Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
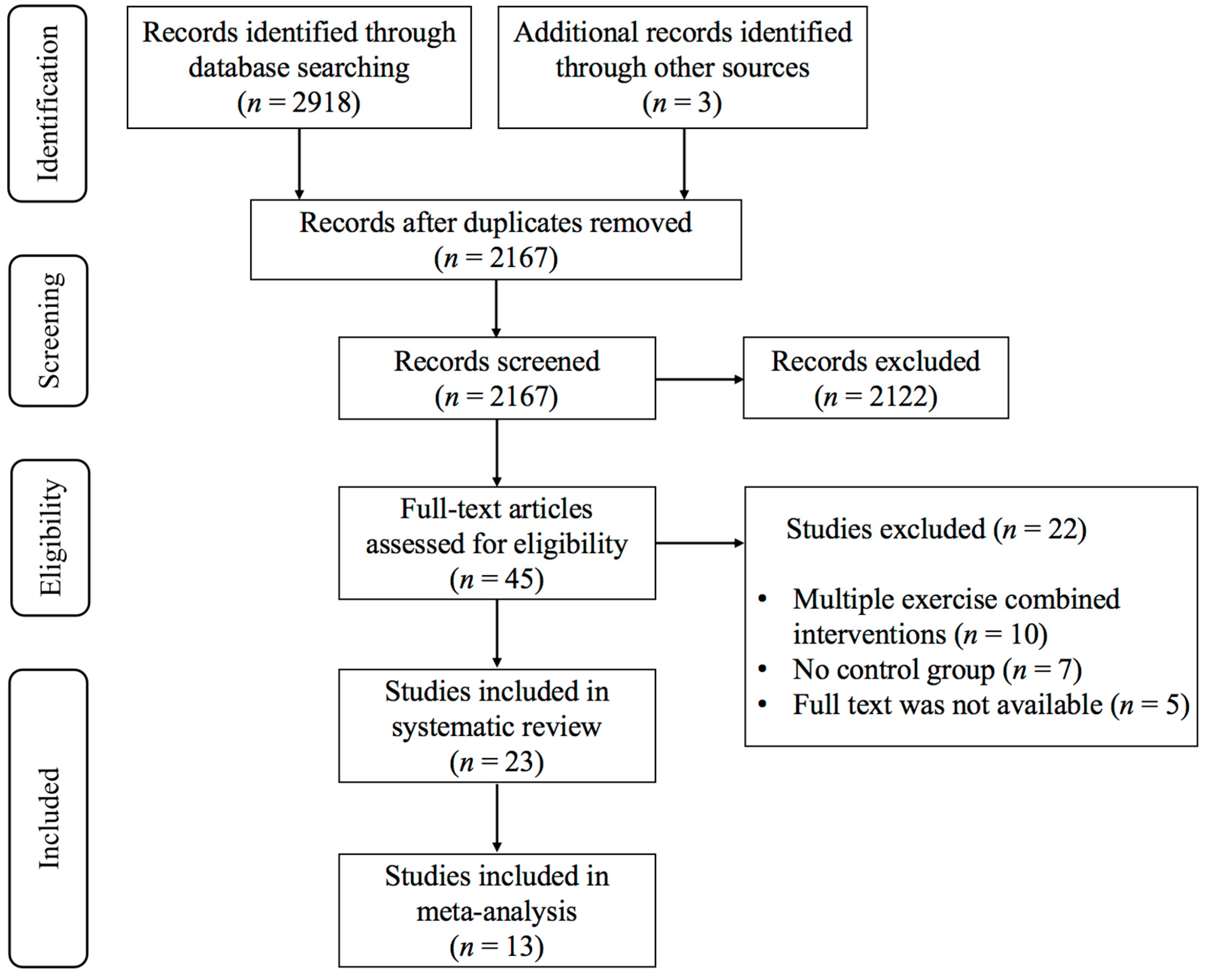
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
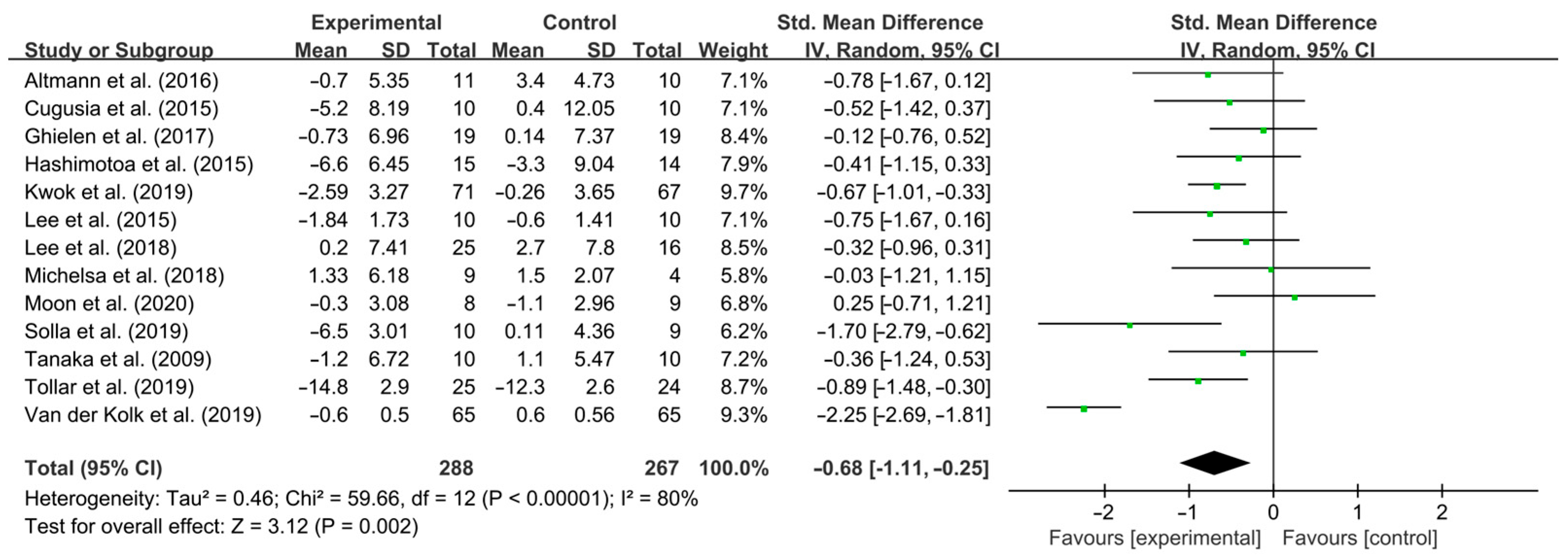
3.3. Meta-Analysis Results
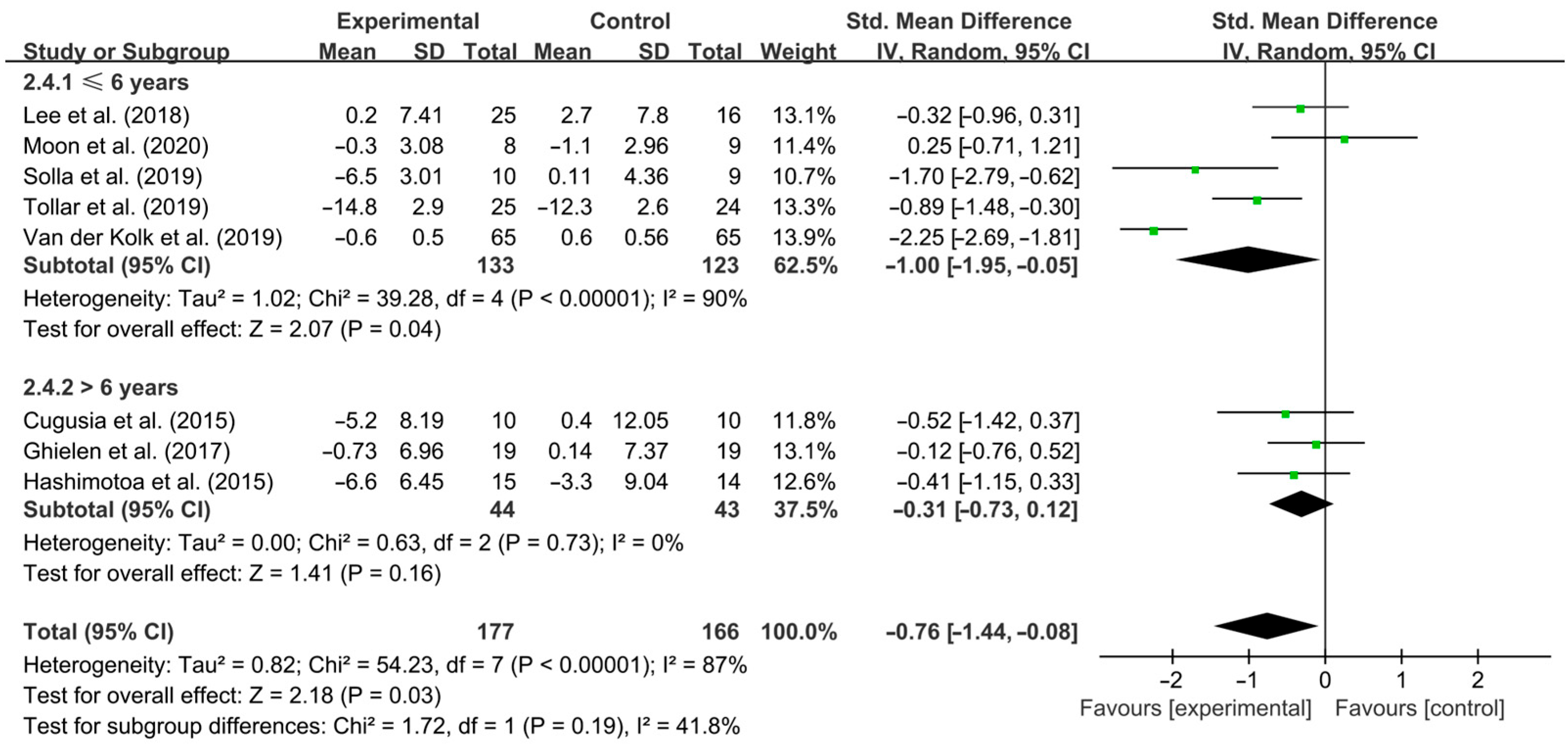
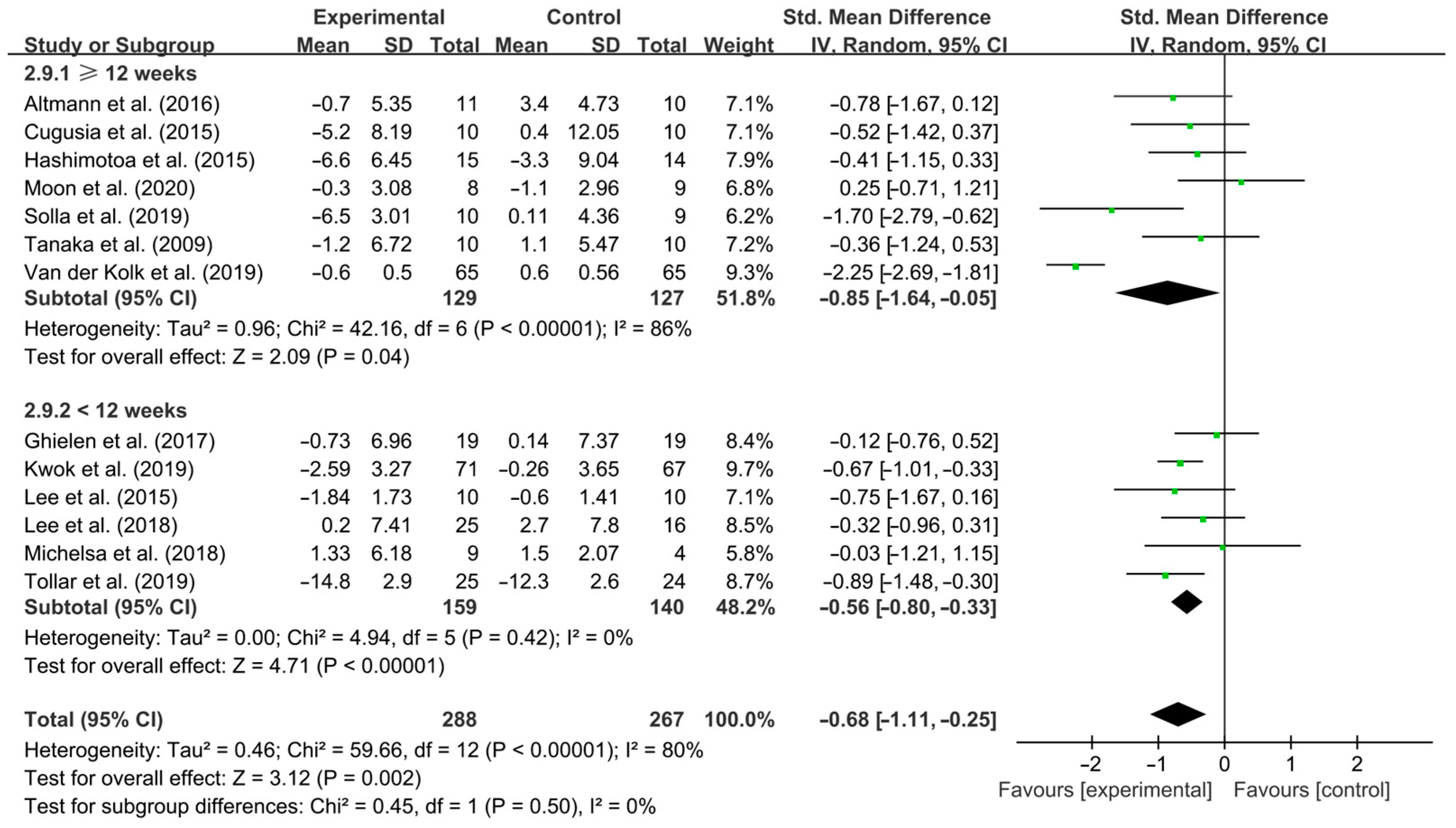
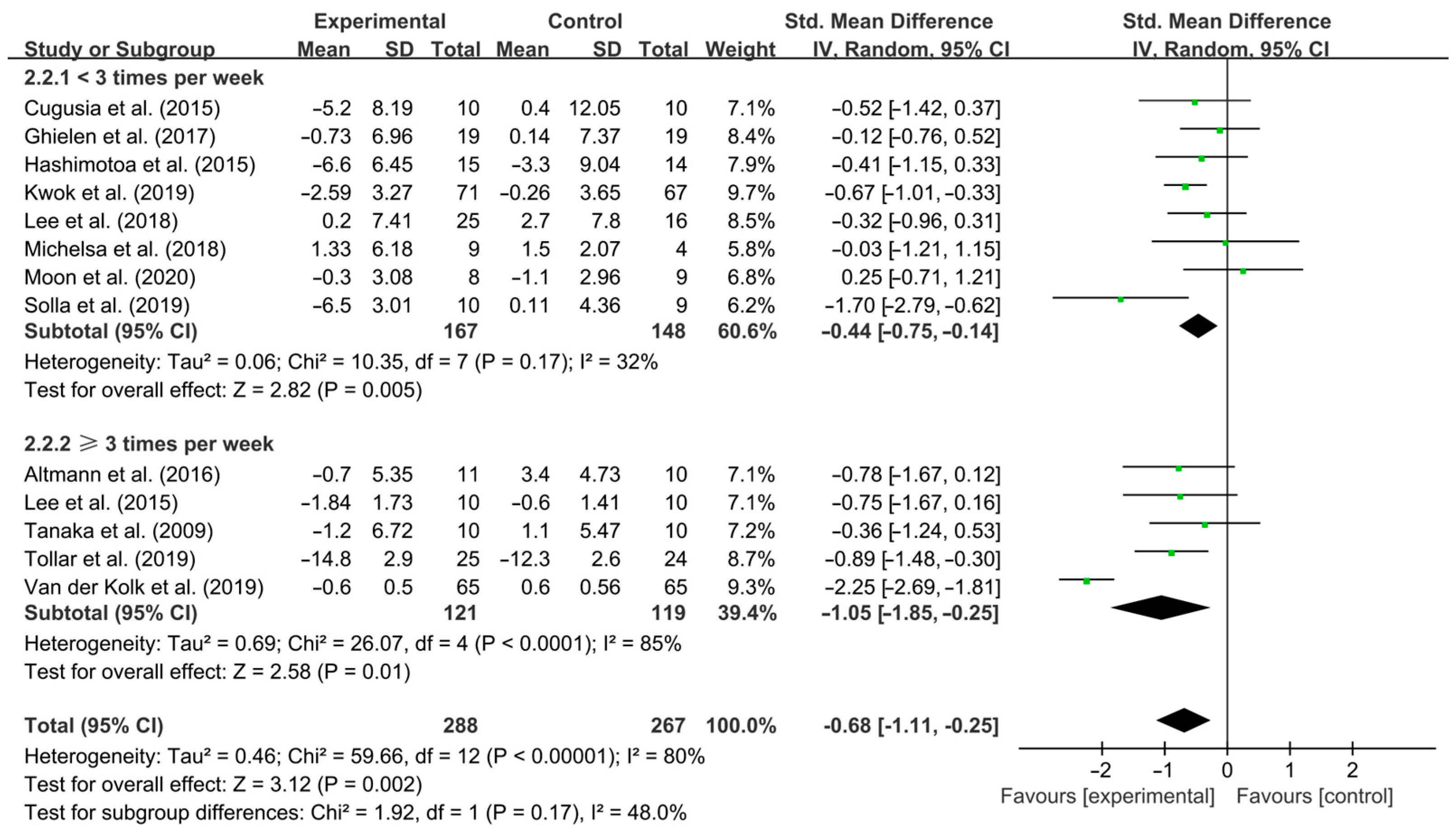
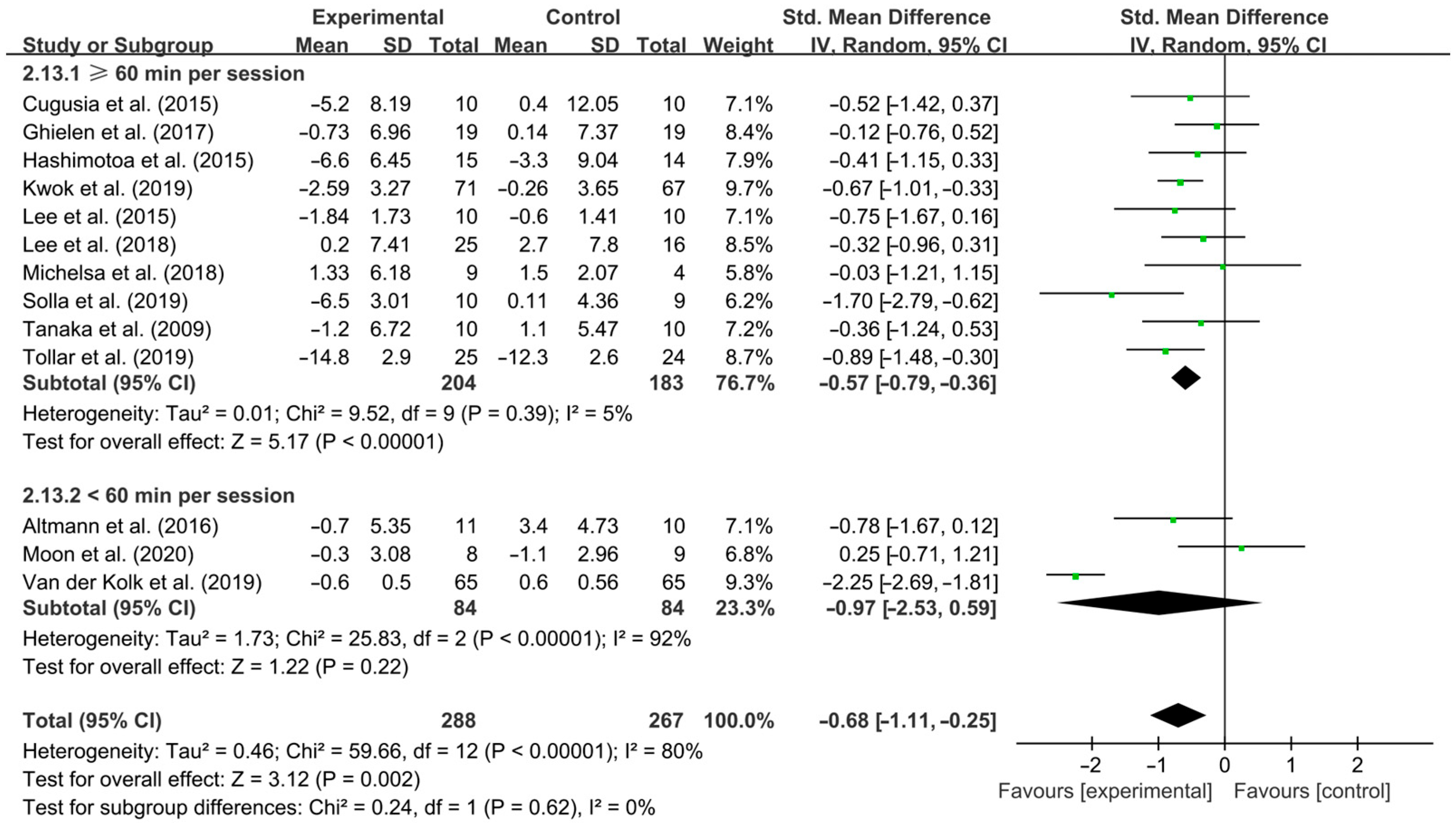
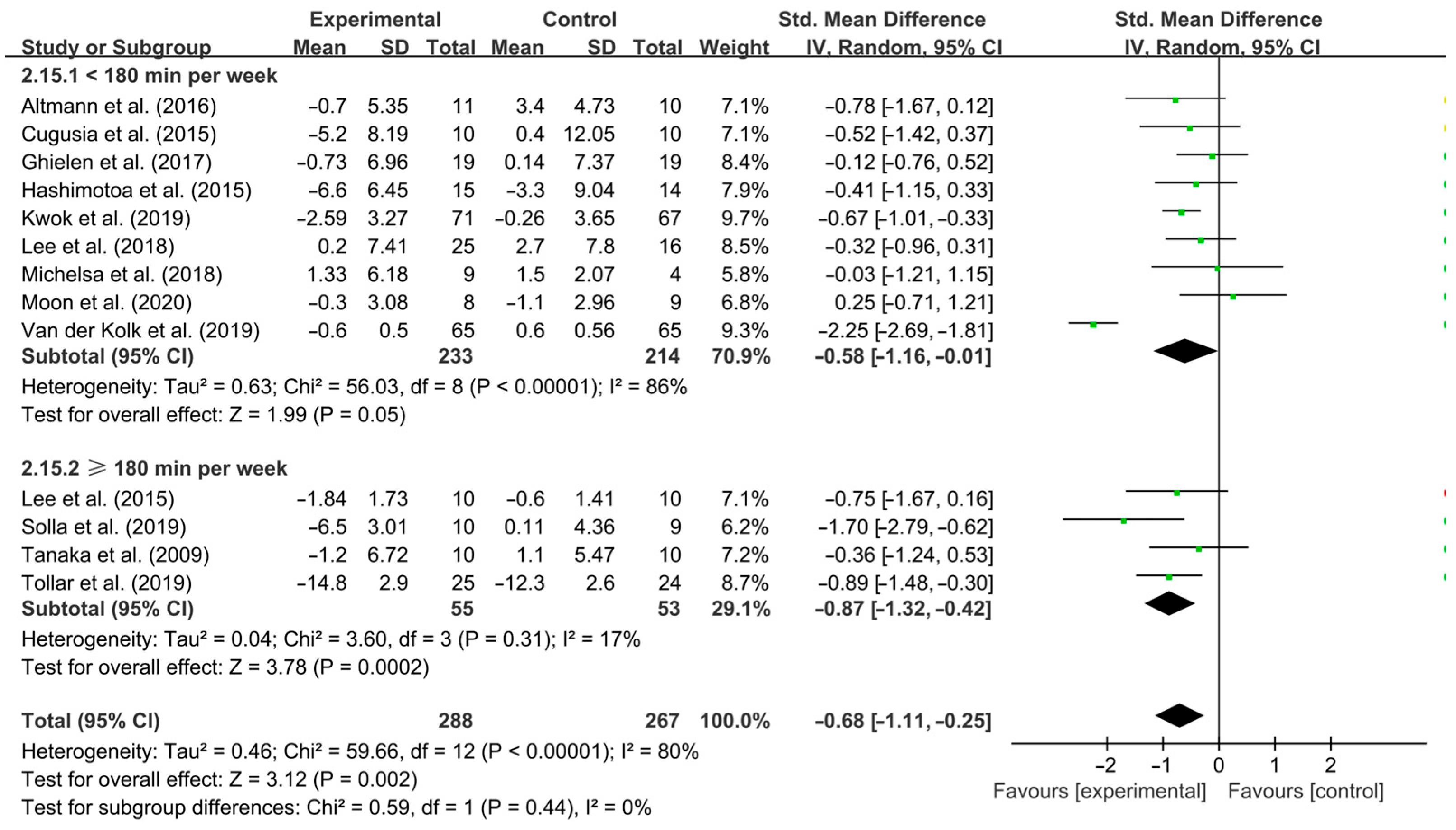
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
3.5. Risk of Bias
3.6. Publication Bias
3.7. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in PD Patients
4.3. Effects of Different Exercise Design Parameters on Depressive Symptoms in PD Patients
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| DA | Dopamine |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| EG | Experimental group |
| CG | Control group |
| NR | No report |
| BDI | Beck Depression Inventory |
| BDI-II | Beck Depression Inventory-II |
| SDS | Self-rating Depression Scale |
| HADS | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale |
| GDS | Geriatric Depression Scale |
| CES-D | Epidemiologic Studies Depression |
| VO2max | Maximal oxygen uptake |
| HRmax | Maximal heart rate |
| HRR | Heart rate reserve |
| RPE | Rating of perceived exertion |
| NE | Norepinephrine |
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| LC | Locus coeruleus |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor protein 3 |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-α |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine’s |
References
- Cong, S.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Cong, S. Prevalence and clinical aspects of depression in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 129 studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 141, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, S.G.; Savitt, J.M. Parkinson’s Disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.C.; Chan, L.L.; Tan, L.C.; Tan, E.K. Depression, anxiety, and apathy in Parkinson’s disease: Insights from neuroimaging studies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.A.; Schrag, A. Psychosis, apathy, depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, Z.; Mrklas, K.J.; Roberts, D.J.; Jette, N.; Pringsheim, T.; Holroyd-Leduc, J. Detecting depression in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2016, 87, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijnders, J.S.; Ehrt, U.; Weber, W.E.; Aarsland, D.; Leentjens, A.F. A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 183–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, W.M.; Richard, I.H.; DeLong, M.R. Prevalence, etiology, and treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Logroscino, G.; Hernán, M.A. Use of antidepressants and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A prospective study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, L.; Brayne, C. A systematic review of depression and mental illness preceding Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2006, 113, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, O.; Ikeda, K.; Cridebring, D.; Takazawa, T.; Yoshii, Y.; Iwasaki, Y. Neurobiology of depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Dis. 2011, 2011, 143547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M. Depression in Parkinson’s disease: Its prevalence, diagnosis, and neurochemical background. J. Neurol. 