Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
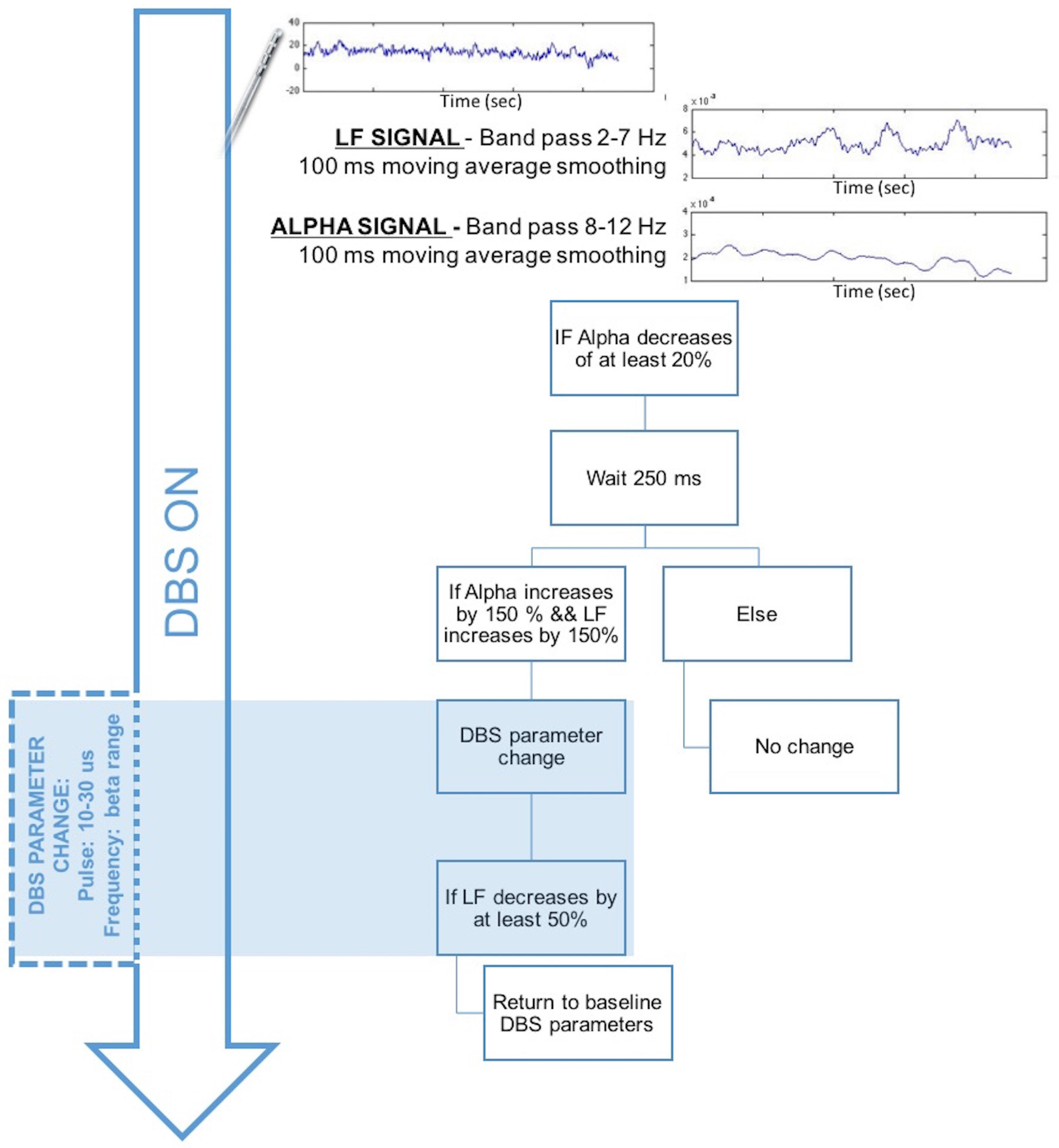
2. The LFP-Based aDBS Concept
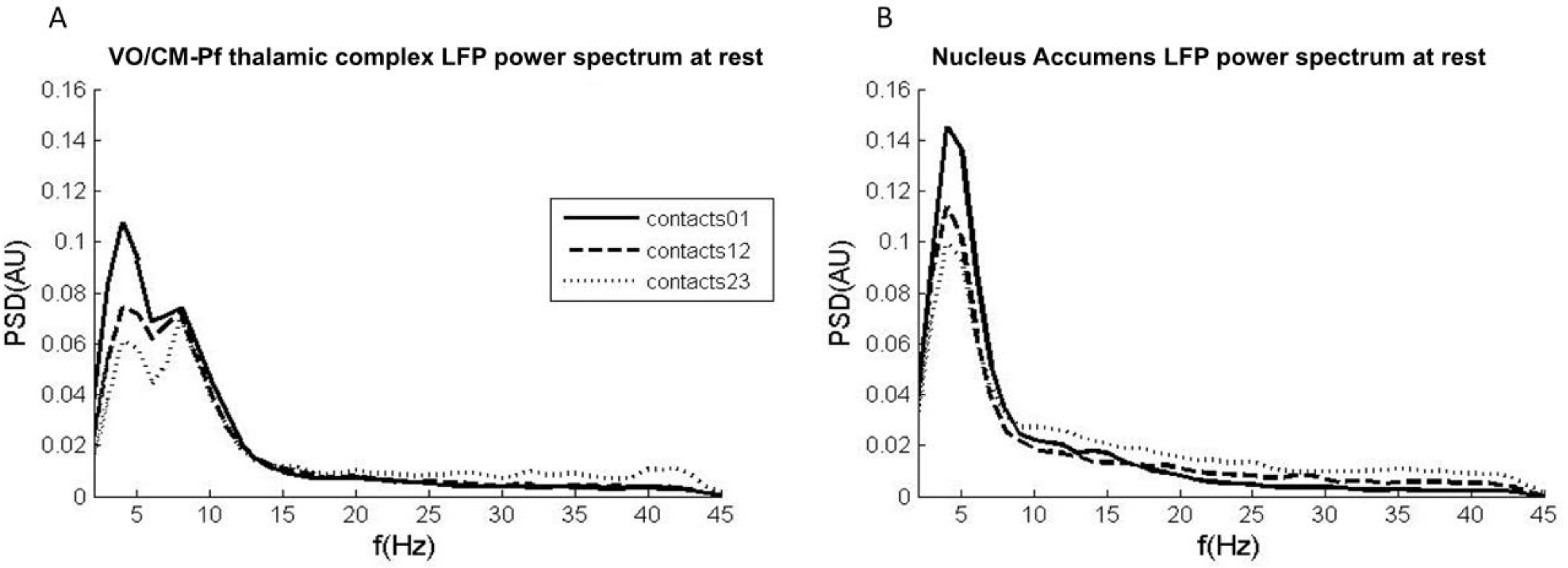
2.1. Experiment 1: LFPs in Tourette Syndrome at Rest
2.1.1. Methods and Participants
2.1.2. Results
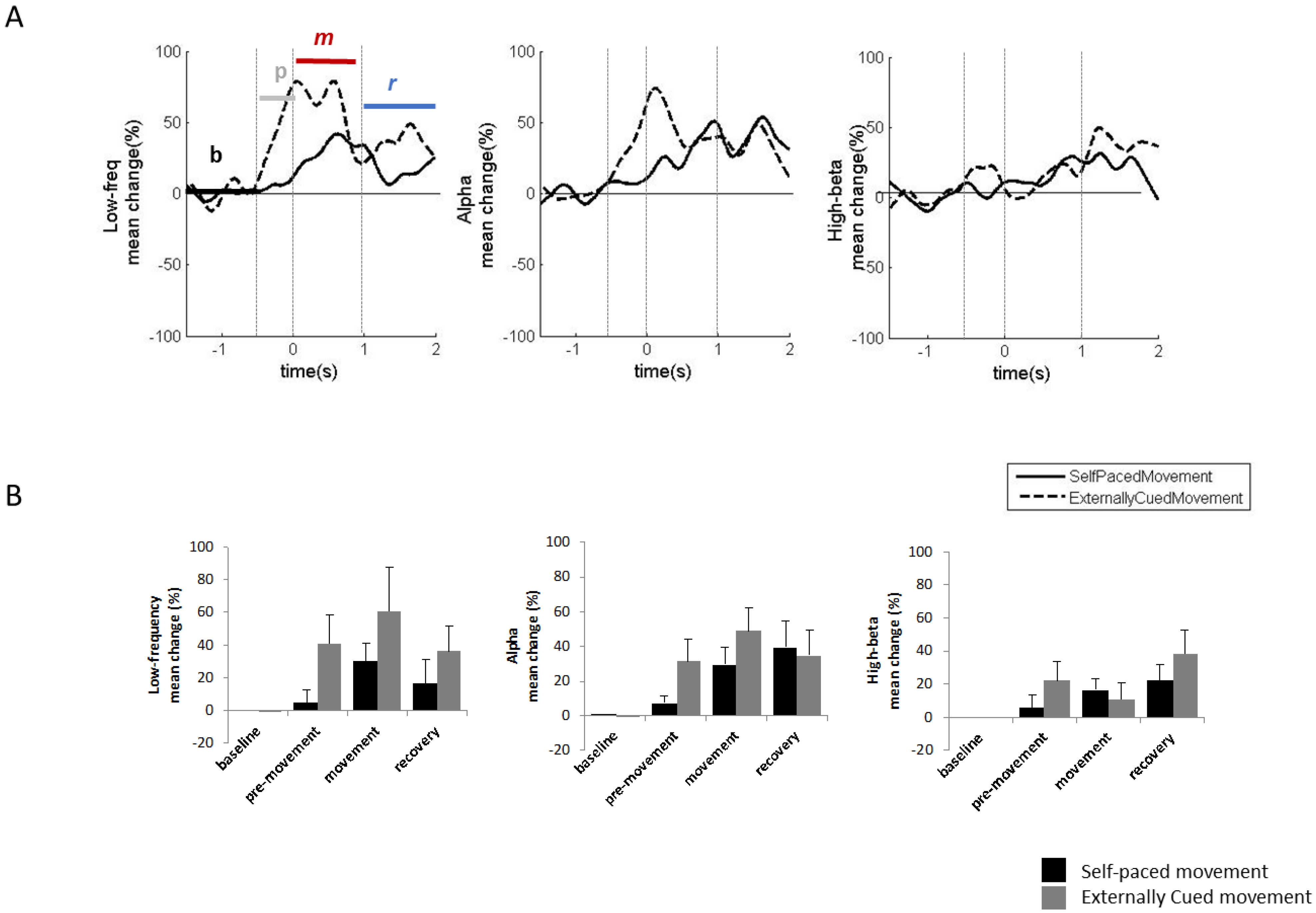
2.2. Experiment 2: LFPs in Tourette Syndrome during Voluntary Movements
2.2.1. Methods and Participants
2.2.2. Results
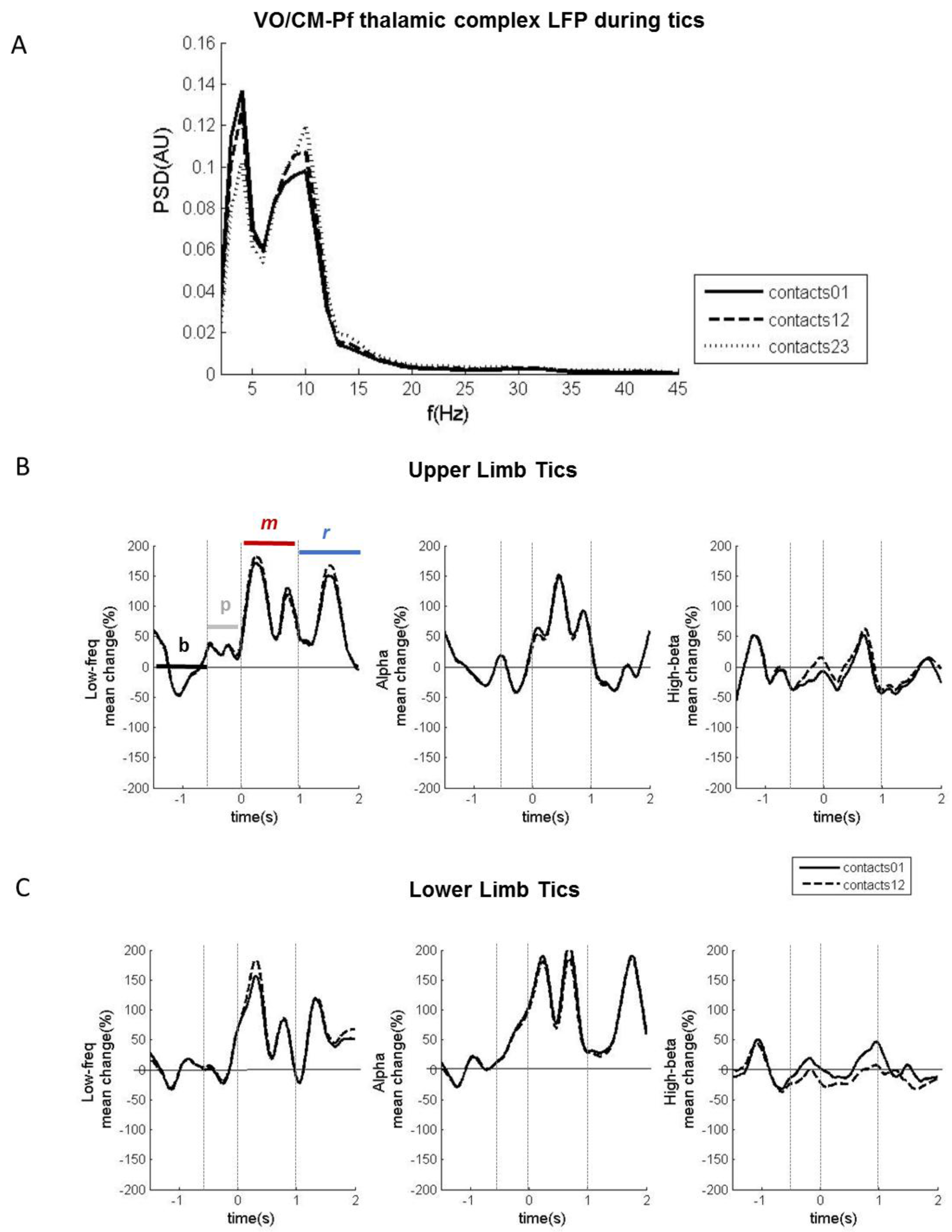
2.3. Experiment 3: LFPs during Involuntary Movements
2.3.1. Results
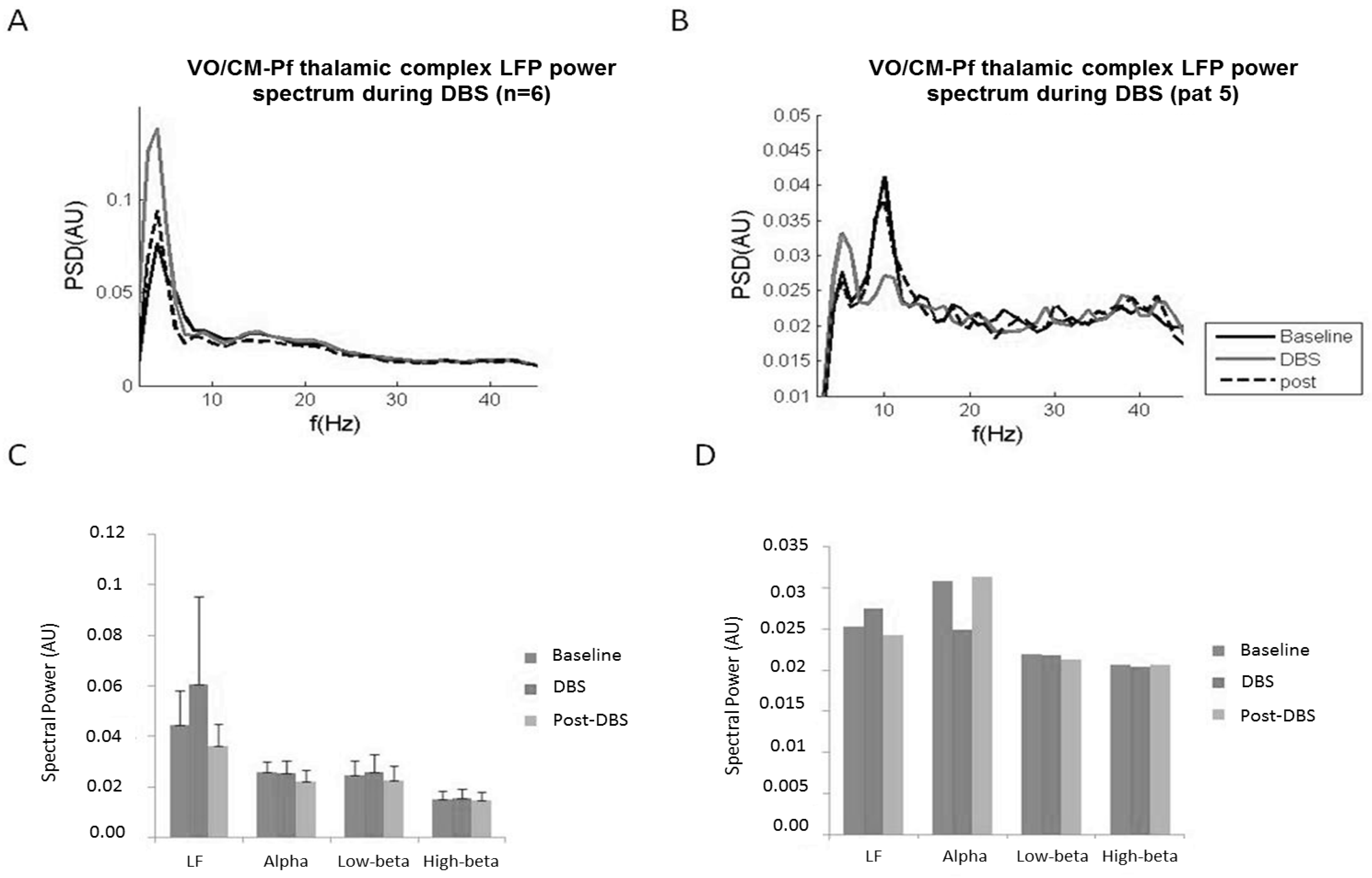
2.4. Experiment 4: Chronic LFP Recordings during DBS
2.4.1. Methods and Participants
2.4.2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kious, B.M.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Shprecher, D.R. Treatment-Refractory Tourette Syndrome. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 70, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, L.E.; Mink, J.W.; Woods, D.W.; Porta, M.; Servello, D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Silburn, P.A.; Foltynie, T.; Walker, H.C.; Shahed-Jimenez, J.; et al. Tourette Syndrome Deep Brain Stimulation: A Review and Updated Recommendations. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 448–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krack, P.; Martinez-Fernandez, R.; del Alamo, M.; Obeso, J.A. Current Applications and Limitations of Surgical Treatments for Movement Disorders: Surgical Treatments For Movement Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Pouratian, N. Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette Syndrome. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, M.-L.; Houeto, J.