NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis in Liver Pathophysiology: The Emerging Relevance of Nrf2 Inducers
Abstract
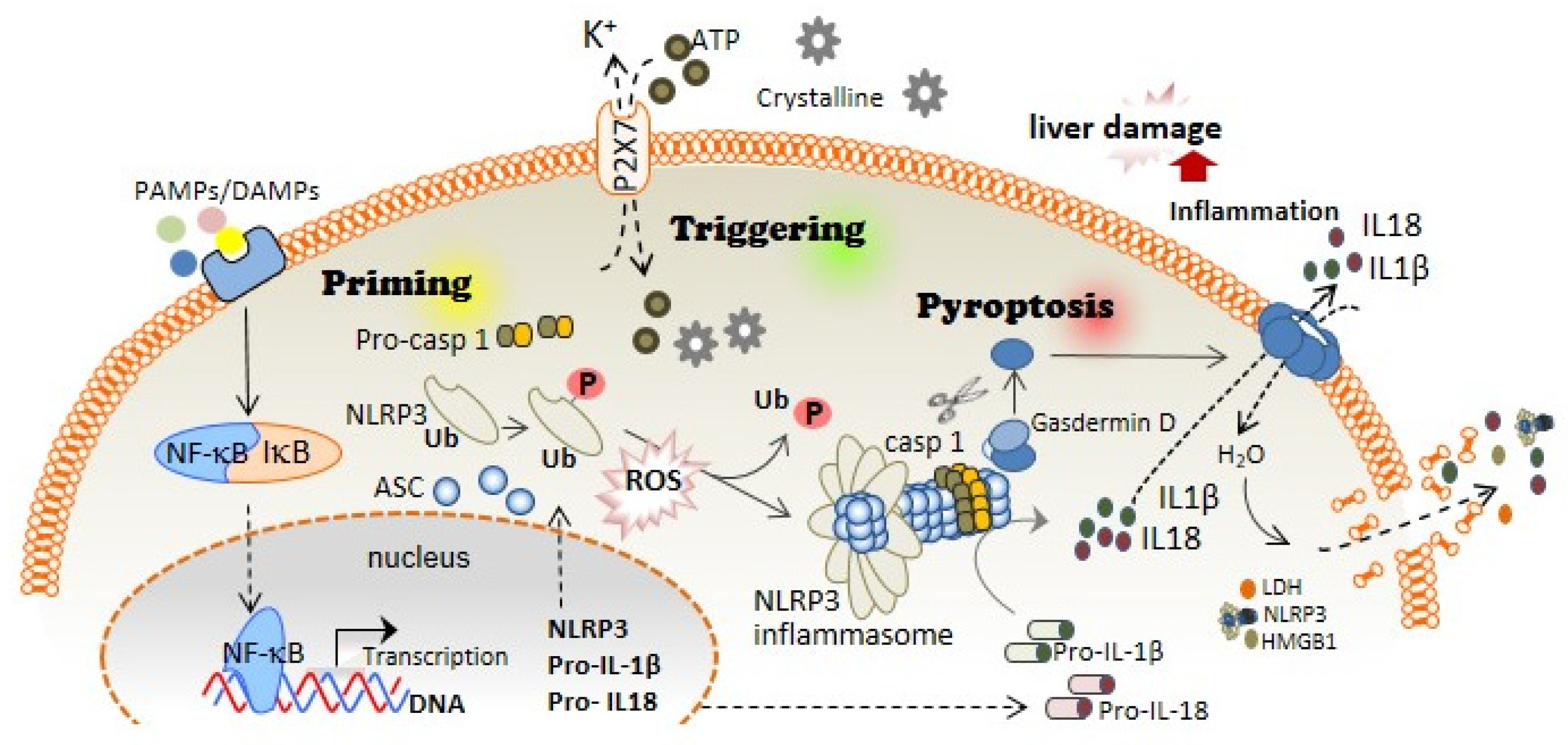
:1. Inflammasomes and Pyroptotic Cell Death
2. Inflammasome and Pyroptosis as an Essential Inflammatory Pathway in Liver Diseases
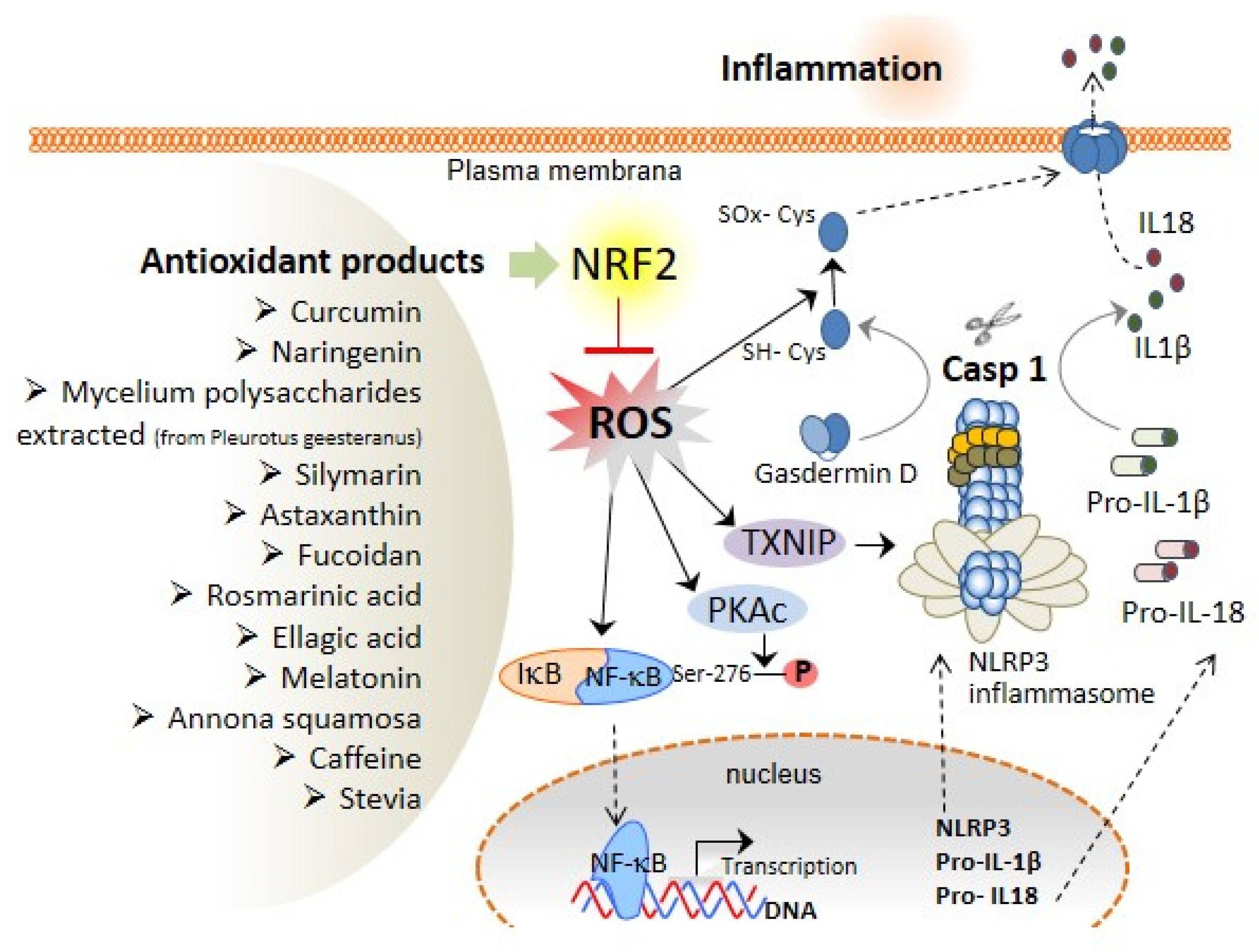
3. The Association of Oxidative Stress with NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Liver Diseases
4. Role of Antioxidant Compounds with Nrf2 Activation Properties in the Prevention of Liver Diseases
5. Clinical Trials with Nrf2-Activating Antioxidants: Results and Side Effects
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIM2 | Absent in melanoma 2 |
| ALD | Alcoholic liver disease |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment and activation domain |
| ASH | Alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CAPS | Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome |
| CARD | Caspase activation and recruitment domain |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| GSDMD | Gasdermin D |
| HAMPs | Homeostasis-altering molecular processes |
| HBV | Chronic viral hepatitis B |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group box 1 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| IL | Interleukin |
| KCs | Kupffer cells |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NLR | Leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NOD | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor |
| P2X7R | P2X purinoceptor 7 |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PEITC | Phenethyl isothiocyanate |
| PKAc | ROS-dependent cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| PSC | Primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| PYD | Pyrin domain |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TXNIP | Thioredoxin-interacting protein |
References
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-β. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Nunez, G. Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, J.P.; Lovering, R.C.; Alnemri, E.S.; Bertin, J.; Boss, J.M.; Davis, B.K.; Flavell, R.A.; Girardin, S.E.; Godzik, A.; Harton, J.A.; et al. The NLR gene family: A standard nomenclature. Immunity 2008, 28, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Yu, X.Y.; Shen, Z.; Song, Y.H. Inflammasomes as therapeutic targets in human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Luheshi, N.M.; Compan, V.; High, S.; Whitehead, R.C.; Flitsch, S.; Kirov, A.; Prudovsky, I.; Swanton, E.; Brough, D. Deubiquitinases regulate the activity of caspase-1 and interleukin-1beta secretion via assembly of the inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutz, A.; Kolbe, C.C.; Stahl, R.; Horvath, G.L.; Franklin, B.S.; van Ray, O.; Brinkschulte, R.; Geyer, M.; Meissner, F.; Latz, E. NLRP3 inflammasome assembly is regulated by phosphorylation of the pyrin domain. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrin, P. P2X7 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Partners in crime. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 187, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.N.R.; Bittner, Z.A.; Shankar, S.; Liu, X.; Chang, T.H.; Jin, T.; Tapia-Abellan, A. Recent insights into the regulatory networks of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs248344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2114–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, S.B.; Miao, E.A. Gasdermins: Effectors of pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Xia, S.; Liu, X.; Lieberman, J.; Wu, H. Cryo-EM structure of the gasdermin A3 membrane pore. Nature 2018, 557, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Magupalli, V.G.; Pablo, J.L.; Dong, Y.; Vora, S.M.; Wang, L.; Fu, T.M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Greka, A.; et