2001, 248 (Suppl. 3), III5–III11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmerle, A.M.; Herman, J.P.; Seroogy, K.B. Stress, depression and Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armento, M.E.; Stanley, M.A.; Marsh, L.; Kunik, M.E.; York, M.K.; Bush, A.L.; Calleo, J.S. Cognitive behavioral therapy for depression and anxiety in Parkinson’s disease: A clinical review. J. Park. Dis. 2012, 2, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assogna, F.; Pellicano, C.; Savini, C.; Macchiusi, L.; Pellicano, G.R.; Alborghetti, M.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G.; Pontieri, F.E. Drug Choices and Advancements for Managing Depression in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, L. Depression and Parkinson’s disease: Current knowledge. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaki, J.M.; Shannon, K.; Voon, V.; Ravina, B.; Kleiner-Fisman, G.; Anderson, K.; Shulman, L.M.; Gronseth, G.; Weiner, W.J. Practice Parameter: Evaluation and treatment of depression, psychosis, and dementia in Parkinson disease (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2006, 66, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, I.H. Depression and apathy in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2007, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Rizvi, M.A.; Ali, M.; Mondal, A.C. Neurobiology of depression in Parkinson’s disease: Insights into epidemiology, molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 85, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhai, J.; Kong, Z.; Li, X. Effects of Exercise Interventions on Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2025, 7, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, P. Neurotransmission in Parkinson’s disease: Beyond dopamine. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robison, L.S.; Swenson, S.; Hamilton, J.; Thanos, P.K. Exercise Reduces Dopamine D1R and Increases D2R in Rats: Implications for Addiction. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Lim, B.V.; Baek, D.; Ryu, D.S.; Seo, J.H. Stress-Induced Depression Is Alleviated by Aerobic Exercise Through Up-Regulation of 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A Receptors in Rats. Int. Neurourol. J. 2015, 19, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, H.; Deslandes, A.C.; de Moraes, H.; Mouta, R.; Ribeiro, P.; Piedade, R.; Laks, J. Effects of exercise on electroencephalographic mean frequency in depressed elderly subjects. Neuropsychobiology 2010, 61, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, D.; Fox, I.; Gozzer, P.; Trentin, F.; Papola, D. Exercise for Depressive Symptoms in Parkinson Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, Ed000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, K.; Zhang, S.; Tao, X.; Li, G.