A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Learning and Memory in Prolonged Aluminum-Exposure-Induced Neurotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sources of Information and Search Strategies
2.2. Selection of Studies and Data Collection
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Methodological Quality, Transparency, and Reporting Standards of Studies
2.6. Statistical Data Analysis
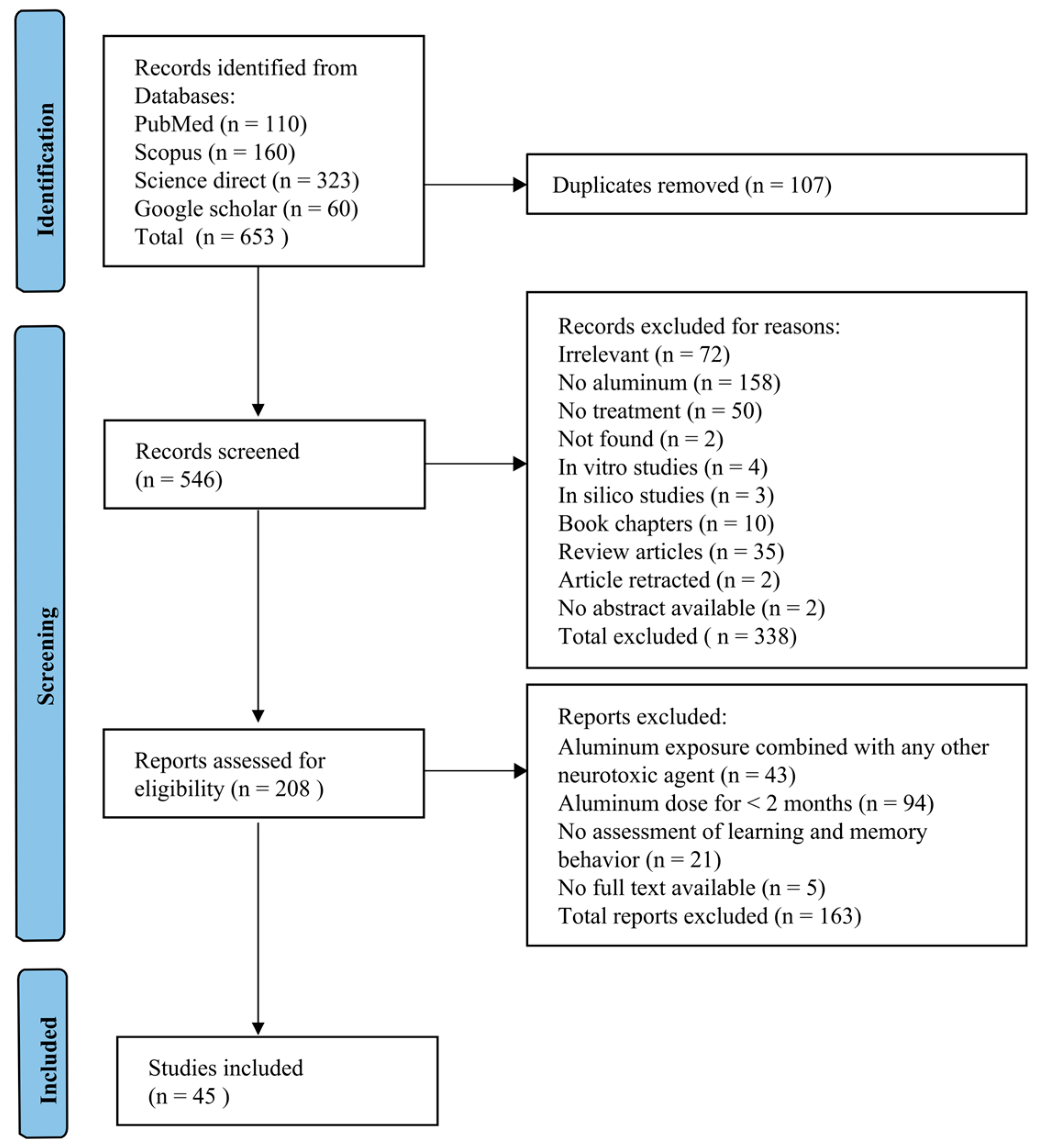
3. Results
3.1. Study Inclusion
3.2. Study Characteristics
| Study | Aluminum, Dose, Duration, and Route | Pharmacological Agent, Dose, Duration, and Route | Combination | Animal Sex, Strain, Age, and Weight | Anaesthesia Dose | Behaviors Accessing Learning and Memory | Properties of Pharmacological Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [38] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Memantine 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | - | Male Wistar rats (90–100 days old) 190 to 230 g | N/M (no dissection) | MWM, PAT, RAM, OFT, RRT | Enhance cognitive functions |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [61] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Rivastigmine 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2.5 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | - | Male Wistar albino rats (90 days old) 190–240 g | N/M (no dissection) | OFT, MWM, RAM, PAT, RRT | Cholinesterase inhibition |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2022 [37] | AlCl3 hexahydrate 80 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Naproxen 20 mg/kg 14 days i.p. | Rivastigmine (1 mg/kg) | Male albino Wistar rats (age N/M) 180–220 g | Thiopental sodium (50 mg/kg) | NOR, PAT, MWM | Cholinergic inhibition Anti-inflammatory Anti-apoptotic |
| Abdel-Zaher et al., 2017 [62] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 90 days i.p. | Citicoline 100 mg/kg 90 days i.p. | - | Male albino Wistar rats (age N/M) 180–220 g | N/M | MWM, PAT, RAM | Anti-oxidant |
| Allagui et al., 2014 [63] | AlCl3 50 mg/kg 120 days Oral gavage | Melatonin 10 mg/kg 120 days i.p. | - | Male Wistar rats Young (60 days) and old (720 days old) Weight N/M | N/M | OFT, RAM, EPM | Anti-oxidant Neuroprotective Cognitive enhancement Enhance neuronal health |
| Alzahrani et al., 2020 [64] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Azilsartan (3.5 mg and 7 mg/kg), Perindopril (0.5 mg and 1 mg/kg), 60 days Oral gavage | - | Male Wister rats (42–56 days old) 180–220 g | N/M | Y maze | Anti-inflammatory (reduces TNF-α) Reduces amyloidogenic activity Anti-oxidant (reduces lipid peroxidation) |
| Amjad and Umesalma, 2015 [65] | AlCl3 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Centella asiatica 500 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Either sex Wistar albino rats (age N/M) 120–150 g | Diethyl ether (dose N/M) | HWM, LA by actophotometer, RRT | Anti-oxidant Restore cholinergic neurotransmission |
| Azib et al., 2019 [66] | AlCl3 100 p.p.m./day 60 days Oral | Pistacia lentiscus L. leaves extract 150 and 300 p.p.m./day 60 days Oral | - | Male adult albino mice (age N/M) 18–25 g | N/M | Head dipping, Black and White test, EPM, MWM | Prevents oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation Anti-inflammatory |
| Azib et al., 2020 [67] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Fraxinus angustifolia Vahl. bark extract 150 and 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male NMRI mice (age N/M) 26 ± 2 g | N/M | LA, Black and White test, MWM | Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Anti-apoptotic Direct inhibition of Aβ-aggregation |
| Bhargava et al., 2023 [14] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral gavage | Cassia tora extract 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral gavage | Memantine (20 mg/kg) | Male Wistar rats (age N/M) 200 ± 20 g | Halothane (dose N/M) | MWM | Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Cognitive enhancement Neurotransmitter regulation |
| Campos et al., 2022 [68] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 90 days Oral | Chrysin 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg 45 days Oral gavage | - | Male Swiss mice (about 60 days old) 25–30 g | Ketamine and xylazine hydrochloride (dose N/M) | OFT, Chimney Test, Step-Down Avoidance | Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotective |
| Cao et al., 2017 [69] | AlCl3 150 mg/kg 90 days Oral | Hypericum perforatum extract 150 and 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male Wistar rats (42–49 days old) 185–200 g | Sodium pentobarbital (dose N/M) | OFT, MWM | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidative Neuroprotective Learning and memory enhancing |
| Cheng et al., 2014 [70] | AlCl3 171.8 mg/kg 70 days Oral | Apple (Ralls) polyphenol extract 200 mg/kg 70 days Oral | - | Male Wistar rats (49 days old) 160–180 g | N/M | SDIA, MWM | Anti-oxidant Metal-chelating Anti-apoptotic |
| Dibacto et al., 2022 [71] | AlCl3 75 mg/kg 60 days Esophageal gavage | Xylopia parviflora 150 and 300 mg/kg 60 days Esophageal gavage | Donepezil (5 mg/kg) and curcumin (100 mg/kg) | Female Wistar rats (456 days old) 200–220 g | N/M | MWM, OFT | Anti-oxidant Cholinesterase inhibition |
| Firdaus et al., 2022 [21] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Centella asiatica 150, 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male Charles Foster strain rats (age N/M) 200–260 g | N/M | Y maze, OFT | AchE inhibition Cognitive enhancement Cellular protection |
| Gadouche et al., 2018 [72] | AlCl3 500 mg/kg 84 days Oral | Pomegranate juice 500 mg/kg 90 days Oral | - | Female Swiss albino mice (428 days old) 18.5 ± 1.98 g | N/M | LA, FST, EPM, MWM | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidant Anti-apoptotic |
| García et al., 2009 [60] | Aluminum lactate 1 mg of Al/g of diet 183 days Oral | Melatonin 10 mg/kg 183 days Oral | - | Female transgenic (Tg2576) and wild-type mice (152 days old) Weight N/M | Ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) | OFT, MWM | No significant protective effect |
| Gong et al., 2005 [73] | AlCl3 500 mg/kg (60 days, i.g.) + 1600 p.p.m. (up to 152 days, in drinking water) Up to 183 days Oral | Ginkgo biloba leaf extract 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg 60 days i.g. | - | Male Wistar rats (56–84 days old) 200–250 g | 35% chloral hydrate (dose N/M) | MWM | Anti-oxidant Neuroprotective Anti-apoptotic |
| Gothwal et al., 2019 [74] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Rivastigmine (in 3 delivery systems: pure RIV, PAMAM- RIV, Lf-RIV) 2 mg/kg 14 days i.p. | - | Either sex Swiss albino mice (20–25 g) (age N/M) | N/M | ORM | Neuroprotective Cognitive enhancer Cholinergic-supportive as it inhibits AChE |
| Guo et al., 2016 [75] | Aluminum gluconate 200 mg/kg 100 days i.g. | Misoprostol 30, 60, and 120 μg/kg 100 days i.g | - | Sprague Dawley male rats (age N/M) 200–250 g | N/M | MWM | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidant Anti-apoptotic effects (by modulating the PGES-PGE2-EPs signaling pathway) |
| Justin Thenmozhi et al., 2017 [76] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Hesperidin 100 mg/kg 60 days i.g. | - | Male albino Wistar rats (70–84 days old) 200–225 g | N/M | RAM, EPM, PAT | Improve learning and memory Anti-oxidative Anti-apoptotic |
| Justin-Thenmozhi et al., 2018 [77] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Hesperidin 100 mg/kg 60 days i.g. | - | Male albino Wistar rats (70–84 days old) 200–225 g | Ketamine chloride (24 mg/kg) | Y maze, NOR, RRT | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidative Anti-apoptotic Neuroprotective Learning and memory enhancing |
| Kakkar and Kaur, 2011 [78] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 126 days Oral gavage | Curcumin (free curcumin: 50 mg/kg) (solid lipid nanoparticles of curcumin: 1, 12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg) 42 days Oral gavage | Rivastigmine (1.5 mg/kg) | Male Lacca mice (56–84 days old) 15–25 g | N/M | MWM | Improve brain histopathology Improve cognition Anti-oxidant |
