ApoE3 vs. ApoE4 Astrocytes: A Detailed Analysis Provides New Insights into Differences in Cholesterol Homeostasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Sterol Quantification by GC-MS
2.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR
2.4. Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blotting
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ApoE Intra- and Extracellular Levels Are Altered in ApoE4 Astrocytes
3.2. ApoE4 Astrocytes Show Different Expression Levels of Several Lipid-Related Genes
3.3. ApoE4 Astrocytes Are Characterized by a Lower Cholesterol Synthesis
3.4. Oxysterol Profile Is Different in ApoE4 Astrocytes
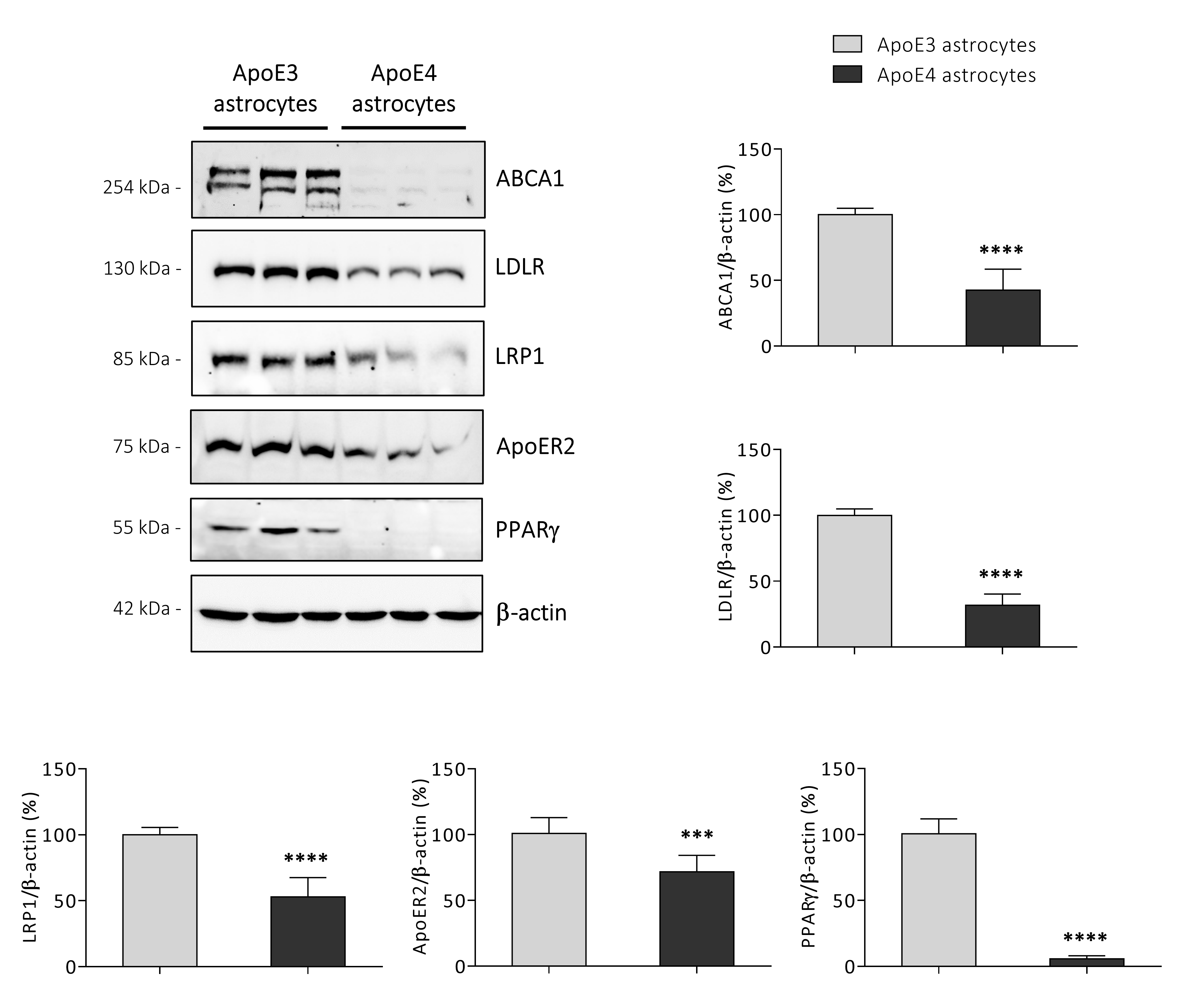
3.5. ApoE4 Astrocytes Synthetize Lower Amounts of KEY Proteins Involved in Cholesterol Homeostasis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C.; Small, G.W.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 1993, 261, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiman, E.M.; Arboleda-Velasquez, J.F.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Huentelman, M.J.; Beach, T.G.; Caselli, R.J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Myers, A.J.; Hardy, J.; et al. Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer’s dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5000-person neuropathological study. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Paolo, G.; Kim, T.W. Linking lipids to Alzheimer’s disease: Cholesterol and beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koriath, C.; Lashley, T.; Taylor, W.; Druyeh, R.; Dimitriadis, A.; Denning, N.; Williams, J.; Warren, J.D.; Fox, N.C.; Schott, J.M.; et al. ApoE4 lowers age at onset in patients with frontotemporal dementia and tauopathy independent of amyloid-beta copathology. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 11, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, D.W.; Heckman, M.G.; Murray, M.E.; Soto, A.I.; Walton, R.L.; Diehl, N.N.; van Gerpen, J.A.; Uitti, R.J.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; et al. APOE epsilon4 is associated with severity of Lewy body pathology independent of Alzheimer pathology. Neurology 2018, 91, e1182–e1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahley, R.W. Central Nervous System Lipoproteins: ApoE and Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Herz, J.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein E receptors: Normal biology and roles in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staurenghi, E.; Giannelli, S.; Testa, G.; Sottero, B.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Gamba, P. Cholesterol Dysmetabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Starring Role for Astrocytes? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Testa, G.; Gargiulo, S.; Staurenghi, E.; Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G. Oxidized cholesterol as the driving force behind the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loera-Valencia, R.; Goikolea, J.; Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Merino-Serrais, P.; Maioli, S. Alterations in cholesterol metabolism as a risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s disease: Potential novel targets for treatment. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrouk, A.; Debbabi, M.; Bezine, M.; Karym, E.M.; Badreddine, A.; Rouaud, O.; Moreau, T.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; El Ayeb, M.; Nasser, B.; et al. Lipid Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Leoni, V.; Meaney, S. Oxysterols and neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Aspects Med. 2009, 30, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcw, J.; Qian, L.; Pipalia, N.H.; Chao, M.J.; Liang, S.A.; Shi, Y.; Jain, B.R.; Bertelsen, S.E.; Kapoor, M.; Marcora, E.; et al. Cholesterol and matrisome pathways dysregulated in astrocytes and microglia. Cell 2022, 185, 2213–2233.e2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Seo, J.; Gao, F.; Feldman, H.M.; Wen, H.L.; Penney, J.; Cam, H.P.; Gjoneska, E.; Raja, W.