Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain Through Increased PD-1 Expression in Female Mice
Abstract
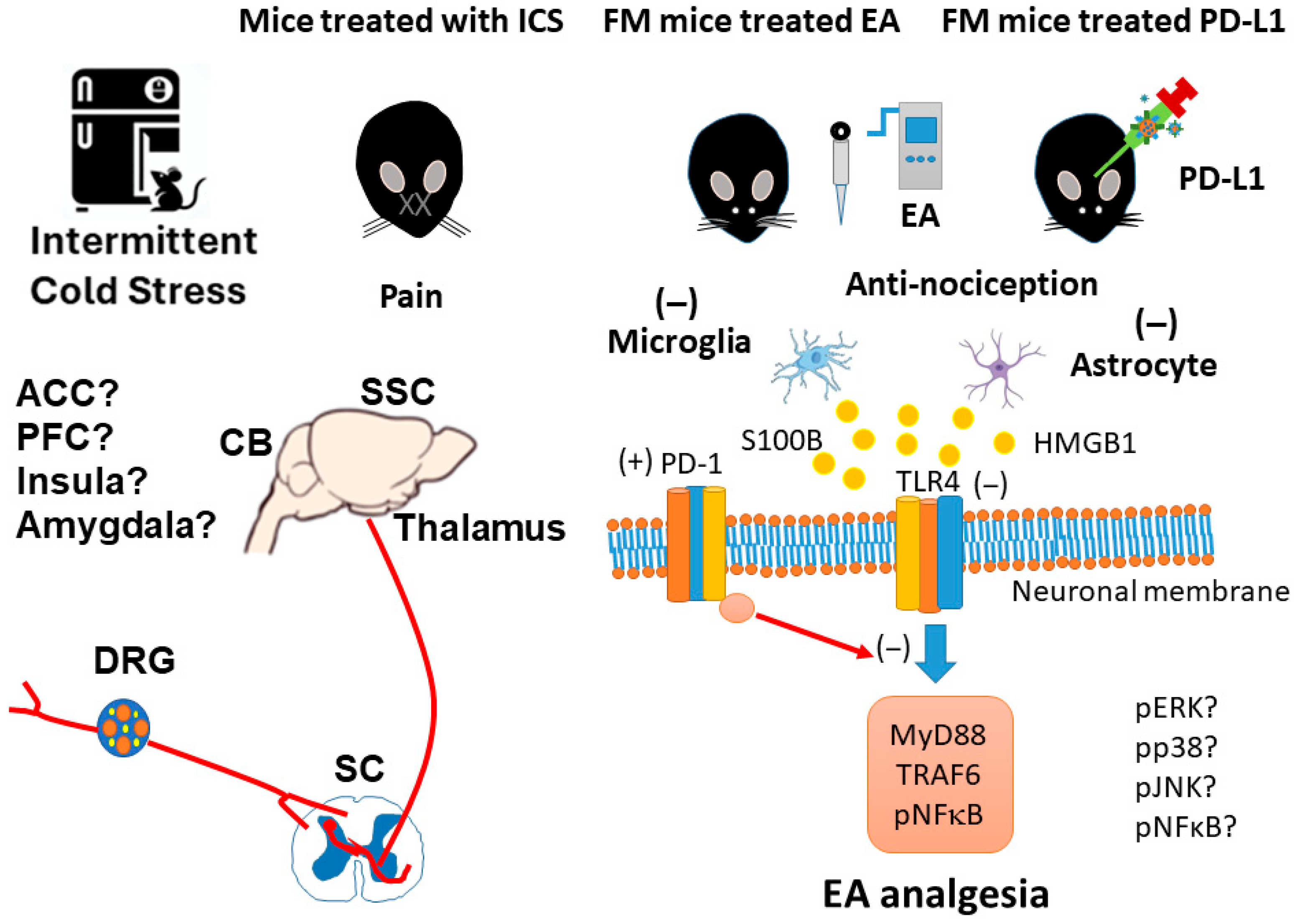
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Fibromyalgia Pain Model
2.2. Electroacupuncture
2.3. Monitoring of Nociceptive Behavior
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Injection of Intracerebral Ventricles with PD-L1
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
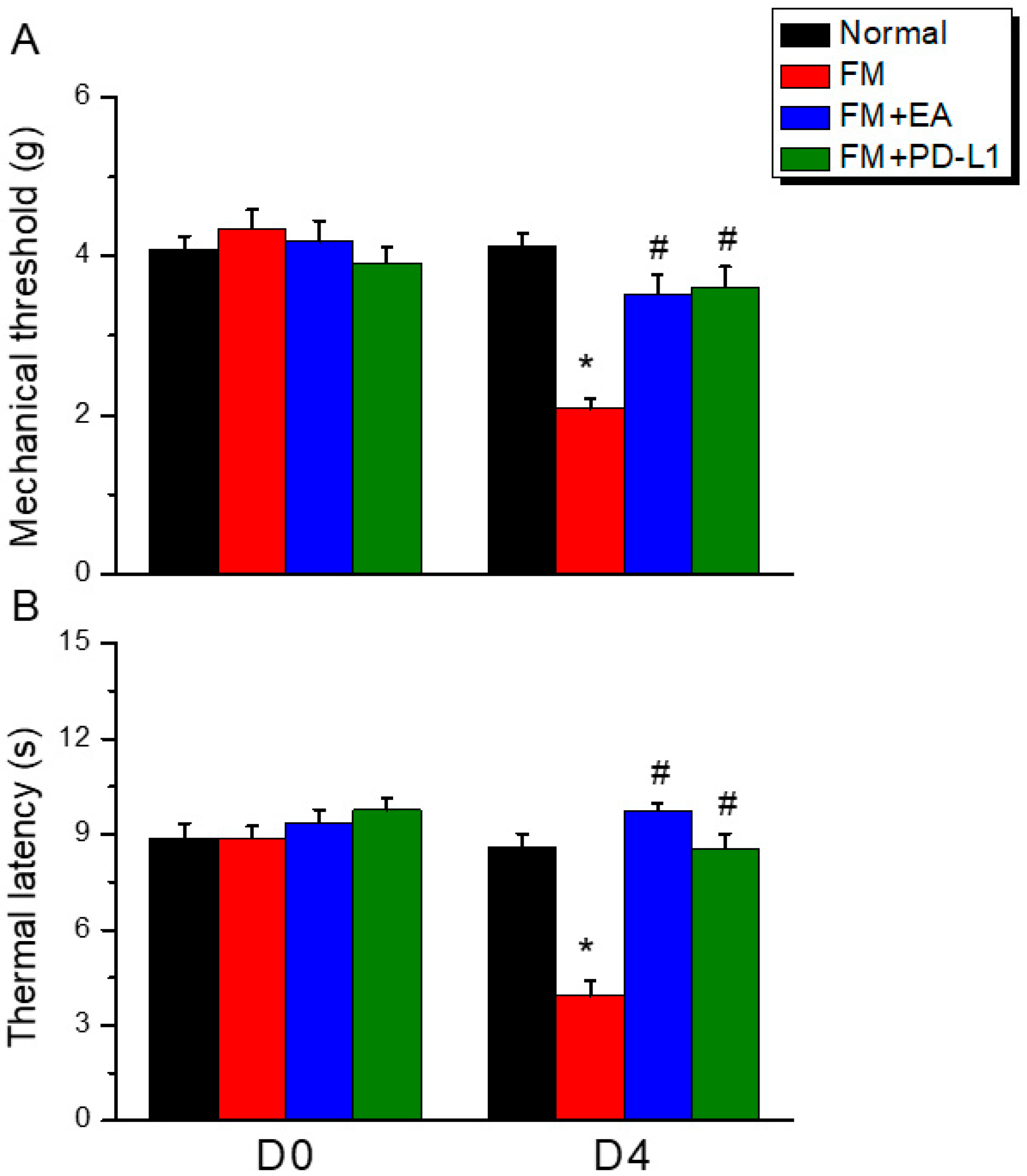
3.1. EA or PD-L1 Injection Relieved Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in an Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced FM Mouse Model
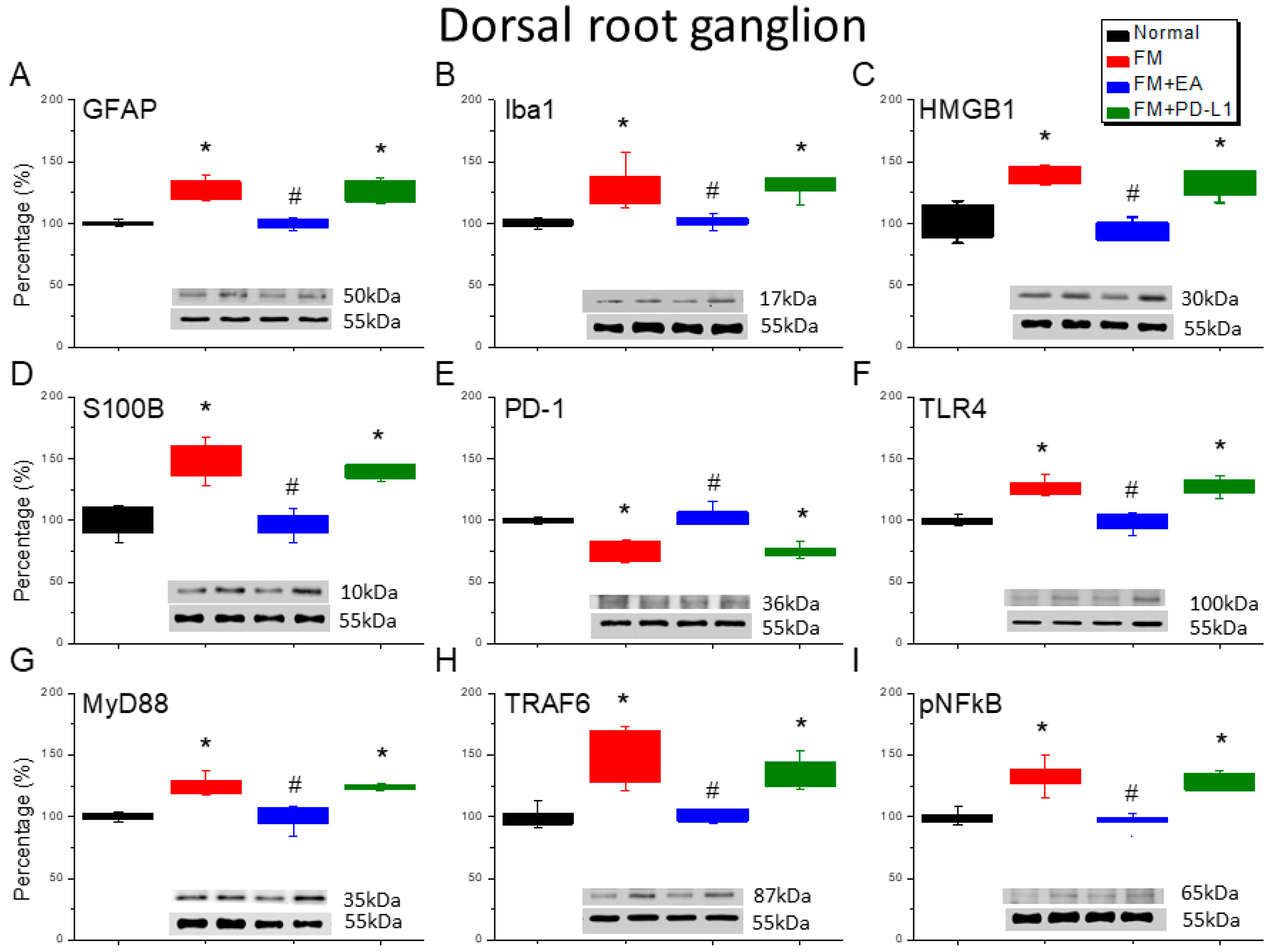
3.2. Beneficial Effects of EA or PD-L1 on Fibromyalgia Pain Were Mediated via Microglia, Astrocytes, and PD-1 Pathway in the Mouse DRG
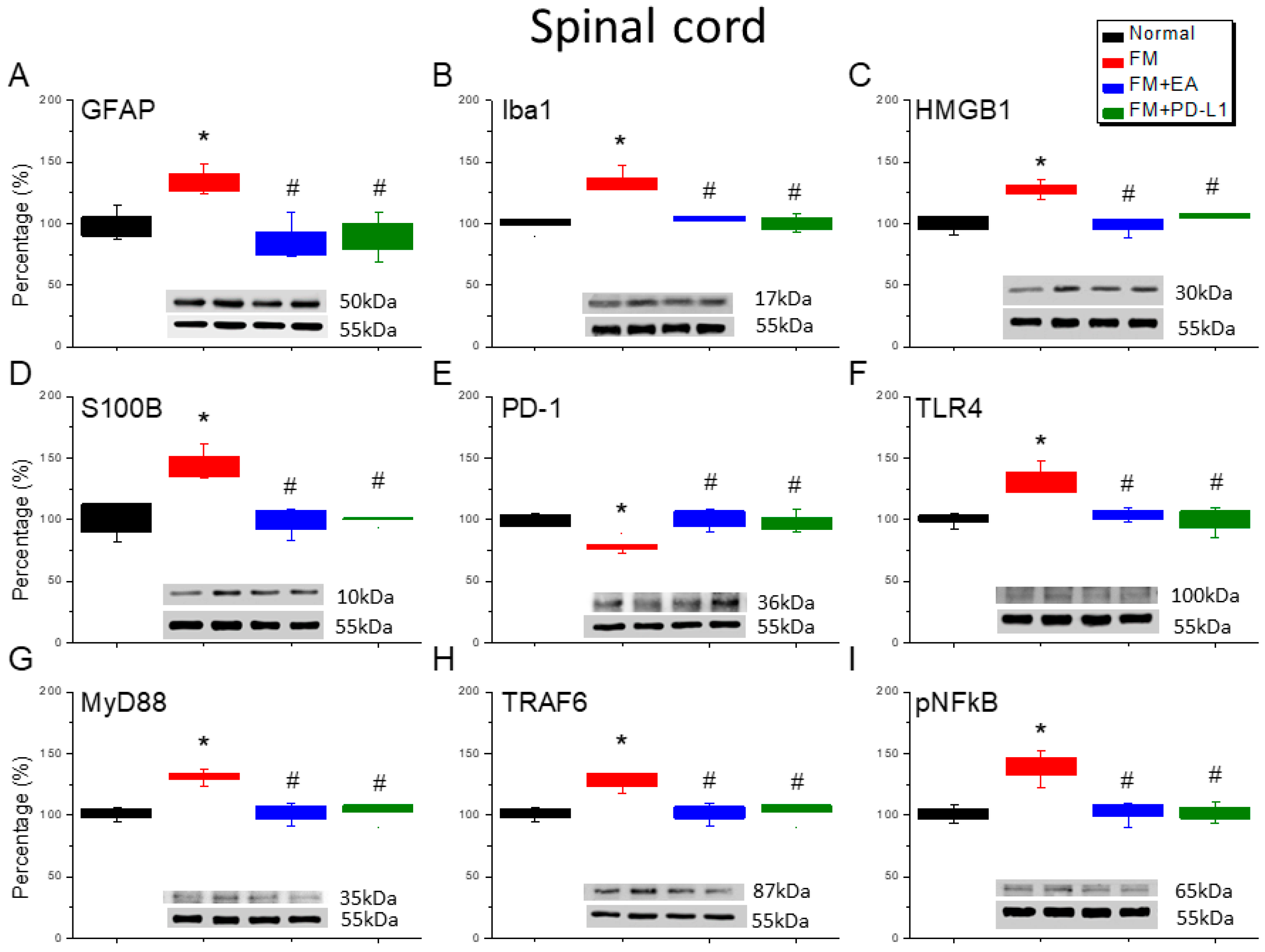
3.3. EA and PD-L1 Treatment Reduced FM Pain in the Spinal Cord
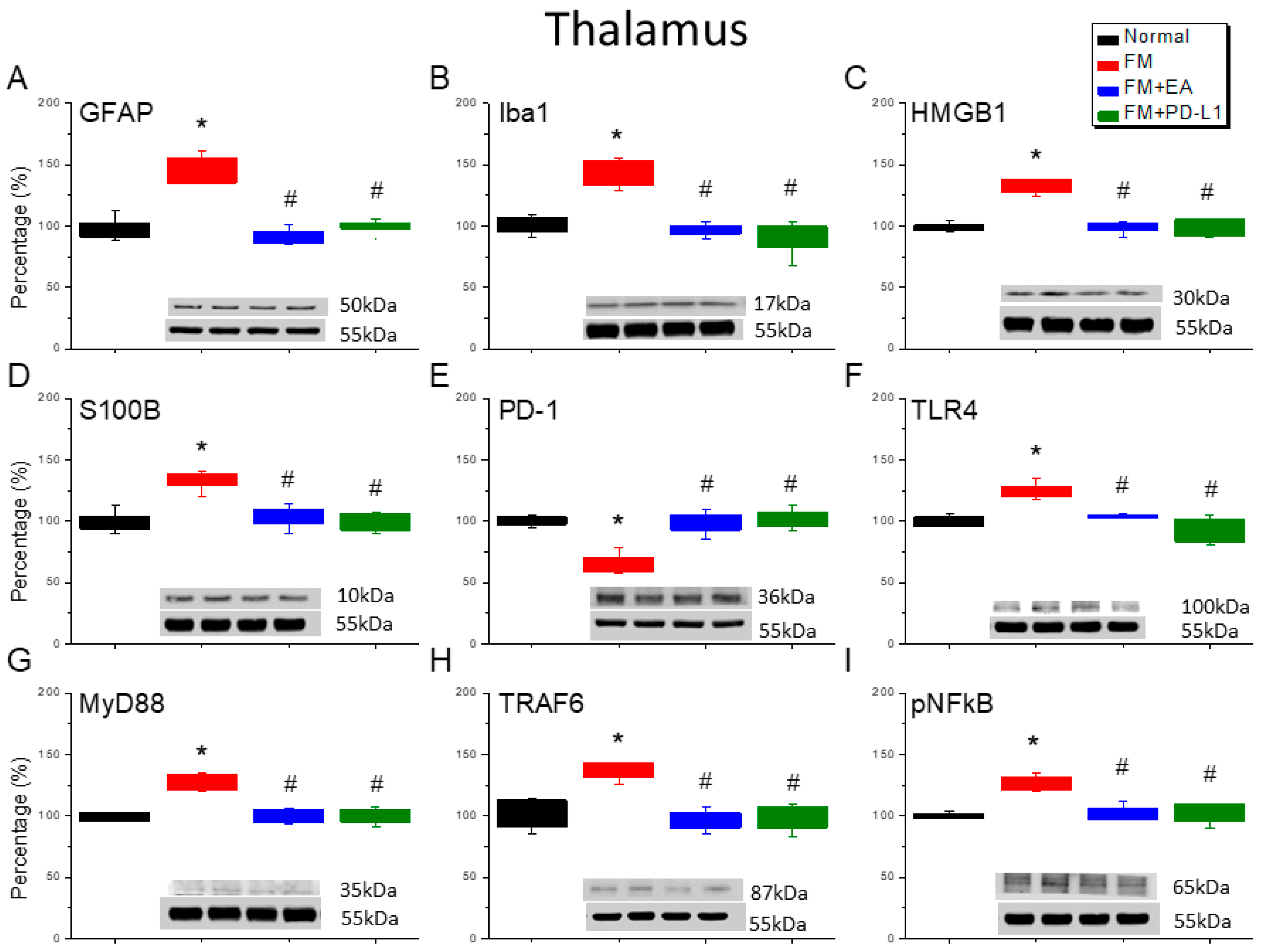
3.4. 2 Hz EA or PD-L1 Treatment Can Reverse Microglial/Astrocytic Activation and TLR4 Accumulation in the Thalamus of FM Mice
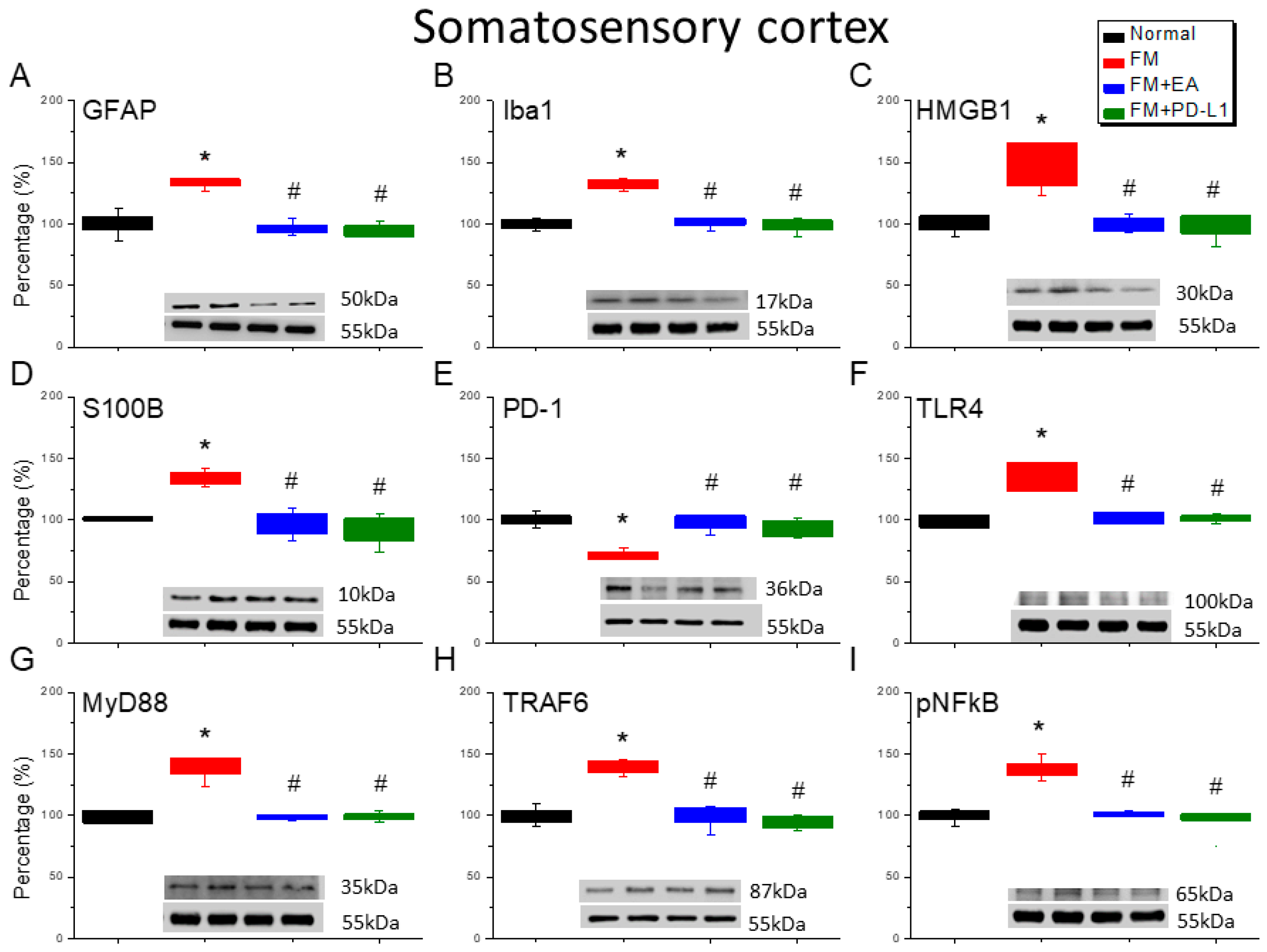
3.5. EA or PD-L1 Treatment Reduced FM Pain by Inhibiting the Microglia/Astrocyte-TLR4 Pathway in the Somatosensory Cortex
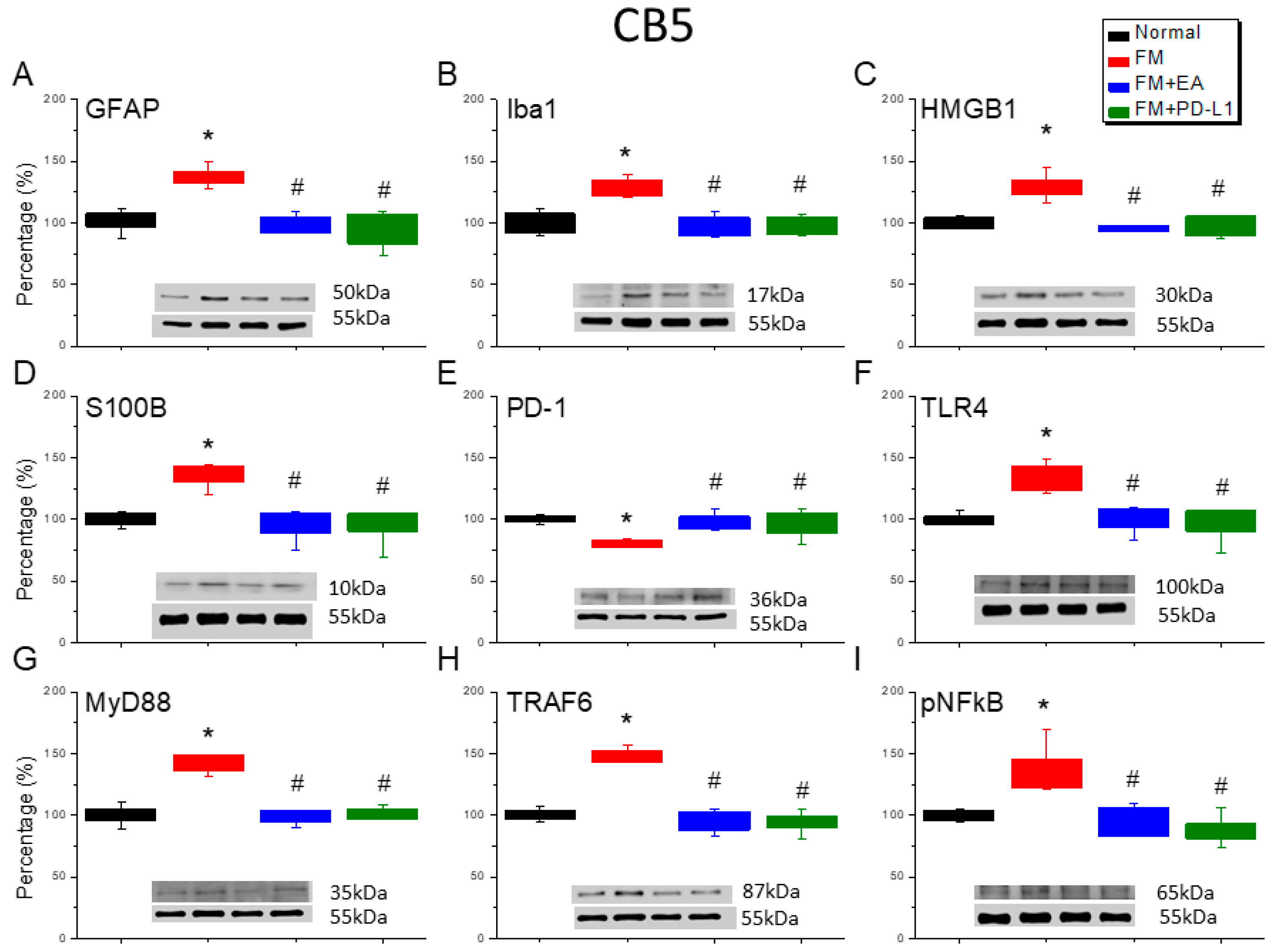
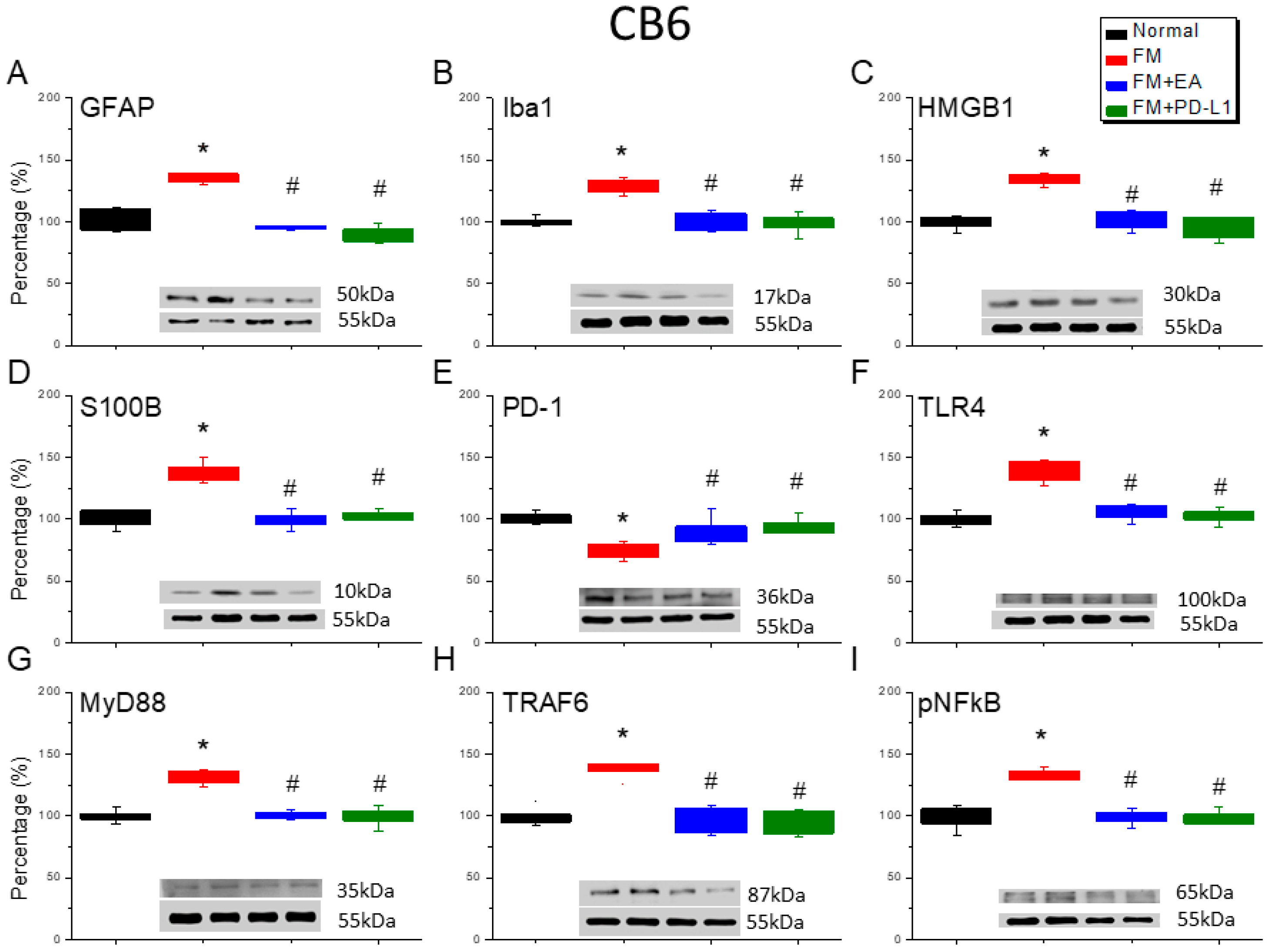
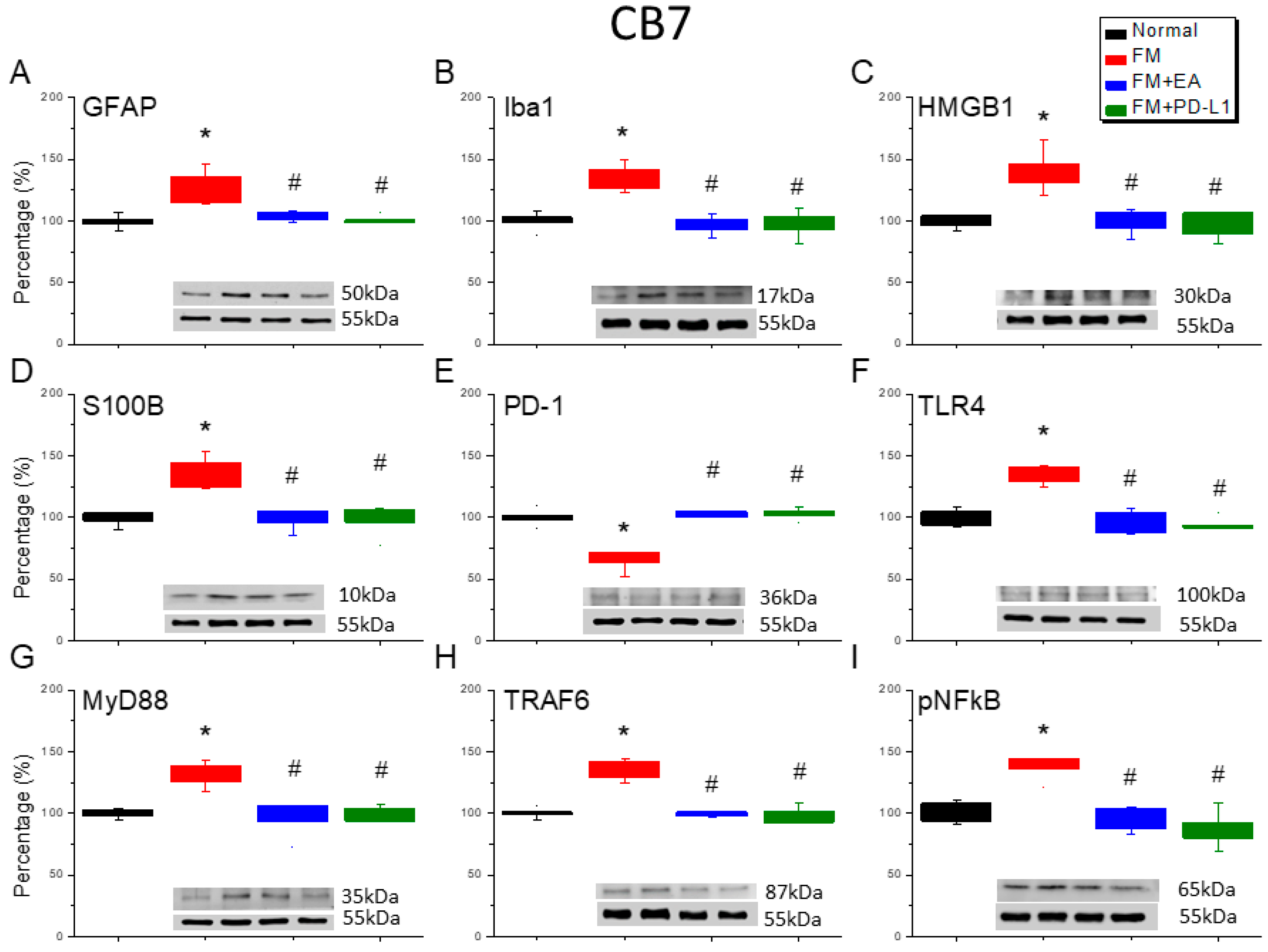
3.6. Cold Stress Induced Fibromyalgia Pain by Increasing the Microglia/Astrocyte-TLR4 Pathway in the CB5-7, an Effect Reversed by EA and PD-L1 Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex |
| CB | Cerebellum |
