Abstract
The Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) Neurogenic locus NOTCH homolog protein (NOTCH) crosstalk has emerged as a critical regulatory axis in the progression of solid cancers, especially lung, affecting tumor growth and resistance to therapy. NRF2 is a master transcription factor that orchestrates the cellular antioxidant response, while NOTCH signaling is involved in the cell–cell communication processes by influencing the patterns of gene expression and differentiation. Although frequently altered independently, genetic and epigenetic dysregulation of both NRF2 and NOTCH pathways often converge to deregulate oxidative stress responses and promote tumor cell survival. Recent findings reveal that the NRF2/NOTCH interplay extends beyond canonical signaling, contributing to metabolic reprogramming and reshaping the tumor microenvironment (TME) to promote cancer malignancy. Emerging scientific evidences highlight the key role of biochemical and metabolomic changes within NRF2–NOTCH crosstalk, in contributing to cancer progression and metabolic reprogramming, beyond facilitating the adaptation of cancer cells to the TME. Actually, the effects of the NRF2–NOTCH bidirectional interaction in either supporting or suppressing lung tumor phenotypes are still unclear. This review explores the molecular mechanisms underlying NRF2–NOTCH crosstalk in lung cancer, highlighting the impact of genetic and epigenetic deregulation mechanisms on neoplastic processes, modulating the TME and driving the metabolic reprogramming. Furthermore, we discuss therapeutic opportunities for targeting this regulatory network, which may open new avenues for overcoming drug resistance and improving clinical outcomes in lung cancer.
1. Introduction
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) and Neurogenic locus NOTCH homolog protein (NOTCH) are master regulators of signaling pathways that orchestrate several biological and cellular behaviors as well as cell proliferation, self-renewal, differentiation, and response to physical and chemical insults [1]. NOTCH1–NOTCH4 receptors belong to single-pass trans-membrane family proteins that are activated by canonical ligands belonging to the Delta-like and Serrate/Jagged families. They are essential for the determination of cell fate and the maintenance of homeostasis in multiple tissues and organs [2]. However, in solid cancers, NOTCH signaling can be considered as a two-sided coin, since, on the one hand, it contributes to guide tumor growth but, on the other hand, it has been reported that its oncogenic properties could switch towards a suppressor role where cell proliferation and survival are strongly limited by cellular context [3].
The transcription factor NRF2, encoded by NFE2L2 gene, exerts a protective activity in counteracting the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS are generated during mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and in response to xenobiotics [4,5]. Under cellular stress, NRF2 dissociates from the binding with its negative regulator Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1), moves into the nucleus and activates the transcription of several cytoprotective genes through the interaction with their antioxidant response elements (AREs) [6]. In an oncogenic context, the aberrant activation of NRF2 leads to elevated oxidative stress tolerance, enhanced proliferation, tumor progression, and altered metabolic reprogramming, that collectively contribute to resistance against chemotherapy and radiotherapy [7]. It would be interesting to investigate whether an increased efficacy of chemo- and radiotherapy and a reduced lung cancer cell resistance may arise from dual pharmacological targeting of NRF2 and NOTCH pathways, so as to represent a promising therapeutic strategy in preclinical and clinical studies [8,9].
Over the past nine years, critical progress has significantly reshaped the understanding of NRF2–NOTCH crosstalk in lung cancer. First, new mechanistic insights revealed that NRF2 directly activates NOTCH1 transcription by binding antioxidant response elements (AREs) within its promoter, establishing a stress-responsive transcriptional axis [10]. Conversely, canonical NOTCH targets such as Hairy and Enhancer of Split 1 (HES1) and Hairy/Enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1 (HEY1) have been shown to modulate NRF2 target gene expression, forming a functional feedback loop that coordinates redox homeostasis with proliferation and cell differentiation [11]. This bidirectional regulatory architecture was not discussed in our prior review [12]. Second, recent work has uncovered a major role of epigenetic modulation—such as aberrant promoter methylation of NFE2L2 and NOTCH genes or histone remodeling via Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) and Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)—in fine-tuning NRF2–NOTCH signaling output, thus linking chromatin state to redox and developmental signaling plasticity [13]. Third, the metabolic dimension of the NRF2–NOTCH interplay has emerged as a key node of convergence, with coordinated regulation of glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway, and glutaminolysis contributing to metabolic reprogramming, NADPH production, and antioxidant defense [14]. The increasing evidence in this field significantly expands the know-how on functional NRF2–NOTCH crosstalk and connects to hallmark features of tumor progression and treatment resistance.
Finally, in terms of scope, the present manuscript offers a substantial and systematic expansion beyond our previous review. The reported and updated literature includes critical findings on emerging regulatory layers and crosstalk mechanisms, not previously addressed [12]. While our prior review focused predominantly on genetic and transcriptional aspects of NRF2 and NOTCH signaling, the present work increases the coverage to include: (1) epigenetic deregulation, not only related to DNA methylation but also included histone acetylation/methylation patterns, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) that modulate NRF2–NOTCH signaling [15]; (2) tumor metabolism, describing how NRF2-driven glycolytic flux and glutaminolysis interact with NOTCH-mediated metabolic shifts under hypoxia [16]; (3) post-translational modifications including phosphorylation, ubiquitination events that fine-tune the stability, localization, and activity of NRF2 and NOTCH proteins (e.g., KEAP1-Cullin 3 (CUL3)-NRF2 axis) [17].
By integrating these multi-layered regulatory mechanisms [18], here we present a more comprehensive genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic evidence underlying NRF2 and NOTCH signaling, underlining the importance of this crosstalk as a potential molecular target to provide new insights into therapeutic strategies for patients with lung tumors.
2. NRF2 Signaling: From Physiological Guardian to Oncological Role
Physiologically, cells respond to stress by activating molecular and energy-related processes to restore homeostasis, increasing catabolic activity and oxidative phosphorylation, which leads to ROS accumulation and oxidative stress [5,19]. To survive, tumor cells exploit antioxidant systems linked to enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase (CAT), while hijacking transcription factors, including Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) domain proteins, named for the basic amino acid residues in the alpha-helical regions, to regulate gene expression and sustain malignant growth [6,20].
A subfamily of these transcription factors, the Cap ‘n’ Collar (CNC) proteins, possesses a 43-amino acid conserved region (CNC domain) at the N-terminal portion [21]. One of the main transcription factors within the CNC-Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) protein family is NRF2, which serves as a master regulator of stress responses under physiological condition. Cancer cells can manipulate the NRF2-KEAP1 cellular pathway to survival and progress [22]. In response to endogenous or exogenous stressors, NRF2 forms a transcriptional complex with its direct heterodimeric partner, small Maf (sMaf), and co-factors such as CREB-binding protein (CBP)/p300. This complex binds to numerous ARE of genes, implicated in cellular adaptation and homeostasis maintenance [23]. The NRF2 pathway is finely regulated by a ubiquitination system that operates under normal cellular homeostasis when an active stress response is unnecessary [24]. The proteasomal ubiquitination system continuously degrades NRF2 by polyubiquitination of NRF2 at seven key lysine residues via KEAP1, an adaptor protein of CUL3–ring-box 1 (RBX1)-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [25] (Figure 1).
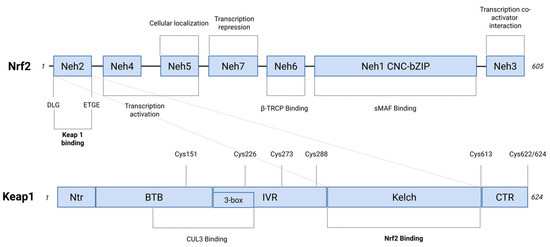
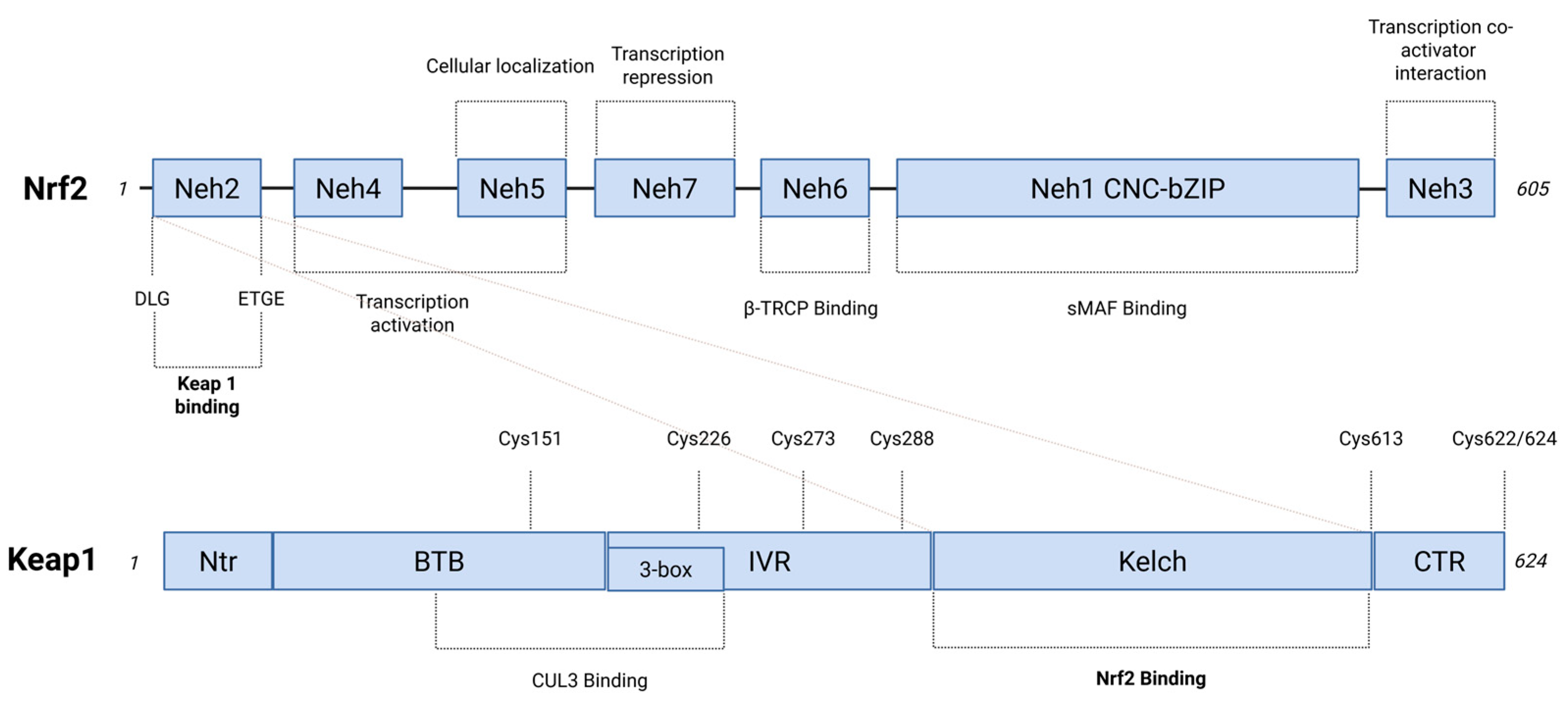
Figure 1.
Functional NRF2 and KEAP1 proteins domains. On the top, NRF2 is a 605 amino acid protein that consists of seven functional domains (Neh1–Neh7), each of which leads to the modulation of both NRF2 transcriptional activity and protein stability. KEAP1-binding region is located within the amino-terminal Neh2 domain that contains Asp-Leu-Gly (DLG) and Glu-Thr-Gly-Glu (ETGE) motifs. The β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TRCP) interaction occurs in the Neh6 domain. The binding to sMAF (small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma) transcription factors takes place through the Neh1 domain. This interaction affects Cap ‘n’ Collar basic leucine zipper (CNC-bZIP) motif, which is responsible for mediating the binding of AREs (antioxidant response elements). The figure includes the functional roles from Neh1 to Neh7 domains. On the bottom, five domains represent the structure of the KEAP1 protein (624 amino acids residues): Ntr (the N-terminal region), Broad complex, Tramtrack, and Bric-a-brac (BTB), intervening region (IVR), double glycine repeat (DGR) that consists of six kelch repeats, which is involved in the binding sites that interact with NRF2 (Kelch), CTR (C-terminal region). The BTB and IVR domains are involved in Cullin 3 (CUL3) binding, leading to the formation of E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. A dashed line indicates the KEAP1 stress-sensing function by linking the three regions that define the H2O2 stress sensor center (Created with BioRender.com, Licensing and Agreement number EZ285EVYX5, accessed on 15 April 2025).
The activity of NRF2 is regulated by two primaries KEAP1-dependent and KEAP1-independent pathways [6,26]. In the KEAP1-dependent pathway, thiol-reactive compounds, such as ROS, induce conformational changes in KEAP1, preventing NRF2 ubiquitination. These conformational changes are facilitated by sensor amino acids such as cysteine residues of KEAP1, which undergo modifications upon reacting with ROS [24]. The accumulation of NRF2 in the cytoplasm promotes its translocation into the nucleus, where it functions as a transcription factor by binding to AREs of several genes [27]. Once homeostasis is restored, NRF2 is exported back to the cytosol via KEAP1, which enters the nucleus through karyopherin alpha 6 (KPNa6), [28]. Additionally, KEAP1 itself can be subjected to ubiquitination. Under stress conditions, a key regulator of this process is Sequestosome 1 (p62), which binds to KEAP1, thereby disrupting its interaction with NRF2. This interaction facilitates KEAP1 degradation via the autophagy–lysosomal pathway, mediated by the vesicular protein complex LC3 [6]. KEAP1-independent NRF2 regulation involves proteins that compete with KEAP1 for NRF2 binding, as protein kinases that modulate NRF2 interactions with the ubiquitination complex [6]. Other transcription factors, such as nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), may also play a role in NRF2 regulation, although the precise interconnections between these pathways remain unclear [29].
Notably, KEAP1 has been shown to bind to Inhibitory kappa B kinase beta (IKKβ), promoting its ubiquitination and degradation [30]. Additionally, the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) transcription factors contribute to KEAP1-independent NRF2 regulation by activating both ARE and xenobiotic-responsive elements (XREs) found in proximity within the promoters of several NRF2-regulated genes, including NRF2 itself [31]. Beyond these mechanisms, many post-transcriptional regulatory processes, such as microRNA (miRNA)-mediated regulation, phosphorylation, and acetylation, can also influence NRF2 activity, contributing to its nuclear exclusion and degradation [32].
Given its ability to protect cells, NRF2 plays a dual role in cellular homeostasis [33]. While it serves as a guardian of cellular defense under normal conditions, it can also transition into a proto-oncogene when hijacked by tumor cells, contributing to treatment resistance [34]. NRF2 is a key regulator of antioxidant response and cellular detoxification, mediating the transcription of genes such as glutamate–cysteine ligase catalytic/modifier subunit (GCLC/M) and glutathione S-reductase (GSR), which are essential for glutathione synthesis and recycling [35]. It also regulates heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), peroxiredoxin-1/4, superoxide dismutases (SODs), thioredoxin (TRX), thioredoxin reductase 1 (TRXR1), and aldo-keto reductases (AKRs), all of which play crucial roles in detoxifying xenobiotic compounds [36]. Studies on NRF2-knockout mice have demonstrated the importance of this pathway, revealing an absence of cytoprotective effects, increased tissue damage, and heightened carcinogenesis [22].
