The Role of Fucoxanthin as a Potent Nrf2 Activator via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Axis against Amyloid-β Peptide-Induced Oxidative Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Aβ Preparation
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Evaluation of Cell Viability
2.4. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Apoptosis
2.5. Cell Cycle Assay
2.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Intracellular Free Calcium Level
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.9. In Silico Docking Simulation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fucoxanthin Attenuated Aβ25-35-Mediated G0/G1 Phase Arrest and Cell Death via Reducing ROS Production
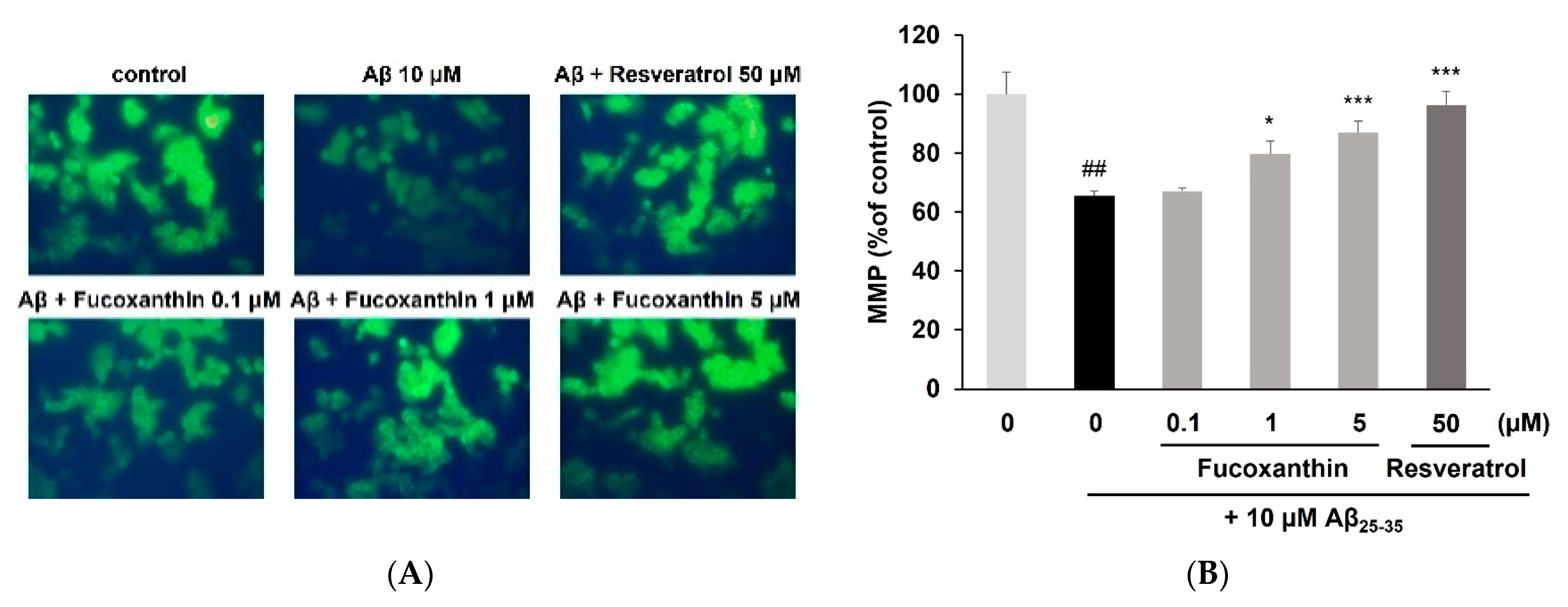
3.2. Fucoxanthin Enhanced Mitochondrial Recovery and Regulated Apoptosis
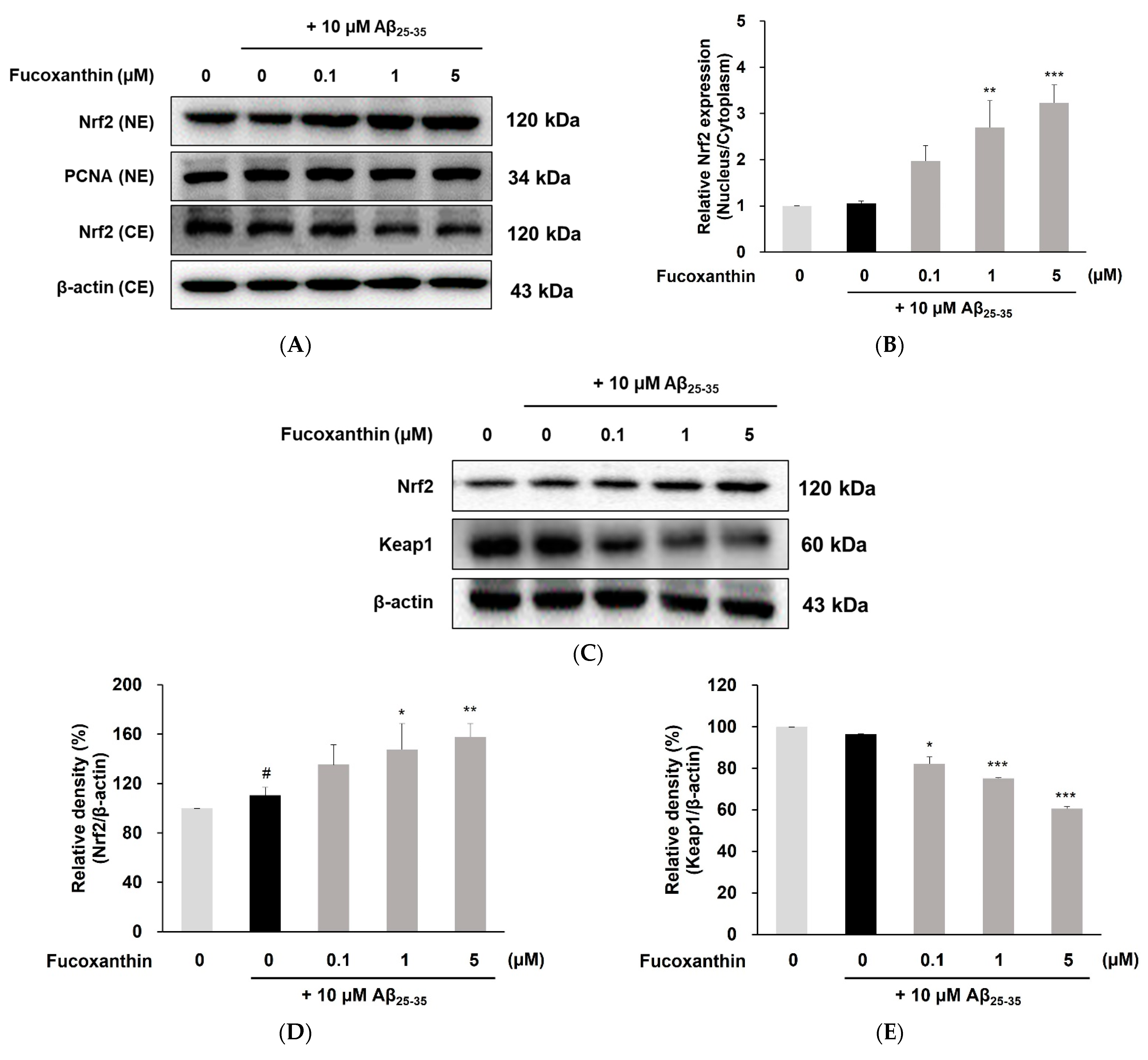
3.3. Fucoxanthin Up-Regulated Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2 and Gene Expression of Phase-II Enzyme on PC12 Cell Injury Caused by Aβ25-35
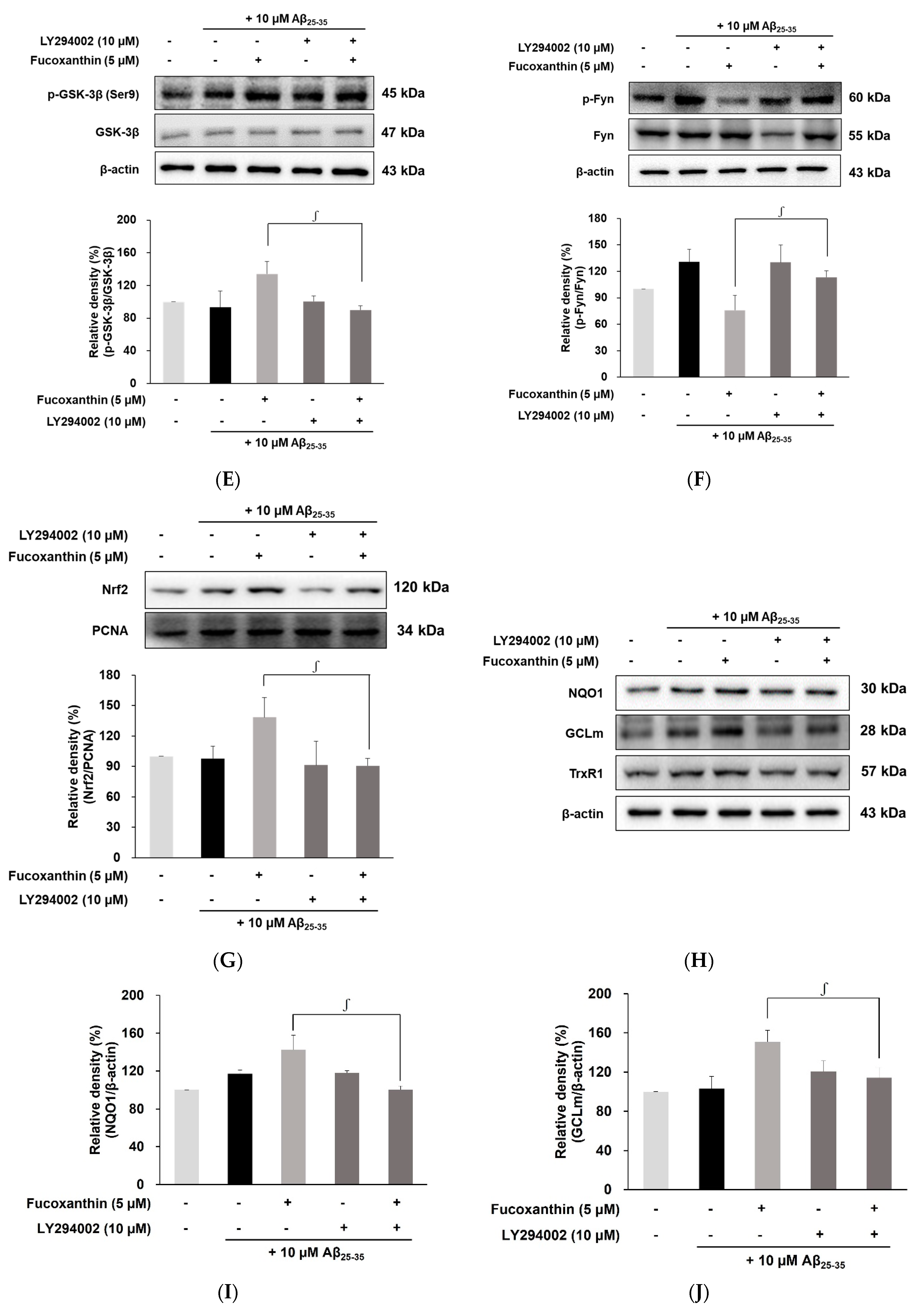
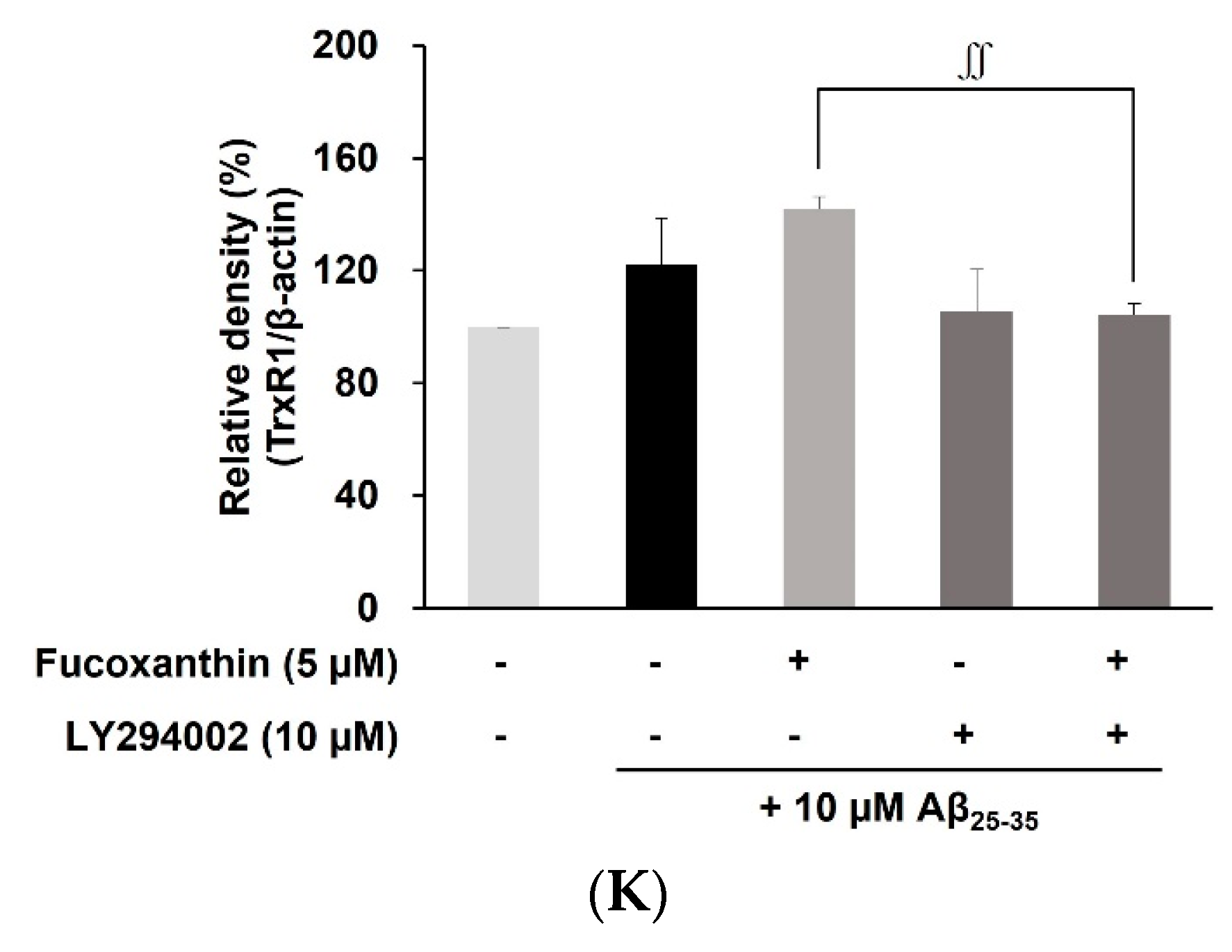
3.4. Fucoxanthin Modulated Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Signaling against Aβ Neuronal Damage
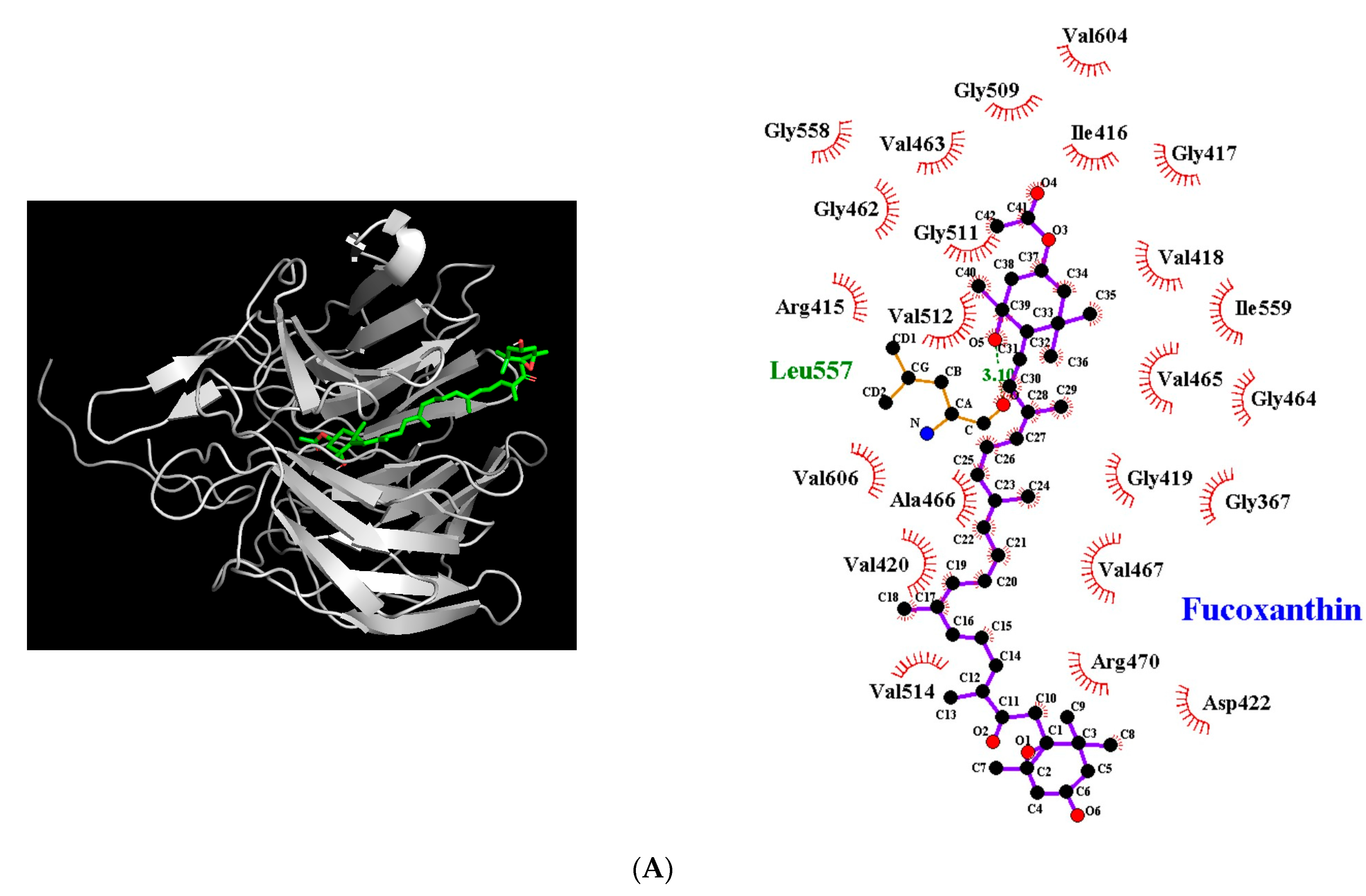
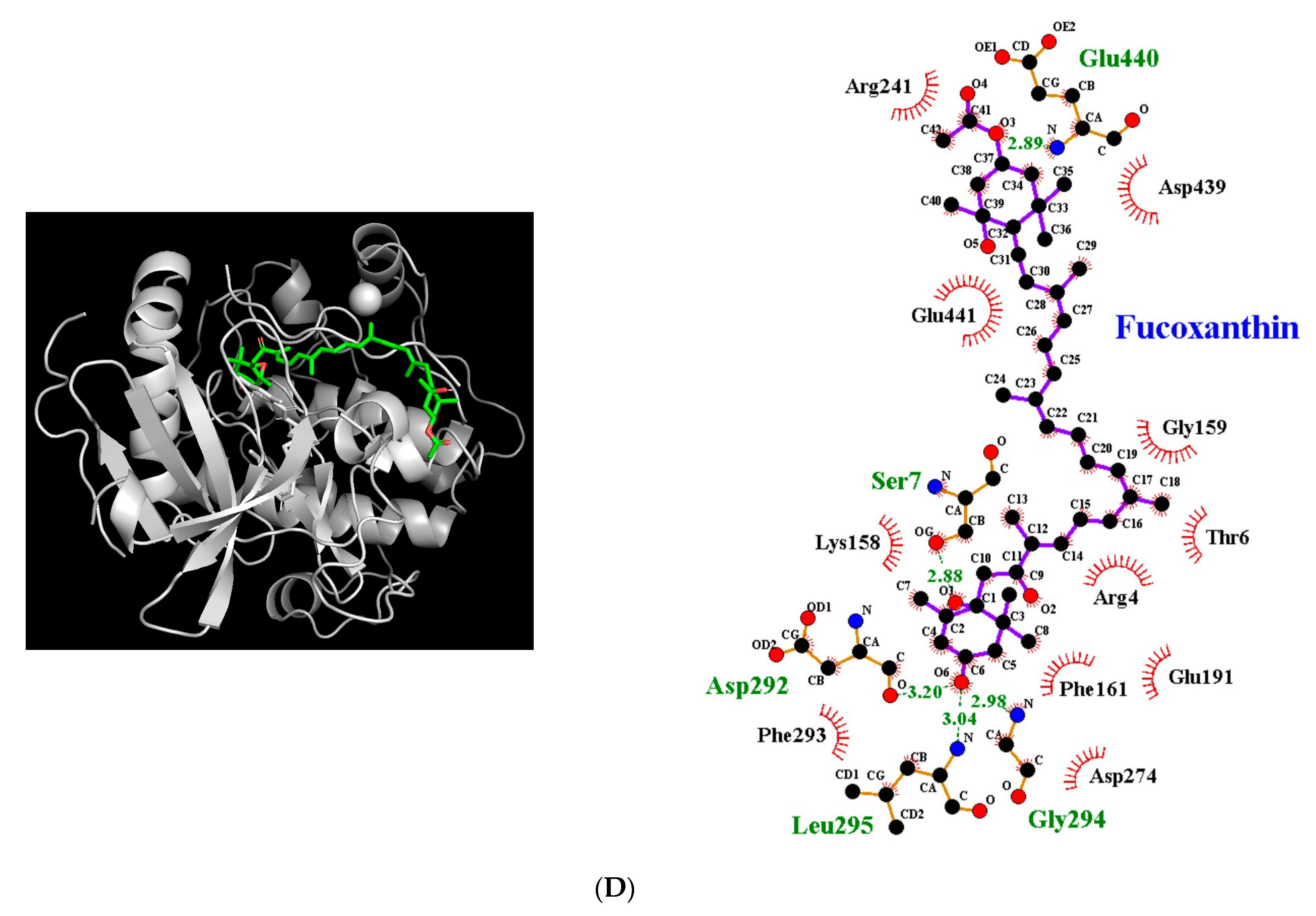
3.5. Molecular Docking Simulation between Fucoxanthin and Target Proteins in Antioxidant Defense System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, L.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X. Andrographolide protects PC12 cells against β-amyloid-induced autophagy-associated cell death through activation of the Nrf2-mediated p62 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H., 3rd. Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Lauderback, C.M. Lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in Alzheimer’s disease brain: Potential causes and consequences involving amyloid β-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuner, K.; Schütt, T.; Kurz, C.; Eckert, S.H.; Schiller, C.; Occhipinti, A.; Mai, S.; Jendrach, M.; Eckert, G.P.; Kruse, S.E.; et al. Mitochondrion-derived reactive oxygen species lead to enhanced amyloid beta formation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Chang, P.; Dai, X.L.; Jiang, Z.F. Protective effects of curcumin on amyloid-β-induced neuronal oxidative damage. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Manda, G.; Hassan, A.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Barbas, C.; Daiber, A.; Ghezzi, P.; León, R.; López, M.G.; Oliva, B.; et al. Transcription Factor NRF2 as a Therapeutic Target for Chronic Diseases: A Systems Medicine Approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 348–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzovino, A.; Chiang, S.; Brown, B.E.; Hawkins, C.L.; Richardson, D.R.; Huang, M.L. Molecular Alterations in a Mouse Cardiac Model of Friedreich Ataxia: An Impaired Nrf2 Response Mediated via Upregulation of Keap1 and Activation of the Gsk3β Axis. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2858–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, P.; Rojo, A.I.; Evrard-Todeschi, N.; Innamorato, N.G.; Cotte, A.; Jaworski, T.; Tobón-Velasco, J.C.; Devijver, H.; García-Mayoral, M.F.; Van Leuven, F.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by the glycogen synthase kinase 3/β-TrCP axis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 3486–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Rizvi, F.; Kakkar, P. PHLPP2 down regulation influences nuclear Nrf2 stability via Akt-1/Gsk3β/Fyn kinase axis in acetaminophen induced oxidative renal toxicity: Protection accorded by morin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Chauhan, O.P.; Mishra, A. Edible seaweeds: A potential novel source of bioactive metabolites and nutraceuticals with human health benefits. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 740054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slegers, P.M.; Helmes, R.J.K.; Draisma, M.; Broekema, R.; Vlottes, M.; van den Burg, S.W.K. Environmental impact and nutritional value of food products using the seaweed Saccharina latissima. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Shnimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Cancer chemoprevention by carotenoids. Molecules 2012, 17, 3202–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Nishikawa, S.; Beppu, F.; Tsukui, T.; Abe, M.; Hosokawa, M. The allenic carotenoid fucoxanthin, a novel marine nutraceutical from brown seaweeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Kong, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Fucoxanthin: A promising medicinal and nutritional ingredient. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 723515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.A.; Ali, M.Y.; Choi, R.J.; Jeong, H.O.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, J.S. Kinetics and molecular docking studies of fucosterol and fucoxanthin, BACE1 inhibitors from brown algae Undaria pinnatifida and Ecklonia stolonifera. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, F.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, K.; Jin, J.; et al. Fucoxanthin Inhibits β-Amyloid Assembly and Attenuates β-Amyloid Oligomer-Induced Cognitive Impairments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4092–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, L.; Yu, J.; Xiang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Cui, W.; He, S.; Wang, Q. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid, Reverses Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Mice and Inhibits Acetylcholinesterase in Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Youn, K.; Jun, M. Protective effect of sargahydroquinoic acid against Aβ25-35-evoked damage via PI3K/Akt mediated Nrf2 antioxidant defense system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Han, J.; Lee, N.; Yoon, J.H.; Youn, K.; Ha, H.J.; Yoon, E.; Kim, D.H.; Jun, M. Neuroprotective Effects of