Decreased Neuron Density and Increased Glia Density in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (Brodmann Area 25) in Williams Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Brain Tissue
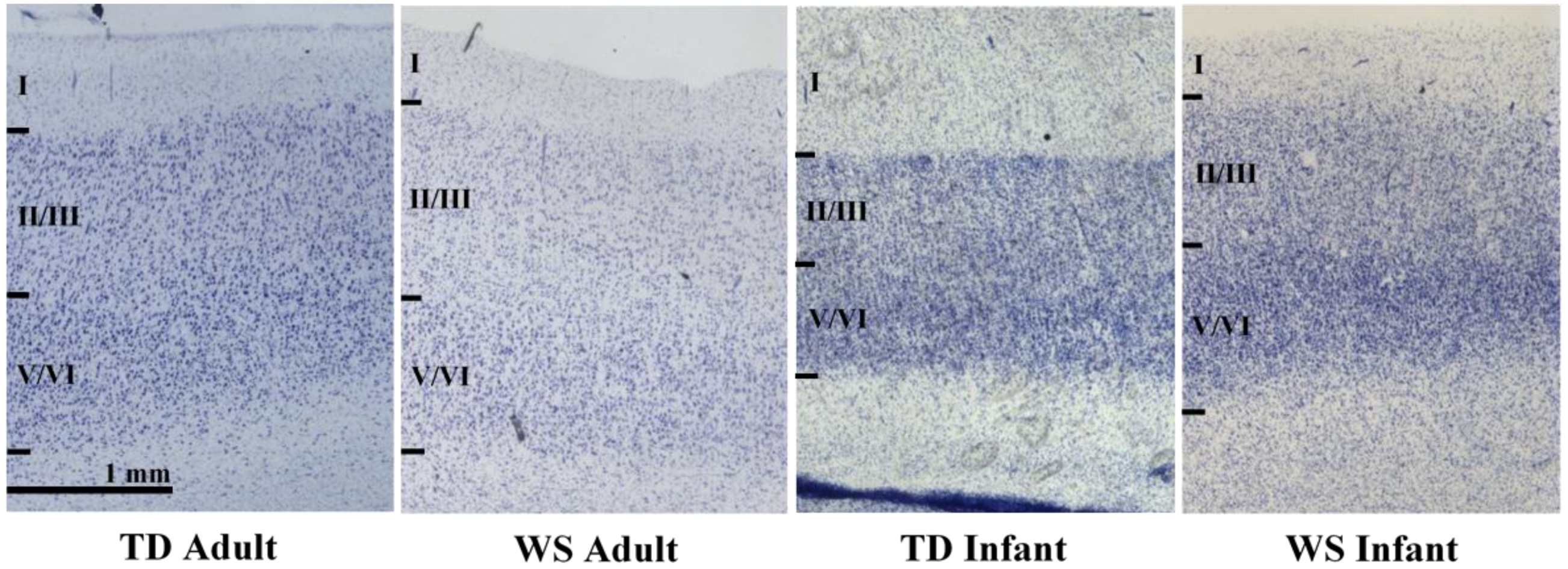
2.2. Regions of Interest
2.3. Processing of Tissue
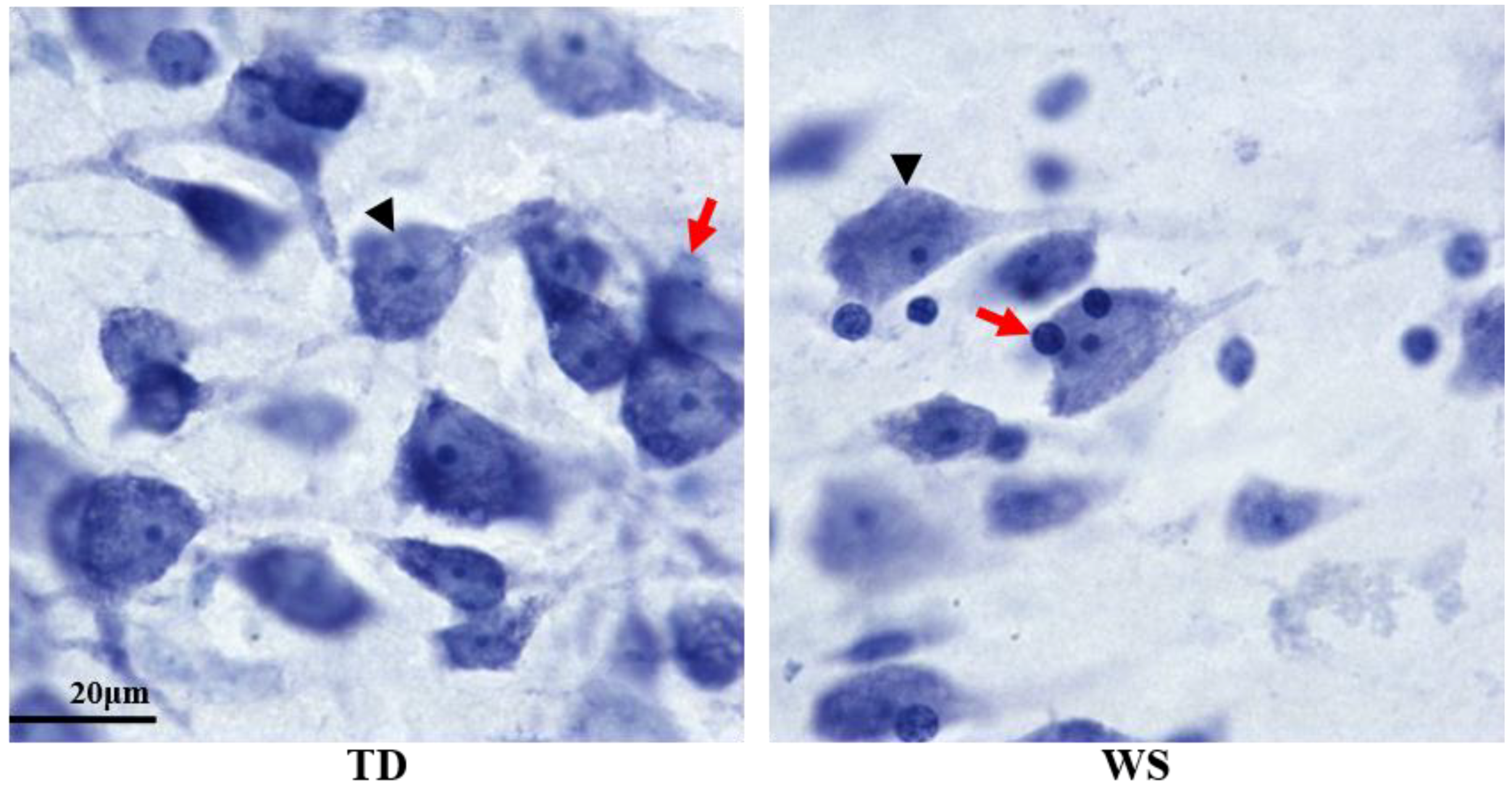
2.4. Unbiased, Design-Based Stereology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
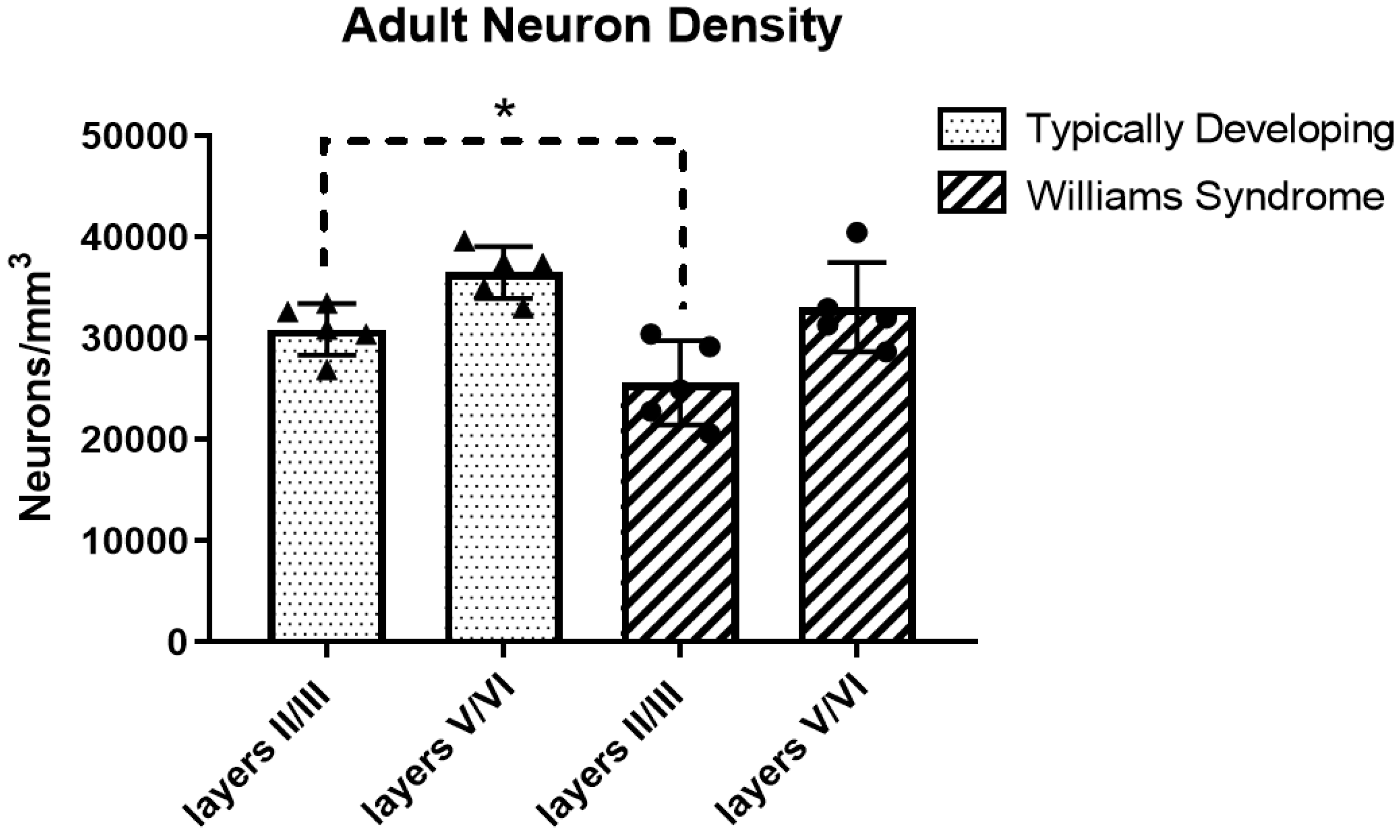
3.1. Adult Neuron Density
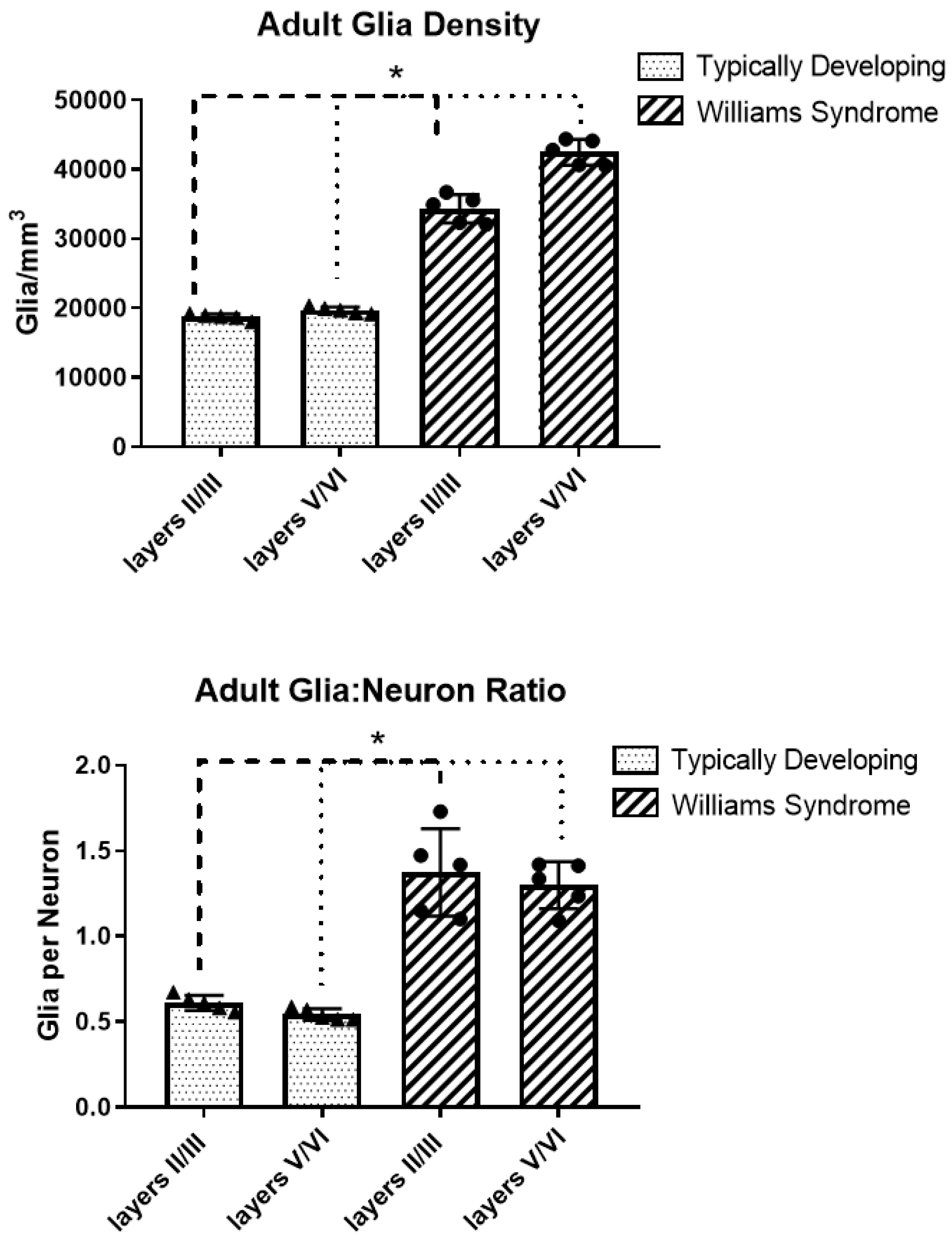
3.2. Adult Glia Density and Glia to Neuron Ratio
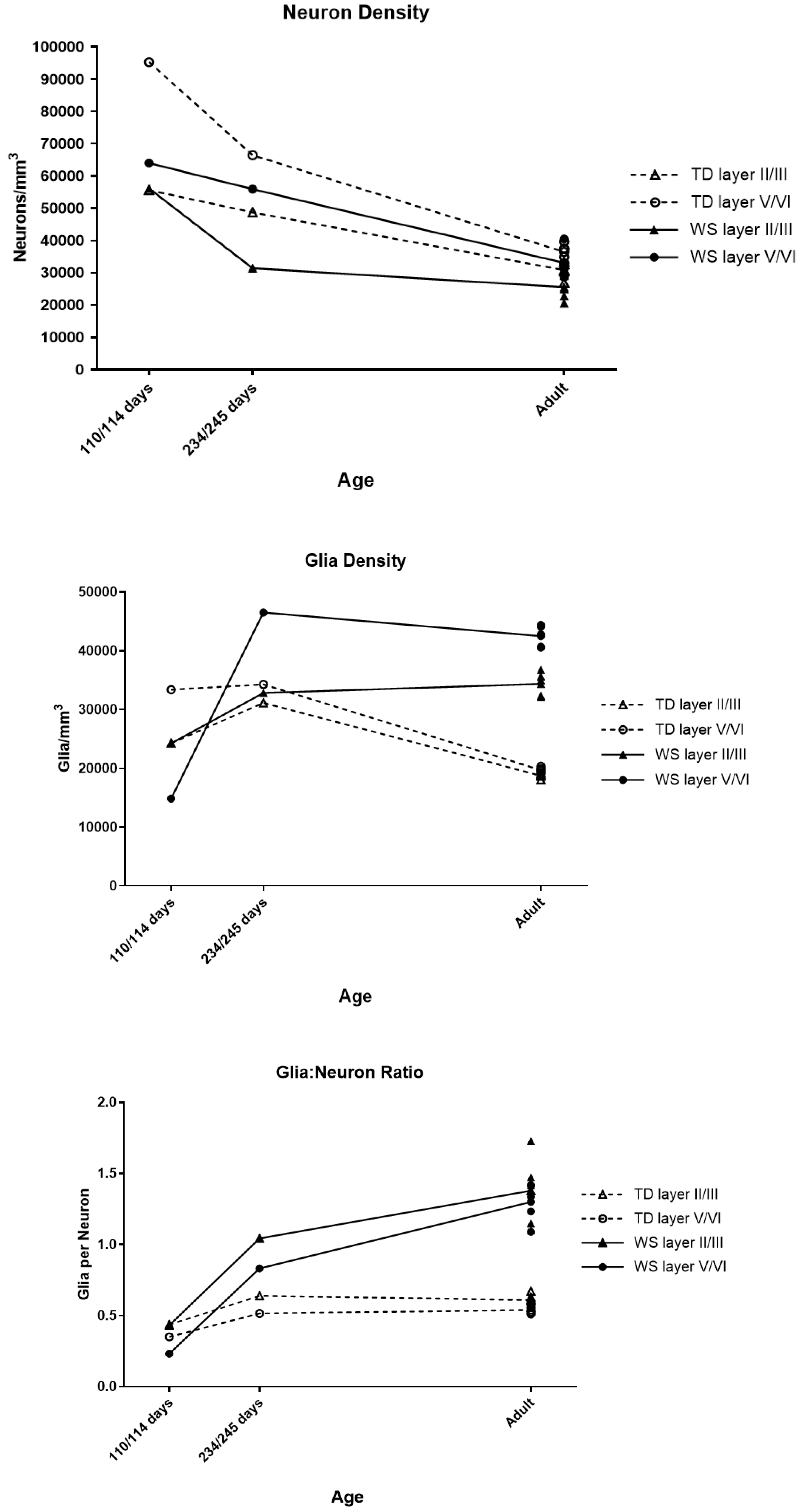
3.3. Infant Neuron Density, Glia Density, and Glia to Neuron Ratio
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strømme, P.; Bjømstad, P.G.; Ramstad, K. Prevalence Estimation of Williams Syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2002, 17, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellugi, U.; Lichtenberger, L.; Jones, W.; Lai, Z.; St. George, M.I. The Neurocognitive Profile of Williams Syndrome: A Complex Pattern of Strengths and Weaknesses. J Cognit. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Thomas, M.; Annaz, D.; Humphreys, K.; Ewing, S.; Brace, N.; Duuren, M.V.; Pike, G.; Grice, S.; Campbell, R. Exploring the Williams syndrome face-processing debate: The importance of building developmental trajectories. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 1258–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, T.F.; Bellugi, U.; Korenberg, J.R.; Graham, J. “Everybody in the world is my friend” hypersociability in young children with Williams syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2004, 124A, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Tasman, B.P.; Mervis, C.B. Distinctive Personality Characteristics of 8-, 9-, and 10-Year-Olds with Williams Syndrome. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2003, 23, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geschwind, D.H. Genetics of autism spectrum disorders. Trends Cognit. Sci. 2011, 15, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miles, J.H. Autism spectrum disorders—A genetics review. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merla, G.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Micale, L.; Fusco, C. Copy number variants at Williams–Beuren syndrome 7q11.23 region. Human Genet. 2010, 128, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.C.; Brown, T.T.; Bartsch, H.; Kuperman, J.M.; Hagler, D.J.; Schork, A.; Searcy, Y.; Bellugi, U.; Halgren, E.; Dale, A.M. Williams syndrome-specific neuroanatomical profile and its associations with behavioral features. NeuroImage: Clin. 2017, 15, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meda, S.A.; Pryweller, J.R.; Thornton-Wells, T.A. Regional Brain Differences in Cortical Thickness, Surface Area and Subcortical Volume in Individuals with Williams Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, A.L.; Eckert, M.A.; Rose, F.E.; Karchemskiy, A.; Kesler, S.; Chang, M.; Reynolds, M.F.; Kwon, H.; Galaburda, A. An Experiment of Nature: Brain Anatomy Parallels Cognition and Behavior in Williams Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 5009–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mobbs, D.; Eckert, M.A.; Mills, D.; Korenberg, J.; Bellugi, U.; Galaburda, A.M.; Reiss, A.L. Frontostriatal Dysfunction During Response Inhibition in Williams Syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, W.; Bellugi, U.; Lai, Z.; Chiles, M.; Reilly, J.; Lincoln, A.; Adolphs, R. II. Hypersociability in Williams Syndrome. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.A.; Coltheart, M.; Langdon, R. The neuropsychological basis of hypersociability in Williams and Down syndrome. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Hariri, A.R.; Munoz, K.E.; Mervis, C.B.; Mattay, V.S.; Morris, C.A.; Berman, K.F. Neural correlates of genetically abnormal social cognition in Williams syndrome. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, R.; Brown, T.T.; Järvinen, A.M.; Erhart, M.; Korenberg, J.R.; Bellugi, U.; Halgren, E. Structural integrity of the limbic–prefrontal connection: Neuropathological correlates of anxiety in Williams syndrome. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, C.H.; Brown, C.; Bellugi, U.; Semendeferi, K. Neuron density is decreased in the prefrontal cortex in Williams syndrome. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, K.L.; Lew, C.H.; Hrvoj-Mihic, B.; Groeniger, K.M.; Halgren, E.; Bellugi, U.; Semendeferi, K. Increased glia density in the caudate nucleus in williams syndrome: Implications for frontostriatal dysfunction in autism. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferry, A.T.; Öngür, D.; An, X.; Price, J.L. Prefrontal cortical projections to the striatum in macaque monkeys: Evidence for an organization related to prefrontal networks. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 425, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, C.H.; Groeniger, K.M.; Bellugi, U.; Stefanacci, L.; Schumann, C.M.; Semendeferi, K. A postmortem stereological study of the amygdala in Williams syndrome. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, C.C.; Fehr, E. The neurobiology of rewards and values in social decision making. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbas, H.; Zikopoulos, B. Sequential and parallel circuits for emotional processing in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Orbitofront. Cortex 2006, 1, 57–93. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, C.M.; Amaral, D.G. Stereological Analysis of Amygdala Neuron Number in Autism. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7674–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, J.T.; Barger, N.; Amaral, D.G.; Schumann, C.M. Stereological Study of Amygdala Glial Populations in Adolescents and Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentería, M.E. Cerebral Asymmetry: A Quantitative, Multifactorial, and Plastic Brain Phenotype. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2012, 15, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zilles, K.; Schleicher, A.; Langemann, C.; Amunts, K.; Morosan, P.; Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Schormann, T.; Mohlberg, H.; Bürgel, U.; Steinmetz, H.; et al. Quantitative analysis of sulci in the human cerebral cortex: Development, regional heterogeneity, gender difference, asymmetry, intersubject variability and cortical architecture. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1997, 5, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öngür, D.; Ferry, A.T.; Price, J.L. Architectonic subdivision of the human orbital and medial prefrontal cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 460, 425–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombrowski, S.M.; Hilgetag, C.C.; Barbas, H. Quantitative Architecture Distinguishes Prefrontal Cortical Systems in the Rhesus Monkey. Cereb. Cortex 2001, 11, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benes, F.M.; Davidson, J.; Bird, E.D. Quantitative Cytoarchitectural Studies of the Cerebral Cortex of Schizophrenics. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1986, 43, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oblak, A.L.; Rosene, D.L.; Kemper, T.L.; Bauman, M.L.; Blatt, G.J. Altered posterior cingulate cortical cyctoarchitecture, but normal density of neurons and interneurons in the posterior cingulate cortex and fusiform gyrus in autism. Autism Res. 2011, 4, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smiley, J.F.; Konnova, K.; Bleiwas, C. Cortical thickness, neuron density and size in the inferior parietal lobe in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 136, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cabezas, M.Á.; John, Y.J.; Barbas, H.; Zikopoulos, B. Distinction of Neurons, Glia and Endothelial Cells in the Cerebral Cortex: An Algorithm Based on Cytological Features. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, S.; Petrides, M. Quantitative demonstration of comparable architectonic areas within the ventromedial and lateral orbital frontal cortex in the human and the macaque monkey brains. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, S.; Petrides, M. Architecture and morphology of the human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 2777–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenlocher, P.R. Morphometric study of human cerebral cortex development. Neuropsychologia 1990, 28, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrvoj-Mihic, B.; Hanson, K.L.; Lew, C.H.; Stefanacci, L.; Jacobs, B.; Bellugi, U.; Semendeferi, K. Basal Dendritic Morphology of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons in Williams Syndrome: Prefrontal Cortex and Beyond. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chailangkarn, T.; Trujillo, C.A.; Freitas, B.C.; Hrvoj-Mihic, B.; Herai, R.H.; Yu, D.X.; Brown, T.T.; Marchetto, M.C.; Bardy, C.; McHenry, L.; et al. A human neurodevelopmental model for Williams syndrome. Nature 2016, 536, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitew, S.; Hay, C.M.; Peckham, H.; Xiao, J.; Koenning, M.; Emery, B. Mechanisms regulating the development of oligodendrocytes and central nervous system myelin. Neuroscience 2014, 276, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Dorr, N.P.; Takahashi, N.; McInnes, L.A.; Elder, G.A.; Buxbaum, J.D. Haploinsufficiency of Gtf2i, a gene deleted in Williams Syndrome, leads to increases in social interactions. Autism Res. 2011, 4, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, O.A.; Fuentealba, L.C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Rowitch, D.H. Astrocyte Development and Heterogeneity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molofsky, A.V.; Krenick, R.; Ullian, E.; Tsai, H.; Deneen, B.; Richardson, W.D.; Barres, B.A.; Rowitch, D.H. Astrocytes and disease: A neurodevelopmental perspective. Genes. Dev. 2012, 26, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Pucci, L.; Bezzi, P. Astrocytes and Microglia and Their Potential Link with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Mechanisms of astrocyte development and their contributions to neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 27, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, Y.; Paolicelli, R.C.; Sforazzini, F.; Weinhard, L.