Depletion of Small HDL Subclasses Predicts Poor Survival in Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. NMR Spectroscopy Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
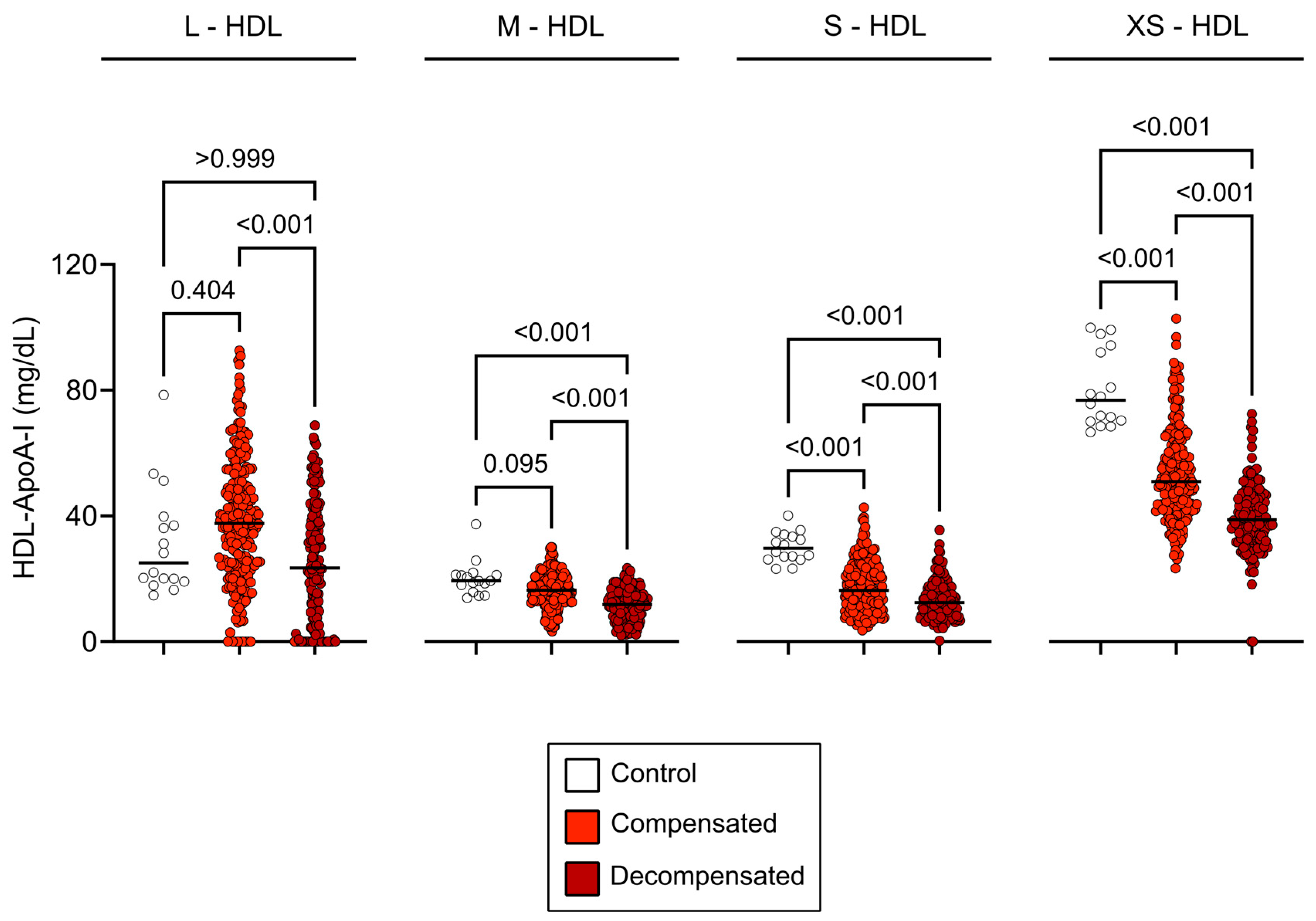
3.2. HDL Subclass Distribution in Cirrhosis
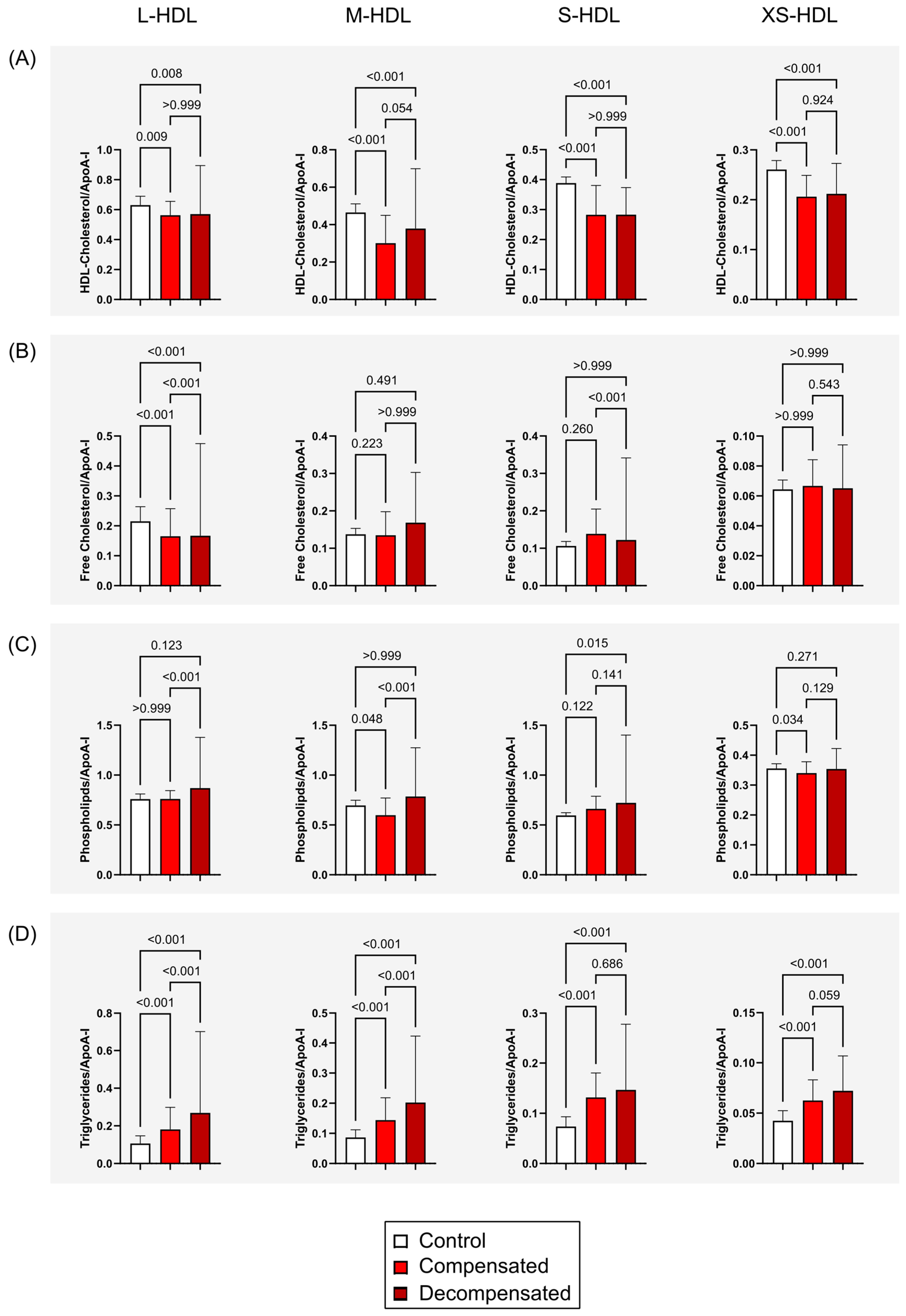
3.3. Composition of HDL Subclasses in Patients with Cirrhosis
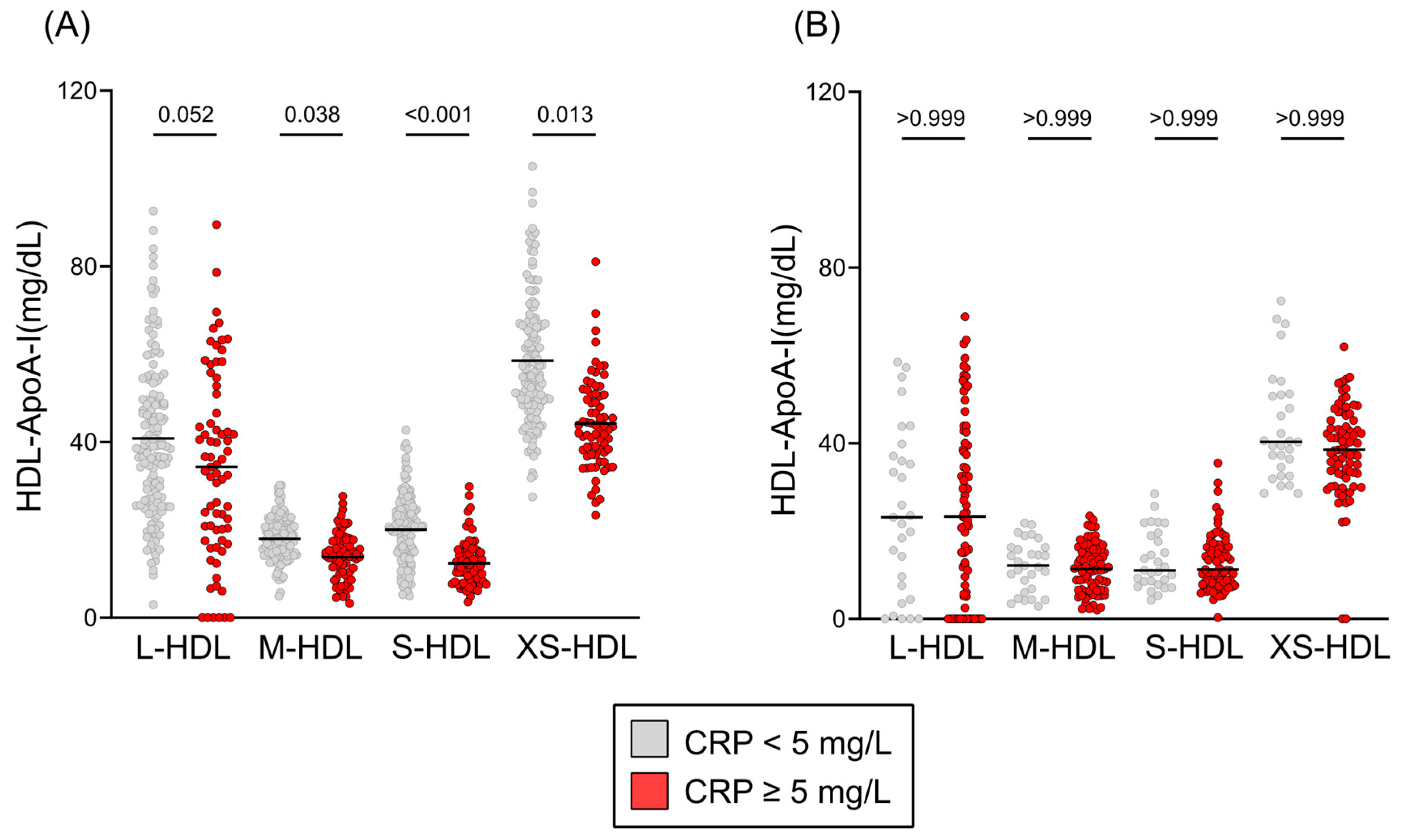
3.4. Inflammation, Etiology of Liver Failure, and HDL Subclass Distribution
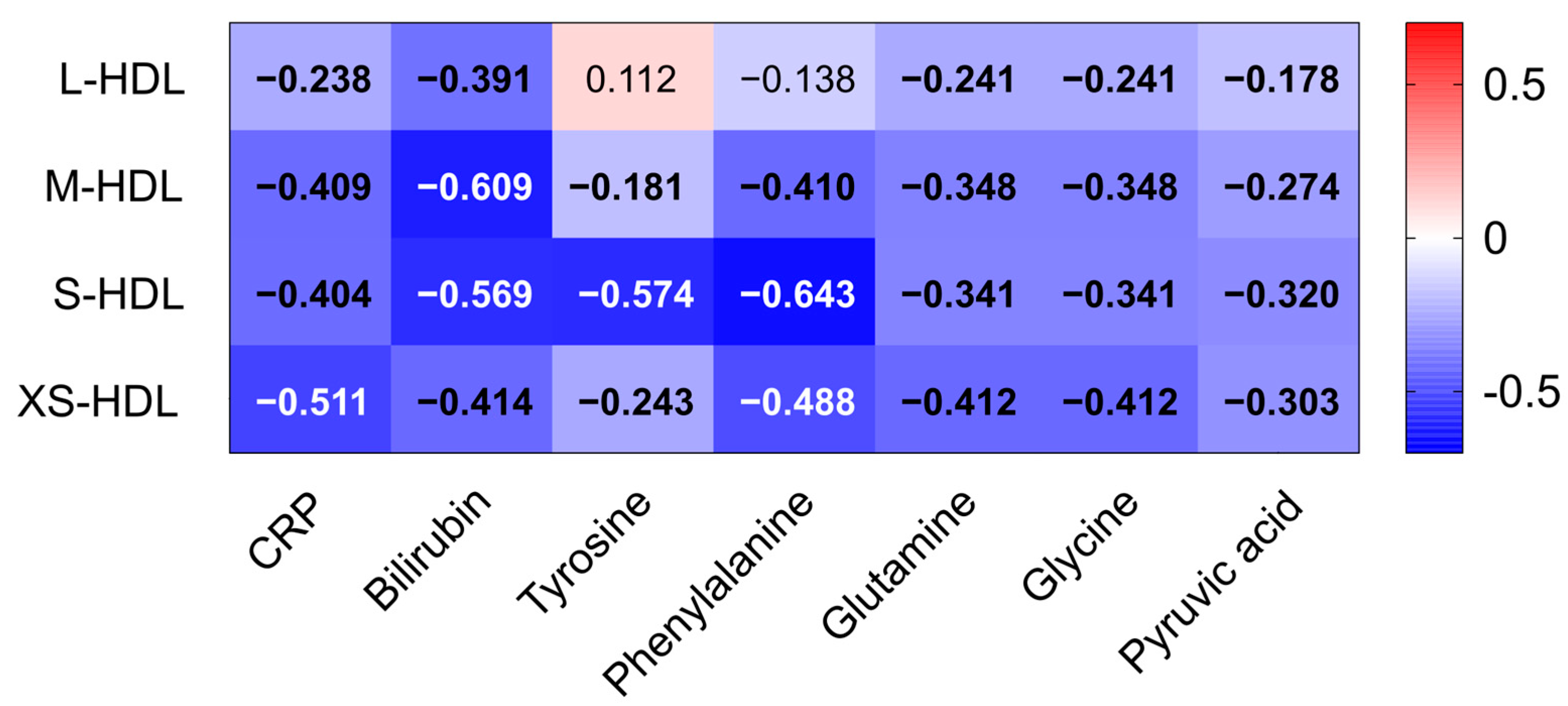
3.5. Associations of HDL Subclasses with Markers of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Liver Dysfunction
3.6. HDL Subclasses and Mortality in Compensated and Decompensated Cirrhosis
3.7. HDL Subclasses as Predictors of Mortality in Liver Cirrhosis
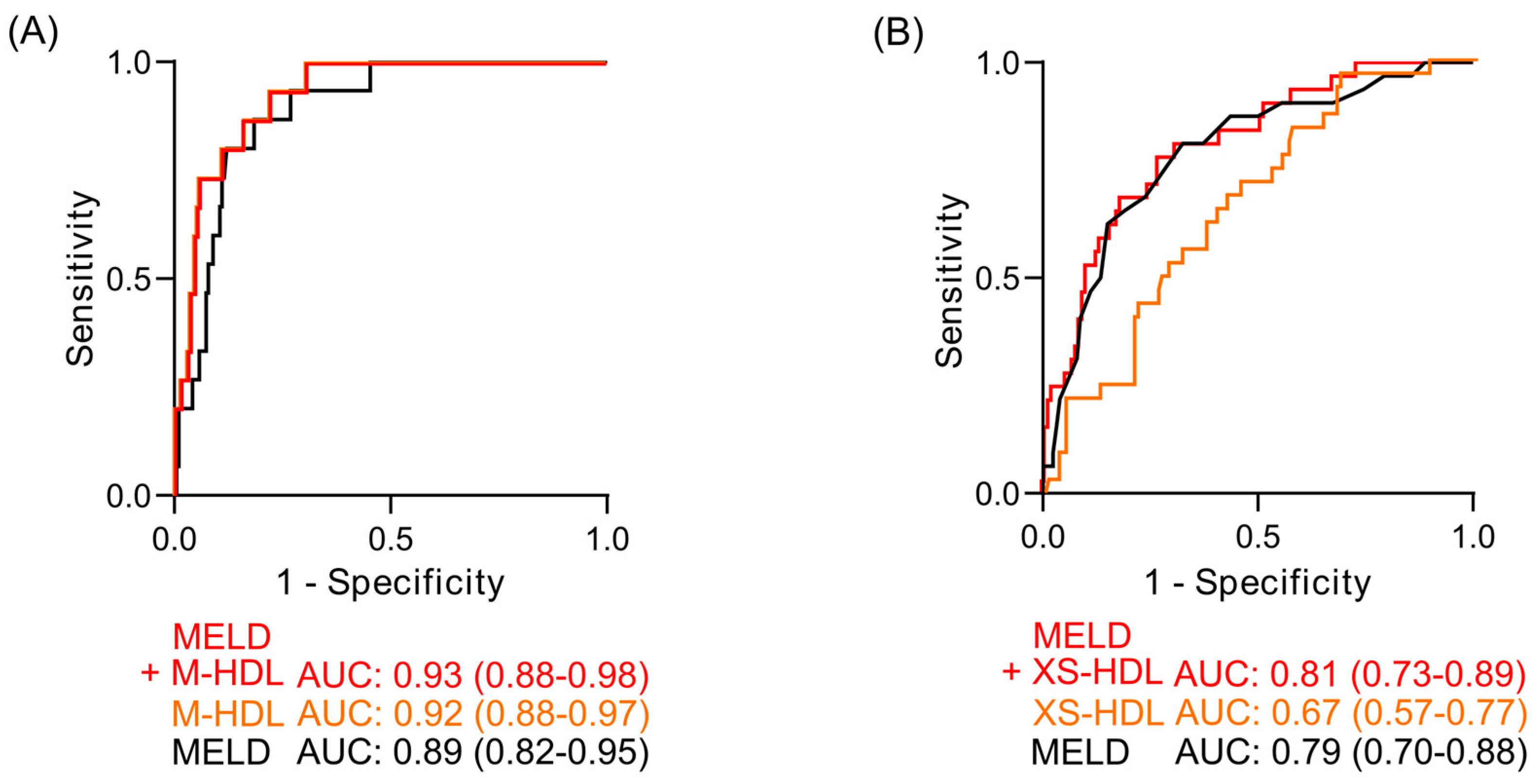
3.8. Receiver Operating Characteristic Analyses of HDL Subclasses as Mortality Predictors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ApoA-I | apolipoprotein-A-I |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CETP | cholesteryl ester transfer protein |
| CRP | c-reactive protein |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| LCAT | lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase |
| L-HDL | large HDL |
| LPL | lipoprotein lipase |
| MELD | model for end-stage liver disease |
| M-HDL | medium HDL |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| S-HDL | small HDL |
| SR-BI | scavenger receptor B1 |
| XS-HDL | extra small HDL |
References
