Inhibitory Projections in the Mouse Auditory Tectothalamic System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surgery
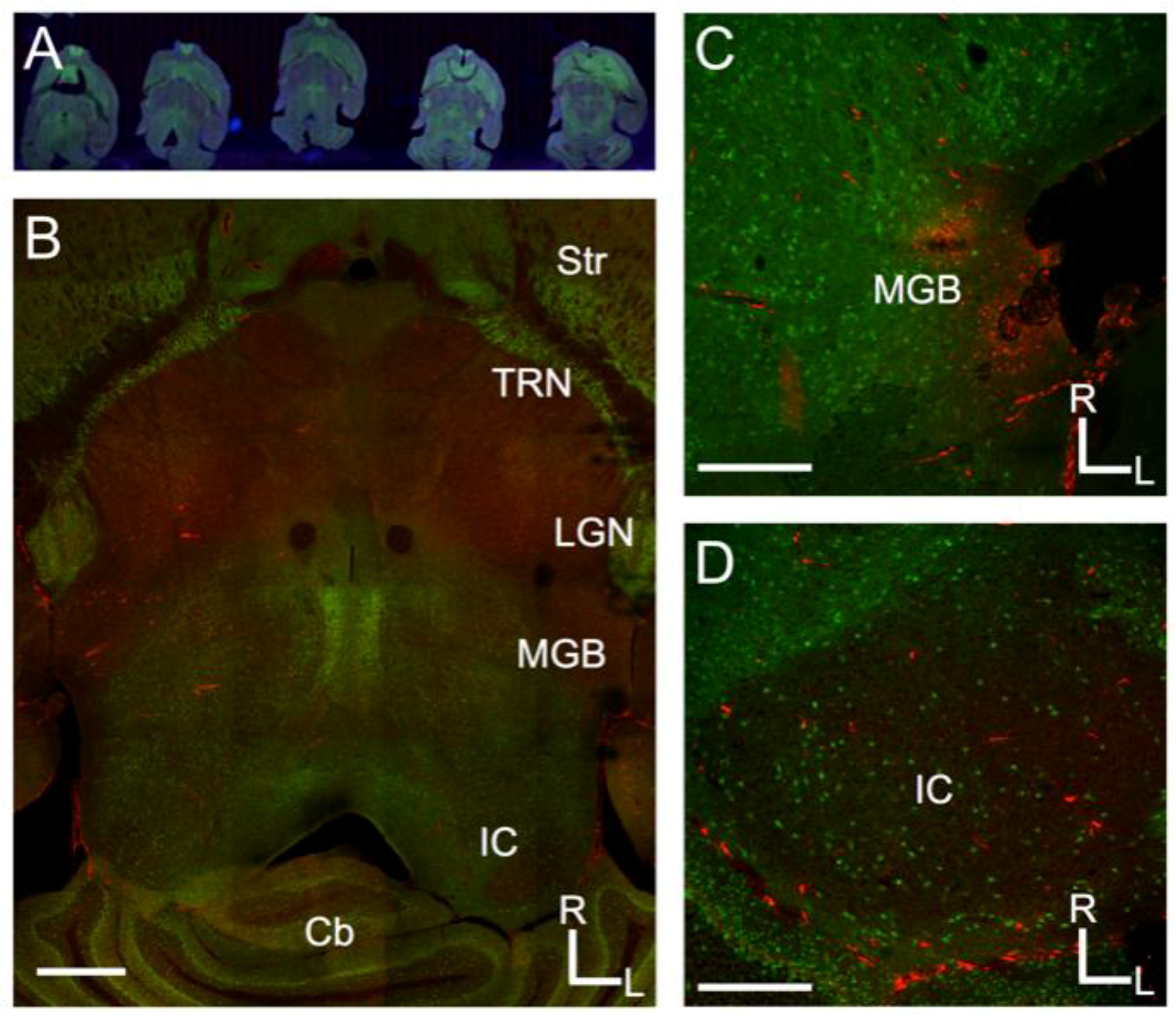
2.2. Histology and Imaging
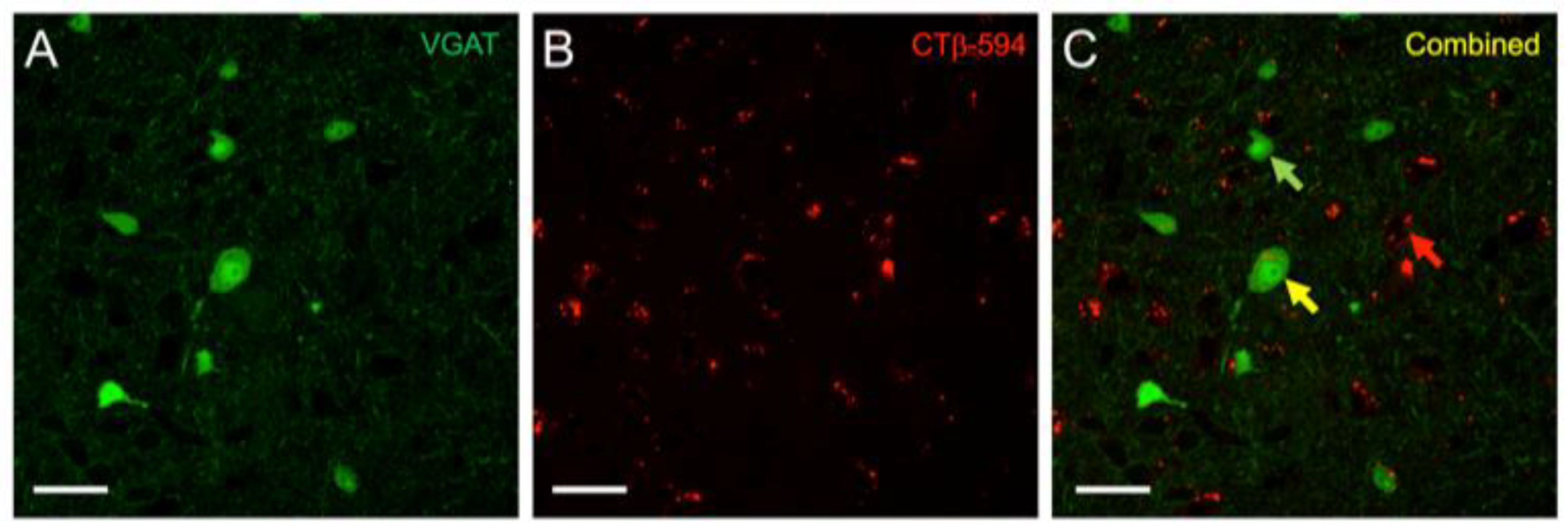
3. Results
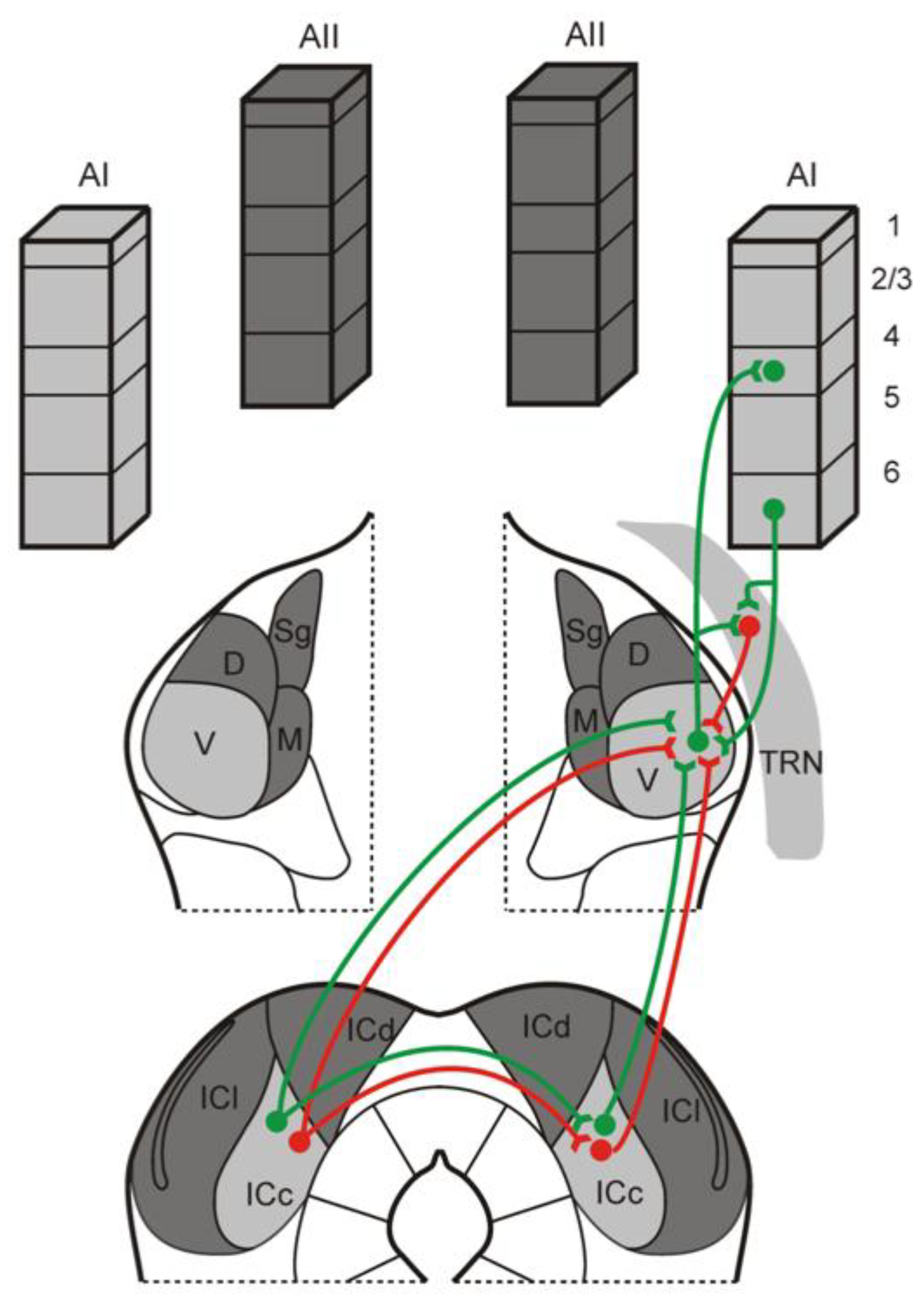
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peruzzi, D.; Bartlett, E.; Smith, P.H.; Oliver, D.L. A monosynaptic gabaergic input from the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate body in rat. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3766–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerci, W.J.; Coleman, J.R. Anatomy of the rat medial geniculate body. I. Cytoarchitecture, myeloarchitcture, and neocortical connectivity. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990, 297, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calford, M.B.; Aitkin, L.M. Ascending projections to the medial geniculate body of the cat: Evidence for multiple, parallel auditory pathways through thalamus. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 2365–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.A.; Diehl, J.J.; Larue, D.T. Projections of auditory cortex to the medial geniculate body of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 430, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenstrup, J.J. The tectothalamic system. In The Inferior Colliculus; Winer, J.A., Schreiner, C.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 200–230. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Winer, J.A. Connections of cat auditory cortex: I. Thalamocortical system. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 507, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budinger, E.; Heil, P.; Scheich, H. Functional organization of auditory cortex in the mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). IV. Connections with anatomically characterized subcortical structures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 2452–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Mothe, L.A.; Blumell, S.; Kajikawa, Y.; Hackett, T.A. Thalamic connections of the auditory cortex in marmoset monkeys: Core and medial belt regions. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 496, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Winer, J.A. Auditory thalamocortical projections in the cat: Laminar and areal patterns of input. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 427, 302–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.H.; Uhlrich, D.J.; Manning, K.A.; Banks, M.I. Thalamocortical projections to rat auditory cortex from the ventral and dorsal divisions of the medial geniculate nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizley, J.K.; Nodal, F.R.; Nelken, I.; King, A.J. Functional organization of ferret auditory cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, E.; Llano, D.A.; Sherman, S.M. Different