Comparative Study Regarding the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Pine (Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris) Bark Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Samples and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Extraction
2.4. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
2.5. Total Tannin Content (TTC)
2.6. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
2.7. UPLC-PDA Analysis
2.8. Antioxidant Activity (AOA) Assays
2.8.1. DPPH Assay
2.8.2. ABTS Assay
2.9. Antibacterial Activity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
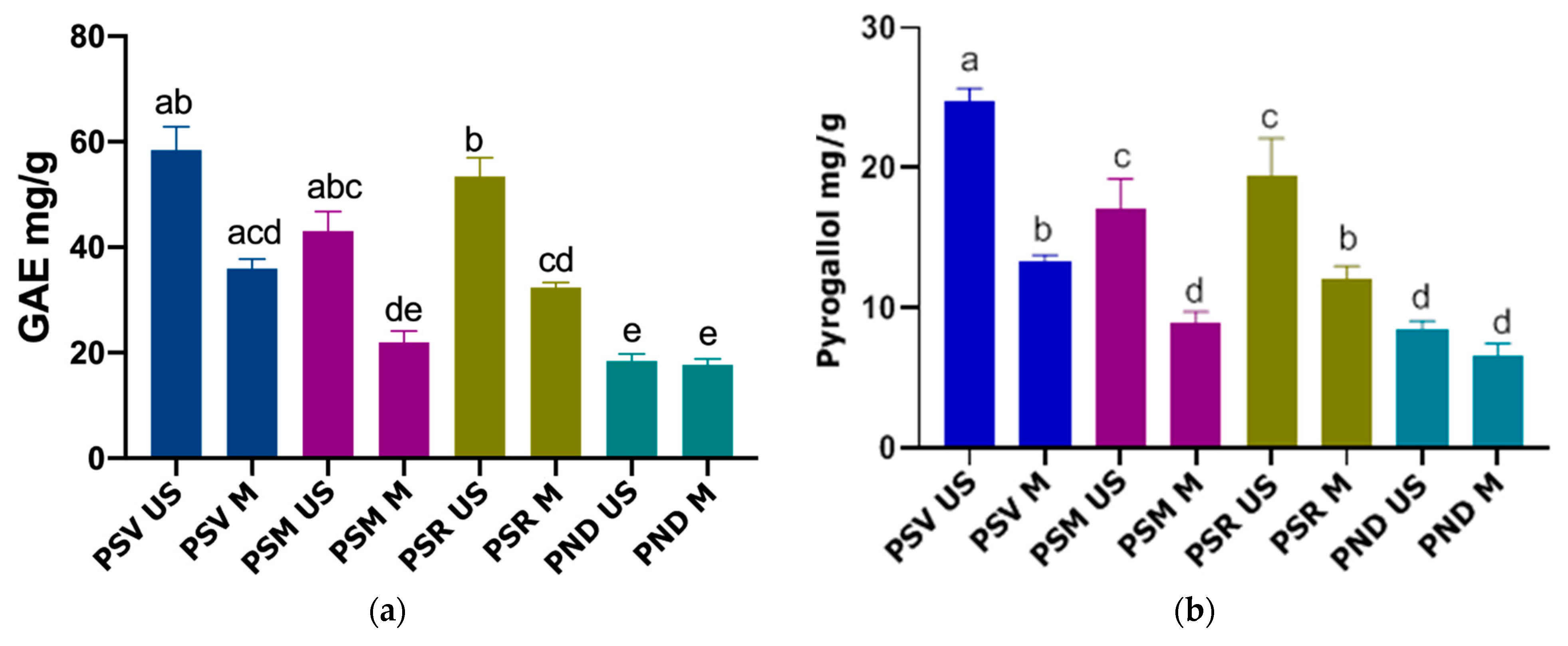
3.1. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
3.2. Total Tannin Content (TTC)
3.3. Volatile Compounds Analysis
3.4. UPLC Analysis
3.5. Antioxidant Activity (AOA)
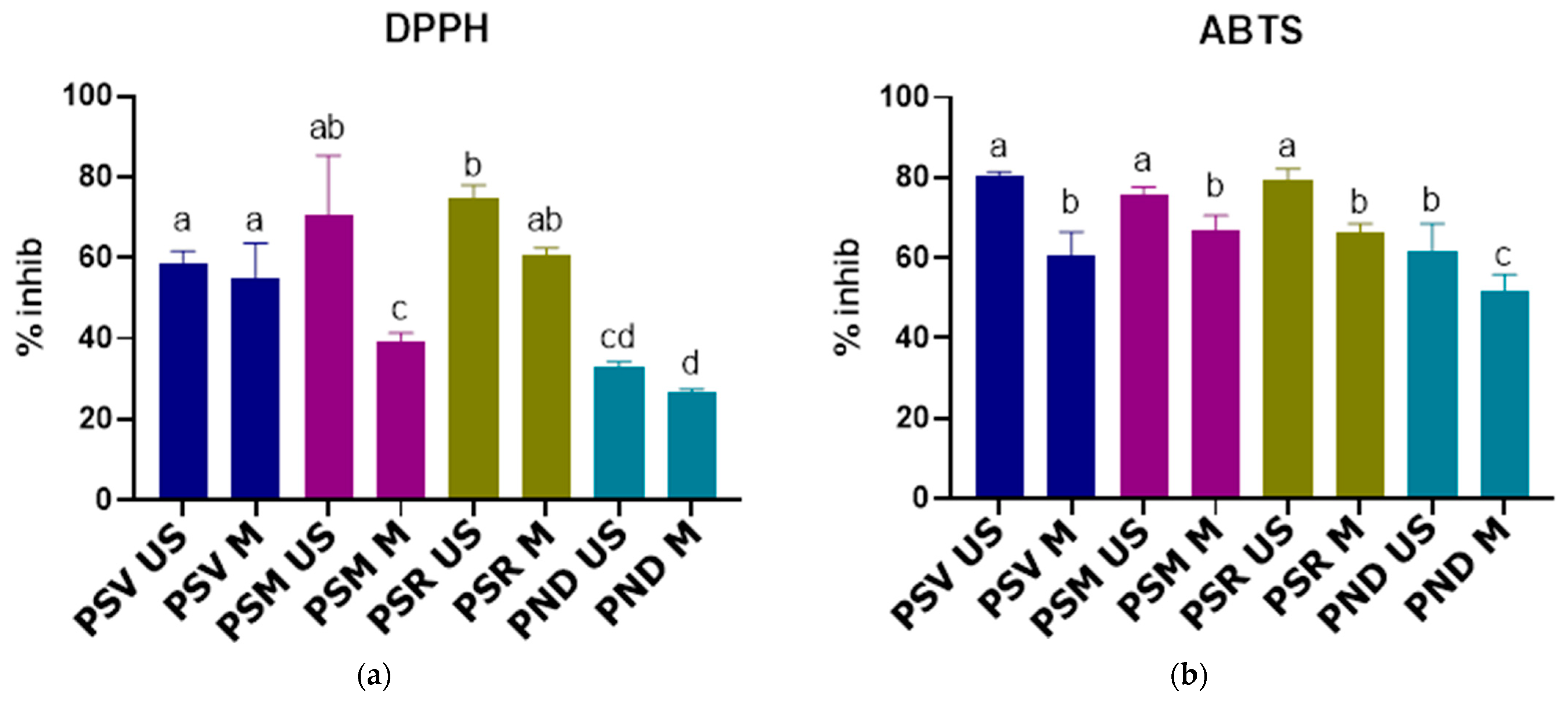
3.5.1. DPPH Assay
3.5.2. ABTS Assay
3.6. Antibacterial Activity
3.6.1. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923
3.6.2. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ATCC 43300
3.6.3. Gram-Negative Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coșarcă, S.-L.; Moacă, E.-A.; Tanase, C.; Muntean, D.L.; Pavel, I.Z.; Dehelean, C.A. Spruce and Beech Bark Aqueous Extracts: Source of Polyphenols, Tannins and Antioxidants Correlated to in vitro Antitumor Potential on Two Different Cell Lines. Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Złotek, U.; Mikulska, S.; Nagajek, M.; Świeca, M. The Effect of Different Solvents and Number of Extraction Steps on the Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Basil Leaves (Ocimum basilicum L.) Extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, C.; Coșarcă, S.; Muntean, D.-L. A Critical Review of Phenolic Compounds Extracted from the Bark of Woody Vascular Plants and Their Potential Biological Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Sood, P.; Citovsky, V. The Roles of Plant Phenolics in Defence and Communication during Agrobacterium and Rhizobium Infection: Phenolics in Agrobacterium and Rhizobium Infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.-A.; Dow, J.M.; Molinaro, A.; Parrilli, M. Invited Review: Priming, Induction and Modulation of Plant Defence Responses by Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides. J. Endotoxin Res. 2007, 13, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittel, P.; Robatzek, S. Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs) Probe Plant Immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparło, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant Properties of Catechins: Comparison with Other Antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implication in Various Diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Allium Cepa Extract: A Green Approach. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roleira, F.M.F.; Tavares-da-Silva, E.J.; Varela, C.L.; Costa, S.C.; Silva, T.