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. APOE4 Causes Widespread Molecular and Cellular Alterations Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Phenotypes in Human iPSC-Derived Brain Cell Types. Neuron 2018, 98, 1141–1154.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, B.C.; Kluemper, J.; Johnson, L.A. Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells 2019, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, M.; Fryer, J.D.; Sullivan, P.M.; Christopher, E.A.; Wahrle, S.E.; DeMattos, R.B.; O’Dell, M.A.; Fagan, A.M.; Lashuel, H.A.; Walz, T.; et al. Production and characterization of astrocyte-derived human apolipoprotein E isoforms from immortalized astrocytes and their interactions with amyloid-beta. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 19, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testa, G.; Staurenghi, E.; Zerbinati, C.; Gargiulo, S.; Iuliano, L.; Giaccone, G.; Fanto, F.; Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Gamba, P. Changes in brain oxysterols at different stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Their involvement in neuroinflammation. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Civra, A.; Leoni, V.; Caccia, C.; Sottemano, S.; Tonetto, P.; Coscia, A.; Peila, C.; Moro, G.E.; Gaglioti, P.; Bertino, E.; et al. Antiviral oxysterols are present in human milk at diverse stages of lactation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 193, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, V.; Nury, T.; Vejux, A.; Zarrouk, A.; Caccia, C.; Debbabi, M.; Fromont, A.; Sghaier, R.; Moreau, T.; Lizard, G. Mitochondrial dysfunctions in 7-ketocholesterol-treated 158N oligodendrocytes without or with alpha-tocopherol: Impacts on the cellular profil of tricarboxylic cycle-associated organic acids, long chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, oxysterols, cholesterol and cholesterol precursors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 169, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risso, D.; Leoni, V.; Canzoneri, F.; Arveda, M.; Zivoli, R.; Peraino, A.; Poli, G.; Menta, R. Presence of cholesterol oxides in milk chocolates and their correlation with milk powder freshness. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, S.M.; Kirschner, A.W.T.; Lindner, K.; Rust, R.; Budny, V.; Wolski, W.E.; Gavin, A.C.; Nitsch, R.M.; Tackenberg, C. APOE2, E3, and E4 differentially modulate cellular homeostasis, cholesterol metabolism, and inflammatory response in isogenic iPSC-derived astrocytes. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.R.; Busra Luleci, H.; Oommen, A.M.; Varma, S.; Blackshear, C.T.; Griswold, M.E.; An, Y.; Roberts, J.A.; O’Brien, R.; Pletnikova, O.; et al. Abnormal brain cholesterol homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease-a targeted metabolomic and transcriptomic study. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Bernardo, A.; Walker, D.; Kanegawa, T.; Mahley, R.W.; Huang, Y. Profile and regulation of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) expression in the CNS in mice with targeting of green fluorescent protein gene to the ApoE locus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4985–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lane-Donovan, C.; Wong, W.M.; Durakoglugil, M.S.; Wasser, C.R.; Jiang, S.; Xian, X.; Herz, J. Genetic Restoration of Plasma ApoE Improves Cognition and Partially Restores Synaptic Defects in ApoE-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10141–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, C.; Guo, Z.D.; He, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Sun, X.C. Apolipoprotein E Affects In Vitro Axonal Growth and Regeneration via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Strickland, M.R.; Soranno, A.; Holtzman, D.M. Apolipoprotein E: Structural Insights and Links to Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. Neuron 2021, 109, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, C.; Wang, H.; Ho, C.M.W. A mechanism for lipid binding to apoE and the role of intrinsically disordered regions coupled to domain-domain interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6292–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, N.; Krammer, E.M.; Stengel, F.; Adams, Q.; Van Liefferinge, F.; Hubin, E.; Chaves, R.; Efremov, R.; Aebersold, R.; Vandenbussche, G.; et al. Lipidated apolipoprotein E4 structure and its receptor binding mechanism determined by a combined cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics approach. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bussy, A.; Snider, B.J.; Coble, D.; Xiong, C.; Fagan, A.M.; Cruchaga, C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Gordon, B.A.; Hassenstab, J.; Bateman, R.J.; et al. Effect of apolipoprotein E4 on clinical, neuroimaging, and biomarker measures in noncarrier participants in the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 75, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Donohue, M.C.; Raman, R.; Sun, C.K.; Yaari, R.; Holdridge, K.; Siemers, E.; Johnson, K.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Team, A.S. Association of Factors With Elevated Amyloid Burden in Clinically Normal Older Individuals. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Blazey, T.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Cruchaga, C.; Su, Y.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Gordon, B.A. Longitudinal brain imaging in preclinical Alzheimer disease: Impact of APOE epsilon4 genotype. Brain 2018, 141, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Sonnenschein, L.S.; Viechtbauer, W.; Ramakers, I.H.; Verhey, F.R.; Visser, P.J. Predictive value of APOE-epsilon4 allele for progression from MCI to AD-type dementia: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, G.A.; Burns, M.P.; Weeber, E.J.; Rebeck, G.W. Young APOE4 targeted replacement mice exhibit poor spatial learning and memory, with reduced dendritic spine density in the medial entorhinal cortex. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomon-Zimri, S.; Boehm-Cagan, A.; Liraz, O.; Michaelson, D.M. Hippocampus-related cognitive impairments in young apoE4 targeted replacement mice. Neurodegener. Dis. 2014, 13, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liraz, O.; Boehm-Cagan, A.; Michaelson, D.M. ApoE4 induces Abeta42, tau, and neuronal pathology in the hippocampus of young targeted replacement apoE4 mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wilson, W.A.; Moore, S.D.; Mace, B.E.; Maeda, N.; Schmechel, D.E.; Sullivan, P.M. Human apoE4-targeted replacement mice display synaptic deficits in the absence of neuropathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 18, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsodendris, N.; Nelson, M.R.; Rao, A.; Huang, Y. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s Disease: Findings, Hypotheses, and Potential Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Seo, J. ApoE4-Induced Cholesterol Dysregulation and Its Brain Cell Type-Specific Implications in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Davis, M.D.; Martens, Y.A.; Shinohara, M.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Younkin, S.G.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G. APOE epsilon4/epsilon4 diminishes neurotrophic function of human iPSC-derived astrocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, P.M.; Han, B.; Liu, F.; Mace, B.E.; Ervin, J.F.; Wu, S.; Koger, D.; Paul, S.; Bales, K.R. Reduced levels of human apoE4 protein in an animal model of cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bales, K.R.; Liu, F.; Wu, S.; Lin, S.; Koger, D.; DeLong, C.; Hansen, J.C.; Sullivan, P.M.; Paul, S.M. Human APOE isoform-dependent effects on brain beta-amyloid levels in PDAPP transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6771–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riddell, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Atchison, K.; Warwick, H.K.; Atkinson, P.J.; Jefferson, J.; Xu, L.; Aschmies, S.; Kirksey, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism on brain ApoE levels. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11445–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fote, G.M.; Geller, N.R.; Efstathiou, N.E.; Hendricks, N.; Vavvas, D.G.; Reidling, J.C.; Thompson, L.M.; Steffan, J.S. Isoform-dependent lysosomal degradation and internalization of apolipoprotein E requires autophagy proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs258687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hayashi, H.; Zou, K.; Sawamura, N.; Fujita, S.C.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoform-dependent lipid release from astrocytes prepared from human ApoE3 and ApoE4 knock-in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29919–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farkas, M.H.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Shepherd, V.L.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S.; Swift, L.L. The recycling of apolipoprotein E and its amino-terminal 22 kDa fragment: Evidence for multiple redundant pathways. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fryer, J.D.; Demattos, R.B.; McCormick, L.M.; O’Dell, M.A.; Spinner, M.L.; Bales, K.R.; Paul, S.M.; Sullivan, P.M.; Parsadanian, M.; Bu, G.; et al. The low density lipoprotein receptor regulates the level of central nervous system human and murine apolipoprotein E but does not modify amyloid plaque pathology in PDAPP mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25754–25759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basak, J.M.; Verghese, P.B.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.; Holtzman, D.M. Low-density lipoprotein receptor represents an apolipoprotein E-independent pathway of Abeta uptake and degradation by astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13959–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, R.; Landreth, G.E. LXR Regulation of Brain Cholesterol: From Development to Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.; Chai, A.B.; Gelissen, I.C.; Brown, A.J. Balancing cholesterol in the brain: From synthesis to disposal. Explor. Neuroprotective Ther. 2022, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieweg, K.; Schaller, H.; Pfrieger, F.W. Marked differences in cholesterol synthesis between neurons and glial cells from postnatal rats. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milagre, I.; Nunes, M.J.; Gama, M.J.; Silva, R.F.; Pascussi, J.M.; Lechner, M.C.; Rodrigues, E. Transcriptional regulation of the human CYP46A1 brain-specific expression by Sp transcription factors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkhem, I.; Leoni, V.; Svenningsson, P. On the fluxes of side-chain oxidized oxysterols across blood-brain and blood-CSF barriers and origin of these steroids in CSF (Review). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 188, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosch, A.R.; Imagawa, D.K.; Jutric, Z. Bile Metabolism and Lithogenesis: An Update. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 99, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutjohann, D.; Breuer, O.; Ahlborg, G.; Nennesmo, I.; Siden, A.; Diczfalusy, U.; Bjorkhem, I. Cholesterol homeostasis in human brain: Evidence for an age-dependent flux of 24S-hydroxycholesterol from the brain into the circulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9799–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abildayeva, K.; Jansen, P.J.; Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Bloks, V.W.; Bakker, A.H.; Ramaekers, F.C.; de Vente, J.; Groen, A.K.; Wellington, C.L.; Kuipers, F.; et al. 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol participates in a liver X receptor-controlled pathway in astrocytes that regulates apolipoprotein E-mediated cholesterol efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12799–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.J.; Jessup, W. Oxysterols: Sources, cellular storage and metabolism, and new insights into their roles in cholesterol homeostasis. Mol. Aspects Med. 2009, 30, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.M.; Kasimov, M.R.; Zefirov, A.L. Brain Cholesterol Metabolism and Its Defects: Linkage to Neurodegenerative Diseases and Synaptic Dysfunction. Acta Nat. 2016, 8, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, F.