| Kumar et al., 2019 [79] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Artesunate 28 mg/kg + Rivastigmine 1 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Memantine (20 mg/kg) | Male Wistar albino rats (age N/M) 150–250 g | N/M | PAT | Memory enhancing Anti-inflammatory Synergistic |
| Li et al., 2018 [80] | AlCl3 50 mg/kg 60 days Subcutaneous injection | Isorhynchophylline 20 and 40 mg/kg 56 days i.g. | Donepezil (5 mg/kg) | Male Balb-c mice (121 days old) 25–30 g | N/M | RAM | Anti-oxidant (suppress NF-κB signaling pathway) Enhance learning and memory |
| Liu et al., 2010 [81] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Soy isoflavones 60 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | - | Kunming male mice (age N/M) 20 g | N/M | PAT | Improve learning and memory |
| Luo et al., 2007 [82] | AlCl3 1600 p.p.m. 243 days Oral | Icariin 60 and 120 mg/kg 91 days Oral gavage | - | Male Wistar rats (age N/M) 400–500 g | N/M | MWM | Anti-oxidant effects Decreased Aβ1–40 levels |
| Mohamed et al., 2023 [83] | AlCl3 175 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Echinacea purpurea extract 250 mg/kg 60 days Oral | Rivastigmine (0.3 mg/kg) | Male Wistar rats (age N/M) 150–170 g | Thiopental sodium (50 mg/kg) | Y maze, FST, NOR | Anti-oxidant Learning and memory enhancing AchE inhibitor |
| Nampoothiri et al., 2017 [84] | AlCl3 175 mg/kg 60 days Oral gavage | Insulin 0.5 insulin units/kg 60 days i.p. | Glucose (200 mg/kg), Rivastigmine (1 mg/kg) | Male Wistar rats (90 days old) 200–220 g | N/M | MWM | No significant neuroprotective properties |
| Nehru and Bhalla, 2007 [85] | AlCl3 40 mg/kg 60 days Oral gavage | Centrophenoxine 100 mg/kg 42 days after Al i.p. | - | Female Sprague Dawley rats (age N/M) 160–200 g | N/M | AAT, PAT | Cholinergic and cognitive enhancing Neurotransmitter restorative |
| Pan et al., 2015 [86] | Aluminum gluconate 200 mg/kg 100 days i.g. | Beraprost sodium 6, 12, and 24 μg/kg 100 days i.g. | - | Male Sprague Dawley rats (56 days old) 200–250 g | 4% chloral hydrate (1 mL/100 g) | MWM | Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotective |
| Prabhakar, 2020 [87] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Naringin 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg 30 days Oral | Donepezil (0.75 mg/kg) | Either sex Wistar rats (age N/M) 180–210 g | N/M | OFT, RAM, RRT, MWM | Anti-oxidant Neuroprotective Cholinergic restoration |
| Qi-Hai et al., 2006 [88] | AlCl3 50 g/L (30 days, gastrogavage) + 1.6 g/L (60 days, in drinking water) 3 months Oral | Ginkgo biloba leaf extract 50, 100, 200 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male Wistar rats (56–84 days old) 200–250 g | 35% chloral hydrate (1 mL/kg) | MWM | Anti-oxidant Inhibit AChE expression Neuroprotective |
| Rapaka et al., 2021 [89] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 168 days Oral | Benincasa hispida 250, 500 mg/kg 112 days Oral gavage | - | Male Sprague-Dawley rats (84 days old) 200–250 g | Ether anaesthesia (dose N/M) | MWM, Y maze | Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidative Neuroprotective Learning and memory enhancing |
| Ravi et al., 2018 [20] | AlCl3 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral catheter | Caesalpinia crista methanolic extract 100 and 400 mg/kg 60 days Oral catheter | Rivastigmine (1.5 mg/kg) | Male Wistar albino rats (age N/M) 180–200 g | N/M | MWM, LA | AChE inhibition Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory |
| Ravi et al., 2020 [90] | AlCl3 300 mg/kg 60 days Oral catheter | Cassia tora extract 100, 400 mg/kg 60 days Oral catheter | Rivastigmine (1.5 mg/kg) | Male Wistar albino rats (age N/M) 180–200 g | Sodium pentobarbitone (100 mg/kg) | MWM, LEA | Anti-amyloid aggregation Memory and cognitive protection Neuroprotective Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Pro-neurotrophic Cholinergic protection Improvement in motor skills |
| Rijal et al., 2019 [91] | AlCl3 10 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Phenylpropanoids; para-methoxycinnamic acid and ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate 50 mg and 100 mg/kg 20 days Oral | Rivastigmine (1 mg/kg) and Memantine (20 mg/kg) | Male Wistar rats (121 days old) 250–300g | N/M | OFT, MWM | Anti-oxidant Neuroprotective (AChE modulation, reduces oxidative stress) |
| Saba et al., 2017 [23] | AlCl3 40 mg/kg 60 days i.g. | Rasa Sindoor 2 g/kg 30 days i.g. | - | C57BL/6J male mice (60 days old) Weight N/M | Urethane (1.5 g/kg) | MWM | Improve cognitive functions and memory Maintain neurotransmitter cycling and GABAergic TCA cycle |
| Sethi et al., 2009 [36] | AlCl3 50 mg/kg 180 days Oral | Curcumin 30 mg/kg 180 days Oral gavage | - | Male albino Wistar rats Young (121 days old) and old (547 days old) Weight N/M | Ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) | MWM, OFT | Anti-oxidant activity Membrane stabilization PKC regulation Neuronal protection Cognitive enhancement Anxiolytic effects |
| Shalaby et al., 2023 [92] | AlCl3 50 mg/kg 60 days Subcutaneous injection | Ginsenoside Rb1 70 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male albino mice (121 days old) 25–30 g | 5% chloral hydrate (dose N/M) | PAT | Anti-oxidant Anti-apoptotic Aβ and tau inhibition Anti-inflammatory |
| Singh et al., 2018 [24] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral gavage | EGCG (Epigallocatechin-gallate) and EGCG-loaded nanoparticles 10 mg/kg 30 days Oral gavage | - | Male Swiss albino Wistar rats (age N/M) 200–250 g | N/M | MWM, OFT, NOR | Anti-amyloidogenic Anti-oxidant Neuroprotective Cholinergic restoration |
| Thenmozhi et al., 2016 [93] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 60 days i.p. | Tannoids of Emblica officinalis 100 mg/kg 60 days Oral | - | Male albino Wistar rats (70–84 days old) 200–225 g | N/M | PAT, EPM, RAM | Anti-oxidant Anti-apoptotic Prevent tau hyperphosphorylation (by activating the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway) |
| Thirunavukkarasu et al., 2012 [94] | AlCl3 100 mg/kg 90 days Oral | Manasamitra vatakam 100 mg/kg 90 days Oral | - | Male adult Wistar albino rats (age N/M) 200–220 g | N/M | EPM, AAT | Cell-protective Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory |
| Zakrzeska et al., 2023 [59] | AlCl3 200 mg/kg 120 days Oral gavage | Betulin 100 mg/kg 60 days i.g. | Cyclodextrin (100 mg/kg) | Adult Wistar rats (age N/M) 220–250 g | Ether anaesthesia (dose N/M) | MWM, BWT | Anti-oxidant Anti-inflammatory Anti-apoptotic AchE enhancement (betulin in combination with cyclodextrin enhances spatial memory and lowers β-amyloid, TNF-α, and APLP2 levels) |
| Zhao et al., 2013 [95] | AlCl3 200 mg/kg 183 days Oral | Ginsenoside Rb1 20 mg/kg 121 days Oral | - | Female ICR mice (60 days old) Weight N/M | Sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg) | MWM | Prevent tau hyperphosphorylation Improve learning and memory |
3.3. Outcomes of Studies
| Study | Treatment Agent | Behavioral Outcomes | Biochemical Outcomes | Molecular Outcomes | Histological Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [38] | Memantine | Improved learning and memory (MWM, RAM, PAT) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [61] | Rivastigmine | Improvement in locomotion and exploration (open field test, Rotarod), enhancement in learning and memory (MWM, RAM, PAT) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2022 [37] | Naproxen | Improved memory and cognitive performance (MWM, NOR, PAT) | ↓ hippocampal AChE activity | N/A | Partial restoration of Purkinje cell morphology cerebellar cortex (H and E staining) (IHC) |
| Abdel-Zaher et al., 2017 [62] | Citicoline | ↓ reference and working memory errors (RAM), improved escape latency and swimming (MWM), ↑ step-through latency (PAT) | ↓ MDA, ↓ glutamate and ↓ nitrite levels, ↑ GSH levels in the hippocampus | N/A | N/A |
| Allagui et al., 2014 [63] | Melatonin | Improved cognitive and memory functions (RAM) | ↓ TBAR levels ↑ SOD, CAT, GPx, and AchE | N/A | Enhanced cellular structure ↓ vacuolization ↓ cellular depletion ↓ Pyknotic nuclei (H and E staining of hippocampus and neocortex) |
| Alzahrani et al., 2020 [64] | Azilsartan and Perindopril | Improved spatial working memory (↑ spontaneous alternation %age, Y maze) | ↓ AChE, ↓ MDA, and ↓ TNF-α, no significant change in NO, ↓ Aβ42 plaques, ↓ neurofibrillary tangles | N/A | Preserved the structure in DG and CA3 hippocampal regions, ↓ vacuolation and ↓ neuronal degeneration (H and E staining) |