However, the loss of NRF2’s protective function is not solely due to its exploitation by tumor cells [37]. Dysregulation of the pathway at the physiological level leads to alterations in the cellular microenvironment, which, when chronically exposed to stress factors, undergoes aging processes that may culminate in tumorigenesis [38]. Persistent inflammation drives oxidative stress, which in turn disrupts NRF2 homeostasis [24,39]. This persistent activation can result in sustained pathway upregulation, promoting the survival of precancerous lesions that would otherwise undergo elimination, and thereby contributing to tumor initiation and progression [40].
In addition to external factors, genetic and epigenetic alterations also play a role in converting NFE2L2 into a proto-oncogene. In this context, NRF2 intersects key oncogenic pathways, including Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS), v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF), and MYC (c-myc), and provides protection from ROS and sustains the reducing environment necessary for anabolic metabolism in proliferating cells [41]. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway, loss of Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) signaling also work in concert with NRF2 to promote tumor growth [42]. The interaction of NRF2 with estrogen receptors also contributes to the dual role of NRF2 in cellular processes. The interplay between estrogens and NRF2 suggests a cytoprotective effect mediated by female hormones [43]. Studies have shown that 17β-estradiol (E2) enhances cell viability, reduces ROS production, activates Akt signaling, and inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), leading to increased NRF2 activity [44]. This results in upregulated HO-1 expression and SOD activity, which mitigate the neurotoxic effects of homocysteine [45]. In mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), E2 treatment induces nuclear translocation of NRF2 enhancing tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced NF-κB activation and upregulates its downstream target, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) [46]. Alternatively, tumor cells can exploit this mechanism to enhance their defenses against oxidative stress, thereby improving survival and proliferation [47]. Moreover, 17β-estradiol cooperates with ER-α36- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) signaling, further amplifying NRF2 activation and promoting cell proliferation [44]. This interaction can activate the Ras/PI3K/PTEN/Akt pathway, which enhances NRF2 nuclear translocation and stability, ultimately contributing to tumor progression [42].
Finally, NRF2 dysregulated may contribute to tumorigenesis by suppressing apoptosis and promoting cancer cell survival via the tumor protein 53 (p53), often referred to as the “guardian of the genome” due its crucial role in maintaining genomic integrity [48,49]. NRF2 can influence p53 regulation through the induction of Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2), which in turn inhibits p53 activity [37].
3. Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms of KEAP1 and NFE2L2 and Their Role in Lung Cancer Development and Progression
Somatic mutations of KEAP1 and NFE2L2 genes are frequent in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLCs), and show specific molecular pattern linked to different histological subtypes of lung cancer [50]. More specifically, and as reported in many other scientific contexts, The Cancer Genome Atlas Network (TCGA) reported the recurrence of these mutations in lung adenocarcinomas (LUADs, 23% of cases) and in lung squamous cell carcinomas (LUSC, 34% of cases), respectively [51,52,53].
KEAP1 loss-of-function (LOF) and NFE2L2 gain-of-function (GOF) mutations exhibited a mutually exclusive pattern, demonstrating that the overexpression of NRF2 may contribute as pivotal mechanism in the selection of specific cancers or stages of tumor progression, including lung cancer [54]. A total of 174 somatic mutations in KEAP1 have been found, predominantly clustering in the intervening region (IVR) domain with missense/pathogenic significance (e.g., p.D236H, p.E242K, p.S243C, p.R272C, p.D294Y) [55]. Chemical modifications of cysteines within these domains disrupted the NRF2-KEAP1 interactions [17]. Meanwhile, KEAP1 gene mutations at KELCH1-6 domains (e.g., p.R320Q, p.G364C, p.L413R, p.A466P, p.W544C, p.G570V), which interact with N-terminal Neh2 domain of NRF2, resulted in a dysregulated ability of KEAP1 to repress NRF2 [56,57,58,59].
Additionally, KEAP1 heterozygous mutations contribute to NRF2 hyperactivation, as the loss of both KEAP1 gene copies is not a critical event [60]. This can be explained by mutations in the Kelch-like domain acting with a dominant negative effect by forming heterodimers with wild-type proteins and disrupting NRF2 association [61]. On the other hand, somatic mutations in NFE2L2 gene were found to be mainly located in the protein domains of DLG or ETGE (e.g., p.D29N, p.R34G, p.E79K, p.G81V). Aminoacidic NRF2 changes inhibited KEAP1-mediated NRF2 degradation, leading to its stabilization, abnormal nuclear accumulation with constitutive activation of cytoprotective enzymes [62].
Interestingly, most mutations that occurred in KEAP1 or NFE2L2 genes aligned with a smoking-associated mutational signature that predominates in early tumorigenesis, although only a very small subset showed a tendency to co-occur [63]. In LUSC, these genetic alterations recurred in about a third of all diagnosed cases, more frequently these are mutational events combined with copy number variations (CNVs) [51]. Over the years, in a pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) cohort, Fernandez-Cuesta and colleagues identified KEAP1 genetic alterations as a specific molecular hallmark with adenocarcinoma-like features [64].
KEAP1 mutations frequently coexist with other genetic alterations, suggesting cooperative events that drive their selection [65]. For example, it has been reported that KEAP1 alterations often co-occur with STK11 (serine/threonine kinase 11) and KRAS mutations in LUAD; likewise, NFE2L2 and TP53 co-mutations but in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) [50]. KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinomas often carried loss-of-function mutations in KEAP1 [66], and co-mutations involving the PI3K-AKT-mTOR and NRF2 pathways, such as NFE2L2 amplification combined with loss of STK11, have also been observed [67].
Tao and collaborators were among the first to offer compelling evidences that oncogenic KRAS upregulates NRF2 transcription levels via 12-O-tetradecanoylphorphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) at the exon 1 within its promoter region. In a murine model, they demonstrated that the inhibition of NRF2 pathway effectively contributed to overcome KRAS-mediated chemoresistance [68]. Similarly, in the context of resistance to targeted therapy, NFE2L2 mutations may enhance cell survival under crizotinib treatment, enabling the acquisition of additional resistance mutations over time [69]. Arbour and collaborators identified a molecular subtype of KRAS-mutant NSCLC with co-mutations in KEAP1 and NFE2L2 genes, where patients had significantly shorter overall survival (OS), and a reduced duration of platinum-based chemotherapy response compared to other KRAS-mutant NSCLC patients [70].
These findings supported previous preclinical studies highlighting the role of NRF2-KEAP1 pathway deregulation in increasing resistance to radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy agents [71,72]. In this context, KEAP1-driven co-mutations were also found unresponsive to immunotherapy, despite high tumor mutational burden (TMB), with a decreased OS in LUAD patients [73]. In this subtype of lung cancer, Zavitsanou and coworkers demonstrated that KEAP1-mutant tumors were able to suppress dendritic cell and T cell responses, creating an immunosuppressive phenotype that could drive resistance to immunotherapy. Using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats—CRISPR associated protein 9 (CRISPR-Cas9) editing revealed that NRF2 pathway hyperactivation might contribute to impaired immune responses in KEAP1-mutant tumors in LUAD antigenic model and LUAD patient samples [74].
Given the significant impact of NRF2-KEAP1 genetic alterations on treatment resistance and patient outcome, the modulation of this pathway represents a promising therapeutic strategy [75]. Goeman et al. defined a distinct molecular subtype of chemotherapy-resistant and shorter OS and progression-free survival (PFS) in LUAD patients based on NFE2L2 and KEAP1 mutations profiling. Additionally, this study reported that KEAP1 mutations were enriched in patients with high TMB but were associated with low T-cell infiltration, suggesting a key role for KEAP1 alterations in immune evasion [76].
Similarly, KEAP1 mutations were found to be associated with poorer clinical outcomes in LUAD patients receiving pembrolizumab in combination with carboplatin and pemetrexed, the standard first-line treatment options for driver-negative non-squamous NSCLC [77]. As a result, these findings suggested an enhanced NRF2 activity and functional inactivation of KEAP1 in order to discriminate a molecular signature of specific subtype of NSCLC, defined by resistance to treatment and accelerated disease progression [78].
Beyond genetic mutations, the NRF2-KEAP1 pathway is also controlled by epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, miRNAs and lncRNAs expression, which play a pivotal role in the regulation of gene expression without altering DNA sequence [56]. Ongoing research in this field aims to develop interventions targeting NRF2-KEAP1 epigenetic modifications that can be reversible or inherited during cell division, with the potential for chemoprevention, overcoming resistance and improving prognosis for NSCLC patients [79].
Recently, Elshaer and colleagues reported that DNA methylation alterations were associated with KEAP1 mutations in LUAD patients, potentially shaping the NRF2 regulatory network functions. Using the Illumina Infinium Human DNA Methylation 450 K array platform, they demonstrated that the 8-gene signature of NRF2 targets exhibited low cytosine-guanine (CpG) dinucleotides methylation and increased gene expression levels in patients harboring KEAP1 mutations [80].
DNA methylation of KEAP1 has been more frequently studied than NFE2L2 across multiple cancer models, revealing distinct methylation patterns at KEAP1 promoter region when comparing normal and tumor lung tissues [81,82,83]. In vitro, Muscarella et al. reported that approximately 50% of NSCLC and 42% of SCLC cell lines showed a global DNA methylation at the KEAP1 promoter, thus reducing gene expression. Moreover, an epigenetic screening of 47 NSCLC patient samples revealed KEAP1 methylation in 47% of cases by quantitative methylation-specific PCR (qMSP) to detect a distinct group of CpG sites [84].
Methylation studies have revealed significant changes in KEAP1 epigenetic patterns in cancer cells from lung and other sides, mainly at CpG sites level at 5′ end, where the main KEAP1 CpG island was located [85,86]. More specifically, the first seven single CpG sites (1–7, P1a region) that were found to be significantly more methylated compared to the last six CpG sites (8–13, P1b region) at the P1 promoter region of lung cancer cells [87]. Previous studies have validated the binding of transcription factors, Specificity protein (Sp-1) and Activator Protein 2 (AP-2) to the KEAP1 promoter region at P1a region. As consequence, in lung cancer cells this binding is inhibited due to hypermethylation, suggesting the epigenetic interference in the modulation of KEAP1 expression in cancer cells [88]. Our group recently developed OPERA_MET-A, a multigene Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) panel, designed to detect differentially methylated cytosines across multiple solid cancer-related genes with notable results [89]. The NGS analysis confirms that the CpG methylation patterns of KEAP1 promoter can occur symmetrically in double-stranded, thus corroborating the effect of hypermethylation in suppressing KEAP1 gene expression and function [89]. Moreover, since aberrant methylation is reversible through epigenetic drugs, treatment of lung cancer cell lines, including lung carcinoid, small cell lung cancer (SCLC), and adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC), with the DNA methylation inhibitor 5′-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine; DAC) can restore KEAP1 expression by demethylating its promoter P1 region. Additionally, an inverse correlation was observed between KEAP1 expression and promoter methylation following DAC treatment [87].
Another pharmacological approach using DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitor genistein has been shown to induce demethylation of KEAP1 CpG promoter islands, leading to increased transcript levels with an overexpression of NRF2, GSS (Glutathione synthetase), and HO-1 transcription levels [90]. Moreover, epigenetic regulation of NRF2 is influenced by extra-terminal (BET) proteins, which interact with acetylated lysine residues on histones and non-histone proteins to either activate or repress NRF2-dependent genes [91]. Li and colleagues focused on the role of histone modification that regulates NFE2L2 repression through EZH2, a component of the polycomb PRC2 complex. EZH2 has been shown to inhibit lung cancer cell proliferation by silencing NFE2L2 expression, which led to an increased trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) marks at its promoter [92].
Murray-Stewart and collaborators demonstrated that histone deacetylation could reactivate another epigenetic alteration in NRF2-KEAP1 signaling pathway. This involves miR-200a, which has been shown to destabilize KEAP1 mRNA levels in lung tumor cell lines resistant to polyamine analogs [93]. NRF2-dependent regulation of miR-1 and miR-206 plays a crucial role in NSCLC proliferation and tumorigenesis by modulating the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). In primary tumor samples, these miRNAs were inversely correlated with PPP gene expression, while elevated expression of NRF2 target genes was associated with poor prognosis [94].
The overexpression of miR-155 mimic, designed to restore the endogenous miRNA activity, enhanced colony formation and cell migration while leading to a reduction in apoptosis in the human lung ASC resistant A549 (A549R) cell line [95]. This effect was significantly associated with high NRF2, NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) and HO-1 transcription levels. Conversely, the inhibition of miR-155 expression strongly reduced NRF2, NQO1, and HO-1 expression, accompanied with a decreasing in B cell lymphoma gene 2 (BCL2)/BCL-2-associated protein X (BAX) ratio. Finally, these results suggested that miR-155 mediated chemotherapy resistance by activating NRF2 signaling pathway with an inhibition of cellular apoptotic process [95].
Similarly, Duan and coworkers demonstrated that miR-421 overexpression in A549 lung cancer cells directly targeted 3′-untranslated region (3′UTR) of KEAP1 gene, leading to its downregulation with an increased proliferation and invasion but decreasing apoptosis process [96]. In addition, Yin and colleagues investigated the role of miR-144-3p in drug resistance in a set of lung cancer cells [97]. In this context, the expression of miR-144-3p was activated by NRF2 upon the binding to AREs in its promoter region. The targeting of this miRNA led to the downregulation of NRF2, resulting in decreased gene expression levels that were found to be associated with cisplatin resistance [97].
Furthermore, preliminary data were reported on miRNAs interacting with NRF2 and KEAP1 by gene expression profiling [98]. Our group demonstrated that the downregulation of miR-27 family (miR-27a and miR-27b) and the upregulation of miR-200 family (miR-200a), could significantly modulate NRF2-KEAP1 activity in NSCLC and SCLC cell lines panels, as well as in a training set of 29 tumors and adjacent normal tissues from NSCLC patients [99].
Interesting findings came from smoke and cancer-associated lncRNA 1 (SCAL1) and Nuclear LUCAT1 (NLUCAT1) in lung cancer cells through the regulation of oxidative stress. SCAL1 is considered the first NRF2-activated lncRNA, which is identified in airway epithelial cells against oxidative stress [100]. It has been reported that there are increased levels of SCAL1 upon cigarette smoking, with a significant correlation with NFE2L2 mutations [101]. Recently, Moreno Leon et al. reported that the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent transcription decreased the hypoxia-dependent expression of NLUCAT1, an NRF2-induced lncRNA [102]. Using CRISPR-Cas9, they demonstrated that NLUCAT1 knockdown in lung adenocarcinoma cells caused a lower proliferation rates, while an increasing ROS levels and sensitivity to cisplatin-induced apoptosis was found. These evidences suggested that this lncRNA is involved in the regulation of the NRF2-mediated antioxidant response with an impact on cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells [103].
A summary of genetic, epigenetic, and molecular alterations of the NRF2-KEAP1 pathway in lung cancer and their clinical significance is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
An overview of NRF2-KEAP1 pathway alterations in lung cancer, covering genetic mutations, epigenetic modifications, associated molecular mechanisms, and clinical implications.
