Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization Driven by TWEAK Promotes Neovascularization and Reduces Brain Damage in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. ICH Rat Model
2.3. Experimental Groups
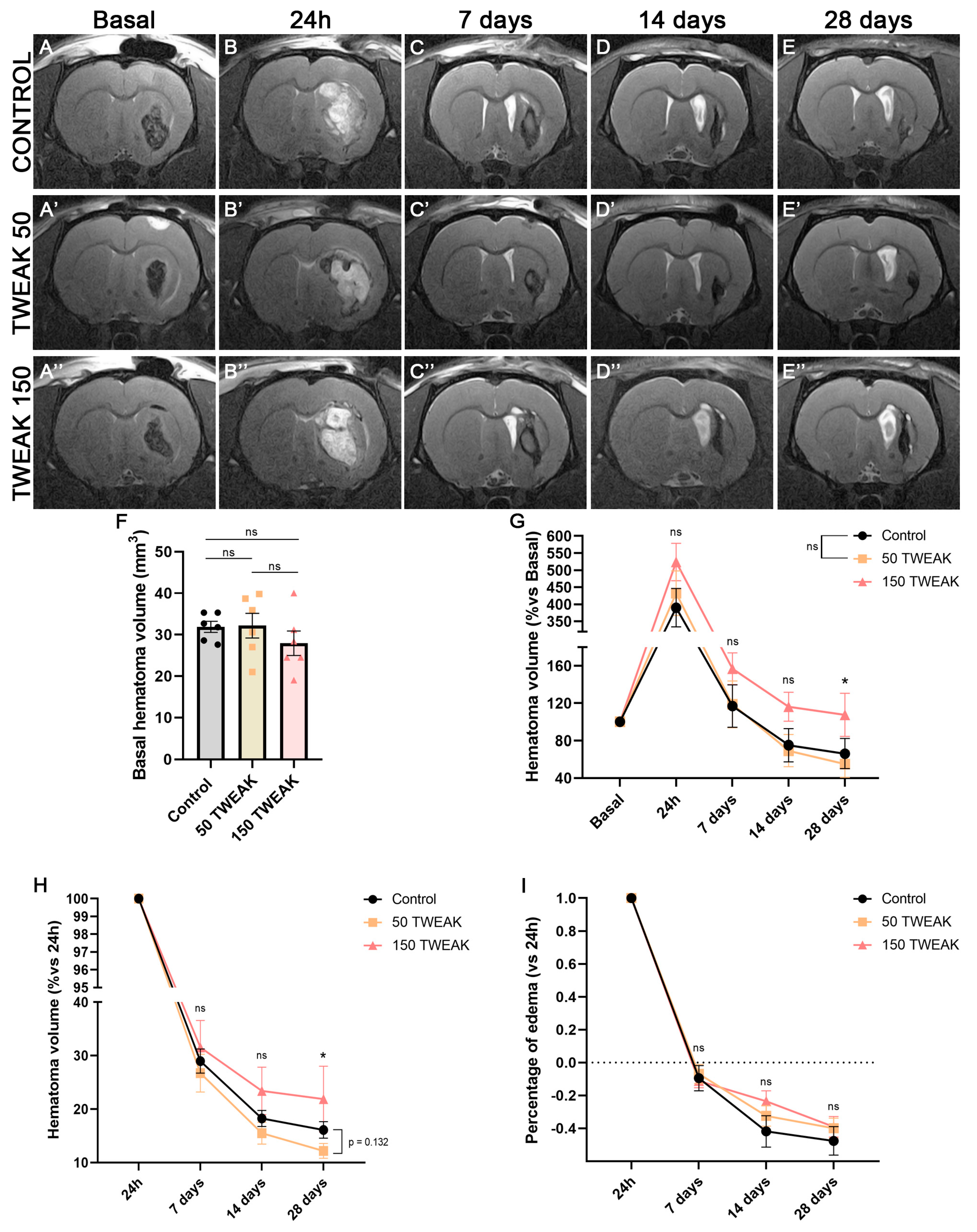
2.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protocol
2.5. Bederson Scale
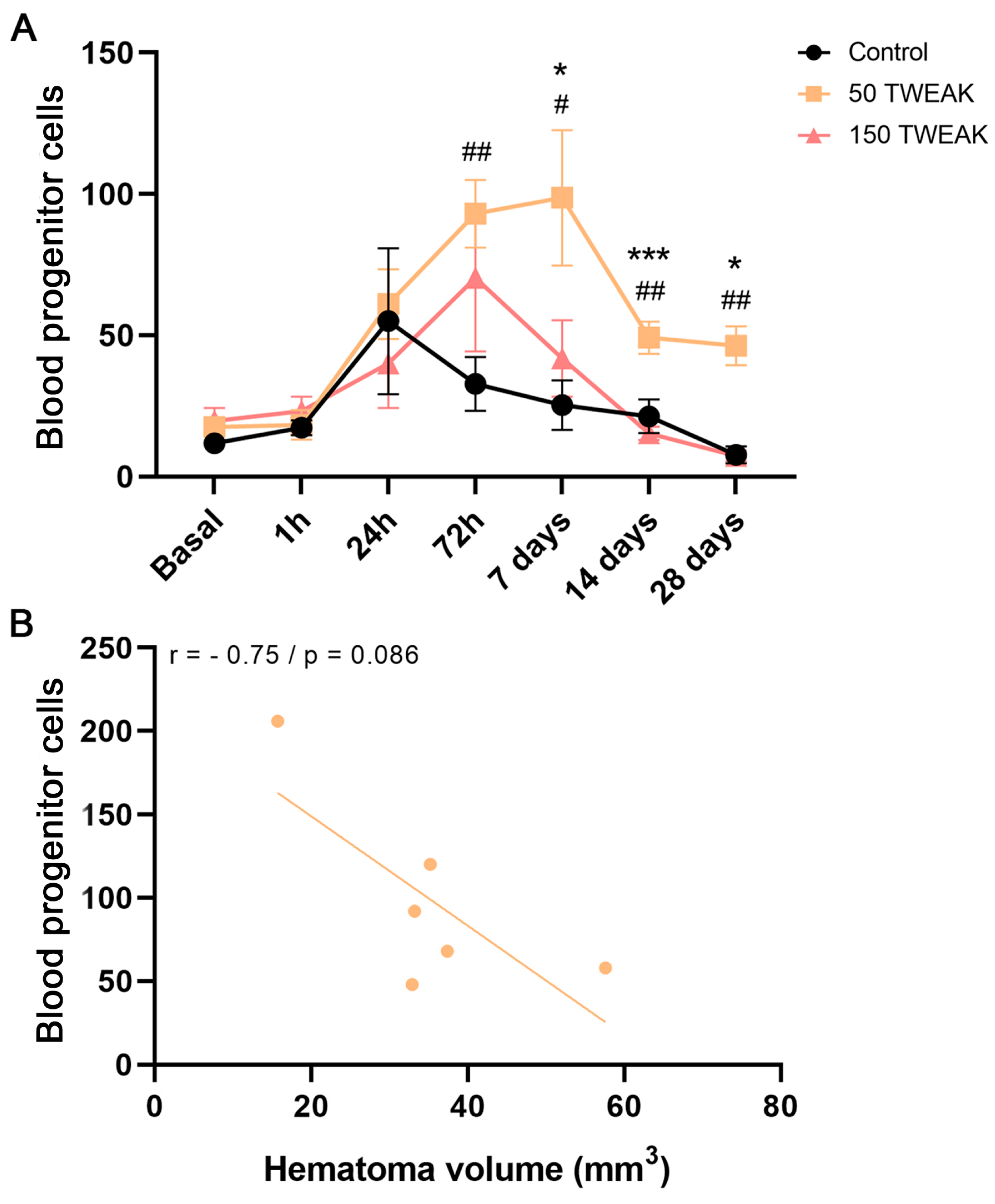
2.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Blood Progenitor Cells
2.7. Tissue Processing
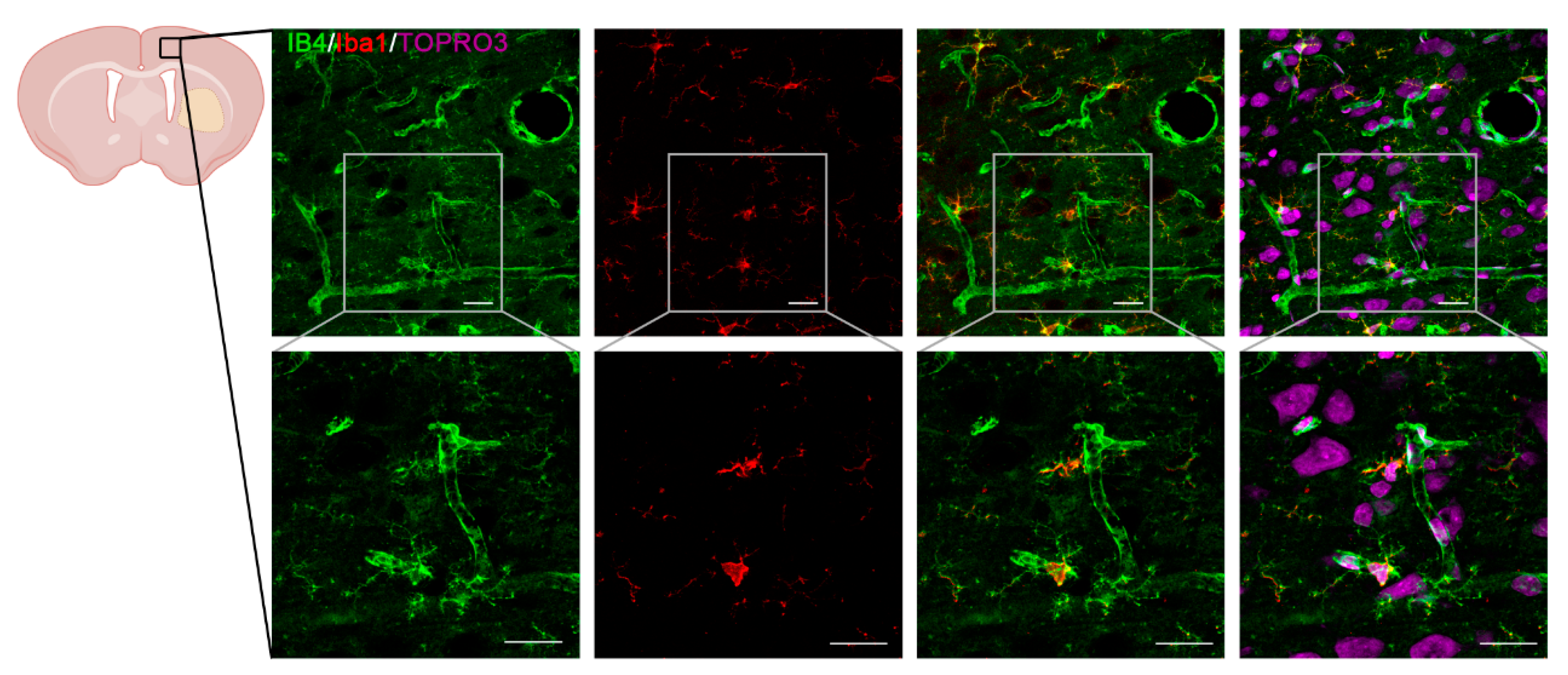
2.8. Immunofluorescence Protocol
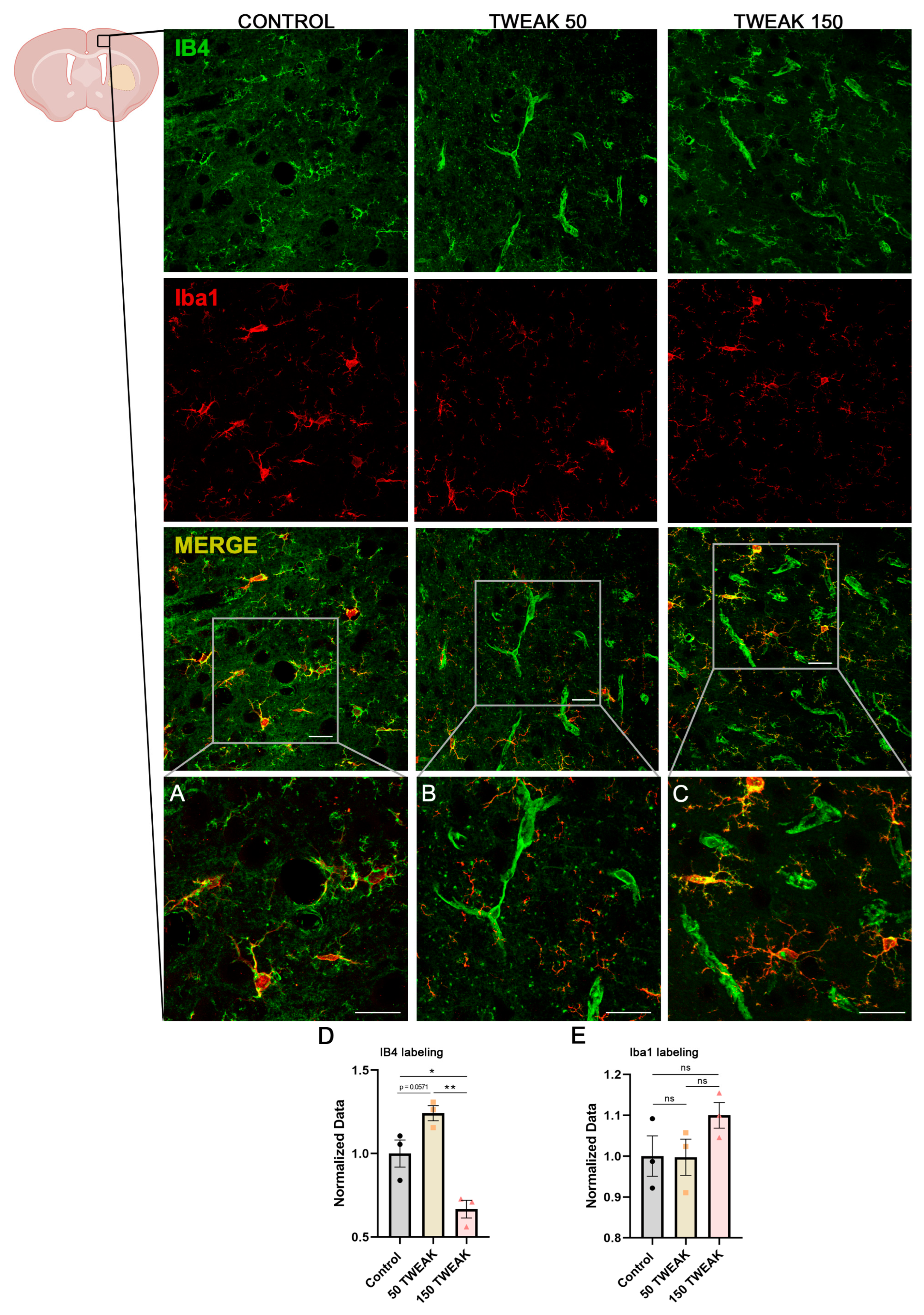
2.9. Immunofluorescence Quantifications
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. rTWEAK Decreases Long-Term Hematoma Volume After ICH Induction
3.2. rTWEAK Promotes and Maintains Long-Term Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization
3.3. rTWEAK Enhanced Cortical Neovascularization
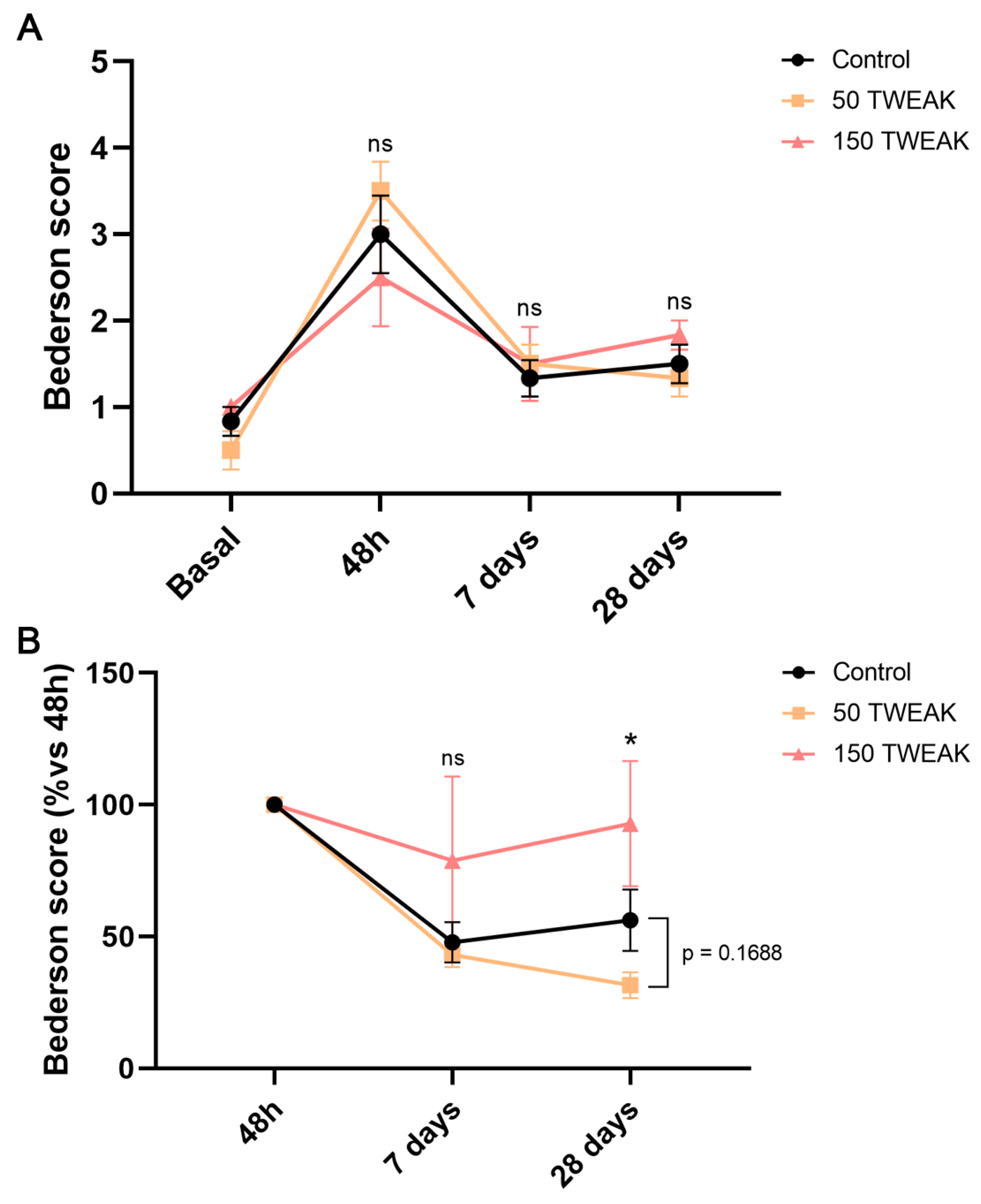
3.4. The Effect of rTWEAK Treatments on Neurological Recovery
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| EPCs | Endothelial progenitor cells |
| ICH | Non-traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| rTWEAK | Recombinant TWEAK |
| PB | Phosphate buffer |
| RARE | Rapid Acquisition Relaxation Enhancement |
| STAIR | Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable |
| TWEAK | TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis |
References
- Carhuapoma, L.; Murthy, S.; Shah, V.A. Outcome Trajectories after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Semin. Neurol. 2024, 44, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffge, D.J.; Fandler-Höfler, S.; Du, Y.; Goeldlin, M.B.; Jolink, W.M.; Klijn, C.J.; Werring, D.J. Intracerebral haemorrhage—Mechanisms, diagnosis and prospects for treatment and prevention. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhou, H.J.; Luo, J.K.; Huang, J.F.; Yang, Q.D.; Li, X.Q. Cerebral angiogenesis after collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1175, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.L.; Zhou, H.J.; Tang, T.; Luo, J.K.; Cui, H.J. Temporal profile of angiogenesis and expression of extracellular matrix-related genes in rat brains following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci. Prog. 2022, 105, 368504221115509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Schallert, T.; Keep, R.F.; Wu, J.