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Plant Derived and Dietary Phenolic Antioxidants: Anticancer Properties. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboubi, A.; Asgarpanah, J.; Sadaghiyani, P.N.; Faizi, M. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content and Antibacterial Activity of Punica Granatum L. Var. Pleniflora Flowers (Golnar) against Bacterial Strains Causing Foodborne Diseases. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Camargo, A.C.; Regitano-d’Arce, M.A.B.; Rasera, G.B.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G.; do Prado-Silva, L.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Shahidi, F. Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids of Peanut By-Products: Antioxidant Capacity and Antimicrobial Effects. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, V.N.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.M.; Santos, E.S.; Morais, L.P.; Tintino, S.R.; Freitas, T.S.; Geraldo, Y.S.; Pereira, R.L.S.; Cruz, R.P.; Menezes, I.R.A.; et al. Antimicrobial and Enhancement of the Antibiotic Activity by Phenolic Compounds: Gallic Acid, Caffeic Acid and Pyrogallol. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Silva, S.; Henriques, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Decoction, Infusion and Hydroalcoholic Extract of Cultivated Thyme: Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities, and Phenolic Characterisation. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guendouze-Bouchefa, N.; Madani, K.; Chibane, M.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L.; Hauchard, D.; Kiendrebeogo, M.; Stévigny, C.; Okusa, P.N.; Duez, P. Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Three Ericaceae from Algeria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Evaluation of Bioactive Properties and Phenolic Compounds in Different Extracts Prepared from Salvia officinalis L. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Activity of Phenolic Compounds from Plant Origin against Candida Species. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 648–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elansary, H.O.; Salem, M.Z.M.; Ashmawy, N.A.; Yessoufou, K.; El-Settawy, A.A.A. In Vitro Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antioxidant Activities of Eucalyptus Spp. Leaf Extracts Related to Phenolic Composition. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2927–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Narita, R.; Nishimura, H.; Marumoto, S.; Yamamoto, S.P.; Ouda, R.; Yatagai, M.; Fujita, T.; Watanabe, T. Antiviral Activity of Phenolic Derivatives in Pyroligneous Acid from Hardwood, Softwood, and Bamboo. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medini, F.; Megdiche, W.; Mshvildadze, V.; Pichette, A.; Legault, J.; St-Gelais, A.; Ksouri, R. Antiviral-Guided Fractionation and Isolation of Phenolic Compounds from Limonium Densiflorum Hydroalcoholic Extract. C. R. Chim. 2016, 19, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Mohammadi-Kamalabadi, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Amjad, L.; Salimzadeh, L. Determination of Antioxidant Activity, Phenolic Contents and Antiviral Potential of Methanol Extract of Euphorbia spinidens Bornm (Euphorbiaceae). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Han, J.; Xiao, H.; Qiao, J.; Han, M. Effect of Tea Polyphenol Compounds on Anticancer Drugs in Terms of Anti-Tumor Activity, Toxicology, and Pharmacokinetics. Nutrients 2016, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.M.A.; Ates, S.; Olgun, Ç.; Gür, M. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Some Industrial Tree Bark Extracts. BioResources 2019, 14, 5657–5671. [Google Scholar]
- Karonen, M.; Ha, M.; Nieminen, R.; Klika, K.D.; Loponen, J.; Ovcharenko, V.V.; Moilanen, E.; Pihlaja, K. Phenolic Extractives from the Bark of Pinus sylvestris L. and Their Effects on Inflammatory Mediators Nitric Oxide and Prostaglandin E2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7532–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, E.; Cepeda, A.; Gualillo, O.; Perez-Fernandez, R. In-Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Pinus sylvestris and Plantago lanceolata Extracts: Effect on Inducible NOS, COX-1, COX-2 and Their Products in J774A.1 Murine Macrophages. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesil-Celiktas, O.; Ganzera, M.; Akgun, I.; Sevimli, C.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Bedir, E. Determination of Polyphenolic Constituents and Biological Activities of Bark Extracts from Different Pinus Species: Biological Activities of Pine Bark Extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.A.; Thakkar, J.H.; Patel, P.; Santani, D. Lipase Inhibitory and Anti-Obesity Effect of The Hydro Alcoholic Extract of Pinus sylvestris Bark. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 1213–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Digrak, M.; Ilçim, A.; Alma, M.H. Antimicrobial Activities of Several Parts of Pinus brutia, Juniperus oxycedrus, Abies cilicia, Cedrus libani and Pinus nigra. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.-L.; Cui, Y.-Y. Pine Bark Extracts: Nutraceutical, Pharmacological, and Toxicological Evaluation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, C.; Domokos, E.; Coșarcă, S.; Miklos, A.; Imre, S.; Domokos, J.; Dehelean, C.A. Study of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) Bark. BioResources 2018, 13, 2247–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.; Mocan, A.; Coșarcă, S.; Gavan, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Gheldiu, A.-M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Muntean, D.-L.; Crișan, O. Biological and Chemical Insights of Beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) Bark: A Source of Bioactive Compounds with Functional Properties. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rangel, J.C.; Benavides, J.; Heredia, J.B.