-L.; Thobois, S.; Bataille, B.; Guenot, M.; Worbe, Y.; Hartmann, A.; Czernecki, V.; Bardinet, E.; Yelnik, J.; et al. Anterior Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette’s Syndrome: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudorfer, C.; El Majdoub, F.; Hunsche, S.; Richter, K.; Sturm, V.; Maarouf, M. Deep Brain Stimulation of the H Fields of Forel Alleviates Tics in Tourette Syndrome. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A. Deep Brain Stimulation in Gilles de La Tourette Syndrome: Killing Several Birds with One Stone? F1000Research 2016, 5, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servello, D.; Zekaj, E.; Saleh, C.; Zanaboni Dina, C.; Porta, M. Sixteen Years of Deep Brain Stimulation in Tourette’s Syndrome: A Critical Review. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2016, 60, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dowd, R.S.; Pourfar, M.; Mogilner, A.Y. Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: A Single-Center Series. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, C.; Hasler, G. Deep Brain Stimulation for Psychiatric Disorders: Is There an Impact on Social Functioning? Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, A.Y.J.M.; Duits, A.A.; Leentjens, A.F.G.; Schruers, K.; van Kranen-Mastenbroek, V.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Temel, Y.; Ackermans, L. Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Tourette Syndrome: Clinical Evidence for Increasing Disbalance of Therapeutic Effects and Side Effects at Long-Term Follow-Up. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.; Pogosyan, A.; Neal, S.; Zavala, B.; Zrinzo, L.; Hariz, M.; Foltynie, T.; Limousin, P.; Ashkan, K.; FitzGerald, J.; et al. Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation in Advanced Parkinson Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.; Arlotti, M.; Ardolino, G.; Cogiamanian, F.; Marceglia, S.; Di Fonzo, A.; Cortese, F.; Rampini, P.M.; Priori, A. Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation in a Freely Moving Parkinsonian Patient. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.; Arlotti, M.; Marceglia, S.; Cogiamanian, F.; Ardolino, G.; Fonzo, A.D.; Lopiano, L.; Scelzo, E.; Merola, A.; Locatelli, M.; et al. Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation Controls Levodopa-Induced Side Effects in Parkinsonian Patients. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2017, 32, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, P.J.; Opri, E.; Shute, J.B.; Molina, R.; Bowers, D.; Ward, H.; Foote, K.D.; Gunduz, A.; Okun, M.S. Scheduled, Intermittent Stimulation of the Thalamus Reduces Tics in Tourette Syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 29, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okun, M.S.; Foote, K.D.; Wu, S.S.; Ward, H.E.; Bowers, D.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Malaty, I.A.; Goodman, W.K.; Gilbert, D.M.; Walker, H.C.; et al. A Trial of Scheduled Deep Brain Stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: Moving Away From Continuous Deep Brain Stimulation Paradigms. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Telkes, I.; Viswanathan, A.; Ince, N.F. GPi Oscillatory Activity Differentiates Tics from the Resting State, Voluntary Movements, and the Unmedicated Parkinsonian State. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bour, L.J.; Ackermans, L.; Foncke, E.M.J.; Cath, D.; van der Linden, C.; Visser Vandewalle, V.; Tijssen, M.A. Tic Related Local Field Potentials in the Thalamus and the Effect of Deep Brain Stimulation in Tourette Syndrome: Report of Three Cases. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shute, J.B.; Okun, M.S.; Opri, E.; Molina, R.; Rossi, P.J.; Martinez-Ramirez, D.; Foote, K.D.; Gunduz, A. Thalamocortical Network Activity Enables Chronic Tic Detection in Humans with Tourette Syndrome. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceglia, S.; Servello, D.; Foffani, G.; Porta, M.; Sassi, M.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Rosa, M.; Barbieri, S.; Priori, A. Thalamic Single-Unit and Local Field Potential Activity in Tourette Syndrome. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2010, 25, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, A.; Giannicola, G.; Rosa, M.; Marceglia, S.; Servello, D.; Sassi, M.; Porta, M. Deep Brain Electrophysiological Recordings Provide Clues to the Pathophysiology of Tourette Syndrome. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlotti, M.; Rosa, M.; Marceglia, S.; Barbieri, S.; Priori, A. The Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation Challenge. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 28, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Williams, D. Basal Ganglia Local Field Potential Activity: Character and Functional Significance in the Human. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2510–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foffani, G.; Bianchi, A.M.; Baselli, G.; Priori, A. Movement-Related Frequency Modulation of Beta Oscillatory Activity in the Human Subthalamic Nucleus. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceglia, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Priori, A. What Neurophysiological Recordings Tell Us about Cognitive and Behavioral Functions of the Human Subthalamic Nucleus. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannicola, G.; Rosa, M.; Servello, D.; Menghetti, C.; Carrabba, G.; Pacchetti, C.; Zangaglia, R.; Cogiamanian, F.; Scelzo, E.; Marceglia, S.; et al. Subthalamic Local Field Potentials after Seven-Year Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 237, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinás, R.R.; Ribary, U.; Jeanmonod, D.; Kronberg, E.; Mitra, P.P. Thalamocortical Dysrhythmia: A Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Syndrome Characterized by Magnetoencephalography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15222–15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceglia, S.; Bianchi, A.M.; Baselli, G.; Foffani, G.; Cogiamanian, F.; Modugno, N.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Priori, A.; Cerutti, S. Interaction between Rhythms in the Human Basal Ganglia: Application of Bispectral Analysis to Local Field Potentials. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Frech, F.; Zamarbide, I.; Alegre, M.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C.; Guridi, J.; Manrique, M.; Valencia, M.; Artieda, J.; Obeso, J.A. Slow Oscillatory Activity and Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2006, 129, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servello, D.; Porta, M.; Sassi, M.; Brambilla, A.; Robertson, M.M. Deep Brain Stimulation in 18 Patients with Severe Gilles de La Tourette Syndrome Refractory to Treatment: The Surgery and Stimulation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, P. The