Clinical Relevance of Peripheral Interleukins in Drug-Naive First-Episode Psychosis: Symptom-Specific Associations from the PANSS Dimensions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Blood Sampling and Laboratory Procedures
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics
3.2. Serum Concentrations of Interleukins in Patients and Healthy Controls
3.3. Diagnostic Value of Interleukins—ROC Analysis
3.4. Association of Interleukins with the PANSS Scale Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PANSS | Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale |
| FEDN | First-Episode Drug-Naive |
| IL | Interleukin |
References
- Al-Diwani, A.A.J.; Pollak, T.A.; Irani, S.R.; Lennox, B.R. Psychosis: An autoimmune disease? Immunology 2017, 152, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, C.; Elsworthy, R.J.; Upthegrove, R.; Wood, S.J.; Aldred, S. Inflammation in first-episode psychosis: The contribution of inflammatory biomarkers to the emergence of negative symptoms, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2022, 146, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, G.M.; Cousins, L.; Deakin, J.; Lennox, B.R.; Yolken, R.; Jones, P.B. Inflammation and immunity in schizophrenia: Implications for pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upthegrove, R.; Manzanares-Teson, N.; Barnes, N.M. Cytokine function in medication-naive first episode psychosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 155, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, É.M.; Khandaker, G.M. Cytokines in psychosis: From mechanism towards treatment and prediction. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Bialas, A.R.; De Rivera, H.; Davis, A.; Hammond, T.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Tooley, K.; Presumey, J.; Baum, M.; Van Doren, V.; et al. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature 2016, 530, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R. Evaluating the Hypothesis That Schizophrenia Is an Inflammatory Disorder. Focus 2020, 18, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, K.A.; Kusnecov, A.W.; Silverstein, S.M. Inflammation and the two-hit hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Van Os, J.; Morrison, A.P.; Ross, C.A. Childhood trauma, psychosis and schizophrenia: A literature review with theoretical and clinical implications. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2005, 112, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, T.A.; Drndarski, S.; Stone, J.M.; David, A.S.; McGuire, P.; Abbott, N.J. The blood–brain barrier in psychosis. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. A clinical perspective of IL-1β as the gatekeeper of inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.J.; Liu, S.S.; Zhou, S.Y.; Luo, J.H. Interleukin-2 inhibits NMDA receptor-mediated currents directly and may differentially affect subtypes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavăl, D.; Gherghel-Pavăl, N.; Căpățînă, O.O.; Stan, A.; Micluția, I.V.; Giné-Servén, E. The Importance of Cerebrospinal Fluid Investigation in First-episode Psychosis. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2023, 96, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, N.; Weidinger, E.; Leitner, B.; Schwarz, M.J. The role of inflammation in schizophrenia. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzi, E.; Bartoli, F.; Crocamo, C.; Clerici, M.; Carrà, G. Acute variations of cytokine levels after antipsychotic treatment in drug-naïve subjects with a first-episode psychosis: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 77, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, B.; Brunet-Lecomte, M.; Martelli, C.; Benyamina, A. Kinetics of Cytokine Levels during Antipsychotic Treatment in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Zare-Shahabadi, A.; Rezaei, N. Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: An Updated Review. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.J.; Buckley, P.; Seabolt, W.; Mellor, A.; Kirkpatrick, B. Meta-Analysis of Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: Clinical Status and Antipsychotic Effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillinger, T.; D’Ambrosio, E.; McCutcheon, R.; Howes, O.D. Is psychosis a multisystem disorder? A meta-review of central nervous system, immune, cardiometabolic, and endocrine alterations in first-episode psychosis and perspective on potential models. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 24, 776–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicola, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Hepgul, N.; Di Forti, M.; Aitchison, K.J.; Janiri, L.; Murray, R.M.; Dazzan, P.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Serum and gene expression profile of cytokines in first-episode psychosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 31, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bartolomeis, A.; Barone, A.; Vellucci, L.; Mazza, B.; Austin, M.C.; Iasevoli, F.; Ciccarelli, M. Linking Inflammation, Aberrant Glutamate-Dopamine Interaction, and Post-synaptic Changes: Translational Relevance for Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment: A Systematic Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6460–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerrigter, D.; Weickert, T.W.; Lenroot, R.; O’Donnell, M.; Galletly, C.; Liu, D.; Burgess, M.; Cadiz, R.; Jacomb, I.; Catts, V.S.; et al. Using blood cytokine measures to define high inflammatory biotype of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carril Pardo, C.; Oyarce Merino, K.; Vera-Montecinos, A. Neuroinflammatory Loop in Schizophrenia, Is There a Relationship with Symptoms or Cognition Decline? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.K.; Quirion, R. Interleukin-2 as a neuroregulatory cytokine. Brain Res. Rev. 1995, 21, 246–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Bartoli, F.; Carrà, G.; Stańczykiewicz, B.; Gładka, A.; Frydecka, D.; Samochowiec, J.; Jarosz, K.; Hadryś, T.; Miller, B.J. Immune-inflammatory markers and psychosis risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 127, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, A.; Martorell, L.; Montalvo, I.; Ortega, L.; Monseny, R.; Vilella, E.; Labad, J. Increased serum interleukin-6 levels in early stages of psychosis: Associations with at-risk mental states and the severity of psychotic symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovcanin, M.; Jovanovic, I.; Radosavljevic, G.; Djukic Dejanovic, S.; Bankovic, D.