4. NOTCH Signaling Hub in Lung Cancer: A Central Regulator of Tumor Progression
Dysregulation of NRF2 and NOTCH transcription factors is frequently observed in tumorigenesis, as their related-aberrant signaling can lead to uncontrolled proliferation, impaired differentiation, and resistance to apoptosis [104]. Among these, the NOTCH pathway stands out as a critical regulator of cellular processes linked to both normal development and cancer progression [105]. NOTCH signaling plays a pivotal role in maintaining stemness and orchestrating organogenesis, requiring precise regulatory control [106]. While proper NOTCH activity ensures orderly cellular differentiation, its dysregulation is frequently linked to carcinogenesis [107].
NOTCH plays a context-dependent role in cancer, acting as an oncogene in several malignancies via hyperactivation [108], but also as a tumor suppressor in specific settings [109]. It is fundamental in the regulation of differentiation and tissue repair following injury [2], and it is essential for developmental processes across various organs including skeletal, hepatic, cardiac, and hematopoietic systems. A hallmark of NOTCH-mediated development is its temporal coordination of control overgrowth and differentiation, contributing it to promote or inhibit proliferation based on context [110]. In cancer, deregulated NOTCH signaling leads to epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) [111], cancer stem-like cell maintenance [106], angiogenesis [112], and modulation of TME through immune cell recruitment and stromal interactions [113].
Like other receptor-mediated signaling pathways, NOTCH network comprises three key components: receptors, ligands, and downstream effectors [2]. In mammals, there are four NOTCH receptors (NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4, which are transmembrane proteins consisting of three main segments: NOTCH extracellular domain (NECD), that mediates ligand binding; a transmembrane domain (TMD), that anchors the receptor in the membrane; a NOTCH intracellular domain (NICD), that functions as the active signaling component upon cleavage (Figure 2). Five ligands interact with the extracellular domain of NOTCH receptors, classified into two groups based on their structural features: Serrate-like ligands: Jagged1 (JAG1) and Jagged2 (JAG2), which contain a cysteine-rich domain; delta-like ligands: DLL1, DLL3, and DLL4, which lack the cysteine-rich domain [114,115].
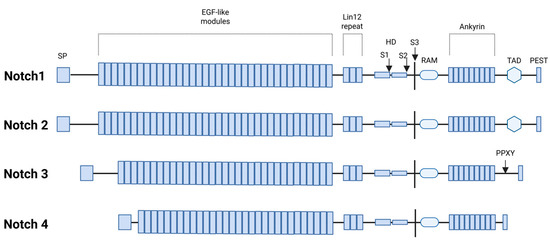
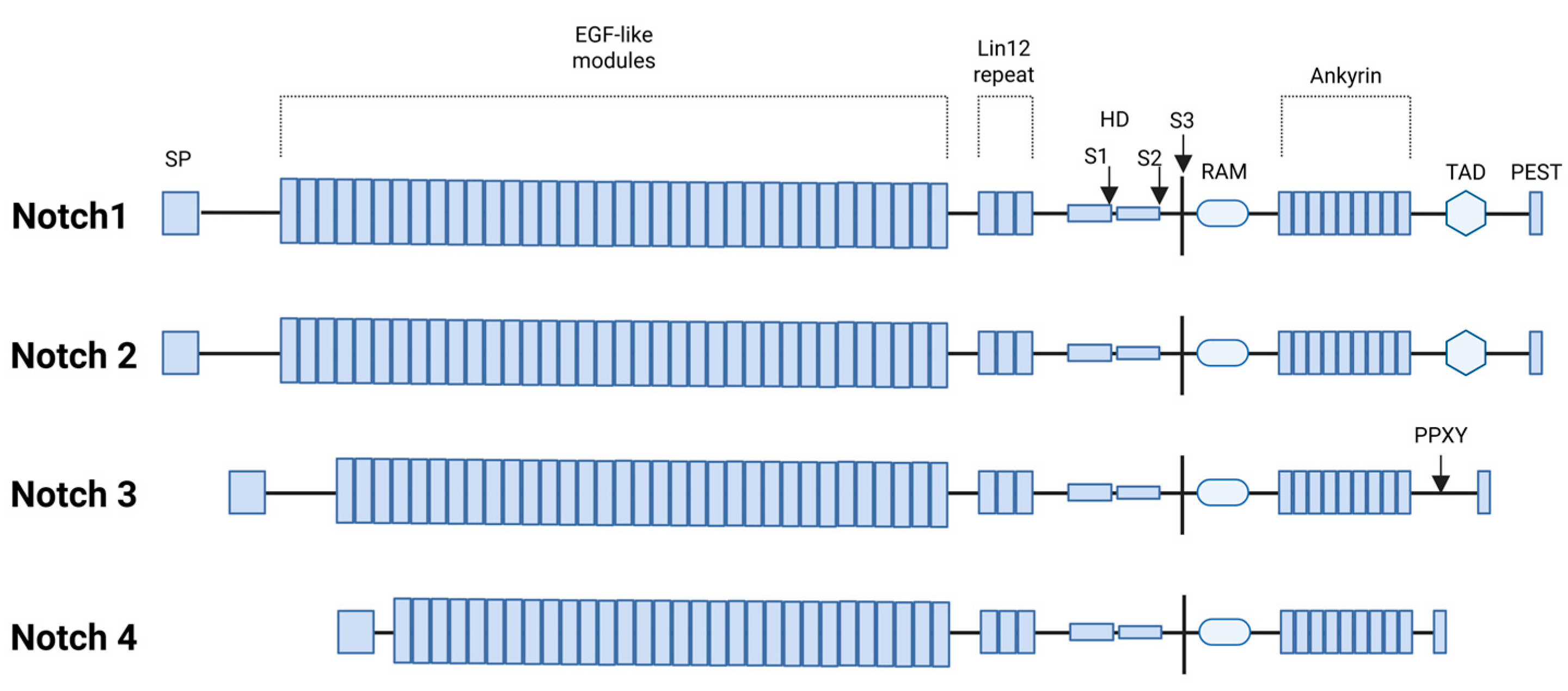
Figure 2.
Functional domains of human NOTCH1-4 proteins: signal peptide (SP), epidermal growth factor-like repeats (EGF), LIN-12 repeat (LNR) as receptors for intercellular signals, heterodimerization domain (HD), S1/S2/S3 proteolytic cleavage sites, RBP-Jkappa-associated module (RAM), transcriptional activation domain (TAD), and the polypeptide sequence rich in proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T) residues. Additionally, the NOTCH3 receptor contains a proline-rich Pro-Pro-x-Tyr (PPXY) motif that serves as a recognition site for the WW domain-containing protein 2 (WWP2), an endocytic regulatory protein (Created with BioRender.com, Licensing and Agreement number RY285EXIU5, accessed on 15 April 2025).
Following ligand–receptor interaction, a cascade of proteolytic cleavages releases the NICD, which translocate into the nucleus and interact with co-activator and co-repressor complexes to regulate the transcription of target genes [116]. These downstream effects shape diverse cellular outcomes, underscoring the pathway’s critical role in normal development as well as in oncogenic transformation.
Going into detail, we can distinguish between a canonical and non-canonical NOTCH signaling pathway [117]. In the canonical pathway, the NICD is released following metalloprotease-mediated proteolytic cleavage. The final cleavage is performed by γ-secretase, enabling NCID to translocate into the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences to promote gene transcription [118]. Proteolytic cleavage can also occur at the endosomal level during vesicular trafficking processes, adding another layer of regulation [119].
In the canonical pathway, NOTCH likely interacts with complex transcriptional machinery, led by the CBF-1/suppressor of hairless/Lag1 (CSL) complex [120]. CSL recruits various co-transcription factors that modulate gene expression, ensuring precise control of developmental and cellular processes [121].
However, NOTCH can also signal through non-canonical pathways, interacting with key molecular regulators such as NF-κB, mTOR, PTEN, AKT, wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt), and Hippo signaling [2]. Non-canonical ligands lack the essential Delta/Serrate/Lag-2 (DSL) domain required for interaction with NOTCH [122]. These ligands include a structurally diverse group of proteins, including integral membrane proteins and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked membrane proteins [123]. Although non-canonical ligands may have important biological functions, their roles have been insufficiently explored in vivo, and their impact on organ development and disease progression remains not fully understood.
Moreover, NOTCH signaling plays a crucial role in sustaining tumor growth under hypoxic conditions, thereby reducing the efficacy of pharmacological and radiotherapeutic interventions [124]. This ability to support cell survival in low-oxygen environments underscores the role of NOTCH as a key factor in tumor aggressiveness and therapy resistance [125]. The four isoforms of the NOTCH receptor have been found both overexpressed and mutated in patients with lung cancer. Gene sequencing analyses have revealed NOTCH gene mutations in various human cancers, particularly in both NSCLC and SCLC [126,127]. These mutations contribute to tumor initiation and progression by promoting stem cell self-renewal, enhancing cellular plasticity, and fostering resistance to therapy [128].
The role of NOTCH family protein as oncogenes or tumor suppressors is complex; NOTCH1 has also been shown to be a tumor suppressor and overexpressed in association with lymph node metastases in patients with NSCLC [126]. NOTCH1 has been much more associated with stem-like characteristics and self-renewal capacity of NSCLC cells; NOTCH2 in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways with growth and development of NSCLC; NOTCH3 has been linked to TGF-β-mediated EMT processes via transcriptional repression of Zinc finger E-box binding protein 1 (ZEB1), NOTCH4 has also been associated with anti-tumor immunity, promoting the infiltration of diverse immune cells populations [129].
NOTCH involvement in EMT has been associated with reduced E-cadherin (E-cadherin) and Snail expression leading to destabilization of the epithelial structure in an intricate signaling network mediated by TGF-β; hyper-activation of cyclins D1 was also associated with EMT in NOTCH signaling [130]. From TCGA data and global analysis of expression profiles, it has been reported that in both LUSC and LUAD opposing roles of NOTCH1 has been revealed, being a suppressor in LUAD and an oncogene in LUSC [105]. High levels of Jag1, DLL1, NOTCH1, and NOTCH2 mRNA were associated with better OS in lung adenocarcinoma patients, while Jag2, DLL3, and NOTCH3 mRNA correlated with poor survival [131].
The opposing prognostic roles of Jag1 and Jag2 were attributed to their mutual inhibition, as Jag1 and Jag2 levels were inversely regulated [132]. NOTCH2 expression was lower in NSCLC patients compared to healthy lung tissue [133]. Additionally, NOTCH3 gene polymorphisms (G684A and C381T) were linked to increased lung cancer susceptibility [134]. Finally, ligands, such as DLL3, play a crucial role in the differentiation plasticity of SCLC tumor cells, influencing cell proliferation, EMT, chemotherapy resistance and the expression of immune biomarkers. DLL3, widely expressed in SCLC tumor cells, represents a promising therapeutic target [135].
Given the pleiotropic nature of NOTCH signaling, therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway must carefully balance its dual role in tumorigenesis. While NOTCH inhibitors show promise in treating specific cancers, they must be precisely tailored to avoid disrupting their essential physiological functions involved in tissue homeostasis and regeneration [136].
The physiopathological overview of the NRF2–NOTCH axis and their crosstalk is illustrated in Figure 3A, while Figure 3B depicts the potential consequences of dysfunctional activation.
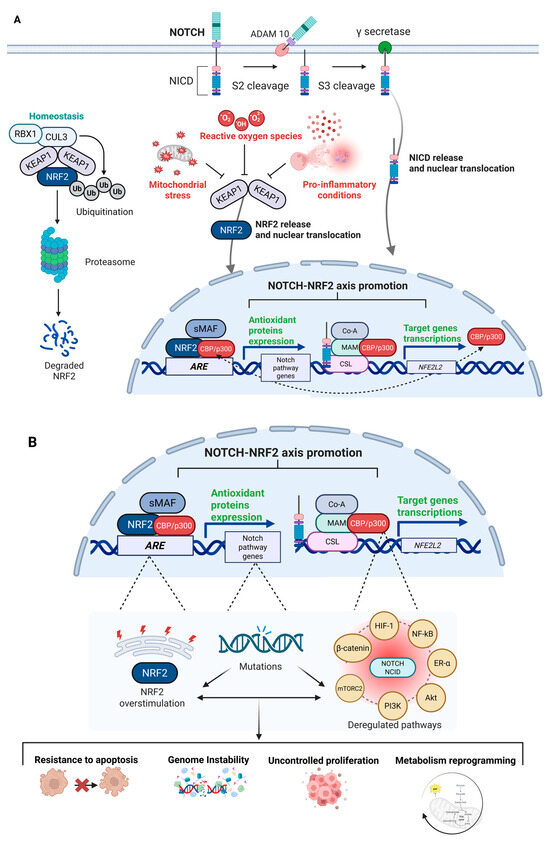
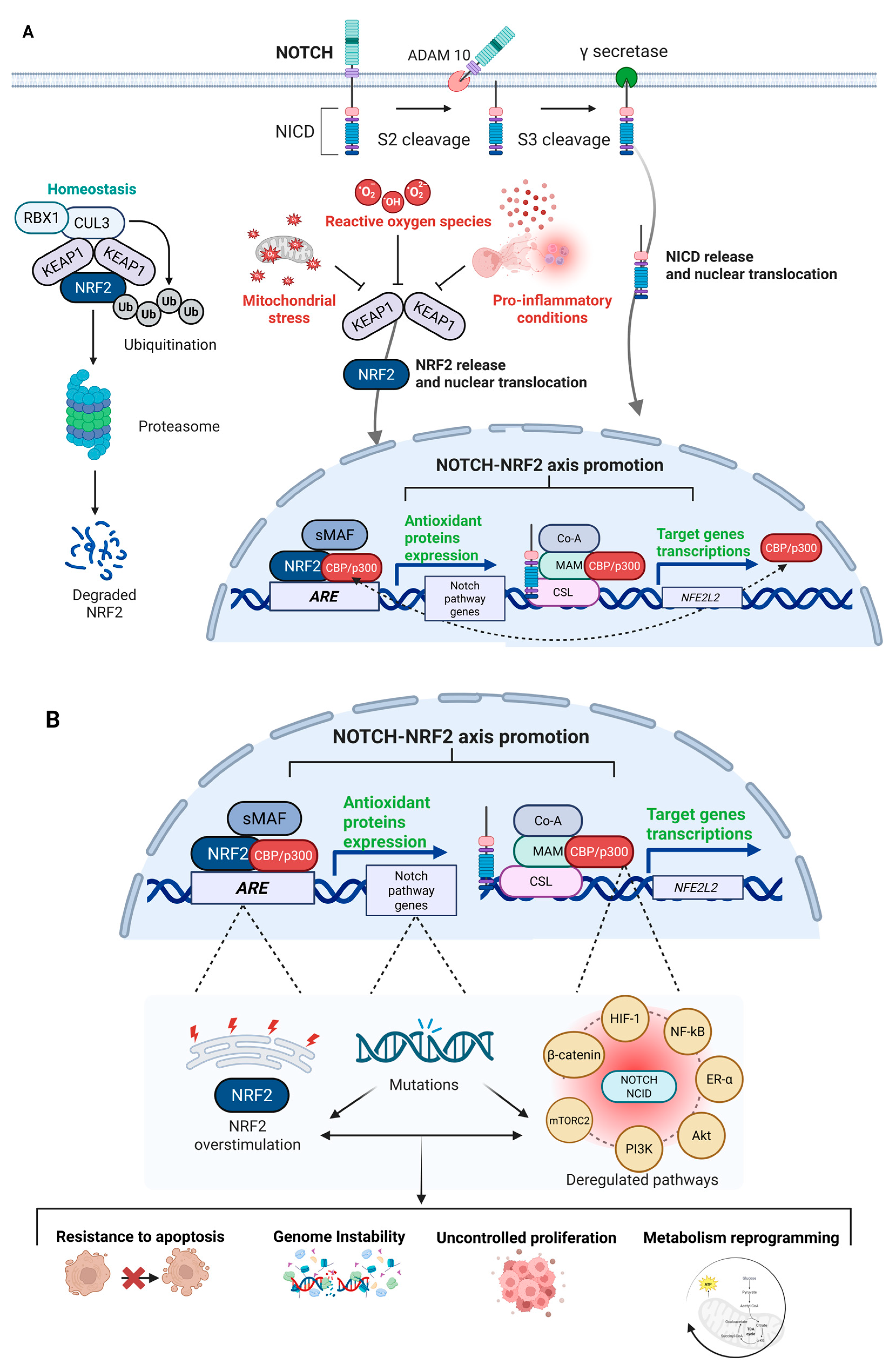
Figure 3.