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A. The Folin–Ciocalteu Assay Revisited: Improvement of Its Specificity for Total Phenolic Content Determination. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5990–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia, 7th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tanase, C.; Cosarca, S.; Toma, F.; Mare, A.; Cosarca, A.; Man, A.; Miklos, A.; Imre, S. Antibacterial Activities of Spruce Bark (Picea abies L.) Extract and Its Components Against Human Pathogens. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondet, V.; Brand-Williams, W.; Berset, C. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Antioxidant Activity Using the DPPH Free Radical Method. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved Abts Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.; Miklos, A.; Imre, S.; Boz, I. Antibacterial Activities of Beech Bark (Fagus sylvatica L.). Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 17, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, C.; Berta, L.; Coman, N.A.; Roșca, I.; Man, A.; Toma, F.; Mocan, A.; Nicolescu, A.; Jakab-Farkas, L.; Biró, D.; et al. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using the Spruce Bark Extract. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrypnik, L. Comparative Study on Radical Scavenging Activity and Phenolic Compounds Content in Water Bark Extracts of Alder (Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.), Oak (Quercus robur L.) and Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Zikeli, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; Kroslakova, I.; Mayer, I.; Pichelin, F.; Matteucci, G. Characterization of Pinus nigra Var. Laricio [Maire] Bark Extracts at the Analytical and Pilot Scale. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspé, E.; Fernández, K. The Effect of Different Extraction Techniques on Extraction Yield, Total Phenolic, and Anti-Radical Capacity of Extracts from Pinus Radiata Bark. Ind. Crop Prod. 2011, 34, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, M.; Chadni, M.; Barba, F.J.; Grimi, N.; Bals, O.; Vorobiev, E. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols from Quercus Bark. Ind. Crop Prod. 2015, 77, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelová, D.; Škulcová, D.; Legerská, B.; Horník, M.; Ondrejovič, M. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenols and Antioxidants from Picea Abies Bark. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 314–315, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Zeidler, A.; Böhm, M.; Mohamed, M.E.A.; Ali, H.M. GC/MS Analysis of Oil Extractives from Wood and Bark of Pinus sylvestris, Abies alba, Picea abies, and Larix decidua. Bioresources 2015, 10, 7725–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgenç, Ö. Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds by SPME-GC-FID/MS from Six Coniferous and Nine Deciduous Tree Bark Species Grown in Turkey. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumm, R.; Tiemann, T.; Schulz, S.; Hilker, M. Analysis of Volatiles from Black Pine (Pinus nigra): Significance of Wounding and Egg Deposition by a Herbivorous Sawfly. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3221–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Luz Cádiz-Gurrea, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Segura-Carretero, A. Pine Bark and Green Tea Concentrated Extracts: Antioxidant Activity and Comprehensive Characterization of Bioactive Compounds by HPLC–ESI-QTOF-MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20382–20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesil-Celiktas, O.; Otto, F.; Parlar, H. A Comparative Study of Flavonoid Contents and Antioxidant Activities of Supercritical CO2 Extracted Pine Barks Grown in Different Regions of Turkey and Germany. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T.; Nebehaj, E.; Stefanovits-Bányai, É.; Albert, L. Antioxidant Capacity and Total Phenol Content of Beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) Bark Extracts. Ind. Crop Prod. 2015, 77, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tálos-Nebehaj, E.; Albert, L.; Visi-Rajczi, E.; Hofmann, T. Combined Multi-Assay Evaluation of the Antioxidant Properties of Tree Bark. Acta Silv. Lignaria Hung. 2019, 15, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio-Kaila, T.; Kyyhkynen, A.; Rautkari, L.; Siitonen, A. Antibacterial Effects of Extracts of Pinus sylvestris and Picea abies against Staphylococcus Aureus, Enterococcus Faecalis, Escherichia Coli, and Streptococcus Pneumoniae. BioResources 2015, 10, 7763–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jin, H.; Xiao, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q. The Simultaneous Loading of Catechin and Quercetin on Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Effective Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agent. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jung, J.; Zhao, Y. Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Catechins and Catechins–Zn Complex Loaded β-Chitosan Nanoparticles of Different Particle Sizes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklasińska-Majdanik, M.; Kępa, M.; Wojtyczka, R.D.; Idzik, D.; Wąsik, T.J. Phenolic Compounds Diminish Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcus Aureus Clinical Strains. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | PND US | PSM US | PSR US | PSV US | PND M | PSM M | PSR M | PSV M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-pinene | 2152.84 ± 6.38 | 621.48 ± 10.04 | 1272.23 ± 4.25 | 782.34 ± 3.61 | 2412.14 ± 6.98 | 885.40 ± 0.25 | 1826.10 ± 11.48 | 1018.04 ± 6.03 |
| β-pinene | 3239.12 ± 2.60 | 3332.87 ± 3.67 | 3006.23 ± 4.18 | 1218.91 ± 3.65 | 3794.11 ± 17.60 | 3422.53 ± 16.44 | 3517.65 ± 0.36 | 1669.02 ± 2.66 |
| Camphene | 44.59 ± 2.41 | 25.18 ± 2.08 | 55.05 ± 0.30 | 42.73 ± 1.29 | 47.77 ± 0.30 | 39.20 ± 0.16 | 53.24 ± 0.15 | 70.14 ± 0.09 |
