Abstract
The p47phox is a key regulatory subunit of Nox2-containing NADPH oxidase (Nox2) that by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) plays an important role in Angiotensin II (AngII)-induced cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. However, the signalling pathways of p47phox in the heart remains unclear. In this study, we used wild-type (WT) and p47phox knockout (KO) mice (C57BL/6, male, 7-month-old, n = 9) to investigate p47phox-dependent oxidant-signalling in AngII infusion (0.8 mg/kg/day, 14 days)-induced cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. AngII infusion resulted in remarkable high blood pressure and cardiac hypertrophy in WT mice. However, these AngII-induced pathological changes were significantly reduced in p47phox KO mice. In WT hearts, AngII infusion increased significantly the levels of superoxide production, the expressions of Nox subunits, the expression of PKCα and C-Src and the activation of ASK1 (apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1), MKK3/6, ERK1/2, p38 MAPK and JNK signalling pathways together with an elevated expression of apoptotic markers, i.e., γH2AX and p53 in the cardiomyocytes. However, in the absence of p47phox, although PKCα expression was increased in the hearts after AngII infusion, there was no significant activation of ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs signalling pathways and no increase in apoptosis biomarker expression in cardiomyocytes. In conclusion, p47phox-dependent redox-signalling through ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs plays a crucial role in AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
1. Introduction
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NADPH oxidase, or Nox) is a membrane-bound enzyme that by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) plays important role in the regulation of cellular function. So far, seven isoforms of the catalytic component of Nox have been identified namely Nox1–5, and durox 1–2 [1]. Angiotensin II is a vasoconstricting peptide (Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe) of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system involved in the regulation of blood pressure and other aspects of organ functions [2]. Oxidative stress and inflammation due to the activation of a Nox2-contaninig NADPH oxidase (Nox2) has been found to play an essential role in mediating AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and failure [1,2,3,4,5]. Nox2 is a multi-subunit enzyme consisting of two membrane-bound subunits, p22phox and Nox2 (also named gp91phox), and four cytosolic regulatory subunits, i.e., p40phox, p47phox, p67phox and rac1. The p47phox is a key regulatory subunit of Nox2 enzyme [2,6,7]. The phosphorylation of p47phox initiates the process of coordination and association of regulatory subunits with membrane-bound p22phox/Nox2 complex, and the subsequent O2●− production [2,6].
In the mammalian heart, the p47phox is expressed in the myocardium, epicardium and coronary vessels [1]. In cardiomyocytes p47phox had been reported to co-localise with F-actin and cortactin in order to facilitate the translocation of the cytosolic regulatory subunits to the p22phox/Nox2 complex [8,9]. Under pathological conditions, p47phox was suggested to link oxidative stress with the hypertrophic growth of cardiomyocytes through the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), i.e., extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) [10,11]. In response to oxidative stress, the redox-sensitive MAPK kinase (MKK) to MAPKs signalling pathways are activated, which in turn promote the activities of pro-apoptotic signalling molecules such as p53, γH2AX and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) leading to cardiac damage [12,13,14]. Genetic ablation of p47phox attenuated AngII-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice [15], and reduced the level of cardiac hypertrophy after experimental myocardial infarction [16].
Despite the importance of p47phox as a key regulator of Nox2-derived ROS production in the heart, its signalling pathways and functional complexity in AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte damage remained unclear. There was insufficient information about the upstream and downstream signalling pathways of p47phox in the hearts. In the current study, we investigated the role of p47phox and its oxidant-signalling pathways in the hearts using a murine model of AngII-infusion-induced cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in WT and p47phox KO mice. The complex role of p47phox in the myocardium was investigated by examining AngII-induced cardiac oxidative stress, the expressions of Nox subunits, the expression of PKCα and C-Src (both were involved in p47phox phosphorylation). We also examined the levels of AngII-induced p47phox phosphorylation, the activation of redox-sensitive ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs and the expression of pro-apoptotic markers, i.e., γH2AX and p53 in the cardiomyocytes. Our results suggested that p47phox oxidant-signalling through ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs played a vital role in mediating cardiac hypertrophic response and the expression of apoptotic markers in cardiomyocytes in response to AngII challenge. Knockout of p47phox inhibited the activation of these stress signalling pathways and protected hearts from AngII-induced oxidative damages.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
AngII was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Amersham, UK); NADPH was purchased from Fisher Scientific (Loughborough, UK); dihydroethidium (DHE) was purchased from Invitrogen (Loughborough, UK); FITC-labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA, Catalogue No. L-4895) was from Sigma-Aldrich. Primary antibodies to p47phox, p22phox, Nox1, Nox2, Nox4, p38-MAPK, ERK1/2, phos-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) and total JNK, phos-Akt (Ser473) and total Akt were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA); antibodies to β-actin, phos-MKK3(Ser189)/6(Ser207) and phos-ASK1 (Thr845), total MKK3/6, γH2AX (Ser139/Tyr142) were purchased from Cell Signalling Technology (London, UK); Antibodies to phos-p47phox (Ser359), phos-p38-MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) and phos-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Nox2-ds-tat (Nox2tat, [H]-RKKRRQRRRCSTRVRRQL-[NH2]) were provided by PeptideSynthetics (PPR Ltd., Fareham, UK). Other reagents, chemicals and antibodies, unless specified, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Animals
All studies were performed following protocols approved by the Ethics Committees of the Surrey and Reading Universities and the Home Office under the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 UK. The p47phox KO mice on a 129sv background were initially obtained from the European mouse mutant archive, and backcrossed to C57BL/6 for ten generations at the animal units in the University of Surrey [17]. Littermates of wild-type and p47phox KO mice at the age of 7-months were randomly grouped into control and AngII groups (n = 9 per group). The dose of AngII (0.8 mg/kg/day) was chosen based on the literature and our own pilot experiments to produce significant cardiac hypertrophy effectively. AngII was delivered to mice through osmotic minipumps (ALZET osmotic pumps, DURECT Corporation, Cupertino, CA, USA) for 14 days. The control group was infused with saline. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP) were measured using a computerised tail-cuff system (CODA, Kent Scientific, Torrington, CT, USA) on conscious mice following one week of training with the instrument [18]. Mice were used at the end of two weeks of AngII infusion. Bodyweight and heart weight were measured, and the tissues were harvested and stored in −80 °C freezer for experimental use.