Baicalein, Wogonin, and Oroxylin A on Amyloid Beta-Induced Toxicity via NF-κB/MAPK Pathway Modulation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, K.; Jun, M. Geraniin Protects PC12 Cells Against Aβ25-35-Mediated Neuronal Damage: Involvement of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Youn, K.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, M.R.; Yoon, E.; Kim, O.Y.; Jun, M. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Property of Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava on Aβ25-35-Induced Damage in PC12 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Lee, N.; Youn, K.; Jo, M.R.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, D.S.; Ho, C.T.; Jun, M. Dieckol Ameliorates Aβ Production via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Regulated APP Processing in SweAPP N2a Cell. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yan, J.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Chu, S.F.; Zhu, C.G.; Guo, Q.L.; Shi, J.G.; Chen, N.H. 20C, a bibenzyl compound isolated from Gastrodia elata, protects PC12 cells against rotenone-induced apoptosis via activation of the Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrup, K.; Neve, R.; Ackerman, S.L.; Copani, A. Divide and die: Cell cycle events as 21 triggers of nerve cell death. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9232–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bai, X.; Yu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Ginsenoside re inhibits ROS/ASK-1 dependent mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and activation of Nrf2-antioxidant response in beta-amyloid-challenged SHSY5Y cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Guo, Y.; Fang, Y. Moderate activation of autophagy regulates the intracellular calcium ion concentration and mitochondrial membrane potential in beta-amyloid-treated PC12 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 618, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.D.; Garcia, J.A.; Anantula, Y.; Rellick, S.L.