Putamen Stiffness Declines with Age and Is Associated with Implicit Sequence Learning Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli and Apparatus
2.3. Stimulus Sequences
2.4. Design and Procedure
2.4.1. Serial Reaction Time Task
2.4.2. Generate Task
2.5. Behavioral Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Serial Reaction Time Task
2.5.2. Generation Task
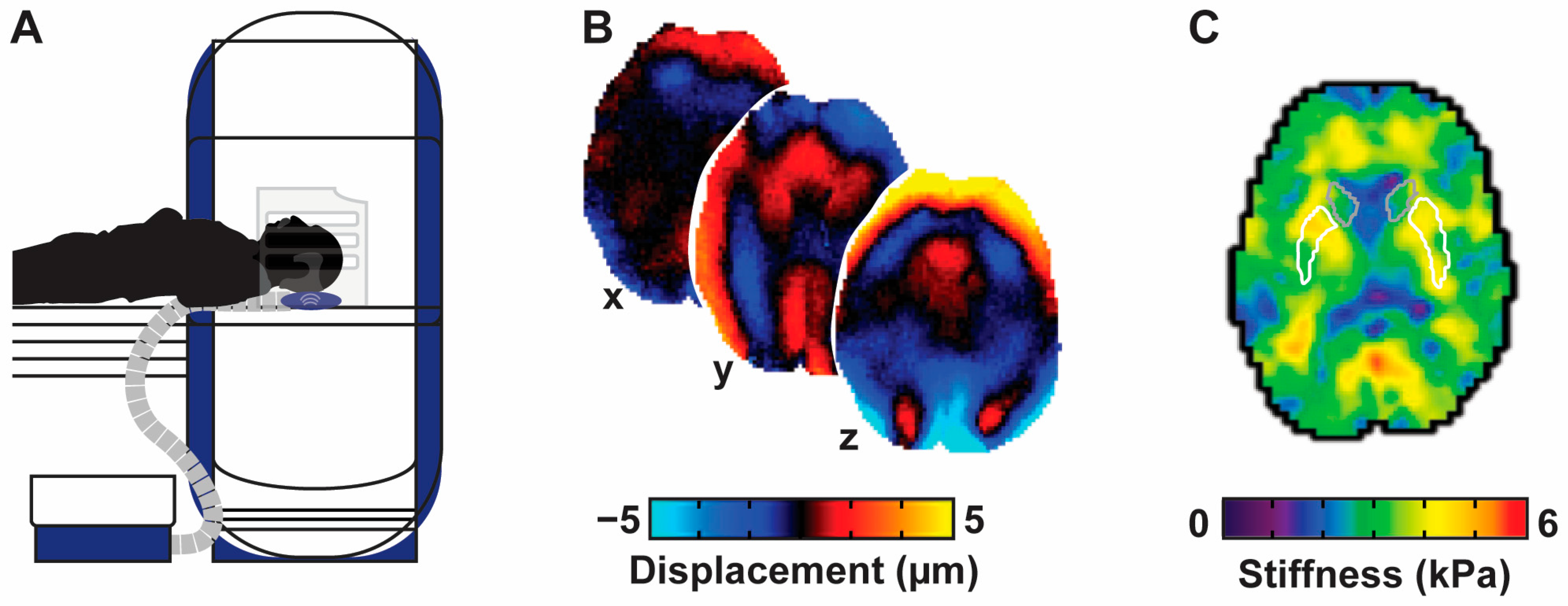
2.6. MRI Apparatus
2.7. Volume Acquisition and Processing
2.8. MRE Acquisition and Processing
2.9. Regions of Interest and Neuroimaging Outcome Measures
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
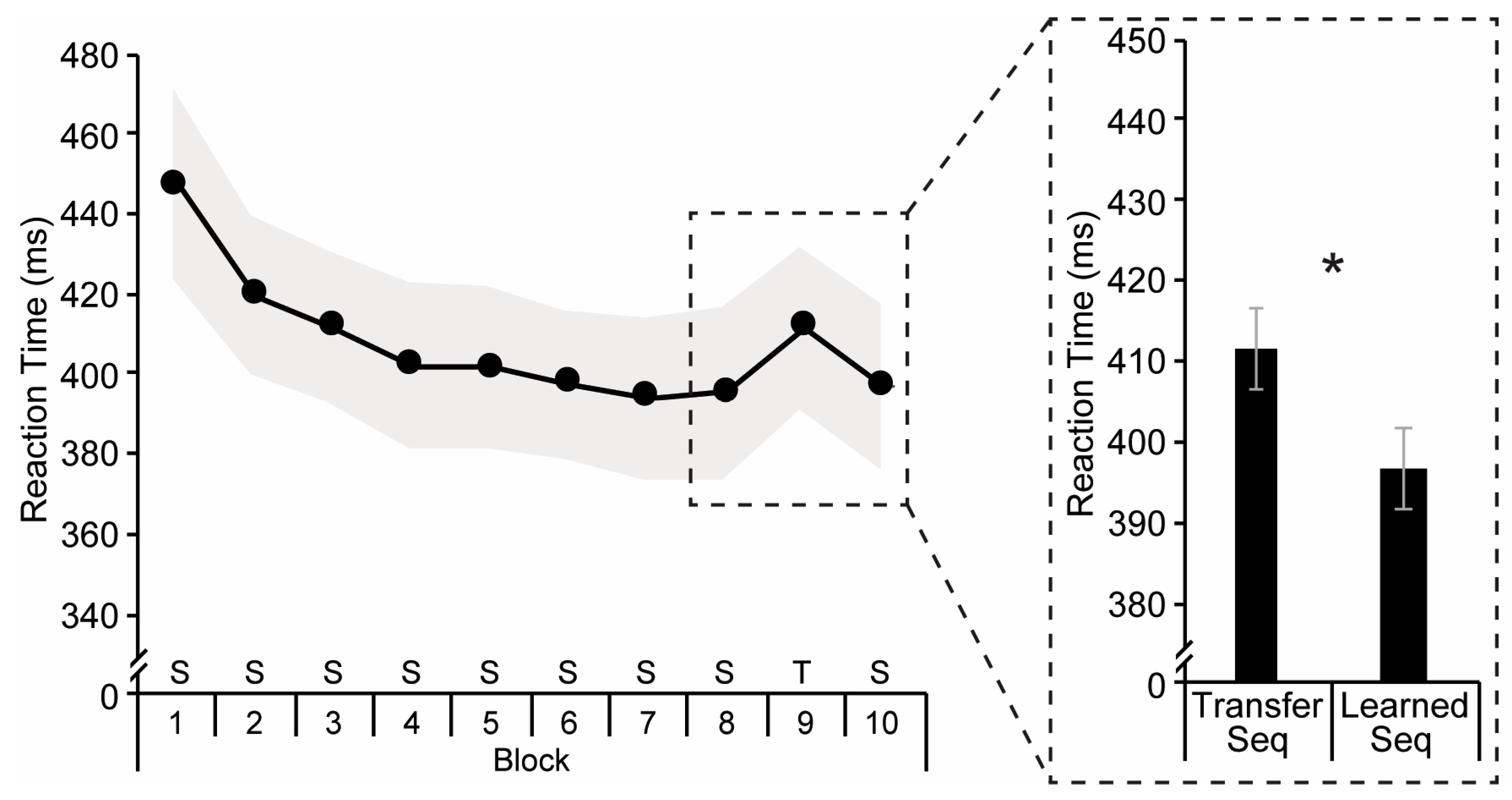
3.1. Implicit Sequence Learning
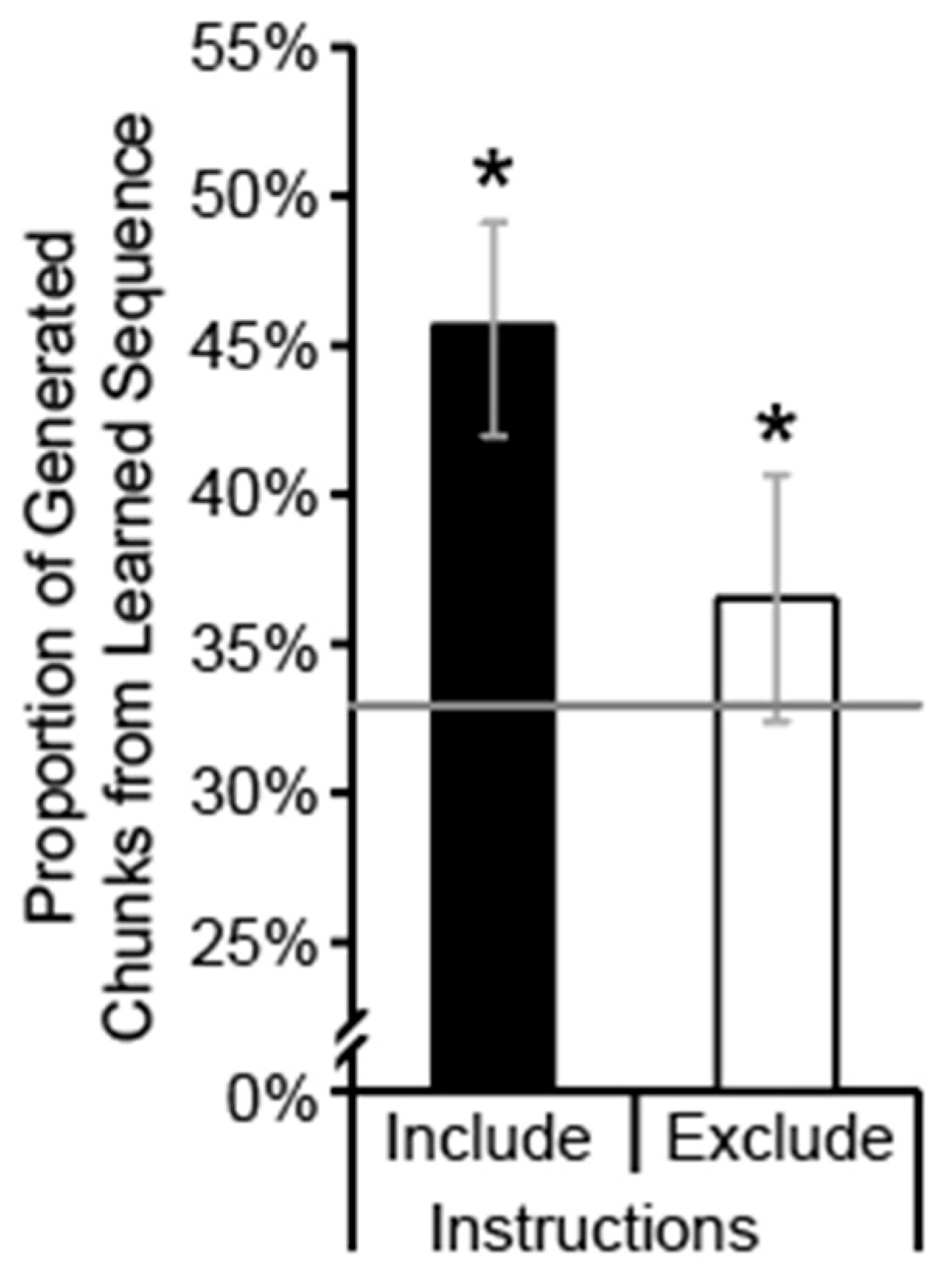
3.2. Explicit Sequence Knowledge
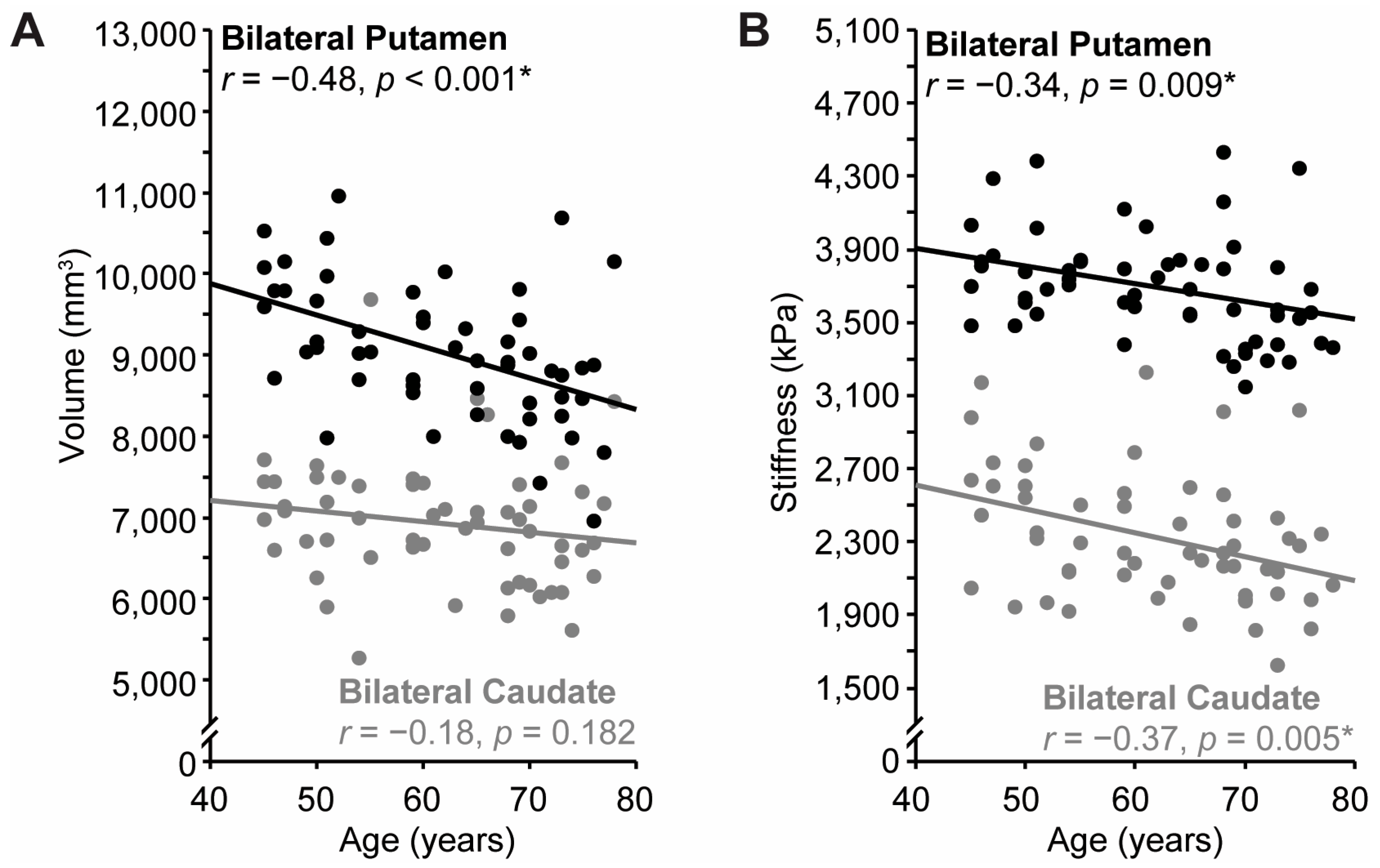
3.3. Effects of Age
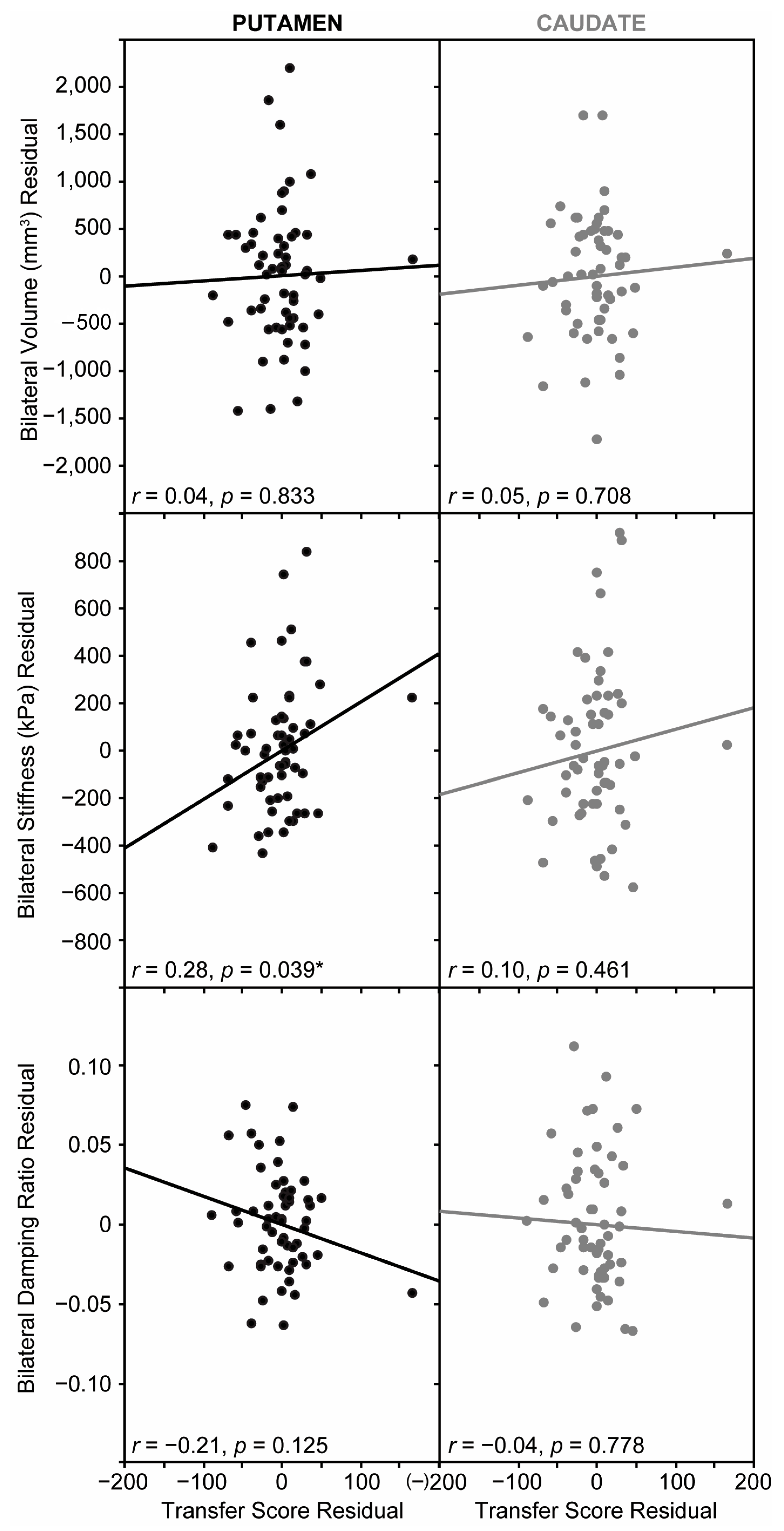
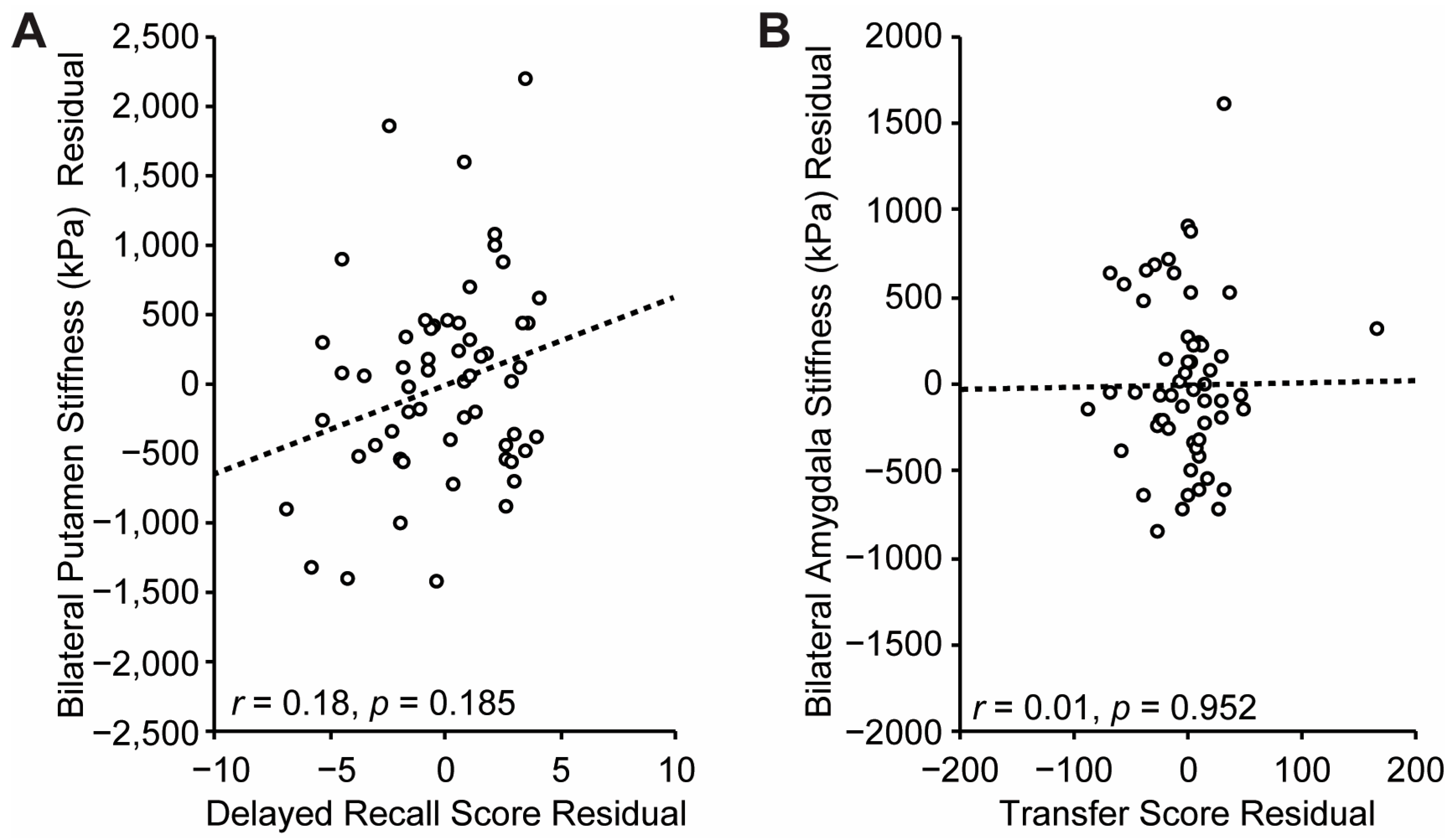
3.4. Relationship Between Striatal Structure and Sequence Learning
3.5. Control Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRE | Magnetic Resonance Elastography |
| SRTT | Serial Reaction Time Task |
| RT | Reaction Time |
| CVLT | California Verbal Learning Test |
References
- Koch, F.-S.; Sundqvist, A.; Thornberg, U.B.; Nyberg, S.; Lum, J.A.G.; Ullman, M.T.; Barr, R.; Rudner, M.; Heimann, M. Procedural Memory in Infancy: Evidence from Implicit Sequence Learning in an Eye-Tracking Paradigm. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2020, 191, 104733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frensch, P.A.; Miner, C.S. Effects of Presentation Rate and Individual Differences in Short-Term Memory Capacity on an Indirect Measure of Serial Learning. Mem. Cognit. 1994, 22, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.H.; Howard, D.V. Age Differences in Implicit Learning of Higher Order Dependencies in Serial Patterns. Psychol. Aging 1997, 12, 634–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janacsek, K.; Shattuck, K.F.; Tagarelli, K.M.; Lum, J.A.G.; Turkeltaub, P.E.; Ullman, M.T. Sequence Learning in the Human Brain: A Functional Neuroanatomical Meta-Analysis of Serial Reaction Time Studies. NeuroImage 2020, 207, 116387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidle, M.; Thompson, W.H.; Albrecht, F.; Franzén, E. Implicit Motor Sequence Learning in People with Mild to Moderate Parkinson’s Disease: Behavior and Related Brain Function. J. Park. Dis. 2023, 13, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.M.; Lum, J.A.G.; Ullman, M.T. A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Serial Reaction Time Task Performance in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropsychology 2014, 28, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, G.M.; Jackson, S.R.; Harrison, J.; Henderson, L.; Kennard, C. Serial Reaction Time Learning and Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence for a Procedural Learning Deficit. Neuropsychologia 1995, 33, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-S.; Reading, S.A.J.; Brashers-Krug, T.; Calhoun, V.D.; Ross, C.A.; Pearlson, G.D. Functional MRI Study of a Serial Reaction Time Task in Huntington’s Disease. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2004, 131, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.; Nissen, M.J. Procedural Learning Is Impaired in Huntington’s Disease: Evidence from the Serial Reaction Time Task. Neuropsychologia 1991, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, N.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Head, D.; Gunning-Dixon, F.; Acker, J.D. Differential Aging of the Human Striatum: Longitudinal Evidence. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Nissen, M.J.; Bullemer, P. Attentional Requirements of Learning: Evidence from Performance Measures. Cognit. Psychol. 1987, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, B.A.; DiGirolamo, G.J.; Keele, S.W. Sequence Learning. Trends Cogn. Sci. 1998, 2, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarb, H.; Schumacher, E.H. Generalized Lessons about Sequence Learning from the Study of the Serial Reaction Time Task. Adv. Cogn. Psychol. 2012, 8, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Ivry, R.I.; Keele, S.W. Attention and Structure in Sequence Learning. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1990, 16, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, S.T.; Hazeltine, E.; Ivry, R.B. Abstract and Effector-Specific Representations of Motor Sequences Identified with PET. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9420–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroost, N.; Coomans, D. Is Sequence Awareness Mandatory for Perceptual Sequence Learning: An Assessment Using a Pure Perceptual Sequence Learning Design. Acta Psychol. 2018, 183, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willingham, D.B.; Nissen, M.J.; Bullemer, P. On the Development of Procedural Knowledge. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1989, 15, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, K.E.; Stadler, M.A. Implicit Learning of a Nonverbal Sequence in Younger and Older Adults. Psychol. Aging 1995, 10, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, I.J.; Howard, J.H.; Howard, D.V. Age-Related Differences in Implicit Learning of Subtle Third-Order Sequential Structure. J. Gerontol. B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2007, 62, P98–P103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.V.; Howard, J.H.; Japikse, K.; DiYanni, C.; Thompson, A.; Somberg, R. Implicit Sequence Learning: Effects of Level of Structure, Adult Age, and Extended Practice. Psychol. Aging 2004, 19, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyon, J.; Gabitov, E.; Vahdat, S.; Lungu, O.; Boutin, A. Current Issues Related to Motor Sequence Learning in Humans. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 20, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penhune, V.B.; Steele, C.J. Parallel Contributions of Cerebellar, Striatal and M1 Mechanisms to Motor Sequence Learning. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefcsik, T.; Nemeth, D.; Janacsek, K.; Hoffmann, I.; Scialabba, J.; Klivenyi, P.; Ambrus, G.G.; Haden, G.; Vecsei, L. The Role of the Putamen in Cognitive Functions—A Case Study. Learn. Percept. 2009, 1, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, L.A.; Edwards, J.D.; Siengsukon, C.S.; Vidoni, E.D.; Wessel, B.D.; Linsdell, M.A. Motor Sequence Chunking Is Impaired by Basal Ganglia Stroke. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 92, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakil, E.; Kahan, S.; Huberman, M.; Osimani, A. Motor and Non-Motor Sequence Learning in Patients with Basal Ganglia Lesions: The Case of Serial Reaction Time (SRT). Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Gunning-Dixon, F.; Head, D.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Williamson, A.; Acker, J.D. Aging, Sexual Dimorphism, and Hemispheric Asymmetry of the Cerebral Cortex: Replicability of Regional Differences in Volume. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Lindenberger, U.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Head, D.; Williamson, A.; Dahle, C.; Gerstorf, D.; Acker, J.D. Regional Brain Changes in Aging Healthy Adults: General Trends, Individual Differences and Modifiers. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkattan, A.; Mahdy, A.; Eltomey, M.; Ismail, R. A Study of Volumetric Variations of Basal Nuclei in the Normal Human Brain by Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkur Shankar, S.; Ballal, S.; Shubha, R. Study of Normal Volumetric Variation in the Putamen with Age and Sex Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M. The Cognitive Consequences of Structural Changes to the Aging Brain. In Handbook of the Psychology of Aging; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 73–91. ISBN 978-0-12-380882-0. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.R.; Xu, Y.-C.; Waring, S.C.; O’Brien, P.C.; Smith, G.E.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Kokmen, E. Memory and MRI-Based Hippocampal Volumes in Aging and AD. Neurology 2000, 54, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning-Dixon, F.M.; Raz, N. Neuroanatomical Correlates of Selected Executive Functions in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective MRI Study. Neuropsychologia 2003, 41, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, D.; Kennedy, K.M.