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. A systematic review and meta-analysis on effects of aerobic exercise in people with Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, G.; He, H.; Lv, Y. Effects of Different Intensities and Durations of Aerobic Exercise on Vascular Endothelial Function in Middle-Aged and Elderly People: A Meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 803102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattari, E.; Pereira-Junior, P.P.; Neto, G.A.; Lamego, M.K.; Moura, A.M.; de Sá, A.S.; Rimes, R.R.; Manochio, J.P.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Mura, G.; et al. Effects of chronic exercise on severity, quality of life and functionality in an elderly Parkinson’s disease patient: Case report. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2014, 10, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dağ, F.; Çimen, Ö.B.; Doğu, O. The effects of arm crank training on aerobic capacity, physical performance, quality of life, and health-related disability in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 191, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kolk, N.M.; Overeem, S.; de Vries, N.M.; Kessels, R.P.; Donders, R.; Brouwer, M.; Berg, D.; Post, B.; Bloem, B.R. Design of the Park-in-Shape study: A phase II double blind randomized controlled trial evaluating the effects of exercise on motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashi, H.; Taguchi, T.; Ueta, Y.; Mitoma, H.; Aizawa, H. Association of daily physical activity with cognition and mood disorders in treatment-naive patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghielen, I.; van den Heuvel, O.A.; de Goede, C.J.; Houniet-de Gier, M.; Collette, E.H.; Burgers-Bots, I.A.; Rutten, S.; Kwakkel, G.; Vermunt, K.; van Vliet, B.; et al. BEWARE: Body awareness training in the treatment of wearing-off related anxiety in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2015, 16, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanns, M.; Mastel-Smith, B.; Donnell, R.; Quarles, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Wang, T. Counterpunching to improve the health of people with Parkinson’s disease. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2021, 33, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobágyi, T.; Sipos, D.; Borbély, G.; Áfra, G.; Reichardt-Varga, E.; Sántha, G.; Nieboer, W.; Tamási, K.; Tollár, J. Detraining Slows and Maintenance Training Over 6 Years Halts Parkinsonian Symptoms-Progression. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 737726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Hübsch, T.; Pyfer, D.; Kielwein, K.; Fimmers, R.; Klockgether, T.; Wallner, U. Qigong exercise for the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, controlled pilot study. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2006, 21, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.K.; Robbins, K.; Wagner, K.; Colgrove, Y.M. A randomized controlled pilot study of the therapeutic effects of yoga in people with Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Yoga 2015, 8, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urrutia, M.; Ivy, C.; Pohl, P.S.; Denney, L. Boxing to Improve Sleep Quality and Daytime Sleepiness in Individuals with Parkinson Disease: Pilot Study. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2020, 36, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, L.J.; Stegemöller, E.; Hazamy, A.A.; Wilson, J.P.; Bowers, D.; Okun, M.S.; Hass, C.J. Aerobic Exercise Improves Mood, Cognition, and Language Function in Parkinson’s Disease: Results of a Controlled Study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2016, 22, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugusi, L.; Solla, P.; Serpe, R.; Carzedda, T.; Piras, L.; Oggianu, M.; Gabba, S.; Di Blasio, A.; Bergamin, M.; Cannas, A.; et al. Effects of a Nordic Walking program on motor and non-motor symptoms, functional performance and body composition in patients with Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRehabilitation 2015, 37, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghielen, I.; van Wegen, E.E.H.; Rutten, S.; de Goede, C.J.T.; Gier, M.H.-D.; Collette, E.H.; Burgers-Bots, I.A.L.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Kwakkel, G.; Vermu, K.N.; et al. Body awareness training in the treatment of wearing-off related anxiety in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Results from a pilot randomized controlled trial. J. Psychosom. Res. 2017, 103, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Takabatake, S.; Miyaguchi, H.; Nakanishi, H.; Naitou, Y. Effects of dance on motor functions, cognitive functions, and mental symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: A quasi-randomized pilot trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.Y.Y.; Kwan, J.C.Y.; Auyeung, M.; Mok, V.C.T.; Lau, C.K.Y.; Choi, K.C.; Chan, H.Y.L. Effects of Mindfulness Yoga vs Stretching and Resistance Training Exercises on Anxiety and Depression for People with Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Chae, Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Yin, C.; Jung, W.S.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, S.N.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H. Turo (Qi Dance) Program for Parkinson’s Disease Patients: Randomized, Assessor Blind, Waiting-List Control, Partial Crossover Study. Explore 2018, 14, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Song, H.S. Effect of virtual reality dance exercise on the balance, activities of daily living, and depressive disorder status of Parkinson’s disease patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, K.; Dubaz, O.; Hornthal, E.; Bega, D. “Dance Therapy” as a psychotherapeutic movement intervention in Parkinson’s disease. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 40, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Sarmento, C.V.M.; Steinbacher, M.; Smirnova, I.V.; Colgrove, Y.; Lai, S.M.; Lyons, K.E.; Liu, W. Can Qigong improve non-motor symptoms in people with Parkinson’s disease-A pilot randomized controlled trial? Complement. Ther. Clin. Pr. 2020, 39, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solla, P.; Cugusi, L.; Bertoli, M.; Cereatti, A.; Della Croce, U.; Pani, D.; Fadda, L.; Cannas, A.; Marrosu, F.; Defazio, G.; et al. Sardinian Folk Dance for Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2019, 25, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Quadros, A.C., Jr.; Santos, R.F.; Stella, F.; Gobbi, L.T.; Gobbi, S. Benefits of physical exercise on executive functions in older people with Parkinson’s disease. Brain Cogn. 2009, 69, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollár, J.; Nagy, F.; Hortobágyi, T. Vastly Different Exercise Programs Similarly Improve Parkinsonian Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Gerontology 2019, 65, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kolk, N.M.; de Vries, N.M.