Plasma Nitrate Levels Are Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Are Not Altered by Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Early Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aim, Design and Setting of the Study
2.2. Patient Characteristics
2.3. Dietary and Laboratory Assessments
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
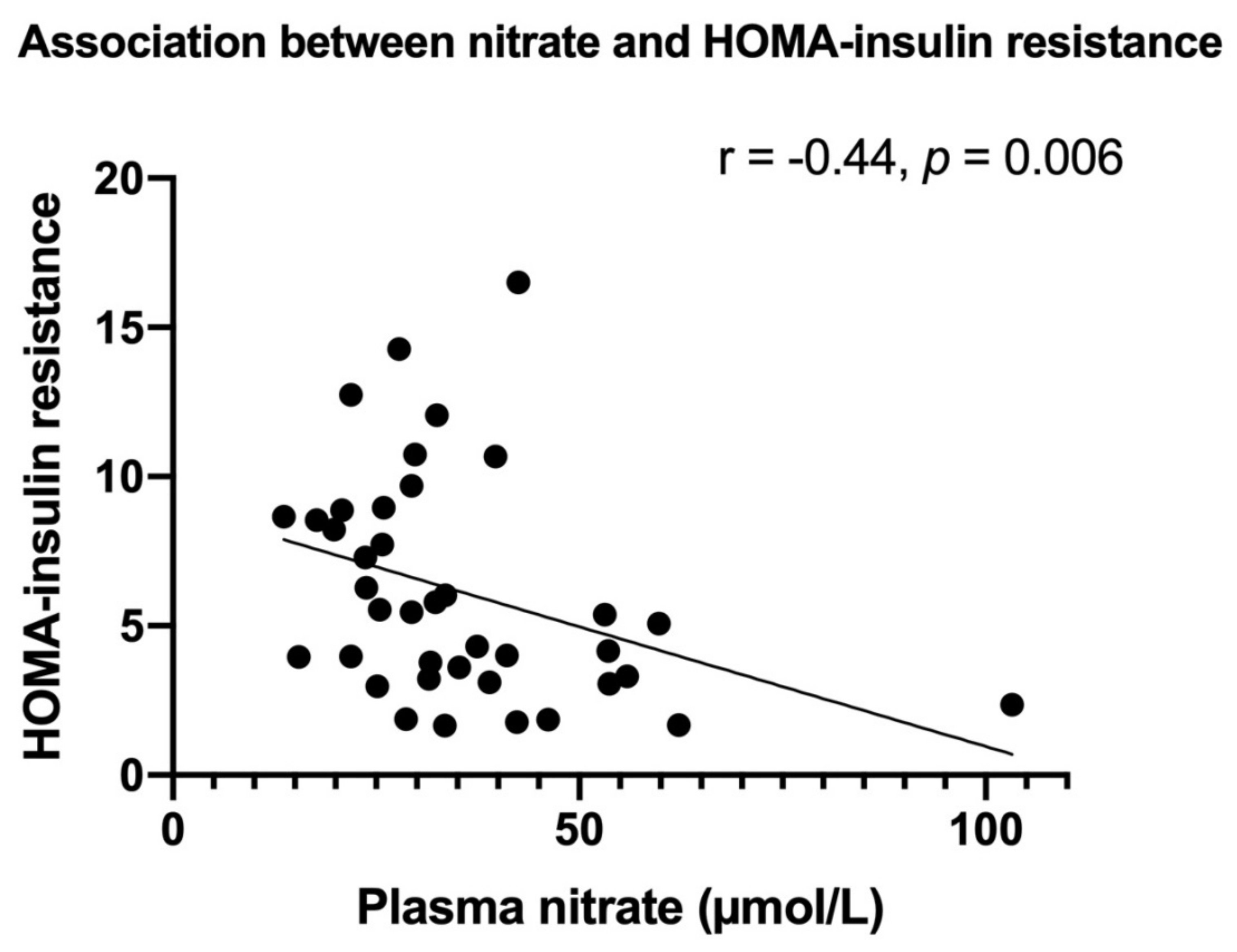
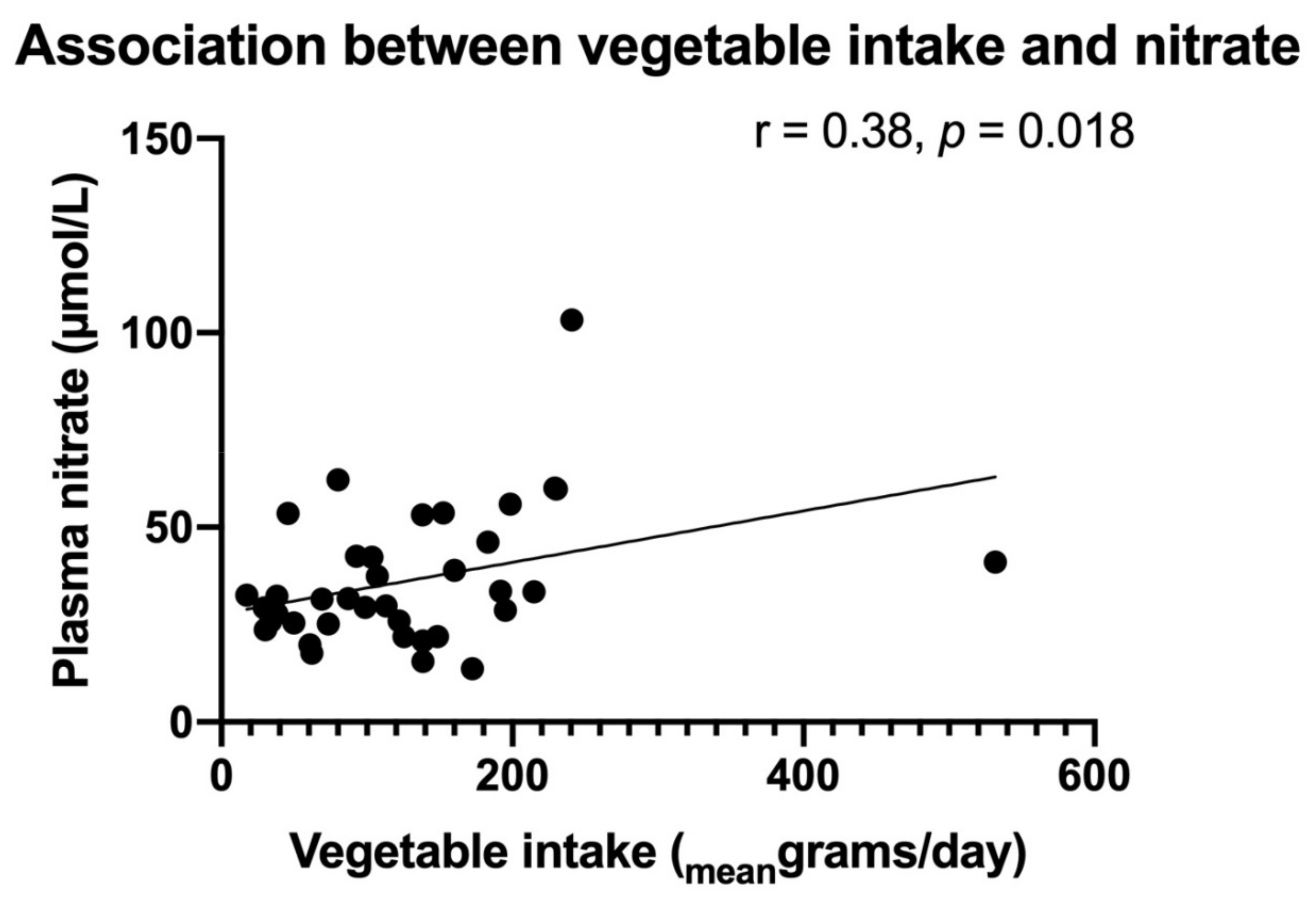
3.1. Stable End-Products of NO in Relation to MetS Markers
3.2. Effects of the DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin
3.2.1. Effects of Linagliptin Treatment on Nitrate and Nitrite Plasma Concentrations
3.2.2. Linagliptin Effects on MetS Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee; Punthakee, Z.; Goldenberg, R.; Katz, P. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes, Prediabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42 (Suppl. S1), S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Herder, C.; Schneitler, S.; Rathmann, W.; Haastert, B.; Schneitler, H.; Winkler, H.; Bredahl, R.; Hahnloser, E.; Martin, S. Low-grade inflammation, obesity, and insulin resistance in adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K. Akash MSH Mechanism of Generation of Oxidative Stress and Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: How Are They Interlinked? J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folli, F.; Corradi, D.; Fanti, P.; Davalli, A.; Paez, A.; Giaccari, A.; Perego CMuscogiuri, G. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus micro-and macrovascular complications: Avenues for a mechanistic-based therapeutic approach. Curr. Diabetes. Rev. 2011, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förstermann, U.; Xia, N.; Li, H. Roles of Vascular Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, E.W.; Stegeman, C.A.; Tiebosch, A.T.; Tegzess, A.M.; van Goor, H. Expression of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthases, formation of peroxynitrite and reactive oxygen species in human chronic renal transplant failure. Am. J. Transplant. 2002, 2, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzirad, R.; González-Muniesa, P.; Ghasemi, A. Hypoxia in Obesity and Diabetes: Potential Therapeutic Effects of Hyperoxia and Nitrate. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5350267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Jeddi, S. Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 2017, 70, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmann, T.S.; Brondani, L.A.; Boucas, A.P.; Rheinheimer, J.; de Souza, B.M.; Canani, L.H.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. Nitric oxide levels in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nitric Oxide 2016, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Majumder, B.; Bhattacharyya, S. Assessment of serum nitrate-nitrite ratio vis-a-vis insulin sensitivity and resistance in type 2 diabetics in a tertiary hospital in Eastern India. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchi-Alves, L.M.; Carnio, E.C. Is There Any Correlation between Insulin Resistance and Nitrate Plasma Concentration in White Coat Hypertensive Patients? Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2009, 2009, 376735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nácul, A.P.; Andrade, C.D.; Schwarz, P.; de Bittencourt, P.I., Jr. Spritzer PM Nitric oxide and fibrinogen in polycystic ovary syndrome: Associations with insulin resistance and obesity. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2007, 133, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.R.; Feelisch, M. Therapeutic uses of inorganic nitrite and nitrate: From the past to the future. Circulation 2008, 117, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Carlström, M.; Weitzberg, E. Metabolic Effects of Dietary Nitrate in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, X. Effects of spinach nitrate on insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction markers and inflammation in mice with high-fat and high-fructose consumption. Food. Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 32010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glorie, L.; D’Haese, P.C.; Verhulst, A. Boning up on DPP4, DPP4 substrates, and DPP4-adipokine interactions: Logical reasoning and known facts about bone related effects of DPP4 inhibitors. Bone 2016, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.R.H.; Jain, P.; Sagor, M.A.T. Reza HM DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin prevents inflammation and oxidative stress of heart and kidney in two kidney and one clip (2K1C) rats. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solini, A.; Rossi, C.; Duranti, E.; Taddei, S.; Natali, A.; Virdis, A. Saxagliptin prevents vascular remodeling and oxidative stress in db/db mice. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and cyclooxygenase. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2016, 76, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Jacob, R.F.; Kubant, R.; Walter, M.F.; Bellamine, A.; Jacoby, A.; Mizuno, Y.; Malinski, T. Effect of enhanced glycemic control with saxagliptin on endothelial nitric oxide release and CD40 levels in obese rats. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergmark, B.A.; Cannon, C.P.; White, W.B.; Jarolim, P.; Liu, Y.; Bonaca, M.P.; Zannad, F.; Morrow, D.A. Baseline adiponectin concentration and clinical outcomes among patients with diabetes and recent acute coronary syndrome in the EXAMINE trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, S.; Murata, K.; Betou, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Ishihara, Y.; Imataka, K.; Uchida, A.; Monguchi, K.; Kaneko, R.; Fujiwara, R.; et al. Effect of trelagliptin on vascular endothelial functions and serum adiponectin level in patients with type 2 diabetes: A preliminary single-arm prospective pilot study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamers, D.; Famulla, S.; Wronkowitz, N.