| CCL2 | Chemokine ligand 2 |
| CCR2 | Chemokine receptor 2 |
| DRG | Dorsal root ganglion |
| EA | Electroacupuncture |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| HMGB1 | High-mobility group protein B1 |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| ICS | Intermittent cold stress |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death ligand 1 |
| pERK | Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| pNF-kB | Phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. |
| S100B | S100 calcium-binding protein B |
| SC | Spinal cord |
| SCI | Spinal cord injury |
| SHP-1 | Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 |
| SSC | Somatosensory cortex |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TRAF6 | TNF Receptor Associated Factor 6 |
| TRPM2 | Transient receptor potential channel melastatin 2 |
References
- Plaut, S. Suggesting a mechanism for acupuncture as a global percutaneous needle fasciotomy that respects tensegrity principles for treating fibromyalgia. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 952159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Ko, Y.C.; Chow, L.H.; Hsiao, F.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, P.N.; Chen, W.T. Salivary cortisol is associated with cognitive changes in patients with fibromyalgia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlejohn, G. Neurogenic neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia and complex regional pain syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordon, B.; Orduna, E.; Vilades, E.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Puebla-Guedea, M.; Polo, V.; Larrosa, J.M.; Pablo, L.E.; Vicente, M.J.; et al. Analysis of Retinal Layers in Fibromyalgia Patients with Premium Protocol in Optical Tomography Coherence and Quality of Life. Curr. Eye Res. 2022, 47, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lin, I.Y.; Chuang, K.T.; Lin, Y.W. Eicosapentaenoic acid alleviates fibromyalgia-like pain by modulating microglia, astrocytes, and toll-Like receptor 4 signaling in the mice cerebellum. Nutr. Neurosci. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, F.F.; Becker, M.W.; Blatt, C.R.; Ziegelmann, P.K.; da Silva Dal Pizzol, T.; Pilger, D. Comparative efficacy of amitriptyline, duloxetine and pregabalin for treating fibromyalgia in adults: An overview with network meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, L.P. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Thakur, P.; Kumar, R.; Kaur, S.; Saini, R.V.; Saini, A.K. Biological markers for the effects of yoga as a complementary and alternative medicine. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwantwi, L.B. Overcoming anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade resistance: The role of macrophage, neutrophils and mast cells in the tumor microenvironment. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 3077–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lay, M.; Chang, W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ji, R.R. PD-L1 inhibits acute and chronic pain by suppressing nociceptive neuron activity via PD-1. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdabi, S.; Asadian, F.; Kiani, R.; Khademi, B.; Haghshenas, M.R.; Erfani, N. Simultaneous Expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in Peripheral and Central Immune Cells and Tumor Cells in the Benign and Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors Microenvironment. Head Neck Pathol. 2023, 17, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, W.; Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Tan, J.; Simons, D.L.; Hu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, Y.; et al. PD-L1-expressing tumor-associated macrophages are immunostimulatory and associate with good clinical outcome in human breast cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; You, Z. Inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and TNF-alpha up-regulate PD-L1 expression in human prostate and colon cancer cells. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 184, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hamrouni, A.; Wolowiec, D.; Coiteux, V.; Kuliczkowski, K.; Hetuin, D.; Saudemont, A.; Quesnel, B. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-gamma and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood 2007, 110, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Zheng, X.; Niu, M.; Zhu, S.; Ge, H.; Wu, K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current advances and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, J.; Jiang, H. Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3083–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Liu, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, H.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Intermittent theta-burst stimulation improves motor function by inhibiting neuronal pyroptosis and regulating microglial polarization via TLR4/NFkappaB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chen, W.; Ni, X.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Tang, L.; Weng, J. Metformin, Macrophage Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 682853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, F.Z.; Arulsamy, A.; Retinasamy, T.; Shaikh, M.F. The Role of High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) in Neurodegeneration: A Systematic Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 2221–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.X.; Chi, G.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ru, Y.X.; Luo, Z.L.; Yan, W.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, M.; et al. IL-37 suppresses the sustained hepatic IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha production and T cell-dependent liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 69, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyires, K.; Toth, E.V.; Zadori, S.Z. Gut inflammation: Current update on pathophysiology, molecular mechanism and pharmacological treatment modalities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1063–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Su, K.P. Clinical efficacy and immune effects of acupuncture in patients with comorbid chronic pain and major depression disorder: A double-blinded, randomized controlled crossover study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 110, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Optogenetic modulation of electroacupuncture analgesia in a mouse inflammatory pain model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.W.