Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
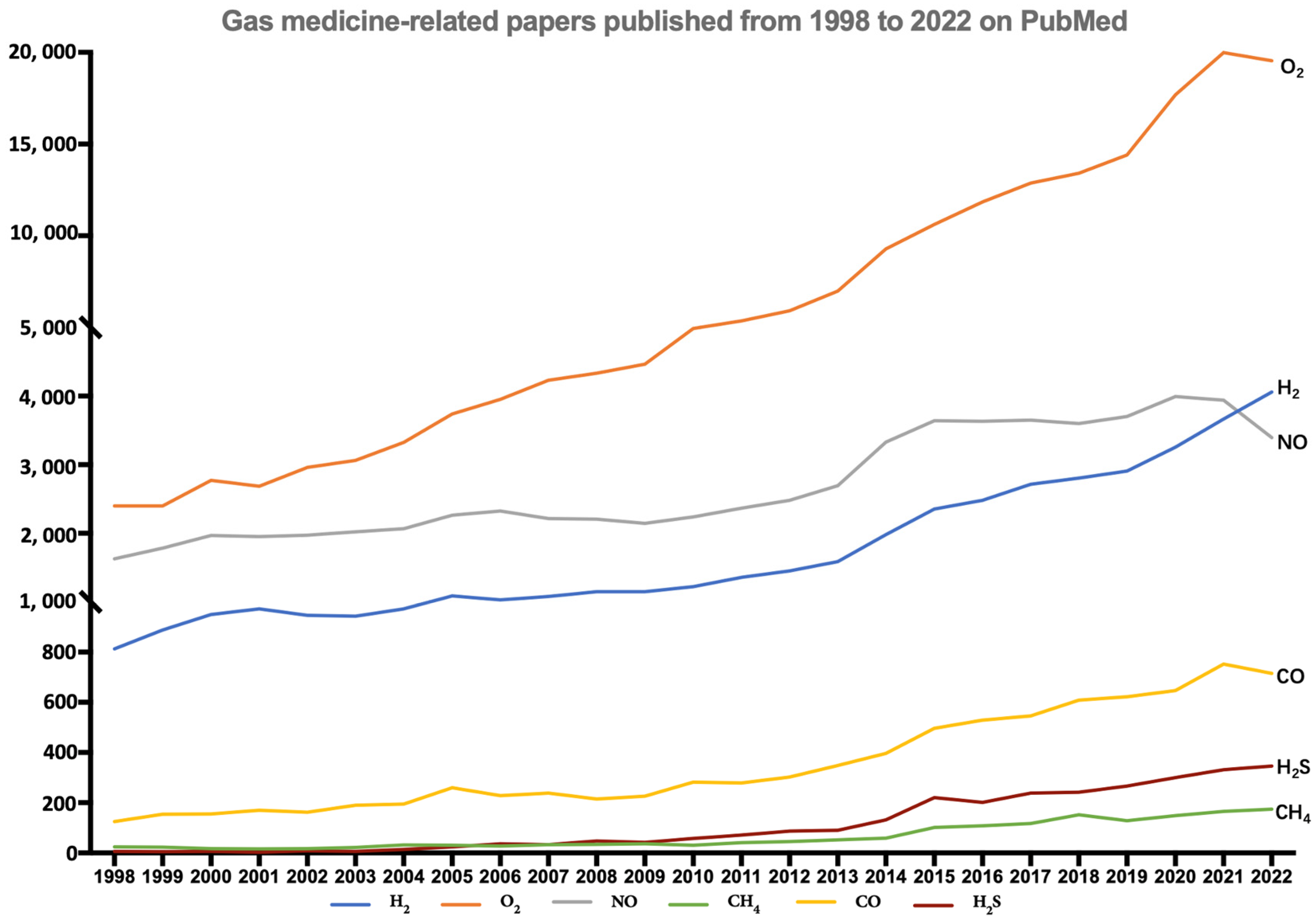
2. History of H2 Medicine
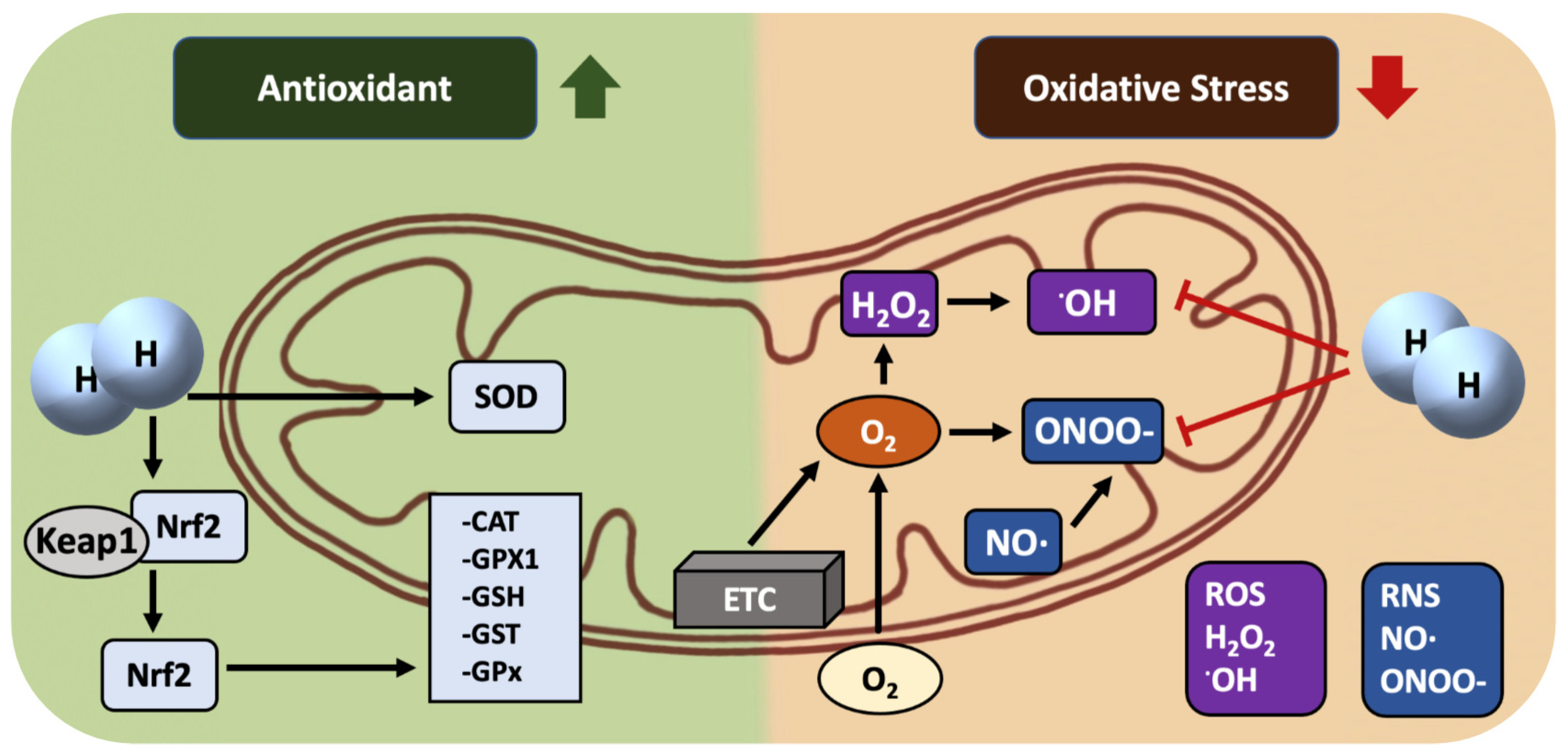
3. H2: A Mitochondria-Targeting Molecule/Nutrient Rather Than a Selective •OH Scavenger
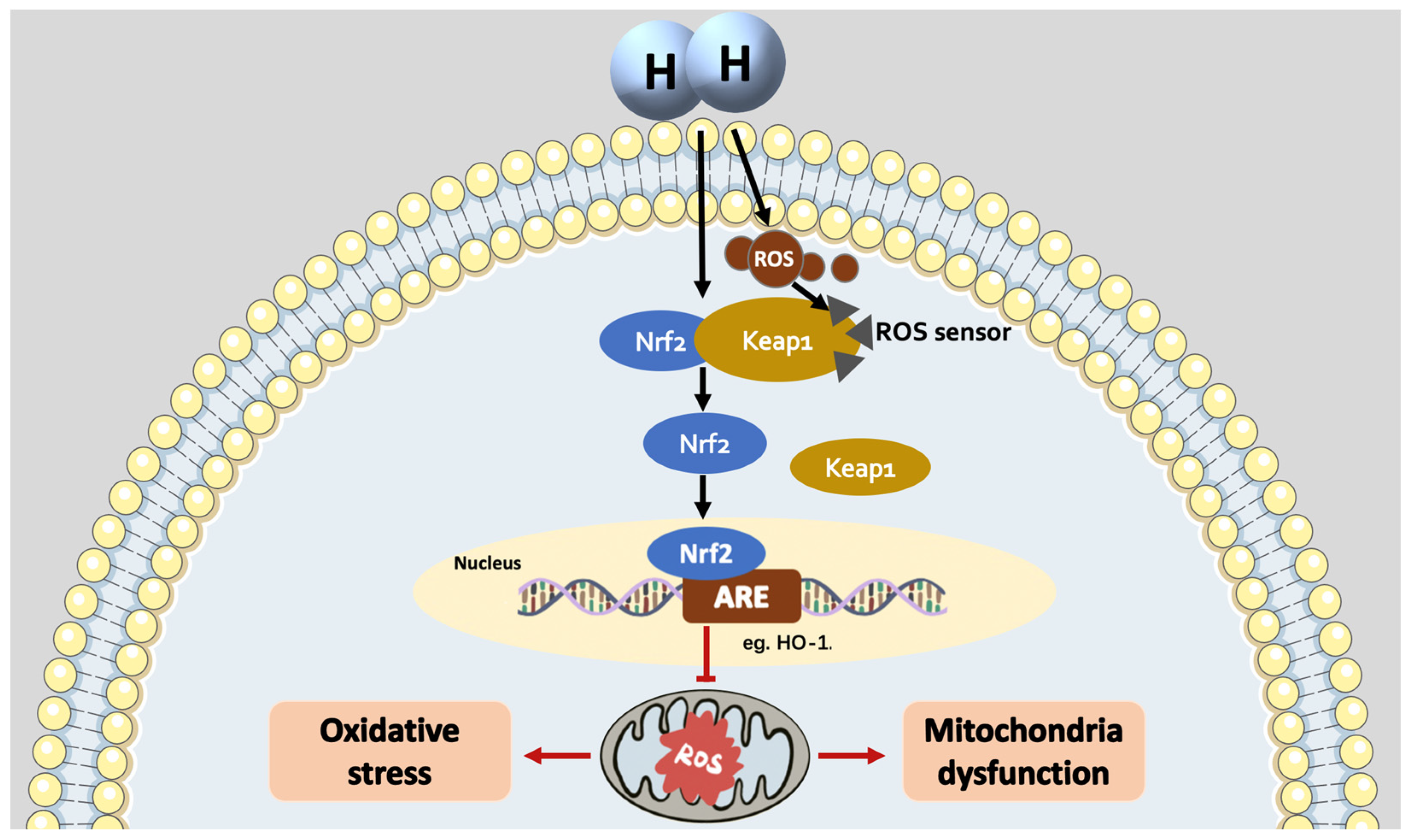
4. The Mechanisms of H2 as an Nrf2 Activator
5. The Medical Effects of H2: Focus on the Effect on Mitochondria
5.1. Effects of H2 on Respiratory System Diseases
5.2. Effects of H2 on Cardiovascular System Diseases
5.3. Effects of H2 on Nervous System Diseases
5.4. Effects of H2 on Digestive System Diseases
5.5. Effects of H2 on Metabolic Syndrome
5.6. The Others
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, J.W.; Shakir, D.; Batie, M.; Frost, M.; Rocha, S. Oxygen-sensing mechanisms in cells. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3888–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Ichinose, F.; Bloch, D.B.; Zapol, W.M. Inhaled nitric oxide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccarina, D.; Lauritano, E.C.; Gabrielli, M.; Franceschi, F.; Ojetti, V.; Gasbarrini, A. The role of methane in intestinal diseases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, D.; Sethi, J.; Choi, A.M. Carbon monoxide-dependent signaling. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabil, O.; Motl, N.; Banerjee, R. H2S and its role in redox signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.F.; Sun, X.J.; Xia, Z.F. Hydrogen resuscitation, a new cytoprotective approach. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.M. Hydrogen as a selective antioxidant: A review of clinical and experimental studies. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M.D. Production and excretion of hydrogen gas in man. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969, 281, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Zhao, L.; Shen, M.; Noda, M.; Qin, S.; Long, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, J. Hydrogen medicine: A rising star in gas medicine. Tradit. Med. Mod. Med. 2020, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dole, M.; Wilson, F.R.; Fife, W.P. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: A possible treatment for cancer. Science 1975, 190, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, X. Experimental Confirmation on the Role of Hydrogen for the Meaning of Life. J. Zibo Norm. Coll. 2013, 1, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Wei, C. New scientific topics—A preliminary study on the significance of hydrogen in life activities.ity of qi and its application prospect. J. Shandong Norm. Univ. 1999, 2, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selec.tively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Kajiyama, S.; Amano, A.; Kondo, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Handa, S.; Takahashi, R.; Fukui, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N.; et al. Hydrogen-rich pure water prevents superoxide formation in brain slices of vitamin C-depleted SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Kang, Z.; Cai, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Denoble, P.J.; Tao, H.; Sun, X. Hydrogen-rich saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiya, M.; Sato, K.; Silva, M.J.; Ouhara, K.; Do, P.M.; Shanmugam, K.T.; Kawai, T. Hydrogen from intestinal bacteria is protective for Concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penders, J.; Kissner, R.; Koppenol, W.H. ONOOH does not react with H2: Potential beneficial effects of H2 as an antioxidant by selective reaction with hydroxyl radicals and peroxynitrite. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, K.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen Gas Protects against Intestinal Injury in Wild Type but not NRF2 Knockout Mice with Severe Sepsis by Regulating HO-1 and HMGB1 Release. Shock 2017, 48, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyspler, R.; Ticha, A.; Schierbeek, H.; Galkin, A.; Zadak, Z. The Evaluation and Quantitation of Dihydrogen Metabolism Using Deuterium Isotope in Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, M.; Masuda, A.; Ohno, K.; Ichihara, M.; Kojima, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, M. Molecular hydrogen suppresses FcepsilonRI-mediated signal transduction and prevents degranulation of mast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dong, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhuang, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Hydrogen: A Novel Option in Human Disease Treatment. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8384742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, F.; Xue, Y.; Qin, S. Progress in clinical research on the use of hydrogen molecules in preventive health care. Chin. J. Geriatr. Care 2023, 21, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Ma, S.N.; Zhao, P.X.; Zhang, X.; Lebaron, T.W.; Yan, X.L.; Ma, X.M. Molecular hydrogen suppresses glioblastoma growth via inducing the glioma stem-like cell differentiation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.A.J.; Hartley, R.C.; Cochemé, H.M.; Murphy, M.P. Mitochondrial pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhi, X.; Weng, W.; Pan, P.; Cao, L.; Ji, F.; et al. Inhalation of Hydrogen of Different Concentrations Ameliorates Spinal Cord Injury in Mice by Protecting Spinal Cord Neurons from Apoptosis, Oxidative Injury and Mitochondrial Structure Damages. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Song, R.; Pang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Propofol inhibits parthanatos via ROS-ER-calcium-mitochondria signal pathway in vivo and vitro. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Targeting molecular hydrogen to mitochondria: Barriers and gateways. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 94, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Ibi, T.; Sahashi, K.; Ichihara, M.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K. Open-label trial and randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of hydrogen-enriched water for mitochondrial and inflammatory myopathies. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Smith, R.A. Drug delivery to mitochondria: The key to mitochondrial medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 41, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J.M.; Neupert, W. Protein transport into mitochondria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Recent progress toward hydrogen medicine: Potential of molecular hydrogen for preventive and therapeutic applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen is a novel antioxidant to efficiently reduce oxidative stress with potential for the improvement of mitochondrial diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, X.; Ohta, S.; Sun, X. Review and prospect of the biomedical effects of hydrogen. Med. Gas Res. 2014, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ohta, S.; Zhang, J.H. Discovery of a hydrogen molecular target. Med. Gas Res. 2023, 13, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ames, B.N. Reducing mitochondrial decay with mitochondrial nutrients to delay and treat cognitive dysfunction, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wertz, K.; Weber, P.; Zhang, P. Targeting mitochondrial biogenesis for preventing and treating insulin resistance in diabetes and obesity: Hope from natural mitochondrial nutrients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Gao, P.; Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Long, J. Central and Peripheral Metabolic Defects Contribute to the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Targeting Mitochondria for Diagnosis and Prevention. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 1188–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, E.; Yan, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Shen, H.; Sun, X.; Feng, Z.; et al. Coral calcium hydride prevents hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese rats: A potent mitochondrial nutrient and phase II enzyme inducer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 103, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, Z.; Cao, K.; Liu, J.; Xu, H. Hydrogen-rich and hyperoxygenate saline inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury through mediating NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. Env. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.; Qu, K.; Wang, R.; Tai, M.H.; Lei Lei, J.C.; Wu, Q.F.; Wang, Z.X. A review of hydrogen as a new medical therapy. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2012, 59, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Laher, I.; Kura, B.; Slezak, J. Hydrogen gas: From clinical medicine to an emerging ergogenic molecule for sports athletes (1). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kurokawa, R.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. A “philosophical molecule”, hydrogen may overcome senescence and intractable diseases. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, C.F.; Ping, N.N.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.X.; Yuan, S.H.; Zibrila, A.I.; Soong, L.; Liu, J.J. Hydrogen-rich water alleviates cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity via the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xie, K. High concentration of hydrogen gas alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatbonton-Schwager, T.; Yagishita, Y.; Joshi, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Srinivasan, H.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. A Point Mutation at C151 of Keap1 of Mice Abrogates NRF2 Signaling, Cytoprotection in Vitro, and Hepatoprotection in Vivo by Bardoxolone Methyl (CDDO-Me). Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 104, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xia, J.; Liang, L.; Lei, C.; Hu, Y.; Cai, X.; et al. SLC27A5 deficiency activates NRF2/TXNRD1 pathway by increased lipid peroxidation in HCC. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D.; Hannink, M. Distinct cysteine residues in Keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventive agents and oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8137–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Chun, K.