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 2002, 33, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pías-Peleteiro, J.; Campos, F.; Perez-Mato, M.; Lopez-Arias, E.; Rodriguez-Yanez, M.; Castillo, J.; Sobrino, T. Endothelial Progenitor Cells as a Therapeutic Approach for Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodia, A.; Ouro, A.; Sargento-Freitas, J.; Aramburu-Núñez, M.; Pías-Peleteiro, J.M.; Hervella, P.; Rosell, A.; Ferreira, L.; Castillo, J.; Romaus-Sanjurjo, D. Unraveling the potential of endothelial progenitor cells as a treatment following ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 940682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, K.; Yoder, M.C. Tissue regeneration using endothelial colony-forming cells: Promising cells for vascular repair. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Chan, S.J.; Mandeville, E.T.; Park, J.H.; Bruzzese, M.; Montaner, J.; Arai, K.; Rosell, A.; Lo, E.H. Protective Effects of Endothelial Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Mitochondria in Brain Endothelium. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. Paracrine mechanisms of endothelial progenitor cells in vascular repair. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, T.; Hurtado, O.; Moro, M.A.; Rodri, M.; Castellanos, M.; Brea, D.; Moldes, O.; Blanco, M.; Arenillas, J.F.; Leira, R. The increase of circulating endothelial progenitor cells after acute ischemic stroke is associated with good outcome. Stroke 2007, 38, 2759–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrino, T.; Pérez-Mato, M.; Brea, D.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; Blanco, M.; Castillo, J. Temporal profile of molecular signatures associated with circulating endothelial progenitor cells in human ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, Y. Changes in serum vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin concentrations associated with circulating endothelial progenitor cells after acute ischemic stroke. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska, E.; Gołąb-Janowska, M.; Bajer-Czajkowska, A.; Machalińska, A.; Ustianowski, P.; Rybicka, M.; Kłos, P.