Physiopathological NRF2–NOTCH axis overview. General overview of the NRF2–NOTCH axis, highlighting the main factors and protein complexes involved in the activation of both pathways. (A) Under homeostatic conditions, KEAP1 directs NRF2 towards ubiquitination and subsequent degradation via the proteasome complex. During stress conditions—often linked to altered energy metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction, and accumulation of ROS, which amplify pro-inflammatory signals—KEAP1 undergoes conformational changes that allow NRF2 to translocate into the nucleus, where it functions as a transcription factor by binding to AREs to initiate a cytoprotective response. Similarly, under physiological conditions, the NOTCH pathway regulates normal development and cell differentiation, thereby contributing to cellular homeostasis. Upon ligand binding, the NOTCH receptor undergoes a series of proteolytic cleavages, culminating in cleavage by γ-secretase, which releases the NICD. NICD then translocates to the nucleus, where it acts as a transcriptional regulator of specific target genes. NICD can interact with the promoter of the NFE2L2 gene to stimulate NRF2 transcription, or it can cooperate with transcriptional co-activators such as CBP/p300 to enhance the transcriptional activity of NRF2 on its target genes. Conversely, NRF2 can upregulate components of the NOTCH pathway by binding to AREs located in the promoters of various genes, including those involved in NOTCH signaling, thereby promoting their expression. Beyond these direct mechanisms, the interconnection between the NOTCH and NRF2 pathways is part of a much broader and more intricate signaling network, with multiple intermediate pathways activated by both axes (Created with BioRender.com, Licensing and Agreement number YR285EY4B1, accessed on 15 April 2025). (B) Mutations or dysregulation within the NRF2–NOTCH axis can lead to aberrant and dysfunctional activation. In cancer, hyperactivation of NRF2—often triggered by persistent stress signals—can be exploited by tumor cells to survive hostile conditions and may in turn contribute to increased NOTCH signaling. Likewise, deregulated NOTCH activity can either upregulate or fail to appropriately activate NRF2. Beyond their oncogenic potential, the deregulation of NOTCH and NRF2 activities can affect a multitude of downstream effectors, such as HIF-1, NF-κB, ER-α, AKT, PI3K, mTORC2, and β-catenin. The deregulation of these interconnected pathways facilitates the acquisition of a set of cancer hallmarks as well as resistance to apoptosis, genomic instability, uncontrolled proliferation, and metabolic reprogramming. The biological complexity of NRF2–NOTCH axis defines its ability to rewire multiple tumor-promoting networks, fueling cancer development and progression (Created with BioRender.com, Licensing and Agreement number ST285EYE6Y, accessed on 15 April 2025). Abbreviations: KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NRF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Cul3, Cullin 3; RBX1, RING-box protein 1; Ub, Ubiquitin; NOTCH, Neurogenic Locus NOTCH Homolog; ADAM10, A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease 10; NICD, NOTCH Intracellular Domain; sMAF, Small Musculoaponeurotic Fibrosarcoma oncogene homologs; CBP/p300, CREB-binding protein/E1A-binding protein p300; ARE, Antioxidant Response Element; Co-A, Co-Activator; MAM, Mastermind-like protein; CSL, CBF-1/suppressor of hairless/Lag1; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; HIF-1, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; ER-α, Estrogen Receptor alpha; Akt, Protein Kinase B; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; mTORC2, Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 2; β-Catenin, Beta-Catenin.
5. Genetic and Epigenetics Hallmarks of NOTCH in Lung Cancer
The alterations characterizing NOTCH signaling during lung cancer pathogenesis might be finely tuned either by somatic mutations and epigenetic modifications, acting as a double-edge sword for its progression [137]. In a recent study, a targeted deep sequencing was conducted assessing 48 tumor-related genes on 153 samples from 55 LUAD and LUSC patients using different sources: formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues, pleural effusion supernatant, pleural effusion cell sediments, white blood cells, oral epithelial cells, and plasma [138].
Mutations were detected in 96% of patients and in 83% of the selected genes, therefore exhibiting a characteristic mutational pattern. Among them, NOTCH1 was one of the top eight mutated genes (36.4%) making it the second most frequently altered gene after TP53 [138]. Notably, 70% of plasma samples harbored NOTCH1 mutations, a frequency significantly higher than the 20% observed in tumor tissues. Furthermore, copy number loss of NOTCH1 was detected in 21% of patients, underscoring the gene’s susceptibility to both sequence-level mutations and structural loss [138]. These mutations included a heterogeneous group of missense mutations: synonymous mutations, and nonsense (truncating) mutations. Many of these mutations clustered within functional domains such as the calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like repeats (EGF) domain, the EGF-like domain, the (Lin-12/NOTCH repeat (LNR) domain, the Ankyrin repeats, and the proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T) as well as PEST domain. Notably, the presence of synonymous mutations, which can influence splicing or gene regulation, suggesting potential regulatory roles beyond direct protein alteration [138].
Among these mechanisms, Westhoff et al. demonstrated that NOTCH1 expression in lung cancer relies on NUMB Endocytic Adaptor Protein (NUMB) activity and somatic mutations acquisition. As contextual evidence, they demonstrated an inverse correlation between Numb, regulated post-translationally in lung cancer, and NOTCH1 accumulation, supported by the expression analysis of the NOTCH-target gene HES family bHLH transcription factor 1 (HES1). Despite the significative inverse correlation, the authors were able to identify an increased expression of HES1 along with a sustained expression of NUMB, hinting towards a possible gain-of-function NOTCH1 mutations [139]. Corroborating this scenario, they identified four different heterozygous mutations by sequencing the entire C-terminal region of the NOTCH1 on the 49 NSCLC cohort, eventually also showing predictive features for a poor prognosis in the TP53-mutated subgroup [139].
In line with this, Huang et al. recently assessed NOTCH1 mutations in 55 out of 963 patients with NSCLC, accounting for 5.7% of cases; a similar percentage to the one they found by further analyzing two public available databases [140]. Of note, mutations were more common in male patients 65 years old at least, smokers and patients with squamous-cell carcinoma. An independent work showed that SNPs affected both NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 genes in lung biopsies obtained from smoker patients [141].
Interestingly, the median of tumor mutational burden for NOTCH1 mutated tumors was significantly higher than for NOTCH1 wild-type tumors, because of the alterations in DNA damage and repair-related genes. Among the most affected pathways, the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling was overactivated in this context [142]. Therefore, Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in NOTCH1 mutated tumors was significantly higher than in NOTCH1 wild-type tumors, therefore enriching the milieu in CD8+ T cells, hallmarks of a highly inflammatory tumor microenvironment [140]. NOTCH1, however, is not the only gene mutated from the NOTCH family. It has been reported indeed that a chromosomal translocation involving t(15;19) regulates NOTCH3 expression in 40% of lung cases, leading to the overexpression of a full-length functional protein [143].
Besides the plethora of mutations that have been reported affecting NOTCH members, a further regulation level relies on the epigenetic control of this family of genes. However, only a few evidences are pointing to the epigenetics control sitting upstream NOTCH regulation. The assessment of NUMB expression in public array databases revealed a marked decrease in its expression of lung cancer. These data correlate with a significant hypermethylation of its promoter, as confirmed by assessing this epigenetic modification of tumor biopsies in comparison to healthy tissues [144]. Consequently, NOTCH cascade is activated, eventually promoting cancer stem cell-like properties and resistance to chemotherapy in NSCLC cell lines.
There is an increasing need to overcome NOTCH expression to counteract lung cancer progression [127]. In this context, it has been shown that Sirtuin proteins, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent deacetylases and ADP-ribosyl transferases (class III histone deacetylase enzymes, HDAC), are involved in regulating NOTCH1 expression via DNMT1. Subramani et al. showed that SIRT6 silencing might represent a strategy for mitigating lung cancer progression; upon its knockdown DNMT1 is acetylated and stabilized, therefore promoting NOTCH1 promoter methylation, and thus repressing its expression [145].
On this basis, Su et al. recently reported that DNMTs activity in NSCLC cell lines can also be modulated by Evodiamine, an alkaloid derived from Euodiae Fructus [146]. The extract exerts its activity by reducing cell viability in vitro and in vivo in rodent models. Furthermore, this alkaloid induced G2/M cell cycle arrest, inhibited cell migration and reduced stemness in cultured NSCLC cells. These outcomes appear to be closely linked to increased NOTCH3 methylation, which occurs following treatment with the extract due to the stabilization of DNMTs [146].
More recently reported epigenetic modification affecting NOTCH family members’ expression involves the non-coding RNAs. It has been reported that miR-34a inhibited the NOTCH signaling pathway by reducing the expression of HES-1, NOTCH1, and Survivin, leading to decreased cell growth and invasiveness and promoting apoptosis in NSCLC cells [147]. Xue et al. also explained the contribution of miR-200 in this context. They reported that miR-200 mediated the interaction between LUAD cells and neighboring cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by targeting the NOTCH ligands Jagged1 and Jagged2, which in turn activated the NOTCH signaling pathway in CAFs and ultimately inhibited lung ASC metastasis [148].
Similarly, cells stably overexpressing lncRNA-p21 and upregulated Jagged1 promote NOTCH1 activation, thus suggesting another mechanism by which lncRNAs modulate NOTCH cascade. In addition to this, lncRNA AGAP2 Antisense RNA 1 (AGAP2-AS1), it has been described to activate the NOTCH signaling pathway in lung cancer cells by upregulating NOTCH2 through the sequestration of miR-296, ultimately promoting malignant cellular behaviors [149]. Likewise, lncRNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 11 (SNHG11) enhanced NOTCH3 expression sponging miR-193a-5p, thereby activating the NOTCH signaling pathway and facilitating the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. The circ_0000190 was shown to reverse luteolin-induced suppression of lung cancer progression by activating the NOTCH1 signaling pathway sponging miR-130a-3p [150,151]. A recent scientific report also highlighted the significative overexpression of lncRNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) in NSCLC tissues and cell lines, where it promoted NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Corroborating this, silencing of PVT1 suppressed the expression of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and inhibited the activation of the NOTCH1 signaling pathway. The mechanism involves EZH2-mediated methylation of the miR-497 promoter, which suppresses miR-497 transcription and results in the upregulation of its target, YAP1. This cascade ultimately activates the NOTCH signaling pathway, thereby promoting epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion, and metastasis [152].
Overall, all these findings highlight the intricate regulatory network governing NOTCH signaling in lung cancer, where genetic mutations and non-coding RNAs collectively shape tumor progression, microenvironment interactions, and therapeutic responses [153]. Table 2 summarizes the alterations targeting NOTCH signaling in lung cancer, highlighting genetic mutations, epigenetic modifications, miRNAs and non-coding RNAs and their impact on clinical outcomes.

Table 2.
Overview of alterations in NOTCH signaling in lung cancer, focusing on mutations, epigenetic modifications, and molecular mechanisms, along with their potential clinical implications.
6. Modulation of NRF2–NOTCH Signaling Across Lung Cancer Subtypes and Treatment Responses
The interaction between NRF2 and NOTCH signaling pathways is increasingly recognized as context-dependent, with variable effects across different lung cancer subtypes and under distinct therapeutic pressures [11]. Genetic analyses have shown that the mutational landscape of NFE2L2 differs significantly between LUAD and LUSC [154]. Specifically, KEAP1 mutations are more commonly observed in LUAD, whereas NFE2L2 mutations predominantly occur in LUSC [72].
In LUAD, mutations in KEAP1, STK11, NRF2, and SMARCA4, which drive the redox-high phenotype, have been shown to be associated with a reduction in tissue-resident memory CD8⁺ T cells, thereby attenuating the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors [155]. In this histology, activating mutations in NFE2L2 or loss-of-function mutations in KEAP1 lead to constitutive activation of NRF2, which has been linked to tumor progression and chemoresistance [71]. Furthermore, NRF2 activation can upregulate the components of the NOTCH pathway, promoting a stem-like phenotype that enhances resistance to chemotherapy and targeted therapies, like EGFR inhibitors (EGFRi) [7].
In LUSC, the NFE2L2 mutations are also common and correlate with increased resistance to radiotherapy [156]. Interestingly, NRF2 activation in LUSC has been shown to suppress NOTCH signaling, which in turn disrupts differentiation pathways, leading to enhanced cell proliferation and survival [157]. Moreover, NRF2-driven chemoresistance in LUSC can also be attributed to its role in modulating the cellular response to cisplatin and other DNA-damaging drugs [158]. In a high-grade neuroendocrine (NE) cancer, like SCLC, where KEAP1 mutations are less frequent, epigenetic silencing of KEAP1 can represent a leading mechanism to aberrantly activate NRF2, contributing to chemoresistance, particularly to agents like etoposide and platinum-based therapies [83].
The interplay between NRF2 and NOTCH in SCLC is particularly notable, as NOTCH signaling is often suppressed, leading to the maintenance of the NE phenotype, which is typically associated with poor prognosis and therapy resistance [135]. Basically, on one hand, the inhibition of NRF2 activity has demonstrated potential in reversing chemoresistance in preclinical models; on the other, the modulation of NOTCH signaling is under investigation as a strategy to promote cellular differentiation and enhance tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy [159].
These findings suggest that NRF2 and NOTCH pathways cooperate in modulating tumor cell survival and therapeutic resistance, underscoring the need for novel therapeutic strategies that target both pathways simultaneously.
7. Clinically Relevant Mutations and Epigenetic Modifiers of the NRF2-KEAP1 and NOTCH Pathways in Lung Cancer
Several specific genetic and epigenetic alterations affecting the NRF2 and NOTCH pathways have been identified in many clinical cohorts of lung cancer patients, and they hold significant potential for improving patients’ stratification and guiding therapeutic decision [7]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the activation of the NRF2 pathway contributes to resistance against various anticancer therapies, with early-stage NSCLC patients harboring KEAP1 or NFE2L2 mutations exhibiting a higher risk of local recurrence following radiotherapy [160,161]. Furthermore, recent studies suggest that the activation of the NRF2-KEAP1 pathway correlates with poorer OS post-chemotherapy. In particular, patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring mutations in KEAP1, NFE2L2, or CUL3 showed significantly shorter time to treatment failure and OS following first-line platinum doublet chemotherapy, compared to matched controls [71].