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhu, X. Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels predicting poor outcomes in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1001411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trieb, M.; Horvath, A.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Spindelboeck, W.; Stadlbauer, V.; Taschler, U.; Curcic, S.; Stauber, R.E.; Holzer, M.; Pasterk, L.; et al. Liver disease alters high-density lipoprotein composition, metabolism and function. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacina, F.; Pirillo, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Norata, G.D. HDL in Immune-Inflammatory Responses: Implications beyond Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieb, M.; Rainer, F.; Stadlbauer, V.; Douschan, P.; Horvath, A.; Binder, L.; Trakaki, A.; Knuplez, E.; Scharnagl, H.; Stojakovic, T.; et al. HDL-related biomarkers are robust predictors of survival in patients with chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Chandler, V.; Chakraborty, S. Oxidative Stress–Induced Liver Damage and Remodeling of the Liver Vasculature. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontush, A.; Chapman, M.J. Antiatherogenic small, dense HDL—Guardian angel of the arterial wall? Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2006, 3, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B.; Davidson, W.S.; Fayad, Z.A.; Fuster, V.; Goldstein, J.; Hellerstein, M.; Jiang, X.-C.; Phillips, M.C.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux and Atheroprotection. Circulation 2012, 125, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, P.J.; Nicholls, S.; Rye, K.-A.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M. Antiinflammatory Properties of HDL. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Stadler, J.T.; Marsche, G. HDL-based therapeutics: A promising frontier in combating viral and bacterial infections. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 260, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camont, L.; Chapman, M.J.; Kontush, A. Biological activities of HDL subpopulations and their relevance to cardiovascular disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.S.; Khokhar, A.A.; May, H.T.; Kulkarni, K.R.; Blaha, M.J.; Joshi, P.H.; Toth, P.P.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Anderson, J.L.; Knight, S.; et al. on behalf of the Lipoprotein Investigators Collaborative (LIC). HDL cholesterol subclasses, myocardial infarction, and mortality in secondary prevention: The lipoprotein investigators collaborative. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pammer, A.; Klobučar, I.; Stadler, J.T.; Meissl, S.; Habisch, H.; Madl, T.; Frank, S.; Degoricija, V.; Marsche, G. Impaired HDL antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions are linked to increased mortality in acute heart failure patients. Redox Biol. 2024, 76, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duparc, T.; Ruidavets, J.-B.; Genoux, A.; Ingueneau, C.; Najib, S.; Ferrières, J.; Perret, B.; Martinez, L.O. Serum level of HDL particles are independently associated with long-term prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease: The GENES study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsløf, M.; Pedersen, K.M.; Afzal, S.; Smith, G.D.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Lower levels of small HDL particles associated with increased infectious disease morbidity and mortality: A population-based cohort study of 30,195 individuals. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Is a Distinct Syndrome That Develops in Patients With Acute Decompensation of Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streese, L.; Habisch, H.; Deiseroth, A.; Carrard, J.; Infanger, D.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Madl, T.; Hanssen, H. Lipoprotein Subclasses Independently Contribute to Subclinical Variance of Microvascular and Macrovascular Health. Molecules 2022, 27, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, P.; Kiwanuka, E.; Vettore, M.; Barazzoni, R.; Zanetti, M.; Cecchet, D.; Orlando, R. Phenylalanine and tyrosine kinetics in compensated liver cirrhosis: Effects of meal ingestion. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G598–G604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Darabi, M.; Tubeuf, E.; Canicio, A.; Lhomme, M.; Frisdal, E.; Lanfranchi-Lebreton, S.; Matheron, L.; Rached, F.; Ponnaiah, M.; et al. Free cholesterol transfer to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) upon triglyceride lipolysis underlies the U-shape relationship between HDL-cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-González, J.A.; Martínez-Sierra, C.; Rodriguez-Ramos, C.; Macías, M.A.; Rendón, P.; Díaz, F.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, C.; Martín-Herrera, L. Implication of inflammation-related cytokines in the natural history of liver cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2004, 24, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauneuf, B.; Champigneulle, B.; Soummer, A.; Mongardon, N.; Charpentier, J.; Cariou, A.; Chiche, J.-D.; Mallet, V.; Mira, J.-P.; Pène, F. Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with septic shock. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Linde-Zwirble, W.T.; Lidicker, J.; Clermont, G.; Carcillo, J.; Pinsky, M.R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1303. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/fulltext/2001/07000/epidemiology_of_severe_sepsis_in_the_united.2.aspx (accessed on 27 February 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.B.; Nair, P.; Koshy, A.K.; Krishnapriya, S.; Greeshma, C.R.; Venu, R.P. Role of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) as a Clinical Predictor of Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease (CLD). Int. J. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 1795851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbois, A.; Thabut, D.; Tazi, K.A.; Rudler, M.; Mohammadi, M.S.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Bennani, H.; Bezeaud, A.; Tellier, Z.; Guichard, C.; et al. Ex vivo effects of high-density lipoprotein exposure on the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in patients with severe cirrhosis†. Hepatology 2009, 49, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, N.A.; Gonzalez-Aldaco, K.; Roman, S.; Panduro, A. Chapter 9-The Immune System and Viral Hepatitis. In Liver Pathophysiology; Muriel, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumstark, D.; Pagel, P.; Eiglsperger, J.; Pfahlert, V.; Huber, F. NMR spectroscopy—A modern analytical tool for serum analytics of lipoproteins and metabolites. LaboratoriumsMedizin 2015, 38, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, J.E.; Andreassen, T.; Olsen, D.A.; Vestergaard, K.; Madsen, J.S.; Kristensen, S.R.; Pedersen, S. Serum