Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals and Experimental Groups
2.3. Behavioral Tests
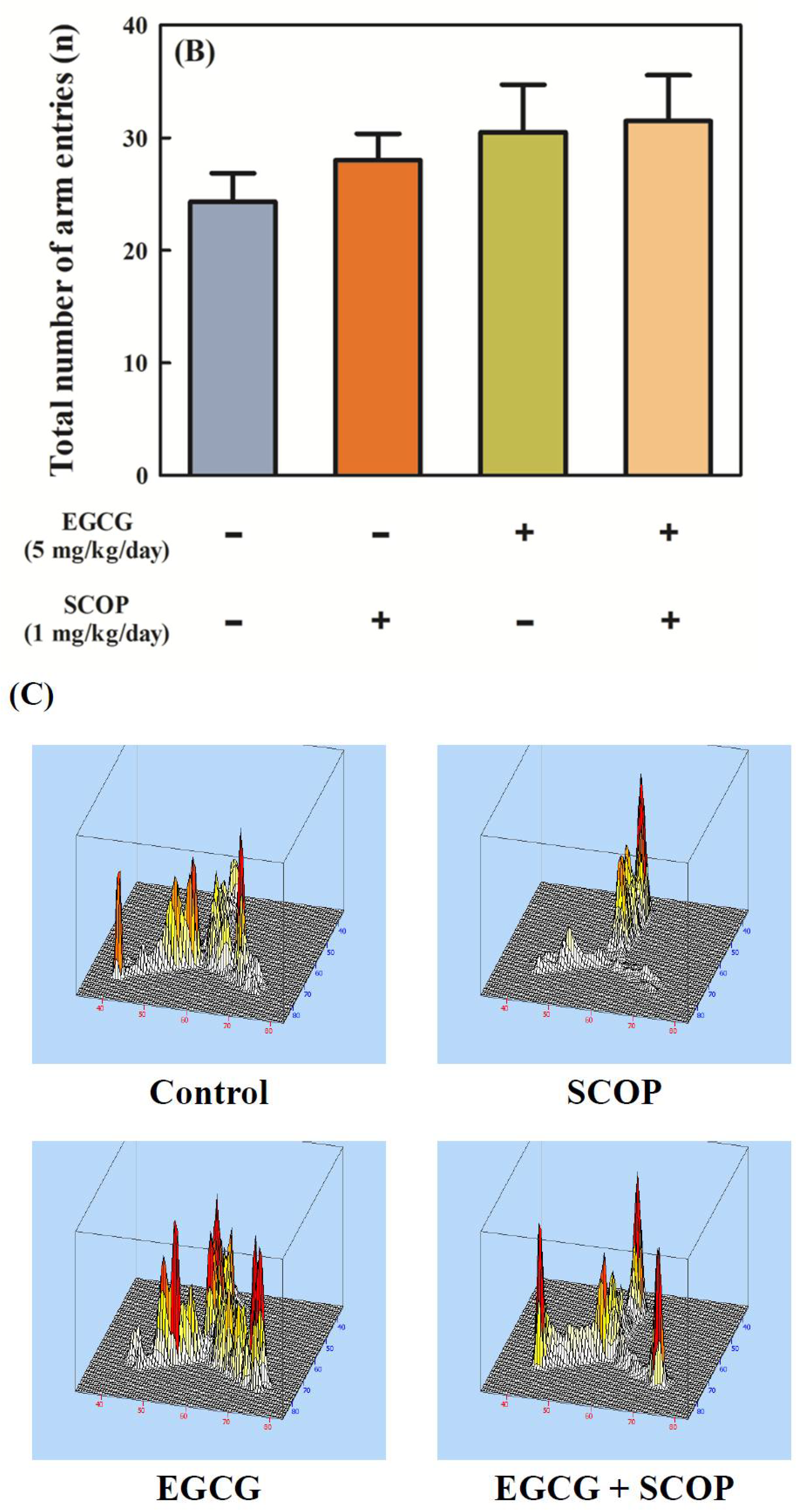
2.3.1. Y-Maze Test
2.3.2. Passive Avoidance Test
2.3.3. Morris Water Maze Test
2.4. Biochemical Assays
2.4.1. Preparation of Hippocampus Homogenate
2.4.2. Measurement of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
2.4.3. Measurement of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
2.4.4. Measurement of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Level
2.5. Electrophysiological Experiments
2.5.1. Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Culture
2.5.2. Preparation of Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Tissue on MEA
2.5.3. Induction of LTP in Organotypic Hippocampal Slices
2.5.4. Electrophysiology Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of EGCG on Short-Term Spatial Memory in the Y-Maze Test
3.2. Effects of EGCG on Short-Term Learning and Memory in the Passive Avoidance Test
3.3. Effects of EGCG on Long-Term Spatial Learning and Memory in the Morris Water Maze Test
3.4. Effects of EGCG on Cholinergic Function in the Hippocampus
3.5. Effects of EGCG on SOD Activity and MDA Level in the Hippocampus
3.6. Effects of EGCG on LTP in Organotypic Hippocampal Slices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Vieira, T.H.; Guimaraes, I.M.; Silva, F.R.; Ribeiro, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease: Targeting the cholinergic system. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.-D.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.V.; Kumar, H.; Cho, D.-Y.; Yun, Y.-S.; Choi, D.-K. Toxin-induced experimental models of learning and memory impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Khadragy, M.F.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Moneim, A.E.A. Neuroprotective effects of Citrus reticulata in scopolamine-induced dementia oxidative stress in rats. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, R.; Mehan, S.; Khanna, D.; Kalra, S. Ameliorative treatment with ellagic acid in scopolamine induced Alzheimer’s type memory and cognitive dysfunctions in rats. Austin J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 2, 1053. [Google Scholar]
- Karthivashan, G.; Park, S.-Y.; Kweon, M.-H.; Kim, J.; Haque, M.E.; Cho, D.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Cho, E.-A.; Ganesan, P.; Choi, D.-K. Ameliorative potential of desalted Salicornia europaea L. extract in multifaceted Alzheimer’s-like scopolamine-induced amnesic mice model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.Y.; Li, F.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.R. Enteromorpha prolifera extract improves memory in scopolamine-treated mice via downregulating amyloid-β expression and upregulating BDNF/TrkB pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, C.-S.; Jeong, H.W.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, D.-O. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects of purified flavonol glycosides and aglycones in green tea. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasanth, M.I.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Tencomnao, T. A review of the role of green tea (Camellia sinensis) in antiphotoaging, stress resistance, neuroprotection, and autophagy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, L.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, Y.-C. Quantitative analysis of major constituents in green tea with different plucking periods and their antioxidant activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 9173–9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.A.; Mandal, A.K.A.; Khan, Z.A. Potential neuroprotective properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-O.; Lee, C.Y. Comprehensive study of vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of various polyphenolics in scavenging a free radical and its structural relationship. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjo, F.; Goto, K.; Seto, R.; Suzuki, M.; Sakai, M.; Hara, Y. Scavenging effects of tea catechins and their derivatives on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Iguchi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hoshino, M.; Hara, A.; Takagaki, A.; Nanjoc, F.; et al. Blood brain barrier permeability of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate, its proliferation-enhancing activity of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, and its preventive effect on age-related cognitive dysfunction in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.-B.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhong, X.; Yao, W.-F.; Wei, M.-J. Increased BBB permeability contributes to EGCG-caused cognitive function improvement in natural aging rats: Pharmacokinetic and distribution analyses. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Arendash, G.W.; Hou, H.; Fernandez, F.; Jensen, M.; Runfeldt, M.; Shytle, R.D.; Tan, J. Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces β-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2008, 1214, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, R.; De Sola, S.; Pons, M.; Duchon, A.; de Lagran, M.M.; Farré, M.; Fitó, M.; Benejam, B.; Langohr, K.; Rodriguez, J.; et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a DYRK1A inhibitor, rescues cognitive deficits in Down syndrome mouse models and in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, W.; Mao, Z.; Qu, Z.; Luan, S.; Jia, L.; Kan, M. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling, cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 516, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Liu, C.; Wan, X.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z. Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates bladder dysfunction via suppression of oxidative stress in a rat model of partial bladder outlet obstruction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1393641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppini, L.; Buchs, P.-A.; Muller, D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Asseburg, H.; Kuntz, S.; Muller, W.E.; Eckert, G.P. Effects of polyphenols on brain ageing and Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on mitochondria. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 46, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierres, J.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Agostinho, P.; Marisco, P.C.; Vieira, J.M.; Rosa, M.M.; Bohnert, C.; Rubin, M.A.; Morsch, V.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of anthocyanins on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarter, M.; Bodewitz, G.; Stephens, D.N. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist β-carbolines. Psychopharmacology 1988, 94, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-Y.; Lee, C.; Park, G.H.; Jang, J.-H. Amelioration of scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment by α-pinene in C57BL/6 mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 4926815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, H.J.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J.-M.; Choi, S.J.; Cho, H.-Y.; Hong, B.; Kim, H.-K.; Kimd, E.; Shin, D.-H. Naringenin from Citrus junos has an inhibitory effect on acetylcholinesterase and a mitigating effect on amnesia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2004, 17, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ögren, S.O.; Stiedl, O. Passive avoidance. In Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology, 2nd ed.; Stolerman, I.P., Price, L.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ainge, J.A.; Tamosiunaite, M.; Woergoetter, F.; Dudchenko, P.A. Hippocampal CA1 place cells encode intended destination on a maze with multiple choice points. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9769–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- deIpolyi, A.R.; Rankin, K.P.; Mucke, L.; Miller, B.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. Spatial cognition and the human navigation network in AD and MCI. Neurology 2007, 69, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliebs, R.; Arendt, T. The cholinergic system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K. Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Luo, D.; Li, L.; Tan, R.-R.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Qin, J.; Zhu, L.; Luo, N.-C.; Xu, T.-T.; Zhang, R.; et al. Ethyl acetate extract components of Bushen-Yizhi Formula provides neuroprotection against scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, V.K.; Singh, T.G.; Garg, N.; Dhiman, S.; Gupta, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Najda, A.; Walasek-Janusz, M.; Kamel, M.; Albadrani, G.M.; et al. Dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s disease: A role for chronic stress? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, S.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, U.; Kim, D.-O.; Choi, S.-G.; Heo, H.J. Anti-amyloidogenic properties of an ethyl acetate fraction from Actinidia arguta in Aβ1–42-induced ICR mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3264–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Park, S.K.; Guo, T.J.; Kang, J.Y.; Ha, J.S.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, U.; Heo, H.J. Anti-amnesic effect of Dendropanax morbifera via JNK signaling pathway on cognitive dysfunction in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 312, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, R.A. A brief history of long-term potentiation. Neuron 2017, 93, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuoka, T.; Uwada, J.; Kudo, M.; Yoshiki, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Nishio, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Muramatsu, I. Augmentation of endogenous acetylcholine uptake and cholinergic facilitation of hippocampal long-term potentiation by acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Neuroscience 2019, 404, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batalha, V.; Pego, J.; Fontinha, B.; Costenla, A.; Valadas, J.; Baqi, Y.; Radjainia, H.; Müller, C.; Sebastião, A.; Lopes, L. Adenosine A2A receptor blockade reverts hippocampal stress-induced deficits and restores corticosterone circadian oscillation. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, E.-S.; Kim, H.-B.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.-O.; Han, S.-M.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.-H. Loganin enhances long-term potentiation and recovers scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 171, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Mirshekar, M.A. Diosmin is neuroprotective in a rat model of scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-B.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.-S.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.-H. p-Coumaric acid enhances long-term potentiation and recovers scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-J.; Hwang, E.-S.; Kim, K.J.; Maeng, S.; Heo, H.J.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, D.-O. Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010001
Kim M-J, Hwang E-S, Kim KJ, Maeng S, Heo HJ, Park J-H, Kim D-O. Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Jeong, Eun-Sang Hwang, Kwan Joong Kim, Sungho Maeng, Ho Jin Heo, Ji-Ho Park, and Dae-Ok Kim. 2022. "Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats" Antioxidants 11, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010001
APA StyleKim, M.-J., Hwang, E.-S., Kim, K. J., Maeng, S., Heo, H. J., Park, J.-H., & Kim, D.-O. (2022). Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Antioxidants, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010001





