Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression: A Retrospective Study on an ADNI Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Analyses of CSF and Plasma Samples
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Features of Participants
3.2. CSF and Plasma Biomarkers in AD Patients Stratified on the Basis of Their RoP
3.3. Predictive Ability of Biomarkers and Confounding Variables for RoP in AD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A/T/N | Amyloid/Tau/Neurodegeneration |
| Aβ | Β-Amyloid |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| APD | Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| bl | Baseline |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CLEIA | Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| FD | Fast Decliners |
| FDG-PET | Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography |
| FTD | Frontotemporal Dementia |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NfL | Neurofilament Light Chain |
| p-Tau | Phosphorylated Tau |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RoP | Rate of Progression |
| SD | Slow Decliners |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SiMoA | Single-Molecule Array |
| t-Tau | Total Tau |
| TBI | Traumatic Brain Injury |
References
- Amiri, F.; Safiri, S.; Shamekh, A.; Abolghasemi, S.; Mansournia, M.A.; Rabiee, M.; Abbasi, N.; Rezaei, N.; Shafiee, A.; Ghaffari, M.; et al. Prevalence, Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life Years Due to Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias in Middle East and North Africa, 1990–2021. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease at 25 Years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”: A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Burnham, S.; Bourgeat, P.; Brown, B.; Ellis, K.A.; Salvado, O.; Szoeke, C.; Macaulay, S.L.; Martins, R.; Maruff, P.; et al. Amyloid β Deposition, Neurodegeneration, and Cognitive Decline in Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O.; Seibyl, J.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Bittner, T.; Lifke, V.; Corradini, V.; Eichenlaub, U.; Batrla, R.; et al. CSF Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease Concord with Amyloid-β PET and Predict Clinical Progression: A Study of Fully Automated Immunoassays in BioFINDER and ADNI Cohorts. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a Biological Definition of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; et al. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, B.C.; Thompson, P.M.; Brinton, R.D. Age, APOE and Sex: Triad of Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 160, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, R.S.; Massman, P.; Dunn, J.K. A Method for Estimating Progression Rates in Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansart, M.; Epelbaum, S.; Bassignana, G.; Bône, A.; Bottani, S.; Cattai, T.; Couronné, R.; Faouzi, J.; Koval, I.; Louis, M.; et al. Predicting the Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Machine Learning: A Systematic, Quantitative and Critical Review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojjati, S.H.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Khazaee, A.; Babajani-Feremi, A.; for The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Predicting Conversion from MCI to AD Using Resting-State fMRI, Graph Theoretical Approach and SVM. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 282, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as Biomarkers in Neurological Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilament Proteins as Biomarkers to Monitor Neurological Diseases and the Efficacy of Therapies. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 689938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Neurological Disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; The NFL Group. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiardi, S.; Quadalti, C.; Mammana, A.; Dellavalle, S.; Zenesini, C.; Sambati, L.; Pantieri, R.; Polischi, B.; Romano, L.; Suffritti, M.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Plasma P-Tau181, NfL, and GFAP in a Clinical Setting Cohort of Prevalent Neurodegenerative Dementias. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light with Neurodegeneration in Patients with Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Skillbäck, T.; Mattsson, N.