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Kuan, T.S.; Hong, C.Z. Needling therapy for myofascial pain: Recommended technique with multiple rapid needle insertion. Biomedicine 2014, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Yen, C.M.; Hsu, H.C.; Liao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Chemogenetics Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in Mice Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain through TRPV1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, A.I.W.; Su, H.; Su, K.P. Transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) modulates the therapeutic effects for comorbidity of pain and depression: The common molecular implication for electroacupuncture and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, G. Effect Size Guidelines for Individual and Group Differences in Physiotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Xu, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Electroacupuncture Alleviates CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via PD-L1/PD-1-SHP-1 Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Bang, S.; Donnelly, C.R.; Chen, O.; Tao, X.; Mirando, A.J.; Hilton, M.J.; Ji, R.R. PD-1 blockade inhibits osteoclast formation and murine bone cancer pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3603–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Sun, K.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Lin, F.; Sun, X.; Luo, X.; Ren, C.; Lu, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. PD-L1 Improves Motor Function and Alleviates Neuropathic Pain in Male Mice After Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting MAPK Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 670646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.; Wang, W. PD-L1 and PD-1 expressed in trigeminal ganglia may inhibit pain in an acute migraine model. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Niu, K.; Guo, J.; Tu, J.; Ma, B.; An, J. Dexmedetomidine attenuates postoperative spatial memory impairment after surgery by reducing cytochrome C. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandlem, V.K.K.; Rivera, A.; Khan, Z.; Quazi, S.H.; Deba, F. TLR4 induced TRPM2 mediated neuropathic pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1472771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.; Qian, G.; Zhao, G. Kaempferol exerts a neuroprotective effect to reduce neuropathic pain through TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1678–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggiss, E.A.; Rosario, R.C.; de Lima, R.A.; Silva, P.A.; Moreira, R.M.; da Silva, K.P.; de Farias, C.L.; Dos Santos, V.Q.; Simoes, R.P.; Santos, A.T.S.; et al. Pulsed Laser Acupuncture in the Treatment of Pain and Heart Rate Variability in Fibromyalgia Patients: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 13, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakawa, Y.; Saito, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Oka, H.; Miki, K.; Yukioka, M.; Itoh, K. Effects of Acupuncture Therapy on Drug-Resistant Fibromyalgia: An Exploratory Single-Arm Nonrandomized Trial. Med. Acupunct. 2022, 34, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, J.; Ying, X.; Gu, X.; Tan, Q.; Tu, W.; Lou, X.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain caused by SNL by promoting M2 microglia polarization through PD-L1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 123, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, I.-H.; Chen, W.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Liao, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain Through Increased PD-1 Expression in Female Mice. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090976
Hsiao I-H, Chen W-H, Lin M-C, Hsu H-C, Liao H-Y, Lin Y-W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain Through Increased PD-1 Expression in Female Mice. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(9):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090976
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, I-Han, Wei-Hung Chen, Ming-Chia Lin, Hsin-Cheng Hsu, Hsien-Yin Liao, and Yi-Wen Lin. 2025. "Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain Through Increased PD-1 Expression in Female Mice" Brain Sciences 15, no. 9: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090976
APA StyleHsiao, I.-H., Chen, W.-H., Lin, M.-C., Hsu, H.-C., Liao, H.-Y., & Lin, Y.-W. (2025). Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain Through Increased PD-1 Expression in Female Mice. Brain Sciences, 15(9), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090976






