Shikimic Acid Mitigates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Jejunal Barrier Injury in Mice via Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animal
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. HE Staining
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.5.1. Determination of T-AOC, MDA, GSH Levels and SOD Activities in Serum
2.5.2. Determination of DAO, D-LA Levels in Jejunum Tissue
2.5.3. Determination of TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1β Levels in Jejunum Tissue
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscope
2.7. Jejunum Tissue qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7.1. RNA Acquisition and Primer Design
2.7.2. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Microbial 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
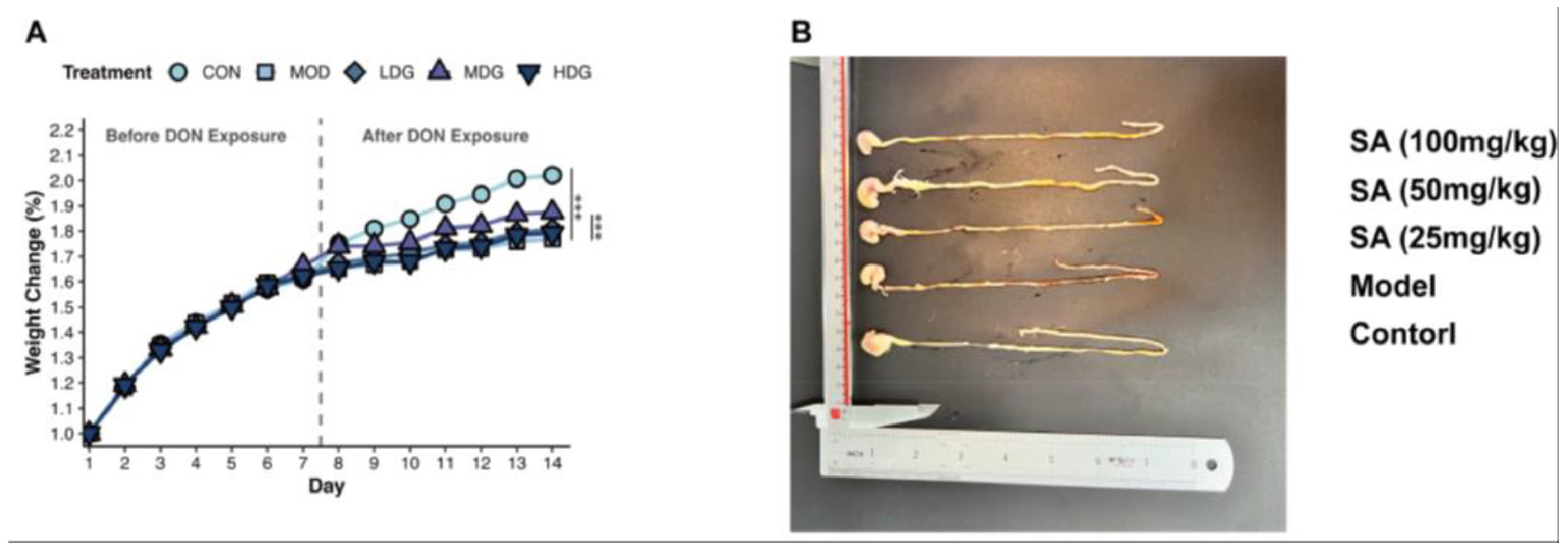
3.1. SA Mitigates DON-Induced Impairment of Mice Growth
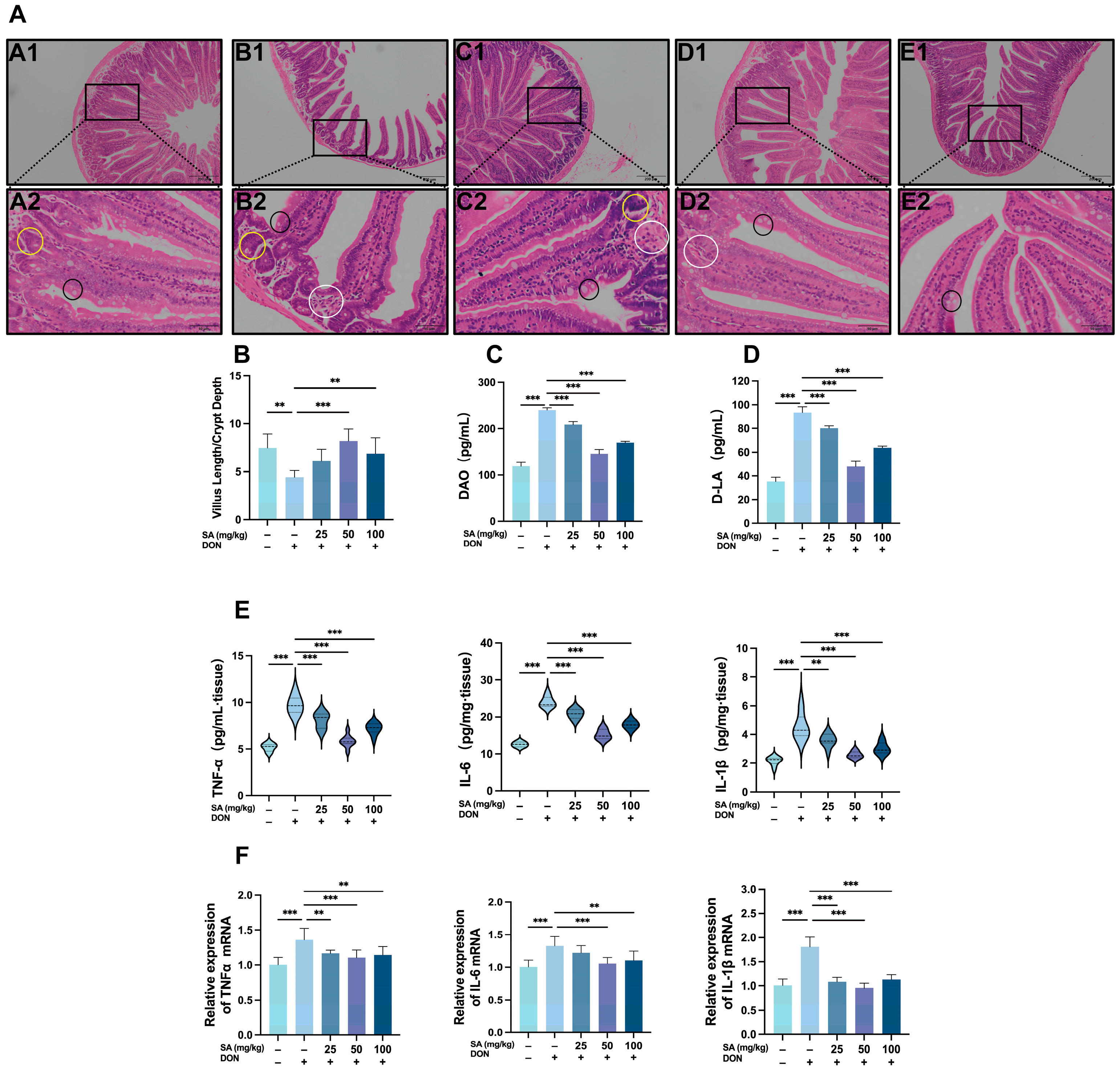
3.2. SA Alleviates DON-Induced Damage to the Jejunal Intestinal Barrier in Mice
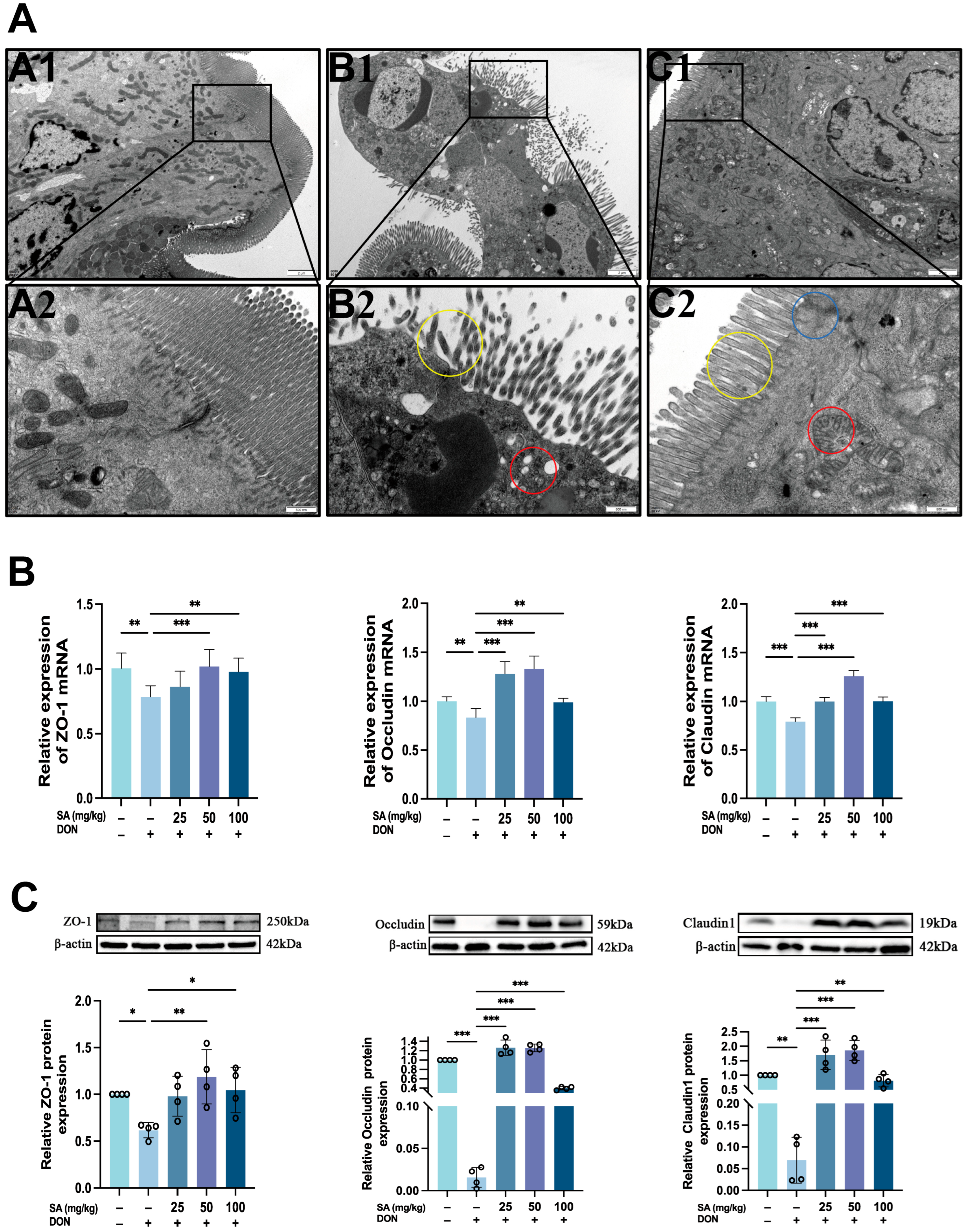
3.3. Effects of DON and SA on Tight Junctions in Mouse Jejunal Tissue
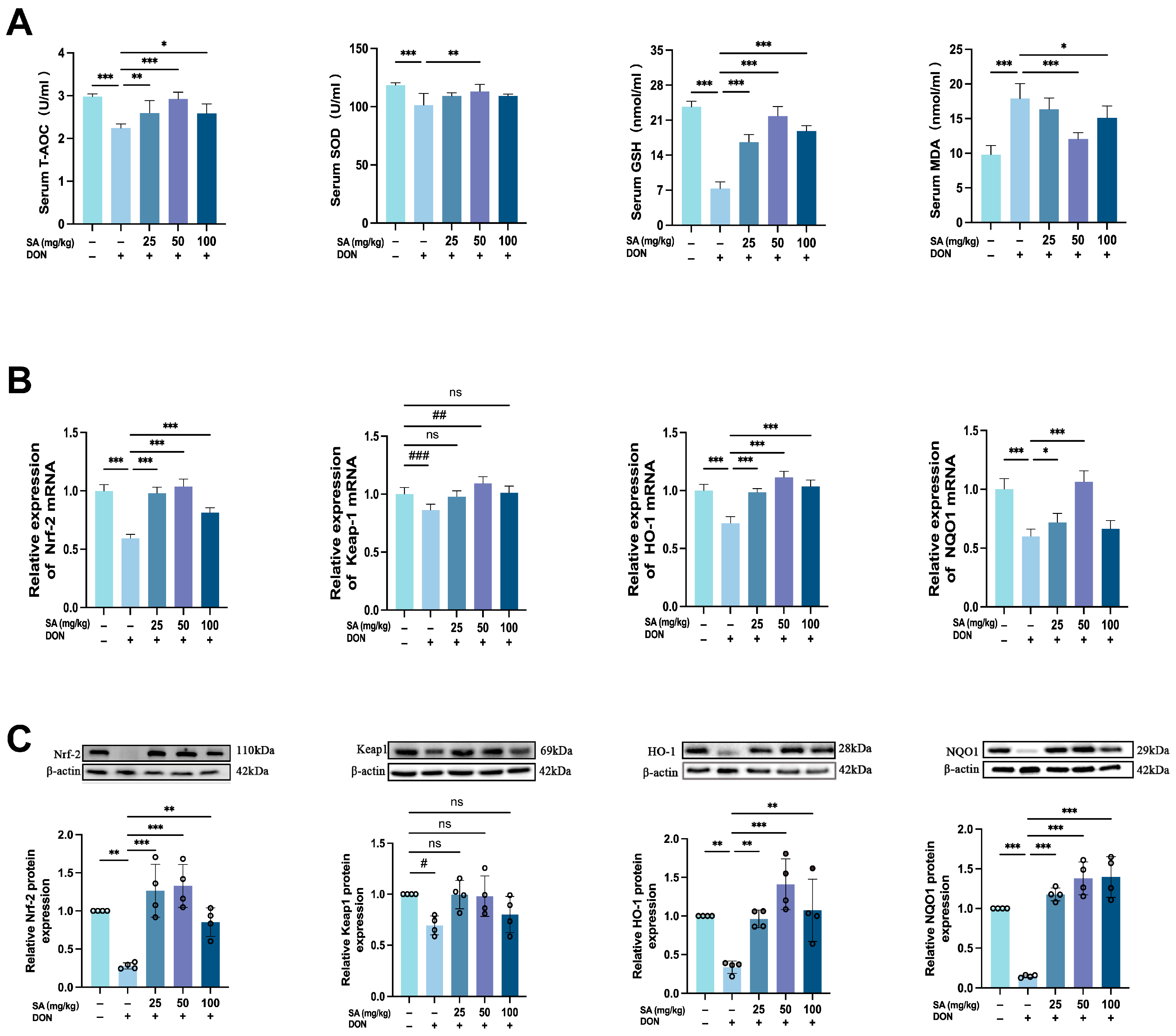
3.4. SA Mitigates DON-Induced Jejunal Oxidative Stress in Mice by Enhancing the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway
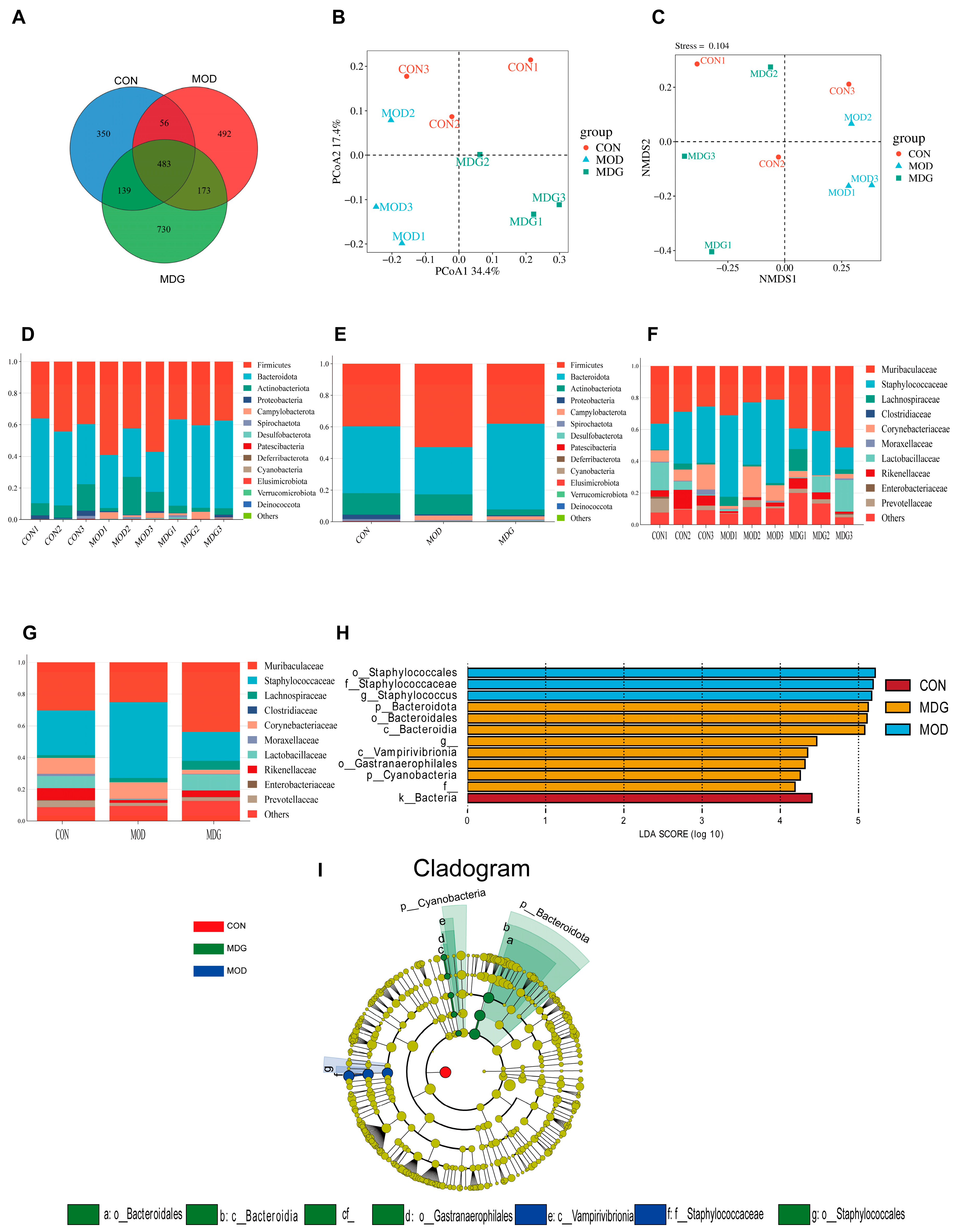
3.5. Effect of SA on DON-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SA | Shikimic Acid |
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
References
- Murakami, S.; Kusano, Y.; Okazaki, K.; Akaike, T.; Motohashi, H. NRF2 signalling in cytoprotection and metabolism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Tatar, M.; Gong, R. Keap1-independent Nrf2 regulation: A novel therapeutic target for treating kidney disease. Redox Biol. 2025, 82, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarah, M.W. The Deoxynivalenol Challenge. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; He, W.; Yang, J. Possible Toxic Mechanisms of Deoxynivalenol (DON) Exposure to Intestinal Barrier Damage and Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota in Laying Hens. Toxins 2022, 14, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panisson, J.C.; Wellington, M.O.; Bosompem, M.A.; Nagl, V.