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Nowacki, P.; et al. Increased circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke: The role of endothelin-1. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 325, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pías-Peleteiro, J.; Pérez-Mato, M.; López-Arias, E.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; Blanco, M.; Campos, F.; Castillo, J.; Sobrino, T. Increased Endothelial Progenitor Cell Levels are Associated with Good Outcome in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tousoulis, D.; Andreou, I.; Antoniades, C.; Tentolouris, C.; Stefanadis, C. Role of inflammation and oxidative stress in endothelial progenitor cell function and mobilization: Therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis 2008, 201, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halurkar, M.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Bihl, J.C. EPC-EXs improve astrocyte survival and oxidative stress through different uptaking pathways in diabetic hypoxia condition. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebing, J.; Arana, J.A.; Salzmann, S.; Wajant, H. Analyzing the signaling capabilities of soluble and membrane TWEAK. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1155, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche, Y.; Bourdon, P.R.; Xu, H.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Scott, H.; Hession, C.; Garcia, I.; Browning, J.L. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32401–32410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkles, J.A. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: Discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, E.R.; Pana, T.A.; Barlas, R.S.; Metcalf, A.K.; Potter, J.F.; Myint, P.K. Elevated inflammatory biomarkers and poor outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 6330–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Cook, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y. A potential fate decision landscape of the TWEAK/Fn14 axis on stem and progenitor cells: A systematic review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Ju, C.