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, N.C.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Curcumin induces stabilization of Nrf2 protein through Keap1 cysteine modification. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Muramatsu, A.; Saito, R.; Iso, T.; Shibata, T.; Kuwata, K.; Kawaguchi, S.I.; Iwawaki, T.; Adachi, S.; Suda, H.; et al. Molecular Mechanism of Cellular Oxidative Stress Sensing by Keap1. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 746–758.e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00099-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Inoue, J.; Iso, T.; Wells, G.; Moore, T.W.; Mizushima, T.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kasai, T.; Kamei, T.; et al. Molecular basis for the disruption of Keap1-Nrf2 interaction via Hinge & Latch mechanism. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen may activate the transcription factor Nrf2 to alleviate oxidative stress through the hydrogen-targeted porphyrin. Aging Pathobiol. Ther. 2023, 5, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Gong, W.; Ding, W.; He, Q. Fe-porphyrin: A redox-related biosensor of hydrogen molecule. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xue, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Ma, T.; Zhao, M.; Gu, Q.; Qin, S. Hydrogen inhalation alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in metabolic syndrome rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Ito, M.; Ohsawa, I. Molecular hydrogen protects against oxidative stress-induced SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell death through the process of mitohormesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Shigemura, N.; Huang, C.S.; Masutani, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, K.; Peng, X.; Takahashi, T.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. Hydrogen gas reduces hyperoxic lung injury via the Nrf2 pathway in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L646–L656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iketani, M.; Sakane, I.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, M.; Ohsawa, I. H(2)-induced transient upregulation of phospholipids with suppression of energy metabolism. Med. Gas Res. 2023, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, A.A.; Passaglia, P.; Santos, B.M.; Rodrigues-Santos, I.; Flores, R.A.; Batalhão, M.E.; Stabile, A.M.; Cárnio, E.C. Chronic molecular hydrogen inhalation mitigates short and long-term memory loss in polymicrobial sepsis. Brain Res. 2020, 1739, 146857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Feng, J.; Lian, N.; Yang, M.; Xie, K.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen gas alleviates blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive dysfunction of septic mice in an Nrf2-dependent pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, K.; Cai, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, D. Hydrogen gas protects against delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning in a rat model. Neurol. Res. 2020, 42, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Huan, L.; Huang, F.; Cui, Y.; Lin, Z. Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Attenuates Seawater Instillation-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the Nrf2 Pathway in Rabbits. Inflammation 2016, 39, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.G.; Xie, K.L.; Han, H.Z.; Wang, W.N.; Liu, D.Q.; Wang, G.L.; Yu, Y.H. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of molecular hydrogen in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Surg. 2013, 11, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Yu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Hou, L.; Chen, S.; Xiong, L.; Wang, G. Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine polymicrobial sepsis via reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1 release. Shock 2010, 34, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen gas inhibits high-mobility group box 1 release in septic mice by upregulation of heme oxygenase 1. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 196, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Z. Molecular hydrogen is a potential protective agent in the management of acute lung injury. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.C.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, Y.L.; Huang, B.S.; Zhuo, Y.F.; Xu, G.H. Hydrogen gas protects against serum and glucose deprivation-induced myocardial injury in H9c2 cells through activation of the NF-E2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase 1 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, K.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, T.; Yu, Y. Molecular hydrogen protects mice against polymicrobial sepsis by ameliorating endothelial dysfunction via an Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates chemotherapy-induced ovarian injury via regulation of oxidative stress. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.C.; Devendran, S.; Méndez-García, C.; Mythen, S.M.; Wright, C.L.; Fields, C.J.; Hernandez, A.G.; Cann, I.; Hylemon, P.B.; Ridlon, J.M. Bile acid oxidation by Eggerthella lenta strains C592 and DSM 2243(T). Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Gallenga, C.E.; Tetè, G.; Caraffa, A.; Ronconi, G.; Younes, A.; Toniato, E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K. How to reduce the likelihood of coronavirus-19 (CoV-19 or SARS-CoV-2) infection and lung inflammation mediated by IL-1. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, A.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K. Protective effects of hydrogen gas against sepsis-induced acute lung injury via regulation of mitochondrial function and dynamics. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Shen, J. Hydrogen, a potential safeguard for graft-versus-host disease and graft ischemia-reperfusion injury? Clinics 2016, 71, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Huang, C.S.; Tochigi, N.; Lee, S.; Shigemura, N.; Billiar, T.R.; Okumura, M.; Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y. Inhaled hydrogen gas therapy for prevention of lung transplant-induced ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Fang, X.; Meng, C.; Xing, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Zhou, H. Lung inflation with hydrogen during the cold ischemia phase decreases lung graft injury in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Shigemura, N.; Kawamura, T.; Noda, K.; Isse, K.; Stolz, D.B.; Billiar, T.R.; Toyoda, Y.; Bermudez, C.A.; Lyons-Weiler, J.; et al. Profiling molecular changes induced by hydrogen treatment of lung allografts prior to procurement. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, W.; Deng, Y.; Shao, A. Molecular hydrogen: A potential radioprotective agent. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, Y.; Ohsawa, I.; Terasaki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kunugi, S.; Dedong, K.; Urushiyama, H.; Amenomori, S.; Kaneko-Togashi, M.; Kuwahara, N.; et al. Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L415–L426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsin, K.; Sittiwangkul, R.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Hydrogen therapy as a potential therapeutic intervention in heart disease: From the past evidence to future application. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2023, 80, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F. Protective Mechanism and Clinical Application of Hydrogen in Myocardial Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2020, 23, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Jia, L.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Long, J.; Li, Y. Hydrogen Inhalation is Superior to Mild Hypothermia in Improving Cardiac Function and Neurological Outcome in an Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Model of Rats. Shock 2016, 46, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.L.; Cheng, L.; Ren, J.D.; Fang, C.; Xiang, K.; Xu, H.T.; Tang, L.J.; Wang, T.; Tian, F.Z. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in grafts after pancreas transplantations by reducing oxidative stress in rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 281985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.; Xie, K. Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in myocardial I/R injury via PINK-mediated autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Cai, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. Early Aerobic Exercise Combined with Hydrogen-Rich Saline as Preconditioning Protects Myocardial Injury Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 187, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shigemura, N.; Kawamura, T.; Wang, Y.; Masutani, K.; Sun, X.; Toyoda, Y.; Bermudez, C.A.; Nakao, A. Hydrogen-supplemented drinking water protects cardiac allografts from inflammation-associated deterioration. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ. Transplant. 2012, 25, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in Studies of Molecular Hydrogen against Sepsis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, A.; Xie, K.; Yu, Y. Protective Effects of Hydrogen on Myocardial Mitochondrial Functions in Septic Mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1568209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, N.; Tong, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Heart Dysfunction by Restoring Fatty Acid Oxidation in Rats by Mitigating C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation. Shock 2015, 44, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.S.; Zheng, H. Chronic hydrogen-rich saline treatment reduces oxidative stress and attenuates left ventricular hypertrophy in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 365, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; He, B.