From Waste to Functional Feed Ingredient: Biochemical and SHK-1 Cell Line Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Aquaculture Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Nutritional Composition, and Total Polyphenol Concentration
2.2. Cellular Culture
2.3. MTT Assays
2.4. Cellular Antioxidation
2.5. Cellular Proliferation
2.6. Protein Standardization
2.7. Starvation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
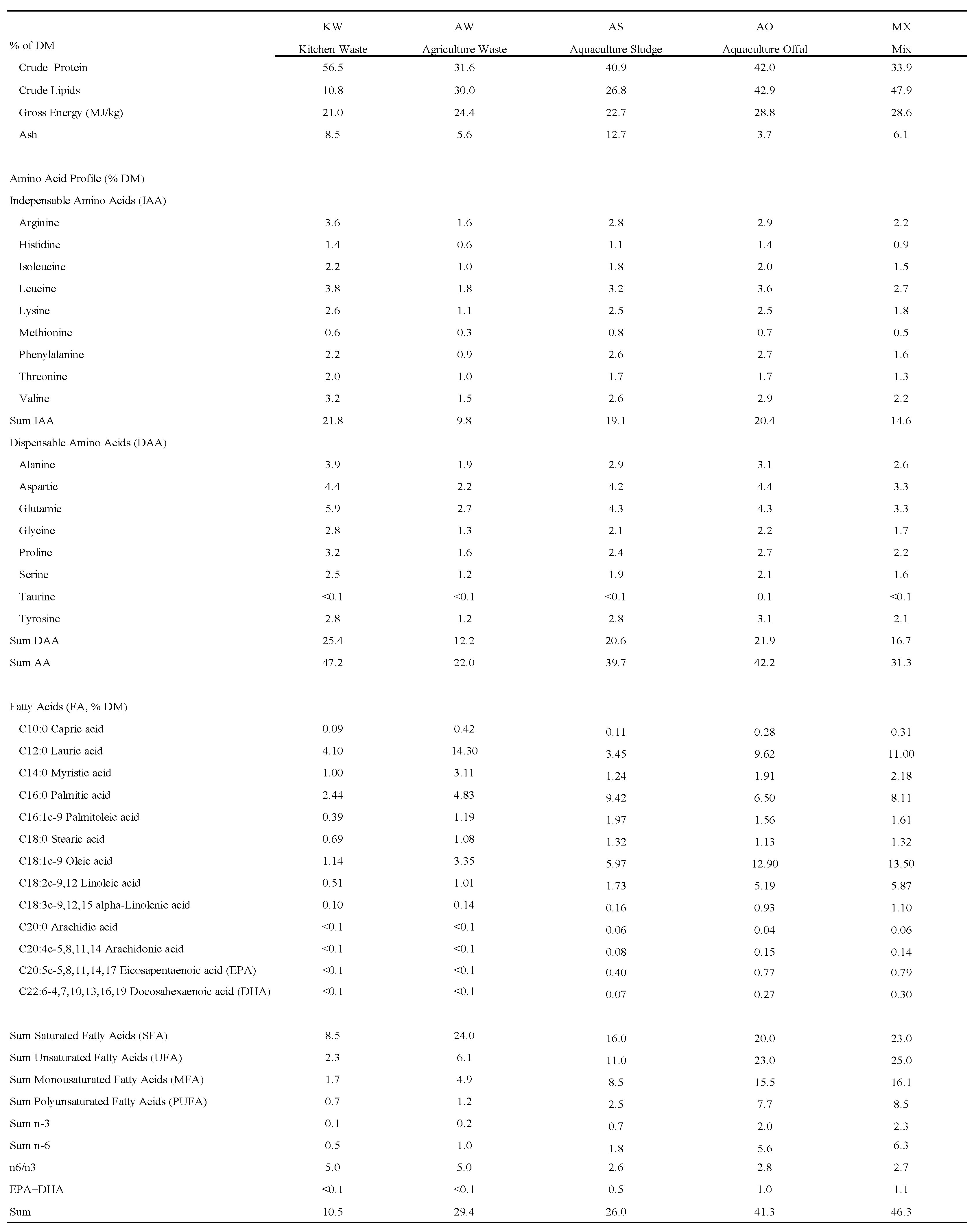
3.1. Cellular Antioxidation
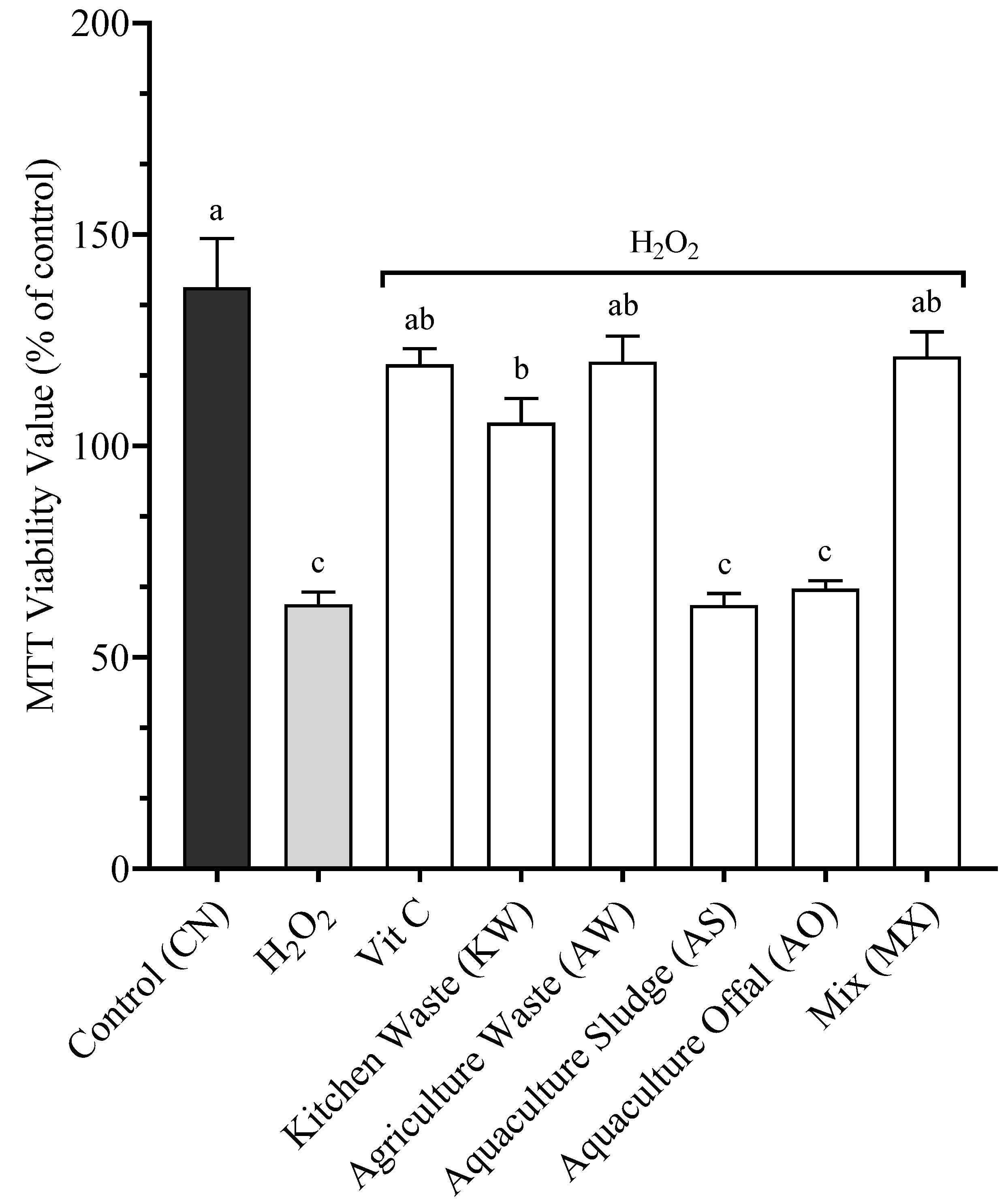
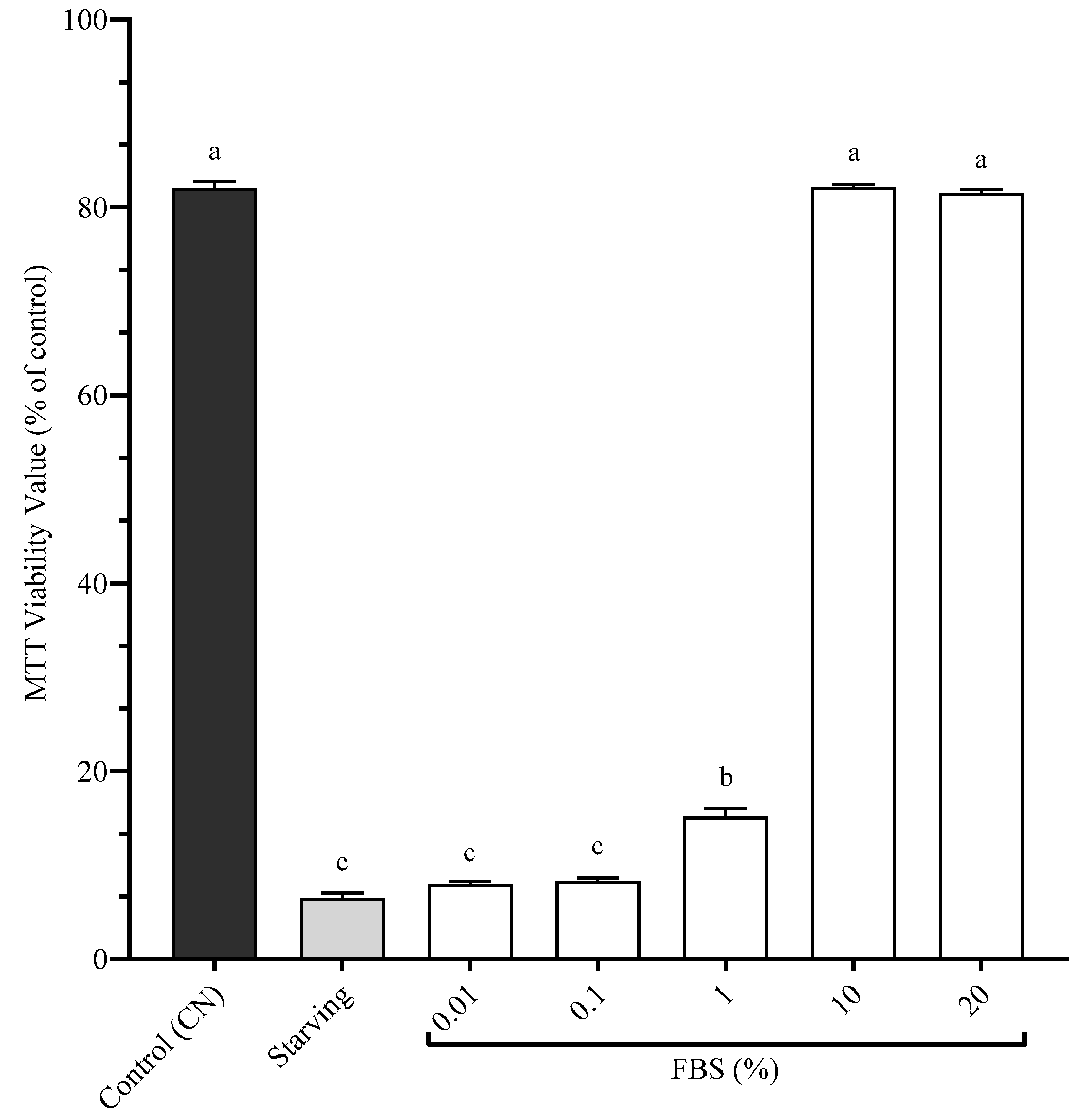
3.2. Cellular Proliferation
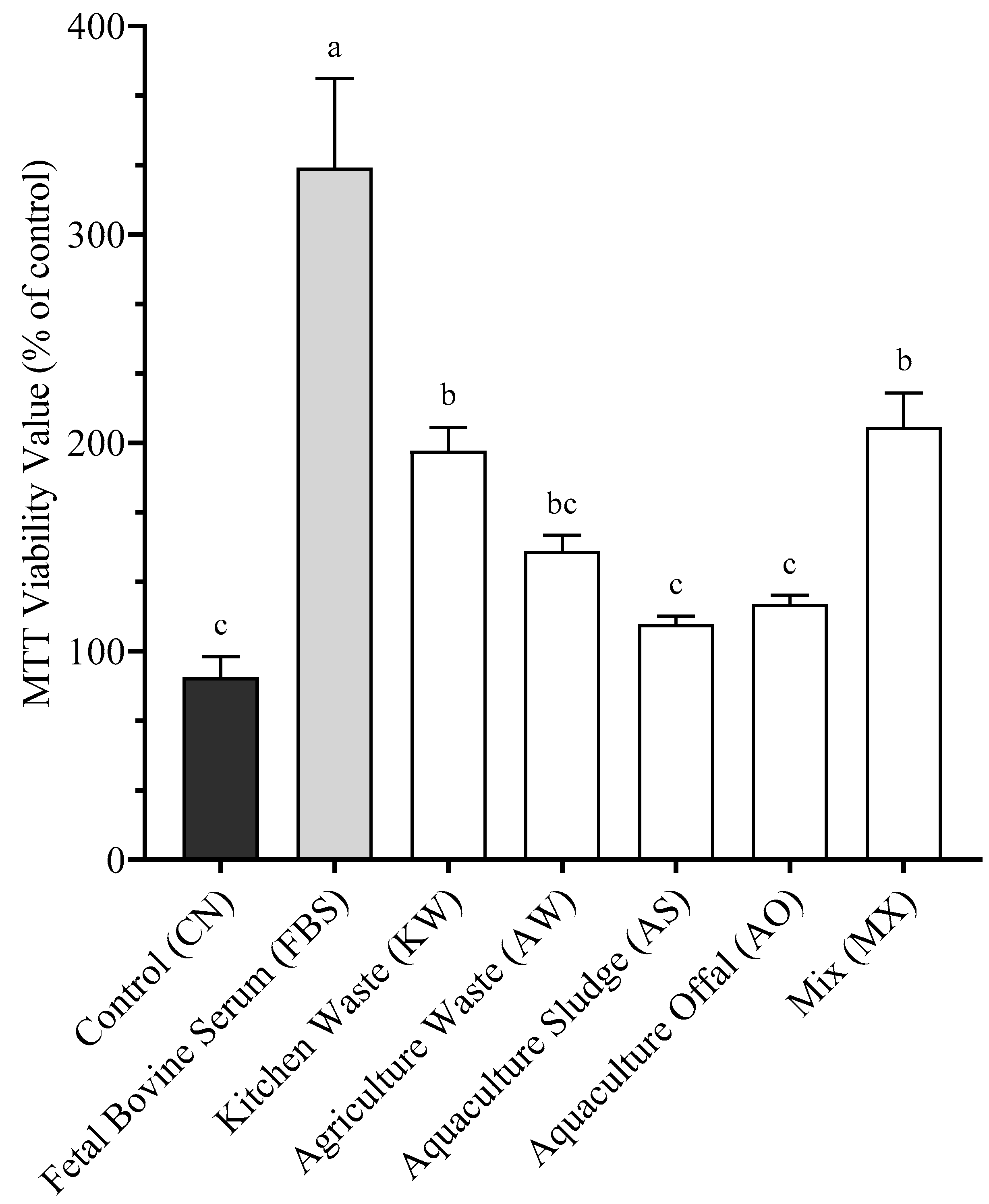
3.3. Protein Standardization
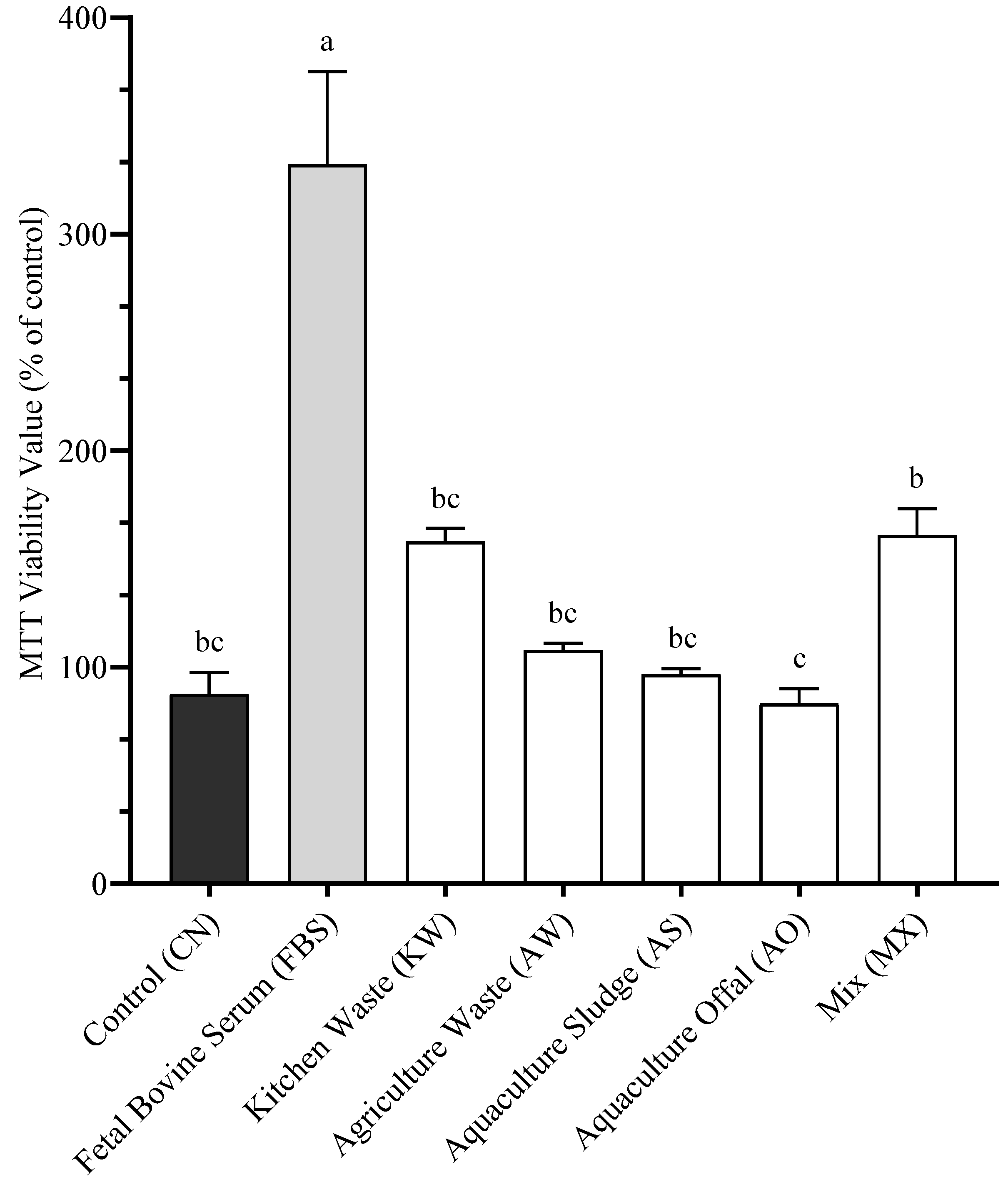
3.4. Cellular Starvation
4. Discussion
4.1. Antioxidation
4.2. Proliferation
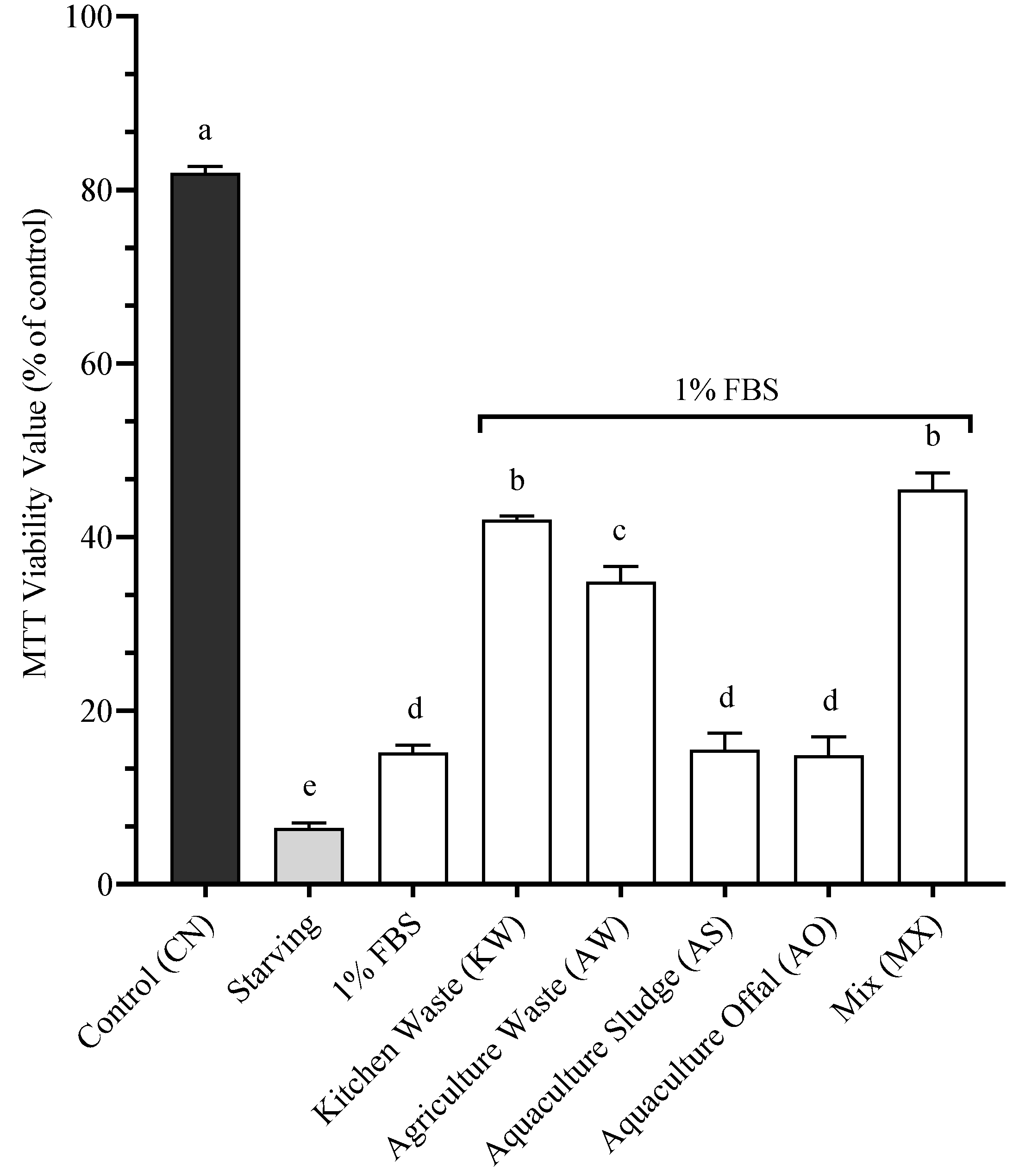
4.3. Proliferation (Standardized Protein)
4.4. Starvation
4.5. Relevance of Oxidative Stress in Aquaculture
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AO | Aquaculture Offal (diet) |
| AS | Aquaculture Sludge (diet) |
| AW | Agricultural Waste (diet) |
| BSFL | Black Soldier Fly Larvae |
| BSFLM | Black Soldier Fly Larvae Meal |
| CN | Control (complete medium + 10% FBS + 1% antibiotic/antimycotic) |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| KW | Kitchen Waste (diet) |
| MTT | [3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] (assay) |
| MX | Mixed Waste (diet) |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SHK-1 | Salmon Head Kidney—1 (cell line from Salmo salar) |
| Vit C | Vitamin C (positive control in antioxidation assay) |
Appendix A
References
- Lock, E.R.; Arsiwalla, T.; Waagbø, R. Insect larvae meal as an alternative source of nutrients in the diet of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) postsmolt. Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 22, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, S.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Fontinha, F.; Martins, N.; Monroig, Ó.; Peres, H. Black soldier fly larvae meal as a potential modulator of immune, inflammatory, and antioxidant status in gilthead seabream juveniles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 271, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weththasinghe, P.; Rocha, S.D.C.; Øyås, O.; Lagos, L.; Hansen, J.Ø.; Mydland, L.T.; Øverland, M. Modulation of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) gut microbiota composition and predicted metabolic capacity by feeding diets with processed black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meals and fractions. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawole, F.J.; Labh, S.N.; Hossain, M.S.; Overturf, K.; Small, B.C.; Welker, T.