Lipoprotein Profiling by NMR Spectroscopy Reveals Alterations in HDL-1 and HDL-2 Apo-A2 Subfractions in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Dong, J. Effect of serum lipid subfractions on nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy’s ability to detect coronary atherosclerosis early. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 2023, 4, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compensated Cirrhosis (n = 205) | Decompensated Cirrhosis (n = 158) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58 (52–63) | 58 (51–66) | 0.092 |
| Gender (female) | 52 (25.4) | 61 (38.6) | 0.007 |
| MELD Score | 11.60 (8.82–16.12) | 18.00 (13.00–22.25) | <0.001 |
| Albumin | 3.90 (3.30–4.40) | 3.00 (2.60–3.40) | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin [mg/dL] | 1.39 (0.80–2.87) | 2.83 (1.40–6.79) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine [mg/dL] | 0.83 (0.72–1.02) | 0.90 (0.73–1.55) | 0.004 |
| INR | 1.29 (1.17–1.49) | 1.46 (1.27–1.85) | <0.001 |
| WBC | 5.14 (3.90–6.63) | 5.70 (4.20–8.25) | 0.007 |
| CRP | 3.05 (1.20–8.03) | 15.50 (4.6–38.10) | <0.001 |
| Total Cholesterol | 175.36 (43.45–336.91) | 119.79 (92.32–151.17) | <0.001 |
| HDL-Cholesterol | 43.37 (0.06–85.13) | 28.30 (20.04–40.44) | <0.001 |
| Etiology | <0.001 | ||
| Alcohol | 123 (55.40) | 62 (39.20) | |
| Virus | 36 (16.20) | 51 (32.30) | |
| Other | 54 (24.3) | 28 (17.70) | |
| 90-day mortality | 8 (3.90) | 32 (20.30) | <0.001 |
| 12 months mortality | 15 (7.30) | 55 (34.80) | <0.001 |
| Compensated | Decompensated | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | HR (95% CI) Per 1 SD | p-Value | HR (95% CI) Per 1 SD | p-Value |