Use of Fast Fourier Transform for the Estimation of Power Spectra: A Method Based on Time Averaging over Short, Modified Periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoustics 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Fumagalli, M.; Giannicola, G.; Marceglia, S.; Lucchiari, C.; Servello, D.; Franzini, A.; Pacchetti, C.; Romito, L.; Albanese, A.; et al. Pathological Gambling in Parkinson’s Disease: Subthalamic Oscillations during Economics Decisions: STN Oscillations in Gambling. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanna, A.E.; Black, K.J.; Hallett, M.; Voon, V. Neurobiology of the Premonitory Urge in Tourette’s Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Treatment Implications. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 29, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, A.; Bagic, A.; Boudreau, E.A.; Hanakawa, T.; Pagan, F.; Mari, Z.; Bara-Jimenez, W.; Aksu, M.; Garraux, G.; Simmons, J.M.; et al. Neuroimaging of Neuronal Circuits Involved in Tic Generation in Patients with Tourette Syndrome. Neurology 2007, 68, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, L.; Foffani, G.; Marceglia, S.; Bracchi, F.; Barbieri, S.; Priori, A. An Electronic Device for Artefact Suppression in Human Local Field Potential Recordings during Deep Brain Stimulation. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlotti, M.; Rossi, L.; Rosa, M.; Marceglia, S.; Priori, A. An External Portable Device for Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) Clinical Research in Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FMorand-Beaulieu, S.; Leclerc, J.; Valois, P.; Lavoie, M.; O’Connor, K.; Gauthier, B. A