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Raz, N. Age Differences in Perseveration: Cognitive and Neuroanatomical Mediators of Performance on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Williamson, A.; Gunning-Dixon, F.; Head, D.; Acker, J.D. Neuroanatomical and Cognitive Correlates of Adult Age Differences in Acquisition of a Perceptual-Motor Skill. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 51, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.C.; Huston, J.; Ehman, R.L. MR Elastography of the Brain and Its Application in Neurological Diseases. NeuroImage 2019, 187, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthupillai, R.; Lomas, D.J.; Rossman, P.J.; Greenleaf, J.F.; Manduca, A.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic Resonance Elastography by Direct Visualization of Propagating Acoustic Strain Waves. Science 1995, 269, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Bertalan, G.; Meierhofer, D.; Klein, C.; Schreyer, S.; Steiner, B.; Wang, S.; Vieira Da Silva, R.; Infante-Duarte, C.; Koch, S.; et al. Brain Maturation Is Associated with Increasing Tissue Stiffness and Decreasing Tissue Fluidity. Acta Biomater. 2019, 99, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, I.; Jöhrens, K.; Würfel, J.; Braun, J. Structure-Sensitive Elastography: On the Viscoelastic Powerlaw Behavior of in Vivo Human Tissue in Health and Disease. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5672–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schregel, K.; Tysiak, E.; Garteiser, P.; Gemeinhardt, I.; Prozorovski, T.; Aktas, O.; Merz, H.; Petersen, D.; Wuerful, J.; Sinkus, R. Demyelination Reduces Brain Parenchymal Stiffness Quantified in Vivo by Magnetic Resonance Elastography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6650–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitberger, K.-J.; Sack, I.; Krefting, D.; Pfüller, C.; Braun, J.; Paul, F.; Wuerfel, J. Brain Viscoelasticity Alteration in Chronic-Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, A.; Guo, J.; Prokscha, T.; Meyer, T.; Hirsch, S.; Braun, J.; Sack, I.; Scheel, M. In Vivo Waveguide Elastography: Effects of Neurodegeneration in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.C.; Jones, D.T.; Jack, C.R.; Glaser, K.J.; Senjem, M.L.; Manduca, A.; Felmlee, J.P.; Carter, R.E.; Ehman, R.L.; Huston, J. Regional Brain Stiffness Changes across the Alzheimer’s Disease Spectrum. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 10, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.C.; Huston, J.; Jack, C.R.; Glaser, K.J.; Manduca, A.; Felmlee, J.P.; Ehman, R.L. Decreased Brain Stiffness in Alzheimer’s Disease Determined by Magnetic Resonance Elastography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 34, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.; Sousa, N. Magnetic Resonance Elastography of the Ageing Brain in Normal and Demented Populations: A Systematic Review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 4207–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, L.V.; Schwarb, H.