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Sarkar, S.N.; Brown, C.M.; Simpkins, J.W. Amyloid-β Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction via a Ca2+-Driven Upregulation of Oxidative Phosphorylation and Superoxide Production in Cerebrovascular Endothelial Cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 75, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedskog, L.; Pinho, C.M.; Filadi, R.; Rönnbäck, A.; Hertwig, L.; Wiehager, B.; Larssen, P.; Gellhaar, S.; Sandebring, A.; Westerlund, M.; et al. Modulation of the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interface in Alzheimer’s disease and related models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7916–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Hou, S.S.; Snyder, A.C.; Kharitonova, E.K.; Russ, A.N.; Das, S.; Fan, Z.; Muzikansky, A.; Garcia-Alloza, M.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; et al. Increased mitochondrial calcium levels associated with neuronal death in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, A.; Missineo, A.; Gallo, M.; Cerretani, M.; Fezzardi, P.; Tomei, L.; Cicero, D.O.; Altamura, S.; Santoprete, A.; Ingenito, R.; et al. Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) drug discovery: Biochemical toolbox to develop NRF2 activators by reversible binding of Kelch-like ECHassociated protein 1 (KEAP1). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 631, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Gan, K.A.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A. Increased Alzheimer’s disease like pathology in the APP/PS1DeltaE9 mouse model lacking Nrf2 through modulation of autophagy. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanninen, K.; Malm, T.M.; Jyrkkänen, H.K.; Goldsteins, G.; Keksa-Goldsteine, V.; Tanila, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 protects against beta amyloid. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2008, 39, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanninen, K.; Heikkinen, R.; Malm, T.; Rolova, T.; Kuhmonen, S.; Leinonen, H.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Tanila, H.; Levonen, A.L.; Koistinaho, M.; et al. Intrahippocampal injection of a lentiviral vector expressing Nrf2 improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16505–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, C.P.; Glass, C.A.; Montgomery, M.B.; Lindl, K.A.; Ritson, G.P.; Chia, L.A.; Hamilton, R.L.; Chu, C.T.; Jordan-Sciutto, K.L. Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Han, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, M.; Wu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, Y.; Niu, T.; Chen, J.; et al. Fucoxanthin Prevents 6-OHDA-Induced Neurotoxicity by Targeting Keap1. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6688708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culbreth, M.; Aschner, M. GSK-3β, a double-edged sword in Nrf2 regulation: Implications for neurological dysfunction and disease. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebel, G.; Stemmelin, J.; Lopez-Grancha, M.; Boulay, D.; Boquet, G.; Slowinski, F.; Pichat, P.; Beeské, S.; Tanaka, S.; Mori, A.; et al. The selective GSK3 inhibitor, SAR502250, displays neuroprotective activity and attenuates behavioral impairments in models of neuropsychiatric symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease in rodents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liu, X. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Oxidative Damage by Activating the Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway to Protect the Kidney from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7444430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, I.; Cao, M.; Su, Z.Y.