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L. Elevated serum level of type-2 cytokine and low IL-17 in first episode psychosis and schizophrenia in relapse. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Il-6 in inflammation, Immunity, And disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovcanin, M.M.; Jovanovic, I.; Radosavljevic, G.; Pantic, J.; Janicijevic, S.M.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Borovcanin, M.M.; Jovanovic, I.; Radosavljevic, G.; et al. Interleukin-6 in schizophrenia-Is there a therapeutic relevance? Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, G.M.; Zammit, S.; Burgess, S.; Lewis, G.; Jones, P.B. Association between a functional interleukin 6 receptor genetic variant and risk of depression and psychosis in a population-based birth cohort. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, S.; Stip, E.; Sepehry, A.A.; Gendron, A.; Bah, R.; Kouassi, E. Inflammatory Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Quantitative Review. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, R.; Yang, Z.; Shurin, G.; Chengappa, K.N.R.; Brar, J.S.; Gubbi, A.V.; Rabin, B.S. Serum interleukin-6 concentration in schizophrenia: Elevation associated with duration of illness. Psychiatry Res. 1994, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.; Noonan, D.M.; Abdalalem, E.; Goletti, D.; Sansone, C.; Calabrone, L.; Albini, A. The multifaceted nature of IL-10: Regulation, role in immunological homeostasis and its relevance to cancer, COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1161067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.W.; De Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severance, E.G.; Gressitt, K.L.; Stallings, C.R.; Origoni, A.E.; Khushalani, S.; Leweke, F.M.; Dickerson, F.B.; Yolken, R.H. Discordant patterns of bacterial translocation markers and implications for innate immune imbalances in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 148, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, M.; Ceresér, K.M.; Goi, P.D.; Fries, G.R.; Teixeira, A.L.; Fernandes, B.S.; Belmonte-De-Abreu, P.S.; Kauer-Sant’Anna, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Gama, C.S. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: Differences in pro- and anti-inflammatory balance. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2011, 33, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwarz, E.; Guest, P.C.; Rahmoune, H.; Harris, L.W.; Wang, L.; Leweke, F.M.; Rothermundt, M.; Bogerts, B.; Koethe, D.; Kranaster, L.; et al. Identification of a biological signature for schizophrenia in serum. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Bocchio Chiavetto, L.; Bignotti, S.; Battisa Tura, G.J.; Pioli, R.; Boin, F.; Kenis, G.; Bosmans, E.; De Jongh, R.; Altamura, C.A. Increased serum interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 in schizophrenic patients resistant to treatment with neuroleptics and the stimulatory effects of clozapine on serum leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 54, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovão, N.; Prata, J.; Vondoellinger, O.; Santos, S.; Barbosa, M.; Coelho, R. Peripheral Biomarkers for First-Episode Psychosis—Opportunities from the Neuroinflammatory Hypothesis of Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Investig. 