Analysis of data from the Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) cohort demonstrated that KEAP1 and/or NFE2L2 genetic alterations could be significantly associated with increased TMB and elevated PD-L1 expression with a greater clinical benefit from immunotherapy than from other treatment modalities, suggesting potential predictive value of these mutations in guiding immunotherapeutic strategies [162]. Notably, mutations in STK11 and KEAP1 genes markedly influence the prognosis of patients with advanced NSCLC, especially when they co-occur with KRAS mutations, offering substantial potential to improve patient stratification for immunotherapy and thereby enhance clinical outcomes [163]. On the other side, several mutational landscape of the NOTCH gene family (particularly NOTCH1 and NOTCH3), observed in a subset of SCLC, supports a context-dependent tumor-suppressive role. This underscores the importance of future research to investigate the clinically actionable impact of NOTCH loss, especially concerning treatment resistance and disease relapses in plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) [164].
On the epigenetic front, in molecularly stratified subpopulations of NSCLC, particularly in LUAD and LUSC cases lacking KRAS mutations, our group demonstrated a strong positive correlation has been observed between KEAP1 promoter hypermethylation and elevated NRF2 mRNA expression, along with increased expression of multiple ARE-driven target genes. Notably, the epigenetic silencing of KEAP1 was specifically linked to KRAS wild-type status in both LUAD and LUSC, being present in the KRAS wild-type subpopulations and absent in patients with KRAS mutations [165].
As expected, the hyperactivation of NRF2 leads to resistance across a wide spectrum of conventional and novel treatments, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy [166]. More recently, NRF2-KEAP1 pathway alterations have been associated with resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitor therapies [167], highlighting their potential utility in identifying patients who may benefit from NRF2-targeted inhibitors or redox-based combination treatments. Stratifying patients based on KEAP1 or NFE2L2 mutational status is increasingly being utilized to guide treatment decisions, including the exclusion of patients from ICI monotherapy trials due to their poor predicted response [168].
Moreover, integrated biomarker profiling that includes KEAP1/NFE2L2, NOTCH, and KRAS/STK11 alterations may improve the identification of molecular subtypes associated with therapeutic resistance and worse clinical outcomes.
8. Metabolic Roles of NRF2 and NOTCH in Lung Cancer
Emerging evidence highlights the critical interplay between the NRF2 and NOTCH signaling pathways in lung cancer, where they also cooperate to reprogram metabolism in support of tumor growth, redox homeostasis, and therapy resistance [169,170,171]. This metabolic reprogramming enables cancer cells to meet increased energetic and biosynthetic demands through enhanced glycolysis, glutaminolysis, lipid catabolism, and antioxidant defense [172]. NOTCH signaling contributes by upregulating MYC, a master regulator of metabolism, in a genotype- and tissue-specific manner [173], while NRF2 regulates ROS homeostasis via induction of enzymes like NQO1, glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM), and heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1) [174,175,176].
NRF2 knockdown in NSCLC cell lines dramatically increases endogenous ROS levels and enhances sensitivity to radiation therapy [177]. Moreover, NRF2-mediated ROS homeostasis contributes to chemoresistance through the PI3K/Akt pathway [178]. The regulation of ROS by NRF2 has far-reaching metabolic consequences. It enhances nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) production by upregulating key enzymes such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1), malic enzyme 1 (ME1), and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (PGD), thereby supporting both redox homeostasis and biosynthetic pathways [94,178,179].
A recent work by Weiss-Sadan and colleagues has revealed that NRF2 activation can induce NADH-reductive stress, creating a metabolic vulnerability in lung cancer [180]. This study demonstrates that NRF2 activation, either through pharmacological inhibition of KEAP1 or genetic mutations, leads to an imbalance in the NADH/NAD+ ratio, which disrupts mitochondrial function and sensitizes cancer cells to Complex I inhibition [180]. In NSCLC, NRF2 activation is associated with the overexpression of NADPH-producing enzymes and NADPH oxidases (NOX2 and NOX4), which together help maintain redox balance and fuel critical biosynthetic pathways essential for cancer cell growth [181,182].
In lung cancer cells, NRF2 activation correlates with increased lactate production and glucose uptake, conferring tumor aggressiveness in terms of invasion and metastasis [183]. Recent studies have identified in lung adenocarcinoma a metabolic phenotype (MP-III), characterized by high glycolytic activity and low lipid metabolism, associated with poor prognosis and metastatic potential [184]. This phenotype is driven by mutations in TP53 and KEAP1, as well as deletions in SETD2 (SET domain containing 2) and PBRM1 (Polybromo 1) [184]. Notably, NRF2 hyperactivation in NSCLC is also linked to hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α), further amplifying glycolytic activity by enhancing the expression of several key genes including hexokinase 2 (HK2), phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3), pyruvate kinase isozymes M2 (PKM2) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) [185].
Concurrently, NOTCH-driven SCCs display elevated expression of glycolytic and serine biosynthesis enzymes, including aldolase A (ALDOA), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1), and serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2), supporting nucleotide synthesis and antioxidant defense [186]. NOTCH signaling also promotes glutaminolysis by upregulating glutaminase (GLS), glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 2 (GOT2), and malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2), thereby fueling tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates and supporting reductive carboxylation [187].
These chemical reactions and pathways also involve glutathione metabolism. In fact, NRF2 controls NADPH synthesis by modulating the expression of enzymes that, such as ME1 and IDH1 [170,188]. NADPH provides the reducing equivalent necessary for the glutathione regeneration, via glutathione reductase (GR) and also serves as a cofactor for TRXR1 and NQO1, showing a clear correlation between the cellular redox status and metabolic functions regulated by NRF2. NRF2 enhances the synthesis of glutathione (GSH) by upregulating glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) and GSS, which helps counteract oxidative stress. Elevated GSH levels in LUSC contribute to resistance against radiation and chemotherapy [189,190].
NRF2 supports GSH metabolism by increasing cystine uptake via solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) and enhancing the expression of GCL and GSS, thereby strengthening antioxidant defenses and contributing to chemoresistance [188,189]. In addition, NOTCH-driven metabolic phenotypes include upregulation of nucleotide biosynthesis enzymes like nucleotide biosynthesis enzymes such as cytidine triphosphate synthase 1 (CTPS1) and guanosine monophosphate synthetase (GMPS), further linking metabolic reprogramming to therapy resistance [186].
In terms of lipid metabolism, NRF2 inhibits de novo lipogenesis via repression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), while promoting fatty acid oxidation (FAO) through the activation of genes such as carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and CD36, sustaining energy production under stress and minimizing lipid-induced ferroptosis [191]. These adaptations are accompanied by high expression of FAO genes like CPT1A, facilitating ROS clearance and tumor progression [192].
Among the numerous functions carried out by NRF2, its role as transcriptional activator of anti-ferroptosis genes is essential, as it prevents lipid peroxidation and the accumulation of free iron. In fact, the SLC7A11 cystine-glutamate transporter system and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) are two key regulators of ferroptosis process that are directly regulated upstream by NRF2 [193,194]. Recent studies have shown that cancer cells can evade ferroptosis induced by SLC7A11 or GPX4 inhibition through activation of the NRF2-ARE pathway, and that inhibiting NRF2 may help overcome this resistance to ferroptotic cell death [195,196].
NRF2 also modulates iron homeostasis by regulating ferritin heavy chain (FTH1) and HMOX1, which protect cells from ferroptosis [197]. Moreover, Mindbomb E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1 (MIB1), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, was able to stimulate NRF2 degradation in a NOTCH-independent manner, rendering cancer more responsive to ferroptosis inducers [198]. MIB1 knockout induces NRF2 accumulation and resistance to ferroptosis, indicating that MIB1 may function as a positive regulator of ferroptosis through targeted NRF2 degradation [198]. In NSCLC, it has been documented that NRF2 activation stabilizes BTB and CNC Homology 1 (BACH1), a pro-metastatic transcription factor, by reducing free heme levels [183].
Finally, antioxidants like N-acetylcysteine and vitamin E can paradoxically promote lung cancer metastasis by reducing free heme levels and stabilizing BACH1, which activates glycolytic genes (HK2 and GAPDH) to increase glucose uptake and lactate production [183]. Recent studies highlight the role of the Coenzyme Q (CoQ) and Ferroptosis Suppressor Protein 1 (FSP1) axis in mediating ferroptosis resistance in KEAP1-mutant tumors, presenting a promising novel therapeutic target [199].
The major metabolic pathways modulated by NRF2 and NOTCH signaling in the progression of lung cancer are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Main metabolic mechanisms modulated via NRF2–NOTCH axis in lung cancer.
9. Targeting NRF2 and NOTCH Pathways in Lung Cancer: Current Drugs, Emerging Strategies, and Clinical Relevance
The therapeutic targeting of NRF2 and NOTCH pathways in lung cancer has emerged as a promising approach due to their critical roles in cancer cell survival, resistance to therapy, and tumor progression. Aberrant activation of NRF2 has been linked to increased tumorigenicity and unfavourable prognosis in lung cancer [158], making it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention [9,75]. Given the interplay between NRF2 and NOTCH signaling, alterations in these pathways have substantial therapeutic implications, particularly in terms of their prognostic value, utility as predictive biomarkers of treatment response, and overall impact on patient outcomes [11].
In lung cancer, genetic and epigenetic alterations affecting the NRF2 and NOTCH signaling pathways have emerged as key determinants of tumor behaviour and clinical outcome. Activating mutations in NFE2L2 or inactivating mutations of its negative regulator KEAP1 promote oxidative stress resistance, metabolic reprogramming, and immune evasion [56]. Similarly, mutations in NOTCH receptors, particularly missense variants affecting ligand-binding or ankyrin domains, can result in ligand-independent activation, contributing to altered cell fate decisions and suppression of tumor suppressor functions [2]. These molecular events are associated with poor prognosis, reduced OS and PFS, and resistance to conventional therapies, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies such as those with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), and immunotherapy [201].
Recent genomic and functional studies have increasingly underscored the prognostic impact of alterations in the NRF2–NOTCH signaling on distinct lung cancer subtypes. Constitutive activation of the NRF2 pathway, mainly resulting from KEAP1 loss-of-function or NFE2L2 gain-of-function mutations, occurs in approximately 20–30% of NSCLCs, especially LUAD and LUSC, as previously reported [158]. In NSCLC, aberrant activation of NRF2 not only enhances oxidative stress resistance and therapeutic tolerance, but also modulates NOTCH1 signaling, influencing apoptotic responses following radiation exposure. This functional interaction contributes to therapy resistance and may define more aggressive disease phenotypes [202].
In large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas (LCNECs), mutations in genes regulating NRF2 activity and members of the NOTCH receptor family are frequently observed, particularly in NSCLC-like LCNECs, where NOTCH pathway mutations help to discriminate them from classical adenocarcinomas [203]. Conversely, SCLC-like LCNECs show a higher incidence of KEAP1 and NFE2L2 mutations, uncommon in canonical SCLC but frequent in squamous cell carcinoma, suggesting divergent developmental trajectories influenced by these pathways [204]. Recently, high NRF2 expression in NSCLC patients were found to be correlated with poorer OS and PFS following chemotherapy or EGFR TKIs treatment, suggesting NRF2 as a potential marker of tumor aggressiveness and a valuable tool for prognosis and optimizing treatment strategies [205].
Moreover, pan-cancer analyses have revealed recurrent co-mutations in KEAP1, NFE2L2, and NOTCH1, supporting a cooperative role in driving tumor progression. These co-alterations may amplify oncogenic signaling and reinforce treatment resistance, thereby correlating with worse clinical outcomes [77,206].
Taken together, disruptions in the NRF2–NOTCH axis emerge as key prognostic indicators in lung cancer, with potential utility in molecular stratification and targeted therapeutic strategies. Moving into predictive insights, KEAP1 and NFE2L2-mutant tumors exhibit reduced responsiveness to immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), likely due to an immunosuppressive microenvironment, characterized by low tumor mutational burden, reduced interferon signaling, and decreased CD8+ T cell infiltration. This may suggest an important predictive value of pharmacologic inhibition of NRF2 as a strategy to restore therapeutic sensitivity, which is currently under preclinical investigation [207].
Given its complex role in lung cancer, NOTCH signaling is emerging as a prognostic and predictive cancer biomarker, as its aberrant activation contributes to tumor progression, therapeutic resistance, and increased recurrence in both NSCLC and SCLC [2].
Clinical findings have shown that elevated NOTCH3 expression was a predictor of different aggressive tumor behaviours, such as advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis in a well-defined cohort of NSCLC patients [208] and, later, it has been found to be correlated with reduced sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy in NSCLC. These findings suggested a role for NOTCH3 in driving the advancement and chemoresistance of NSCLC and supporting the potential role of NOTCH3 as a predictive biomarker for treatment response in this cohort of patients [126].
Importantly, emerging data point to a context-dependent predictive role of NOTCH mutations in immunotherapy. Among NOTCH alterations, NOTCH1 mutations have been linked to an increase in MHC class I expression and T-cell infiltration, two features that may sensitize NSCLC patients to ICIs, corroborating the idea that specific NOTCH mutations could serve as independent predictive biomarkers in the prognosis of NSCLC patients treated with ICIs [209].
By making tumor cells more susceptible to oxidative stress, NRF2 inhibitors, like Brusatol [210,211,212] and ML385 [213,214], have been studied for their capacity to prevent NRF2 activation and improve the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiation therapy [215,216]. Drugs targeting the NRF2 pathway also frequently block downstream antioxidant genes that support cancer cell survival or prevent the pathway’s interaction with KEAP1, a negative regulator of NRF2 [215].
Several approaches for the NOTCH pathway are being investigated. Gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), such as DAPT [83,217] and RO4929097 [218], seem to be promising in preclinical studies for their ability to block the cleavage of NOTCH receptors, preventing downstream signaling activation [219]. These inhibitors, by disrupting the aberrant activation of NOTCH signaling, can arrest tumor growth in lung cancer cells. However, because of its intricate involvement in maintaining normal tissue homeostasis, NOTCH signaling has proven difficult to target, and the therapeutic window is still limited because of possible adverse consequences such as immune suppression [11].
Additional tactics include the use of small compounds to alter the way NOTCH interacts with its downstream effectors and monoclonal antibodies, as well as tarextumab [135], that target NOTCH receptors or ligands, with intriguing results [220]. NOTCH signaling inhibitors are often explored in combination with other therapies to improve treatment efficacy, particularly in NSCLC and SCLC [8]. NOTCH inhibitors, especially GSIs, are sometimes used in combination with standard chemotherapy or targeted therapies to overcome drug resistance. For example, blocking NOTCH signaling can make cancer cells more sensitive to traditional chemotherapy agents (like cisplatin) and targeted agents (like EGFRi) [221].