| Amjad and Umesalma, 2015 [65] | Centella asiatica | Improved spatial memory, ↓ task latency (Hebb–Williams maze), improved neuromuscular coordination (Rotarod test), improved locomotor activity | ↑ MDA levels, ↑ SOD, ↑ CAT, ↑ GST, ↑ GSH, ↓ LPO, SOD, CAT, attenuated AChE levels | N/A | Preserved cell membrane integrity and improved histoarchitecture (in cortex, striatum, hypothalamus, and hippocampus, H and E staining), ↓ Nissl bodies, marked reduction in neuronal cell loss (Nissl’s staining) |
| Azib et al., 2019 [66] | Pistacia lentiscus L. leaves extract | Improved memory (MWM), ↓ anxiety (head dipping, Black and White, EPM) | ↓ lipid-peroxidation-maintained SOD and CAT activity, stabilized total thiol levels | N/A | Preserved cerebral cortex morphology, ↓ neuronal loss, and ↓ vacuolation (H and E staining) |
| Azib et al., 2020 [67] | Fraxinus angustifolia Vahl. bark extract | Improved locomotor activity (open field test), ↓ anxiety (Black and White test), improved memory (MWM) | ↓ lipid peroxidation, ↑ cell viability in PC12 cells, ↓ MDA in synaptosomes | N/A | Preserved brain cortex structure, reduced vacuolation and neuronal loss (H and E staining) |
| Bhargava et al., 2023 [14] | Cassia tora extract | Improve learning and memory (MWM) | ↓ AChE and MAO activities normalized pro-inflammatory markers (↓ IL-6, ↓ IL-1β, ↓ TNF-α, ↓ IFN-γ), amyloid markers (↓ Aβ-42, ↑ Aβ-40) ↓ lipid peroxidation ↑ (CAT, SOD, GSH, GPx, GR, GST) | N/A | Protective effect (in cortex and hippocampus, H and E staining) |
| Campos et al., 2022 [68] | Chrysin | Improve non-spatial long-term memory (Step-Down Avoidance Test), improved motor function (Chimney Test) | ↓ MDA, ↑ SOD, CAT, and GSH levels, ↓ LPO, ↓ AChE activity, ↓ carbonylated protein levels | ↓ pro-inflammatory cytokines; ↓ iNOS, ↓ TNFα, ↓ IL-1β in microglial THP-1 cells | Preserved hippocampal and cortical morphology, ↓ vacuolation and pyknosis (H and E staining) |
| Cao et al., 2017 [69] | Hypericum perforatum extract | Improved cognitive function (MWM) | ↓ AchE, ↓ glutamic acid, ↑ noradrenaline, and ↑ dopamine ↓ SOD, ↓ GSH, ↑ ROS, ↑ TBARS | ↓ IL-6, ↓ IL-1β, ↓ TNF-α, and ↓ MHC class II | ↓ Aβ42 and amyloid plaques in the hippocampus (Congo red staining) |
| Cheng et al., 2014 [70] | Apple (Ralls) polyphenol extract | Improved spatial memory (MWM), preserved cognitive performance (Step-Down Inhibitory Avoidance) | ↑ AChE and CK activity, ↑ ATP synthesis, ↓ MDA, ↑ SOD and CAT levels | ↓ Aβ accumulation, ↓ neurofibrillary degeneration | Preserved cerebral cortex morphology, ↓ neuronal vacuolation and congestion (H and E staining) |
| Dibacto et al., 2022 [71] | Xylopia parviflora | Improved memory and locomotion (MWM, open field) | ↓ AChE and BChE, ↑ SOD, ↑ CAT, ↑ GSH, ↓ MDA, and ↓ NO levels, ATPases activities Assay: ↑ Na+, K+-ATPase, ↑ Mg+2-ATPase activities, ↑ Mg+2 levels, and ↓ Ca+2 levels | N/A | Improvement of the hippocampal structure (H and E staining) |
| Firdaus et al., 2022 [21] | Centella asiatica | Improved stress and coping behaviors (Y maze) Increased ambulation | ↓ MDA and AChE, ↓ SOD and ↓ CAT in cerebrum and cerebellum | N/A | Increase cell count, normalize cell structure H and E staining (cerebrum) |
| Gadouche et al., 2018 [72] | Pomegranate juice | Improved memory and cognitive function (MWM), ↓ anxiety (EPM), ↓ immobility time (forced swim test) | ↓ aluminum accumulation in brain tissue | N/A | Preserved cerebral cortex and hippocampal structure, ↓ neuronal loss and ↓ vacuolization (H and E staining) |
| García et al., 2009 [60] | Melatonin | No significant results | No significant decrease in aluminum levels in the brain’s hippocampus, cerebellum, and cortex | N/A | N/A |
| Gong et al., 2005 [73] | Ginkgo biloba leaf extract | Improved spatial learning and memory (↓ escape latency and searching distance, MWM) | N/A | N/A | ↓ expression of APP and caspase-3 (IHC) Free-floating incubation SABC method |
| Gothwal et al., 2019 [74] | Rivastigmine | Improved memory and discrimination (ORM) | No significant differences in dopamine or DOPAC | N/A | ↓ AChE activity levels, better neuronal integrity (AChE Histo-Enzymology) |
| Guo et al., 2016 [75] | Misoprostol | Improved spatial learning and memory (MWM) | ↓ MDA levels, ↑ SOD | ↓ PGE2, mPGES-1, EP2, and EP4, ↑ EP3 | ↓ hippocampal neuron death restored neuronal structure (H and E staining) |
| Justin Thenmozhi et al., 2017 [76] | Hesperidin | Improved memory (RAM, EPM, PAT) | ↓TBARS ↑ SOD, GSH, CAT, and GPx in brain cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum | ↓ pro-apoptotic (Bax) ↑ anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2) | N/A |
| Justin-Thenmozhi et al., 2018 [77] | Hesperidin | Improved memory and motor coordination (Y maze, NOR) | ↓ Cytosole cytochrome c, caspase-3,8 and 9 levels ↓ GFAP, Iba-1, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-4 and 6, COX-2, and iNOS | ↓ pTau and CDK5 levels (enhanced Aβ clearance through upregulation of IDE, ↑ phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) and GSK-3β) | N/A |
| Kakkar and Kaur, 2011 [78] | Curcumin (solid lipid nanoparticles of curcumin and free curcumin) | Improved memory (MWM) Improvement was more effective with solid lipid nanoparticles of curcumin than free curcumin | ↓ AchE, LPO, SOD, CAT, GSH (curcumin solid lipid nanoparticles more effective) | N/A | Normal neurons with intact nucleus and astrocytes No vacuolization or spongiosis and degenerated neurons (H and E staining of lateral sections of the brain) |
| Kumar et al., 2019 [79] | Artesunate + Rivastigmine | Improved learning and memory (PAT) | N/A | N/A | Protective effect on brain histology (H and E staining) |
| Li et al., 2018 [80] | Isorhynchophylline | Improved learning and memory (RAM) | ↑ SOD, ↓ MDA, ↑ CAT ↑ GSH, ↓ ACHE, and no significant effect on BuChE | ↓ phosphorylation of IκBα and NF-κB p65 | N/A |
| Liu et al., 2010 [81] | Soy isoflavones | Improved learning and memory (PAT) | ↓ ACHE ↑ glutamic acid and aspartic acid levels in cortex and hippocampus | N/A | N/A |
| Luo et al., 2007 [82] | Icariin | Improved spatial memory (↓ escape latency and searching distance, ↑ exploring time in the target area, MWM) | ↑ SOD, ↓ MDA in the hippocampus | N/A | Attenuated Aβ1-40 levels in the hippocampus (IHC), free-floating incubation and SABC method |
| Mohamed et al., 2023 [83] | Echinacea purpurea extract | Improved spatial and short-term memory (Y maze), improved long-term memory (NOR) and depressive-like behaviors (forced swim) | Inhibited Acholinesterase restored oxidative balance | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α cytokines | Normalize cell structure, no amyloid plaques in cortex (H and E and Congo red staining), improved histology (CA 3,4 and DG region of hippocampus, H and E staining) |
| Nampoothiri et al., 2017 [84] | Insulin | Memory improvement not observed (MWM) | ↓ blood glucose ↑ AChE, and the results were not significant compared to AlCl3 ↑ GSH in brain hippocampus and frontal cortex, showing oxidative stress | N/A | N/A |
| Nehru and Bhalla, 2007 [85] | Centrophenoxine | Improved memory (active and passive avoidance) | Restored AChE activity (up to 93% increase in the cerebrum) Restored levels of DA, norepinephrine, and serotonin in all brain regions | N/A | N/A |
| Pan et al., 2015 [86] | Beraprost sodium | Improved cognitive and memory functions (MWM) | ↓ MDA and restored SOD activity ↓ 6-k-PGF1α levels | ↓ PGIS mRNA expression ↓ IP mRNA expression | Improved histopathological changes of hippocampal neurons (H and E staining) |
| Prabhakar, 2020 [87] | Naringin | Improved locomotor and exploratory activity, ↓ latency time (MWM), ↑ memory performance (MWM RAM) | ↓ AChE, ↓ MDA, ↑ SOD, and ↑ CAT levels | N/A | N/A |
| Qi-Hai et al., 2006 [88] | Ginkgo biloba leaf extract | Improved spatial memory, ↓ escape latency and search distance (MWM) | N/A | N/A | Reversed AChE levels to near-normal in high doses, ↓ AChE expression (in high dose of extract) (free-floating staining and SABC method) |
