Alterations in Motor Cortical Representation of Muscles Following Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Electromyography (EMG)
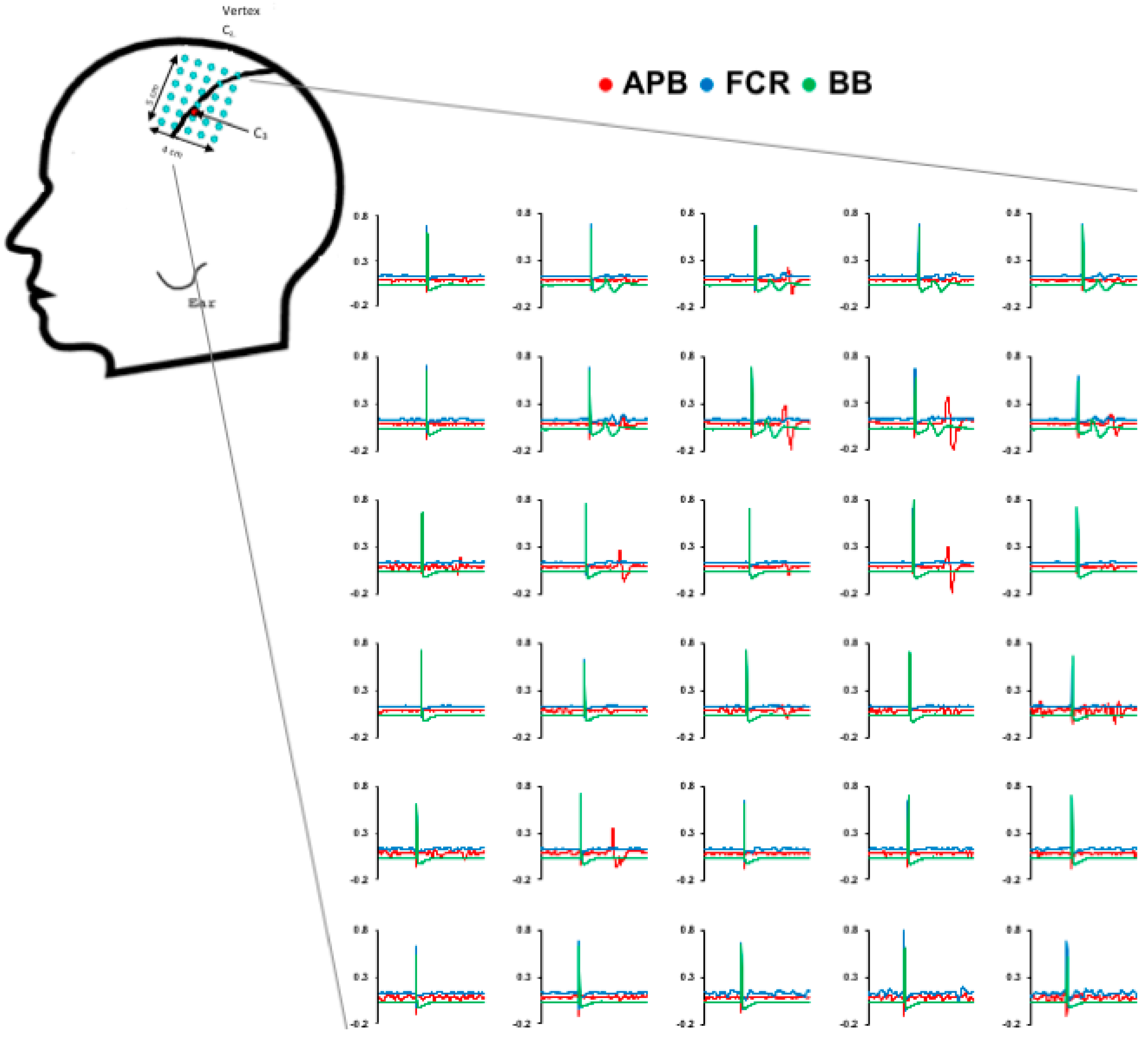
2.3. M1 Mapping Protocol
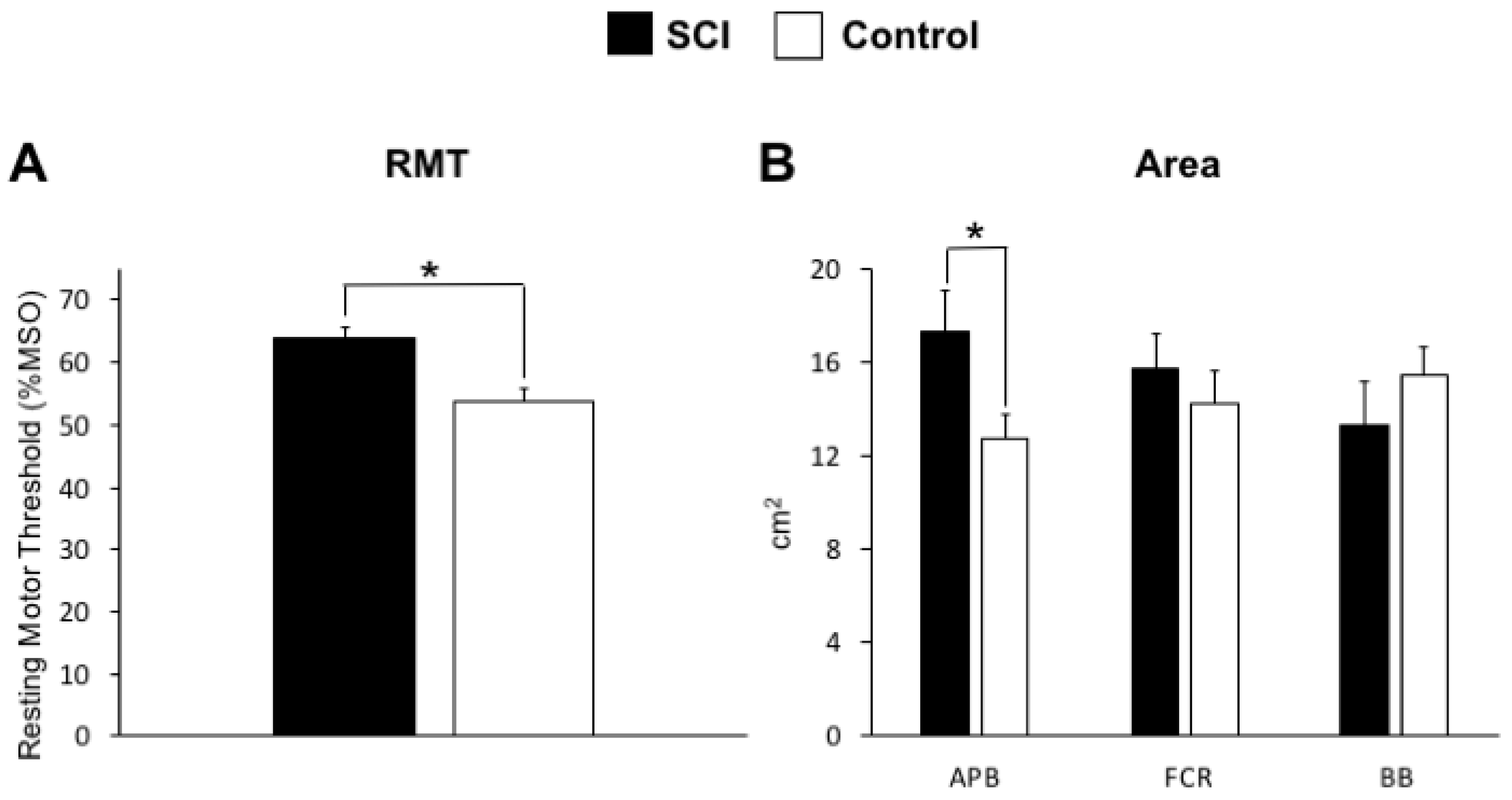
2.4. Resting Motor Threshold
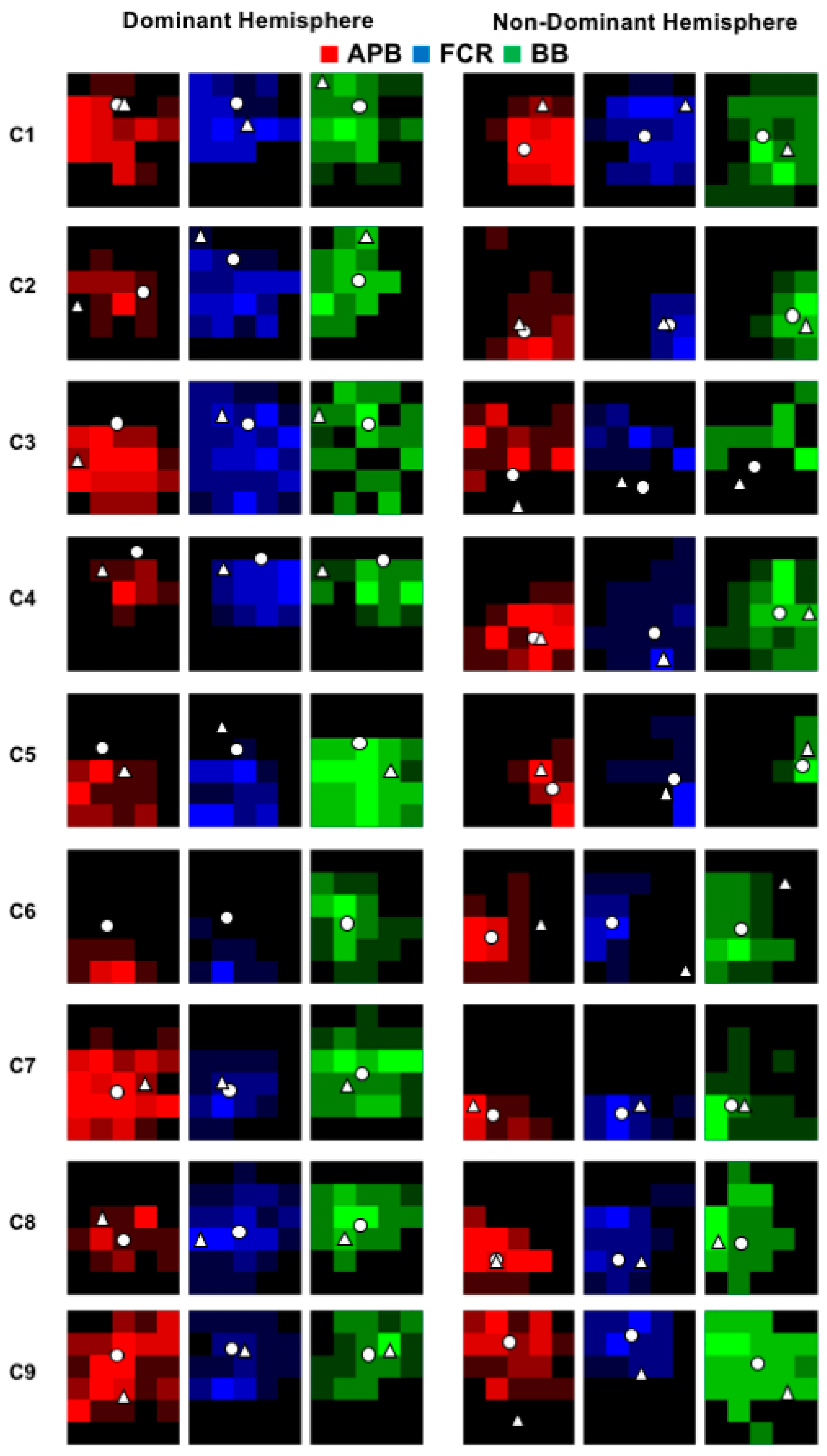
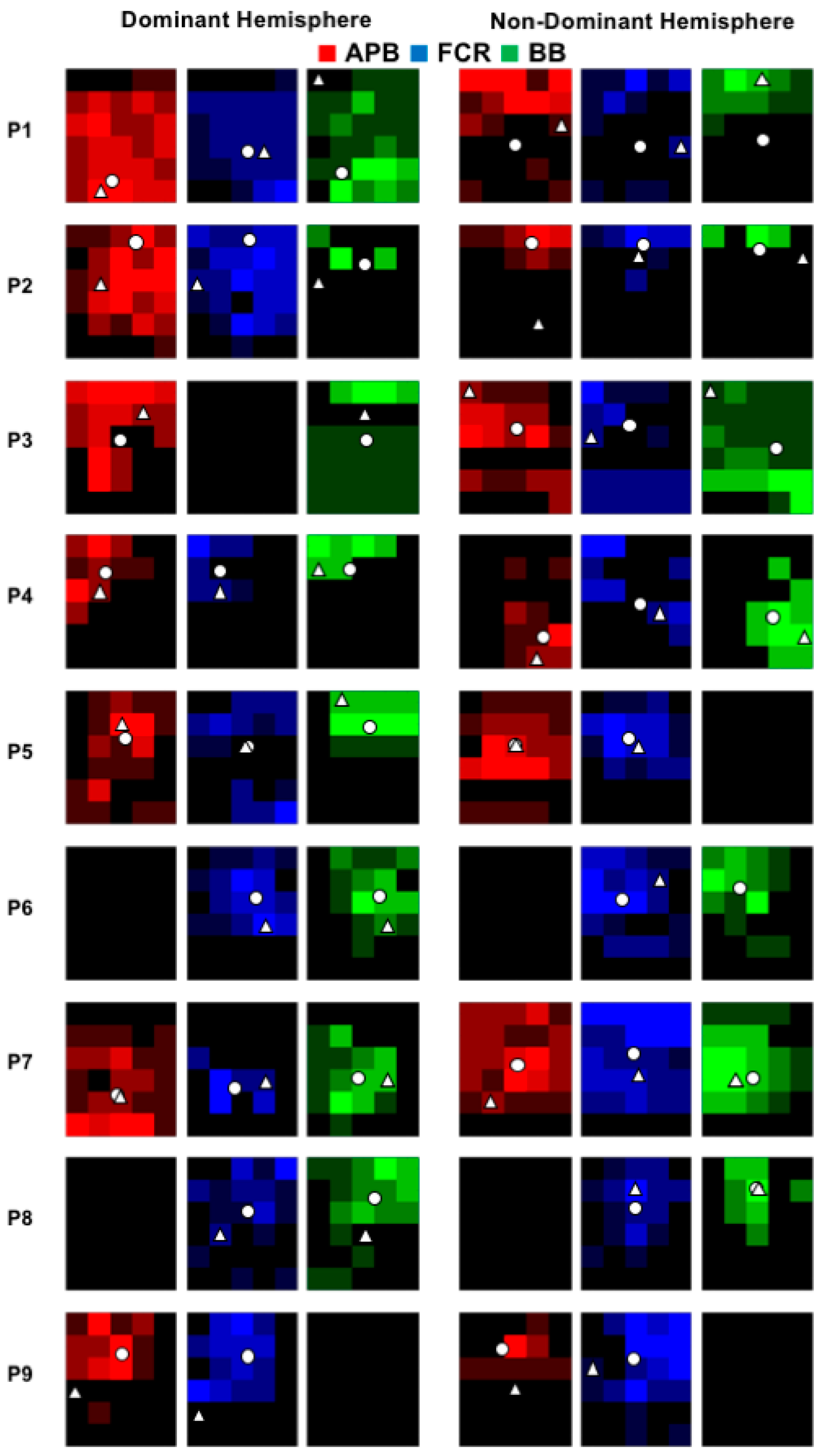
2.5. Analysis of M1 Maps
2.6. Statistical Analysis
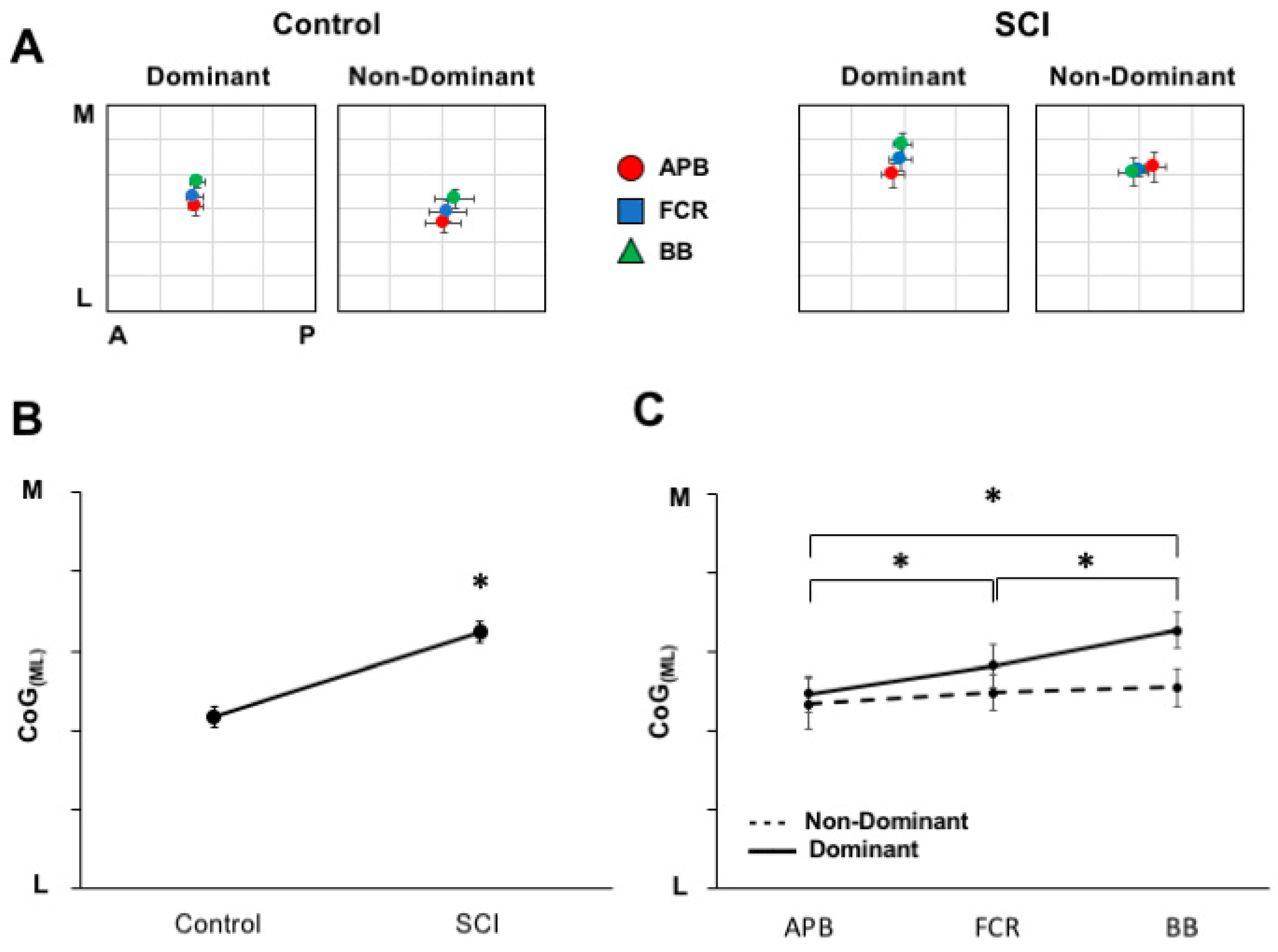
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, L.G.; Roth, B.J.; Wassermann, E.M.; Topka, H.; Fuhr, P.; Schultz, J.; Hallett, M. Magnetic stimulation of the human cerebral cortex, an indicator of reorganization in motor pathways in certain pathological conditions. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1991, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Ruit, M.; Perenboom, M.J.L.; Grey, M.J. TMS brain mapping in less than two minutes. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon, K.A.; Oliviero, A.; Aguilar, J.; Foffani, G. Cortical reorganization after spinal cord injury: Always for good? Neuroscience 2014, 283, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkiewicz, M.T.; Mikulis, D.J.; McIlroy, W.E.; Fehlings, M.G.; Verrier, M.C. Sensorimotor cortical plasticity during recovery following spinal cord injury: A longitudinal fMRI study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2007, 21, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Field-Fote, E.C. Functional and corticomotor changes in individuals with tetraplegia following unimanual or bimanual massed practice training with somatosensory