2.3. Measurement of Cross-Sectional Cardiomyocyte Sizes
Left ventricular cryosections (8 µm) were prepared and fixed in freshly prepared 1% formaldehyde phosphate-buffered solution. Cardiomyocytes in the cardiac sections were outlined by FITC-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) that binds to glycoproteins of the cell membrane, and is routinely used for the staining of cardiac sarcolemma to determine cross sectional area or myocyte density [19]. Staining was visualised under the A1R confocal microscope (Nikon, Chiyoda, Japan) (20–40× magnification, 1024 × 1024 pixels)). Cross-sectional cardiomyocyte sizes were measured according to the method published previously [19,20] using software of ImageJ 1.50i (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA). For statistical analyses, cardiomyocyte sizes were obtained from at least three microscopic areas per section, three cross sections per heart and nine mice per group.
2.4. Measurement of ROS Production
ROS production was measured using the homogenates of left ventricular tissues. The homogenates were used immediately for the ROS measurement as described previously using three independent methods [4]. Lucigenin (5 µM)-chemiluminescence was used for measuring real-time NADPH-dependent O2●− production in heart homogenates detected using a 96-well microplate luminometer (Molecular Devices, Wokingham, UK). Catalase (300 U/mL)-inhibitable amplex red (6.25 µM) assay was used for measuring the H2O2 production in heart homogenates detected using FluoStar OPTIMA (BMG LabTech, Aylesbury, UK). DHE (2 µM)-fluorescence was used to measure in situ ROS production by cardiac sections, and images were captured using Nikon Eclipse Ti2-E inverted microscope and the DHE fluorescence intensities were quantified. The specificity of the lucigenin and DHE assays for the detection of O2●− was confirmed by using tiron (10 mM), a non-enzymatic O2●− scavenger, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (200 U/mL). The enzymatic sources of O2●− production were investigated using different enzyme inhibitors, i.e., L-NAME (N-nitroarginine methyl ester, 100 μM, nitric oxide synthase inhibitor), rotenone (100 μM, mitochondrial complex-1 enzyme inhibitor), diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) (20 μM, flavoprotein inhibitor), oxypurinol (100 μM, xanthine oxidase inhibitor) and Nox2tat (a specific peptide Nox2 inhibitor, 10 µM) [21]. Individual inhibitor was added into the wells loaded with homogenates and incubated for 10 min at room temperature before the measurement of ROS production.
2.5. Immunoblotting
Immunoblotting was performed exactly as described previously [4,18] using the left ventricular tissue homogenates. β-actin detected in the same sample was used as a loading control. For the quantification of phosphorylation of MAPKs, the total levels of the same protein in the same sample were pre-tested and justified for equal loading and used as loading controls for the quantification of phosphorylated proteins. The results were captured by BioSpectrum AC imaging system (UVP, Upland, CA, USA). The optical density of the bands was quantified and normalised to the relevant loading controls.
2.6. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
These experiments were performed as described previously [18]. The left ventricular tissue cryosections (8 µm) were fixed with 1:1 methanol: acetone solution for 10 min at −20 degree. All buffers and reagents were freshly prepared and kept on ice before use. Sections were then blocked using 2% bovine albumin serum (BSA) in PBS with 0.1% Triton X-100. BSA (2%) was used in the place of primary antibodies as a negative control. Primary antibodies were used at 1:100 dilutions in 0.2% BSA/PBS. Biotin-conjugated secondary antibodies were used at 1:1000 dilution in 0.2% BSA/PBS and detected using streptavidin-FITC or streptavidin-Cy3. Images were captured by Nikon A1R confocal microscope, and the fluorescent intensities (Fluo-intensity) were quantified. For statistical analysis, at least five random fields per section with three sections per heart were used per animal and nine animals were used per group. The control background fluorescence captured from sections without primary antibody was deducted and the results were expressed as Fluo-intensity.
2.7. Statistics
The Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7.0. Two-way ANOVA plus Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used for multiple-group significance testing and for testing repeated measures of blood pressure. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test was employed for other data analyses where it was appropriate. p ≤ 0.05 was denoted as statistically significant. Nine mice per group were used for statistical analysis. Results were presented as mean ± SD unless specified in the figure legends.