| Rapaka et al., 2021 [89] | Benincasa hispida | Improved memory (MWM, Y maze) | ↑ AchE, DA, and serotonin levels in the cortex and hippocampus ↓ MDA, ↑ SOD and GSH, ↓ TNF-α, and ↓ IL-1β | ↑ Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, showing enhanced anti-oxidant defense | Histopathological examination revealed preserved neuronal structure, ↓ amyloid plaques and neurodegeneration (H and E staining of hippocampal CA3) |
| Ravi et al., 2018 [20] | Caesalpinia crista methanolic extract | Improved spatial memory (MWM) | ↓ AChE activity restored anti-oxidant enzyme levels (CAT, GSH, GST), ↓ MDA | ↓ pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β); ↑ BDNF levels | Improved cell morphology, partial restoration of morphology of Purkinje cells ↑ GFAP, ↓ caspase-3, and ↑ Nestin expression (IHC) (H and E staining) Hippocampus and cerebellum |
| Ravi et al., 2020 [90] | Cassia tora extract | Improve spatial memory (MWM) Restore motor activity | ↓ Tthioflavin-T fluorescence, ↓ Aβ1–42 aggregation ↑ CAT, GPx, GST ↓ MDA, ↓ AChE ↓ TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β mRNA levels ↑ BDNF level | N/A | ↑ Density of mature Pyramidal cell ↓ Pyknotic neurons: cytoarchitecture: ameliorate pyramidal cell layer alignment (Cresyl violet hippocampal CA3 and CA1) |
| Rijal et al., 2019 [91] | Phenylpropanoids; para-methoxycinnamic acid and ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate | Improved spatial memory, ↓ escape latency (MWM) | Restored CAT and ↓ TBARS levels in the hippocampus and cortex, ↓ hippocampal AChE activity | N/A | N/A |
| Saba et al., 2017 [23] | Rasa Sindoor | Improved memory (MWM) | ↑ glutamate, GABA, and aspartate in cortex, hippocampus, and striatum | N/A | Aβ plaques in aluminum-treated group (IHC of cortex and hippocampus of aluminum and control group only) |
| Sethi et al., 2009 [36] | Curcumin | Anxiety ↓ (open field) Memory performance improved (MWM) | Cytosolic PKC activity: ↓ in young; ↑ in old Bound PKC activity: maintained, lipid peroxidation ↓ Na–K-ATPase activity ↑ | N/A | Normal cytoplasm and intact cellular organelles (histological assessment using transmission electron microscopy of cortical cells) |
| Shalaby et al., 2023 [92] | Ginsenoside Rb1 | Enhanced memory, ↑ latency into the dark chamber (PAT) | ↓ MDA, ↑ SOD, ↓ AChE levels, ↓ Aβ 40 and phosphorylated tau | N/A | Restoration of normal neuronal architecture, ↓ shrinkage and vacuolation (H and E staining), ↑ surviving neurons (Nissl’s staining), ↑ synaptophysin, ↓ cleaved caspase-3, Iba-1 ↓ GFAP ↓ expression (IHC) |
| Singh et al., 2018 [24] | EGCG (Epigallocatechin-gallate) and EGCG-loaded nanoparticles | ↑ locomotor activity (open field) ↑ recognition memory (NOR) ↑ spatial and working memory (MWM) | ↓ AChE ↓ ROS ↓ NO | ↓ Aβ1–42, AChE, APP, and GSK3β ↑ PDK1 | ↓ reduced neurofibrillary tangles ↓ Aβ1–42 (H and E staining of cortex and hippocampus) |
| Thenmozhi et al., 2016 [93] | Tannoids of Emblica officinalis | Improved reference and working memory (RAM), improved cognitive performance (EPM, PAT) | ↓ lipid peroxidation (TBARS) and ↑ GSH, ↑ SOD, ↑ CAT, ↑ GPx levels in the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum | ↓ Bax, ↓ caspase -3 and 9, ↓ cytosolic cytochrome c, and ↑ Bcl-2 and ↑ mitochondrial cytochrome c expression | N/A |
| Thirunavukkarasu et al., 2012 [94] | Manasamitra vatakam | Improved memory performance (active-avoidance), ↓ anxiety (EPM) | ↑ AChE, SOD, CAT, GPx, and GSH levels; ↓ LPO | ↓ aluminum concentration in the cortex and hippocampus, ↓ HSP70 protein and mRNA expression | ↓ neuronal shrinkage, vacuolated cytoplasm cellular depletion and necrosis (cerebral cortex and hippocampus, H and E staining) |
| Zakrzeska et al., 2023 [59] | Betulin | Improved spatial memory (MWM), improved motor coordination (beam walking test) | ↓ Aβ1-42, ↓ TNF-α and ↓ APLP2 levels, ↑ AChE activity, ↑ anti-oxidant enzymes (GSH, GR, GSTs), ↓ oxidative stress markers, ↓ GSSG, ↓ G6PD, and ↓ GPO | N/A | N/A |
| Zhao et al., 2013 [95] | Ginsenoside Rb1 | Improved learning and memory (MWM) | N/A | Reduced tau phosphorylation (by restoring levels of ↓ active p-GSK3 and ↑ PP2A) in the cortex and hippocampus | ↓ p-tau staining, restore p-GSK3 and PP2A (in hippocampal CA3, IHC) |
3.4. Behaviors to Access Learning and Memory
| Behavior Name | Number of Studies in Which Behavior Is Assessed |
|---|---|
| Morris water maze | 29 |
| Open field | 12 |
| Passive avoidance task | 10 |
| Elevated plus maze | 10 |
| Radial arm maze | 8 |
| Locomotor activity | 5 |
| Novel object recognition | 4 |
| Y maze | 4 |
| Object recognition memory | 2 |
| Rota rod | 2 |
| Active avoidance test | 2 |
| Forced swim | 2 |
| Step-down inhibitory avoidance | 2 |
| Black and White test | 2 |
| Hebb–Williams maze | 2 |
| Head dipping | 1 |
3.5. The Methodological Quality of the Included Studies
| Study | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | Total 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [38] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ☓ | 5 |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [61] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ☓ | 5 |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2022 [37] | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Abdel-Zaher et al., 2017 [62] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Allagui et al., 2014 [63] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Alzahrani et al., 2020 [64] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Amjad and Umesalma, 2015 [65] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | 6 |
| Azib et al., 2019 [66] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Azib et al., 2020 [67] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Bhargava et al., 2023 [14] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Campos et al., 2022 [68] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Cao et al., 2017 [69] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Cheng et al., 2014 [70] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Dibacto et al., 2022 [71] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Firdaus et al., 2022 [21] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Gadouche et al., 2018 [72] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| García et al., 2009 [60] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Gong et al., 2005 [73] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Gothwal et al., 2019 [74] | ✓ | ☓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Guo et al., 2016 [75] | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Justin Thenmozhi et al., 2017 [76] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Justin-Thenmozhi et al., 2018 [77] | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Kakkar and Kaur, 2011 [78] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Kumar et al., 2019 [79] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Li et al., 2018 [80] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Liu et al., 2010 [81] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Luo et al., 2007 [82] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ☓ | 5 |
| Mohamed et al., 2023 [83] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Nampoothiri et al., 2017 [84] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Nehru and Bhalla, 2007 [85] | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ☓ | 5 |
| Pan et al., 2015 [86] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8 |
| Prabhakar, 2020 [87] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Qi-Hai et al., 2006 [88] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | 6 |
| Rapaka et al., 2021 [89] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Ravi et al., 2018 [20] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Ravi et al., 2020 [90] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Rijal et al., 2019 [91] | ✓ | ☓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 5 |
| Saba et al., 2017 [23] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Sethi et al., 2009 [36] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ☓ | 6 |
| Shalaby et al., 2023 [92] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 8 |
| Singh et al., 2018 [24] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 7 |