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y.; Fang, M.; Kong, A.N. Fucoxanthin Elicits Epigenetic Modifications, Nrf2 Activation and Blocking Transformation in Mouse Skin JB6 P+ Cells. AAPS J. 2018, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.W.; Na, S.J.; Kim, W.K. Antioxidant effects of fucoxanthin rich powder in rats fed with high fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Beppu, F.; Hosokawa, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Nutraceutical characteristics of the brown sea-weed carotenoid fucoxanthin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 686, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Maoka, T. Allenic and cumulenic lipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2007, 46, 328–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, R.K.; Bhaskar, N.; Baskaran, V. Comparative effects of beta-carotene and fucoxanthin on retinol deficiency induced oxidative stress in rats. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2009, 331, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, S.; Narayan, B.; Vallikannan, B. Fucoxanthin restrains oxidative stress induced by retinol deficiency through modulation of Na(+)K(+)-ATPase and antioxidant enzyme activities in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, F.; Niwano, Y.; Tsukui, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Single and repeated oral dose toxicity study of fucoxanthin (FX), a marine carotenoid, in mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Product Size (bp) | Genbank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQO1 | F: ATGGCGGTGAGAAGAGCCCTG R: ACCCTTGTCATACATGGTGGC | 64 | 408 | XM_032887917 |
| GCLm | F: AGACCGGGAACCTGCTCAAC R: CATCACCCTGATGCCTAAGC | 55 | 1111 | NM_017305 |
| TrxR1 | F: CAATGAAAAGACCGGGAAGA R: CACAGCAGCCATACTCCAAA | 60 | 224 | NM_001351984 |
| GAPDH | F: CATCACCATCTTCCAGGAGCG R: TGACCTTGCCCACAGCCTTG | 60 | 443 | NM_017008 |
| Target Protein | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | No. of H-Bonds | H-Bonding Residues | H-Bond Length (Å) | van der Waals Residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2-Keap1 | −9.4 | 1 | Leu557 | 3.10 | Gly367, Arg415, Ile416, Gly417, Val418, Gly419, Val420, Asp422, Gly462, Val463, Gly464, Val465, Ala466, Val467, Arg470, Gly509, Gly511, Val512, Val514, Gly558, Ile559, Val604, Val606 |