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Johnson, C.L. Aging Brain Mechanics: Progress and Promise of Magnetic Resonance Elastography. NeuroImage 2021, 232, 117889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, T.; Motosugi, U.; Sasaki, Y.; Kakegawa, T.; Sato, K.; Glaser, K.J.; Ehman, R.L.; Onishi, H. Influence of Age on Global and Regional Brain Stiffness in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, I.; Beierbach, B.; Wuerfel, J.; Klatt, D.; Hamhaber, U.; Papazoglou, S.; Martus, P.; Braun, J. The Impact of Aging and Gender on Brain Viscoelasticity. NeuroImage 2009, 46, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, I.; Streitberger, K.-J.; Krefting, D.; Paul, F.; Braun, J. The Influence of Physiological Aging and Atrophy on Brain Viscoelastic Properties in Humans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, L.V.; Johnson, C.L.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Perrins, M.; Littlejohn, A.; van Beek, E.J.R.; Roberts, N.; Starr, J.M. High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Elastography Reveals Differences in Subcortical Gray Matter Viscoelasticity between Young and Healthy Older Adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 65, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.L.; Schwarb, H.; Horecka, K.M.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Hillman, C.H.; Kramer, A.F.; Cohen, N.J.; Barbey, A.K. Double Dissociation of Structure-Function Relationships in Memory and Fluid Intelligence Observed with Magnetic Resonance Elastography. NeuroImage 2018, 171, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarb, H.; Johnson, C.L.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Cohen, N.J. Medial Temporal Lobe Viscoelasticity and Relational Memory Performance. NeuroImage 2016, 132, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarb, H.; Johnson, C.L.; Dulas, M.R.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Holtrop, J.L.; Watson, P.D.; Wang, J.X.; Voss, J.L.; Sutton, B.P.; Cohen, N.J. Structural and Functional MRI Evidence for Distinct Medial Temporal and Prefrontal Roles in Context-Dependent Relational Memory. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 1857–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgorio, P.L.; Hiscox, L.V.; Daugherty, A.M.; Sanjana, F.; McIlvain, G.; Pohlig, R.T.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Martens, C.R.; Schwarb, H.; Johnson, C.L. Structure-Function Dissociations of Human Hippocampal Subfield Stiffness and Memory Performance. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 7957–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, L.V.; Johnson, C.L.