Since NOTCH signaling is involved in immune cell regulation and the maintenance of cancer stem cells, combining NOTCH inhibitors with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs, such as anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1) has been explored. This strategy may enhance the immune response against lung tumors [222]. While these drugs are still being tested in clinical trials, they represent exciting prospects for enhancing lung cancer treatment.
Emerging data also highlight potential crosstalk between NRF2 and NOTCH signaling axes, which may synergistically drive tumor aggressiveness and resistance phenotypes, resulting in significant clinical implications as detailed in this section [223]. Given their multifaceted roles, integrative profiling of NRF2 and NOTCH alterations, at genomic, transcriptomic, and protein levels, could improve patient stratification and guide the development of combination strategies (e.g., NRF2 or NOTCH inhibitors with ICIs or standard therapies) aimed at overcoming resistance and improving durable clinical responses in lung cancer.
However, challenges such as toxicity, tumor heterogeneity, and resistance need to be addressed before these inhibitors can become mainstream treatments for lung cancer [224]. Table 4 summarizes the targeting of NRF2 and NOTCH pathways, their associated mechanisms of action, and relevant drugs.

Table 4.
Drugs targeting NRF2 and NOTCH pathways and related mechanisms of action.
10. Multi-Omics and Emerging Technologies: Current Advances and Future Directions
Emerging technologies, particularly single-cell multi-omics, are poised to significantly enhance the understanding of the NRF2–NOTCH signaling pathways, which are crucial in various biological processes and diseases. These technologies allow us to perform a detailed analysis of cellular heterogeneity, molecular interactions and functional states across tumor microenvironments [230]. In this context, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and chromatin accessibility assays (scATAC-seq) hold great value and can be effectively applied to dissect NRF2- and NOTCH-driven transcriptional and epigenetic programs at a cell-specific level. These approaches are able to cover context-dependent interactions, such as NRF2 binding to AREs in regulatory regions of NOTCH1 or repression of NRF2 target genes by NOTCH effectors [231].
Although Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) remains the gold standard for profiling chromatin-protein interactions, its high input material requirements pose significant challenges for applications at the single-cell level [232]. By profiling histone marks and transcription factor occupancy associated with NRF2, KEAP1, and NOTCH proteins, CUT&Tag (Cleavage Under Targets and Tagmentation) facilitates the identification of dynamic chromatin accessibility changes and regulatory element activity that govern their gene expression and functional status [230]. These approaches could be further strengthened by integrative proteogenomic techniques, such as Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing (CITE-seq) and RNA Expression and Protein Sequencing (REAP-seq), single-cell multi-omics platforms that simultaneously quantify gene expression and surface protein levels within individual cells, providing a powerful means to dissect oxidative stress responses, immune modulation, and the regulatory dynamics underlying NRF2–NOTCH pathway crosstalk [233].
To contextualize NRF2–NOTCH pathway activity within the native tissue environment, spatial transcriptomics platforms such as 10× Genomics Visium and Slide-seq retain spatial information, enabling precise mapping of pathway activation and its interactions with stromal and immune components across distinct tumor niches [234]. Finally, functional studies employing perturbation sequencing, which combines Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-mediated gene perturbations with single-cell transcriptomic readouts, have revealed critical vulnerabilities and adaptive dependencies that tumor cells acquire upon loss of KEAP1, NFE2L2, or NOTCH1, thereby uncovering potential targets for therapeutic intervention [235,236].
Despite their great potential, these technologies face key challenges, particularly in data integration and clinical translation, highlighting the need for standardized methods, longitudinal sampling, and validation in relevant models to effectively exploit single-cell multi-omics and identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in the NRF2–NOTCH axis in lung cancer.
11. Conclusions
The dynamic crosstalk between NRF2 and NOTCH signaling pathways plays a pivotal role in lung cancer biology, since their reciprocal regulation influences tumor initiation, progression, and therapy resistance [10].
Key takeaways from this review include: (1) NRF2 can transcriptionally activate NOTCH1, while NOTCH signaling regulates NRF2 activity via RBPJ, illustrating a bidirectional and context-specific interaction [11]; (2) both pathways can function as oncogenes or tumor suppressors, depending on tumor subtype and microenvironmental cues [7]; (3) genetic alterations, such as KEAP1, NFE2L2 and NOTCH1 mutations, significantly impact on their signaling networks [237]; (4) epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and ncRNAs, add another layer of regulation, contributing to pathway deregulation in NSCLC [238]; (5) metabolic reprogramming, a hallmark of aggressive tumors, further modulates NRF2–NOTCH interactions, driving phenotype plasticity and drug resistance [169,186]; (6) therapeutic implications: advances in high-throughput and single-cell multi-omics technologies now allow for a more comprehensive analysis of the crosstalk between these pathways, paving the way for the development of NRF2–NOTCH inhibitors and the implementation of personalized therapeutic strategies [239].
Overall, understanding the intricate NRF2–NOTCH axis provides a promising framework for designing innovative strategies to improve therapeutic responses and clinical outcomes in lung cancer patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.T. and F.P.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S., F.T., G.G., S.B. and F.P.F.; writing—review and editing, F.T., L.A.M. and F.P.F.; visualization, A.S., F.T., F.D., G.G., S.B., F.P.F. and L.A.M.; supervision, F.P.F. and L.A.M.; project administration, F.P.F.; funding acquisition, L.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ricerca Corrente Program, Italian Ministry of Health and by the “5 × 1000” voluntary contributions to Fondazione IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wakabayashi, N.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Kensler, T.W. Crosstalk between Nrf2 and Notch signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Lin, W.; Long, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Chu, Q. Notch signaling pathway: Architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Assoro, A.B.; Leon-Ferre, R.; Braune, E.B.; Lendahl, U. Roles of Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Colombrita, C.; Guagliano, E.; Sapienza, M.; Ravagna, A.; Cardile, V.; Scapagnini, G.; Santoro, A.M.; Mangiameli, A.; Butterfield, D.A.; et al. Protective effect of carnosine during nitrosative stress in astroglial cell cultures. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00099-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Ortega, M.; Carrera, A.C.; Garrido, A. Role of NRF2 in Lung Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Minari, R.; Cortellini, A.; Rolfo, C.D.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Notch pathway in small-cell lung cancer: From preclinical evidence to therapeutic challenges. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 42, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouremamali, F.; Pouremamali, A.; Dadashpour, M.; Soozangar, N.; Jeddi, F. An update of Nrf2 activators and inhibitors in cancer prevention/promotion. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimta, A.A.; Cenariu, D.; Irimie, A.; Magdo, L.; Nabavi, S.M.; Atanasov, A.G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Role of Nrf2 Activity in Cancer Development and Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Xue, C.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Li, L. Notch signaling pathway in cancer: From mechanistic insights to targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparaneo, A.; Fabrizio, F.P.; Muscarella, L.A. Nrf2 and Notch Signaling in Lung Cancer: Near the Crossroad. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7316492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Wu, C.; Tang, L.; Bian, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Targeting epigenetic and post-translational modifications of NRF2: Key regulatory factors in disease treatment. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBlasi, J.M.; DeNicola, G.M. Dissecting the Crosstalk between NRF2 Signaling and Metabolic Processes in Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Dashwood, R.H. Epigenetic Regulation of NRF2/KEAP1 by Phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Suzen, S.; Saso, L. The NRF2/KEAP1 Axis in the Regulation of Tumor Metabolism: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qu, Y.; Mao, C.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, D.; Sun, X. Post-translational modifications of Keap1: The state of the art. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1332049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wicha, M.S. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Redox Metabolism to Enhance Therapy Responses. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A.B.; Samal, R.R.; Bhol, N.K.; Duttaroy, A.K. Cellular Red-Ox system in health and disease: The latest update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, L.; Mesgarzadeh, J.; Xu, I.; Powers, E.T.; Wiseman, R.L.; Bollong, M.J. Defining the Functional Targets of Cap‘n’collar Transcription Factors NRF1, NRF2, and NRF3. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Arfuso, F.; Bian, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Antioxidant response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Fujikawa, N.; Komatsu, M.; Ishii, T.; Unno, M.; Akaike, T.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 degradation by autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13561–13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Inoue, J.; Iso, T.; Wells, G.; Moore, T.W.; Mizushima, T.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kasai, T.; Kamei, T.; et al. Molecular basis for the disruption of Keap1-Nrf2 interaction via Hinge & Latch mechanism. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xiao, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, M. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: A key mechanism in the occurrence and development of cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1381467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, P. The Nrf2 transcription factor: A multifaceted regulator of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. Plus 2021, 10, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskomic, M.; Tomic, A.; Barbaric, L.; Matic, A.; Kindl, D.C.; Matovina, M. KEAP1-NRF2 Interaction in Cancer: Competitive Interactors and Their Role in Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2025, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Wakabayashi, N.; Misra, V.; Biswal, S.; Lee, G.H.; Agoston, E.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. NRF2 modulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling: Influence on adipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7188–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dayalan Naidu, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Regulating Nrf2 activity: Ubiquitin ligases and signaling molecules in redox homeostasis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2025, 50, 179–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubarak, M.M.; Pagano Zottola, A.C.; Larrieu, C.M.; Cuvellier, S.; Daubon, T.; Martin, O.C.B. Exploring the multifaceted role of NRF2 in brain physiology and cancer: A comprehensive review. Neurooncol. Adv. 2024, 6, vdad160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, X.; Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, C. Tumor initiation and early tumorigenesis: Molecular mechanisms and interventional targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganjac, M.; Milkovic, L.; Sunjic, S.B.; Zarkovic, N. The NRF2, Thioredoxin, and Glutathione System in Tumorigenesis and Anticancer Therapies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismann, C.; Arlt, A.; Sebens, S.; Schafer, H. Cytoprotection “gone astray”: Nrf2 and its role in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotblat, B.; Melino, G.; Knight, R.A. NRF2 and p53: Januses in cancer? Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbai, O.; Torrisi, F.; Fabrizio, F.P.; Rabbeni, G.; Perrone, L. Effect of the Mediterranean Diet (MeDi) on the Progression of Retinal Disease: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Liu, K. Inflammation in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities from new insights. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo-Correa, E.; Silva-Aguero, J.F.; Calle, X.; Chiong, M.; Henriquez, M.; Garcia-Rivas, G.; Latorre, M.; Parra, V. Estrogen signaling as a bridge between the nucleus and mitochondria in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 968373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Warabi, E. Mechanism of Rapid Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Activation via Membrane-Associated Estrogen Receptors: Roles of NADPH Oxidase 1, Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). Antioxidants 2019, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Tseng, Y.T.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Lo, Y.C. Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant defense and cell survival signaling are upregulated by 17beta-estradiol in homocysteine-treated dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neuroendocrinology 2013, 97, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.H.; Kim, N.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.N.; Surh, Y.J. 17-beta estradiol exerts anti-inflammatory effects through activation of Nrf2 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, J.; Tang, D.; Yang, L.; Chen, X. Oxidative cell death in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordani, M.; Garufi, A.; Benedetti, R.; Tafani, M.; Aventaggiato, M.; D’Orazi, G.; Cirone, M. Recent Advances on Mutant p53: Unveiling Novel Oncogenic Roles, Degradation Pathways, and Therapeutic Interventions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalera, S.; Mazzotta, M.; Cortile, C.; Krasniqi, E.; De Maria, R.; Cappuzzo, F.; Ciliberto, G.; Maugeri-Sacca, M. KEAP1-Mutant NSCLC: The Catastrophic Failure of a Cell-Protecting Hub. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Suzuki, A.; Shitara, M.; Okuda, K.; Hikosaka, Y.; Moriyama, S.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. Keap1 mutations in lung cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.; Jonsson, M.; Lauss, M.; Brunnstrom, H.; Jonsson, P.; Borg, A.; Jonsson, G.; Ringner, M.; Planck, M.; Staaf, J. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of lung carcinoma reveals one neuroendocrine and four adenocarcinoma epitypes associated with patient outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6127–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Oncogene-Stimulated Congestion at the KEAP1 Stress Signaling Hub Allows Bypass of NRF2 and Induction of NRF2-Target Genes that Promote Tumor Survival. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, N.J.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, Y.R.; An, C.H.; Lee, S.H. Somatic mutations of the KEAP1 gene in common solid cancers. Histopathology 2012, 60, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Sparaneo, A.; Trombetta, D.; Muscarella, L.A. Epigenetic versus Genetic Deregulation of the KEAP1/NRF2 Axis in Solid Tumors: Focus on Methylation and Noncoding RNAs. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2492063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.L.; Heath, A.P.; Ferretti, V.; Varmus, H.E.; Lowy, D.R.; Kibbe, W.A.; Staudt, L.M. Toward a Shared Vision for Cancer Genomic Data. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, V.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Ames, S.; Hoque, M.O.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Sidransky, D.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Iijima, K.; Miyamoto, M.; Nakahara, I.; Tanaka, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Yokota, J.; Sakiyama, T.; et al. Loss of Keap1 function activates Nrf2 and provides advantages for lung cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz, A.; Kloska, D.; Forman, H.J.; Jozkowicz, A.; Grochot-Przeczek, A. Beyond repression of Nrf2: An update on Keap1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 157, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerins, M.J.; Ooi, A. A catalogue of somatic NRF2 gain-of-function mutations in cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellyer, J.A.; Padda, S.K.; Diehn, M.; Wakelee, H.A. Clinical Implications of KEAP1-NFE2L2 Mutations in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Peifer, M.; Lu, X.; Sun, R.; Ozretic, L.; Seidal, D.; Zander, T.; Leenders, F.; George, J.; Muller, C.; et al. Frequent mutations in chromatin-remodelling genes in pulmonary carcinoids. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Hayashi, M.; Zavitsanou, A.M.; Papagiannakopoulos, T. NRF2: KEAPing Tumors Protected. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.A.; Ding, S.; Kersbergen, A.; Dong, X.; Song, J.Y.; Xie, Y.; Reljic, B.; Li, K.; Vince, J.E.; Rathi, V.; et al. Distinct initiating events underpin the immune and metabolic heterogeneity of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wang, S.; Moghaddam, S.J.; Ooi, A.; Chapman, E.; Wong, P.K.; Zhang, D.D. Oncogenic KRAS confers chemoresistance by upregulating NRF2. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7430–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krall, E.B.; Wang, B.; Munoz, D.M.; Ilic, N.; Raghavan, S.; Niederst, M.J.; Yu, K.; Ruddy, D.A.; Aguirre, A.J.; Kim, J.W.; et al. KEAP1 loss modulates sensitivity to kinase targeted therapy in lung cancer. Elife 2017, 6, e18970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Jordan, E.; Kim, H.R.; Dienstag, J.; Yu, H.A.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Lito, P.; Berger, M.; Solit, D.B.; Hellmann, M.; et al. Effects of Co-occurring Genomic Alterations on Outcomes in Patients with KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Hellyer, J.A.; Stehr, H.; Hoang, N.T.; Niu, X.; Das, M.; Padda, S.K.; Ramchandran, K.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.; et al. Role of KEAP1/NFE2L2 Mutations in the Chemotherapeutic Response of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R.; Scheffler, M.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Ihle, M.A.; Kron, A.; Rauer, M.; Ueckeroth, F.; Konig, K.; Michels, S.; Fischer, R.; et al. Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of KEAP1- and NFE2L2-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC). Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, D.; Mazzotta, M.; Scalera, S.; Terrenato, I.; Sperati, F.