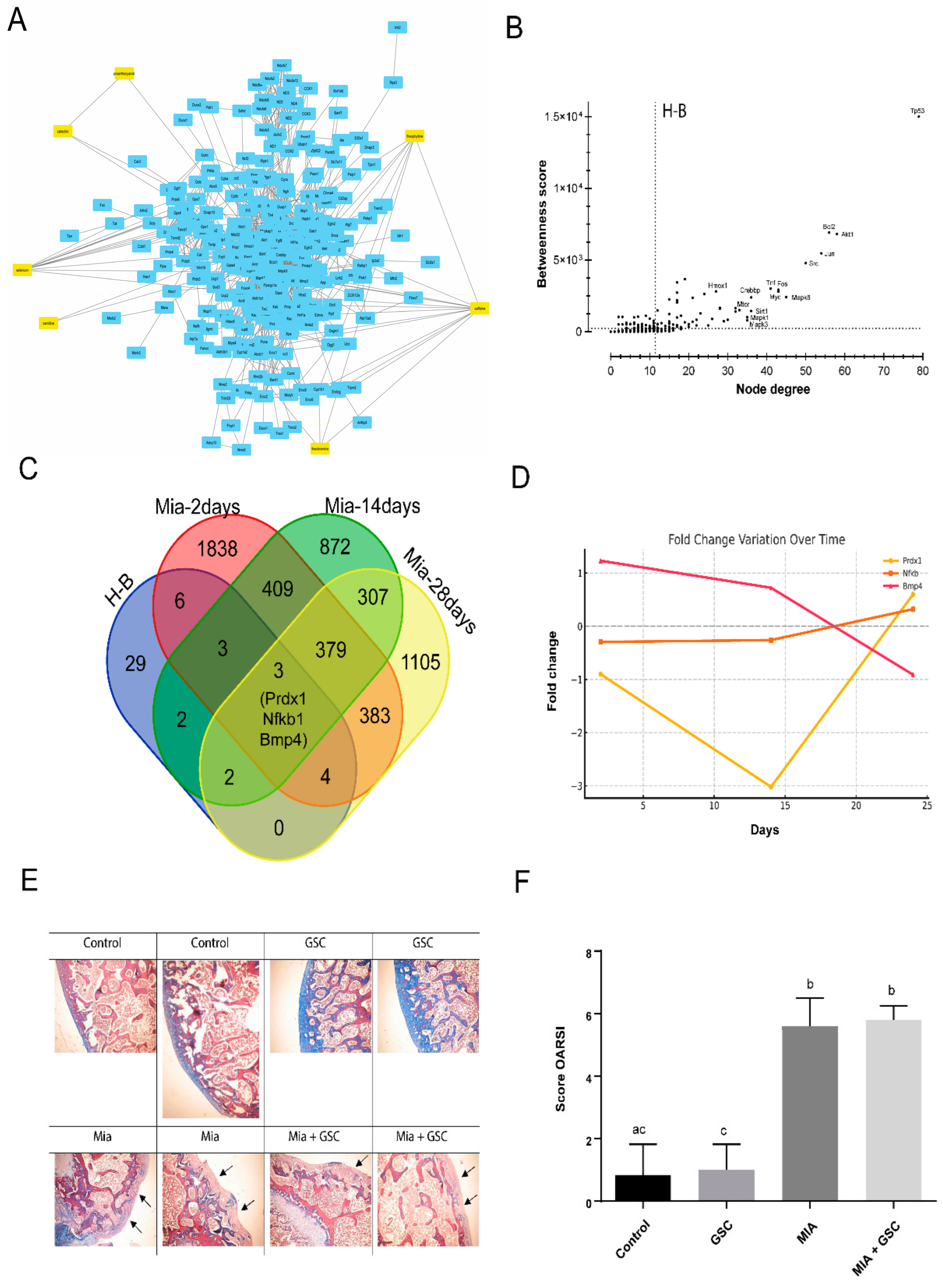
3.7. Systems Biology Analysis and Histological Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e508–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, L.A. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: Clinical. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Mak, C.C.H.; Sharma, V.; To, K.; Khan, W. Mendelian Randomization Studies of Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis: A PRISMA Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altay, M.A.; Erturk, C.; Bilge, A.; Yapti, M.; Levent, A.; Aksoy, N. Evaluation of prolidase activity and oxidative status in patients with knee osteoarthritis: Relationships with radiographic severity and clinical parameters. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erturk, C.; Altay, M.A.; Selek, S.; Kocyigit, A. Paraoxonase-1 activity and oxidative status in patients with knee osteoarthritis and their relationship with radiological and clinical parameters. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altindag, O.; Erel, O.; Aksoy, N.; Selek, S.; Celik, H.; Karaoglanoglu, M. Increased oxidative stress and its relation with collagen metabolism in knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.M.; Guilak, F.; Weinberg, J.B.; Fermor, B. Reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in interleukin-1-mediated DNA damage associated with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, G.; Wang, W. Reactive oxygen species: The 2-edged sword of osteoarthritis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 344, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetsos, P.; Papavassiliou, A.G. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.L.; Gabrielides, C.; Davidson, R.K.; Swingler, T.E.; Clark, I.M.; Wallis, G.A.; Boot-Handford, R.P.; Kirkwood, T.B.; Taylor, R.W.; Young, D.A. Superoxide dismutase downregulation in osteoarthritis progression and end-stage disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ao, M.; Dong, B.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Xu, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Curcumin in the Inflammatory Diseases: Status, Limitations and Countermeasures. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4503–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X. Protective Effect of Resveratrol on Knee Osteoarthritis and its Molecular Mechanisms: A Recent Review in Preclinical and Clinical Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 921003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses the global interleukin-1beta-induced inflammatory response in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Cao, G.; Ba, X.; Jiang, H. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate promotes extracellular matrix and inhibits inflammation in IL-1beta stimulated chondrocytes by the PTEN/miRNA-29b pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Majeed, S.; Narayanan, N.K.; Nagabhushanam, K. A pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a novel Boswellia serrata extract in the management of osteoarthritis of the knee. Phytother. Res. PTR 2019, 33, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, J.; Grygiel-Gorniak, B.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Zingiber Officinale Roscoe: The Antiarthritic Potential of a Popular Spice-Preclinical and Clinical Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Rescigno, A.; Dettori, T.; Calina, D.; Docea, A.O.; Singh, L.; Cebeci, F.; Ozcelik, B.; Bhia, M.; Dowlati Beirami, A.; et al. Avocado-Soybean Unsaponifiables: A Panoply of Potentialities to Be Exploited. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Feng, D.; Gong, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Natural products in osteoarthritis treatment: Bridging basic research to clinical applications. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolin, V.F.; Azzolin, V.F.; da Silva Maia, R.; Mastella, M.H.; Sasso, J.S.; Barbisan, F.; Bitencourt, G.R.; de Azevedo Mello, P.; Ribeiro, E.M.A.; Ribeiro, E.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy indicators of guarana and Brazil nut extract carried in nanoparticles of coenzyme Q10: Evidence from human blood cells and red earthworm experimental model. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2024, 191, 114828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, K.N.; Paula Barbosa, A.; de Freitas, A.A.; Alvarenga, L.F.; Padua, R.M.; Gomes Faraco, A.A.; Braga, F.C.; Vianna-Soares, C.D.; Castilho, R.O. TNF-alpha inhibition, antioxidant effects and chemical analysis of extracts and fraction from Brazilian guarana seed powder. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manica-Cattani, M.F.; Hoefel, A.L.; Azzolin, V.F.; Montano, M.A.E.; da Cruz Jung, I.E.; Ribeiro, E.E.; Azzolin, V.F.; da Cruz, I.B.M. Amazonian fruits with potential effects on COVID-19 by inflammaging modulation: A narrative review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macan, T.P.; Magenis, M.L.; Damiani, A.P.; Monteiro, I.O.; Silveira, G.B.; Zaccaron, R.P.; Silveira, P.C.L.; Teixeira, J.P.F.; Gajski, G.; Andrade, V.M. Brazil nut consumption reduces DNA damage in overweight type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2024, 895, 503739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Vinceti, M. Selenium and immune function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental human studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastgoo, S.; Fateh, S.T.; Nikbaf-Shandiz, M.; Rasaei, N.; Aali, Y.; Zamani, M.; Shiraseb, F.; Asbaghi, O. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers in adults: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2173–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.; Azzolin, V.F.; Rodrigues Dos Passos, G.; Turra, B.O.; Alves, A.O.; Bressanim, A.C.M.; Canton, L.E.L.; Vieira Dos Santos, A.C.; Mastella, M.H.; Barbisan, F.; et al. A coffee enriched with guarana, selenium, and l-carnitine (GSC) has nutrigenomic effects on oxi-inflammatory markers of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients: A pilot study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 71, 104515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.; da Cruz, I.B.M.; Ribeiro, E.E.; Pillar, D.M.; Turra, B.O.; Praia, R.S.; Barbisan, F.; Alves, A.O.; Sato, D.K.; Assmann, C.E.; et al. Safety indicators of a novel multi supplement based on guarana, selenium, and L-carnitine: Evidence from human and red earthworm immune cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2021, 150, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonsy, J.L.; Ghandehari, J.; Dickenson, A.H. Differential analgesic effects of morphine and gabapentin on behavioural measures of pain and disability in a model of osteoarthritis pain in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernihough, J.; Gentry, C.; Malcangio, M.; Fox, A.; Rediske, J.; Pellas, T.; Kidd, B.; Bevan, S.; Winter, J. Pain related behaviour in two models of osteoarthritis in the rat knee. Pain 2004, 112, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, R.E.; Evans, M.G.; Bove, S.; Morenko, B.; Kilgore, K. Mono-iodoacetate-induced histologic changes in subchondral bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotibial joints: An animal model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orita, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Miyagi, M.; Ochiai, N.; Inoue, G.; Eguchi, Y.; Kamoda, H.; Arai, G.; Toyone, T.; Aoki, Y.; et al. Pain-related sensory innervation in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rat knees that gradually develops neuronal injury in addition to inflammatory pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, P.; Pai, M.; Blomme, E.A.; Hsieh, G.C.; Decker, M.W.; Honore, P. Pharmacological modulation of movement-evoked pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 613, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijn, C.M.; Krijnen, H.; Menting-Hermeling, S.; Coenen, A.M. Decapitation in rats: Latency to unconsciousness and the ‘wave of death’. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzsch, A.M.; Bachmann, H.; Furst, P.; Biesalski, H.K. Improved analysis of malondialdehyde in human body fluids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, O.; Andersen, J.M.; Aarnes, H.; Fonnum, F. Evaluation of the probes 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate, luminol, and lucigenin as indicators of reactive species formation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccol, R.; da Silveira, K.L.; Manzoni, A.G.; Abdalla, F.H.