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Yan, G.; He, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, G. TWEAK promotes endothelial progenitor cell vasculogenesis to alleviate acute myocardial infarction via the Fn14-NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4019–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potrovita, I.; Zhang, W.; Burkly, L.; Hahm, K.; Lincecum, J.; Wang, M.Z.; Maurer, M.H.; Rossner, M.; Schneider, A.; Schwaninger, M. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis-induced neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8237–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, R.; Gongora, M.C.; Winkles, J.A.; Yepes, M. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis increases the permeability of the neurovascular unit through nuclear factor-kappa B pathway activation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10094–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, M.; Brown, S.A.; Moore, E.G.; Smith, E.P.; Lawrence, D.A.; Winkles, J.A. A soluble Fn14-Fc decoy receptor reduces infarct volume in a murine model of cerebral ischemia. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Winkles, J.A.; Gongora, M.C.; Polavarapu, R.; Michaelson, J.S.; Hahm, K.; Burkly, L.; Friedman, M.; Li, X.-J.; Yepes, M. TWEAK-Fn14 pathway inhibition protects the integrity of the neurovascular unit during cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2007, 27, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Sobrino, T.; López-Arias, E.; Ugarte, A.; Sánchez-Arias, J.A.; Vieites-Prado, A.; de Miguel, I.; Oyarzabal, J.; Páramo, J.A.; Campos, F. CM352 Reduces Brain Damage and Improves Functional Recovery in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Lado, N.; López-Arias, E.; Iglesias-Rey, R.; Díaz-PlatasSantiago, L.; Medín-AguerreAnxo, S.; Fernández-FerreiroAdrián, A.; Posado-FernándezLara, A.; García-VarelaManuel, L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.; Campos, F. [18F]-FMISO PET/MRI Imaging Shows Ischemic Tissue around Hematoma in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, C.; Changotra, H.; Wedhas, N.; Qin, X.; Wergedal, J.E.; Kumar, A. TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a potent skeletal muscle-wasting cytokine. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva-Candal, A.; Vieites-Prado, A.