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Pallocca, M.; Corleone, G.; Krasniqi, E.; Pizzuti, L.; et al. KEAP1-driven co-mutations in lung adenocarcinoma unresponsive to immunotherapy despite high tumor mutational burden. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavitsanou, A.M.; Pillai, R.; Hao, Y.; Wu, W.L.; Bartnicki, E.; Karakousi, T.; Rajalingam, S.; Herrera, A.; Karatza, A.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; et al. KEAP1 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma promotes immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Saso, L. Potential Applications of NRF2 Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8592348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeman, F.; De Nicola, F.; Scalera, S.; Sperati, F.; Gallo, E.; Ciuffreda, L.; Pallocca, M.; Pizzuti, L.; Krasniqi, E.; Barchiesi, G.; et al. Mutations in the KEAP1-NFE2L2 Pathway Define a Molecular Subset of Rapidly Progressing Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addeo, A.; Passaro, A.; Malapelle, U.; Banna, G.L.; Subbiah, V.; Friedlaender, A. Immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harbouring driver mutations. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 96, 102179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Fan, P.D.; Qeriqi, B.; Namakydoust, A.; Daly, B.; Ahn, L.; Kim, R.; Plodkowski, A.; Ni, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Targeting NFE2L2/KEAP1 Mutations in Advanced NSCLC With the TORC1/2 Inhibitor TAK-228. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, M.; ElManawy, A.I.; Hammad, A.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Integrated data analysis reveals significant associations of KEAP1 mutations with DNA methylation alterations in lung adenocarcinomas. Aging 2020, 12, 7183–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Kong, A.N. Epigenetic regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y.; Kong, A.N. Regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling: The role of epigenetics. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2016, 1, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Sparaneo, A.; Gorgoglione, G.; Battista, P.; Centra, F.; Delli Muti, F.; Trombetta, D.; Centonza, A.; Graziano, P.; Rossi, A.; et al. Effects of KEAP1 Silencing on NRF2 and NOTCH Pathways in SCLC Cell Lines. Cancers 2024, 16, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, L.A.; Parrella, P.; D’Alessandro, V.; la Torre, A.; Barbano, R.; Fontana, A.; Tancredi, A.; Guarnieri, V.; Balsamo, T.; Coco, M.; et al. Frequent epigenetics inactivation of KEAP1 gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; An, J.; Ji, F.; Jiao, H.; Sun, H.; Zhou, D. Hypermethylation of the Keap1 gene in human lung cancer cell lines and lung cancer tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.W.; Lu, R.J.; Jayasinghe, R.G.; Foltz, S.M.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Geffen, Y.; Wendl, M.C.; Lazcano, R.; Kolodziejczak, I.; Song, Y.; et al. Integrative multi-omic cancer profiling reveals DNA methylation patterns associated with therapeutic vulnerability and cell-of-origin. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1567–1585.e1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Sparaneo, A.; Centra, F.; Trombetta, D.; Storlazzi, C.T.; Graziano, P.; Maiello, E.; Fazio, V.M.; Muscarella, L.A. Methylation Density Pattern of KEAP1 Gene in Lung Cancer Cell Lines Detected by Quantitative Methylation Specific PCR and Pyrosequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wu, B.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zhou, D. A possible gene silencing mechanism: Hypermethylation of the Keap1 promoter abrogates binding of the transcription factor Sp1 in lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Castellana, S.; Centra, F.; Sparaneo, A.; Mastroianno, M.; Mazza, T.; Coco, M.; Trombetta, D.; Cingolani, N.; Centonza, A.; et al. Design and experimental validation of OPERA_MET-A panel for deep methylation analysis by next generation sequencing. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 968804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, B.; Jin, X.; Li, P.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, F.; Li, Q. Genistein mediates the selective radiosensitizing effect in NSCLC A549 cells via inhibiting methylation of the keap1 gene promoter region. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27267–27279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Bohmann, D. BET-ting on Nrf2: How Nrf2 Signaling can Influence the Therapeutic Activities of BET Protein Inhibitors. Bioessays 2018, 40, e1800007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Tang, N.; Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Shen, S.; Niu, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, Z. The polycomb group protein EZH2 inhibits lung cancer cell growth by repressing the transcription factor Nrf2. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3000–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray-Stewart, T.; Hanigan, C.L.; Woster, P.M.; Marton, L.J.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Histone deacetylase inhibition overcomes drug resistance through a miRNA-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Happel, C.; Manna, S.K.; Acquaah-Mensah, G.; Carrerero, J.; Kumar, S.; Nasipuri, P.; Krausz, K.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Dewi, R.; et al. Transcription factor NRF2 regulates miR-1 and miR-206 to drive tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2921–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Lai, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. miR-155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.G.; Wang, M.F.; Cao, Y.B.; Dan, L.; Li, R.Z.; Fan, X.X.; Khan, I.; Lai, H.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Hsiao, W.W.; et al. MicroRNA-421 confers paclitaxel resistance by binding to the KEAP1 3’UTR and predicts poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Shi, D.; Zhai, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Qin, J. miR-144-3p regulates the resistance of lung cancer to cisplatin by targeting Nrf2. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3479–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahizadeh, R.; Vatankhah, M.A.; Safari, A.; Danesh, H.; Nazmi, N.; Gholizadeh, P.; Soozangar, N.; Jeddi, F. The interplay between microRNAs and Nrf2 signaling in human cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.; Sparaneo, A.; Castellana, S.; Mazza, T.; Trombetta, D.; Graziano, P.; Rossi, A.; Fazio, V.; Muscarella, L. 17P—REDOXI-miRNA of Keap1/Nrf2 axis in lung tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. 2), ii5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.R.V.; Ferrer, J.L.M.; Garcia, R.L. Concomitant and decoupled effects of cigarette smoke and SCAL1 upregulation on oncogenic phenotypes and ROS detoxification in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, P.; Statt, S.; Chen, C.H.; Liang, E.; Campbell, C.; Wu, R. Characterization of a novel long noncoding RNA, SCAL1, induced by cigarette smoke and elevated in lung cancer cell lines. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Leon, L.; Gautier, M.; Allan, R.; Ilie, M.; Nottet, N.; Pons, N.; Paquet, A.; Lebrigand, K.; Truchi, M.; Fassy, J.; et al. The nuclear hypoxia-regulated NLUCAT1 long non-coding RNA contributes to an aggressive phenotype in lung adenocarcinoma through regulation of oxidative stress. Oncogene 2019, 38, 7146–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Sparaneo, A.; Muscarella, L.A. NRF2 Regulation by Noncoding RNAs in Cancers: The Present Knowledge and the Way Forward. Cancers 2020, 12, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, K.; Viswakarma, N.; Rana, A.; Rana, B. Transcription Factors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusewicz, D.; Orzechowska, M.; Bednarek, A.K. Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer-Review with Bioinformatic Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, F.H. Emerging role of Notch in stem cells and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 279, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Kaur, B.; Han, H.; Yu, J. The Notch signaling pathway: A potential target for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.M.; Jana, S.; Singhal, J.; Horne, D.; Awasthi, S.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Notch signaling in breast cancer: From pathway analysis to therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 461, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, C.S.; Radtke, F. Notch as a tumour suppressor. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Jiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; He, W. Emerging role of tumor cell plasticity in modifying therapeutic response. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Sarkar, F.H. The role of Notch signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during development and tumor aggressiveness. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, A.; Gutierrez-Garcia, A.K.; Guenter, R.; Rose, J.B.; Beck, A.W.; Chen, H.; Ren, B. Notch Signaling in Vascular Endothelial Cells, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Progression: An Update and Prospective. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 642352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P. Novel insights into Notch signaling in tumor immunity: Potential targets for cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Franco, D.; Kalra, R.; Draper, I.; Pacak, C.A.; Asakura, A.; Kang, P.B. The Notch signaling pathway in skeletal muscle health and disease. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, N.; Sharma, V.; Mutsuddi, M.; Mukherjee, A. Notch signalling: Multifaceted role in development and disease. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 3030–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdik, T.R.; Crow, J.J.; Lawton, T.; Munroe, C.J.; Theriault, H.; Wood, T.M.; Albig, A.R. Notch intracellular domains form transcriptionally active heterodimeric complexes on sequence-paired sites. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, O.; Sprinzak, D. Notch signaling in development and homeostasis. Development 2023, 150, dev201138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-kappaB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Wu, P.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Chang, Y.T.; Bhore, N.; Wu, P.F.; Liao, Y.F. Quantitative Measurement of gamma-Secretase-mediated Amyloid Precursor Protein and Notch Cleavage in Cell-based Luciferase Reporter Assay Platforms. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, 56795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez Rodriguez, F.; Sanlidag, S.; Sahlgren, C. Mechanical regulation of the Notch signaling pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2023, 85, 102244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Lamarca, M.J.; Falo-Sanjuan, J.; Stojnic, R.; Abdul Rehman, S.; Muresan, L.; Jones, M.L.; Pillidge, Z.; Cerda-Moya, G.; Yuan, Z.; Baloul, S.; et al. Activation of the Notch Signaling Pathway In Vivo Elicits Changes in CSL Nuclear Dynamics. Dev. Cell 2018, 44, 611–623.e617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, W.H.; Deng, W.M. Ligand-Independent Mechanisms of Notch Activity. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jia, G.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chao, Y.; Bao, J.; Su, Z.; Qu, Q.; Li, D. Molecular insights into biogenesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor proteins. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Niu, Y.; Xie, M.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Notch signaling, hypoxia, and cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1078768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Malhotra, J.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Emerging Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Zhou, X.L.; Lai, S.Q.; Liu, J.C. Notch signaling and non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3415–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Shaji, A.; Chammaa, M.; Pawlik, E.; Fernandez-Valdivia, R. Notch Transduction in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wartmann, T.; Jauch, K.W.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cells and their niche: Perspectives for future therapeutic targets and strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dong, M.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wen, D. Notch signaling and targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 585, 216647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wu, H.; Han, N.; Xu, H.; Chu, Q.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K. Notch signaling and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer: Biological significance and therapeutic application. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.C.; Jing, L.; Ruan, Z.P.; Yao, Y.; Nan, K.J.; Guo, H. Notch Signaling Components: Diverging Prognostic Indicators in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2016, 95, e3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Ahn, Y.H.; Gibbons, D.L.; Tran, H.T.; Creighton, C.J.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Qin, F.X.; Kurie, J.M. Distinct biological roles for the notch ligands Jagged-1 and Jagged-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17766–17774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, A.; Mazur, P.K.; Anton, M.; Rudelius, M.; Schwamborn, K.; Feuchtinger, A.; Behnke, K.; Walch, A.; Braren, R.; Peschel, C.; et al. Opposing role of Notch1 and Notch2 in a Kras(G12D)-driven murine non-small cell lung cancer model. Oncogene 2015, 34, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagci, E.; Degirmenci, I.; Ozbayer, C.; Ak, G.; Saydam, F.; Metintas, M. Common Variants rs3815188 and rs1043994 on Notch3 Gene Confer Susceptibility to Lung Cancer: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2019, 38, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q. Targeting the Notch signaling pathway and the Notch ligand, DLL3, in small cell lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, F.; Maillard, I. Therapeutic Targeting of Notch Signaling: From Cancer to Inflammatory Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 649205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebel, C.; Lendahl, U. Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1235–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Ai-Dherasi, A.; Zheng, F.; Tian, J.; et al. Targeted deep sequencing from multiple sources demonstrates increased NOTCH1 alterations in lung cancer patient plasma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5673–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, B.; Colaluca, I.N.; D’Ario, G.; Donzelli, M.; Tosoni, D.; Volorio, S.; Pelosi, G.; Spaggiari, L.; Mazzarol, G.; Viale, G.; et al. Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22293–22298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Cao, H.; Yao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Bai, Q.; Hu, H. NOTCH1 Mutations Predict Superior Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Immunotargets Ther. 2023, 12, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, P.; Hong, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, X. Cigarette smoke enhances initiation and progression of lung cancer by mutating Notch1/2 and dysregulating downstream signaling molecules. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115128–115139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lastwika, K.J.; Wilson, W., 3rd; Li, Q.K.; Norris, J.; Xu, H.; Ghazarian, S.R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kawabata, S.; Taube, J.M.; Yao, S.; et al. Control of PD-L1 Expression by Oncogenic Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, T.P.; Gazdar, A.F.; Virmani, A.K.; Sepetavec, T.; Hande, K.R.; Minna, J.D.; Roberts, J.R.; Carbone, D.P. Chromosome 19 translocation, overexpression of Notch3, and human lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Heredia, J.M.; Verdugo Sivianes, E.M.; Lucena-Cacace, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Carnero, A. Numb-like (NumbL) downregulation increases tumorigenicity, cancer stem cell-like properties and resistance to chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63611–63628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, P.; Nagarajan, N.; Mariaraj, S.; Vilwanathan, R. Knockdown of sirtuin6 positively regulates acetylation of DNMT1 to inhibit NOTCH signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Cell. Signal. 2023, 105, 110629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Yang, X.; Deng, J.H.; Huang, Q.J.; Huang, S.C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zheng, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.L.; Liu, Z.Q. Evodiamine, a Novel NOTCH3 Methylation Stimulator, Significantly Suppresses Lung Carcinogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Geamanu, A.; Goja, A.; Sarkar, F.H.; Gupta, S.V. Delta-tocotrienol suppresses Notch-1 pathway by upregulating miR-34a in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2668–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Chuang, C.H.; Prosser, H.M.; Fuziwara, C.S.; Chan, C.; Sahasrabudhe, N.; Kuhn, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Biton, A.; et al. miR-200 deficiency promotes lung cancer metastasis by activating Notch signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Genes. Dev. 2021, 35, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 enhances radiotherapy immunity in lung cancer by reducing microRNA-296 and elevating NOTCH2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, L. LncRNA SNHG11 accelerates the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via activating Notch pathways. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 234, 153849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Gong, E.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, X. Luteolin suppresses lung cancer progression through targeting the circ_0000190/miR-130a-3p/notch-1 signaling pathway. J. Chemother. 2023, 35, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.H.G.; Xie, J.H.; Zeng, Q.Y.; Dai, S.H.H.; Wang, Y.; Wan, X.M.; Liu, J.C.H. lncRNA PVT1 Promotes Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Through EZH2-Mediated Activation of Hippo/NOTCH1 Signaling Pathways. Cell J. 2021, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; Elsayed, A.M.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Amero, P.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C. An Overview of the Immune Modulatory Properties of Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Potential Use as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Noncoding RNA 2023, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandara, D.R.; Hammerman, P.S.; Sos, M.L.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Hirsch, F.R. Squamous cell lung cancer: From tumor genomics to cancer therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.W.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.C.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.R.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.R.; Deng, J.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; et al. Redox(high) phenotype mediated by KEAP1/STK11/SMARCA4/NRF2 mutations diminishes tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells and attenuates the efficacy of immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2024, 13, 2340154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, F. Prevalence and Associations of Co-occurrence of NFE2L2 Mutations and Chromosome 3q26 Amplification in Lung Cancer. Glob. Med. Genet. 