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Kumar, V. Insect (black soldier fly larvae) oil as a potential substitute for fish or soy oil in the fish meal-based diet of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, C.; Ahilan, B.; Felix, N.; Uma, A.; Chidambaram, P.; Prabu, E. Replacement of fish oil with black soldier fly larvae oil and vegetable oils: Effects of growth, whole-body fatty acid profile, digestive enzyme activity, haemato-biochemical responses and muscle growth-related gene expression of juvenile striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Aksoy, J.; Beck, B.H. Frass from Black Soldier Fly Larvae, Hermetia illucens, as a Possible Functional Dietary Ingredient in Channel Catfish Feed. Fishes 2023, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Eljack, R.; Beck, B.H.; Peatman, E. Nutritional evaluation of frass from black soldier fly larvae as potential feed ingredient for Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Yamamoto, F.; Rawles, S.D.; Webster, C.D. Type of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae frass influences the nutritional value when included in a prepared diet for Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquaculture 2024, 589, 740946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Ferreti, P.; Chavez, V.; Herrera, H.; Lara, C.; Parodi, J. Modelos in vitro para el desarrollo de una acuicultura sustentable. La aplicación del modelo de líneas celulares. Rev. De Investig. Veter. Del Peru 2025, 36, e27350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Yashwanth, B.S.; Trudeau, V.; Lakra, W.S. Role and relevance of fish cell lines in advanced in vitro research. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Tan, X.; You, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M. Growth and Fatty Acid Composition of Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Are Influenced by Dietary Fat Sources and Levels. Animals 2022, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Cranfill, K.; McGuire, M.A.; Mosley, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Newton, L.; Sealey, W.; Sheppard, C.; Irving, S. Fish offal recycling by the black soldier fly produces a foodstuff high in omega-3 fatty acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbland, P.; Alyokhin, A.; Perkins, L.B.; Peterson, M. Dose-Dependent Retention of Omega-3 Fatty Acids by Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Econ. Èntomol. 2020, 113, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camperio, J.; Suarez, J.A.; Simonton, J.; Paresky, E.; Parodi, J.; Benetti, D.D. Valorizing Organic Waste Through Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens): A Sustainable Solution for Aquafeeds with Key Nutrients and Natural Bioactive Polyphenols. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musembi, J.P.; Owino, E.A.; Oyieke, F.A.; Tanga, C.M.; Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Cheseto, X.; Egonyu, J.P. Efficient agri-food waste valorization using mealworm (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) into nutrient-rich biomass for food and feed. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2024, 117, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, P.; Tanga, C.M.; Osuga, I.; Windisch, W.; Subramanian, S. Experimental feeding studies with crickets and locusts on the use of feed mixtures composed of storable feed materials commonly used in livestock production. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 255, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Luparelli, A.V.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Effect of the rearing substrate on total protein and amino acid composition in black soldier fly. Foods 2021, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Ottoboni, M.; Klootwijk, C.; Ovyn, A.; Deboosere, S.; De Meulenaer, B.; Michiels, J.; Eeckhout, M.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on different organic waste substrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, E.; da Cunha-Borges, V.; Cantero-Bahillo, E.; Fornari, T.; García-Risco, M.R.; Martin, D. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae accumulate bioactive compounds that modulate antioxidant activity when reared with bioactive agrifood by-products. Food Res. Int. 2025, 219, 117013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Yousefi, M.; Karimi, M.; Fadaei Raieni, R.; Dadar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Benefits of Dietary Polyphenols and Polyphenol-Rich Additives to Aquatic Animal Health: An Overview. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 478–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, R.; Sirdaarta, J.; White, A.; Cock, I.E. Inhibition of Caco-2 and HeLa proliferation by Terminalia carpentariae C. T. White and Terminalia grandiflora Benth. extracts: Identification of triterpenoid components. Pharmacogn. J. 2017, 9, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Shah, M.H.; Al-Dosary, M.A.; Abbasi, A.M. Phytochemical profiling, antioxidant and HepG2 cancer cells’ antiproliferation potential in the kernels of apricot cultivars. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.J.; Romero, A.; Gonzalez-Stegmaier, R.; Dantagnan, P. The effects of supplemented diets with a phytopharmaceutical preparation from herbal and macroalgal origin on disease resistance in rainbow trout against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, P.; Sanchez, R.; Carmona, E.; Astuya, A.; Herrera, H.; Parodi, J. Nucleotides and Effect Over Starving Condition on Fish SHK-1 Cells Model. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2016, 7, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Valenzuela, J.; Mejías, M.; Ortiz, D.; Salgado, P.; Montt, L.; Chávez-Báez, I.; Vera-Tamargo, F.; Mandakovic, D.; Wacyk, J.; Pulgar, R. Increased dietary availability of selenium in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) improves its plasma antioxidant capacity and resistance to infection with Piscirickettsia salmonis. Veter. Res. 2021, 52, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; Olivares, P.; Carmona, E.; Astuya, A.; Herrera, H.; Parodi, J. Fish Nutrition Additives in SHK-1 Cells: Protective Effects of Silymarin. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dannevig, B.H.; Brudeseth, B.E.; Gjøen, T.; Rode, M.; Wergeland, H.I.; Evensen, Ø.; Press, C.M. Characterisation of a long-term cell line (SHK-1) developed from the head kidney of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 1997, 7, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Kumar, A.; Taraji, M.; Lloyd, N.D.R. Assessment of PFDA toxicity on RTgill-W1 cell line via metabolomics and lipidomics approaches. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 284, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.; Peggs, D.; McGurk, C.; Martin, S.A.M. Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT) primary cells and stable cell lines as predictive models for intestinal health in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1023235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Ferretti, P.; Sánchez, R.; de la Paz, L.O.; Parodi, J. A synergy of the nutritional additives taurine and silymarin in salmon farming: Evaluation with the CHSE-214 cellular model. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Ferretti, P.; Chavez, V.; Maguregui, E.; Jiménez, S.; Colom, O.; Parodi, J. Exploring the metabolic and antioxidant potential of solergy: Implications for enhanced animal production. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 41, e00821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Johnson, I.T.; Saltmarsh, M. Polyphenols: Antioxidants and beyond. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 215S–217S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Polyphenols and glycemic control. Nutrients 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Shen, T.; Lou, H. Dietary Polyphenols and Their Biological Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 950–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corino, C.; Rossi, R. Antioxidants in animal nutrition. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 820–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.F.; Revel, J.S.; Maier, C.S. Mitochondria-centric review of polyphenol bioactivity in cancer models. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1589–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belghit, I.; Liland, N.S.