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Columbus, D.A. Urinary and Serum Concentration of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and DON Metabolites as an Indicator of DON Contamination in Swine Diets. Toxins 2023, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Kuča, K.; Humpf, H.U.; Klímová, B.; Cramer, B. Fate of deoxynivalenol and deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside during cereal-based thermal food processing: A review study. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.; Dewangan, J.; Divakar, A.; Kumar Rath, S. Global occurrence of deoxynivalenol in food commodities and exposure risk assessment in humans in the last decade: A survey. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1346–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Long, M. The biological detoxification of deoxynivalenol: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ma, K.; Li, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shan, A. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates DON-induced intestinal damage depending on the enrichment of beneficial bacteria in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Z. Deoxynivalenol Induces Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Damage through RhoA/ROCK Pathway-Mediated Apoptosis and F-Actin-Associated Tight Junction Disruption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 9411–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, N.; Li, J.; Xi, N.; Xu, M.; Wu, F.; Fu, Q.; Yan, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Chlorogenic acid attenuates deoxynivalenol-induced apoptosis and pyroptosis in human keratinocytes via activating Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Zou, T.; You, J. Plant-Derived Polyphenols as Nrf2 Activators to Counteract Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Toxicity Induced by Deoxynivalenol in Swine: An Emerging Research Direction. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, A.; Horgan, K.A.; White, B.; Walls, D. Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone-Synergistic or Antagonistic Agri-Food Chain Co-Contaminants? Toxins 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, I.; Araújo, J.R.; Rolhion, N.; Demignot, S. Jejunum: The understudied meeting place of dietary lipids and the microbiota. Biochimie 2020, 178, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, A.M.; Estévez, R.J. A short overview on the medicinal chemistry of (-)-shikimic acid. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumariya, S.; Grano de Oro, A.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.L.; Joe, B.; Osman, I. Gut microbiota-derived Metabolite, Shikimic Acid, inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Vasconcelos, A.B.S.; Antony, P.J.; Montalvão, M.M.; de Franca, M.N.F.; Hillary, V.E.; Ceasar, S.A.; Liu, D. Natural sources, biosynthesis, biological functions, and molecular mechanisms of shikimic acid and its derivatives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2023, 13, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malki, A.L. Shikimic acid from Artemisia absinthium inhibits protein glycation in diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Y.; You, C.Y.; Dong, K.; You, H.S.; Xing, J.F. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant activities of 3,4-oxo-isopropylidene-shikimic acid. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mo, K.; Tian, G.; Zhou, J.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Huang, X. Shikimic Acid Regulates the NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota to Ameliorate DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8906–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Gao, J.; Huang, W.; Yan, J.; Shan, A.; Gao, X. Curcumin mitigates deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal epithelial barrier disruption by regulating Nrf2/p53 and NF-κB/MLCK signaling in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 167, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; You, C.; Dong, K.; Sun, J.; You, H.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J. Ameliorative effects of 3,4-oxo-isopropylidene-shikimic acid on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dänicke, S.; Valenta, H.; Döll, S. On the toxicokinetics and the metabolism of deoxynivalenol (DON) in the pig. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 58, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; De Pierri, C.R.; Evangelista, A.G.; Gomes, A.; Luciano, F.B. Deoxynivalenol: Toxicology, Degradation by Bacteria, and Phylogenetic Analysis. Toxins 2022, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Shen, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ma, X. PXR Activation Relieves Deoxynivalenol-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress Via Malat1 LncRNA m(6)A Demethylation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Fang, R.; Xue, J.; Yang, K.; Lu, Y. Effects of Catalase on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, Intestinal Morphology, and Microbial Composition in Yellow Broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 802051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csernus, B.; Czeglédi, L. Physiological, antimicrobial, intestine morphological, and immunological effects of fructooligosaccharides in pigs. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2020, 63, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Du, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, G. Protective role of Cecropin AD against LPS-induced intestinal mucosal injury in chickens. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1290182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Leng, Y.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Xing, Y. Probiotics improve intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1546650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhai, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shen, J.; Chu, S.; Focaccia, E.; Tian, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X.; et al. TNF compromises intestinal bile-acid tolerance dictating colitis progression and limited infliximab response. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 2086–2103.e2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonin, C.; Thongboonkerd, V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4436–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Mo, M.; Chen, X.; Chao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; He, N.; Yuan, X.; et al. Targeting inhibition of prognosis-related lipid metabolism genes including CYP19A1 enhances immunotherapeutic response in colon cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, T.K.; Guimarães, A.G.; Oliveira, M.A.; Gasparotto, J.; Serafini, M.R.