2024, 11, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Jin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies in lung squamous cell carcinoma: Mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Daemen, A.; Nickles, D.; Jeon, S.M.; Foreman, O.; Sudini, K.; Gnad, F.; Lajoie, S.; Gour, N.; Mitzner, W.; et al. NRF2 Activation Promotes Aggressive Lung Cancer and Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, Q.; Lu, F.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, N.; Yu, Y.; Ning, Z.; She, T.; et al. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Current status and potential therapeutic targetable role in human cancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1184079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Bai, Y. Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2252–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Hoang, N.T.; Lovejoy, A.; Stehr, H.; Newman, A.M.; Gentles, A.J.; Kong, W.; Truong, D.; Martin, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; et al. Role of KEAP1/NRF2 and TP53 Mutations in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development and Radiation Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, N.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Dong, X.; et al. NFE2L2/KEAP1 Mutations Correlate with Higher Tumor Mutational Burden Value/PD-L1 Expression and Potentiate Improved Clinical Outcome with Immunotherapy. Oncologist 2020, 25, e955–e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knetki-Wroblewska, M.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Krawczyk, P.; Krzakowski, M. Emerging insights into STK11, KEAP1 and KRAS mutations: Implications for immunotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 3718–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodovar, K.; Iams, W.T.; Meador, C.B.; Zhao, Z.; York, S.; Horn, L.; Yan, Y.; Hernandez, J.; Chen, H.; Shyr, Y.; et al. Longitudinal Cell-Free DNA Analysis in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer Reveals Dynamic Insights into Treatment Efficacy and Disease Relapse. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, F.P.; Mazza, T.; Castellana, S.; Sparaneo, A.; Muscarella, L.A. Epigenetic Scanning of KEAP1 CpG Sites Uncovers New Molecular-Driven Patterns in Lung Adeno and Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.; Namani, A.; Elshaer, M.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. “NRF2 addiction” in lung cancer cells and its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 467, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrao, M.V.; Araujo, H.A.; Lamberti, G.; Cooper, A.J.; Akhave, N.S.; Zhou, T.; Delasos, L.; Hicks, J.K.; Aldea, M.; Minuti, G.; et al. Comutations and KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy in Advanced NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckl, W.M.; Ficker, J.H.; Zeitler, G. Clinically relevant prognostic and predictive markers for immune-checkpoint-inhibitor (ICI) therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Meng, D.; Zeng, L.; Zhuang, R.; Huang, S.; Lv, W.; Hu, J. Nrf2 Mediates Metabolic Reprogramming in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Shibata, T.; Nukiwa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignitto, L.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Homer, H.; Jiang, S.; Askenazi, M.; Karakousi, T.R.; Pass, H.I.; Bhutkar, A.J.; Tsirigos, A.; Ueberheide, B.; et al. Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1. Cell 2019, 178, 316–329.e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiliro, C.; Firestein, B.L. Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells Supporting Enhanced Growth and Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuneva, M.O.; Fan, T.W.; Allen, T.D.; Higashi, R.M.; Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T.; Mates, J.M.; Alonso, F.J.; Wang, C.; Seo, Y.; et al. The metabolic profile of tumors depends on both the responsible genetic lesion and tissue type. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M. The KEAP1-NRF2 System in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, L.M.; Behrens, C.; Dong, W.; Suraokar, M.; Ozburn, N.C.; Moran, C.A.; Corvalan, A.H.; Biswal, S.; Swisher, S.G.; Bekele, B.N.; et al. Nrf2 and Keap1 abnormalities in non-small cell lung carcinoma and association with clinicopathologic features. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; Saso, L.; D’Angeli, F.; Calabrese, V.; Intrieri, M.; Scapagnini, G. Astaxanthin as a Modulator of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and Their Crosstalk: Molecular Mechanisms and Possible Clinical Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Siow, R.C.; Mann, G.E. Impaired redox signaling and antioxidant gene expression in endothelial cells in diabetes: A role for mitochondria and the nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2-Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 defense pathway. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hang, Q.; Li, P.; Zhang, P.; Ji, J.; Song, H.; Chen, M.; et al. PI3K/mTOR inhibitors promote G6PD autophagic degradation and exacerbate oxidative stress damage to radiosensitize small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.C.; Cui, J.Y.; Klaassen, C.D. Beneficial role of Nrf2 in regulating NADPH generation and consumption. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Sadan, T.; Ge, M.; Hayashi, M.; Gohar, M.; Yao, C.H.; de Groot, A.; Harry, S.; Carlin, A.; Fischer, H.; Shi, L.; et al. NRF2 activation induces NADH-reductive stress, providing a metabolic vulnerability in lung cancer. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 487–503.e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.L.; Fan, X.X.; Wong, M.P.; Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yao, X.J.; Lu, L.L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yau, L.F.; Tin, V.P.; et al. Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Inducing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation via Methionine 790 Oxidation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Yao, B.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, B. NOX4 supports glycolysis and promotes glutamine metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 101, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiel, C.; Le Gal, K.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Jahangir, C.A.; Kashif, M.; Yao, H.; Ziegler, D.V.; Xu, X.; Ghosh, T.; Mondal, T.; et al. BACH1 Stabilization by Antioxidants Stimulates Lung Cancer Metastasis. Cell 2019, 178, 330–345.e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, L.; Deng, J.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gu, Y.; et al. Identifying metabolic reprogramming phenotypes with glycolysis-lipid metabolism discoordination and intercellular communication for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.S.; Du, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, H.L.; Yu, X.Y.; Shi, Y.T.; Xiong, D.N.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.H. NRF2 facilitates breast cancer cell growth via HIF1a-mediated metabolic reprogramming. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 95, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, K.; Allen, T.D.; Bousamra, M., 2nd; Tan, J.; Mendez-Lucas, A.; Lin, W.; Bah, N.; Chernyavskaya, Y.; MacRae, J.I.; Higashi, R.M.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming and Notch activity distinguish between non-small cell lung cancer subtypes. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Sayin, V.I.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Singh, S.X.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Karakousi, T.R.; Ellis, D.C.; Bhutkar, A.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; et al. Keap1 loss promotes Kras-driven lung cancer and results in dependence on glutaminolysis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Chen, P.H.; Mullarky, E.; Sudderth, J.A.; Hu, Z.; Wu, D.; Tang, H.; Xie, Y.; Asara, J.M.; Huffman, K.E.; et al. NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, B.J.; Stine, Z.E.; Dang, C.V. From Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludtmann, M.H.; Angelova, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Abramov, A.Y.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Nrf2 affects the efficiency of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Biochem. J. 2014, 457, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Vega, M.R.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaugg, K.; Yao, Y.; Reilly, P.T.; Kannan, K.; Kiarash, R.; Mason, J.; Huang, P.; Sawyer, S.K.; Fuerth, B.; Faubert, B.; et al. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C promotes cell survival and tumor growth under conditions of metabolic stress. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, E.; Linher-Melville, K.; Lin, H.X.; Singh, G. Expression of xCT and activity of system xc(-) are regulated by NRF2 in human breast cancer cells in response to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015, 5, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, J.; Roh, J.L. Nrf2 inhibition reverses resistance to GPX4 inhibitor-induced ferroptosis in head and neck cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Cho, P.; Selfors, L.M.; Kuiken, H.J.; Kaul, R.; Fujiwara, T.; Harris, I.S.; Zhang, T.; Gygi, S.P.; Brugge, J.S. 3D Culture Models with CRISPR Screens Reveal Hyperactive NRF2 as a Prerequisite for Spheroid Formation via Regulation of Proliferation and Ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 828–844.e826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Lin, B.; Jin, W.; Tang, L.; Hu, S.; Cai, R. NRF2, a Superstar of Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J.; Cheng, S.; Pei, D.; Zhang, X.; Shu, X. The E3 Ligase MIB1 Promotes Proteasomal Degradation of NRF2 and Sensitizes Lung Cancer Cells to Ferroptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppula, P.; Lei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Mao, C.; Kondiparthi, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Horbath, A.; Das, M.; et al. A targetable CoQ-FSP1 axis drives ferroptosis- and radiation-resistance in KEAP1 inactive lung cancers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Song, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Ji, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Loss of Scribble confers cisplatin resistance during NSCLC chemotherapy via Nox2/ROS and Nrf2/PD-L1 signaling. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Molecular targeted therapy for anticancer treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1670–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Mao, A.; Yan, J.; Sun, C.; Di, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Guo, R.; Zhang, H. Downregulation of Nrf2 promotes radiation-induced apoptosis through Nrf2 mediated Notch signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretic, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhtman, N.; Pietanza, M.C.; Hellmann, M.D.; Naidoo, J.; Arora, A.; Won, H.; Halpenny, D.F.; Wang, H.; Tian, S.K.; Litvak, A.M.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing of Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Reveals Small Cell Carcinoma-like and Non-Small Cell Carcinoma-like Subsets. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3618–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, B.; Tian, W. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of NRF2 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Mermel, C.H.; Robinson, J.T.; Garraway, L.A.; Golub, T.R.; Meyerson, M.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature 2014, 505, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, H. KEAP1-NFE2L2-Mutant NSCLC and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Large Database Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, e85–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.M.; Ye, Y.Z.; Qian, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.B. Notch signaling molecules as prognostic biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, G.; Hu, S.; Bai, Y. The Impact of NOTCH Pathway Alteration on Tumor Microenvironment and Clinical Survival of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Ye, W.; Huang, C.; Lou, B.; Zhang, J.; Yu, D.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Brusatol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via JNK/p38 MAPK/NF-kappab/Stat3/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Ye, W.; Huang, C.; Yu, D.; Chen, H.; Deng, T.; Zhang, F.; Lou, B.; Zhang, J.; Shi, K.; et al. Brusatol Enhances the Chemotherapy Efficacy of Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer via the Nrf2 Signalling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2360427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhu, L.; He, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, B.; Ge, C.; et al. The Nrf2 inhibitor brusatol synergistically enhances the cytotoxic effect of lapatinib in HER2-positive cancers. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Venkannagari, S.; Oh, K.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Rohde, J.M.; Liu, L.; Nimmagadda, S.; Sudini, K.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Gajghate, S.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitor of NRF2 Selectively Intervenes Therapeutic Resistance in KEAP1-Deficient NSCLC Tumors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Moghal, N.; Zou, X.; Fang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Tsao, M.S. The NRF2 antagonist ML385 inhibits PI3K-mTOR signaling and growth of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 5688–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Panieri, E.; Cevik, D.; Suzen, S.; Saso, L. Therapeutic Targeting of the NRF2 Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panieri, E.; Buha, A.; Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Cevik, D.; Kouretas, D.; Veskoukis, A.; Skaperda, Z.; Tsatsakis, A.; Wallace, D.; Suzen, S.; et al. Potential Applications of NRF2 Modulators in Cancer Therapy. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Deng, S.; Guo, W.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Gao, T. Notch pathway inhibition using DAPT, a gamma-secretase inhibitor (GSI), enhances the antitumor effect of cisplatin in resistant osteosarcoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Moon, J.; Redman, B.G.; Chidiac, T.; Flaherty, L.E.; Zha, Y.; Othus, M.; Ribas, A.; Sondak, V.K.; Gajewski, T.F.; et al. Phase 2 study of RO4929097, a gamma-secretase inhibitor, in metastatic melanoma: SWOG 0933. Cancer 2015, 121, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaw, T.R.; Inga, E.; Chen, H.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Dudeja, V.; Bibb, J.A.; Ren, B.; Rose, J.B. Gamma Secretase Inhibitors in Cancer: A Current Perspective on Clinical Performance. Oncologist 2021, 26, e608–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, I.; Miele, L. Notch inhibitors for cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Bakyt, L.; Akhmetkaliyev, A.; Toktarkhanova, D.; Bulanin, D. Re-Sensitizing Cancer Stem Cells to Conventional Chemotherapy Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Ning, N.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Chang, A.E.; Wicha, M.S. Concise Review: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells Using Immunologic Approaches. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiuto, C.J.; Moerland, J.A.; Leal, A.S.; Gallo, K.A.; Liby, K.T. The Multi-Faceted Consequences of NRF2 Activation throughout Carcinogenesis. Mol. Cells 2023, 46, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.H.; Bahrami, A.R.; Matin, M.M. Cancer cell cycle heterogeneity as a critical determinant of therapeutic resistance. Genes. Dis. 2024, 11, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.; Basu, B.; Smith, D.M.; Gopinathan, A.; Evans, J.; Steward, W.P.; Palmer, D.; Propper, D.; Venugopal, B.; Hategan, M.; et al. A phase I trial of the gamma-secretase inhibitor MK-0752 in combination with gemcitabine in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piha-Paul, S.A.; Munster, P.N.; Hollebecque, A.; Argiles, G.; Dajani, O.; Cheng, J.D.; Wang, R.; Swift, A.; Tosolini, A.; Gupta, S. Results of a phase 1 trial combining ridaforolimus and MK-0752 in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means-Powell, J.A.; Mayer, I.A.; Ismail-Khan, R.; Del Valle, L.; Tonetti, D.; Abramson, V.G.; Sanders, M.S.; Lush, R.M.; Sorrentino, C.; Majumder, S.; et al. A Phase Ib Dose Escalation Trial of RO4929097 (a gamma-secretase inhibitor) in Combination with Exemestane in Patients with ER + Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC). Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, F.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, D.; Qiu, W.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; et al. Nicotinamide metabolism face-off between macrophages and fibroblasts manipulates the microenvironment in gastric cancer. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1806–1822.e1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Gills, J.J.; Kawabata, S.; Onozawa, M.; Della Gatta, G.; Ferrando, A.A.; Aplan, P.D.; Dennis, P.A. Inhibition of the NOTCH and mTOR pathways by nelfinavir as a novel treatment for T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, R. Single-cell sequencing to multi-omics: Technologies and applications. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, D.; Cull, A.H.; Rubio-Lara, J.A.; Kent, D.G. Exploiting Single-Cell Tools in Gene and Cell Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 702636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotem, A.; Ram, O.; Shoresh, N.; Sperling, R.A.; Goren, A.; Weitz, D.A.; Bernstein, B.E. Single-cell ChIP-seq reveals cell subpopulations defined by chromatin state. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, R.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Applications of single-cell sequencing in cancer research: Progress and perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Wu, L. Spatial transcriptomics technology in cancer research. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1019111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Replogle, J.M.; Norman, T.M.; Xu, A.; Hussmann, J.A.; Chen, J.; Cogan, J.Z.; Meer, E.J.; Terry, J.M.; Riordan, D.P.; Srinivas, N.; et al. Combinatorial single-cell CRISPR screens by direct guide RNA capture and targeted sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Tan, H.Y.; Bian, Z.X.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. CRISPR-Cas9 library screening approach for anti-cancer drug discovery: Overview and perspectives. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3329–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, S.; Patinen, T.; Jawahar Deen, A.; Pitkanen, S.; Harkonen, J.; Kansanen, E.; Kublbeck, J.; Levonen, A.L. The KEAP1-NRF2 pathway: Targets for therapy and role in cancer. Redox Biol. 2023, 63, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camina, N.; Penning, T.M. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the NRF2-KEAP1 pathway in human lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Kong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z. Advancements and applications of single-cell multi-omics techniques in cancer research: Unveiling heterogeneity and paving the way for precision therapeutics. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2024, 37, 101589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).