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Tibon, J.; Sindre, H.; Nilsen, H.; Hagemann, A.; Sele, V. Aquaculture sludge as feed for black soldier fly: Transfer of chemical and biological contaminants and nutrients. Waste Manag. 2024, 187, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sele, V.; Ali, A.; Liland, N.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Tibon, J.; Araujo, P.; Sindre, H.; Nilsen, H.; Hagemann, A.; Belghit, I. Characterization of nutrients and contaminants in fish sludge from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) production sites—A future resource. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Liu, N.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M. Tolerance and Removal of Four Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Compounds (PAHs) by Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environ. Èntomol. 2020, 49, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalunga, A.; Komakech, A.J.; Karungi, J.; Kabenge, I.; Schwarzböck, T. Black soldier fly larvae composting as a bioremediation approach for heavy metals and pathogens in fecal sludge cake. Discov. Environ. 2025, 3, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, T.; Tafi, E.; Paul, A.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P.; Zibek, S. Current state of chitin purification and chitosan production from insects. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2775–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, S.; de Souza, T.S.P.; Dunshea, F.R.; DiGiacomo, K.; Suleria, H.A.R. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetica illucens) as a sustainable source of nutritive and bioactive compounds, and their consumption challenges. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2023, 64, AN23192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.Z.; Ohta, T.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T. The dipterose of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) induces innate immune response through toll-like receptor pathway in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araujo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.-J. Modulation of nutrient composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae by feeding seaweed-enriched media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.F.N.M.; Seok-Kian, A.Y.; Seng, L.L.; Mustafa, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Shapawi, R. Nutritional value of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae processed by different methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Regulation of cell cycle progression by growth factor-induced cell signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, G.; Ekici, M.; Rössler, O.G. Regulation of cellular proliferation, differentiation and cell death by activated Raf. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasinger, C.; Hofer, A.; Spadiut, O.; Hohenegger, M. Amino Acid Signature in Human Melanoma Cell Lines from Different Disease Stages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, T.; Amemiya, Y.; Sugiyama, R.; Maki, M.; Shibata, H. Amino acid-dependent control of mTORC1 signaling: A variety of regulatory modes. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frendi, S.; Chassac, A.; Veron, K.; Raffenne, J.; Nicolle, R.; Albuquerque, M.; Paradis, V.; Couvelard, A.; Cros, J.; Rebours, V. Protective role of oleic acid against palmitic acid-induced pancreatic fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Imperlini, E.; Nigro, E.; Montagnese, C.; Daniele, A.; Orrù, S.; Buono, P. Biological and nutritional properties of palm oil and palmitic acid: Effects on health. Molecules 2015, 20, 17339–17361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Song, Y.; Fu, K.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D.; He, W.; Yang, L.-L. Energy metabolism in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai-Foenander, A.S.; Kuppusamy, G.; Manogoran, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Ser, H.; Yow, Y.; Goh, K.W.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.): A potential small mighty giant in the field of cosmeceuticals. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsos, E.; Modica, B.; Freel, T. Immunomodulatory potential of black soldier fly larvae: Applications beyond nutrition in animal feeding programs. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendra, K.C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; van Huis, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Heckmann, L.-H.L.; Khanal, S.K. Rethinking organic wastes bioconversion: Evaluating the potential of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.)) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) (BSF). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; Sapere, N.; Visentin, M.; Zella, D.; Scapagnini, G. Enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis with polyphenols: Combined effects of resveratrol and equol in human endothelial cells. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, R.; Lu, Y.; Tang, J. Targeting mitochondria with natural polyphenols for treating Neurodegenerative Diseases: A comprehensive scoping review from oxidative stress perspective. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Sair, A.T.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Ferulic acid restores mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy via AMPK signaling pathway in a palmitate-induced hepatocyte model of metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, I.E.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dudu, A.; Balaș, M.; Voicu, S.; Grecu, I.; Dediu, L.; Dinischiotu, A.; Costache, M. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanisms in response to starvation and refeeding in the intestine of stellate sturgeon (Acipenser stellatus) juveniles from aquaculture. Animals 2021, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.E.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Abellán, E.; Cardenete, G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses after prolonged starvation in Dentex dentex liver. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 139, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, E.; Kentepozidou, E.; Feidantsis, K.; Roufidou, C.; Despoti, S.; Chatzifotis, S. Starvation and re-feeding affect Hsp expression, MAPK activation and antioxidant enzymes activity of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 165, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Ha, J. AMPK activators: Mechanisms of action and physiological activities. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Soto, M.Á.; Carrillo-Fernández, P.; Saez Lancellotti, E.T.; Medina-Jiménez, E.; Mogaburo Alba, J.F.; Catena-Granados, N.; López-Carmona, M.D.; Pérez-Belmonte, L.M.; Prieto Lain, N.; Gómez Hernández, A.I.; et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds: Modulating Mitochondrial Function and Protecting Against Chronic Diseases—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-Mora, A.; Salazar, N.A.; Domenech-Bendaña, A.; Locascio, A.; Bejarano, E.; Gimeno-Mallench, L. Interplay Between Polyphenols and Autophagy: Insights From an Aging Perspective. Front. Biosci. 2025, 30, 25728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal, W.; Fatima, S.; Minahal, Q.; Liaqat, R. Investigating the optimum stocking density of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) for intensive production focused to in-pond raceway system. Sci. Prog. 2024, 107, 00368504241257128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletti, M.; Fonsatti, E.; Leva, F.; Maccatrozzo, L.; Ballarin, C.; Radaelli, G.; Caberlotto, S.; Bertotto, D. Influence of Transportation on Stress Response and Cellular Oxidative Stress Markers in Juvenile Meagre (Argyrosomus regius). Animals 2023, 13, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.V.; Kumar, A.; Middha, S.K.; Paital, B.; Mathur, S.; Johnson, R.; Kademan, A.; Usha, T.; Hemavathi, K.N.; Dayal, S.; et al. Water physicochemical factors and oxidative stress physiology in fish, a review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1240813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Fu, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Aflatoxin B1 Induced Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota Disorder to Increase the Infection of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 2 in Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Mancera, J.M.; Costas, B. The use of dietary additives in fish stress mitigation: Comparative endocrine and physiological responses. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ji, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H. Defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets for juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian): Growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activities, digestive enzyme activities, intestine and hepatopancreas histological structure. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawole, F.J.; Adeoye, A.A.; Tiamiyu, L.O.; Ajala, K.I.; Obadara, S.O.; Ganiyu, I.O. Substituting fishmeal with Hermetia illucens in the diets of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus): Effects on growth, nutrient utilization, haemato-physiological response, and oxidative stress biomarker. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, A.; Zuo, R.; Jiang, Y. Replacement of Commercial Feed with Fresh Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae in Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gawad, E.A.A.; Zahran, E.; Youssuf, H.; Shehab, A.; Matter, A.F. Defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) diets improved hemato-immunological responses, biochemical parameters, and antioxidant activities in Streptococcus iniae-infected Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). BMC Veter Res. 2025, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camperio, J.; Parodi, J.; Olivares-Ferretti, P.; Suarez, J.A.; Benetti, D.D. From Waste to Functional Feed Ingredient: Biochemical and SHK-1 Cell Line Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Aquaculture Nutrition. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101172
Camperio J, Parodi J, Olivares-Ferretti P, Suarez JA, Benetti DD. From Waste to Functional Feed Ingredient: Biochemical and SHK-1 Cell Line Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Aquaculture Nutrition. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(10):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101172
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamperio, Julio, Jorge Parodi, Pamela Olivares-Ferretti, Jorge A. Suarez, and Daniel D. Benetti. 2025. "From Waste to Functional Feed Ingredient: Biochemical and SHK-1 Cell Line Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Aquaculture Nutrition" Antioxidants 14, no. 10: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101172
APA StyleCamperio, J., Parodi, J., Olivares-Ferretti, P., Suarez, J. A., & Benetti, D. D. (2025). From Waste to Functional Feed Ingredient: Biochemical and SHK-1 Cell Line Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Aquaculture Nutrition. Antioxidants, 14(10), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101172