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S.; Ouwens, D.M.; Eckardt, K.; Kaufman, J.M.; Ryden, M.; Müller, S.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a novel adipokine potentially linking obesity to the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, A.; Charkoudian, N.; Schrage, W.; Rizza, R.A.; Basu, R.; Joyner, M.J. Beneficial effects of GLP-1 on endothelial function in humans: Dampening by glyburide but not by glimepiride. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, S.A.; Hovinga-de Boer, M.C.; Heerspink, H.J.; Lefrandt, J.D.; van Roon, A.M.; Lutgers, H.L.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Mulder, D.J. Arterial Stiffness Is Positively Associated With 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography-Assessed Subclinical Vascular Inflammation in People With Early Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Boer, S.A.; Heerspink, H.J.; Juárez Orozco, L.E.; van Roon, A.M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Smit, A.J.; Slart, R.H.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Mulder, D.J. Effect of linagliptin on pulse wave velocity in early type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, controlled 26-week trial (RELEASE). Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rassaf, T.; Bryan, N.S.; Kelm, M.; Feelisch, M. Concomitant presence of N-nitroso and S-nitroso proteins in human plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbrello, M.; Dyson, A.; Pinto, B.B.; Fernandez, B.O.; Simon, V.; Feelisch, M.; Singer, M. Short-term hypoxic vasodilation in vivo is mediated by bioactive nitric oxide metabolites, rather than free nitric oxide derived from haemoglobin-mediated nitrite reduction. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, A.M.; Meijers, W.C.; Pasch, A.; Leuvenink, H.G.; Frenay, A.R.S.; Dekker, M.M.; Feelisch, M.; de Boer, R.A.; van Goor, H. Serum free thiols in chronic heart failure. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulle, A.E.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Kieneker, L.M.; Koning, A.M.; la Bastide-van Gemert, S.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Dijkstra, G.; Faber, K.N.; Dullaart, R.P.; Bakker, S.J.; et al. Serum free thiols predict cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in the general population: A prospective cohort study. BMC. Med. 2020, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Gladwin MT The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.K.; Patterson, A.J.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.K.; Bondonno, C.P.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Ward, N.C.; Hodgson, J.M.; Byles, J.E.; McEvoy, M.A. Dietary Nitrate and Diet Quality: An Examination of Changing Dietary Intakes within a Representative Sample of Australian Women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Born, J.C.; Hammes, H.P.; Greffrath, W.; van Goor, H.; Hillebrands, J.L. DFG GRK International Research Training Group 1874 Diabetic Microvascular Complications (DIAMICOM) Gasotransmitters in Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgen, I.T.; Tascilar, M.E.; Bilir, P.; Boyraz, M.; Guncikan, M.N.; Akay, C.; Dundaroz, R. Oxidative stress in obese children and its relation with insulin resistance. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varzandi, T.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Rohani, S.A.H.; Piryaei, A.; Zadeh-Vakili, A.; Jeddi, S.; Ghasemi, A. Effect of long-term nitrite administration on browning of white adipose tissue in type 2 diabetic rats: A stereological study. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, K.; Nakano, G.; Ehara, N.; Sonoda, K.; Ito, J.; Uchida, H.; Kobayashi, J. Dietary nitrite supplementation improves insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic KKA(y) mice. Nitric Oxide 2015, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J. Fat in all the wrong places. Nature 2002, 415, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrover, I.M.; Spiering, W.; Leiner, T.; Visseren, F.L. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Clinical Relevance and Diagnostic Possibilities. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goossens, G.H. The Metabolic Phenotype in Obesity: Fat Mass, Body Fat Distribution, and Adipose Tissue Function. Obes. Facts. 2017, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Portincasa, P.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Involvement of the leptin-adiponectin axis in inflammation and oxidative stress in the metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kina-Tanada, M.; Sakanashi, M.; Tanimoto, A.; Kaname, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Noguchi, K.; Uchida, T.; Nakasone, J.; Kozuka, C.; Ishida, M.; et al. Long-term dietary nitrite and nitrate deficiency causes the metabolic syndrome, endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular death in mice. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belo, V.A.; Souza-Costa, D.C.; Lacchini, R.; Sertorio, J.T.; Lanna, C.M.; Carmo, V.P.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Adiponectin associates positively with nitrite levels in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Boer, S.A.; Heerspink, H.J.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Hovinga-de Boer, M.C.; van Roon, A.M.; Juárez Orozco, L.E.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Slart, R.H.; Mulder, D.J. Effect of Linagliptin on Arterial (18)F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Uptake: A Randomized Controlled Trial (RELEASE). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1097–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, S.A.; Reijrink, M.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Hoekstra, E.S.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Westra, J.; Mulder, D.J. Angiogenic T cells are decreased in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and recruited by the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor Linagliptin: A subanalysis from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (RELEASE study). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigagli, E.; Luceri, C.; Dicembrini, I.; Tatti, L.; Scavone, F.; Giovannelli, L.; Mannucci, E.; Lodovici, M. Effect of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Circulating Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koren, S.; Shemesh-Bar, L.; Tirosh, A.; Peleg, R.K.; Berman, S.; Hamad, R.A.; Vinker, S.; Golik, A.; Efrati, S. The effect of sitagliptin versus glibenclamide on arterial stiffness, blood pressure, lipids, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, H.; Matsuo, M.; Hishida, A.; Koezuka, R.; Tochiya, M.; Ohata, Y.; Tamanaha, T.; Son, C.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hosoda, K. Effect of linagliptin on oxidative stress markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. Diabetol. Int. 2018, 10, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Rizvi, A.A.; Spinas, G.A.; Rini, G.B.; Berneis, K. Glucose lowering and anti-atherogenic effects of incretin-based therapies: GLP-1 analogues and DPP-4-inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| All (n = 40) | Linagliptin (n = 21) | Placebo (n = 19) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n) | 25 (63%) | 13 (62%) | 12 (63%) |
| Age (years) | 63 (55–67) | 63 (52–66) | 63 (57–69) |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 1.0 (0.0–3.8) | 1 (0–5) | 1 (0–3) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 30 (27–37) | 32 (28–39) | 29 (27–34) |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 7.5 ± 0.92 * | 7.6 ± 0.90 | 7.3 ± 0.95 ^ |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 16 (9.8–25) | 13 (9.6–27) | 18 (9.7–22) |
| HOMA-insulin resistance | 5.4 (3.2–8.7) * | 4.3 (3.2–9.3) | 5.5 (3.7–8.0) ^ |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 45 ± 4.4 | 45 ± 4.3 | 45 ± 4.6 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 1.3 (0.73–3.1) | 1.6 (0.80–2.9) | 1.2 (0.70–3.9) |
| Leukocyte counts (*109/L) | 7.0 ± 1.8 | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 6.7 ± 1.8 |
| Total free thiols (µM) | 426 (399–441) | 411 (374–438) | 430 (413–453) |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.7 ± 0.97 | 4.8 ± 1.2 | 4.6 ± 0.71 |
| High density lipids (mmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.33 | 1.3 ± 0.27 | 1.4 ± 0.39 |
| Low density lipids (mmol/L) | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 3.2 ± 1.2 | 2.9 ± 0.86 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.4 (0.90–2.0) | 1.4 (1.1–2.0) | 1.2 (0.82–2.1) |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate (mL/min*1.73m2) | 85 (79–97) | 91 (81–98) | 81 (66–87) |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 26 (43–20) | 25 (19–41) | 27 (22–43) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 26 (22–33) | 24 (21–28) | 26 (22–33) |
| Gamma-glutamyltransferase (U/L) | 35 (25–47) | 33 (22–39) | 36 (27–64) |
| Nitrate (µmol/L) | 32 (25–42) | 33 (27–48) | 29 (25–43) |
| Nitrite (µmol/L) | 0.19 (0.095–0.33) | 0.14 (0.092–0.35) | 0.20 (0.094–0.33) |