2019, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, H.; Hafizi, S.; Andreazza, A.C.; Mizrahi, R. Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Psychosis and Psychosis Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allswede, D.M.; Buka, S.L.; Yolken, R.H.; Torrey, E.F.; Cannon, T.D. Elevated maternal cytokine levels at birth and risk for psychosis in adult offspring. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 172, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Huang, P.; Peng, L.; Huang, Q. Maternal C-reactive protein and cytokine levels during pregnancy and the risk of selected neuropsychiatric disorders in offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 105, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, M.; Suzumura, A.; Hosoya, H.; Marunouchi, T.; Nagatsu, T. Interleukin-10 inhibits both production of cytokines and expression of cytokine receptors in microglia. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strle, K.; Zhou, J.H.; Shen, W.H.; Broussard, S.R.; Johnson, R.W.; Freund, G.G.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. Interleukin-10 in the brain. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 21, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeboer, A.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Wierinckx, A.; Van Der Jagt, S.; Bristow, A.F.; Leysen, J.E.; Tilders, F.J.H.; Van Dam, A. Expression and regulation of interleukin-10 and interleukin-10 receptor in rat astroglial and microglial cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.; Jie, H.; Duan, Y.; Xiong, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, P.; Kang, M.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Huang, Z.; et al. Different serum protein factor levels in first-episode drug-naive patients with schizophrenia characterized by positive and negative symptoms. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mednova, I.A.; Boiko, A.S.; Kornetova, E.G.; Semke, A.V.; Bokhan, N.A.; Ivanova, S.A. Cytokines as Potential Biomarkers of Clinical Characteristics of Schizophrenia. Life 2022, 12, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asevedo, E.; Rizzo, L.B.; Gadelha, A.; Mansur, R.B.; Ota, V.K.; Berberian, A.A.; Scarpato, B.S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Bressan, R.A.; Brietzke, E. Peripheral interleukin-2 level is associated with negative symptoms and cognitive performance in schizophrenia. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 129, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyaeva, T.; Rukavishnikov, G.; Manakova, E.; Mazo, G. Serum Interleukin-6 in Schizophrenia: Associations with Clinical and Sociodemographic Characteristics. Consort. Psychiatr. 2023, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, K.A.; Cone, J.J.; Rosen, C.; Sharma, R.P. The value of interleukin 6 as a peripheral diagnostic marker in schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydecka, D.; Misiak, B.; Pawlak-Adamska, E.; Karabon, L.; Tomkiewicz, A.; Sedlaczek, P.; Kiejna, A.; Beszłej, J.A. Interleukin-6: The missing element of the neurocognitive deterioration in schizophrenia? The focus on genetic underpinnings, cognitive impairment and clinical manifestation. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The Master Regulator of Immunity to Infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şimşek, Ş.; Ylldlrlm, V.; Çim, A.; Kaya, S. Serum IL-4 and IL-10 Levels Correlate with the Symptoms of the Drug-Naive Adolescents with First Episode, Early Onset Schizophrenia. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, M.H.; Yang, G.G.; Tan, Y.L.; Chen, D.C.; Tan, S.P.; Wang, Z.R.; De Yang, F.; Okusaga, O.; Soares, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y. Decreased interleukin-10 serum levels in first-episode drug-naïve schizophrenia: Relationship to psychopathology. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 156, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bueno, B.; Bioque, M.; Mac-Dowell, K.S.; Barcones, M.F.; Martínez-Cengotitabengoa, M.; Pina-Camacho, L.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, R.; Sáiz, P.A.; Castro, C.; Lafuente, A.; et al. Pro-/Anti-inflammatory Dysregulation in Patients with First Episode of Psychosis: Toward an Integrative Inflammatory Hypothesis of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinowicz, P.; Więdłocha, M.; Zborowska, N.; Dębowska, W.; Podwalski, P.; Misiak, B.; Tyburski, E.; Szulc, A. A Meta-Analysis of the Influence of Antipsychotics on Cytokines Levels in First Episode Psychosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Healthy Controls | FEDN |
|---|---|---|
| Sex n (%) | ||
| Men | 14 (63.6) | 23 (60.5) |
| Women | 8 (36.4) | 15 (39.5) |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 29.91 ± 6.46 | 27.63 ± 6.84 |
| PANSS (mean ± SD) | NA | |
| Positive symptoms | 29.63 ± 4.77 | |
| Negative symptoms | 23.45 ± 6.34 | |
| General psychopathology | 53.47 ± 6.96 | |
| Total score | 106.55 ± 14.47 |
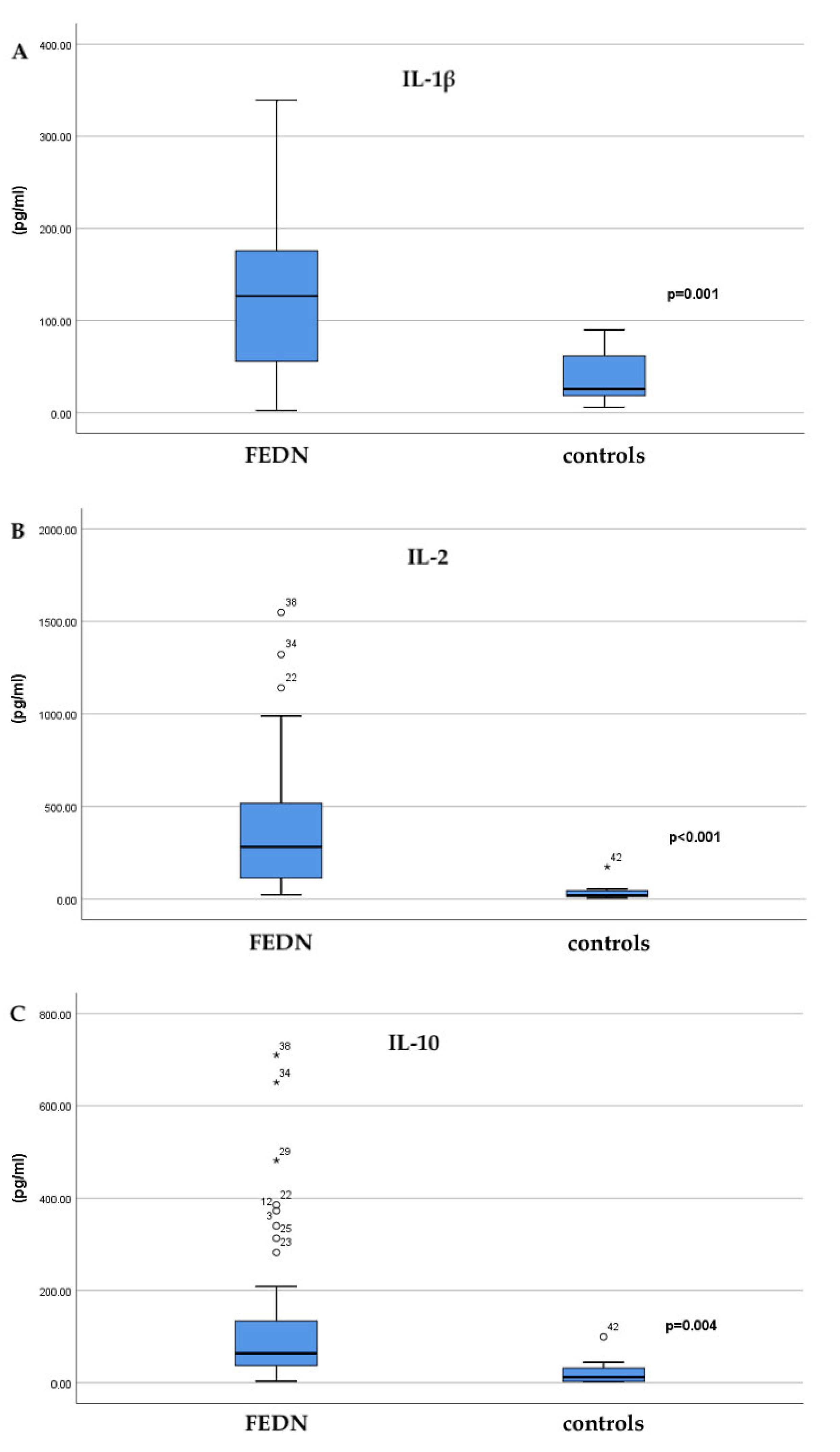
| Interleukin | Healthy Controls (pg/mL; Mean ± SD) | FEDN (pg/mL; Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 37.06 ± 27.61 | 130.14 ± 93.22 | 0.001 |
| IL-2 | 42.15 ± 55.59 | 395.7 ± 380.29 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 | 5.01 ± 4.28 | 9.13 ± 12.90 | 0.698 |
| IL-10 | 24.20 ± 33.43 | 140.65 ± 176.84 | 0.004 |
| Interleukin | AUC | 95%CI | Cut Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 0.842 | 0.659–0.981 | 99.18 | 65.0 | 100.0 | <0.001 |
| IL-2 | 0.917 | 0.759–1.000 | 77.02 | 95.0 | 83.3 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 | 0.396 | 0.187–0.625 | 13.56 | 25.0 | 100.0 | 0.451 |
| IL-10 | 0.817 | 0.565–1.000 | 44.62 | 70.0 | 83.3 | <0.001 |
| PANSS | IL-1β | IL-2 | IL-6 | IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ/p | ||||
| Total score | 0.146/0.382 | 0.070/0.688 | 0.79/0.719 | 0.225/0.174 |
| Positive symptoms | 0.053/0.735 | 0.046/0.785 | 0.065/0.733 | −0.006/0.970 |
| P1 | −0.074/0.660 | −0.123/0.483 | −0.276/0.202 | −0.042/0.804 |
| P2 | −0.025/0.880 | −0.041/0.815 | −0.081/0.715 | 0.058/0.727 |
| P3 | −0.022/0.893 | −0.060/0.732 | −0.064/0.773 | 0.078/0.643 |
| P4 | −0.082/0.624 | −0.087/0.621 | −0.122/0.581 | −0.087/0.603 |
| P5 | −0.371/0.022 | −0.164/0.348 | 0.094/0.669 | −0.309/0.059 |