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M.; Rey, R.I.; Argibay, B.; Mirelman, D.; Sobrino, T.; Rodríguez-Frutos, B.; Castillo, J.; Campos, F. Blood glutamate grabbing does not reduce the hematoma in an intracerebral hemorrhage model but it is a safe excitotoxic treatment modality. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2015, 35, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, M.; Benatar, M.; Fisher, M.; Savitz, S.I. Methodological quality of animal studies of neuroprotective agents currently in phase II/III acute ischemic stroke trials. Stroke 2009, 40, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bederson, J.B.; Pitts, L.H.; Tsuji, M.; Nishimura, M.C.; Davis, R.L.; Bartkowski, H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986, 17, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadini, G.P.; Sartore, S.; Schiavon, M.; Albiero, M.; Baesso, I.; Cabrelle, A.; Agostini, C.; Avogaro, A. Diabetes impairs progenitor cell mobilisation after hindlimb ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.; Sobrino, T.; Agulla, J.; Bobo-Jiménez, V.; Ramos-Araque, M.E.; Duarte, J.J.; Gómez-Sánchez, J.C.; Bolaños, J.P.; Castillo, J.; Almeida, Á. Neovascularization and functional recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage is conditioned by the Tp53 Arg72Pro single-nucleotide polymorphism. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.N.; Wang, Y.C.; Lund, J.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Leal, J.A.; Wiley, S.R. TWEAK induces angiogenesis and proliferation of endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8455–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, S.R.; Cassiano, L.; Lofton, T.; Davis-Smith, T.; Winkles, J.A.; Lindner, V.; Liu, H.; Daniel, T.O.; Smith, C.A.; Fanslow, W.C. A novel TNF receptor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis. Immunity 2001, 15, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Nakayama, M.; Nakano, H.; Fukuchi, Y.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Pro-inflammatory effect of TWEAK/Fn14 interaction on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, A.; Browning, B.; Lukashev, M.; Sizing, I.; Thompson, J.S.; Benjamin, C.D.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Ambrose, C.; Zheng, T.S.; Burkly, L.C. Dual role for TWEAK in angiogenic regulation. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, P.J.; Richards, C.M.; Brown, S.A.; Hanscom, H.N.; Buschman, J.; Thangada, S.; Hla, T.; Williams, M.S.; Winkles, J.A. TWEAK is an endothelial cell growth and chemotactic factor that also potentiates FGF-2 and VEGF-A mitogenic activity. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Fàbregas, J.; Crespo, J.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Peña, E.; Marín, R.; Dinia, L.; Jiménez-Xarrié, E.; Fernández-Arcos, A.; Pérez-Pérez, J.; et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in acute ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva-Candal, A.; Pérez-Mato, M.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; López-Dequidt, I.; Pumar, J.M.; Ávila-Gómez, P.; Sobrino, T.; Campos, F.; Castillo, J.; Hervella, P. The presence of leukoaraiosis enhances the association between sTWEAK and hemorrhagic transformation. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva-Candal, A.; López-Dequidt, I.; Rodriguez-Yañez, M.; Ávila-Gómez, P.; Pumar, J.M.; Castillo, J.; Sobrino, T.; Campos, F.; Iglesias-Rey, R.; Hervella, P. sTWEAK is a marker of early haematoma growth and leukoaraiosis in intracerebral haemorrhage. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2021, 6, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Neurological Inflammation: A Mini Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkly, L.C.; Michaelson, J.S.; Hahm, K.; Jakubowski, A.; Zheng, T.S. TWEAKing tissue remodeling by a multifunctional cytokine: Role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in health and disease. Cytokine 2007, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Xiang, H.; Guo, L.; Chen, R.; Zhao, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, P.; Lu, H.; Chen, S. TWEAK/Fn14 promotes oxidative stress through AMPK/PGC-1α/MnSOD signaling pathway in endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal-Matute, J.; Fernandez-Laso, V.; Sastre, C.; Llamas-Granda, P.; Egido, J.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Zalba, G.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. TWEAK/Fn14 interaction promotes oxidative stress through NADPH oxidase activation in macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samidurai, M.; Tarale, P.; Janarthanam, C.; Estrada, C.G.; Gordon, R.; Zenitsky, G.