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Dornelles, G.L.; Barbisan, F.; Passos, D.F.; Casali, E.A.; de Andrade, C.M.; et al. Antioxidant, hepatoprotective, genoprotective, and cytoprotective effects of quercetin in a murine model of arthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.P.; Kiesow, L.A. Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25 °C (with molar extinction coefficients of H2O2 solutions in the UV). Anal. Biochem. 1972, 49, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worek, F.; Mast, U.; Kiderlen, D.; Diepold, C.; Eyer, P. Improved determination of acetylcholinesterase activity in human whole blood. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 288, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Reprint of: Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 726, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Pineda, M.; Aguilar, M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: Specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzker, K.P.; Gay, S.; Jimenez, S.A.; Ostergaard, K.; Pelletier, J.P.; Revell, P.A.; Salter, D.; van den Berg, W.B. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: Grading and staging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt Lda, S.; Zeidan-Chulia, F.; Yatsu, F.K.; Schnorr, C.E.; Moresco, K.S.; Kolling, E.A.; Gelain, D.P.; Bassani, V.L.; Moreira, J.C. Guarana (Paullinia cupana Mart.) prevents beta-amyloid aggregation, generation of advanced glycation-end products (AGEs), and acrolein-induced cytotoxicity on human neuronal-like cells. Phytother. Res. PTR 2014, 28, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, G.S.; Canuto, K.M.; Ribeiro, P.R.V.; de Brito, E.S.; Nascimento, M.M.; Zocolo, G.J.; Coutinho, J.P.; de Jesus, R.M. Chemical profiling of guarana seeds (Paullinia cupana) from different geographical origins using UPLC-QTOF-MS combined with chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Santos, A.; von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P.; Kuhn, M. STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D380–D384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardoni, G.; Tosadori, G.; Faizan, M.; Spoto, F.; Fabbri, F.; Laudanna, C. Biological network analysis with CentiScaPe: Centralities and experimental dataset integration. F1000Research 2014, 3, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillan-Fresco, M.; Franco-Trepat, E.; Alonso-Perez, A.; Jorge-Mora, A.; Lopez-Fagundez, M.; Pazos-Perez, A.; Gualillo, O.; Gomez, R. Caffeine, a Risk Factor for Osteoarthritis and Longitudinal Bone Growth Inhibition. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Yen, C.C.; Huang, L.W.; Hu, Y.C.; Huang, T.C.; Hsieh, B.S.; Chang, K.L. Selenium Lessens Osteoarthritis by Protecting Articular Chondrocytes from Oxidative Damage through Nrf2 and NF-kappaB Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. Effect of l-Carnitine Supplementation on Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, R.P.; Lima, F.D.; Carvalho, N.R.; Bresciani, G.; Royes, L.F. Caffeine effects on systemic metabolism, oxidative-inflammatory pathways, and exercise performance. Nutr. Res. 2020, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Min Kim, T.; Kwon, G.; Park, J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jin, E.J. Targeting ROS in osteoclasts within the OA environment: A novel therapeutic strategy for osteoarthritis management. J. Tissue Eng. 2024, 15, 20417314241279935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.L.; Lyon, M.; Chapman, E.A.