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Portelius, E.; Shaw, L.M.; Weiner, M.W.; Blennow, K.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Concentration with Alzheimer Disease Progression. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, S.; Syrjanen, J.A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Skoog, I.; Waern, M.; Hagen, C.E.; van Harten, A.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; et al. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein with Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment Among Individuals Without Cognitive Impairment. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Bathala, P.; Kale, S.S.; Campbell, C.T.; Stengelin, M.; Sando, S.B.; Prassas, I.; Diamandis, E.P.; Bråthen, G. CSF Neurofilament Light May Predict Progression from Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, V.; Colletti, T.; Ribisi, P.; Tarantino, D.; Mosca, V.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M.; Piccoli, T. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilaments Light-Chain Differentiate Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression (RoP): A Preliminary Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preische, O.; Schultz, S.A.; Apel, A.; Kuhle, J.; Kaeser, S.A.; Barro, C.; Gräber, S.; Kuder-Buletta, E.; LaFougere, C.; Laske, C.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Dynamics Predicts Neurodegeneration and Clinical Progression in Presymptomatic Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomucci, G.; Mazzeo, S.; Bagnoli, S.; Ingannato, A.; Leccese, D.; Berti, V.; Padiglioni, S.; Galdo, G.; Ferrari, C.; Sorbi, S.; et al. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease in Subjective Cognitive Decline and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Andreasson, U.; Derfuss, T.; Lindberg, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Liman, V.; Norgren, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Comparison of Three Analytical Platforms for Quantification of the Neurofilament Light Chain in Blood Samples: ELISA, Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Piccoli, T.; Vidali, M.; Cuffaro, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Iacolino, G.; Giglio, V.R.; Lupo, F.; Alongi, P.; Bivona, G.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers Measured by Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2020, 80, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Basic Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration: A Critical Update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, R.S.; Pavlik, V.; Massman, P.; Rountree, S.; Darby, E.; Chan, W. Predicting Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2010, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.L.; Unverzagt, F.; LaMantia, M.A.; Khan, B.A.; Boustani, M.A. Risk Factors for the Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.M.; Mapstone, M.; Gardner, M.N.; Sandoval, T.C.; McCrary, J.W.; Guillily, M.D.; Reilly, L.A.; DeGrush, E. Women Have Farther to Fall: Gender Differences between Normal Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease in Verbal Memory Engender Better Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease in Women. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2011, 17, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraghavan, V.; Klein, S.; Fani, L.; Ham, L.S.; Vrooman, H.; Ikram, M.K.; Niessen, W.J.; Bron, E.E.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Analyzing the Effect of APOE on Alzheimer’s Disease Progression Using an Event-Based Model for Stratified Populations. Neuroimage 2021, 227, 117646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.A.; Choudhury, K.R.; Rathakrishnan, B.G.; Marks, D.M.; Petrella, J.R.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Marked Gender Differences in Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment over 8 Years. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 1, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Blood Biomarkers: Democratizing Alzheimer’s Diagnostics. Neuron 2020, 106, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planalp, E.M.; Langhough, R.E.; Jonaitis, E.M.; Clark, L.R.; Hermann, B.P.; Betthauser, T.J.; Gallagher, C.L.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. Synaptic Markers Are Associated with Cognitive Decline after Accounting for Amyloid Burden among an At-Risk Alzheimer’s Disease Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Al Khleifat, A.; Leuzy, A.; van der Ende, E.