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Vyssotski, A.L.; Bifone, A.; Gozzi, A.; Ragozzino, D.; et al. Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Wei, J.; Dilley, G.; Pittman, S.D.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Overholser, J.C.; Roth, B.L.; Stockmeier, C.A. Morphometric evidence for neuronal and glial prefrontal cell pathology in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.T.; Chana, G.; Pardo, C.A.; Achim, C.; Semendeferi, K.; Buckwalter, J.; Courchesne, E.; Everall, I.P. Microglial Activation and Increased Microglial Density Observed in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garey, L. When cortical development goes wrong: Schizophrenia as a neurodevelopmental disease of microcircuits. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessaris, N.; Fogarty, M.; Iannarelli, P.; Grist, M.; Wegner, M.; Richardson, W.D. Competing waves of oligodendrocytes in the forebrain and postnatal elimination of an embryonic lineage. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Mayer-Proschel, M.; Rao, M.S. Gliogenesis in the central nervous system. Glia 2000, 30, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orentas, D.M.; Miller, R.H. Regulation of oligodendrocyte development. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998, 18, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homem, C.C.F.; Repic, M.; Knoblich, J.A. Proliferation control in neural stem and progenitor cells. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohwi, M.; Doe, C.Q. Temporal fate specification and neural progenitor competence during development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, Q.; Yang, C.-P.; Liu, Z.; Sugino, K.; Mok, K.; He, Y.; Ito, M.; Nern, A.; Otsuna, H.; Lee, T. Stem Cell-Intrinsic, Seven-up-Triggered Temporal Factor Gradients Diversify Intermediate Neural Progenitors. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.I.; Kern, J.K. Evidence of microglial activation in autism and its possible role in brain underconnectivity. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011, 7, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courchesne, E.; Mouton, P.R.; Calhoun, M.E.; Semendeferi, K.; Ahrens-Barbeau, C.; Hallet, M.J.; Barnes, C.C.; Pierce, K. Neuron Number and Size in Prefrontal Cortex of Children with Autism. JAMA 2011, 306, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnea-Goraly, N.; Kwon, H.; Menon, V.; Eliez, S.; Lotspeich, L.; Reiss, A.L. White matter structure in autism: Preliminary evidence from diffusion tensor imaging. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 55, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, A.; Choi, E.Y.; Jones, R.M.; Castellanos, F.X.; Mukerji, A. Imaging the Striatum in Autism Spectrum Disorder; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Monk, C.S.; Weng, S.-J.; Wiggins, J.L.; Kurapati, N.; Louro, H.M.C.; Carrasco, M.; Maslowsky, J.; Risi, S.; Lord, C. Neural circuitry of emotional face processing in autism spectrum disorders. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010, 35, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Subject | Age at Death | Sex | Hemisphere | PMI (h) | Cause of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS 7 | 114 days | M | R | <30 | Multiorgan failure |
| TD 5883 | 110 days | M | R | 34 | Sudden unexplained death in infancy |
| WS 2 | 245 days | F | R | N/A | Sudden infant death syndrome |
| TD 4392 | 234 days | F | R | 13 | Intussuseption of Meckel’s diverticulum |
| WS 10 | 18 years | M | R | 24 | Cardiac complications |
| TD 4916 | 19 years | M | R | 5 | Drowning |
| WS 15 | 24 years | F | R | 20 | Pneumonia, Sepsis |
| TD 5350 | 25 years | F | R | 26 | Sepsis |
| WS 1 | 31 years | M | R | 26 | Cardiac complications |
| TD 5539 | 31 years | M | R | 24 | Acute drug intoxication |
| WS 14 | 42 years | F | R | 18 | Cardiac complications |
| TD 5445 | 42 years | F | R | 10 | Pulmonary thromboembolism |
| WS 9 | 43 years | F | R | 12 | Cardiac complications |
| TD 4636 | 43 years | F | R | 19 | Pulmonary thromboembolism |
| Cortical Layers | II/III | V/VI |