| Total HDL-ApoA-I | 0.43 (0.21–0.87) | 0.019 | 0.75 (0.49–1.15) | 0.189 |
| L-HDL-ApoA-I | 0.49 (0.23–1.04) | 0.063 | 0.83 (0.54–1.28) | 0.399 |
| M-HDL-ApoA-I | 0.09 (0.03–0.33) | <0.001 | 0.73 (0.46–1.16) | 0.178 |
| S-HDL-ApoA-I | 0.10 (0.03–0.39) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.54–1.55) | 0.730 |
| XS-HDL-ApoA-I | 0.24 (0.10–0.58) | 0.001 | 0.46 (0.28–0.78) | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pammer, A.; Madl, T.; Habisch, H.; Kerbl-Knapp, J.; Rainer, F.; Stadlbauer, V.; Horvath, A.; Douschan, P.; Stauber, R.E.; Marsche, G. Depletion of Small HDL Subclasses Predicts Poor Survival in Liver Cirrhosis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060664
Pammer A, Madl T, Habisch H, Kerbl-Knapp J, Rainer F, Stadlbauer V, Horvath A, Douschan P, Stauber RE, Marsche G. Depletion of Small HDL Subclasses Predicts Poor Survival in Liver Cirrhosis. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(6):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060664
Chicago/Turabian StylePammer, Anja, Tobias Madl, Hansjörg Habisch, Jakob Kerbl-Knapp, Florian Rainer, Vanessa Stadlbauer, Angela Horvath, Philipp Douschan, Rudolf E. Stauber, and Gunther Marsche. 2025. "Depletion of Small HDL Subclasses Predicts Poor Survival in Liver Cirrhosis" Antioxidants 14, no. 6: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060664
APA StylePammer, A., Madl, T., Habisch, H., Kerbl-Knapp, J., Rainer, F., Stadlbauer, V., Horvath, A., Douschan, P., Stauber, R. E., & Marsche, G. (2025). Depletion of Small HDL Subclasses Predicts Poor Survival in Liver Cirrhosis. Antioxidants, 14(6), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14060664