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Benedet, A.L.; Pascoal, T.A.; Lleó, A.; Parnetti, L.; et al. A Multicentre Validation Study of the Diagnostic Value of Plasma Neurofilament Light. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, M.M.; Syrjanen, J.A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Vemuri, P.; Skoog, I.; Machulda, M.M.; Kremers, W.K.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.; et al. Plasma and CSF Neurofilament Light: Relation to Longitudinal Neuroimaging and Cognitive Measures. Neurology 2019, 93, e252–e260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Cullen, N.C.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Association Between Longitudinal Plasma Neurofilament Light and Neurodegeneration in Patients with Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, L.E.; Karlsson, J.E.; Karlsson, J.O.; Persson, L.I.; Wikkelsø, C. Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases Have Increased Levels of Neurofilament Protein in CSF. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Bertolotto, A.; Engelborghs, S.; Hampel, H.; Simonsen, A.H.; Kapaki, E.; Kruse, N.; Le Bastard, N.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Recommendations to Standardize Preanalytical Confounding Factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers: An Update. Biomark. Med. 2012, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Gray, E.; Pearce, N.; Petzold, A.; Norgren, N.; Giovannoni, G.; Fratta, P.; Sidle, K.; Fish, M.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain: A Prognostic Biomarker in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurology 2015, 84, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, F.; Steinacker, P.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Kassubek, J.; Oeckl, P.; Halbgebauer, S.; Tumani, H.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Dorst, J.; Feneberg, E.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum for the Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Portelius, E.; Cullen, N.C.; Sandelius, Å.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Höglund, K.; Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; et al. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein Levels with Cognition in Patients with Dementia, Motor Neuron Disease, and Movement Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hamade, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Axtell, R.; Giri, S.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Current and Future Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, J.D.; Woollacott, I.O.C.; Dick, K.M.; Brotherhood, E.; Gordon, E.; Fellows, A.; Toombs, J.; Druyeh, R.; Cardoso, M.J.; Ourselin, S.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain Protein Is a Measure of Disease Intensity in Frontotemporal Dementia. Neurology 2016, 87, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Häsler, L.M.; Lambert, M.; Kaeser, S.A.; Gräber-Sultan, S.; Obermüller, U.; Kuder-Buletta, E.; la Fougere, C.; Laske, C.; Vöglein, J.; et al. Comparative neurofilament light chain trajectories in CSF and plasma in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, M. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Plasma for Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeo, S.; Ingannato, A.; Giacomucci, G.; Manganelli, A.; Moschini, V.; Balestrini, J.; Cavaliere, A.; Morinelli, C.; Galdo, G.; Emiliani, F.; et al. Plasma neurofilament light chain predicts Alzheimer’s disease in patients with subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cullen, N.C.; Leuzy, A.; Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, L.; Allué, J.A.; Proctor, N.K.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Individualized Prognosis of Cognitive Decline and Dementia in Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on Plasma Biomarker Combinations. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, P.S.J.; Poole, T.; O’Connor, A.; Heslegrave, A.; Ryan, N.S.; Liang, Y.; Druyeh, R.; Mead, S.; Blennow, K.; Schott, J.M.; et al. Longitudinal Measurement of Serum Neurofilament Light in Presymptomatic Familial Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioni, A.; Raho, E.M.; Manzoli, L.; Koch, G.; Flacco, M.E.; Di Lorenzo, F. Blood phosphorylated Tau181 reliably differentiates amyloid-positive from amyloid-negative subjects in the Alzheimer’s disease continuum: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 17, e70068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Dubarbie, F.; Guerra-Ruiz, A.; López-García, S.; Lage, C.; Fernández-Matarrubia, M.; Nevado-Cáceres, Á.; Rivera-Sánchez, M.; Valera-Barrero, A.; Pozueta-Cantudo, A.; García-Martínez, M.; et al. Prestazioni diagnostiche del p-tau217 plasmatico in una coorte di pazienti con problemi di memoria utilizzando la piattaforma automatizzata Lumipulse. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Vidali, M.; Scazzone, C.; Piccoli, T.; Gambino, C.M.; Bivona, G.; Giglio, R.V.; Ciaccio, A.M.; La Bella, V.; et al. Neurogranin as a Reliable Biomarker for Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, L.; Gambino, C.M.; Lo Sasso, B.; Bivona, G.; Milano, S.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Piccoli, T.; La Bella, V.; Ciaccio, M. Neurogranin as a Novel Biomarker in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | SD (n = 42) | FD (n = 45) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 75.5 (71.1–79.625) | 75.7 (68.2–79.6) | 0.810 |
| Gender (M/F) | 29/13 | 24/21 | 1 |
| Follow-up (years) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 0.459 |
| MMSE bl A (scores) | 24 (22–25) | 22 (21–25) | 0.093 |
| Apo E ε4 (%) | 71 | 67 | 0.980 |
| Variables | Median Values (IQR) | rho | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| RoP (n.a.) | ) | / | / |
| Aβ42 (pg/mL) | 593.6 (455.25–750.2) | −0.089 | 0.410 |
| tTau (pg/mL) | 358.9 (278.75–450.85) | 0.083 | 0.442 |
| pTau (pg/mL) | 37.72 (28.13–54.355) | −0.030 | 0.781 |
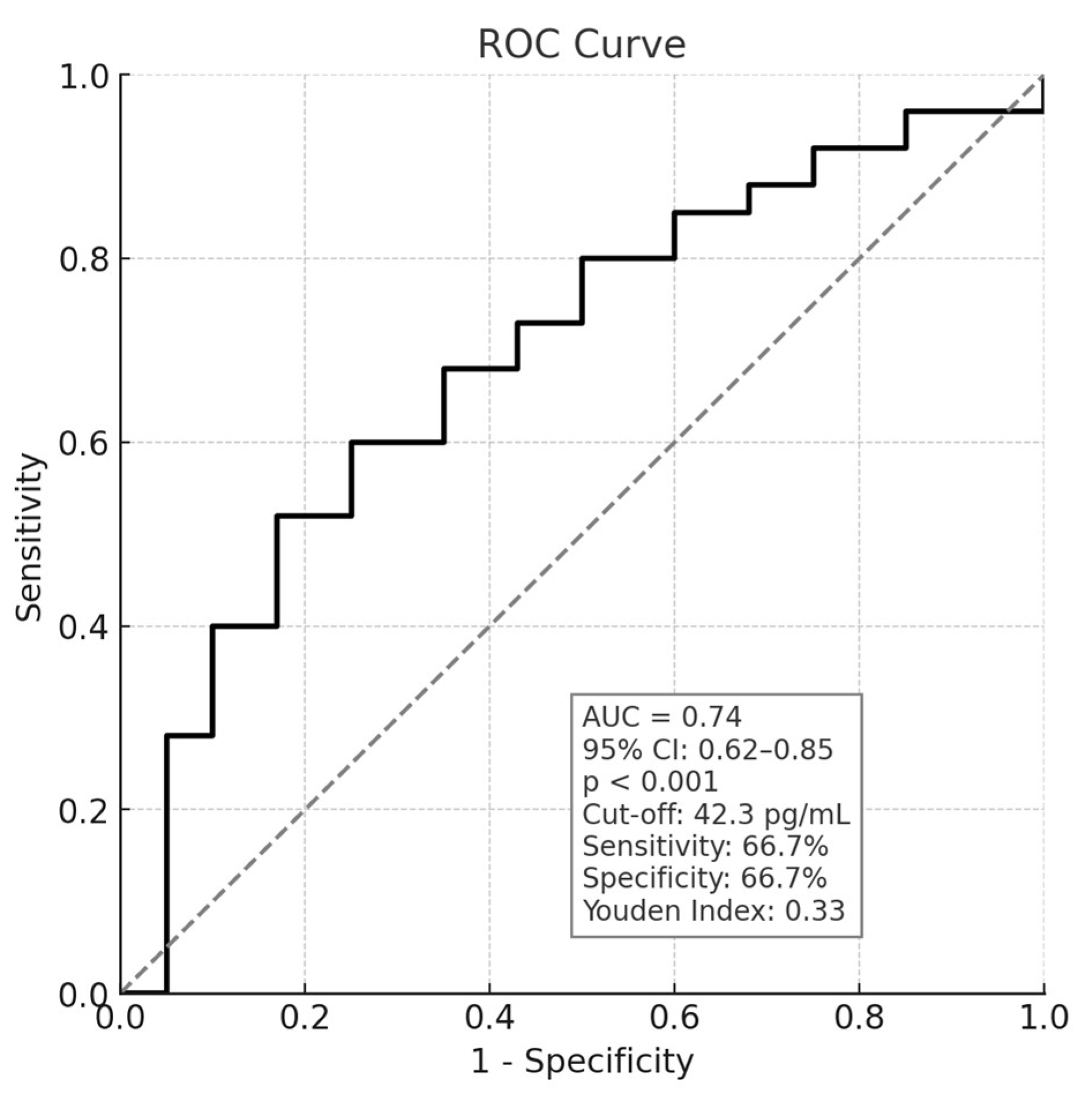
| Plasma NfL (pg/mL) | 42.3 (32.8–63.05) | 0.446 | <0.001 |
| Variables | SD (n = 42) | FD (n = 45) | Effect Size | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42 (pg/mL) | 651.2 (496.575–808.75) | 576.4 (447.8–653.9) | 0.622 | 0.0507 |
| tTau (pg/mL) | 362.35 (268.4–452.775) | 353.7 (286.5–445.4) | 0.490 | 0.875 |
| pTau (pg/mL) | 37.97 (27.883–64.228) | 37.41 (28.64–47.67) | 0.530 | 0.631 |
| Plasma NfL (pg/mL) | 36.9 (30.75–45.975) | 61.4 (39.8–90.1) | 0.410 | <0.001 |
| RoP FD | B | SE A | OD (95%C.I.) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma NfL (>cut off) | 1.386 | 0.455 | 4.0 (1.64–9.76) | 0.0023 |
| Aβ42 (path.) | 0.788 | 0.442 | 2.2 (0.92–5.23) | 0.074 |
| t-Tau (path.) | 0.098 | 0.451 | 1.1 (0.46–2.68) | 0.582 |
| p-Tau (path.) | −0.775 | 0.534 | 0.46 (0.16–1.31) | 0.256 |
| Model | RoP FD | B | SE | p | AIC | BIC | LL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | NfL > cut-off | −0.735 | 0.278 | 0.008 | 92.69 | 97.62 | −44.34 |
| 1 | base + Aβ42 | −1.710 | 0.540 | 0.002 | 87.86 | 95.26 | −40.93 |
| 2 | base + pTau | −0.603 | 0.311 | 0.053 | 93.80 | 101.20 | −43.90 |
| 3 | base + tTau | −0.914 | 0.357 | 0.010 | 94.00 | 101.40 | −44.00 |
| 4 | base + APOE ε4 | −0.968 | 0.479 | 0.043 | 94.31 | 101.71 | −44.15 |
| 5 | base + MMSE bl | 3.271 | 3.179 | 0.304 | 93.03 | 100.42 | −43.51 |
| 6 | base + Aβ42 + pTau | −1.577 | 0.555 | 0.004 | 88.83 | 98.69 | −40.41 |
| 7 | base + Aβ42 + tTau | −1.926 | 0.601 | 0.001 | 89.11 | 98.97 | −40.56 |
| 8 | base + Aβ42 + pTau + tTau | −1.833 | 0.607 | 0.003 | 89.34 | 101.67 | −39.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virga, G.; Marco, B.D.; Blandino, V.; Piccoli, T. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression: A Retrospective Study on an ADNI Cohort. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090924
Virga G, Marco BD, Blandino V, Piccoli T. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression: A Retrospective Study on an ADNI Cohort. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(9):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090924
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirga, Giuseppe, Bruno Di Marco, Valeria Blandino, and Tommaso Piccoli. 2025. "Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression: A Retrospective Study on an ADNI Cohort" Brain Sciences 15, no. 9: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090924
APA StyleVirga, G., Marco, B. D., Blandino, V., & Piccoli, T. (2025). Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain in Patients Affected by Alzheimer’s Disease with Different Rate of Progression: A Retrospective Study on an ADNI Cohort. Brain Sciences, 15(9), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15090924