| Thenmozhi et al., 2016 [93] | ✓ | ☓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ☓ | 4 |
| Thirunavukkarasu et al., 2012 [94] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ? | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Zakrzeska et al., 2023 [59] | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
| Zhao et al., 2013 [95] | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | 6 |
3.6. Transparency and Reporting Standards of Studies
| Study | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | Total Score 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [38] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 10 |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2011 [61] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 10 |
| Abdel-Aal et al., 2022 [37] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Abdel-Zaher et al., 2017 [62] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 10 |
| Allagui et al., 2014 [63] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 11 |
| Alzahrani et al., 2020 [64] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Amjad and Umesalma, 2015 [65] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| Azib et al., 2019 [66] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Azib et al., 2020 [67] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Bhargava et al., 2023 [14] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Campos et al., 2022 [68] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 15 |
| Cao et al., 2017 [69] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 13 |
| Cheng et al., 2014 [70] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 12 |
| Dibacto et al., 2022 [71] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| Firdaus et al., 2022 [21] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| Gadouche et al., 2018 [72] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| García et al., 2009 [60] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Gong et al., 2005 [73] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 11 |
| Gothwal et al., 2019 [74] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| Guo et al., 2016 [75] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 11 |
| Justin Thenmozhi et al., 2017 [76] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Justin-Thenmozhi et al., 2018 [77] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 14 |
| Kakkar and Kaur, 2011 [78] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Kumar et al., 2019 [79] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Li et al., 2018 [80] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| Liu et al., 2010 [81] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Luo et al., 2007 [82] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Mohamed et al., 2023 [83] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 14 |
| Nampoothiri et al., 2017 [84] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Nehru and Bhalla, 2007 [85] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Pan et al., 2015 [86] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 13 |
| Prabhakar, 2020 [87] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 10 |
| Qi-Hai et al., 2006 [88] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Rapaka et al., 2021 [89] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 14 |
| Ravi et al., 2018 [20] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 11 |
| Ravi et al., 2020 [90] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Rijal et al., 2019 [91] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Saba et al., 2017 [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Sethi et al., 2009 [36] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Shalaby et al., 2023 [92] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| Singh et al., 2018 [24] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 12 |
| Thenmozhi et al., 2016 [93] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Thirunavukkarasu et al., 2012 [94] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 12 |
| Zakrzeska et al., 2023 [59] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Zhao et al., 2013 [95] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
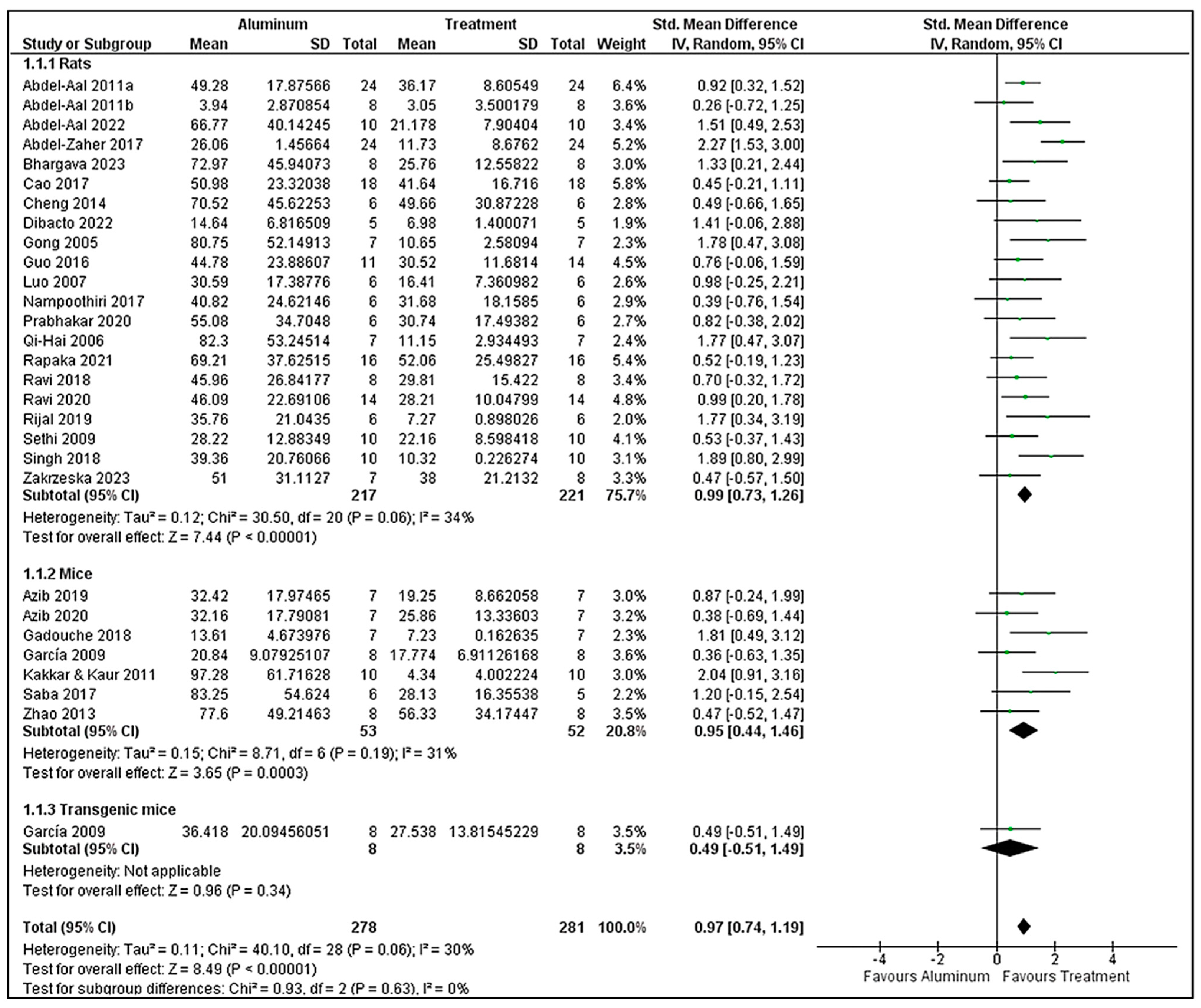
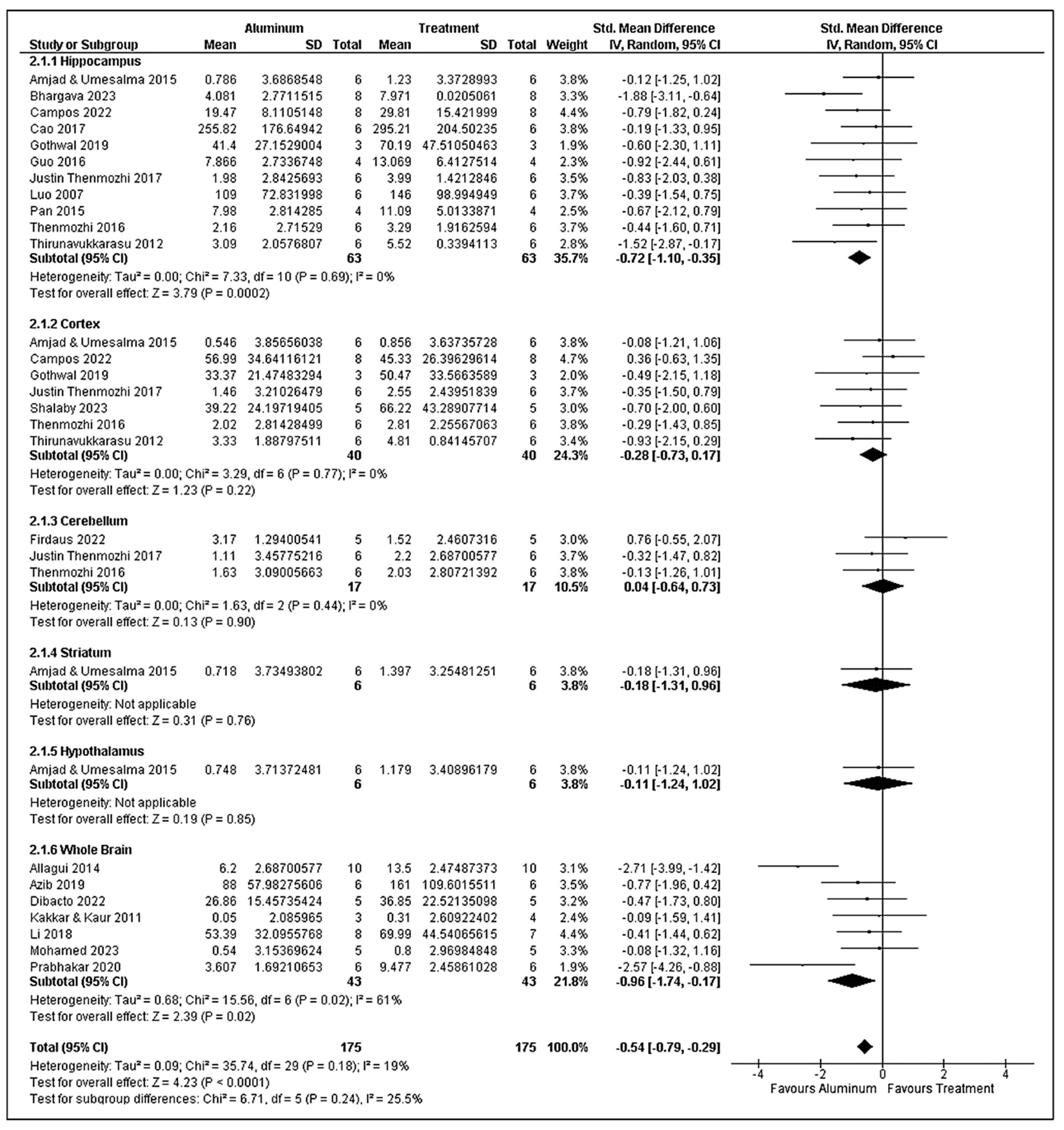
3.7. Morris Water Maze Analysis
3.8. Superoxide Dismutase Analysis
3.9. Catalase Analysis
3.10. Risk of Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Evidence Summary and Interpretation
4.2. Methodological Considerations
4.3. Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, N.; Gaurav, S.S.; Kumar, A. Molecular basis of aluminium toxicity in plants: A review. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, J.M. Aluminum poisoning of humanity and Earth’s biota by clandestine geoengineering activity: Implications for India. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 2173–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, F.S.; Al Zubaidy, I.A.H.; Bassioni, G. A comparison of aluminum leaching processes in tap and drinking water. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 3118–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, U.; Seifert, M. Oral intake of aluminum from foodstuffs, food additives, food packaging, cookware and pharmaceutical preparations with respect to dietary regulations. Trace Elem. Electrolytes 2006, 23, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokel, R.A. Aluminum in Food—The Nature and Contribution of Food Additives; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Volume 203, pp. 203–228. [Google Scholar]
- Hardisson, A.; Revert, C.; Gonzales-Weler, D.; Rubio, C. Aluminium exposure through the diet. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.F.; Cabrera, C.; Lorenzo, M.L.; López, M.C. Aluminium content of drinking waters, fruit juices and soft drinks: Contribution to dietary intake. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 292, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, V.; Jacqmin-Gadda, H.; Commenges, D.; Helmer, C.; Dartigues, J.-F. Aluminum and silica in drinking water and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease or cognitive decline: Findings from 15-year follow-up of the PAQUID cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.T.; Viraraghavan, T.; Subramanian, K.S. Aluminium in drinking water: An overview. Water Sa 1999, 25, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Renke, G.; Almeida, V.B.P.; Souza, E.A.; Lessa, S.; Teixeira, R.L.; Rocha, L.; Sousa, P.L.; Starling-Soares, B. Clinical outcomes of the deleterious effects of aluminum on neuro-cognition, inflammation, and health: A review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q. Overview of the relationship between aluminum exposure and health of human being. In Neurotoxicity of Aluminum; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Rahimzadeh, M.R.; Kazemi, S.; Amiri, R.J.; Pirzadeh, M.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Aluminum poisoning with emphasis on its mechanism and treatment of intoxication. Emerg. Med. Int. 2022, 1, 1480553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïr, K.; Kharoubi, O.; Taïr, O.A.; Hellal, N.; Benyettou, I.; Aoues, A. Aluminium-induced acute neurotoxicity in rats: Treatment with aqueous extract of Arthrophytum (Hammada scoparia). J. Acute Dis. 2016, 5, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, V.P.; Netam, A.K.; Singh, R.; Sharma, P. Cassia tora Mitigates Aluminium Chloride Induced Alterations in Pro-inflammatory Cytokines, Neurotransmitters, and Beta-amyloid and Tau Protein Markers in Wistar Rats. Toxicol. Int. 2023, 30, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.R. An aluminum-based rat model for Alzheimer’s disease exhibits oxidative damage, inhibition of PP2A activity, hyperphosphorylated tau, and granulovacuolar degeneration. J. Irong. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, S.; Millen, N.; González, M.; del Carmen Contini, M.; Elías, M.M. Alterations of the renal function and oxidative stress in renal tissue from rats chronically treated with aluminium during the initial phase of hepatic regeneration. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1858–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, S.; del Carmen Contini, M.; González, M.; Millen, N. Melatonin reduces oxidative damage induced by aluminium in rat kidney. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 190, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Du, Y.; Xue, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, B. Aluminum induces neurodegeneration and its toxicity arises from increased iron accumulation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 199.e1–199.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalny, A.V.; Aschner, M.; Jiang, Y.; Gluhcheva, Y.G.; Tizabi, Y.; Lobinski, R.; Tinkov, A.A. Molecular mechanisms of aluminum neurotoxicity: Update on adverse effects and therapeutic strategies. Adv. Neurotoxicol. 2021, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.K.; Ramesh, B.N.; Mundugaru, R.; Vincent, B. Multiple pharmacological activities of Caesalpinia crista against aluminium-induced neurodegeneration in rats: Relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdaus, Z.; Kumar, D.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, T.D. Centella asiatica alleviates AlCl3-induced cognitive impairment, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration by modulating cholinergic activity and oxidative burden in rat brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelodun, S.T.; Ishola, O.A.; Abijo, A.Z.; Olatunji, S.Y.; Owolabi, J.O.; Olanrewaju, J.A.; Adekomi, D.A. Aluminium chloride-induced hippocampal damage: CA3 hippocampal subfield involvement and the neuroprotective role of Buchholzia coriacea ethanolic seed extract. Phytomed. Plus 2021, 1, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, K.; Rajnala, N.; Veeraiah, P.; Tiwari, V.; Rana, R.K.; Lakhotia, S.C.; Patel, A.B. Energetics of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission in aluminum chloride model of Alzheimer’s disease: Reversal of behavioral and metabolic deficits by Rasa Sindoor. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.A.; Bhardwaj, V.; Ravi, C.; Ramesh, N.; Mandal, A.K.A.; Khan, Z.A. EGCG nanoparticles attenuate aluminum chloride induced neurobehavioral deficits, beta amyloid and tau pathology in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebai, O.; Djebli, N.E. Chronic exposure to aluminum chloride in mice: Exploratory behaviors and spatial learning. Adv. Biol. Res. 2008, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, C.; Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.; Bai, C.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, L.; et al. Aluminium chloride impairs long-term memory and downregulates cAMP-PKA-CREB signalling in rats. Toxicology 2014, 323, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asili, E.; Sharifzadeh, M. Effects of Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) on spatial memory: Association with oxidative stress. J. Pharm. Health Sci. 2011, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Q. Aluminium-maltolate-induced impairment of learning, memory and hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats. Ind. Health 2012, 50, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaquat, L.; Sadir, S.; Batool, Z.; Tabassum, S.; Shahzad, S.; Afzal, A.; Haider, S. Acute aluminum chloride toxicity revisited: Study on DNA damage and histopathological, biochemical and neurochemical alterations in rat brain. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xing, W.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, X. Effects of chronic aluminum exposure on memory through multiple signal transduction pathways. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 29, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Duan, X.; Zhang, L. Effects of Subchronic Aluminum Exposure on Learning, Memory, and Neurotrophic Factors in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, D.D.; Aydemir, I.; Alizade, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Aksu, F. Investigation of Behavioral Changes and Histopathological Changes in the Brain in Alzheimer’s Modeled Mice with Aluminium Chloride (AlCl3). Cyprus J. Med. Sci. 2025, 10, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Dayem, D.A.M.; Ahmed, A.F.; Abdel Hafez, S.M.N.; Gamal El-Tahawy, N.F.; Abdel-Aleem, S. Possible effects of aluminum chloride induced toxicity on hippocampus of adult male albino rats. Minia J. Med. Res. 2023, 34, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inohana, M.; Eguchi, A.; Nakamura, M.; Nagahara, R.; Onda, N.; Nakajima, K.; Saegusa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Shibutani, M. Developmental exposure to aluminum chloride irreversibly affects postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis involving multiple functions in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, P.; He, S.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Conti, P.; Boscolo, P. The relationship between Bcl-2 gene expression and learning & memory impairment in chronic aluminum-exposed rats. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 12, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, P.; Jyoti, A.; Hussain, E.; Sharma, D. Curcumin attenuates aluminium-induced functional neurotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 93, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aal, R.A.; Hussein, O.A.; Elsaady, R.G.; Abdelzaher, L.A. Naproxen as a potential candidate for promoting rivastigmine anti-Alzheimer activity against aluminum chloride-prompted Alzheimer’s-like disease in rats; neurogenesis and apoptosis modulation as a possible underlying mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 915, 174695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R.A.; Assi, A.-A.A.; Kostandy, B.B. Memantine prevents aluminum-induced cognitive deficit in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandeis, R.; Brandys, Y.; Yehuda, S. The use of the Morris water maze in the study of memory and learning. Int. J. Neurosci. 1989, 48, 29–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-Maze for Assessment of Spatial Working and Reference Memory in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.S.; Alterman, C.D.C.; Peçanha, F.M.; Vassallo, D.V.; Mello-Carpes, P.B.; Miguel, M.; Wiggers, G.A. Aluminum Exposure at Human Dietary Levels for 60 Days Reaches a Threshold Sufficient to Promote Memory Impairment in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.B.; Frandsen, T.F. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: A systematic review. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2018, 106, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Espinós, E.; Hernández, V.; Domínguez-Escrig, J.L.; Fernández-Pello, S.; Hevia, V.; Mayor, J.; Padilla-Fernández, B.; Ribal, M.J. Methodology of a systematic review. Actas Urol. Esp. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 42, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, M.R.; O’Collins, T.; Howells, D.W.; Donnan, G.A. Pooling of animal experimental data reveals influence of study design and publication bias. Stroke 2004, 35, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.B.M.; Hooijmans, C.R.; Langendam, M.W.; Van Luijk, J.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Wever, K.E. A protocol format for the preparation, registration and publication of systematic reviews of animal intervention studies. Evid.-Based Preclin. Med. 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallogjeri, D.; Piccirillo, J.F. A Simple Guide to Effect Size Measures. JAMA Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2023, 149, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V. Advances in statistical methods for meta-analysis. New Dir. Program Eval. 1984, 24, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Aloe, A.M. Evaluation of various estimators for standardized mean difference in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P. Statistical Algorithms in Review Manager 5. Statistical Methods Group of the Cochrane Collaboration. 2010. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252093205_Statistical_Algorithms_in_Review_Manager_5 (accessed on 3 August 2025).