al. Gasdermin D pore structure reveals preferential release of mature interleukin-1. Nature 2021, 593, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayagaki, N.; Kornfeld, O.S.; Lee, B.L.; Stowe, I.B.; O’Rourke, K.; Li, Q.; Sandoval, W.; Yan, D.; Kang, J.; Xu, M.; et al. NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature 2021, 591, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja-Mazo, A.; Martin-Sanchez, F.; Gomez, A.I.; Martinez, C.M.; Amores-Iniesta, J.; Compan, V.; Barbera-Cremades, M.; Yague, J.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Anton, J.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is released as a particulate danger signal that amplifies the inflammatory response. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Torre-Minguela, C.; Gomez, A.I.; Couillin, I.; Pelegrin, P. Gasdermins mediate cellular release of mitochondrial DNA during pyroptosis and apoptosis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, P.; Pelegrin, P.; Shao, F. The gasdermins, a protein family executing cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, C.; Abdel-Latif, A.; Smyth, S.S.; Shiroishi, T.; Mackman, N.; Wei, Y.; Tao, M.; et al. Inflammasome activation promotes venous thrombosis through pyroptosis. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. Bacterial endotoxin activates the coagulation cascade through gasdermin D-dependent phosphatidylserine exposure. Immunity 2019, 51, 983–996.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, A.; Akter, A.; Hossain, S.; Sarker, T.; Safa, S.A.; Mustafa, Q.G.; Muhammad, S.A.; Munir, F. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in liver disease. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byass, P. The global burden of liver disease: A challenge for methods and for public health. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieling, R.G.; Wallace, K.; Han, Y.P. Interleukin-1 participates in the progression from liver injury to fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1324–G1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegre, F.; Pelegrin, P.; Feldstein, A.E. Inflammasomes in liver fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calcagno, D.M.; Chu, A.; Gaul, S.; Taghdiri, N.; Toomu, A.; Leszczynska, A.; Kaufmann, B.; Papouchado, B.; Wree, A.; Geisler, L.; et al. NOD-like receptor protein 3 activation causes spontaneous inflammation and fibrosis that mimics human NASH. Hepatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.W.; Cheng, P.C.; Chang, K.C.; Cao, J.P.; Feng, J.L.; Chen, C.C.; Lam, H.Y.P.; Peng, S.Y. Activation of the NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes in a mouse model of Schistosoma mansoni infection. J. Helminthol. 2019, 94, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Xia, M.; Lu, Y.Q.; Wang, M.; Boini, K.M.; Li, P.L.; Tang, W.X. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in mouse hepatic stellate cells during Schistosoma J. infection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39316–39331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chang, B.; Wang, B. Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation by Escherichia coli RNA induces transforming growth factor beta 1 secretion in hepatic stellate cells. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 16, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.H.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Song, S.Z.; Sun, P.; Nan, J.X.; Lian, L.H. Potentiation of hepatic stellate cell activation by extracellular ATP is dependent on P2X7R-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Huang, S.; Ma, X.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Angiotensin(1–7) attenuated Angiotensin II-induced hepatocyte EMT by inhibiting NOX-derived H2O2-activated NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1beta/Smad circuit. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 97, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, X.; Lu, C.; Lian, N.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, S. Tetramethylpyrazine reduces inflammation in liver fibrosis and inhibits inflammatory cytokine expression in hepatic stellate cells by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaul, S.; Leszczynska, A.; Alegre, F.; Kaufmann, B.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, L.A.; Wree, A.; Damm, G.; Seehofer, D.; Calvente, C.J.; et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, H.; Yuan, X.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Ding, Y. Interleukin-10 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells attenuates acute liver failure through inhibiting pyroptosis. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, E194–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.Y.; Cui, W.W.; Gao, H.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.R.; Hou, Y.L.; Jia, Z.H. Jinlida granules ameliorate the high-fat-diet induced liver injury in mice by antagonising hepatocytes pyroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Le, Q.A.; Han, S.Y.; Bae, J.; Shin, H.W.; Kang, H.G.; Han, K.H.; Shin, J.; et al. Sestrin2 protects against cholestatic liver injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, K.; Kageyama, S.; Nakamura, K.; Hirao, H.; Ito, T.; Kojima, H.; Dery, K.J.; Li, X.; Kupiec-Weglinski, J.W. Myeloid Ikaros-SIRT1 signaling axis regulates hepatic inflammation and pyroptosis in ischemia-stressed mouse and human liver. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Wright, S.E.; Kim, S.H.; Srivastava, S.K. Phenethyl isothiocyanate: A comprehensive review of anti-cancer mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.J.; Liu, X.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ruan, J.; Luo, X.; Lou, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, K.; An, N.; Li, S.; Bai, M.; Wu, X.; Shen, Y.; Du, R.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Q. Direct inhibition of GSDMD by PEITC reduces hepatocyte pyroptosis and alleviates acute liver injury in mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 825428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, J.; Wree, A.; Tacke, F.; Feldstein, A.E. The NLRP3 inflammasome in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridha, A.R.; Wree, A.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Yeh, M.M.; Johnson, C.D.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Haczeyni, F.; Teoh, N.C.; Savard, C.; Ioannou, G.N.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, M.; Chu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Fan, D.; Nie, Y.; et al. Gasdermin D plays a key role as a pyroptosis executor of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in humans and mice. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, D.W.; Im, G.Y.; Szabo, G.; Mellinger, J.L.; Lucey, M.R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol-Associated Liver Diseases: 2019 Practice Guidance From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 71, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, T.; Huang, Y.; Pang, N.; Jiang, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, J.; Yang, L. Cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucoside inactivates NLRP3 inflammasome and alleviates alcoholic steatohepatitis via SirT1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Petrasek, J.; Satishchandran, A.; Gyongyosi, B.; Saha, B.; Kodys, K.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Inhibition of sterile danger signals, uric acid and ATP, prevents inflammasome activation and protects from alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrasek, J.