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J. Apolipoprotein E metabolism and functions in brain and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Q.W.; Iosbe, I.; Asou, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Expression and regulation of apolipoprotein E receptors in the cells of the central nervous system in culture: A review. J. Am. Aging Assoc. 2001, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.C.; Hu, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Cirrito, J.R.; Kanekiyo, T.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bu, G. Astrocytic LRP1 Mediates Brain Abeta Clearance and Impacts Amyloid Deposition. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hascalovici, J.R.; Song, W.; Liberman, A.; Vaya, J.; Khatib, S.; Holcroft, C.; Laferla, F.; Schipper, H.M. Neural HO-1/sterol interactions in vivo: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2014, 280, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, G.; Staurenghi, E.; Giannelli, S.; Gargiulo, S.; Guglielmotto, M.; Tabaton, M.; Tamagno, E.; Gamba, P.; Leonarduzzi, G. A silver lining for 24-hydroxycholesterol in Alzheimer’s disease: The involvement of the neuroprotective enzyme sirtuin 1. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Giannelli, S.; Staurenghi, E.; Testa, G.; Sottero, B.; Biasi, F.; Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G. The Controversial Role of 24-S-Hydroxycholesterol in Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, V.; Wang, S.; Sima, J.; Bar, R.; Liraz, O.; Gundimeda, U.; Parekh, T.; Chan, J.; Johansson, J.O.; Tang, C.; et al. ApoE4 Alters ABCA1 Membrane Trafficking in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9611–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Opposing effects of viral mediated brain expression of apolipoprotein E2 (apoE2) and apoE4 on apoE lipidation and Abeta metabolism in apoE4-targeted replacement mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinsinger, N.M.; Gachechiladze, M.A.; Rebeck, G.W. Apolipoprotein E Genotype Affects Size of ApoE Complexes in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm-Cagan, A.; Michaelson, D.M. Reversal of apoE4-driven brain pathology and behavioral deficits by bexarotene. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7293–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, A.Y.; Letronne, F.; Fitz, N.F.; Mounier, A.; Wolfe, C.M.; Nam, K.N.; Reeves, V.L.; Kamboh, H.; Lefterov, I.; Koldamova, R. Liver X receptor agonist treatment significantly affects phenotype and transcriptome of APOE3 and APOE4 Abca1 haplo-deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, H.; Rao, R. Amyloid clearance defect in ApoE4 astrocytes is reversed by epigenetic correction of endosomal pH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6640–E6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Bezprozvanny, I. Differences in Recycling of Apolipoprotein E3 and E4-LDL Receptor Complexes-A Mechanistic Hypothesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, X.; Pohlkamp, T.; Durakoglugil, M.S.; Wong, C.H.; Beck, J.K.; Lane-Donovan, C.; Plattner, F.; Herz, J. Reversal of ApoE4-induced recycling block as a novel prevention approach for Alzheimer’s disease. eLife 2018, 7, e40048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Castellano, J.M.; Jiang, H.; Basak, J.M.; Parsadanian, M.; Pham, V.; Mason, S.M.; Paul, S.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Overexpression of low-density lipoprotein receptor in the brain markedly inhibits amyloid deposition and increases extracellular A beta clearance. Neuron 2009, 64, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storer, P.D.; Xu, J.; Chavis, J.; Drew, P.D. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists inhibit the activation of microglia and astrocytes: Implications for multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 161, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, W.; Tyagi, N.; Tyagi, S.C. Role of PPARgamma, a nuclear hormone receptor in neuroprotection. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 48, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Keeney, J.T.; Ibrahimi, S.; Zhao, L. Human ApoE Isoforms Differentially Modulate Glucose and Amyloid Metabolic Pathways in Female Brain: Evidence of the Mechanism of Neuroprotection by ApoE2 and Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention and Early Intervention. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrera, J.; Subramanian, S.; Chiba-Falek, O. Probing the role of PPARgamma in the regulation of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease-associated genes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, A.; Vassiliou, G.; Benoist, F.; McPherson, R. Adipocyte low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein gene expression and function is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11945–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondon-Ortiz, A.N.; Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Martinez-Malaga, J.; Gonzales-Urday, A.L.; Gugnani, K.S.; Bohlke, M.; Maher, T.J.; Pino-Figueroa, A.J. High Concentrations of Rosiglitazone Reduce mRNA and Protein Levels of LRP1 in HepG2 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bujold, K.; Rhainds, D.; Jossart, C.; Febbraio, M.; Marleau, S.; Ong, H. CD36-mediated cholesterol efflux is associated with PPARgamma activation via a MAPK-dependent COX-2 pathway in macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 83, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moosecker, S.; Pissioti, A.; Leidmaa, E.; Harb, M.R.; Dioli, C.; Gassen, N.C.; Yu, S.; Gazea, M.; Catania, C.; Anderzhanova, E.; et al. Brain Expression, Physiological Regulation and Role in Motivation and Associative Learning of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor gamma. Neuroscience 2021, 479, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Sastre, M.; Dumitrescu-Ozimek, L.; Hanke, A.; Dewachter, I.; Kuiperi, C.; O’Banion, K.; Klockgether, T.; Van Leuven, F.; Landreth, G.E. Acute treatment with the PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone and ibuprofen reduces glial inflammation and Abeta1-42 levels in APPV717I transgenic mice. Brain 2005, 128, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, M.; Alderton, C.; Zvartau-Hind, M.; Egginton, S.; Saunders, A.M.; Irizarry, M.; Craft, S.; Landreth, G.; Linnamagi, U.; Sawchak, S. Rosiglitazone monotherapy in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2010, 30, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iketani, R.; Ohno, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamada, H.; Kishino, S. Apolipoprotein E Gene Polymorphisms Affect the Efficacy of Thiazolidinediones for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staurenghi, E.; Leoni, V.; Lo Iacono, M.; Sottero, B.; Testa, G.; Giannelli, S.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Gamba, P. ApoE3 vs. ApoE4 Astrocytes: A Detailed Analysis Provides New Insights into Differences in Cholesterol Homeostasis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112168
Staurenghi E, Leoni V, Lo Iacono M, Sottero B, Testa G, Giannelli S, Leonarduzzi G, Gamba P. ApoE3 vs. ApoE4 Astrocytes: A Detailed Analysis Provides New Insights into Differences in Cholesterol Homeostasis. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(11):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112168
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaurenghi, Erica, Valerio Leoni, Marco Lo Iacono, Barbara Sottero, Gabriella Testa, Serena Giannelli, Gabriella Leonarduzzi, and Paola Gamba. 2022. "ApoE3 vs. ApoE4 Astrocytes: A Detailed Analysis Provides New Insights into Differences in Cholesterol Homeostasis" Antioxidants 11, no. 11: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112168
APA StyleStaurenghi, E., Leoni, V., Lo Iacono, M., Sottero, B., Testa, G., Giannelli, S., Leonarduzzi, G., & Gamba, P. (2022). ApoE3 vs. ApoE4 Astrocytes: A Detailed Analysis Provides New Insights into Differences in Cholesterol Homeostasis. Antioxidants, 11(11), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112168