3. Results
3.1. Knockout p47phox Attenuated AngII Infusion-Induced High Blood Pressure and Cardiac Hypertrophy
The mice used in this study were middle-aged (7-months) which were more susceptible to AngII-induced cardiovascular damages than mice at younger ages. At day 0 (before AngII challenge), there was no significant difference in BP between WT and p47phox KO mice. AngII infusion (14 days) of WT mice markedly increased the systolic BP to an average of 180.3 ± 7.5 mmHg and the diastolic BP to an average of 142.6 ± 10.8 mmHg as compared to saline-infused controls (Figure 1A,B). However, in the absence of p47phox, AngII infusion only caused mild but significant increases in the systolic BP to an average of 150 ± 6 mmHg and the diastolic blood pressure to an average of 118.6 ± 9.7 mmHg (Figure 1A,B). The levels of AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy were expressed as the increases in heart weight (HW) and the HW/body weight (BW) ratios. In WT mice, AngII infusion significantly increased the heart weights (Figure 1C) and the HW/BW ratios (Figure 1D). However, in the p47phox KO mice, AngII induced cardiac hypertrophy was significantly reduced in comparison to WT mice. Although there were increases in HW/BW ratio in AngII-infused p47phox KO mice, these were not statistically significant (Figure 1D). AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy was further examined by measuring cardiomyocyte cross sectional area in the left ventricular tissue sections. The cardiomyocytes were labelled with FITC-WGA, which binds to glycoproteins of the cardiomyocyte membrane and outlines the cardiomyocytes on cross sections [19]. In comparison to saline-infused controls, there were significant increases in the cross-sectional areas of cardiomyocytes in AngII-infused WT hearts, which were significantly reduced in p47phox KO hearts (Figure 1E).
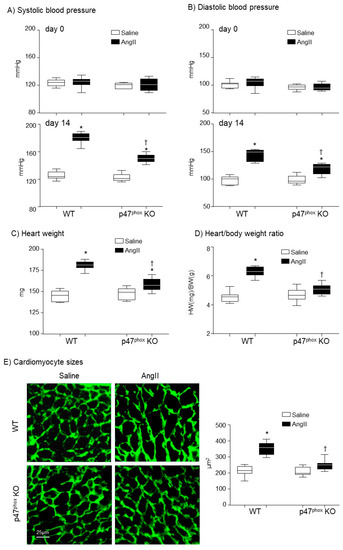
Figure 1.
Development of hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy in AngII-infused WT and p47phox KO mice. (A) Systolic blood pressure. (B) Diastolic blood pressure. Day 0: day of minipump implantation. Day 14: day of minipump removal. (C) Heart weights. (D) Heart weight (HW, mg)/body weight (BW, g) ratio. (E) Left panels: Representative images of cardiomyocyte sizes on the cross-sections of left ventricular tissues. The cardiomyocytes membranes were labelled with WGA-FITC (green). Right panel: Statistical analysis of cardiomyocyte cross-sectional areas (µm2). n = 9 mice per group. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05 for AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group; † p < 0.05, for p47phox KO AngII values versus WT AngII values.
3.2. Knockout p47phox Inhibited AngII-Induced Cardiac Oxidative Stress
The effect of genetic ablation of p47phox on AngII-induced cardiac oxidative stress were first examined by measuring NADPH-dependent O2●− production in heart homogenates using lucigenin chemiluminescence. A representative example of real-time measurements of O2●− production by heart homogenates is shown in the left panel of Figure 2A. Tiron (an O2●− scavenger) was used to confirm the assay specificity. The statistical analyses were shown in the right panel of Figure 2A. Compared to saline-infused WT controls, AngII infusion resulted in 2.6-folds increases in the levels of O2●− production in the WT hearts. However, this was significantly inhibited by knockout of p47phox. Although there were some increases in the levels of O2●− production in AngII infused p47phox KO hearts, they were not statistically significant. The enzymatic sources of AngII-induced O2●− production found in WT hearts were examined using different enzyme inhibitors including L-NAME (nitric oxide synthase inhibitor), rotenone (mitochondrial respiratory chain inhibitor), oxypurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor), apocynin (NADPH oxidase inhibitor), DPI (flavoprotein inhibitor) and Nox2tat (a specific peptide inhibitor of Nox2) (Figure 2B). The O2●− production detected in AngII-infused WT hearts was not affected by rotenone and oxypuronol, but was significantly inhibited by apocynin, Nox2tat or DPI suggesting Nox2 as a major enzymatic source of AngII-induced O2●− production. There was some inhibition of AngII-induced O2●− production by L-NAME, indicating nitric oxide synthase disfunction. SOD (superoxide dismutase) was used to double confirm the detection of O2●−.
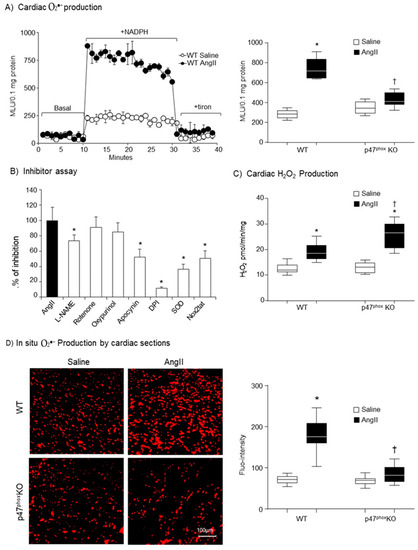
Figure 2.
