Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Equipment
2.2. In Vivo Assay
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Recombinant Expression and Purification of STb
2.5. Measurement of Oxidative-Antioxidant Parameters
2.6. Paraffin Blocks Preparation
2.7. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.9. Real-Time qPCR
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
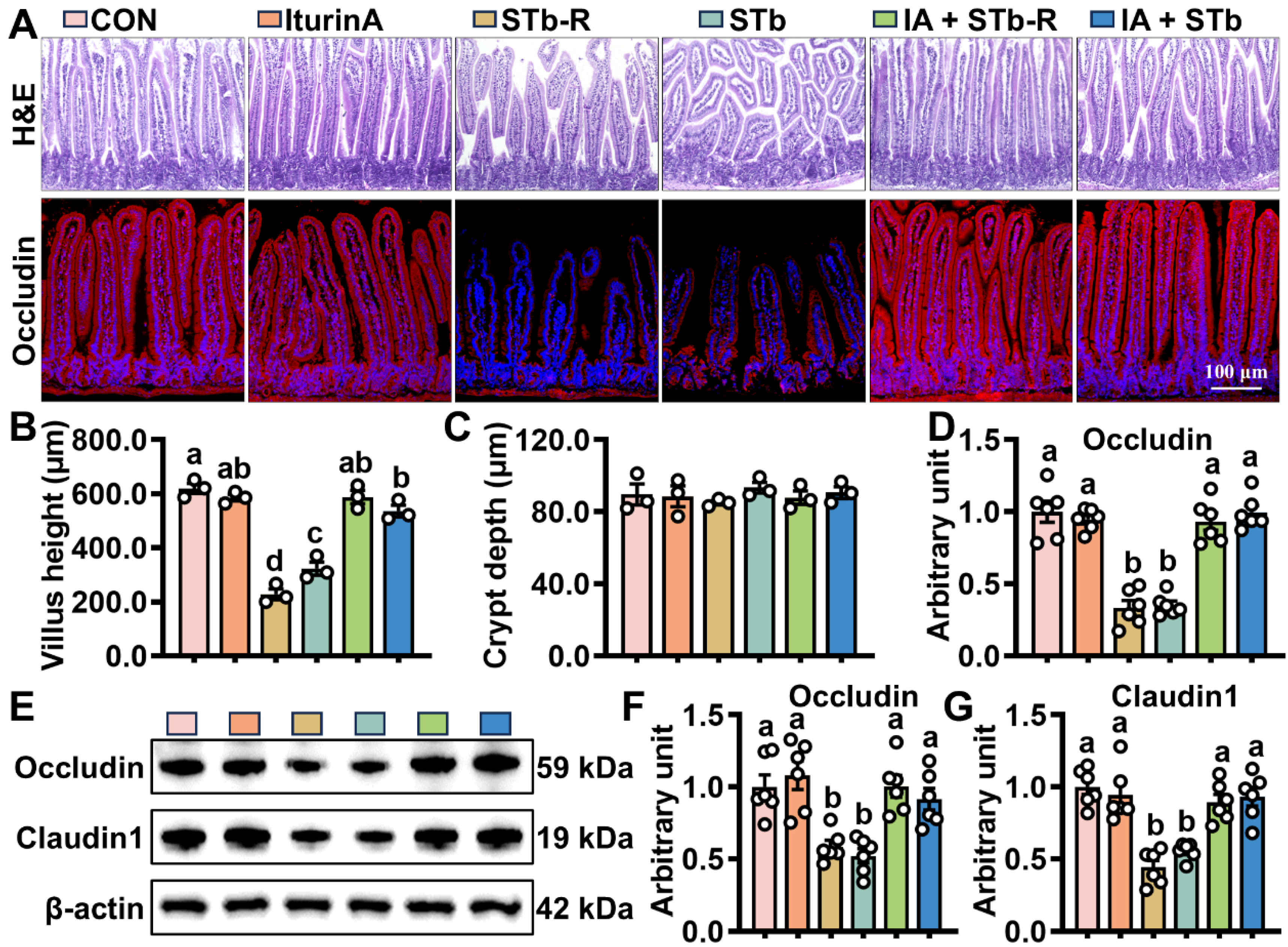
3.1. Iturin A Attenuates STb Damage to Intestinal Epithelial Structures in Mice
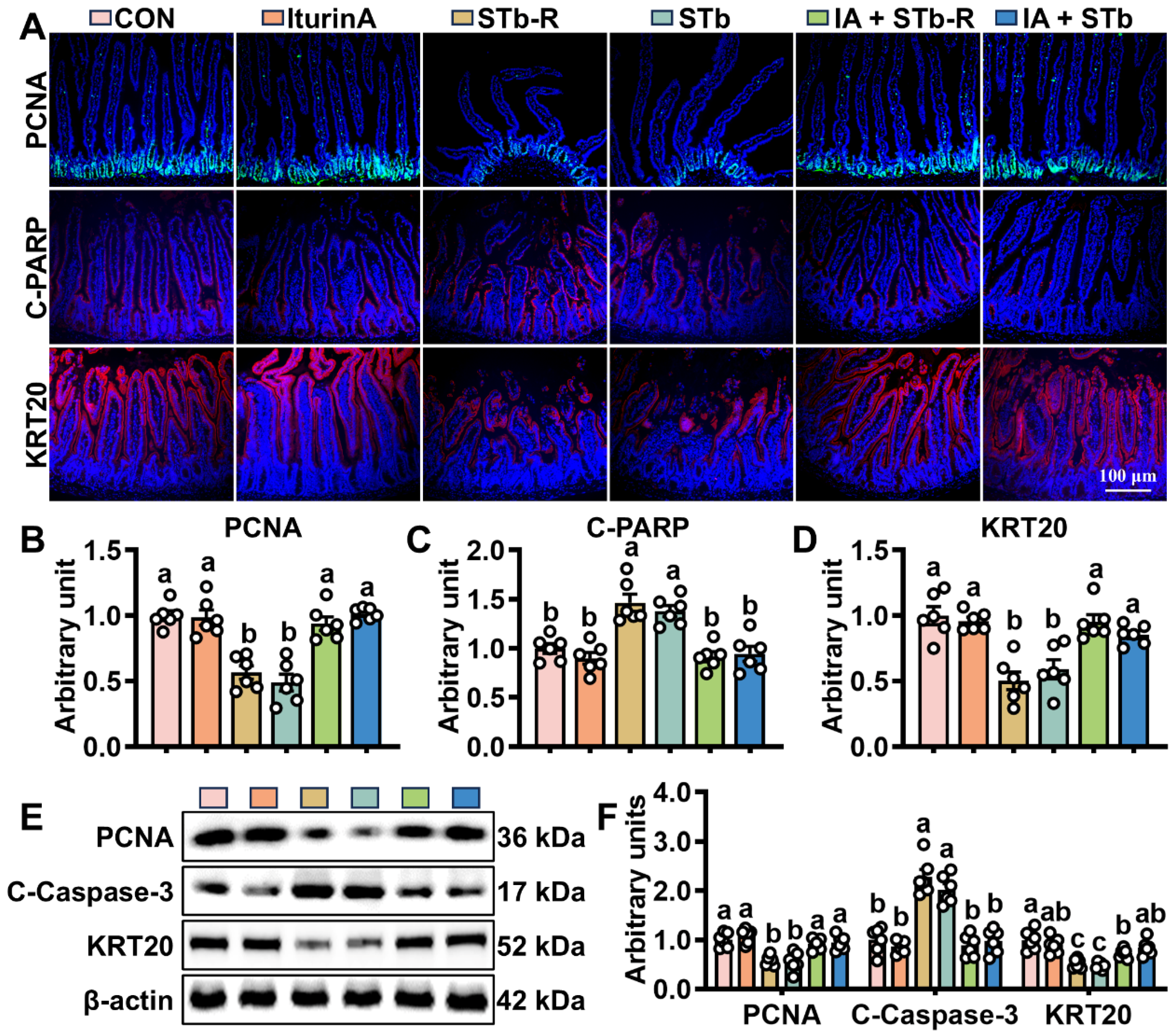
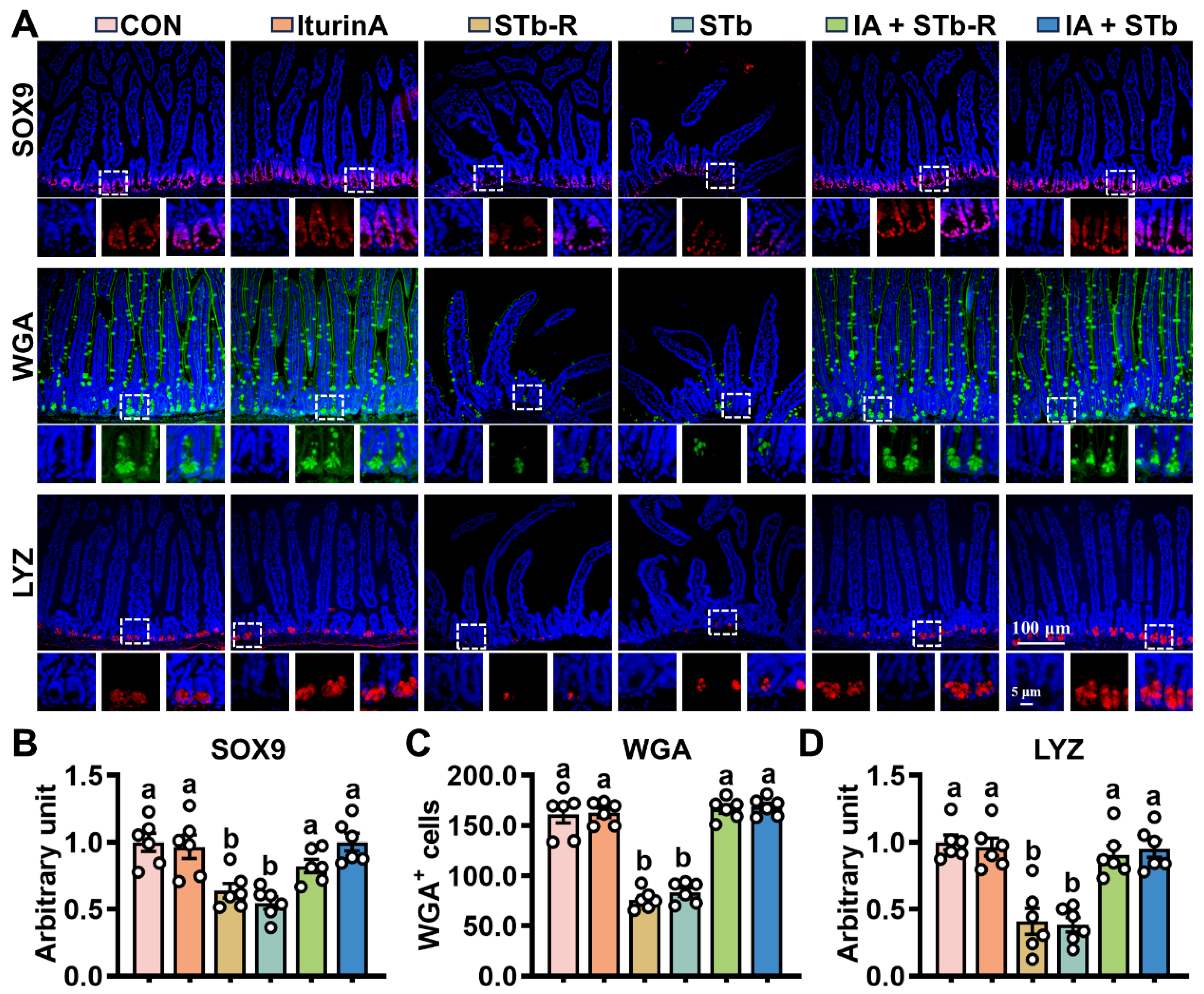
3.2. Iturin A Enhances the Activity of Mouse ISCs After STb Invasion
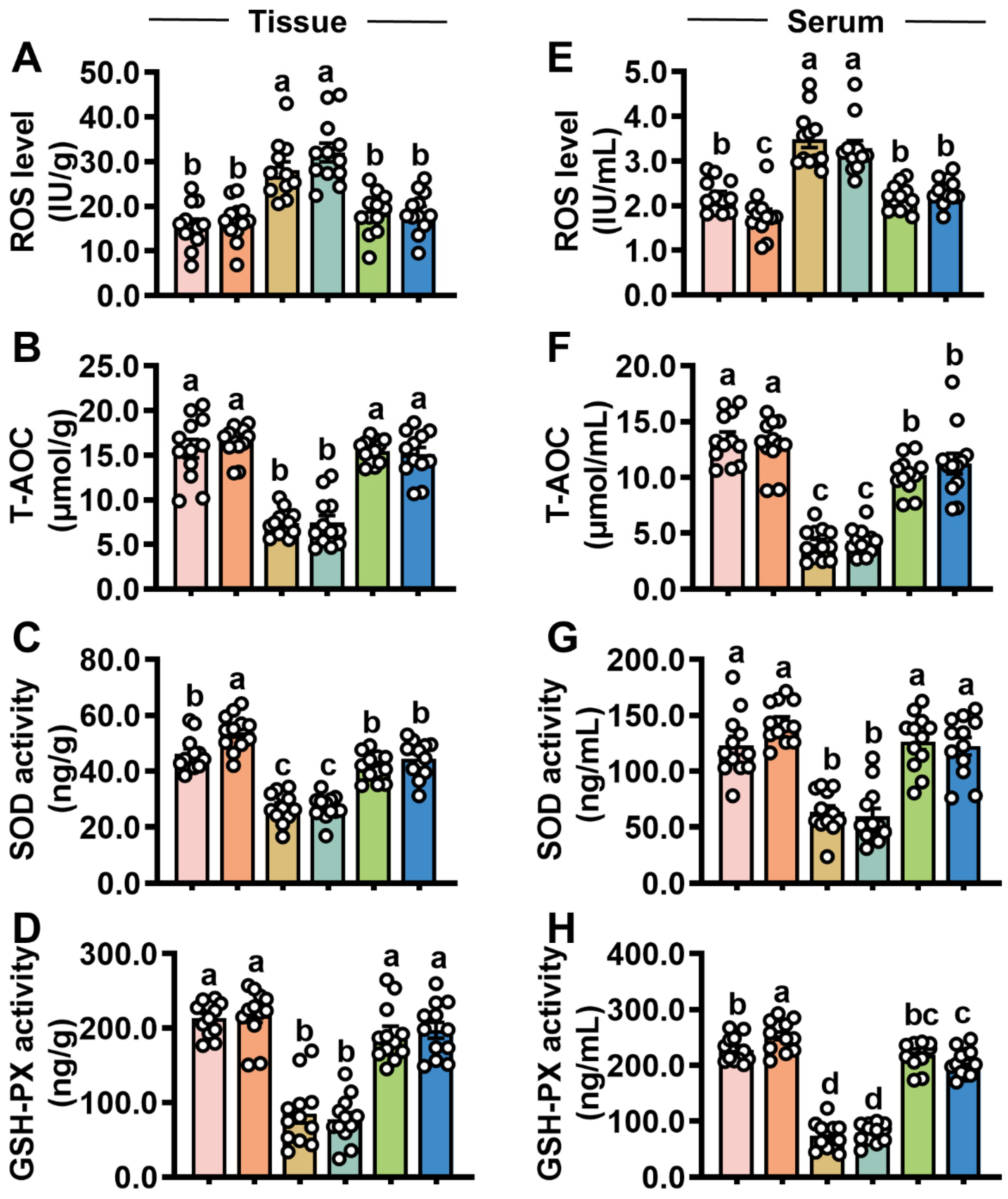
3.3. Iturin A Elevates Intestinal Antioxidant Capacity in Mice After STb Invasion
3.4. Iturin A Promotes Intestinal Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling in Mice Under STb Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvador-Erro, J.; Pastor, Y.; Gamazo, C. Targeting Enterotoxins: Advancing Vaccine Development for Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ETEC. Toxins 2025, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.L.; Zhou, J.Y.; Liang, S.J.; Wang, X.Q. Impaired intestinal stem cell activity in ETEC infection: Enterotoxins, cyclic nucleotides, and Wnt signaling. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, S.; Saleh, M.; Gagnon, J. Impact of the Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin b (STb) on Gut Health and Function. Toxins 2020, 12, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, J.; Viitanen, A.; Fabris, G.; Strutynska, T.; Korzelius, J.; Hietakangas, V. Stem cell mTOR signaling directs region-specific cell fate decisions during intestinal nutrient adaptation. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadi2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Che, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Meng, T.; Xie, H.; Cao, L.; Hao, H. Dual roles of IL-18 in colitis through regulation of the function and quantity of goblet cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, M.; Samuelson, L.C. Paneth Cells: Dispensable yet Irreplaceable for the Intestinal Stem Cell Niche. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 19, 101443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Xiu, M.; Dai, Y.; Wan, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, J. Flos puerariae ameliorates the intestinal inflammation of Drosophila via modulating the Nrf2/Keap1, JAK-STAT and Wnt signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 893758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liang, S.; Zan, G.; Wang, X.; Gao, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J. Selenomethionine Alleviates DON-Induced Oxidative Stress via Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling in the Small Intestinal Epithelium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Mansy, M.S.; Ramadan, M.A.; Aziz, R.K. The biosurfactants iturin, lichenysin and surfactin, from vaginally isolated lactobacilli, prevent biofilm formation by pathogenic Candida. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaraguppi, D.A.; Bagewadi, Z.K.; Patil, N.R.; Mantri, N. Iturin: A Promising Cyclic Lipopeptide with Diverse Applications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, S.; Zhao, X.; Shao, D.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J.; Sun, H. Potential of iturins as functional agents: Safe, probiotic, and cytotoxic to cancer cells. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5580–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, G.X.; Qu, H.Z.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.F.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, J.Y. Matrine disturbs the eimeria necatrix-induced loop of tuft cell-intestinal stem cell-goblet cell by inactivating IL-13/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghdadi, M.B.; Houtekamer, R.M.; Perrin, L.; Rao-Bhatia, A.; Whelen, M.; Decker, L.; Bergert, M.; Pérez-Gonzàlez, C.; Bouras, R.; Gropplero, G.; et al. PIEZO-dependent mechanosensing is essential for intestinal stem cell fate decision and maintenance. Science 2024, 386, eadj7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, H.; Jung, K.B.; Chang, D.H.