stimulation: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2010, 34, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, W.J.; Amassian, V.E.; Traad, M.; Cadwell, J. Focal magnetic coil stimulation reveals motor cortical system reorganized in humans after traumatic quadriplegia. Brain Res. 1990, 510, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletz, L.J.; Belevich, J.K.; Jones, S.M.; Bhushan, A.; Shah, S.H.; Herbison, G.J. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: Cortical motor maps in acute spinal cord injury. Brain Topogr. 1995, 7, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, B.; Hopkins-Rosseel, D.H. Motor cortical mapping of proximal upper extremity muscles following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1997, 35, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, M.; Thickbroom, G.W.; Elder, J.; Rykman, A.; Valls-Sole, J.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Edwards, D.J. The corticomotor projection to liminally-contractable forearm muscles in chronic spinal cord injury: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Spinal Cord 2016, 55, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, P.; Rothwell, J.C.; Craggs, M.; Thompson, A.J.; Bestmann, S. Corticomotor representation to a human forearm muscle changes following cervical spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Thickbroom, G.W.; Mastaglia, F.L. Transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping of the motor cortex in normal subjects. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 118, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicinelli, P.; Traversa, R.; Bassi, A.; Scivoletto, G.; Rossini, P.M. Interhemispheric differences of hand muscle representation in human motor cortex. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, T.; Buchbinder, B.R.; Butler, W.E.; Chiappa, K.H.; Jiang, H.J.; Cosgrove, G.R.; Rosen, B.R. Functional magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation: Complementary approaches in the evaluation of cortical motor function. Neurology 1997, 48, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassermann, E.M.; McShane, L.M.; Hallett, M.; Cohen, L.G. Noninvasive mapping of muscle representations in human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggs, W.J.; Subramanium, B.; Rossi, F. Hand preference and transcranial magnetic stimulation asymmetry of cortical motor representation. Brain Res. 1999, 835, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.D. Targeting Recovery: Priorities of the Spinal Cord-Injured Population. J. Neurotrauma 2004, 21, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshblum, S.C.; Burns, S.P.; Biering-Sorensen, F.; Donovan, W.; Graves, D.E.; Jha, A.; Johansen, M.; Jones, L.; Krassioukov, A.; Mulcahey, M.; et al. International standards for neurological classification of spinal cord injury (Revised 2011). J. Spinal Cord Med. 2011, 34, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talairach, J.; Tournoux, P. Co-Planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain: 3-Dimensional Proportional System: An Approach to Cerebral Imaging, 1st ed.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rossini, P.M.