Cardiac ROS production. (A) Levels of O2●− production measured by lucigenin-chemiluminescence. Left panel: Representative examples of kinetic measurements of O2●− production by WT heart homogenates. NADPH (0.1 mM) was added at 10 min. Tiron (10 mM) was added at 30 min to scavenge O2●−. Right panel: Differences in NADPH-dependent O2●− production measured between 10–30 min shown in the left panel. (B) The effects of different enzyme inhibitors on the levels of O2●− by AngII-infused WT heart homogenates. L-NAME: (NG-nitroarginine methyl ester), NOS inhibitor; Rotenone: mitochondrial respiratory chain inhibitor; Oxypurinol, xanthine oxidase inhibitor; DPI: (diphenyleneiodonium), flavoprotein inhibitor; SOD: (superoxide dismutase). (C) Cardiac H2O2 production detected by amplex red assay. (D) In situ detection of reactive oxygen species production by DHE fluorescence. Left panel: Representative images of DHE staining on cardiac sections; right panel: Quantification of DHE fluorescence intensity. n = 9 per group. Statistical comparisons were done using one-way ANOVA for inhibitor assay, and two-way ANOVA for the rests (panels A, C, D). * p < 0.05 for indicated AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group; † p < 0.05 for p47phox KO AngII values versus WT AngII values.
O2●− is not stable and can be quickly converted to H2O2 in cells. Therefore, we examined cardiac H2O2 production using catalase-inhibitable amplex red assay (Figure 2C). There was no significant difference in the basal (without AngII) levels of H2O2 production between WT and p47phox KO hearts. Compared to saline infused controls, the level of H2O2 production was significantly increased in AngII-infused WT hearts, which might link to the high level of O2●− production. However, in the p47phox KO hearts, although the level of O2●− production showed no change in response to AngII challenge, there was a significant increase in the levels of H2O2 production in AngII-infused p47phox KO hearts as compared to saline controls.
The levels of AngII-induced O2●− production in the hearts were further examined by in situ DHE fluorescence on cardiac cryosections (Figure 2D). There were significant high levels of O2●− production in AngII-infused WT hearts in comparison to saline-infused WT controls. However, there was no significant difference in DHE fluorescence intensities between AngII-infused and saline-infused p47phox KO hearts.
3.3. AngII-Induced Upregulation of Nox Subunits, PKCα and C-Src Protein Kinases and p47phox Phosphorylation in Murine Hearts
The levels of expression of p47phox, p22phox, p67phox, rac1, Nox1, Nox2 and Nox4 in response to AngII infusion were examined in WT and p47phox KO hearts by immunoblotting (Figure 3). The levels of β-actin detected in the same sample were used as loading controls. The p47phox was highly expressed in the WT hearts, but was barely detectable in the p47phox KO hearts. AngII infusion resulted in a great upregulation of the levels of p22phox expression in both WT and p47phox KO hearts without significant difference between the two groups. In comparison to saline infused WT controls, AngII-infusion increased significantly the levels of expression of p47phox, p67phox, rac1 and Nox2 in the WT hearts. However, in the absence of p47phox KO, AngII infusion had no significant effect on the levels of expression of p67phox and Nox2, but increased significantly the levels of p22phox, Nox4 and rac1 expression. Nox1 expression remained the same without significant difference between WT and p47phoxKO hearts.
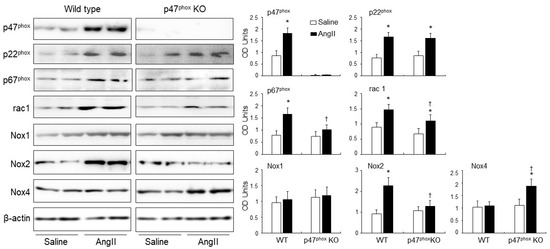
Figure 3.
Expressions of isoforms of the catalytic subunit of Nox (i.e., Nox1. Nox2, Nox4) and other subunits of Nox (p47phox, p22phox, p67phox and rac1) in murine hearts. Left panels: Representative Western blot images. β-actin detected in the same samples were used as loading controls. Right panels: Optical densities (OD) of Western blot bands were quantified and normalised to the levels of β-actin detected in the same samples. n = 9 per group. Statistical comparisons were made using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05 for AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group; † p < 0.05 for p47phox KO AngII values versus WT AngII values.
Protein kinase C alpha (PKCα) is highly expressed in the myocardium [22], and phosphorylates p47phox at multiple serine sites in response to AngII stimulation. [23]. C-Src had been proposed to be an upstream tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p47phox in response to AngII stimulation [24]. Therefore, we examined the levels of expressions of (PKCα) and C-Src together with the levels of p47phox phosphorylation in WT and p47phox KO hearts by immunoblotting (Figure 4A). Compared to saline-infused controls, AngII infusion increased the levels of PKCα expression in both WT and p47phox KO hearts without significant difference between these two groups. However, AngII-induced C-Src expression was only found in WT hearts, but not in p47phox KO hearts suggesting a key role of oxidative stress in cardiac C-Src activation (Figure 4A). Accompanied with increased PKCα expression, there were significant increases in p47phox serine phosphorylation detected using specific antibodies to phos-p47phox.