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Kanthasamy, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis (TWEAK) Enhances Activation of STAT3/NLRC4 Inflammasome Signaling Axis through PKCδ in Astrocytes: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarín, C.; Fernández-Laso, V.; Sastre, C.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Gómez, M.; Zaragoza, C.; Egido, J.; Burkly, L.C.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis or Fn14 deficiency reduce elastase perfusion-induced aortic abdominal aneurysm in mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saas, P.; Boucraut, J.; Walker, P.R.; Quiquerez, A.-L.; Billot, M.; Desplat-Jego, S.; Chicheportiche, Y.; Dietrich, P.-Y. TWEAK stimulation of astrocytes and the proinflammatory consequences. Glia 2000, 32, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, R.; Fang, Z.; You, M.; He, Q.; Hu, B. Microglia Phenotype and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Balance of Yin and Yang. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 765205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Ma, L. Secondary Brain Injury by Oxidative Stress After Cerebral Hemorrhage: Recent Advances. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 853589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Yong, V.W.; Xue, M. Oxidative Stress Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Fan, X. Targeting Oxidative Stress in Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Prospects of the Natural Products Approach. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wälchli, T.; Mateos, J.M.; Weinman, O.; Babic, D.; Regli, L.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Gerhardt, H.; Schwab, M.E.; Vogel, J. Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial tip cells in the postnatal mouse brain. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Zhu, L.; Han, P.; Bai, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Chi, H.