Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase-Positive Neurons in the Brain Cortex of Rats After Administration of Rebaudioside A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Qualitative Histological Evaluation
2.4. Morphomeric Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
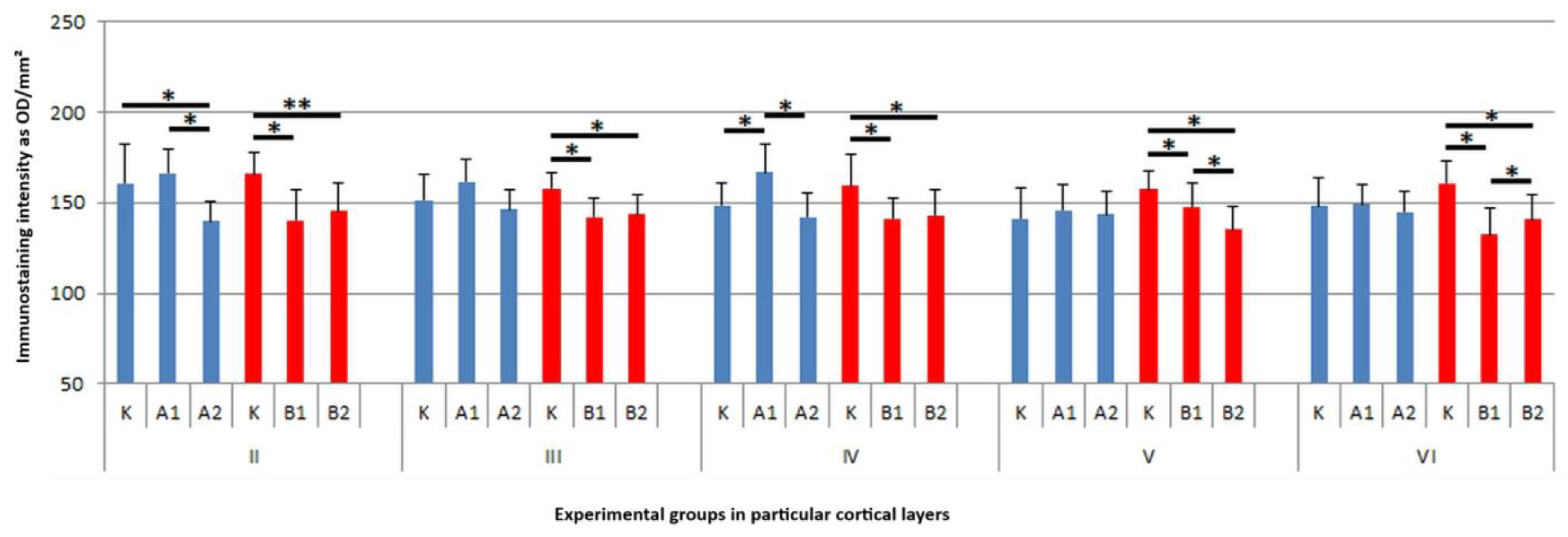
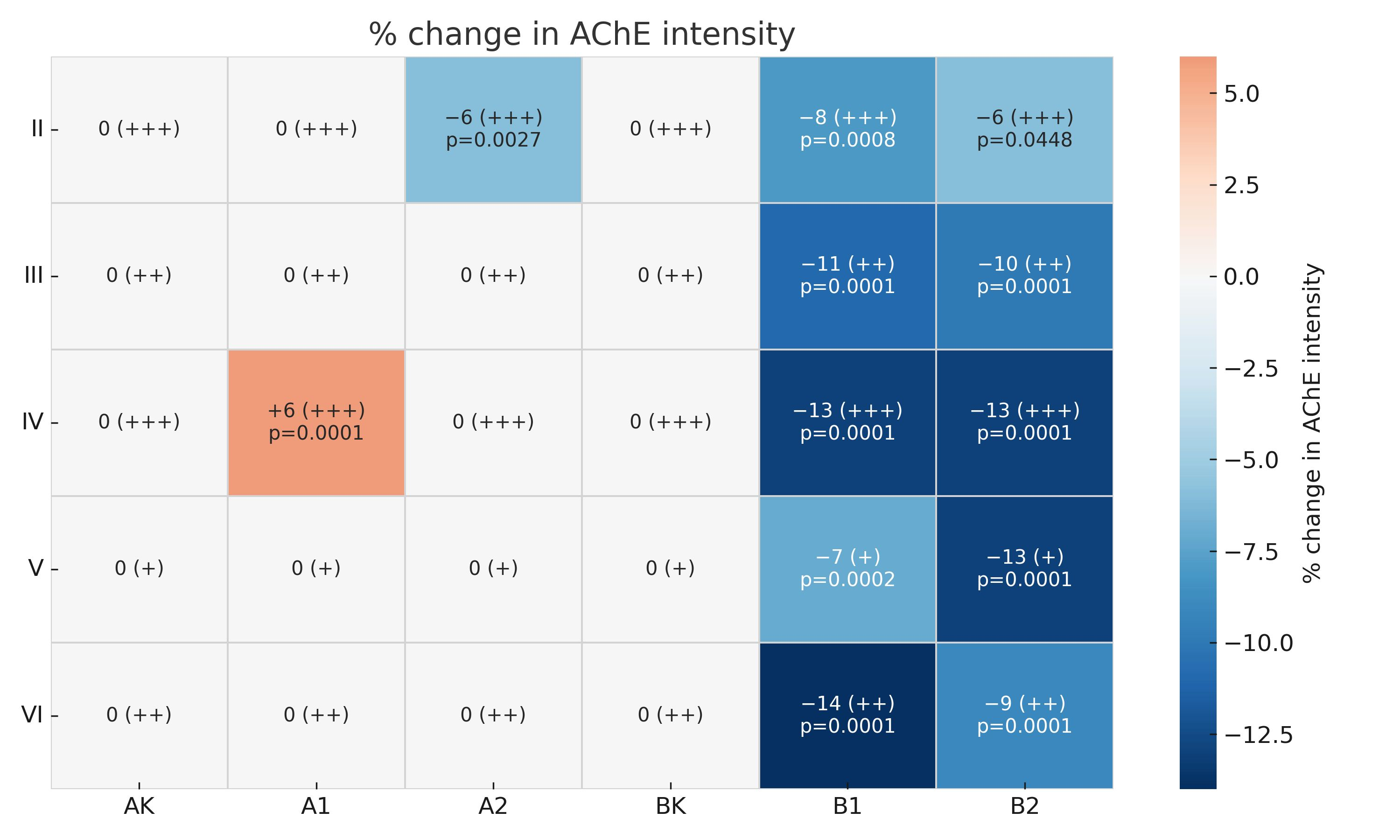
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madan, S.; Ahmad, S.; Singh, G.N.; Kohli, K.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, R.; Garg, M. Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.) Bertoni—A review. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2010, 1, 267–286. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.; Renwick, A.G. Comparative toxicokinetics and metabolism of rebaudioside A, stevioside, and steviol in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S31–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.; Boileau, A.; Winkler, P.; Compton, J.; Prakash, I.; Jiang, X.; Mandarino, D. Pharmacokinetics of rebaudioside A and stevioside after single oral doses in healthy men. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S54–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, S.; Kwok, D. Metabolic fate in adult and pediatric population of steviol glycosides produced from stevia leaf extract by different production technologies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 116, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Paucar, A.M. Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects. Molecules 2023, 28, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoens, C.; Philippaert, K.; Wuyts, C.; Goscinny, S.; Van Hoeck, E.; Van Loco, J.; Billen, J.; de Hoon, J.; Ampe, E.; Vangoitsenhoven, R.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Oral Rebaudioside A in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effects on Glucose Homeostasis: A Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 47, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juyal, D.S.; Kumar, A.; Bisht, G. Effect of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.) extract on memory and acetylcholinesterase activity in young and aged rats. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2010, 2, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Juyal, D.S.; Bisht, G. Kumar A 2010: Memory enhancing effect of ethanolic extract of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.). Int. J. Phytomedicine 2025, 2, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł-Bęben, K.; Tomasz, B.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Antosiewicz, B.; Jakubczyk, A.; Karaś, M.; Rybczyńska, K. Stevia Rebaudiana Bert. Leaf Extracts as a Multifunctional Source of Natural Antioxidants. Molecules 2015, 20, 5468–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, K.; Lanza, E.A.; Martin, S.A.; Myronyuk, N.; Rua, M.; Raffa, R.B. Diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease: Shared pathology and treatment? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 71, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagiakrishnan, K.; Sankaralingam, S.; Ghosh, M.; Mereu, L.; Senior, P. Antidiabetic drugs and their potential role in treating mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Discov. Med. 2013, 16, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Claassen, J.A.H.R.; van Beek, A.H.E.A.; Olde-Rikkert, M.G.M. Short review: Acetylcholinesterase-inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease have opposing effects on blood pressure and cerebral perfusion. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreq, H.; Seidman, S. Acetylcholinesterase—New roles for an old actor. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Sivaprakasam, P.; Vijendra, P.; Waseem, M.; Pandurangan, A.K. A Recent Update on Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Interventions of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 3428–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Dikshit, M.; Nath, C. Profile of acetylcholinesterase in brain areas of male and female rats of adult and old age. Life Sci. 2001, 68, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.P.; Ferreira-Machado, S.C.; Nunes, R.M.; Dantas, F.J.; De Mattos, J.C.; Caldeira-de-Araújo, A. Analysis of genotoxic potentiality of stevioside by comet assay. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.; Poorthuis, R.B.; Mansvelder, H.D. Cholinergic modulation of the medial prefrontal cortex: The role of nicotinic receptors in attention and regulation of neuronal activity. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, V.; Mendoza, C.; Iarkov, A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and learning and memory deficits in Neuroinflammatory diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1179611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elston, G.N. Cortex, Cognition and the Cell: New insights into the pyramidal neuron and prefrontal function. Cereb. Cortex 2003, 13, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, R. Neocortical inhibitory system. Folia Biol. 2009, 55, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orta-Salazar, E.; Cuellar-Lemus, C.A.; Díaz-Cintra, S.; Feria-Velasco, A.I. Cholinergic markers in the cortex and hippocampus of some animal species and their correlation to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurologia 2014, 29, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczek, M.; Gefen, T.; Samimi, M.; Kim, G.; Weintraub, S.; Bigio, E.; Rogalski, E.; Mesulam, M.-M.; Geula, C. Variations in Acetylcholinesterase Activity within Human Cortical Pyramidal Neurons Across Age and Cognitive Trajectories. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Srivastava, U.C. Acetylcholinesterase: A versatile enzyme of nervous system. Ann. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycerz, K.; Jaworska-Adamu, J.; Krawczyk, A.; Arciszewski, M.B. Immunoreactivity of acetylcholinesterase and M1 muscarinic receptors in the hippocampus and striatum of rats treated with Rebaudioside A. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 25, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rycerz, K.; Jaworska-Adamu, J. Immunohistochemical evaluation of the influence of rebaudioside A on neurons containing acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the rat’s hippocampus and striatum. Med. Weter. 