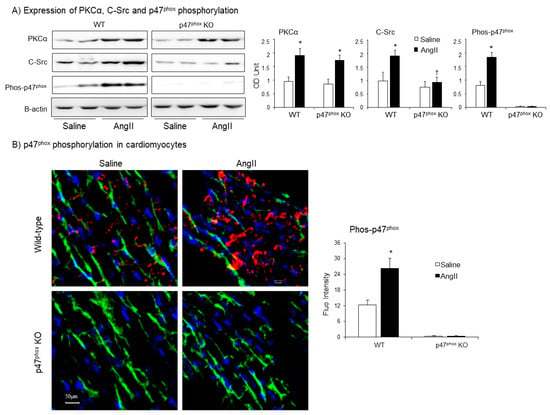
Figure 4.
Expressions of protein kinase C alpha (PKCα), Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src (C-Src) and p47phox phosphorylation in AngII-infused murine hearts. (A) Western blots. Left panels: Representative images. β-actin detected in the same samples were used as loading controls. Right panels: Optical densities (OD) of Western blot bands were quantified and normalised to the levels of β-actin detected in the same samples. (B) Confocal immunofluorescence of cardiac sections. Left panel: Representative immunofluorescence images. Cardiomyocyte cell membrane was labelled by WGA-FITC (green) and p47phox phosphorylation was identified using phos-p47phox specific antibody (Cy3, red). Nuclei were labelled by DAPI (blue). Right panel: Quantification of phos-p47phox fluorescence intensity. n = 9 hearts per group. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. Statistical comparisons were made using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05 for AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group.
AngII-induced p47phox phosphorylation in the myocardium was further examined by confocal immunofluorescence (Figure 4B). The sarcolemma membranes of cardiomyocytes were labelled with FITC-WGA (green), and the nuclei were labelled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) to visualise cardiomyocytes. The phospho-p47phox was labelled by Cy3 (red), and was only detected in WT hearts. AngII infusion significantly increased the levels of p47phox phosphorylation (red) mainly located at the cardiomyocyte gap junctions or at the cell membranes overlapped with FITC-WGA as indicated by the yellow colour (Figure 4B).
3.4. p47phox-Dependent Redox-Signalling through MKK3/6, MAPKs and AKT in AngII-Induced and Cardiac Hypertrophy and Apoptosis
The role of p47phox in modulating AngII signalling in the hearts was examined for the activations of stress-signalling pathways, i.e., mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MKK3/6) and down-stream ERK1/2; p38MAPK, JNK and Akt (Figure 5). The total levels of the same protein in the same samples were pre-tested and used as loading controls. In saline-infused control hearts, there was no significant difference in the levels of phosphorylation of these signalling molecules between WT and p47phoxKO hearts. Compared to saline-infused controls, AngII-infusion resulted in significant increases in the levels of phosphorylation of MKK3/6, ERK1/2, p38 MAPK, JNK and Akt in WT hearts. However, in the absence of p47phox, AngII failed to induce the phosphorylation of these signalling molecules in the hearts (Figure 5).
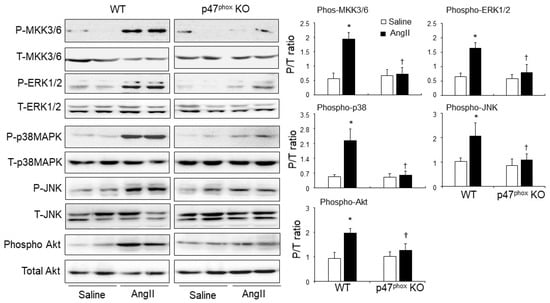
Figure 5.
AngII-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6 (MKK3/6), mitogen-activated protein kinases (i.e., ERK1/2, p38MAPK and JNK) and Akt (also called protein kinase B) in murine hearts. Left panels: Representative immunoblotting images. The total protein bands of each molecule in heart homogenates were pre-tested for equal loading. Right panels: Quantification of the optical densities (OD) of phos-protein bands expressed as phosphorylated/total (P/T) protein ratio. n = 9 mice per group. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. Statistical comparisons were made using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05 for AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group. † p < 0.05 for p47phox KO AngII values versus WT AngII values.
The effects of genetic knockout of p47phox on AngII-induced oxidative damage of cardiomyocytes and apoptotic death was examine by immunoblotting of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and biomarkers for DNA double-strand breaks (γH2AX), and apoptosis (p53) (Figure 6A). The levels of β-actin detected in the same sample were used as loading controls. Compared to saline-infused controls, there were remarkable significant increases in the level of expression of phos-ASK1, γH2AX and p53 in AngII-infused WT mice. However, in the absence of p47phox, there was no significant increase in the expression of these markers of cell DNA damage and apoptosis in after two weeks of AngII-infusion.
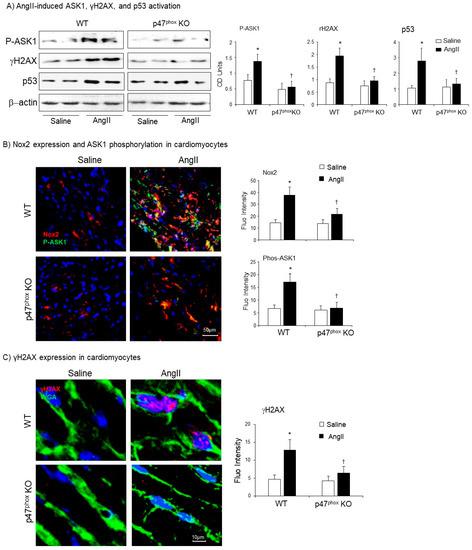
Figure 6.
Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), p53 and phosphorylation of H2A histone family member X (γH2AX) in murine hearts. (A) Western blots for the expressions of phos-ASK1, p53 and γH2AX. Optical densities of protein bands were quantified and normalised to the levels of β-actin detected in the same samples. (B) Confocal immunofluorescence detection of Nox2 (Cy3 labelled, red) and phos-ASK1 expressions (FITC labelled, green) in the cardiac sections. (C) Confocal immunofluorescence detection of γH2AX expression (Cy3-labelled, red) in the cardiac sections. The cardiomyocyte membrane was labelled by WGA-FITC (green), and the nuclei were labelled by DAPI (blue). The specific fluorescent densities were quantified. n = 9 mice per group. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. Statistical comparisons were made using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05, for AngII values versus saline values in the same genetic group. † p < 0.05 for p47phox KO AngII values versus WT AngII values.
The crucial role of p47phox in regulating AngII-induced Nox2 activation and ASK1 activation in the cardiomyocytes were examined using immunofluorescence confocal microscopy (Figure 6B). Low levels of Nox2 expression (red) could be detected in the control hearts (infused with saline) without significant difference between WT and p47phoxKO groups. AngII infusion significantly increased Nox2 expression together with great increases in ASK1 phosphorylation in the WT hearts. AngII-induced Nox2 expression was inhibited in p47phoxKO hearts and there was no change in the levels of ASK1 phosphorylation in response to AngII infusion in p47phoxKO hearts.
The role of p47phox in modulating AngII-induced DNA damage in cardiomyocytes was further demonstrated using immunofluorescence confocal microscopy (Figure 6C). The cardiomyocyte membranes were labelled with FITC-WAG (green), the nuclei were labelled by DAPI. In saline-infused hearts, there was very low level of γH2AX positive staining. However, in AngII-infused WT hearts, there were clear visible γH2AX foci (red) formation detected in the nuclei (blue) of cardiomyocytes as indicated by the pink colour. AngII-induced nuclear expression of γH2A, seen in WT hearts, was significantly inhibited in p47phoxKO hearts. Putting together, our results indicated clearly a key role of p47phox in mediating AngII-induced oxidative stress, activation of stress signalling pathways and oxidative damage of cardiomyocyte DNAs and cell apoptosis.
4. Discussion
AngII is a potent activator of Nox2 enzyme, which by generating ROS is involved in AngII-induced cardiovascular oxidative stress, hypertension, remodelling and organ damage [2,3]. The p47phox is a primary regulatory subunit of Nox2 enzyme, and the phosphorylation of p47phox at multiple serines in the C-terminus is a key step for Nox2 O2●− production [6,17]. However, the signalling pathways of p47phox in the heart remains unclear. The current study by using a disease model of AngII infusion-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy in WT versus p47phoxKO mice, provided novel insights of p47phox-dependent signalling pathways in modulating AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. We discovered that p47phox-dependent regulation of redox-sensitive signalling cascade through ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs is essential in mediating AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and DNA damage in cardiomyocytes. Genetic knockout of p47phox inhibited AngII-induced cardiac ROS production, attenuated ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPK activation and protected cardiomyocyte from AngII-induced hypertrophic growth, DNA damage and apoptosis.
The mice used in this study were 7-month-old, equivalent to humans at the middle-age, and were more susceptible to AngII-induced cardiovascular damages than mice at younger ages. The crucial role of p47phox in mediating AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy was properly controlled using age-matched littermates of p47phoxKO mice subjected to the same experimental procedures. Despite a mild increase in BP found in p47phoxKO mice after two weeks of AngII-infusion, there was no significant cardiac hypertrophy as evaluated using two separate methods, i.e., the changes in HW/BW ratio and cardiomyocyte cross-sectional areas.
NADPH oxidase family contains at least 7 members (Nox1–5 and duox 1–2) [1]. Individual Nox enzyme has distinctive mechanism of activation and functions differently [25,26]. So far, Nox1–2 and Nox4–5 have been found in the hearts [27]. Nox2 relies on p47phox to be active and generates O2●− involved in many diseased conditions [6]. Whereas, Nox4 is autoactivated and plays a protective role in cardiovascular function [27]. In the current study, we found that AngII-infusion induced a great increase in cardiac Nox2 expression together with increased level of O2●− production in the WT hearts. O2●− is short lived and can be quickly converted to H2O2 by SOD as a cellular self-protective mechanism [28]. This explained the mild elevation of H2O2 production observed in AngII-infused WT hearts. However, AngII-infusion of p47phoxKO mice induced a great increase in cardiac Nox4 expression together with a high level of H2O2 production indicating Nox4 was the enzymatic source of AngII-induced H2O2 production in p47phoxKO hearts.
PKCα has been reported to be highly expressed in the hearts [20] and phosphorylates p47phox at multiple serine sites in response to AngII stimulation [21]. C-Src had also been proposed to be an upstream tyrosine kinase of p47phox phosphorylation in response to AngII stimulation [22]. However, a recent study found that C-Src, rather than an upstream kinase of p47phox phosphorylation, was a downstream molecule of p47phox-dependent ROS production in lung inflammation [29]. In the current study, we found that AngII-induced cardiac C-Src activation was oxidant-dependent and was abolished by the knockout of p47phox.