distributions of calbindin and calretinin immunostaining across the medial and dorsal divisions of the mouse medial geniculate body. Hear. Res. 2009, 257, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.A.; Larue, D.T. Evolution of gabaergic circuitry in the mammalian medial geniculate body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3083–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Sherman, S.M. Intrinsic modulators of auditory thalamocortical transmission. Hear. Res. 2012, 287, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Imaizumi, K. Functional convergence of thalamic and intinsic inputs in cortical layers 4 and 6. Neurophysiology 2013, 45, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenstrup, J.J. Frequency organization and responses to complex sounds in the medial geniculate body of the mustached bat. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 2528–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashikawa, T.; Rausell, E.; Molinari, M.; Jones, E.G. Parvalbumin- and calbindin-containing neurons in the monkey medial geniculate complex: Differential distribution and cortical layer specific projections. Brain Res. 1991, 544, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imig, T.J.; Morel, A. Tonotopic organization in ventral nucleus of medial geniculate body in the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 1985, 53, 309–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.A. The functional architecture of the medial geniculate body and the primary auditory cortex. In Springer Handbook of Auditory Research, Volume 1, the Mammalian Auditory Pathways: Neuroanatomy; Webster, D.B., Popper, A.N., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 222–409. [Google Scholar]
- Winer, J.A. The human medial geniculate body. Hear. Res. 1984, 15, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J.E.; Ruggiero, D.A.; Reis, D.J. Projections to the subcortical forebrain from anatomically defined regions of the medial geniculate body in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 242, 182–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morest, D.K. The neuronal architecture of the medial geniculate body of the cat. J. Anat. 1964, 98, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, N.M. The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear conditioning. Hear. Res. 2011, 274, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukano, H.; Horie, M.; Ohga, S.; Takahashi, K.; Kubota, Y.; Hishida, R.; Takebayashi, H.; Shibuki, K. Reconsidering tonotopic maps in the auditory cortex and lemniscal auditory thalamus in mice. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imaizumi, K.; Lee, C.C. Frequency transformation in the auditory lemniscal thalamocortical system. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.A.; Saint Marie, R.L.; Larue, D.T.; Oliver, D.L. Gabaergic feedforward projections from the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8005–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellott, J.G.; Foster, N.L.; Ohl, A.P.; Schofield, B.R. Excitatory and inhibitory projections in parallel pathways from the inferior colliculus to the auditory thalamus. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellott, J.G.; Foster, N.L.; Nakamoto, K.T.; Motts, S.D.; Schofield, B.R. Distribution of gabaergic cells in the inferior colliculus that project to the thalamus. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Sherman, S.M. Topography and physiology of ascending streams in the auditory tectothalamic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, E.L.; Smith, P.H. Effects of paired-pulse and repetitive stimulation on neurons in the rat medial geniculate body. Neuroscience 2002, 113, 957–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Yanagawa, Y.; Imaizumi, K. Commissural functional topography of the inferior colliculus assessed in vitro. Hear Res 2015, 328, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kakizaki, T.; Sakagami, H.; Saito, K.; Ebihara, S.; Kato, M.; Hirabayashi, M.; Saito, Y.; Furuya, N.; Yanagawa, Y. Fluorescent labeling of both gabaergic and glycinergic neurons in vesicular gaba transporter (vgat)–venus transgenic mouse. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, K.B.J.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Winer, J.A. Principles governing auditory cortex connections. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Imaizumi, K.; Schreiner, C.E.; Winer, J.A. Concurrent tonotopic processing streams in auditory cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldaña, E.; Merchán, M.A. Intrinsic and commissural connections of the rat inferior colliculus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 319, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buentello, D.C.; Bishop, D.C.; Oliver, D.L. Differential distribution of gaba and glycine terminals in inferior colliculus of rat and mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Oliver, D.L. Origins of glutamatergic terminals in the inferior colliculus identified by retrograde transport and expresión of vglut1and vglut2 genes. Front. Neuroanat. 2010, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Oliver, D.L. The basic circuit of the ic: Tectothalamic neurons with different patterns of synaptic organization send different messages to the thalamus. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, E.L.; Smith, P.H. Anatomic, intrinsic, and synaptic properties of dorsal and ventral division neurons in rat medial geniculate body. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 81, 1999–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, K.L.; Longo-Guess, C.M.; Gagnon, L.H.