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Anti-inflammatory effect of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 148, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Htun, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Kusaka, T. Hydrogen and therapeutic gases for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Potential neuroprotective adjuncts in translational research. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, M.; Liu, J.; Long, J. Neuroprotective and Preventative Effects of Molecular Hydrogen. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Peng, Y.; Qin, C.; Fan, F.; Liu, J.; Long, J. Hydrogen-rich water improves cognitive impairment gender-dependently in APP/PS1 mice without affecting Aβ clearance. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoritaka, A.; Takanashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nakahara, T.; Ohta, S.; Hattori, N. Pilot study of H2 therapy in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2013, 28, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ji, M.; Jia, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Duan, M. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates neuronal ischemia--reperfusion injury by protecting mitochondrial function in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, B.; Cai, S.; Hui, K.; Yu, G.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Duan, M.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Saline in Global Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Rats: Up-Regulated Tregs and Down-Regulated miR-21, miR-210 and NF-κB Expression. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Hou, L.; Chen, D.; Lin, F.; Chang, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Niu, X.; Wang, H.; Fu, S.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates isoflurane-induced caspase-3 activation and cognitive impairment via inhibition of isoflurane-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and reduction in ATP levels. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Liu, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhu, L.; Sun, X.; Sun, X. Effect of hydrogen-rich water on oxidative stress, liver function, and viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2013, 6, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid signaling in metabolic disease and drug therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 948–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.L.; Gao, J.; Guo, W.J.; Zhou, F.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Su, C.C. Anti-injury effect of hydrogen-enriched water in a rat model of liver injury induced by aflatoxin B(1). Sheng Li Xue Bao 2019, 71, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Shi, L.; Du, D.; Li, H.; Yi, N.; Xi, Y.; Cui, J.; Li, P.; Kang, H.; Noda, M.; et al. Hydrogen-Rich Water Ameliorates Metabolic Disorder via Modifying Gut Microbiota in Impaired Fasting Glucose Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yu, S.; Qin, M.; Mao, Y.; Jin, L.; Che, N.; Liu, S.; Ge, R. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Ameliorates Allergic Rhinitis by Reversing the Imbalance of Th1/Th2 and Up-Regulation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Regulatory T Cells, Interleukin-10, and Membrane-Bound Transforming Growth Factor-β in Guinea Pigs. Inflammation 2018, 41, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Guo, A.; Han, X.; Wu, S.; Chen, C.; Luo, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Hei, Z. Aerosol inhalation of a hydrogen-rich solution restored septic renal function. Aging 2019, 11, 12097–12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xu, L.; Jia, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Alleviates Kidney Fibrosis Following AKI and Retains Klotho Expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Liao, K.S.; Zhao, K.L.; Wang, W.X.; Zuo, T.; Deng, W.H.; Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Guo, W.Y.; He, X.B.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates acute renal injury in sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting ROS and NF-κB pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 685043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Song, Y.; Yi, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ma, S.; Ma, C.; Li, J.; Zhanghuang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, P.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Molecular Hydrogen in Metabolic Diseases from Bench to Bedside. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzavon, Y.M.; Xie, F.; Yi, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhao, P.; Liu, M.; Ma, S.; Ma, X. Long-term and daily use of molecular hydrogen induces reprogramming of liver metabolism in rats by modulating NADP/NADPH redox pathways. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korovljev, D.; Trivic, T.; Drid, P.; Ostojic, S.M. Molecular hydrogen affects body composition, metabolic profiles, and mitochondrial function in middle-aged overweight women. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 187, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuchi, K.; Nishimaki, K.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen suppresses free-radical-induced cell death by mitigating fatty acid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mechanism | Example | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Electrophilic | Cys151-dependent compounds | Bardoxolone methyl Sulforaphane, dimethyl-fumarate |
| Class II | Targets Cys288 | 15d-PGJ2 | |
| Class III | Reacts with any of the three sensor cysteines Cys151/Cys273/Cys288 | 4-HNE, NaAsO2, 9-nitro-octadec-9-enoic acid | |
| Class IV | Targets cysteines Cys77/Cys434 | Pubescenoside A | |
| Class V | Non-electrophilic | Targets Cys226/Cys613/Cys622/Cys624 | H2O2, cadmium chloride, zinc chloride, prostaglandin A2 |
| Class VI | Protein–protein interaction inhibitors (PPIs) | CPUY192018 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, D.; Long, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J. Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122062
Cheng D, Long J, Zhao L, Liu J. Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(12):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122062
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Danyu, Jiangang Long, Lin Zhao, and Jiankang Liu. 2023. "Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System" Antioxidants 12, no. 12: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122062
APA StyleCheng, D., Long, J., Zhao, L., & Liu, J. (2023). Hydrogen: A Rising Star in Gas Medicine as a Mitochondria-Targeting Nutrient via Activating Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant System. Antioxidants, 12(12), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12122062