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Schwarb, H.; Van Beek, E.J.R.; Roberts, N.; Starr, J.M. Hippocampal Viscoelasticity and Episodic Memory Performance in Healthy Older Adults Examined with Magnetic Resonance Elastography. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020, 14, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, K.; Huston, J.; Ehman, R.L.; Manduca, A.; Jack, C.R.; Senjem, M.L.; Vemuri, P.; Murphy, M.C. Associations between Vascular Health, Brain Stiffness and Global Cognitive Function. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destrebecqz, A.; Peigneux, P.; Laureys, S.; Degueldre, C.; Del Fiore, G.; Aerts, J.; Luxen, A.; Van Der Linden, M.; Cleeremans, A.; Maquet, P. The Neural Correlates of Implicit and Explicit Sequence Learning: Interacting Networks Revealed by the Process Dissociation Procedure. Learn. Mem. Cold Spring Harb. Lab. Press 2005, 12, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.L.; Whalen, P.J.; Savage, C.R.; Curran, T.; Kendrick, A.; Brown, H.D.; Bush, G.; Breiter, H.C.; Rosen, B.R. Striatal Recruitment during an Implicit Sequence Learning Task as Measured by Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1997, 5, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeltine, E. Attention and Stimulus Characteristics Determine the Locus of Motor—Sequence Encoding. A PET Study. Brain 1997, 120, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schendan, H.E.; Searl, M.M.; Melrose, R.J.; Stern, C.E. An fMRI Study of the Role of the Medial Temporal Lobe in Implicit and Explicit Sequence Learning. Neuron 2003, 37, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delis, D.C.; Kramer, J.H.; Kaplan, E.; Ober, B.A. California Verbal Learning Test, 2nd ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, W.; Eschman, A.; Zuccolotto, A. E-Prime; Psychology Software Tools Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, J.; Johnson, P. Assessing Implicit Learning with Indirect Tests: Determining What Is Learned about Sequence Structure. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1994, 20, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destrebecqz, A.; Cleeremans, A. Can Sequence Learning Be Implicit? New Evidence with the Process Dissociation Procedure. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2001, 8, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Albert, M.; Dieterich, M.; Haselgrove, C.; van der Kouwe, A.; Killiany, R.; Kennedy, D.; Klaveness, S.; et al. Whole Brain Segmentation: Automated Labeling of Neuroanatomical Structures in the Human Brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, R.L. Memory and Executive Function in Aging and AD: Multiple Factors That Cause Decline and Reserve Factors That Compensate. Neuron 2004, 44, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlvain, G.; Cerjanic, A.M.; Christodoulou, A.G.