Lateralized Brainstem and Cervical Spinal Cord Responses to Aversive Sounds: A Spinal fMRI Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimulus Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. fMRI Scanning Parameters and Preprocessing
2.5. fMRI Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.W.L.; McPhee, R.W.; Stringer, M.D. An evidence-based approach to human dermatomes. Clin. Anat. 2008, 21, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.D.; Kornelsen, J. Emotion-dependent responses in spinal cord neurons: A spinal fMRI study. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIver, T.A.; Kornelsen, J.; Smith, S.D. Limb-specific emotional modulation of cervical spinal cord neurons. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 13, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühholz, S.; Trost, W.; Grandjean, D. The role of the medial temporal limbic system in processing emotions in voice and music. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 123, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, A.B.M.; Wieser, M.J.; Alpers, G.W. Emotional pictures and sounds: A review of multimodal interactions of emotion cues in multiple domains. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Eippert, F.; Weiskopf, N.; Veit, R. The human amygdala is sensitive to the valence of pictures and sounds irrespective of arousal: An fMRI study. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2008, 3, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecteau, S.; Belin, P.; Joanette, Y.; Armony, J.L. Amygdala responses to nonlinguistic emotional vocalizations. Neuroimage 2007, 36, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühholz, S.; Grandjean, D. Processing of emotional vocalizations in bilateral inferior frontal cortex. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zald, D.H.; Pardo, J.V. The neural correlates of aversive auditory stimulation. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeDoux, J.E. Emotion Circuits in the Brain. Focus (Madison) 2009, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zald, D.H. The human amygdala and the emotional evaluation of sensory stimuli. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 41, 88–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Von Kriegstein, K.; Friston, K.; Griffiths, T.D. Features versus feelings: Dissociable representations of the acoustic features and valence of aversive sounds. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14184–14192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannese, A.; Grandjean, D.; Frühholz, S. Amygdala and auditory cortex exhibit distinct sensitivity to relevant acoustic features of auditory emotions. Cortex 2016, 85, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruholz, S.; Ceravolo, L.; Grandjean, D. Specific brain networks during explicit and implicit decoding of emotional prosody. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, N.; Takahashi, O.; Satoda, T.; Matsushima, R. Amygdalo-spinal projections in the macaque monkey. Neurosci. Lett. 1985, 53, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.L.; Amaral, D.G. An autoradiographic study of the projections of the central nucleus of the monkey amygdala. J. Neurosci. 1981, 1, 1242–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.S.; Friston, K.J.; Büchel, C.; Frith, C.D.; Young, A.W.; Calder, A.J.; Dolan, R.J. A neuromodulatory role for the human amygdala in processing emotional facial expressions. Brain 1998, 121, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surguladze, S.A.; Brammer, M.J.; Young, A.W.; Andrew, C.; Travis, M.J.; Williams, S.C.R.; Phillips, M.L. A preferential increase in the extrastriate response to signals of danger. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.F.; Simmons, W.K. Interoceptive predictions in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.D. How do you feel now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeley, W.W.; Menon, V.