| Fyn | −8.1 | 4 | Lys87 Arg163 Lys167 | 3.31 3.12 2.80/3.11 | Leu17, Asn19, Gly20, Gln21, Phe22, Gly88, Ser89, Asp92, Asp130, Arg132, Asp148, Leu151, Ala166, Phe168 |
| GSK-3β | −7.4 | 1 | Ser147 | 2.99 | Gly65, Ser66, Val70, Lys85, Arg144, Arg148, Asp200, Tyr221, Gln254, Pro255, Pro258, Gly259, Asp264, Glu268 |
| Akt | −8.0 | 5 | Ser7 Asp292 Gly294 Leu295 Glu440 | 2.88 3.20 2.98 3.04 2.89 | Arg4, Thr6, Lys158, Gly159, Phe161, Glu191, Arg241, Asp274, Phe293, Asp439, Glu441 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.; Youn, K.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, B.; Kim, D.H.; Jun, M. The Role of Fucoxanthin as a Potent Nrf2 Activator via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Axis against Amyloid-β Peptide-Induced Oxidative Damage. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030629
Lee N, Youn K, Yoon J-H, Lee B, Kim DH, Jun M. The Role of Fucoxanthin as a Potent Nrf2 Activator via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Axis against Amyloid-β Peptide-Induced Oxidative Damage. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(3):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030629
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Nayoung, Kumju Youn, Jeong-Hyun Yoon, Bokyung Lee, Dong Hyun Kim, and Mira Jun. 2023. "The Role of Fucoxanthin as a Potent Nrf2 Activator via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Axis against Amyloid-β Peptide-Induced Oxidative Damage" Antioxidants 12, no. 3: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030629
APA StyleLee, N., Youn, K., Yoon, J.-H., Lee, B., Kim, D. H., & Jun, M. (2023). The Role of Fucoxanthin as a Potent Nrf2 Activator via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn Axis against Amyloid-β Peptide-Induced Oxidative Damage. Antioxidants, 12(3), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030629