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Saha, B.; Satishchandran, A.; Kodys, K.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Metabolic danger signals, uric acid and ATP, mediate inflammatory cross-talk between hepatocytes and immune cells in alcoholic liver disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, L.R.; Randall, M.J.; Ather, J.L.; DePuccio, D.P.; Landry, C.C.; Qian, X.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M.; van der Vliet, A.; Dixon, A.E.; Amiel, E.; et al. Mitochondrial ROS induced by chronic ethanol exposure promote hyper-activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.J.; Kim, T.H.; You, J.S.; Blaya, D.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Kim, S.G. Alcohol dysregulates miR-148a in hepatocytes through FoxO1, facilitating pyroptosis via TXNIP overexpression. Gut 2019, 68, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voican, C.S.; Njiké-Nakseu, M.; Boujedidi, H.; Barri-Ova, N.; Bouchet-Delbos, L.; Agostini, H.; Maitre, S.; Prévot, S.; Cassard-Doulcier, A.M.; Naveau, S.; et al. Alcohol withdrawal alleviates adipose tissue inflammation in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2015, 35, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Torralba, M.G.; Kuelbs, C.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Abraldes, J.G.; Bosques-Padilla, F.; Verna, E.C.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; et al. Intestinal fungal dysbiosis and systemic immune response to fungi in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2020, 71, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkel, P.; Schnabl, B. Bidirectional communication between liver and gut during alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Rajesh, M.; Cao, Z.; Horvath, B.; Park, O.; Wang, H.; Erdelyi, K.; Holovac, E.; Wang, Y.; Liaudet, L.; et al. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 is a key mediator of liver inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Horvath, B.; Rajesh, M.; Varga, Z.V.; Gariani, K.; Ryu, D.; Cao, Z.; Holovac, E.; Park, O.; Zhou, Z.; et al. PARP inhibition protects against alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- .Paldino, E.; D’Angelo, V.; Laurenti, D.; Angeloni, C.; Sancesario, G.; Fusco, F.R. Modulation of Inflammasome and pyroptosis by olaparib, a PARP-1 inhibitor, in the R6/2 mouse model of huntington’s disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanova, E.; Wu, R.; Wang, W.; Yan, R.; Chen, Y.; French, S.W.; Llorente, C.; Pan, S.Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Pyroptosis by caspase11/4-gasdermin-D pathway in alcoholic hepatitis in mice and patients. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, X.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in liver cirrhotic patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyvdas, A.; Georgopoulou, U.; Lazaridis, N.; Hytiroglou, P.; Dimitriadis, A.; Foka, P.; Vassiliadis, T.; Loli, G.; Phillipidis, A.; Zebekakis, P.; et al. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the activation of IL-1β in the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatic inflammation. Cytokine 2018, 110, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.H.; Ding, J.; Xie, X.X.; Yang, X.H.; Wu, X.F.; Chen, Z.X.; Guo, Q.L.; Gao, W.Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, D. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell pyroptosis under oxidative stress through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.P.; Zanetto, A.; Pinto, E.; Battistella, S.; Penzo, B.; Burra, P.; Farinati, F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic viral hepatitis: Where do we stand? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lan, P.; Hou, X.; Han, Q.; Lu, N.; Li, T.; Jiao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z. HBV inhibits LPS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β production via suppressing the NF-κB pathway and ROS production. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lei, Q.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Qin, B. Hepatitis B core antigen can regulate NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in HepG2 cells. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofahi, H.M.; Taylor, N.G.; Hirasawa, K.; Grant, M.D.; Russell, R.S. Hepatitis C virus infection of cultured human hepatoma cells causes apoptosis and pyroptosis in both infected and bystander cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, A.A.; Olson, R.M.; Griffin, S.; Gale, M., Jr. Modulation of calcium signaling pathway by hepatitis C virus core protein stimulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Free radicals, antioxidants, nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2 and liver damage. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2020, 40, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.E.; Tian, B.; Jamaluddin, M.; Boldogh, I.; Vergara, L.A.; Choudhary, S.; Brasier, A.R. RelA Ser276 phosphorylation is required for activation of a subset of NF-kappaB-dependent genes by recruiting cyclin-dependent kinase 9/cyclin T1 complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3623–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, J.R.; Kaszubska, W.; Turcatti, G.; Wells, T.N.; Hay, R.T. Role of cysteine62 in DNA recognition by the P50 subunit of NF-kappa B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubici, C.; Papa, S.; Dean, K.; Franzoso, G. Mutual cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor-kappa B: Molecular basis and biological significance. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6731–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Wang, S.; Boldogh, I.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R. TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB/RelA Ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ROS-dependent PKAc pathway. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Tardivel, A.; Thorens, B.; Choi, I.; Tschopp, J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, R.; Yilmaz, O. The role of reactive-oxygen-species in microbial persistence and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostert, C.; Pétrilli, V.; Van Bruggen, R.; Steele, C.; Mossman, B.T.; Tschopp, J. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 2008, 320, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latz, E. NOX-free inflammasome activation. Blood 2010, 116, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Menu, P.; Tschopp, J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011, 469, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, P.; Garstkiewicz, M.; Grossi, S.; Di Filippo, M.; French, L.E.; Beer, H.D. The crosstalk between Nrf2 and Inflammasomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenkov, N.K.; Menshchikova, E.B.; Tkachev, V.O. Keap1/Nrf2/ARE redox-sensitive signaling system as a pharmacological target. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Molecular mechanisms that link oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Que, R.; Lin, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Inhibition of oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome by Saikosaponin-d alleviates acute liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420950593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Kaji, K.; Sato, S.; Ogawa, H.; Takagi, H.