Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6,3’,4´- and 7,3´,4´-Trihydroxyflavone on 2D and 3D RAW264.7 Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Scaffolds Fabrication
2.3. 2D and 3D Cell Culture and Morphology Characterization
2.4. Cellular Antioxidant Analysis
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. NO Production Assay
2.7. Western Blotting Analysis
2.8. RT-qPCR
2.9. Screening for C-Src Kinase Binding Activity
2.10. Transcriptome Sequencing
2.11. Statistical Analysis
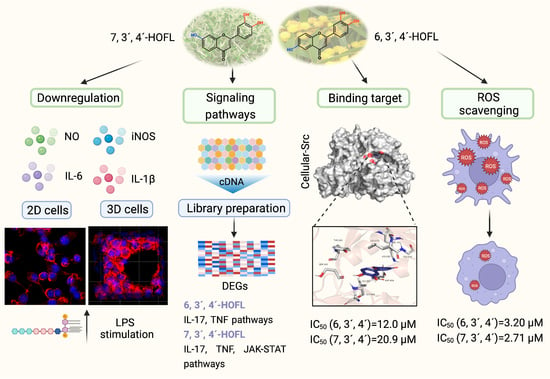
3. Results
3.1. Cellular Antioxidant Activity
3.2. Morphologies of 2D and 3D Macrophages
3.3. NO Inhibition Activity and Cytotoxicity
3.4. Enzymes and Cytokines Suppression Activities
3.5. Anti-Inflammation Mechanisms
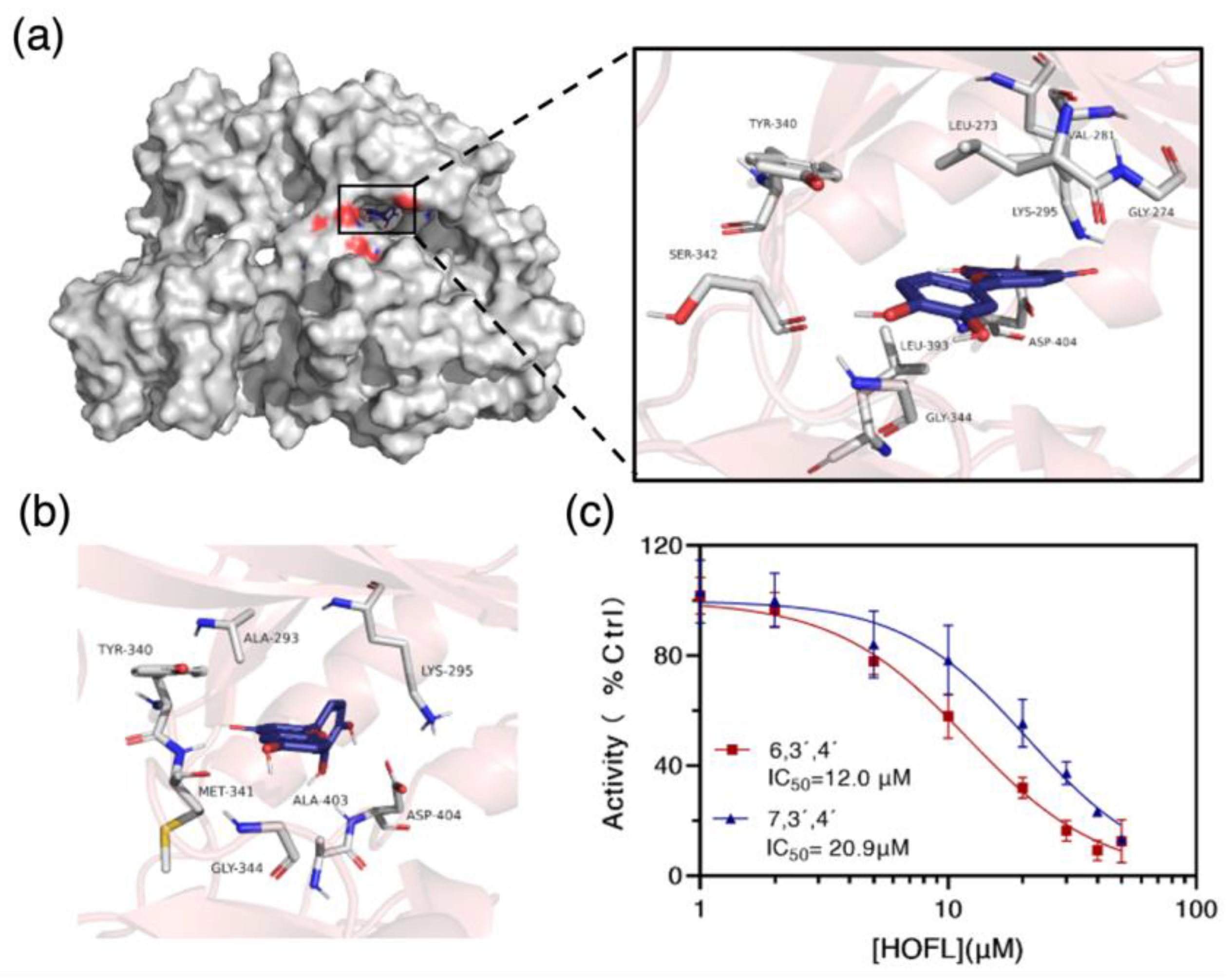
3.6. Binding Targets of 6,3´,4´- and 7,3´,4´-HOFL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three dimensional |
| 6,3´,4´-HOFL | 6,3´,4´-trihydroxyflavone |
| 7,3´,4´-HOFL | 7,3´,4´-trihydroxyflavone |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| CLSM | Confocal laser scanning microscopy |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DCFDA | 2´,7´-dichlorofluorescin diacetate |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EHDJ | Electrohydrodynamic jetting |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FESEM | Field emission scanning electron microscope |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitrite oxidase |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandins E2 |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| tBHP | Tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Yang, B.W.; Yang, S.; Kim, S.; Baek, A.R.; Sung, B.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Choi, G.; et al. Flavonoid-Conjugated Gadolinium Complexes as Anti-Inflammatory Theranostic Agents. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Bian, J.; Huang, D. Anti-Inflammation Activity of Flavones and Their Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7285–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, L.S.; Oliveira, M.S.; Dittz, D.; Sousa, R.W.; Ferreira, P.M.; Pessoa, C.; de P. Varotti, F.; Sanchez, B.A.; Banfi, F.F.; Chaves, M.H. Flavonoids, Cytotoxic, and Antimalarial Activities of Dipteryx lacunifera. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2020, 30, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Zeb, A. Phytochemical profile and pharmacological properties of Trifolium repens. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Morikawa, T.; Ando, S.; Toguchida, I.; Yoshikawa, M. Structural requirements of flavonoids for nitric oxide production inhibitory activity and mechanism of action. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, E.L.S.; Lamhamedi-Cherradi, S.-E.; Burdett, E.; Ramamoorthy, V.; Lazar, A.J.; Kasper, F.K.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Vishwamitra, D.; Demicco, E.G.; Menegaz, B.A. Modeling Ewing sarcoma tumors in vitro with 3D scaffolds. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6500–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, J.; Li, Q.; Yan, C.; Jiang, S.; Mohammadtursun, N. Baicalein inhibits orthotopic human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts via Src/Id1 pathway. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9806062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, J.-P.; Calcagno, A.M.; Varma, S.; Marino, M.; Green, L.J.; Vora, M.I.; Patel, C.; Orina, J.N.; Eliseeva, T.A.; Singal, V. Redefining the relevance of established cancer cell lines to the study of mechanisms of clinical anti-cancer drug resistance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18708–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture models in drug discovery and drug repositioning. Front. Pharmacol 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, V.; Oliveira, J.M.; Correlo, V.M.