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Ferreri, F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; George, M.S.; et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: Basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application: An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ruit, M.; Grey, M.J. The TMS Map Scales with Increased Stimulation Intensity and Muscle Activation. Brain Topogr. 2016, 29, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, J.; Ridding, M.C.; Miles, T.S. Stability of maps of human motor cortex made with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr. 2002, 14, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehlmeier, M.; Dietz, V.; Leenders, K.L.; Roelcke, U.; Missimer, J.; Curt, A. How does the human brain deal with a spinal cord injury? Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 3918–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topka, H.; Cohen, L.G.; Cole, R.A.; Hallett, M. Reorganization of corticospinal pathways following spinal cord injury. Neurology 1991, 41, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudo, R.; Milliken, G.; Jenkins, W.; Merzenich, M. Use-dependent alterations of movement representations in primary motor cortex of adult squirrel monkeys. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Cammarota, A.; Wassermann, E.M.; Brasil, N.J.; Cohen, L.G.; Hallett, M.; Pascual, L.A.; Cammarota, A.; Wassermann, E.M.; Brasil, N.J.; et al. Modulation of motor cortical outputs to the reading hand of braille readers. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Nguyet, D.; Cohen, L.G.; Brasil-Neto, J.P.; Cammarota, A.; Hallett, M. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyč, F.; Boyadjian, A.; Devanne, H. Motor cortex plasticity induced by extensive training revealed by transcranial magnetic stimulation in human. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, A.J.; Thickbroom, G.W.; Byrnes, M.L.; Mastaglia, F.L. Functional reorganisation of the corticomotor projection to the hand in skilled racquet players. Exp. Brain Res. 2000, 130, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, A.; Tamir, D.; Vakil, E.; Zeilig, G. Specific deficit in implicit motor sequence learning following spinal cord injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungu, O.; Frigon, A.; Piché, M.; Rainville, P.; Rossignol, S.; Doyon, J. Changes in Spinal Reflex Excitability Associated with Motor Sequence Learning. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, S.; Lungu, O.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Benali, H.; Doyon, J. Simultaneous brain–cervical cord fMRI reveals intrinsic spinal cord plasticity during motor sequence learning. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, J.; Calabro, F.J.; Perez, M.A. Impaired Organization of Paired-Pulse TMS-Induced I-Waves After Human Spinal Cord Injury. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penfield, W.; Boldrey, E. Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain 1937, 60, 389–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.H. Constraints on somatotopic organization in the primary motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 2125–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotze, M.; Laubis-Herrmann, U.; Topka, H.; Erb, M.; Grodd, W. Reorganization in the Primary Motor Cortex after Spinal Cord Injury—A functional Magnetic Resonance (fMRI) Study. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 1999, 14, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amunts, K.; Jäncke, L.; Mohlberg, H.; Steinmetz, H.; Zilles, K. Interhemispheric asymmetry of the human motor cortex related to handedness and gender. Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, J.; Schnitzler, A.; Witte, O.W.; Freund, H. Handedness and asymmetry of hand representation in human motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, A.; Gut, M.; Binder, M.; Forsberg, L.; Rymarczyk, K.; Urbanik, A. Switching handedness: fMRI study of hand motor control in right-handers, left-handers and converted left-handers. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars). 2012, 72, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Turco, C.V.; El-Sayes, J.; Locke, M.B.; Chen, R.; Baker, S.; Nelson, A.J. Effects of lorazepam and baclofen on short- and long-latency afferent inhibition. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 5267–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.N.; Orekhov, Y.; Ziemann, U. The role of GABAB receptors in intracortical inhibition in the human motor cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sub | Years Since Injury | Injury Level | ASIA Score | Handedness (SCI) | Medications | Control Sub | Handedness (Controls) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.5 | C5–C6 | C | L * | Fesoterodine | 1 | R |
| 2 | 2 | C6–C7 | C | L | Diazepam, preganalin, cyclobenzaprine | 9 | L |
| 3 | 39 | C5 | C | R | None | 3 | R |
| 4 | 14 | C6–C7 | C | R | Baclofen | 4 | R |
| 5 | 17 | C4–C8 | C | R | Botulinum toxin, Percocet | 7 | R |
| 6 | 3 | C4 | C | R | Baclofen, pregabalin | 6 | R |
| 7 | 2 | C3–C4 | C | R | Gabapentin, citalopram | 8 | R |
| 8 | 33 | C6–C7 | C | R | Baclofen, clonazepam | 4 | R |
| 9 | 3 | C5 | C | R | None | 5 | R |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fassett, H.J.; Turco, C.V.; El-Sayes, J.; Nelson, A.J. Alterations in Motor Cortical Representation of Muscles Following Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Humans. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120225
Fassett HJ, Turco CV, El-Sayes J, Nelson AJ. Alterations in Motor Cortical Representation of Muscles Following Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Humans. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(12):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120225
Chicago/Turabian StyleFassett, Hunter J., Claudia V. Turco, Jenin El-Sayes, and Aimee J. Nelson. 2018. "Alterations in Motor Cortical Representation of Muscles Following Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Humans" Brain Sciences 8, no. 12: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120225
APA StyleFassett, H. J., Turco, C. V., El-Sayes, J., & Nelson, A. J. (2018). Alterations in Motor Cortical Representation of Muscles Following Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Humans. Brain Sciences, 8(12), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120225