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Akahane, T.; et al. Sulforaphane ameliorates ethanol plus carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice through the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response and acetaldehyde metabolization with inhibition of the LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 89, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irazabal, M.V.; Torres, V.E. Reactive oxygen species and redox signaling in chronic kidney disease. Cells 2020, 9, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Moreno, M.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Silva-Gomez, J.; Gutierrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Roles of Nrf2 in liver diseases: Molecular, pharmacological, and epigenetic aspects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, S.; Pelegrin, P. Pyroptosis and redox balance in kidney diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohs, A.; Otto, T.; Schneider, K.M.; Peltzer, M.; Boekschoten, M.; Holland, C.H.; Hudert, C.A.; Kalveram, L.; Wiegand, S.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific NRF2 activation controls fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis in steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Crisostomo, I.; Fernandez-Martinez, E.; Carino-Cortes, R.; Betanzos-Cabrera, G.; Bobadilla-Lugo, R.A. Phytosterols and triterpenoids for prevention and treatment of metabolic-related liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Tang, G.Y.; Liu, P.H.; Zhao, C.J.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.B. Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effect of 10 medicinal herbs on CCl4-induced liver injury in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5629–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Casado-Andres, M.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Serrano-Macia, M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L. Nutraceutical properties of polyphenols against liver diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Zobeiri, M.; Parvizi, F.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Marmouzi, I.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Naseri, R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Curcumin in liver diseases: A systematic review of the cellular mechanisms of oxidative stress and clinical perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Aquino, E.; Muriel, P. Beneficial effects of naringenin in liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1679–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, B.; He, X.M.; Li, D.D.; Shi, J.S.; Zhang, F. Naringenin targets on astroglial Nrf2 to support dopaminergic neurons. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shen, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Z.; Wang, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of intracellular mycelium polysaccharides from Pleurotus geesteranus against alcoholic liver diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, J.; Ren, H.; Jia, L. Mycelium Polysaccharides from Termitomyces albuminosus attenuate CCl4-induced chronic liver injury via inhibiting TGFbeta1/Smad3 and NF-kappaB signal pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, L.M.O.; Agostini, L.D.C.; Lima, W.G.; Camini, F.C.; Costa, D.C. Silymarin Attenuates hepatic and pancreatic redox imbalance independent of glycemic regulation in the alloxan-induced diabetic rat model. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2020, 33, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, C.; Wu, J. Astaxanthin in liver health and disease: A potential therapeutic agent. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wei, J.G.; Tu, M.J.; Gu, J.G.; Zhang, W. Fucoidan alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via oxidative stress inhibition and Nrf2 translocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Guo, C.; Wu, J. Fucoidan: Biological activity in liver diseases. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, A.; Boyuk, A.; Ekinci, A.; Alabalik, U.; Turkoglu, A.; Tuncer, M.C.; Ekingen, A.; Deveci, E.; Gulturk, B.; Aday, U. Investigation of antioxidant effects of rosmarinic acid on liver, lung and kidney in rats: A biochemical and histopathological study. Folia Morphol. 2020, 79, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, V.; Solaipriya, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, V. Role of ellagic acid for the prevention and treatment of liver diseases. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xue, H.; Lu, Y. Rosmarinic acid, the main effective constituent of orthosiphon stamineus, inhibits intestinal epithelial apoptosis via regulation of the Nrf2 pathway in mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Jian, T.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Ren, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; et al. Ellagic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells via miR-223/keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhao, L.; Tao, J.; Li, L. Protective role of melatonin in early-stage and end-stage liver cirrhosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7151–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, Z.; Ashrafizadeh, M. Melatonin as a potential modulator of Nrf2. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Arif, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Mujahid, M. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Annona squamosa seed extract against alcohol-induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 43, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Hagen, C.E.; Kumar, S.N.; Park, J.I.; Zimmerman, M.A.; Hong, J.C. Anticholestatic effect of bardoxolone methyl on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, H.; Ikram, M.; Ali, W.; Ahmad, S.; Hahm, J.R.; Kim, M.O. Caffeine may abrogate LPS-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by regulating Nrf2/TLR4 in adult mouse brains. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Buendia-Montano, L.D.; Galindo-Gomez, S.; Hernandez-Aquino, E.; Tsutsumi, V.; Muriel, P. Stevia prevents experimental cirrhosis by reducing hepatic myofibroblasts and modulating molecular profibrotic pathways. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2019, 49, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Flores-Beltran, R.E.; Galindo-Gomez, S.; Vera-Aguilar, E.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Montes, S.; Camacho, J.; Tsutsumi, V.; Muriel, P. Stevia rebaudiana tea prevents experimental cirrhosis via regulation of NF-kappaB, Nrf2, transforming growth factor beta, Smad7, and hepatic stellate cell activation. Phytother. Res. PTR 2018, 32, 2568–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachon, A.U.; Quintal-Novelo, C.; Medina-Escobedo, G.; Castro-Aguilar, G.; Moo-Puc, R.E. Hepatoprotective effect of low doses of caffeine on CCL4-induced liver damage in rats. J. Diet. Suppl. 2017, 14, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Bai, Y. Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2252–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, J.T.; Nguyen, T.; Turgeon, R.D. N-acetylcysteine for non-paracetamol (acetaminophen)-related acute liver failure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD012123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.R., 3rd; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Dalal, D.; Riemersma, R.A.; Appel, L.J.; Guallar, E. Meta-analysis: High-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Tuttle, K.R. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1768–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.H.; Jadoul, M.; Block, G.A.; Chin, M.P.; Ferguson, D.A.; Goldsberry, A.; Meyer, C.J.; O’Grady, M.; Pergola, P.E.; Reisman, S.A.; et al. Effects of bardoxolone methyl on hepatic enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and stage 4 CKD. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Harmful and beneficial role of ROS 2017. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5943635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, S.; Yang, Y.; Konkalmatt, P.; Asico, L.D.; Feranil, J.; Jones, J.; Villar, V.A.; Armando, I.; Jose, P.A. Role of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in the oxidative stress-dependent hypertension associated with the depletion of DJ-1. Hypertension 2015, 65, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel, C.; Kraus, A.C.; Saludes, M.A.; Konkalmatt, P.; Dominguez, A.R.; Asico, L.D.; Latham, P.S.; Offen, D.; Jose, P.A.; Cuevas, S. ND-13, a DJ-1-derived peptide, attenuates the renal expression of fibrotic and inflammatory markers associated with unilateral ureter obstruction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Source | Type of Molecule | Effect on Liver Pathologies | Biological System | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Plants | Polyphenol | NASH; ALD; Liver fibrosis | Rat; Mice | [86] |
| Naringenin | Plants | Flavonoid | ALD; Liver fibrosis; Diabetes-induced hepatotoxicity; Liver Cancer | Rat; Mice; Human; Rabbit | [87,88] |
| Pleurotus geesteranus | Mushroom | Mycelium polysaccharide | ALD; Chronic liver injury | Mice | [89,90] |
| Silymarin | Plants | Extract | Diabetes Type 1-induced hepatotoxicity | Rat | [91] |
| Astaxanthin | Seafood, microalgaes, yeasts | Carotenoid | Liver fibrosis; NAFLD; Liver Cancer, Liver cirrhosis; Hepatic IRI | Rat; Mice; Human | [92] |
| Fucoidan | Brown algae | Sulfuric acid-group-rich polysaccharide | Acute liver injury; Viral Hepatitis; Liver fibrosis; Liver Cancer; Hepatic IRI; NAFLD | Rat; Mice; Human | [93,94] |
| Rosmarinic acid | Plants | Caffeic acid ester | Hepatic IRI | Rat; Mice | [95,96] |
| Ellagic acid | Plants | Polyphenol | Liver fibrosis; NAFLD; Viral Hepatitis | Rat; Mice; Human | [97,98] |
| Melatonin | Plants | Pineal gland hormone | Liver fibrosis; NAFLD; NASH; Liver cirrhosis; Liver injury | Rat; Mice | [99,100] |
| Annona squamosa | Plants | Seed extract | ALD | Rat | [101] |
| Bardoxolone | Semi-synthetic | Triterpenoid | Hepatic IRI | Rat | [102] |
| Stevia | Plants | Diterpene | Liver cirrhosis | Rat; Mice | [103,104] |
| Caffeine | Plants | Alkaloid (Xanthine) | Liver injury | Rat; Mice | [105,106] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurtado-Navarro, L.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Pelegrín, P.; Baroja-Mazo, A.; Cuevas, S. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis in Liver Pathophysiology: The Emerging Relevance of Nrf2 Inducers. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050870
Hurtado-Navarro L, Angosto-Bazarra D, Pelegrín P, Baroja-Mazo A, Cuevas S. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis in Liver Pathophysiology: The Emerging Relevance of Nrf2 Inducers. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(5):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050870
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurtado-Navarro, Laura, Diego Angosto-Bazarra, Pablo Pelegrín, Alberto Baroja-Mazo, and Santiago Cuevas. 2022. "NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis in Liver Pathophysiology: The Emerging Relevance of Nrf2 Inducers" Antioxidants 11, no. 5: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050870
APA StyleHurtado-Navarro, L., Angosto-Bazarra, D., Pelegrín, P., Baroja-Mazo, A., & Cuevas, S. (2022). NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis in Liver Pathophysiology: The Emerging Relevance of Nrf2 Inducers. Antioxidants, 11(5), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050870