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C. Could 3D models of cancer enhance drug screening? Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Bian, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, D. Zein increases the cytoaffinity and biodegradability of scaffolds 3D-printed with zein and poly (ε-caprolactone) composite ink. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18551–18559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Jing, L.; Chen, S.; Leng, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, Z.; Bian, J.; Banjerdpongchai, R.; Poofery, J. Three-Dimensional RAW264. 7 Cell Model on Electrohydrodynamic Printed Poly (ε-Caprolactone) Scaffolds for In Vitro Study of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 4, 7967–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Deng, S.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Hao, L.; Zhang, G.; Su, S.; Xu, X.; Yang, R. 3, 4-seco-Dammarane triterpenoid saponins with anti-inflammatory activity isolated from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarino, A.V.; Kanno, Y.; O’Shea, J.J. Mechanisms and consequences of Jak–STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.O.; Jeong, D.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. ATP-Binding Pocket-Targeted Suppression of Src and Syk by Luteolin Contributes to Its Anti-Inflammatory Action. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagishi, H.; Finkel, T. Unraveling the truth about antioxidants: ROS and disease: Finding the right balance. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, I. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1997, 24, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas, I.; Erenler, R.; Elmastas, M.; Goktasoglu, A. Studies on the antioxidant potential of flavones of Allium vineale isolated from its water-soluble fraction. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P.-G. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.M.; Mytelka, D.S.; Dunwiddie, C.T.; Persinger, C.C.; Munos, B.H.; Lindborg, S.R.; Schacht, A.L. How to improve R&D productivity: The pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, S.G.; Reddy, E.P. JAKs, STATs and Src kinases in hematopoiesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3334–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincheira, R.; Castro, A.F.; Ozes, O.N.; Idumalla, P.S.; Donner, D.B. Type 1 TNF Receptor Forms a Complex with and Uses Jak2 and c-Src to Selectively Engage Signaling Pathways That Regulate Transcription Factor Activity. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Bian, J.; Huang, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6,3’,4´- and 7,3´,4´-Trihydroxyflavone on 2D and 3D RAW264.7 Models. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010204
Wang X, Cao Y, Chen S, Yang X, Bian J, Huang D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6,3’,4´- and 7,3´,4´-Trihydroxyflavone on 2D and 3D RAW264.7 Models. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(1):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010204
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiang, Yujia Cao, Siyu Chen, Xin Yang, Jinsong Bian, and Dejian Huang. 2023. "Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6,3’,4´- and 7,3´,4´-Trihydroxyflavone on 2D and 3D RAW264.7 Models" Antioxidants 12, no. 1: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010204
APA StyleWang, X., Cao, Y., Chen, S., Yang, X., Bian, J., & Huang, D. (2023). Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6,3’,4´- and 7,3´,4´-Trihydroxyflavone on 2D and 3D RAW264.7 Models. Antioxidants, 12(1), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010204