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, E.J.; et al. The secreted protein Amuc_1409 from Akkermansia muciniphila improves gut health through intestinal stem cell regulation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, J.; Sun, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhai, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Sishen Wan enhances intestinal barrier function via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress to improve mice with diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 129, 155541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Zan, G.X.; Zhu, Q.J.; Gao, C.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q. Recombinant Porcine R-Spondin 1 Facilitates Intestinal Stem Cell Expansion along the Crypt-Villus Axis through Potentiating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Homeostasis and Deoxynivalenol Injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10644–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, G.X.; Qin, Y.C.; Xie, W.W.; Gao, C.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, J.Y. Heat stress disrupts intestinal stem cell migration and differentiation along the crypt-villus axis through FAK signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2023, 1870, 119431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cray, P.; Sheahan, B.J.; Dekaney, C.M. Secretory Sorcery: Paneth Cell Control of Intestinal Repair and Homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.E.; Deng, Z.; Kim, S.W. Effects of dietary Lactobacillus postbiotics and bacitracin on the modulation of mucosa-associated microbiota and pattern recognition receptors affecting immunocompetence of jejunal mucosa in pigs challenged with enterotoxigenic F18(+) Escherichia coli. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Zhang, J.; Thacker, P.A.; Qiao, S. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide cecropin AD on performance and intestinal health in weaned piglets challenged with Escherichia coli. Peptides 2012, 35, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, J.; He, L.; Jiang, D.; Huang, S.; Hou, S. The Hydrophobic Amino Acid-Rich Fish Collagen Peptide Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice via Repairing the Intestinal Barrier, Regulating Intestinal Flora and AA Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 25690–25703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Flier, L.G.; Clevers, H. Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Huang, D.G.; Gao, C.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Zou, S.G.; Wang, X.Q. Heat-stable enterotoxin inhibits intestinal stem cell expansion to disrupt the intestinal integrity by downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yan, W.; Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, J. Effects of IRW and IQW on Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota in Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 51, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Jiang, J.; et al. The Antimicrobial Peptide Mastoparan X Protects Against Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection, Inhibits Inflammation, and Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 644887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Solé, F.; Criado-Mesas, L.; Villodre, C.; García, W.C.; Farré, M.; Borda, E.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Folch, J.M.; Solà-Oriol, D.; Pérez, J.F. Porcine Digestible Peptides (PDP) in Weanling Diets Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Gut Barrier Function, Immune Response and Nutrient Transport in Nursery Pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Wei, Y.; Han, S.; Xia, L.; Tan, B.; Yu, J.; Kang, H.; Ma, M.; et al. Effects of Small Peptide Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier of Laying Hens During the Brooding and Growing Periods. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Podio, N.S.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Jiang, S.; Wei, X.; Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Research progress on the regulation of oxidative stress by phenolics: The role of gut microbiota and Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.A.; Liang, S.