2019, 75, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.K.; Jones, C.K.; Newhouse, P.A. The Role of Estrogen in Brain and Cognitive Aging. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, J.F.R.; Klippel, R.A. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Forebrain and Lower Parts of the Brain Stem; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Young, B.; O’Dowd, G.; Woodford, P. Wheater’s Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas, 6th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, A.; Jaworska-Adamu, J.; Rycerz, K. Immunohistochemical evaluation of hippocampal CA1 region astrocytes in 10-day-old rats after monosodium glutamate treatment. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Arzberger, T.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Bodi, I.; Bogdanovic, N.; Braak, H.; Bugiani, O.; Del-Tredici, K.; Ferrer, I.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Staging of neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease: A study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, L.L.; Stabenow, E.; Tavares, M.; Ferraz, A.R.; Capelozzi, V.; Pinhal, M.A.D.S. Immunohistochemistry quantification by a digital computer-assisted method compared to semiquantitative analysis. Clinics 2006, 61, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzuto, J.M.; Nanayakkara, N.P.; Compadre, C.M.; Swanson, S.M.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Guenthner, T.M.; Sparnins, V.L.; Lam, L.K. Characterization of bacterial mutagenicity mediated by 13-hydroxy-ent-kaurenoic acid (steviol) and several structurally-related derivatives and evaluation of potential to induce glutathione S-transferase in mice. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. 1986, 169, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusick, D.J. A critical review of the genetic toxicity of steviol and steviol glycosides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S83–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carakostas, M.C.; Curry, L.L.; Boileau, A.C.; Brusick, D.J. Overview: The history, technical function and safety of rebaudioside A, a naturally occurring steviol glycoside, for use in food and beverages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsudthipong, V.; Muanprasat, C. Stevioside and related compounds: Therapeutic benefits beyond sweetness. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Abdollahi, E.; Sahebkar, A. A Review on the Pharmacology and Toxicology of Steviol Glycosides Extracted from Stevia rebaudiana. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarter, M.; Bruno, J.P. Cortical cholinergic inputs mediating arousal, attentional processing and dreaming: Differential afferent regulation of the basal forebrain by telencephalic and brainstem afferents. Neuroscience 1999, 95, 933–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Asaka, Y.; Kanamura, S. Relationship between immunostaining intensity and antigen content in sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1996, 44, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotto, M.R.; Higley, M.J.; Mineur, Y.S. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: Cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron 2012, 76, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmo, M.E. The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degroot, A.; Parent, M.B. Increasing acetylcholine levels in the hippocampus or entorhinal cortex reverses the impairing effects of septal GABA receptor activation on spontaneous alternation. Learn. Mem. 2000, 7, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Puri, M.; Tiwary, A.K.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Antiamnesic effect of stevioside in scopolamine-treated rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2010, 42, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratiglioni, L.; Winblad, B.; von Strauss, E. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. Major findings from the Kungsholmen Project. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, H.; Soni, M.; Silawat, N.; Mehta, D.; Mehta, B.K.; Jain, D.C. Antidiabetic activity of medium-polar extract from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana Bert. (Bertoni) on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, M.; Kumar, J.; Vajravelu, L.K.; Satheesan, A.; Chaithanya, V.; Murugesan, R. Artificial sweeteners and their implications in diabetes: A review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1411560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sędzikowska, A.; Szablewski, L. Insulin and Insulin Resistance in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badowska-Szalewska, E.; Klejbor, I.; Cecot, T.; Spodnik, J.H.; Moryś, J. Changes in NGF/c-Fos double staining in the structures of the limbic system in juvenile and aged rats exposed to forced swim test. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2009, 69, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rycerz, K.; Balawender, K.; Cassano, T.; Żuryń, A.; Arciszewski, M.B.; Walocha, J.; Wawrzyniak, A. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase-Positive Neurons in the Brain Cortex of Rats After Administration of Rebaudioside A. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080845
Rycerz K, Balawender K, Cassano T, Żuryń A, Arciszewski MB, Walocha J, Wawrzyniak A. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase-Positive Neurons in the Brain Cortex of Rats After Administration of Rebaudioside A. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(8):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080845
Chicago/Turabian StyleRycerz, Karol, Krzysztof Balawender, Tommaso Cassano, Agnieszka Żuryń, Marcin B. Arciszewski, Jerzy Walocha, and Agata Wawrzyniak. 2025. "Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase-Positive Neurons in the Brain Cortex of Rats After Administration of Rebaudioside A" Brain Sciences 15, no. 8: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080845
APA StyleRycerz, K., Balawender, K., Cassano, T., Żuryń, A., Arciszewski, M. B., Walocha, J., & Wawrzyniak, A. (2025). Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Acetylcholinesterase-Positive Neurons in the Brain Cortex of Rats After Administration of Rebaudioside A. Brain Sciences, 15(8), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080845