| Vegetable intake (mean grams/day) | 110 (58–175) ° | 107 (61–153) ® | 122 (50–192) |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 8.3 (6.3–10.5) | 7.3 (5.7–9.9) | 8.5 (6.4–12.6) |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 13 (6.6–25) | 13 (4.6–26) | 13 (8.1–23) |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 139 ± 13 | 139 ± 15 | 138 ± 12 |
| Model 1 (R2 = 0.191, p = 0.005) | Model 2 (R2 = 0.327, p = 0.003) | Model 3 (R2 = 0.345, p = 0.005) | Model 4 (R2 = 0.354, p = 0.014) | Model 5 (R2 = 0.356, p = 0.030) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent: nitrate | St. ß | p-value | St. ß | p-value | St. ß | p-value | St. ß | p-value | St. ß | p-value |
| HOMA-IR | −0.44 | 0.005 | −1.08 | 0.001 | −1.01 | 0.004 | −0.91 | 0.015 | −0.88 | 0.033 |
| BMI | −0.49 | 0.035 | −0.46 | 0.048 | −0.43 | 0.043 | −0.43 | 0.046 | ||
| Interaction variable HOMA-IR * BMI | 1.03 | 0.013 | 1.02 | 0.014 | 0.85 | 0.045 | 0.82 | 0.060 | ||
| CRP | −0.16 | 0.35 | −0.10 | 0.62 | −0.10 | 0.62 | ||||
| Vegetable intake | 0.084 | 0.65 | 0.080 | 0.67 | ||||||
| Gamma-GT | −0.038 | 0.82 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reijrink, M.; De Boer, S.A.; Van Roon, A.M.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Fernandez, B.O.; Feelisch, M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Van Goor, H.; Hillebrands, J.-L.; Mulder, D.J. Plasma Nitrate Levels Are Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Are Not Altered by Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Early Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101548
Reijrink M, De Boer SA, Van Roon AM, Slart RHJA, Fernandez BO, Feelisch M, Heerspink HJL, Van Goor H, Hillebrands J-L, Mulder DJ. Plasma Nitrate Levels Are Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Are Not Altered by Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Early Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(10):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101548
Chicago/Turabian StyleReijrink, Melanie, Stefanie A. De Boer, Anniek M. Van Roon, Riemer H. J. A. Slart, Bernadette O. Fernandez, Martin Feelisch, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Harry Van Goor, Jan-Luuk Hillebrands, and Douwe J. Mulder. 2021. "Plasma Nitrate Levels Are Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Are Not Altered by Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Early Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Antioxidants 10, no. 10: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101548
APA StyleReijrink, M., De Boer, S. A., Van Roon, A. M., Slart, R. H. J. A., Fernandez, B. O., Feelisch, M., Heerspink, H. J. L., Van Goor, H., Hillebrands, J.-L., & Mulder, D. J. (2021). Plasma Nitrate Levels Are Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Are Not Altered by Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Early Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants, 10(10), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101548