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid Neutrophils Drive Inflammation Through Production of Chemokines, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Blasco, D.; Almeida, A.; Bolanos, J.P. Brightness and shadows of mitochondrial ROS in the brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 184, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasagayam, T.P.; Kamat, J.P.; Mohan, H.; Kesavan, P.C. Caffeine as an antioxidant: Inhibition of lipid peroxidation induced by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1282, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Luan, H.Y.; Kang, Z.C.; Wang, C.B. Effects of L-carnitine against oxidative stress in human hepatocytes: Involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, C.N.; Xu, Q.; Ramanujan, V.K. Direct measurement of catalase activity in living cells and tissue biopsies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfante, R.; Di Lascio, S.; Cardani, S.; Fornasari, D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: A new therapeutic perspective in aging-related disorders. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenoproteins and human health: Insights from epidemiological data. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Mahdavi, A.; Mahdavi, R.; Kolahi, S.; Zemestani, M.; Vatankhah, A.M. L-Carnitine supplementation improved clinical status without changing oxidative stress and lipid profile in women with knee osteoarthritis. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricordi, C.; Garcia-Contreras, M.; Farnetti, S. Diet and Inflammation: Possible Effects on Immunity, Chronic Diseases, and Life Span. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34 (Suppl. 1), 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Paniagua, D.; Parron, T.; Alarcon, R.; Requena, M.; Gil, F.; Lopez-Guarnido, O.; Lacasana, M.; Hernandez, A.F. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in blood of workers exposed to non-cholinesterase inhibiting pesticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osz, B.E.; Jitca, G.; Stefanescu, R.E.; Puscas, A.; Tero-Vescan, A.; Vari, C.E. Caffeine and Its Antioxidant Properties-It Is All about Dose and Source. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseeb, A.; Ansari, M.Y.; Haqqi, T.M. Harpagoside suppresses IL-6 expression in primary human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.; Bellemere, G.; Boyer, G.; Ponelle, F.; Bauer, T.; Legeny, M.C.; Baudouin, C.; Henrotin, Y. Composition Analysis and Pharmacological Activity of Avocado/Soybean Unsaponifiable Products Used in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 781389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Degree | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| 0 | Surface and cartilage with intact morphology |
| 1 | Intact surface |
| 2 | Discontinuity surface |
| 3 | Vertical cracks |
| 4 | Erosion |
| 5 | Denudation |
| 6 | Deformation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuanazzi Pasinato, A.; Vargas, J.E.; Spanhol da Silva, J.; Grandó Moretto, J.; Ferreira Teixeira, C.; Farina Azzolin, V.; Mânica da Cruz, I.B.; da Rosa Trevisan, C.; Zub, E.C.; Puga, R.; et al. Guarana, Selenium, and L-Carnitine Supplementation Improves the Oxidative Profile but Fails to Reduce Tissue Damage in Rats with Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070881
Zuanazzi Pasinato A, Vargas JE, Spanhol da Silva J, Grandó Moretto J, Ferreira Teixeira C, Farina Azzolin V, Mânica da Cruz IB, da Rosa Trevisan C, Zub EC, Puga R, et al. Guarana, Selenium, and L-Carnitine Supplementation Improves the Oxidative Profile but Fails to Reduce Tissue Damage in Rats with Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(7):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuanazzi Pasinato, Aline, José Eduardo Vargas, Julia Spanhol da Silva, Joana Grandó Moretto, Cibele Ferreira Teixeira, Verônica Farina Azzolin, Ivana Beatrice Mânica da Cruz, Camile da Rosa Trevisan, Emanuele Cristina Zub, Renato Puga, and et al. 2025. "Guarana, Selenium, and L-Carnitine Supplementation Improves the Oxidative Profile but Fails to Reduce Tissue Damage in Rats with Osteoarthritis" Antioxidants 14, no. 7: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070881
APA StyleZuanazzi Pasinato, A., Vargas, J. E., Spanhol da Silva, J., Grandó Moretto, J., Ferreira Teixeira, C., Farina Azzolin, V., Mânica da Cruz, I. B., da Rosa Trevisan, C., Zub, E. C., Puga, R., Vargas, V. I., León-Mejía, G., & Pillon Barcelos, R. (2025). Guarana, Selenium, and L-Carnitine Supplementation Improves the Oxidative Profile but Fails to Reduce Tissue Damage in Rats with Osteoarthritis. Antioxidants, 14(7), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14070881