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.J.; Johnson, K.R. Genetic background effects on age-related hearing loss associated with cdh23 variants in mice. Hear. Res. 2012, 283, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojima, H. Terminal morphology and distribution of corticothalamic fibers originating from layers 5 and 6 of cat primary auditory cortex. Cereb. Cortex 1994, 4, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, S.M.; Imaizumi, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Lee, C.C. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-labeled perineuronal nets in the mouse inferior colliculus, thalamic reticular nucleus and auditory cortex. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.W. Organization in the auditory sector of the cat’s thalamic reticular nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 390, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, D. The thalamic reticular nucleus: Structure, function and concept. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 46, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomes, D.L.; Bickford, M.E.; Schofield, B.R. Gabaergic circuitry in the dorsal division of the cat medial geniculate nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 453, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C. Thalamic and cortical pathways supporting auditory processing. Brain Lang. 2013, 126, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C. Exploring functions for the non-lemniscal auditory thalamus. Front. Neural Circuits 2015, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Sherman, S.M. Drivers and modulators in the central auditory pathways. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Sherman, S.M. On the classification of pathways in the auditory midbrain, thalamus, and cortex. Hear. Res. 2011, 276, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ipsi IC (n = 3650) | Contra IC (n = 297) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean VGAT+ retrograde cells (%) | 30 ± 2 | 36 ± 5 |
| Mean VGAT− retrograde cells (%) | 70 ± 2 | 64 ± 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clarke, B.A.; Lee, C.C. Inhibitory Projections in the Mouse Auditory Tectothalamic System. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8060103
Clarke BA, Lee CC. Inhibitory Projections in the Mouse Auditory Tectothalamic System. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(6):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8060103
Chicago/Turabian StyleClarke, Blaise A., and Charles C. Lee. 2018. "Inhibitory Projections in the Mouse Auditory Tectothalamic System" Brain Sciences 8, no. 6: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8060103
APA StyleClarke, B. A., & Lee, C. C. (2018). Inhibitory Projections in the Mouse Auditory Tectothalamic System. Brain Sciences, 8(6), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8060103