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. TWEAK is an activator of Hippo-YAP signaling protecting against hepatic Ischemia/ reperfusion injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Park, D.Y.; Bae, H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, S.P.; Jang, S.P.; Kubota, Y.; et al. YAP/TAZ regulates sprouting angiogenesis and vascular barrier maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3441–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.; Morancho, A.; Navarro-Sobrino, M.; Martínez-Saez, E.; Hernández-Guillamon, M.; Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Barceló, V.; Borrás, F.; Penalba, A.; García-Bonilla, L.; et al. Factors secreted by endothelial progenitor cells enhance neurorepair responses after cerebral ischemia in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romaus-Sanjurjo, D.; López-Arias, E.; Rodríguez, C.; Hervella, P.; Rodríguez-Arrizabalaga, M.; Debasa-Mouce, M.; Pías-Peleteiro, J.M.; Iglesias-Rey, R.; Aguiar, P.; Almeida, Á.; et al. Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization Driven by TWEAK Promotes Neovascularization and Reduces Brain Damage in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050601
Romaus-Sanjurjo D, López-Arias E, Rodríguez C, Hervella P, Rodríguez-Arrizabalaga M, Debasa-Mouce M, Pías-Peleteiro JM, Iglesias-Rey R, Aguiar P, Almeida Á, et al. Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization Driven by TWEAK Promotes Neovascularization and Reduces Brain Damage in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050601
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomaus-Sanjurjo, Daniel, Esteban López-Arias, Cristina Rodríguez, Pablo Hervella, Mariña Rodríguez-Arrizabalaga, Manuel Debasa-Mouce, Juan Manuel Pías-Peleteiro, Ramón Iglesias-Rey, Pablo Aguiar, Ángeles Almeida, and et al. 2025. "Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization Driven by TWEAK Promotes Neovascularization and Reduces Brain Damage in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050601
APA StyleRomaus-Sanjurjo, D., López-Arias, E., Rodríguez, C., Hervella, P., Rodríguez-Arrizabalaga, M., Debasa-Mouce, M., Pías-Peleteiro, J. M., Iglesias-Rey, R., Aguiar, P., Almeida, Á., Castillo, J., Ouro, A., & Sobrino, T. (2025). Blood Progenitor Cell Mobilization Driven by TWEAK Promotes Neovascularization and Reduces Brain Damage in a Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Antioxidants, 14(5), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050601