Review of the Neuropsychological Dimensions of Tourette Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Osso, B.; Marazziti, D.; Albert, U.; Pallanti, S.; Gambini, O.; Tundo, A.; Zanaboni, C.; Servello, D.; Rizzo, R.; Scalone, L.; et al. Parsing the Phenotype of Obsessive-Compulsive Tic Disorder (OCTD): A Multidisciplinary Consensus. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2017, 21, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient ID | Gender | Age (Years) | Severe Psychiatric Comorbidity | DBS Target | Preoperative Assessment | 12 Months Assessment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBOCS | YGTSS | YBOCS | YGTSS | |||||
| 1 | m | 39 | Vo/CM-Pf | 12 | 75 | 10 | 40 | |
| 2 | m | 42 | Vo/CM-Pf | 12 | 79 | 11 | 70 | |
| 3 | f | 47 | Vo/CM-Pf | 17 | 45 | 20 | 29 | |
| 4 | m | 40 | Vo/CM-Pf | 3 | 65 | 5 | 35 | |
| 5 | m | 27 | Vo/CM-Pf | 17 | 28 | 0 | 14 | |
| 6 | m | 24 | x | NA | 23 | 79 | 11 | 48 |
| 7 | f | 29 | x | NA | 37 | 70 | 30 | 70 |
| Movement Type | Low-Frequency (2–7 Hz) | Alpha (8–13 Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset (ms) | Duration (ms) | % Change | Onset (ms) | Duration (ms) | % Change | ||
| Voluntary movement | Pre-movement [−500 0] ms | −250 | 250 | +40% | −250 | 250 | +20% |
| Movement [0 1000] ms | 0 | 800 | +60% | 0 | 500 | +60% | |
| Recovery [1000 2000] ms | 800 | 1200 | +20% | 500 | 1500 | +20% | |
| Involuntary movement | Pre-tic [−500 0] ms | - | - | - | −250 | 250 | −20% |
| Tic [0 1000] ms | 0 | 1000 | 150% | 0 | 1000 | 150% | |
| Recovery [1000 2000] ms | 1000 | 2000 | 100% | - | - | - | |