|---|---|---|
| TD | 30,882 ± 2537 | 36,506 ± 2567 |
| WS | 25,594 ± 4157 | 33,094 ± 4417 |
| % Difference | −17% | −9% |
| Cortical Layers | II/III | V/VI |
|---|---|---|
| TD | 18,756 ± 426 | 19,721 ± 465 |
| WS | 34,355 ± 2038 | 42,510 ± 1844 |
| % Difference | +83% | +116% |
| Cortical Layers | II/III | V/VI |
|---|---|---|
| TD | 0.61 | 0.54 |
| WS | 1.38 | 1.30 |
| % Difference | +125% | +140% |
| Age | Layer | Neuron Density | Glia Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 months | II/III | No difference | No difference |
| V/VI | 33% Lower | 16% Lower | |
| 8 months | II/III | 35% Lower | 5% Higher |
| V/VI | 16% Lower | 16% Higher | |
| Adult | II/III | 17% Lower * | 83% Higher * |
| V/VI | 9% Lower | 116% Higher * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilder, L.; Hanson, K.L.; Lew, C.H.; Bellugi, U.; Semendeferi, K. Decreased Neuron Density and Increased Glia Density in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (Brodmann Area 25) in Williams Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120209
Wilder L, Hanson KL, Lew CH, Bellugi U, Semendeferi K. Decreased Neuron Density and Increased Glia Density in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (Brodmann Area 25) in Williams Syndrome. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(12):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120209
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilder, Linnea, Kari L. Hanson, Caroline H. Lew, Ursula Bellugi, and Katerina Semendeferi. 2018. "Decreased Neuron Density and Increased Glia Density in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (Brodmann Area 25) in Williams Syndrome" Brain Sciences 8, no. 12: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120209
APA StyleWilder, L., Hanson, K. L., Lew, C. H., Bellugi, U., & Semendeferi, K. (2018). Decreased Neuron Density and Increased Glia Density in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (Brodmann Area 25) in Williams Syndrome. Brain Sciences, 8(12), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120209