| 3-carene | 80.93 ± 0.13 | 68.25 ± 0.37 | 75.19 ± 0.23 | 82.39 ± 0.55 | 84.17 ± 0.10 | 68.77 ± 0.26 | 91.00 ± 0.13 | 60.27 ± 0.09 |
| α-phellandrene | 10.16 ± 0.18 | 6.38 ± 0.41 | 9.24 ± 0.21 | 7.11 ± 0.22 | 9.75 ± 0.46 | 7.08 ± 0.04 | 11.09 ± 0.04 | 8.00 ± 0.11 |
| Limonene | 97.16 ± 0.09 | 70.31 ± 0.05 | 88.10 ± 0.04 | 73.32 ± 0.25 | 109.90 ± 0.19 | 74.21 ± 0.05 | 94.30 ± 0.05 | 76.67 ± 0.05 |
| Sabinene | 49.08 ± 0.08 | 26.19 ± 0.02 | 30.04 ± 0.04 | 19.22 ± 0.03 | 59.90 ± 0.19 | 31.34 ± 0.23 | 37.31 ± 0.05 | 20.56 ± 0.41 |
| Myrcene | 136.31 ± 0.32 | 112.23 ± 0.23 | 155.31 ± 0.21 | 196.96 ± 0.12 | 139.84 ± 0.29 | 112.70 ± 0.08 | 156.20 ± 0.14 | 198.50 ± 0.46 |
| Tricyclene | 9.27 ± 0.09 | 7.09 ± 0.07 | 7.18 ± 0.15 | 22.14 ± 0.06 | 6.27 ± 0.04 | 8.19 ± 0.18 | 7.88 ± 0.07 | 26.21 ± 0.14 |
| Compound | PND US | PSM US | PSR US | PSV US | PND M | PSM M | PSR M | PSV M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catechin | 0.602 | 1.289 | 1.222 | 8.393 | 0.588 | 0.637 | 1.165 | 0.958 |
| Epicatechin | 2.299 | 5.005 | 3.16 | 37.456 | 3.817 | 1.554 | 3.813 | 18.779 |
| Tested Bacteria | MIC (mg bark/mL Extract) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSV M | PSV US | PSR M | PSR US | PSM M | PSM US | PND M | PND US | |
| Staphyllococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 3.125 | 1.562 | 6.25 | 3.125 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| Methicillin resistant Staphyllococcus aureus (MRSA) ATCC 43300 | 3.125 | 1.562 | 3.125 | 1.562 | 6.25 | 3.125 | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 100 | 50 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 2753 | 100 | 25 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 | >100 | >50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nisca, A.; Ștefănescu, R.; Stegăruș, D.I.; Mare, A.D.; Farczadi, L.; Tanase, C. Comparative Study Regarding the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Pine (Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris) Bark Extracts. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020327
Nisca A, Ștefănescu R, Stegăruș DI, Mare AD, Farczadi L, Tanase C. Comparative Study Regarding the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Pine (Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris) Bark Extracts. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleNisca, Adrian, Ruxandra Ștefănescu, Diana Ionela Stegăruș, Anca Delia Mare, Lenard Farczadi, and Corneliu Tanase. 2021. "Comparative Study Regarding the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Pine (Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris) Bark Extracts" Antioxidants 10, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020327
APA StyleNisca, A., Ștefănescu, R., Stegăruș, D. I., Mare, A. D., Farczadi, L., & Tanase, C. (2021). Comparative Study Regarding the Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Pine (Pinus nigra and P. sylvestris) Bark Extracts. Antioxidants, 10(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020327