- Dettori, J.R.; Norvellm, D.C.; Chapman, J.R. Fixed-Effect vs. Random-Effects Models for Meta-Analysis: 3 Points to Consider. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakopoulou, A.; Mavridis, D.; Salanti, G. How to interpret meta-analysis models: Fixed effect and random effects meta-analyses. BMJ Ment Health 2014, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettori, J.R.; Norvell, D.C.; Chapman, J.R. Seeing the Forest by Looking at the Trees: How to Interpret a Meta-Analysis Forest Plot. Glob. Spine J. 2021, 11, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; IntHout, J.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Rovers, M.M. Meta-analyses of animal studies: An introduction of a valuable instrument to further improve healthcare. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, J.A.; González-Farías, G. A note on the Cook’s distance. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2004, 120, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzeska, A.; Kitlas, P.; Shlyahtun, A.; Jabłoński, R.; Tomulewicz, M.; Szymańska, N. Protective effect of Betulin against aluminium-induced Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration. Acta. Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2023, 80, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, T.; Ribes, D.; Colomina, M.T.; Cabré, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Gómez, M. Evaluation of the protective role of melatonin on the behavioral effects of aluminum in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicology 2009, 265, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R.A.; Assi, A.-A.A.; Kostandy, B.B. Rivastigmine reverses aluminum-induced behavioral changes in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 659, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Zaher, A.O.; Hamdy, M.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.S.; Abd El-hamid, D.H. Protective effect of citicoline against aluminum-induced cognitive impairments in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allagui, M.S.; Feriani, A.; Saoudi, M.; Badraoui, R.; Bouoni, Z.; Nciri, R.; Murat, J.C.; Elfeki, A. Effects of melatonin on aluminium-induced neurobehavioral and neurochemical changes in aging rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 70, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, Y.M.; Sattar, M.A.A.A.; Kamel, F.O.; Ramadan, W.S.; Alzahrani, Y.A. Possible combined effect of perindopril and Azilsartan in an experimental model of dementia in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, S.; Umesalma, S. Protective effect of Centella asiatica against aluminium-induced neurotoxicity in cerebral cortex, striatum, hypothalamus and hippocampus of rat brain-histopathological, and biochemical approach. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Azib, L.; Debbache-Benaida, N.; Da Costa, G.; Atmani-Kilani, D.; Saidene, N.; Bouguellid, G.; Ourabah, A.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Atmani, D. Pistacia lentiscus L. leaves extract and its major phenolic compounds reverse aluminium-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azib, L.; Debbache-Benaida, N.; Da Costa, G.; Atmani-Kilani, D.; Saidene, N.; Bouguellid, G.; Ourabah, A.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Atmani, D. Neuroprotective effects of Fraxinus angustifolia Vahl. bark extract against Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 109, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, H.M.; da Costa, M.; da Silva Moreira, L.K.; da Silva Neri, H.F.; da Silva, C.R.B.; Pruccoli, L.; Dos Santos, F.C.A.; Costa, E.A.; Tarozzi, A.; Ghedini, P.C. Protective effects of chrysin against the neurotoxicity induced by aluminium: In vitro and in vivo studies. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, F.; Xiu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Hypericum perforatum extract attenuates behavioral, biochemical, and neurochemical abnormalities in aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Xi, Y.; Cao, J.; Cao, D.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, W. Protective effect of apple (Ralls) polyphenol extract against aluminum-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in rat. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibacto, R.E.K.; Ambamba, B.D.A.; Ella, F.A.; Nyangono, C.F.B.; Nanhah, J.V.K.; Fonkoua, M.; Minka, R.S.; Ngondi, J.L. The neuroprotective effect of Xylopia parviflora against aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadouche, L.; Djebli, N.; Zerrouki, K. Pomegranate juice attenuates neurotoxicity and histopathological changes of the nervous system induced by aluminum in mice. Phytothérapie 2018, 16, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.-H.; Wu, Q.; Huang, X.-N.; Sun, A.-S.; Shi, J.-S. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on aluminum-induced brain dysfunction in rats. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, A.; Singh, H.; Jain, S.K.; Dutta, A.; Borah, A.; Gupta, U. Behavioral and biochemical implications of dendrimeric rivastigmine in memory-deficit and Alzheimer’s induced rodents. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3789–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Lei, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Ji, C.; Yang, J. Misoprostol reverse hippocampal neuron cyclooxygenase-2 downstream signaling imbalance in aluminum-overload rats. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justin Thenmozhi, A.; William Raja, T.R.; Manivasagam, T.; Janakiraman, U.; Essa, M.M. Hesperidin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis against aluminium chloride induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin-Thenmozhi, A.; Dhivya Bharathi, M.; Kiruthika, R.; Manivasagam, T.; Borah, A.; Essa, M.M. Attenuation of aluminum chloride-induced neuroinflammation and caspase activation through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway by hesperidin in wistar rats. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 34, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, V.; Kaur, I.P. Evaluating potential of curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in aluminium induced behavioural, biochemical and histopathological alterations in mice brain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.E.P.; Bairy, K.L.; Nayak, V.; Reddy, S.K.; Kiran, A.; Ballal, A. Amelioration of aluminium chloride (AlCl3) induced neurotoxicity by combination of rivastigmine and memantine with artesunate in Albino Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Q.; Ip, S.-P.; Zheng, G.-Q.; Xian, Y.-F.; Lin, Z.-X. Isorhynchophylline alleviates learning and memory impairments induced by aluminum chloride in mice. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, T.; Liang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Memory performance, brain excitatory amino acid and acetylcholinesterase activity of chronically aluminum exposed mice in response to soy isoflavones treatment. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nie, J.; Gong, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J. Protective effects of icariin against learning and memory deficits induced by aluminium in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.M.; Shalaby, M.A.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; El-Banna, A.H.; El-Banna, H.A.; Nabil, G. Evaluation of anti-Alzheimer activity of Echinacea purpurea extracts in aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity in rat model. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2023, 128, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nampoothiri, M.; Kumar, N.; Ramalingayya, G.V.; Kutty, N.G.; Krishnadas, N.; Rao, C.M. Effect of insulin on spatial memory in aluminum chloride-induced dementia in rats. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehru, B.; Bhalla, P. Biochemical alterations in rat brain following aluminum exposure: Protection with centrophenoxine. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2007, 89, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, L.; Lei, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, J. Beraprost sodium protects against chronic brain injury in aluminum-overload rats. Behav. Brain Funct. 2015, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prabhakar, O. Naringin attenuates Aluminum induced cognitive deficits in rats. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2020, 54, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi-Hai, G.; Qin, W.; Xie-Nan, H.; An-Sheng, S.; Jing, N.; Jing-Shan, S. Protective effect of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on learning and memory deficit induced by aluminum in model rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2006, 12, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapaka, D.; Bitra, V.R.; Ummidi, R.; Akula, A. Benincasa hispida alleviates amyloid pathology by inhibition of Keap1/Nrf2-axis: Emphasis on oxidative and inflammatory stress involved in Alzheimer’s disease model. Neuropeptides 2021, 88, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.K.; Narasingappa, R.B.; Mundagaru, R.; Girish, T.K.; Vincent, B. Cassia tora extract alleviates Aβ1–42 aggregation processes in vitro and protects against aluminium-induced neurodegeneration in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijal, S.; Changdar, N.; Kinra, M.; Kumar, A.; Nampoothiri, M.; Arora, D.; Shenoy, R.R.; Ranganath Pai, K.S.; Joseph, A.; Mudgal, J. Neuromodulatory potential of phenylpropanoids; para-methoxycinnamic acid and ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate on aluminum-induced memory deficit in rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.M.; Alnasser, S.M.; Khairy, D.A.; Alabiad, M.A.; Alorini, M.; Jaber, F.A.; Tawfeek, S.E. The neuroprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on the cerebral cortex changes induced by aluminium chloride in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: A histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical study. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2023, 129, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, A.J.; Dhivyabharathi, M.; Manivasagam, T.; Essa, M.M. Tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis attenuated aluminum chloride induced apoptosis by suppressing oxidative stress and tau pathology via Akt/GSK-3βsignaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirunavukkarasu, S.V.; Venkataraman, S.; Raja, S.; Upadhyay, L. Neuroprotective effect of Manasamitra vatakam against aluminium induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in the cortex and hippocampus of rat brain. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 35, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Di, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Lai, H.; Lü, Y. Involvement of GSK3 and PP2A in ginsenoside Rb1’s attenuation of aluminum-induced tau hyperphosphorylation. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 241, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorzo, C.; Arias, J.L.; Méndez, M. Are there sex differences in spatial reference memory in the Morris water maze? A large-sample experimental study. Learn. Behav. 2024, 52, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.Z.; Hassan, Z.; Has, A.T.C. Morris water maze: A versatile and pertinent tool for assessing spatial learning and memory. Exp. Anim. 2022, 71, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melbiarta, R.R.; Kalanjati, V.P.; Herawati, L.; Salim, Y.; Othman, Z. Analysis of spatial working memory using the Y-maze on rodents treated with high-calorie diet and moderate-intensity exercise. Folia Medica Indones. 2023, 59, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.K. Spatial learning and memory using a radial arm maze with a head-mounted display. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M. Use of TSD, CSS or CLOSE maze to measure spatial navigation, working memory, Reference memory, memory errors, locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavior in Rats. J. Dent. Oral Care 2022, 1, 01–04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; You, S.; Wang, X. An Open-Field-Based Unimodal Object Recognition Test (OF-UORT) for Assessment of Chronic Stress Effects on Visual and Tactile Unimodal Cognition in Mice. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiabadi, M.; Esmaeili, M.-H.; Haghdoost-Yazdi, H.; Dezfulian, M.; Afshari, Z.H.; Goodarzvand Chegini, K. Effects of prenatal combined stress on passive avoidance learning and memory in rats. Neurophysiology 2018, 50, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulava, A.I.; Volkov, S.V.; Alexandrov, Y.I. A novel avoidance test setup: Device and exemplary tasks. In Advances in Neural Computation, Machine Learning, and Cognitive Research III: Selected Papers from the XXI International Conference on Neuroinformatics, Dolgoprudny, Russia, 7–11 October 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasak, T.; Dujlovic, T.; Barth, A. Aluminum exposure and cognitive performance: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, G.T.; Ugle, S.S.; Bikkad, M.D.; Ingle, S.B. Water aluminium and alzheimer disease. Int. J. Pharma. Bio. Sci. 2015, 6, B608-12. [Google Scholar]