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, H.C. Lycopene Protects Intestinal Epithelium from Deoxynivalenol-Induced Oxidative Damage via Regulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Lin, H.L.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, X.G.; Gao, C.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q. l-Carnosine Protects Against Deoxynivalenol-Induced Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Stem Cells by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Guo, K. Tannic acid alleviates ETEC K88-induced intestinal damage through regulating the p62-keap1-Nrf2 and TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway in IPEC-J2 cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5186–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shang, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, K.; Qiao, J. Clostridium butyricum Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-Induced Oxidative Damage Through Regulating the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Remodeling the Cecal Microbial Community. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 771826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, N.; Huang, H.; Idris, M.; Peng, X.; Xu, F.; Dong, S.; Liu, C. KEAP1 Mutations Drive Tumorigenesis by Suppressing SOX9 Ubiquitination and Degradation. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidlin, C.J.; Zeng, T.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Dodson, M.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. Chronic arsenic exposure enhances metastatic potential via NRF2-mediated upregulation of SOX9. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 402, 115138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Ye, P.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Lei, G.; Zhao, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Lunasin attenuates oxidant-induced endothelial injury and inhibits atherosclerotic plaque progression in ApoE(-/-) mice by up-regulating heme oxygenase-1 via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/ARE pathway. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 4836–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, G.; Basilicata, M.G.; Carrizzo, A.; Adesso, S.; Ostacolo, C.; Sala, M.; Sommella, E.; Ruocco, M.; Cascioferro, S.; Ambrosio, M.; et al. β-Lactoglobulin Heptapeptide Reduces Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Angiotensin II-Induced Vasoconstriction on Mouse Mesenteric Arteries by Induction of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Translocation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1616239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Silva, M.; Pruccoli, L.; Morroni, F.; Sita, G.; Seghetti, F.; Viegas, C.; Tarozzi, A. The Keap1/Nrf2-ARE Pathway as a Pharmacological Target for Chalcones. Molecules 2018, 23, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, S.; Lu, C.; Wan, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Ming, T.; Jim Wang, Z.; Su, X. The novel peptides ICRD and LCGEC screened from tuna roe show antioxidative activity via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE pathway regulation and gut microbiota modulation. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zan, G.-X.; Qu, H.-Z.; Li, X.-Y.; Peng, Q.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Li, R.-S.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Yan, H.-C.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-Q. Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040478
Zan G-X, Qu H-Z, Li X-Y, Peng Q-L, Wang X-F, Li R-S, Zhao Y-G, Yan H-C, Zhou J-Y, Wang X-Q. Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(4):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040478
Chicago/Turabian StyleZan, Geng-Xiu, Hao-Zhan Qu, Xin-Yang Li, Qi-Liang Peng, Xiao-Fan Wang, Run-Sheng Li, Yu-Guang Zhao, Hui-Chao Yan, Jia-Yi Zhou, and Xiu-Qi Wang. 2025. "Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B" Antioxidants 14, no. 4: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040478
APA StyleZan, G.-X., Qu, H.-Z., Li, X.-Y., Peng, Q.-L., Wang, X.-F., Li, R.-S., Zhao, Y.-G., Yan, H.-C., Zhou, J.-Y., & Wang, X.-Q. (2025). Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B. Antioxidants, 14(4), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040478