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Johnson, C.L. OSCILLATE: A Low-Rank Approach for Accelerated Magnetic Resonance Elastography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 88, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.L.; Holtrop, J.L.; Anderson, A.T.; Sutton, B.P. Brain MR Elastography with Multiband Excitation and Nonlinear Motion-Induced Phase Error Correction. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Singapore, 7–13 May 2016; p. 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.L.; Holtrop, J.L.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Weaver, J.B.; Paulsen, K.D.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Sutton, B.P. 3D Multislab, Multishot Acquisition for Fast, Whole-Brain MR Elastography with High Signal-to-Noise Efficiency. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, M.D.J.; Van Houten, E.E.W.; Johnson, C.L.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Sutton, B.P.; Weaver, J.B.; Paulsen, K.D. Multiresolution MR Elastography Using Nonlinear Inversion. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 6388–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, M.D.J.; Johnson, C.L.; Sutton, B.P.; Van Houten, E.E.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Weaver, J.B.; Paulsen, K.D. Including Spatial Information in Nonlinear Inversion MR Elastography Using Soft Prior Regularization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.L.; Schwarb, H.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Anderson, A.T.; Huesmann, G.R.; Sutton, B.P.; Cohen, N.J. Viscoelasticity of Subcortical Gray Matter Structures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 4221–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, A.; Murphy, M.C.; Glaser, K.J.; Manduca, A.; Lake, D.S.; Kruse, S.A.; Jack, C.R.; Ehman, R.L.; Huston, J. Measuring the Effects of Aging and Sex on Regional Brain Stiffness with MR Elastography in Healthy Older Adults. NeuroImage 2015, 111, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgorio, P.L.; Hiscox, L.V.; Daugherty, A.M.; Sanjana, F.; Pohlig, R.T.; Ellison, J.M.; Martens, C.R.; Schwarb, H.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Johnson, C.L. Effect of Aging on the Viscoelastic Properties of Hippocampal Subfields Assessed with High-Resolution MR Elastography. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergs, J.; Morr, A.S.; Silva, R.V.; Infante-Duarte, C.; Sack, I. The Networking Brain: How Extracellular Matrix, Cellular Networks, and Vasculature Shape the In Vivo Mechanical Properties of the Brain. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2402338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimann, F.B.; Müller, S.; Streitberger, K.-J.; Guo, J.; Rot, S.; Ghori, A.; Vajkoczy, P.; Reiter, R.; Sack, I.; Braun, J. MR Elastography in a Murine Stroke Model Reveals Correlation of Macroscopic Viscoelastic Properties of the Brain with Neuronal Density. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, Y.; Arenaza-Urquijo, E.M.; Bartrés-Faz, D.; Belleville, S.; Cantilon, M.; Chetelat, G.; Ewers, M.; Franzmeier, N.; Kempermann, G.; Kremen, W.S.; et al. Whitepaper: Defining and Investigating Cognitive Reserve, Brain Reserve, and Brain Maintenance. Alzheimers Dement. J. Alzheimers Assoc. 2020, 16, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenig, M.C.; Dzialas, V.; Banwinkler, M.; Asendorf, A.; Drzezga, A.; van Eimeren, T. Educational Level and Its Association with Dopamine Transporter Loss in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 115, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, S.T.; Hazeltine, E.; Ivry, R. Functional Mapping of Sequence Learning in Normal Humans. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1995, 7, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarb, H.; Johnson, C.L.; Daugherty, A.M.; Hillman, C.H.; Kramer, A.F.; Cohen, N.J.; Barbey, A.K. Aerobic Fitness, Hippocampal Viscoelasticity, and Relational Memory Performance. NeuroImage 2017, 153, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, L.V.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Johnson, C.L. Evaluation of Cerebral Cortex Viscoelastic Property Estimation with Nonlinear Inversion Magnetic Resonance Elastography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohy, K.E.; Kramer, M.K.; Diano, A.M.; Bailey, O.M.; Delgorio, P.L.; McIlvain, G.; McGarry, M.D.J.; Martens, C.R.; Schwarb, H.; Hiscox, L.V.; et al. Mechanical Properties of the Cortex in Older Adults and Relationships With Personality Traits. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2025, 46, e70147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heselton, H.J.; Anderson, A.T.; Johnson, C.L.; Cohen, N.J.; Sutton, B.P.; Schwarb, H. Putamen Stiffness Declines with Age and Is Associated with Implicit Sequence Learning Outcomes. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090947
Heselton HJ, Anderson AT, Johnson CL, Cohen NJ, Sutton BP, Schwarb H. Putamen Stiffness Declines with Age and Is Associated with Implicit Sequence Learning Outcomes. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(9):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090947
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeselton, Hyeon Jung, Aaron T. Anderson, Curtis L. Johnson, Neal J. Cohen, Bradley P. Sutton, and Hillary Schwarb. 2025. "Putamen Stiffness Declines with Age and Is Associated with Implicit Sequence Learning Outcomes" Brain Sciences 15, no. 9: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090947
APA StyleHeselton, H. J., Anderson, A. T., Johnson, C. L., Cohen, N. J., Sutton, B. P., & Schwarb, H. (2025). Putamen Stiffness Declines with Age and Is Associated with Implicit Sequence Learning Outcomes. Brain Sciences, 15(9), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090947