| P6 | 0.031/0.853 | 0.029/0.867 | 0.170/0.438 | 0.026/0.876 |
| P7 | −0.342/0.036 | −0.107/0.540 | 0.179/0.415 | −0.313/0.056 |
| Negative symptoms | 0.373/0.013 | 0.218/0.189 | 0.068/0.722 | 0.275/0.078 |
| N1 | 0.222/0.181 | 0.058/0.741 | −0.103/0.642 | 0.126/0.450 |
| N2 | 0.065/0.698 | 0.023/0.895 | 0.149/0.498 | 0.204/0.219 |
| N3 | 0.243/0.142 | 0.156/0.372 | −0.017/0.940 | 0.302/0.065 |
| N4 | 0.167/0.317 | −0.020/0.909 | −0.064/0.770 | −0.076/0.650 |
| N5 | 0.097/0.562 | 0.083/0.637 | −0.112/0.612 | 0.168/0.314 |
| N6 | 0.107/0.521 | 0.059/0.737 | 0.271/0.211 | 0.183/0.273 |
| N7 | 0.104/0.534 | −0.146/0.402 | −0.078/0.725 | 0.066/0.696 |
| General psychopathology | 0.375/0.012 | 0.265/0.108 | 0.903/0.626 | 0.364/0.018 |
| G1 | 0.202/0.224 | 0.073/0.676 | −0.246/0.259 | 0.159/0.342 |
| G2 | 0.152/0.362 | 0.161/0.354 | 0.175/0.435 | 0.191/0.252 |
| G3 | 0.219/0.186 | 0.071/0.686 | −0.306/0.156 | 0.110/0.512 |
| G4 | −0.172/0.302 | 0.051/0.770 | 0.403/0.056 | 0.043/0.797 |
| G5 | 0.092/0.584 | 0.084/0.632 | 0.122/0.579 | 0.198/0.234 |
| G6 | 0.209/0.208 | 0.135/0.438 | −0.144/0.511 | 0.125/0.455 |
| G7 | 0.235/0.155 | −0.035/0.840 | 0.026/0.905 | 0.195/0.242 |
| G8 | −0.034/0.841 | 0.017/0.922 | 0.007/0.795 | −0.067/0.690 |
| G9 | −0.089/0.596 | −0.031/0.859 | −0.024/0.914 | −0.004/0.983 |
| G10 | 0.133/0.427 | 0.105/0.548 | 0.225/0.302 | 0.193/0.245 |
| G11 | −0.026/0.875 | −0.105/0.548 | −0.099/0.654 | 0.001/0.997 |
| G12 | −0.002/0.541 | 0.023/0.897 | −0.047/0.832 | 0.021/0.899 |
| G13 | 0.159/0.341 | 0.097/0.580 | 0.381/0.073 | 0.342/0.036 |
| G14 | −0.149/0.370 | −0.062/0.726 | −0.017/0.938 | −0.008/0.961 |
| G15 | 0.103/0.540 | −0.045/0.799 | 0.232/0.287 | 0.227/0.170 |
| G16 | 0.190/0.252 | 0.115/0.512 | 0.247/0.256 | 0.273/0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Binic, I.; Petrovic, J.; Zikic, O.; Golubovic, S.T.; Djordjevic, V.; Stevanovic, M.; Krtinic, D.; Andjelkovic Apostolovic, M. Clinical Relevance of Peripheral Interleukins in Drug-Naive First-Episode Psychosis: Symptom-Specific Associations from the PANSS Dimensions. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090932
Binic I, Petrovic J, Zikic O, Golubovic ST, Djordjevic V, Stevanovic M, Krtinic D, Andjelkovic Apostolovic M. Clinical Relevance of Peripheral Interleukins in Drug-Naive First-Episode Psychosis: Symptom-Specific Associations from the PANSS Dimensions. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(9):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090932
Chicago/Turabian StyleBinic, Iva, Jovana Petrovic, Olivera Zikic, Suzana Tosic Golubovic, Vladimir Djordjevic, Marko Stevanovic, Dane Krtinic, and Marija Andjelkovic Apostolovic. 2025. "Clinical Relevance of Peripheral Interleukins in Drug-Naive First-Episode Psychosis: Symptom-Specific Associations from the PANSS Dimensions" Brain Sciences 15, no. 9: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090932
APA StyleBinic, I., Petrovic, J., Zikic, O., Golubovic, S. T., Djordjevic, V., Stevanovic, M., Krtinic, D., & Andjelkovic Apostolovic, M. (2025). Clinical Relevance of Peripheral Interleukins in Drug-Naive First-Episode Psychosis: Symptom-Specific Associations from the PANSS Dimensions. Brain Sciences, 15(9), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090932