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Keller, J.; Glover, G.H.; Kenna, H.; Reiss, A.L.; Greicius, M.D. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büchel, C.; Dolan, R.J.; Armony, J.L.; Friston, K.J. Amygdala-hippocampal involvement in human aversive trace conditioning revealed through event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10869–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Affective reactions to acoustic stimuli. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, S.P.; Backs, R.W. Cardiac response during auditory selective attention to tones and affective sounds. Psychophysiology 2015, 52, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partala, T.; Surakka, V. Pupil size variation as an indication of affective processing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchely, H.D. Neural mechanisms of autonomic, affective, and cognitive integration. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchley, H.D.; Harrison, N.A. Visceral influence on brain and behavior. Neuron 2013, 77, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessing, W.W. The Lower Brainstem and Bodily Homeostasis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Critchley, H.D.; Mathias, C.J.; Josephs, O.; O’Doherty, J.; Zanini, S.; Dewar, B.K.; Cipolotti, L.; Shallice, T.; Dolan, R.J. Human cingulate cortex and autonomic control: Converging neuroimaging and clinical evidence. Brain 2003, 126, 2139–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchley, H.D.; Wiens, S.; Rotshtein, P.; Öhman, A.; Dolan, R.J. Neural systems supporting interoceptive awareness. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotz, S.A.; Kalberlah, C.; Bahlmann, J.; Friederici, A.D.; Haynes, J.D. Predicting vocal emotion expressions from the human brain. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühholz, S.; Trost, W.; Kotz, S.A. The sound of emotions—Towards a unifying neural network perspective of affective sound processing. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, F.; Banfi, C.; Borgheresi, A.; Fiori, E.; Innocenti, I.; Rossi, S.; Zaccara, G.; Viggiano, M.P.; Cincotta, M. The effect of music on corticospinal excitability is related to the perceived emotion: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Cortex 2013, 49, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeilipoor, N.; Pizzolato, F.; Daffertshofer, A.; Cesari, P. Excitability of motor cortices as a function of emotional sounds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnew, S.K.; Banissy, Z.K.; McGettigan, M.J.; Walsh, C.; Scott, V. Investigating the neural basis of theta burst stimulation to premotor cortex on emotional vocalization perception: A combined TMS-fMRI study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Banissy, M.J.; Sauter, D.A.; Ward, J.; Warren, J.E.; Walsh, V.; Scott, S.K. Suppressing sensorimotor activity modulates the discrimination of auditory emotions but not speaker identity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13552–13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekert, M.; Vingerhoets, G.; Aleman, A. Results of a pilot study on the involvement of bilateral inferior frontal gyri in emotional prosody perception: An rTMS study. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. The International Affective Digitized Sounds; Affective Ratings of Sounds and Instruction Manual; Technical Report B-3; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Stroman, P.W.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.; Backon, M.; Schwab, J.M.; Bosma, R.; Brooks, J.; Cadotte, D.; Carlstedt, T.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cohen-Adad, J.; et al. The current state-of-the-art of spinal cord imaging. NeuroImage 2014, 4, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosma, R.L.; Stroman, P.W. Assessment of data acquisition parameters, and analysis techniques for noise reduction in spinal cord fMRI data. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, J.K.; Figley, C.R.; Stroman, P.W. Applying functional MRI to the spinal cord and brainstem. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 28, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornelsen, J.; Smith, S.D.; McIver, T.A. A neural correlate of visceral emotional responses: Evidence from fMRI of the thoracic spinal cord. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2015, 10, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.D.; Kornelsen, J.; McIver, T.A. Generating facial expressions of disgust activates neurons in the thoracic spinal cord: Aspinal fMRI study. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D.; Kolesar, T.A.; Kornelsen, J.; Smith, S.D. Neural responses to consciously and unconsciously perceived emotional faces: A spinal fMRI study. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, M. Auditory localization. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Squire, L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 721–728. [Google Scholar]
- Rinne, T.; Balk, M.H.; Koistinen, S.; Autti, T.; Alho, K.; Sams, M. Auditory selective attention modulates activation of human inferior colliculus. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 3323–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstege, G. The mesopontine rostromedial tegmental nucleus and the emotional motor system: Role in basic survival behavior. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovick, T.A. The periaqueductal gray-rostral medulla connection in the defence reaction: Efferent pathways and descending control mechanisms. Behav. Brain Res. 1993, 58, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpute, A.B.; Wager, T.D.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Bianciardi, M.; Choi, J.K.; Buhle, J.T.; Wald, L.L.; Barrett, L.F. Identification of discrete functional subregions of the human periaqueductal gray. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17101–17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, K.; Neubert, J.; Pfannmöller, J.; Lotze, M.; Hamm, A.O.; Wendt, J. Fear-potentiated startle processing in humans: Parallel fMRI and orbicularis EMG assessment during cue conditioning and extinction. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 98, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Mobbs, D.; Seymour, B.; Rowe, J.B.; Calder, A.J. The neural signature of escalating frustration in humans. Cortex 2014, 54, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Moulder, B.; Lang, P.J. When good things go bad: The reflex physiology of defense. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 16, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aravamuthan, B.R.; Muthusamy, K.A.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z.; Johansen-Berg, H. Topography of cortical and subcortical connections of the human pedunculopontine and subthalamic nuclei. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, A.; Edlow, B.L.; Immordino-Yang, M.H. The Brainstem in Emotion: A Review. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesulam, M.M. Cholinergic Pathways and the Ascending Reticular Activating System of the Human Brain. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 757, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombes, S.A.; Tandonnet, C.; Fujiyama, H.; Janelle, C.M.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Summers, J.J. Emotion and motor preparation: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study of corticospinal motor tract excitability. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 9, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, A.M.; Van den Wildenberg, W.P.; Van stegeren, A.H.; Hajcak, G.