MAPKs belong to a highly conserved family of Ser-Thr protein kinases and have diverse regulatory roles in normal heart development as well as in pathological cardiac hypertrophic growth and remodelling [30]. MAPK activation in response to Nox2-derived oxidative stress is a crucial signalling pathway involved in the development of cardiovascular abnormalities. Akt is also a redox-sensitive Ser-Thr kinase involved in cardiomyocyte hypertrophic growth and survival. In the current study, we showed that knockout of p47phox attenuated Nox2-derived ROS production, inhibited MKK3/6, MAPK and Akt activation in response to AngII challenge and protected murine hearts from AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy. However, p47phox redox-signalling is a complicated mechanism and we do not know if p47phox is physically a component of these signalling pathways, and how it promotes both the pro- and anti-apoptotic signalling pathways in response to AngII infusion. Further detailed investigation is needed.
ASK1 is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) family that activates downstream MAPKs, JNKs and p38 MAPKs in response to various stresses, such as ROS [13,31]. H2AX is a variant of the H2A protein family and is a component of the histone octamer in nucleosomes [32]. When DNA is damaged and double stranded DNA breaks, H2AX is phosphorylated to form γH2AX. Therefore, γH2AX has been used as a biomarker of DNA damage [32]. The p53 plays an important role in the regulation of cardiomyocyte hypertrophic growth and apoptosis [33]. An important discovery from this study is that ASK1 links p47phox with the activation of MAPKs and the expression of apoptotic markers, i.e., γH2AX and p53, in AngII-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis. We showed that ASK1 was phosphorylated in response to AngII-induced oxidative stress in the WT hearts. Knockout of p47phox, inhibited AngII-induced ASK1 phosphorylation and its down-stream signalling pathways. There was no obvious cardiomyocyte hypertrophic growth and no increase in the expression of apoptosis markers in AngII-infused p47phoxKO hearts. A schematic illustration of AngII-induced p47phox redox signalling pathways examined in this study is shown in Figure 7.
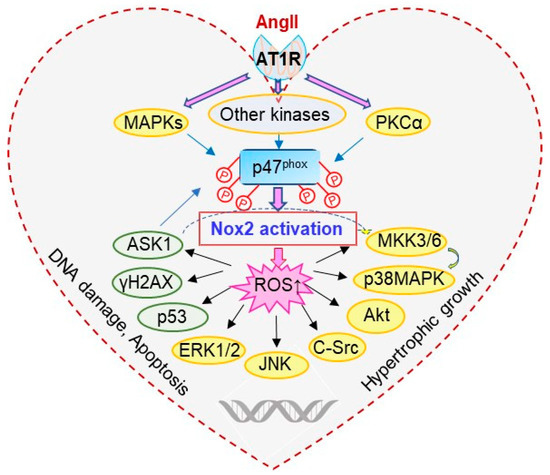
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of p47phox redox-signalling pathways examined.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have reported that p47phox is a key player in mediating AngII-induced oxidative stress signalling cascade from the phosphorylation of ASK1, MKK3/6 and MAPKs to the activation of H2AX and p53 involved in DNA damage and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes. Genetic ablation of p47phox inhibited the cardiac Nox2-derived O2●− production, attenuated the activation of ASK1 and MAPK signalling pathways and protected hearts from AngII-induced hypertrophic growth and DNA damage. Targeting p47phox has great therapeutic potential in preventing or treating AngII-induced cardiac dysfunction and damages.
Author Contributions
F.L.: data generation and analysis; manuscript drafting; L.M.F.: data analysis and critical revising of the manuscript; L.G.: in vivo sample collection and data generation; J.-M.L.: directed the study and finalised manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by an International PhD Studentship of the University of Reading (F.L.) and the British Heart Foundation (grant number: PG/14/85/31161).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All studies were performed following protocols approved by the Review Board of the Ethics Committees of the Surrey and Reading Universities and the Home Office under the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 UK. The animal studies were performed under the Home Office animal work project licences (PPL 70/6729 and PPL 70/7638).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Research material sources and all data that support the findings of this study are provided within this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lassegue, B.; Martin, A.S.; Griendling, K.K. Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases in the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1364–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M.; Douglas, G.; Bendall, J.K.; McNeill, E.; Crabtree, M.J.; Hale, A.B.; Mai, A.; Li, J.M.; McAteer, M.A.; Schneider, J.E.; et al. Endothelial cell-specific reactive oxygen species production increases susceptibility to aortic dissection. Circulation 2014, 129, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.M.; Geng, L.; Cahill-Smith, S.; Liu, F.; Douglas, G.; McKenzie, C.A.; Smith, C.; Brooks, G.; Channon, K.M.; Li, J.M. Nox2 contributes to age-related oxidative damage to neurons and the cerebral vasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3374–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchi, E.; Bargelli, V.; Stillitano, F.; Giordano, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Nassi, P.A.; d’Amati, G.; Cerbai, E.; Nediani, C. Enhanced ROS production by NADPH oxidase is correlated to changes in antioxidant enzyme activity in human heart failure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Benna, J.; Dang, P.M.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Marie, J.C.; Braut-Boucher, F. p47phox, the phagocyte NADPH oxidase/NOX2 organizer: Structure, phosphorylation and implication in diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.M.; Mullen, A.M.; Yun, S.; Wientjes, F.; Brouns, G.Y.; Thrasher, A.J.; Shah, A.M. Essential role of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox in endothelial cell superoxide production in response to phorbol ester and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, V.B.; Wang, Z.; Fan, D.; Zhabyeyev, P.; Basu, R.; Das, S.K.; Wang, W.; Desaulniers, J.; Holland, S.M.; Kassiri, Z.; et al. Loss of p47phox subunit enhances susceptibility to biomechanical stress and heart failure because of dysregulation of cortactin and actin filaments. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, M.; Itoh, K.; Akita, H.; Takano, K.; Oku, S. Identification of an actin-binding site in p47phox an organizer protein of NADPH oxidase. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.M.; Gall, N.P.; Grieve, D.J.; Chen, M.; Shah, A.M. Activation of NADPH oxidase during progression of cardiac hypertrophy to failure. Hypertension 2002, 40, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Mao, Z.; Peng, M.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, X.; Yan, J.; Yuan, W. Extracellular cyclophilin A induces cardiac hypertrophy via the ERK/p47phox pathway. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Penninger, J.M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2838–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soga, M.; Matsuzawa, A.; Ichijo, H. Oxidative Stress-Induced Diseases via the ASK1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 439587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablina, A.A.; Budanov, A.V.; Ilyinskaya, G.V.; Agapova, L.S.; Kravchenko, J.E.; Chumakov, P.M. The antioxidant function of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Gavrila, D.; McCormick, M.L.; Miller, F.J., Jr.; Daugherty, A.; Cassis, L.A.; Dellsperger, K.C.; Weintraub, N.L. Deletion of p47phox attenuates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 2006, 114, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doerries, C.; Grote, K.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Luchtefeld, M.; Schaefer, A.; Holland, S.M.; Sorrentino, S.; Manes, C.; Schieffer, B.; Drexler, H.; et al. Critical role of the NAD(P)H oxidase subunit p47phox for left ventricular remodeling/dysfunction and survival after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meijles, D.N.; Fan, L.M.; Howlin, B.J.; Li, J.M. Molecular insights of p47phox phosphorylation dynamics in the regulation of NADPH oxidase activation and superoxide production. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22759–22770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Fan, L.M.; Mai, A.; Li, J.M. Crucial roles of Nox2-derived oxidative stress in deteriorating the function of insulin receptors and endothelium in dietary obesity of middle-aged mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schipke, J.; Banmann, E.; Nikam, S.; Voswinckel, R.; Kohlstedt, K.; Loot, A.E.; Fleming, I.; Muhlfeld, C. The number of cardiac myocytes in the hypertrophic and hypotrophic left ventricle of the obese and calorie-restricted mouse heart. J. Anat. 2014, 225, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bensley, J.G.; de Matteo, R.; Harding, R.; Black, M.J. Three-dimensional direct measurement of cardiomyocyte volume, nuclearity, and ploidy in thick histological sections. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csanyi, G.; Cifuentes-Pagano, E.; al Ghouleh, I.; Ranayhossaini, D.J.; Egana, L.; Lopes, L.R.; Jackson, H.M.; Kelley, E.E.; Pagano, P.J. Nox2 B-loop peptide, Nox2ds, specifically inhibits the NADPH oxidase Nox2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorn, G.W., II; Force, T. Protein kinase cascades in the regulation of cardiac hypertrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontayne, A.; Dang, P.M.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; El-Benna, J. Phosphorylation of p47phox sites by PKC alpha, beta II, delta, and zeta: Effect on binding to p22phox and on NADPH oxidase activation. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7743–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callera, G.E.; Antunes, T.T.; He, Y.; Montezano, A.C.; Yogi, A.; Savoia, C.; Touyz, R.M. c-Src Inhibition Improves Cardiovascular Function but not Remodeling or Fibrosis in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension. Hypertension 2016, 68, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altenhofer, S.; Radermacher, K.A.; Kleikers, P.W.; Wingler, K.; Schmidt, H.H. Evolution of NADPH Oxidase Inhibitors: Selectivity and Mechanisms for Target Engagement. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 406–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumimoto, H. Structure, regulation and evolution of Nox-family NADPH oxidases that produce reactive oxygen species. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3249–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Murugesan, P.; Huang, K.; Cai, H. NADPH oxidases and oxidase crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases: Novel therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Superoxide dismutases: Role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.C.; Lin, W.N.; Cho, R.L.; Yang, C.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Hsiao, L.D.; Tseng, H.C.; Yang, C.M. Induction of HO-1 by Mevastatin Mediated via a Nox/ROS-Dependent c-Src/PDGFRalpha/PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/ARE Cascade Suppresses TNF-alpha-Induced Lung Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in heart development and diseases. Circulation 2007, 116, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, R.; Hayakawa, T.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H. Therapeutic targets in the ASK1-dependent stress signaling pathways. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2012, 88, 434–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, L.J.; Yang, L.X. Gamma-H2AX—A novel biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks. In Vivo 2008, 22, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Hauck, L.; Grothe, D.; Billia, F. p53 regulates the cardiac transcriptome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).