- Meshitsuka, S.; Aremu, D.A.; Nose, T. A risk of Alzheimer’s disease and aluminum in drinking water. Psychogeriatrics 2002, 2, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, I.; Handra, C.-M.; Naghi, E.; Gurzu, I.-L.; Chirila, M. Vulnerability to Stress and Depression Risk Related to Occupational Exposure to Aluminum. Occup. Dis. Environ. Med. 2022, 10, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, I.; Zugravu, A.; Handra, C.; Segarceanu, A.; Negutu, M.; Fulga, I. Experimental research concerning the effect of aluminium compounds on anxiety in mice. Farmacla 2015, 63, 568–573. [Google Scholar]
- Izadi, S.; Abdolrezaei, M.; Soukhaklari, R.; Moosavi, M. Memory impairment induced by aluminum nanoparticles is associated with hippocampal IL-1 and IBA-1 upregulation in mice. Neurol. Res. 2024, 46, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G.M. Morris water maze. Scholarpedia 2008, 3, 6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Anand, N.; Varma, S.R.; Ramamurthy, S.; Vichitra, C.; Sharma, A.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Essa, M.M. Superoxide dismutase and neurological disorders. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2024, 16, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.; Onodera, K.; Shinkai, T.; Suzuki, S.; Urano, S. Impairment of learning and memory in rats caused by oxidative stress and aging, and changes in antioxidative defense systems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 928, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannan, T.S.; Maker, H.S.; Raes, I.P. Regional distribution of catalase in the adult rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1981, 36, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagepally, B.S.; Balachandar, R.; Kalahasthi, R.; Tripathi, R.; Haridoss, M. Association between aluminium exposure and cognitive functions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, B.; Figgitt, D.P. Memantine. Drugs Aging 2003, 20, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.G.; Rammes, G.; Danysz, W. Pharmacodynamics of Memantine: An Update. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.G.; Stöffler, A.; Danysz, W. Memantine: A NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system-too little activation is bad, too much is even worse. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 699–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, W.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhong, X.; Sha, L.; He, M.; Zheng, Z.H.; Wei, M.J. Memantine improves spatial learning and memory impairments by regulating NGF signaling in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neuroscience 2014, 273, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockrow, J.; Boger, H.; Bimonte-Nelson, H.; Granholm, A.C. Effects of long-term memantine on memory and neuropathology In ts65dn mice, A model for down syndrome. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 221, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shata, A.; Elkashef, W.; Hamouda, M.A.; Eissa, H. Effect of artesunate vs. memantine in aluminum chloride induced model of neurotoxicity in rats. Adv. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.P.; De Lima, M.N.M.; Presti-Torres, J.; Dornelles, A.; Garcia, V.A.; Scalco, F.S.; Guimarães, M.R.; Constantino, L.; Budni, P.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Memantine reduces oxidative damage and enhances long-term recognition memory in aged rats. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.M.; Keating, G.M. Memantine: A review of its use in Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs 2006, 66, 1515–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Wenk, G.L. The neuropharmacological basis for the use of memantine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drug Rev. 2003, 9, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, S.; Ecaterina, V. Spectrophotometrical study of extracts from the herb ST. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum). In Proceedings of the Physical Methods in Coordination and Supramolecular Chemistry, Chişinău, Moldova, 8–9 October 2015; Volume XVIII, p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Douichene, S.; Hammadi, K.; Djebli, N. Neuroprotective effect of Hypericum thymopsis against chronic exposure to aluminum chloride and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 3, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Reus, M.I.; Del Rio, M.A.G.; Iglesias, I.; Elorza, M.; Slowing, K.; Benedi, J. Standardized Hypericum perforatum reduces oxidative stress and increases gene expression of antioxidant enzymes on rotenone-exposed rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, D.A.; Khalifa, A.E.; Attia, A.S.; Eldenshary, E.E.D.S. Hypericum perforatum extract demonstrates antioxidant properties against elevated rat brain oxidative status induced by amnestic dose of scopolamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 76, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.A.M.; Anwar, F.; Hamid, A.A.; Saari, N. Kundur [Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn.]: A potential source for valuable nutrients and functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooja, R.C.; Bharathi, D.R. Benincasa Hispida Reversed D-galactose-induced oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration-Mediated Cognitive Impairment. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 1, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Imran, M.; Rauf, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Shariati, M.A.; Iahtisham-Ul-Haq; IqraYasmin; Shahbaz, M.; Qaisrani, T.B.; Shah, Z.A.; et al. Chrysin: Pharmacological and therapeutic properties. Life Sci. 2019, 235, 116797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Singh, G.; Verma, A. A Comprehensive Review on Therapeutic Potential of Chrysin in Brain Related Disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets-CNS Neurol. Disord. 2022, 22, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajit, R.; Sritawan, N.; Suwannakot, K.; Naewla, S.; Aranarochana, A.; Sirichoat, A.; Pannangrong, W.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Chrysin protects against memory and hippocampal neurogenesis depletion in D-galactose-induced aging in rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Shaikh, M.A.; Haq, S.H.I.U.; Nazir, S. Neuroprotective role of chrysin in attenuating loss of dopaminergic neurons and improving motor, learning and memory functions in rats. Int. J. Health Sci. (Qassim) 2018, 12, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Shooshtari, M.K.; Sarkaki, A.; Mansouri, S.M.T.; Badavi, M.; Khorsandi, L.; Ghasemi Dehcheshmeh, M.; Farbood, Y. Protective effects of Chrysin against memory impairment, cerebral hyperemia and oxidative stress after cerebral hypoperfusion and reperfusion in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, V.C.; Dahleh, M.M.M.; Marques, L.S.; Borstmann, S.M.A.; Viana, C.E.; Pinheiro, F.C.; Balok, F.R.M.; Meichtry, L.B.; Boeira, S.P.; Guerra, G.P. Chrysin modulates the BDNF/TrkB/AKT/Creb neuroplasticity signaling pathway: Acting in the improvement of cognitive flexibility and declarative, working and aversive memory deficits caused by hypothyroidism in C57BL/6 female mice. Neuroscience 2025, 566, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashno, M.; Ghaderi, S.; Nesari, A.; Khorsandi, L.; Farbood, Y.; Sarkaki, A. Chrysin attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced recognition memory decline, and anxiety/depression-like behaviors in rats: Insights into underlying mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, L.C.; Antunes, M.S.; Borges Filho, C.; Del Fabbro, L.; de Gomes, M.G.; Goes, A.T.R.; Donato, F.; Prigol, M.; Boeira, S.P.; Jesse, C.R. Flavonoid Chrysin prevents age-related cognitive decline via attenuation of oxidative stress and modulation of BDNF levels in aged mouse brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 134, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N.; Mandal, S.; Hazra, B.; Sarkar, R.; Biswas, S. Assessment of the Antioxidant and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Activity of Methanolic Extract of Caesalpinia crista Leaf. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 1, 173768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, S.N.; Sakarkar, D.M.; Deshpande, S.S. Pharmacie globale international journal of comprehensive pharmacy learning and memory enhancing activity of ethanolic extract of dried seed kernels of caesalpinia crista Lin. Int. J. Compr. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, N.K.; Negida, A. Sample size calculation guide-part 1: How to calculate the sample size based on the prevalence rate. Adv. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 2, e50. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Jiang, H. Dual effects of ketamine: Neurotoxicity versus neuroprotection in anesthesia for the developing brain. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2014, 26, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M.S.; Fehm, N.P.; Vatankhah, B.; Horn, M. Ketamine/xylazine anesthesia for radiologic imaging of neurologically impaired rats: Dose response, respiratory depression, and management of complications. Comp. Med. 2004, 54, 652–655. [Google Scholar]
- Aronson, J.K. Barbiturates. In Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs, 16th ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 819–826. [Google Scholar]
- Shcherbak, N.S.; Yukina, G.Y.; Gurbo, A.G.; Sukhorukova, E.G.; Sargsian, A.G.; Thomson, V.V.; Galagudza, M.M. Morphofunctional state of microglia and hippocampal neurons in aged rats after anesthesia with chloral hydrate. Reg. Blood Circ. Microcirc. 2022, 21, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, S.K.; Lee, W.A.; Sabato, S.; Mendez, A.A.; Agresta, C.A.; Kelly, G. Halothane anesthesia is neuroprotective in experimental spinal cord injury: Early hemodynamic mechanisms of action. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1993, 80, 59–81. [Google Scholar]
- Schifilliti, D.; Grasso, G.; Conti, A.; Fodale, V. Anaesthetic-Related Neuroprotection. CNS Drugs 2010, 24, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblin, D.D. Urethane: Help or hindrance? Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Roy, S.; Ghosh, D.; Nandi, S.K. Role of animal models in biomedical research: A review. Lab. Anim. Res. 2022, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Patel, B.M. Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery to the Brain. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Animal studies | Ex vivo and in vitro studies |
| Intervention | Aluminum exposure for ≥2 months, and the treatment agent used | Aluminum exposure for <2 months, aluminum exposure combined with any other neurotoxin |
| Comparison | Aluminum group, along with the treatment group | No treatment in the aluminum group |
| Outcomes | Assessment of learning and memory | No learning and memory assessment |
| Parameter | Number of Studies | Egger’s Test (p Value) |
|---|---|---|
| MWM escape latencies | 28 | 1.120 (0.273) |
| SOD levels | 21 | −1.495 (0.146) |
| CAT levels | 18 | −0.610 (0.547) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayat, M.; Khola, N.U.H.; Ahmed, T. A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Learning and Memory in Prolonged Aluminum-Exposure-Induced Neurotoxicity. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080849
Hayat M, Khola NUH, Ahmed T. A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Learning and Memory in Prolonged Aluminum-Exposure-Induced Neurotoxicity. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(8):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080849
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayat, Mahnoor, Noor Ul Huda Khola, and Touqeer Ahmed. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Learning and Memory in Prolonged Aluminum-Exposure-Induced Neurotoxicity" Brain Sciences 15, no. 8: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080849
APA StyleHayat, M., Khola, N. U. H., & Ahmed, T. (2025). A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Pharmacological Agents on Learning and Memory in Prolonged Aluminum-Exposure-Induced Neurotoxicity. Brain Sciences, 15(8), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080849