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Gelain, D.P. Shikimic acid inhibits LPS-induced cellular pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuates mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, E.G.; Mukherjee, T.; Cabral-Fernandes, L.; Rocha, J.D.B.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. How autophagy controls the intestinal epithelial barrier. Autophagy 2022, 18, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Hu, C. Curcumin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury and mitochondrial damage by promoting Parkin dependent mitophagy through AMPK-TFEB signal pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 147, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.A.; Hou, Y.; Yi, D.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, G.; Kong, X.; Yin, Y. Autophagy and tight junction proteins in the intestine and intestinal diseases. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.C.; Higashi, T.; Chiba, H. Tight-junction strand networks and tightness of the epithelial barrier. Microscopy 2023, 72, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, P.; Saha, K.; Nighot, P. Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier Regulation by Novel Pathways. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2025, 31, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight Junction Structure and Function Revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Cui, H.; Deng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Chen, L.; et al. Nickel induces blood-testis barrier damage through ROS-mediated p38 MAPK pathways in mice. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Lin, H.L.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, X.G.; Gao, C.Q.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q. l-Carnosine Protects Against Deoxynivalenol-Induced Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Stem Cells by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magesh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L. Small molecule modulators of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as potential preventive and therapeutic agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 687–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Sha, H. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway in Chronic Diseases. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Dutta, N.; Banerjee, P.; Gajbhiye, R.L.; Sareng, H.R.; Kapse, P.; Pal, S.; Burdelya, L.; Mandal, N.C.; Ravichandiran, V.; et al. Induction of monoamine oxidase A-mediated oxidative stress and impairment of NRF2-antioxidant defence response by polyphenol-rich fraction of Bergenia ligulata sensitizes prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Gao, X.; Cao, Z. Deoxynivalenol Induces Blood-Testis Barrier Dysfunction through Disrupting p38 Signaling Pathway-Mediated Tight Junction Protein Expression and Distribution in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 12829–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sun, X.; Oh, S.F.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Jupp, R.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C.; et al. Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORγ(+) regulatory T cell homeostasis. Nature 2020, 577, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.C.; Yen, T.L.; Huang, C.J.; Hong, K.J. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG as dietary supplement improved survival from lipopolysaccharides-induced sepsis in mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6786–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watad, A.; McGonagle, D.; Anis, S.; Carmeli, R.; Cohen, A.D.; Tsur, A.M.; Ben-Shabat, N.; Luigi Bragazzi, N.; Lidar, M.; Amital, H. TNF inhibitors have a protective role in the risk of dementia in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Results from a nationwide study. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mackay, C.R.; Gershwin, M.E. Immunomodulatory Effects of Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Autoimmune Liver Diseases. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bosch, C.; Boorman, E.; Zunszain, P.A.; Mann, G.E. Short-chain fatty acids as modulators of redox signaling in health and disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Buey, B.; Grasa, L.; Mesonero, J.E.; Latorre, E. Protective role of short-chain fatty acids on intestinal oxidative stress induced by TNF-α. Cell Stress Chaperones 2024, 29, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Target | Primer (5′–3′) | Size | Sequence Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F: TATAAAACCCGGCGGCGCA R: GTCATCCATGGCGAACTGGTG | 118 | NM_007393.5 |