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Joosten, H.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Post, B.; Bloem, B.R. Effectiveness of home-based and remotely supervised aerobic exercise in Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhen, K.; Ren, S.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effect of continuous aerobic exercise on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1043108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heissel, A.; Heinen, D.; Brokmeier, L.L.; Skarabis, N.; Kangas, M.; Vancampfort, D.; Stubbs, B.; Firth, J.; Ward, P.B.; Rosenbaum, S.; et al. Exercise as medicine for depressive symptoms? A systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.; Chen, D.; Zhu, M. Effects of Aerobic Exercise and Mind-Body Exercise in Parkinson’s Disease: A Mixed-Treatment Comparison Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 739115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.L.; Lee, M.; Huang, T.T. Effectiveness of physical activity on patients with depression and Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh Pahlavani, H. Possible role of exercise therapy on depression: Effector neurotransmitters as key players. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 459, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, C.; Anjum, R.; Shakeel, N.U.A. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management strategies. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbatyuk, O.S.; Li, S.; Sullivan, L.F.; Chen, W.; Kondrikova, G.; Manfredsson, F.P.; Mandel, R.J.; Muzyczka, N. The phosphorylation state of Ser-129 in human alpha-synuclein determines neurodegeneration in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Luk, K.C.; Patel, T.P.; Tanik, S.A.; Riddle, D.M.; Stieber, A.; Meaney, D.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 2011, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarsland, D.; Påhlhagen, S.; Ballard, C.G.; Ehrt, U.; Svenningsson, P. Depression in Parkinson disease—Epidemiology, mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 8, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlop, B.W.; Nemeroff, C.B. The role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga-Amaro, R.; Gonzalez, H.; Pacheco, R.; Stehberg, J. Dopamine receptor D3 deficiency results in chronic depression and anxiety. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 274, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, B.; Yong, S.S.; Tian, Z. Effects of Exercise Intervention on Physical and Mental Health of Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Based on ICF-CY. J. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamotte, G.; Rafferty, M.R.; Prodoehl, J.; Kohrt, W.M.; Comella, C.L.; Simuni, T.; Corcos, D.M. Effects of Endurance Exercise Training on The Motor and Non-Motor Features of Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 993. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, T.B.; Schamne, M.G.; Santos, J.R.; Ferro, M.M.; Miyoshi, E.; Prediger, R.D. Exploring Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Depression: Role of Inflammation on the Noradrenergic and Serotonergic Pathways. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, M.J.; Kirilina, E.; Otaduy, M.C.G.; Ivanov, D.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Callaghan, M.F.; Lambert, C.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Pine, K.; Passamonti, L.; et al. Locus coeruleus imaging as a biomarker for noradrenergic dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain 2019, 142, 2558–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Rodriguez, E.; Vegas-Suarez, S.; Morera-Herreras, T.; De Deurwaerdere, P.; Miguelez, C. The Noradrenergic System in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, A.; Krack, P.; Lhommée, E.; Météreau, E.; Klinger, H.; Favre, E.; Le Bars, D.; Schmitt, E.; Bichon, A.; Pelissier, P.; et al. The prominent role of serotonergic degeneration in apathy, anxiety and depression in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 2486–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.Z.; Cheer, J.F.; Tonini, R. Modulating the Neuromodulators: Dopamine, Serotonin, and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupfer, D.J.; Frank, E.; Phillips, M.L. Major depressive disorder: New clinical, neurobiological, and treatment perspectives. Lancet 2012, 379, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.K.; Hartung, H.; Sharp, T.; Temel, Y. Serotonin-dependent depression in Parkinson’s disease: A role for the subthalamic nucleus? Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melancon, M.O.; Lorrain, D.; Dionne, I.J. Changes in markers of brain serotonin activity in response to chronic exercise in senior men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Ren, F.; Liang, H.; Wu, D.; Ji, X.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Efficacy and evaluation of therapeutic exercises on adults with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H. The Effects and Mechanisms of Exercise on the Treatment of Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 705559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; Derry, H.M.; Fagundes, C.P. Inflammation: Depression fans the flames and feasts on the heat. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brites, D.; Fernandes, A. Neuroinflammation and Depression: Microglia Activation, Extracellular Microvesicles and microRNA Dysregulation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of inflammatory markers in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes da Silva, S.; Simões, P.S.; Mortara, R.A.; Scorza, F.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; da Graça Naffah-Mazzacoratti, M.; Arida, R.M. Exercise-induced hippocampal anti-inflammatory response in aged rats. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa e Silva, T.; Longui, C.A.; Rocha, M.N.; Faria, C.D.; Melo, M.R.; Faria, T.G.; de Souza, J.A.; Rizzo, L.V. Prolonged physical training decreases mRNA levels of glucocorticoid receptor and inflammatory genes. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 74, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Aerobic exercise alleviates pyroptosis-related diseases by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 965366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, B.E.G.; Hartmann, T.E.; Marino, F.E.; Skein, M. The Effect of a 12 Week Mixed-Modality Training Intervention on the Cardio-Metabolic Health of Rotational Shift Workers. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2024, 6, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Duan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Ying, J.; et al. Physical exercise promotes brain remodeling by regulating epigenetics, neuroplasticity and neurotrophins. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Sun, J. Serum BDNF discriminates Parkinson’s disease patients with depression from without depression and reflect motor severity and gender differences. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, X.D.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhang, B.S.; Soares, J.C.; Zhang, X.Y. Association of low serum BDNF with depression in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 41, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaepen, K.; Goekint, M.; Heyman, E.M.; Meeusen, R. Neuroplasticity-exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 765–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, C.P.; Kuys, S.S.; Brauer, S.G. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in People with Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 4716197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, B.; Zhen, K.; Du, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer’s disease models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2024, 126, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, F.; Saghazadeh, A.; Rahmani, M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Rezaei, N.; Aghamollaii, V.; Ardebili, H.E. Plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Res. 2019, 1704, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzinger, G.M.; Fisher, B.E.; McEwen, S.; Beeler, J.A.; Walsh, J.P.; Jakowec, M.W. Exercise-enhanced neuroplasticity targeting motor and cognitive circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmolesky, M.T.; Webb, D.L.; Hansen, R.A. The effects of aerobic exercise intensity and duration on levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in healthy men. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mak, M.K.; Wong-Yu, I.S.; Shen, X.; Chung, C.L. Long-term effects of exercise and physical therapy in people with Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.L.; Jiang, W.T.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.D.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, G.R. Exercise, brain plasticity, and depression. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imboden, C.; Gerber, M.; Beck, J.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Pühse, U.; Hatzinger, M. Aerobic exercise or stretching as add-on to inpatient treatment of depression: Similar antidepressant effects on depressive symptoms and larger effects on working memory for aerobic exercise alone. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 276, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasson, L.S.; Nyberg, L.; Axelsson, J.; Kramer, A.F.; Riklund, K.; Boraxbekk, C.J. Higher striatal D2-receptor availability in aerobically fit older adults but non-selective intervention effects after aerobic versus resistance training. Neuroimage 2019, 202, 116044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Lou, S. Aerobic Exercise Improves Synaptic-Related Proteins of Diabetic Rats by Inhibiting FOXO1/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Signaling Pathway and Ameliorating PI3K/Akt Insulin Signaling Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schootemeijer, S.; Darweesh, S.K.L.; de Vries, N.M. Clinical Trial Highlights-Aerobic Exercise for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 12, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, R.; Reaburn, P. Exercise and the treatment of depression: A review of the exercise program variables. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2014, 17, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Frith, E.; Kang, M.; Loprinzi, P.D. Effects of Acute Exercise on Verbal, Mathematical, and Spatial Insight Creativity. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2023, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidong, C.; Wang, X.; Yin, J.; Song, D.; Chen, Z. Effects of physical exercise on working memory in older adults: A systematic and meta-analytic review. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, V.; White, L.J. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor response to aerobic exercise in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 269, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Yang, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Liew, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, H.I.; Suh, Y.H.; Park, H.S.; et al. Dopamine and Cu+/2+ can induce oligomerization of α-synuclein in the absence of oxygen: Two types of oligomerization mechanisms for α-synuclein and related cell toxicity studies. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schootemeijer, S.; van der Kolk, N.M.; Bloem, B.R.; de Vries, N.M. Current Perspectives on Aerobic Exercise in People with Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1418–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollan, R.; Ernst, M.; Lieker, E.; Caro-Valenzuela, J.; Monsef, I.; Dresen, A.; Roheger, M.; Skoetz, N.; Kalbe, E.; Folkerts, A.K. Effects of Resistance Training on Motor- and Non-Motor Symptoms in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 1783–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Yu, L. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080792
Ren H, Zhou Y, Lv Y, Liu X, He L, Yu L. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(8):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080792
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hao, Yilun Zhou, Yuanyuan Lv, Xiaojie Liu, Lingxiao He, and Laikang Yu. 2025. "Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Brain Sciences 15, no. 8: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080792
APA StyleRen, H., Zhou, Y., Lv, Y., Liu, X., He, L., & Yu, L. (2025). Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sciences, 15(8), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080792