| Patient | Gender | Age (Year) | Preoperative Assessment | 12 Months Assessment | DBS Target | Chronic Stimulation for (Years) | Recording Contacts | Impedance of the Recording Contacts (kΩ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBOCS | YGTSS | YBOCS | YGTSS | ||||||||
| 1 | m | 31 | 32 | 92 | 18 | 40 | Vo/CM-Pf | 7 | Right | 46 | 4.5 |
| Left | 02 | 5.1 | |||||||||
| 2 | m | 35 | 21 | 89 | 14 | 38 | Vo/CM-Pf | 5 | Right | 57 | 3 |
| Left | 02 | 6.2 | |||||||||
| 3 | m | 48 | 20 | 78 | 14 | 30 | Vo/CM-Pf | 2 | Left | 12 | 7.6 |
| 4 | f | 25 | 25 | 78 | 19 | 40 | Vo/CM-Pf | N/A | Right | 46 | 4.7 |
| Left | 02 | 3.7 | |||||||||
| 5 | m | 38 | 30 | 42 | 26 | 26 | Vo/CM-Pf | N/A | Right | 46 | 7 |
| 6 | m | 24 | 0 | 28 | 2 | 25 | Vo/CM-Pf | 1 | Right | 47 | 0 |
| Left | 03 | 4.9 | |||||||||
| 7 | f | 39 | 5 | 56 | 11 | 31 | Vo/CM-Pf | 4 | Right | 46 | 5 |
| Left | 02 | 7.3 | |||||||||
| Right | 46 | 3.8 | |||||||||
| 8 | m | 29 | 38 | 69 | 21 | 20 | NA | 3 | Left | 02 | 2.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marceglia, S.; Rosa, M.; Servello, D.; Porta, M.; Barbieri, S.; Moro, E.; Priori, A. Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8010004
Marceglia S, Rosa M, Servello D, Porta M, Barbieri S, Moro E, Priori A. Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarceglia, Sara, Manuela Rosa, Domenico Servello, Mauro Porta, Sergio Barbieri, Elena Moro, and Alberto Priori. 2018. "Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome" Brain Sciences 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8010004
APA StyleMarceglia, S., Rosa, M., Servello, D., Porta, M., Barbieri, S., Moro, E., & Priori, A. (2018). Adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation (aDBS) for Tourette Syndrome. Brain Sciences, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8010004