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Emotional stimuli modulate readiness for action: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 10, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M.S. Neural organization of the defensive behavior system responsible for fear. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 1994, 1, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, P.J.; Davis, M. Emotion, motivation, and the brain: Reflex foundations in animal and human research. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 156, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermans, E.J.; Henckens, M.J.; Roelofs, K.; Fernández, G. Fear bradycardia and activation of the human periaqueductal grey. NeuroImage 2013, 66, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, J.; Löw, A.; Weymar, M.; Lotze, M.; Hamm, A.O. Active avoidance and attentive freezing in the face of approaching threat. NeuroImage 2017, 158, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, K. Freeze for action: Neurobiological mechanisms in animal and human freezing. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2017, 372, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaree, H.A.; Everhart, D.E.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Harrison, D.W. Brain lateralization of emotional processing: Historical roots and a future incorporating dominance. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev. 2005, 4, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, D.; Aleman, A.; Kahn, R.S. Lateralization of amygdala activation: A systematic review of functional neuroimaging studies. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 45, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, L.; Bryden, M.P.; Bulman-Fleming, M.B. Footedness is a better predictor than is handedness of emotional lateralization. Neuropsychologia 1998, 36, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
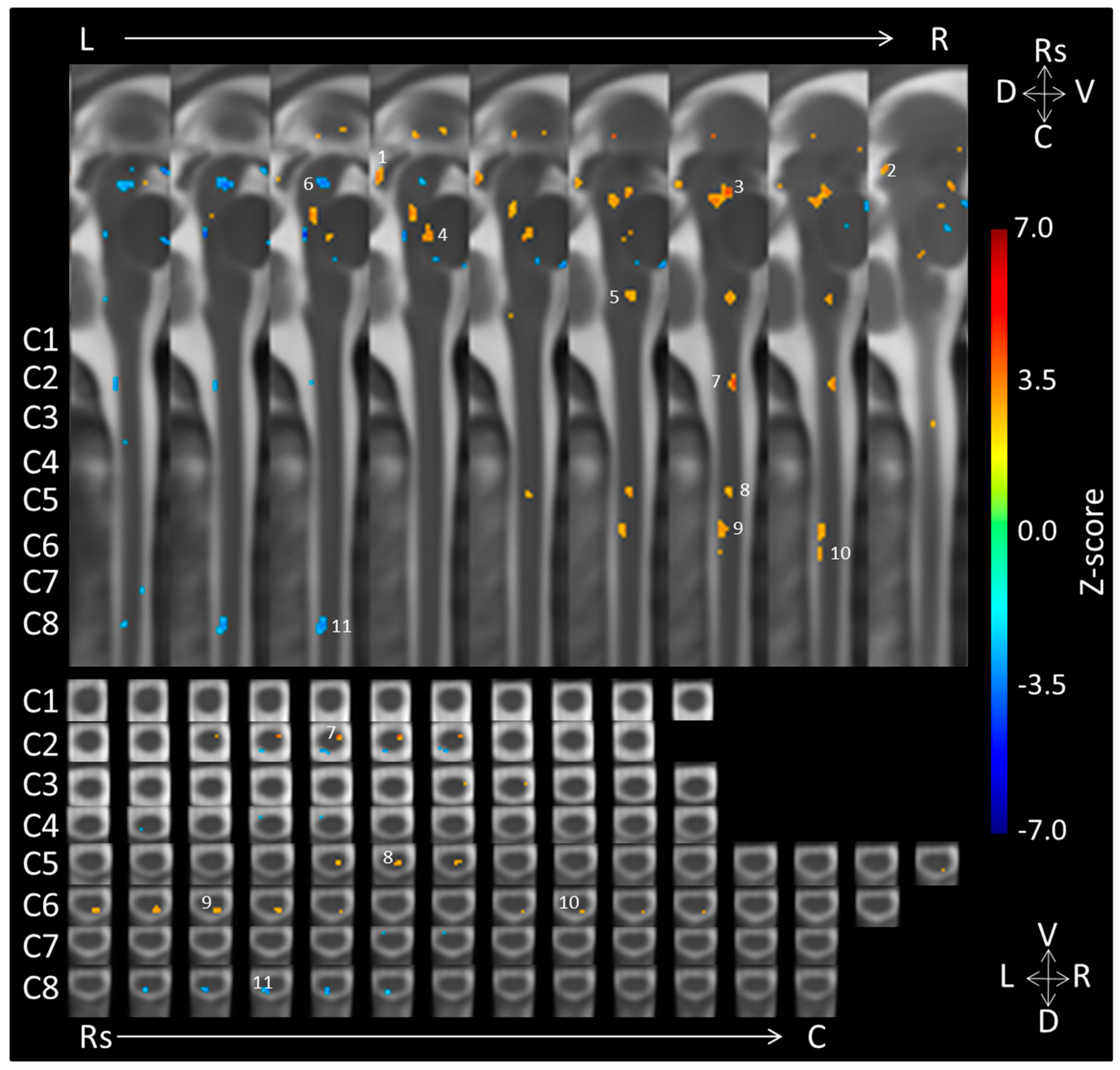
| Location | Side | Dorsal/Ventral | Coordinates (mm) | Voxels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| Negative > Neutral | ||||||
| 1. Midbrain (caudal IC) | Right | −2 | 21 | 27 | 24 | |
| 2. Midbrain (rostral IC/caudal SC) | Right | −7 | 18 | 30 | 8 | |
| 3. Midbrain (Periaqueductal Gray) | Right | Medial | −3 | 9 | 20 | 81 |
| 4. Pons | Medial | Dorsal | −1 | 6 | 10 | 23 |
| 5. Medulla | Right | Medial | −4 | 5 | −8 | 20 |
| Neutral > Negative | ||||||
| 6. Midbrain | Medial/Left | Medial | 1 | 7 | 26 | 39 |
| Location | Side | Dorsal/Ventral | Coordinates (mm) | Voxels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| Negative > Neutral | ||||||
| 7. C2 | Right | Ventral | −4 | 4 | −34 | 13 |
| 8. C5 | Right | Dorsomedial/medial | −3 | 5 | −67 | 13 |
| 9. C6 | Right | Dorsal | −4 | 7 | −78 | 26 |
| 10. C6 | Right | Dorsal | −5 | 8 | −85 | 5 |
| Neutral > Negative | ||||||
| 11. C8 | Medial/Left | Dorsal | 1 | 8 | −107 | 26 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, S.D.; Kolesar, T.A.; Kornelsen, J. Lateralized Brainstem and Cervical Spinal Cord Responses to Aversive Sounds: A Spinal fMRI Study. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8090165
Smith SD, Kolesar TA, Kornelsen J. Lateralized Brainstem and Cervical Spinal Cord Responses to Aversive Sounds: A Spinal fMRI Study. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(9):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8090165
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Stephen D., Tiffany A. Kolesar, and Jennifer Kornelsen. 2018. "Lateralized Brainstem and Cervical Spinal Cord Responses to Aversive Sounds: A Spinal fMRI Study" Brain Sciences 8, no. 9: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8090165
APA StyleSmith, S. D., Kolesar, T. A., & Kornelsen, J. (2018). Lateralized Brainstem and Cervical Spinal Cord Responses to Aversive Sounds: A Spinal fMRI Study. Brain Sciences, 8(9), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8090165