| Keap1 | F: GCCCCGGGACTCTTATTGTG R: TTAGGGGCCCCGCCAT | 101 | NM_001110305.1 |
| Nrf2 | F: ACTACAGTCCCAGCAGAGTGAT R: TCACACACTTTCTGCGTGCT | 109 | NM_001399226.1 |
| NQO1 | F: TCTCTGGCCGATTCAGAGTG R: CCAGACGGTTTCCAGACGTT | 145 | NM_008706.5 |
| HO-1 | F: ACCTTCCCGAACATCGAGACAG R: CAGCTCCTCAAACAGCTCAATG | 150 | NM_010442.2 |
| Claudin 1 | F: TGGGGCTGATCGCAATCTTT R: CACTAATGTCGCCAGACCTGA | 137 | NM_016674.4 |
| Occludin | F: CCCTCTTTCCTTAGGCGACA R: CCCAAGATAAGCGAACCTGC | 95 | NM_001360536.1 |
| ZO-1 | F: CTTCCCGGACTTTTTGTCCCA R: CATTGCTGTGCTCTTAGCGG | 220 | NM_001163574.2 |
| TNF-α | F: ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA R: ATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGT | 212 | NM_001278601.1 |
| IL-1β | F: TGCCACCTTTTGACAGTGATG R: TGATGTGCTGCTGCGAGATT | 138 | NM_008361.4 |
| IL-6 | F: AGACAAAGCCAGAGTCCTTCAG R: TGTGACTCCAGCTTATCTCTTGG | 77 | NM_001314054.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Shikimic Acid Mitigates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Jejunal Barrier Injury in Mice via Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101145
Su Y, Zheng B, Zhou C, Li M, Yuan Y, Wang H, Li B, Wu S, Wu Z, Zhao Y, et al. Shikimic Acid Mitigates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Jejunal Barrier Injury in Mice via Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(10):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yijing, Bin Zheng, Chixiang Zhou, Miaochun Li, Yifeng Yuan, Han Wang, Bei Li, Shiyu Wu, Zhengkun Wu, Yinquan Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Shikimic Acid Mitigates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Jejunal Barrier Injury in Mice via Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota" Antioxidants 14, no. 10: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101145
APA StyleSu, Y., Zheng, B., Zhou, C., Li, M., Yuan, Y., Wang, H., Li, B., Wu, S., Wu, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, W., & Shu, G. (2025). Shikimic Acid Mitigates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Jejunal Barrier Injury in Mice via Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1/NQO1 Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Antioxidants, 14(10), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101145






