SAGEFusionNet: An Auxiliary Supervised Graph Neural Network for Brain Age Prediction as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker
Abstract
1. Introduction
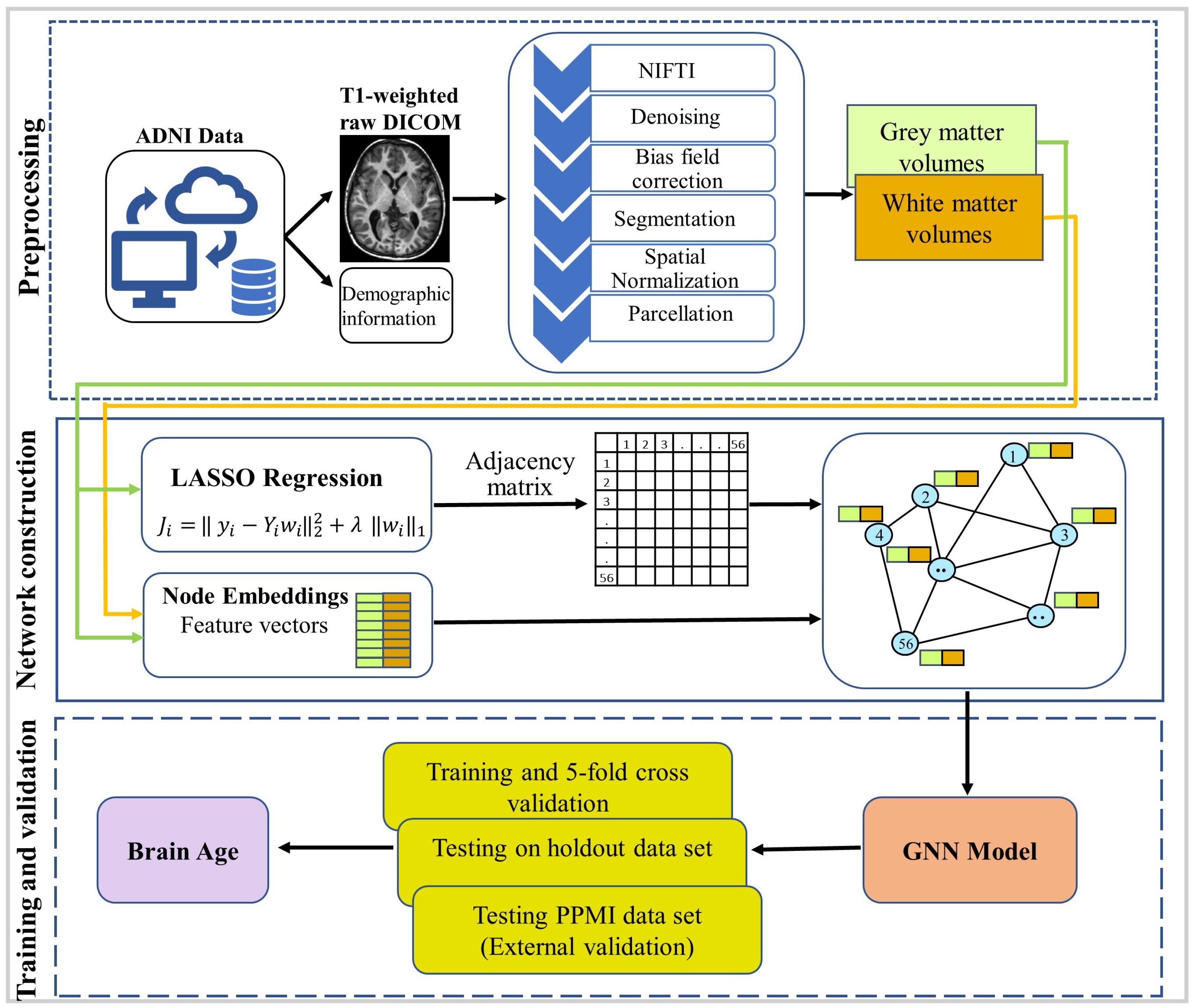
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Description
2.2. Preprocessing

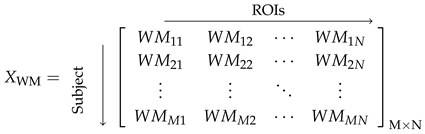
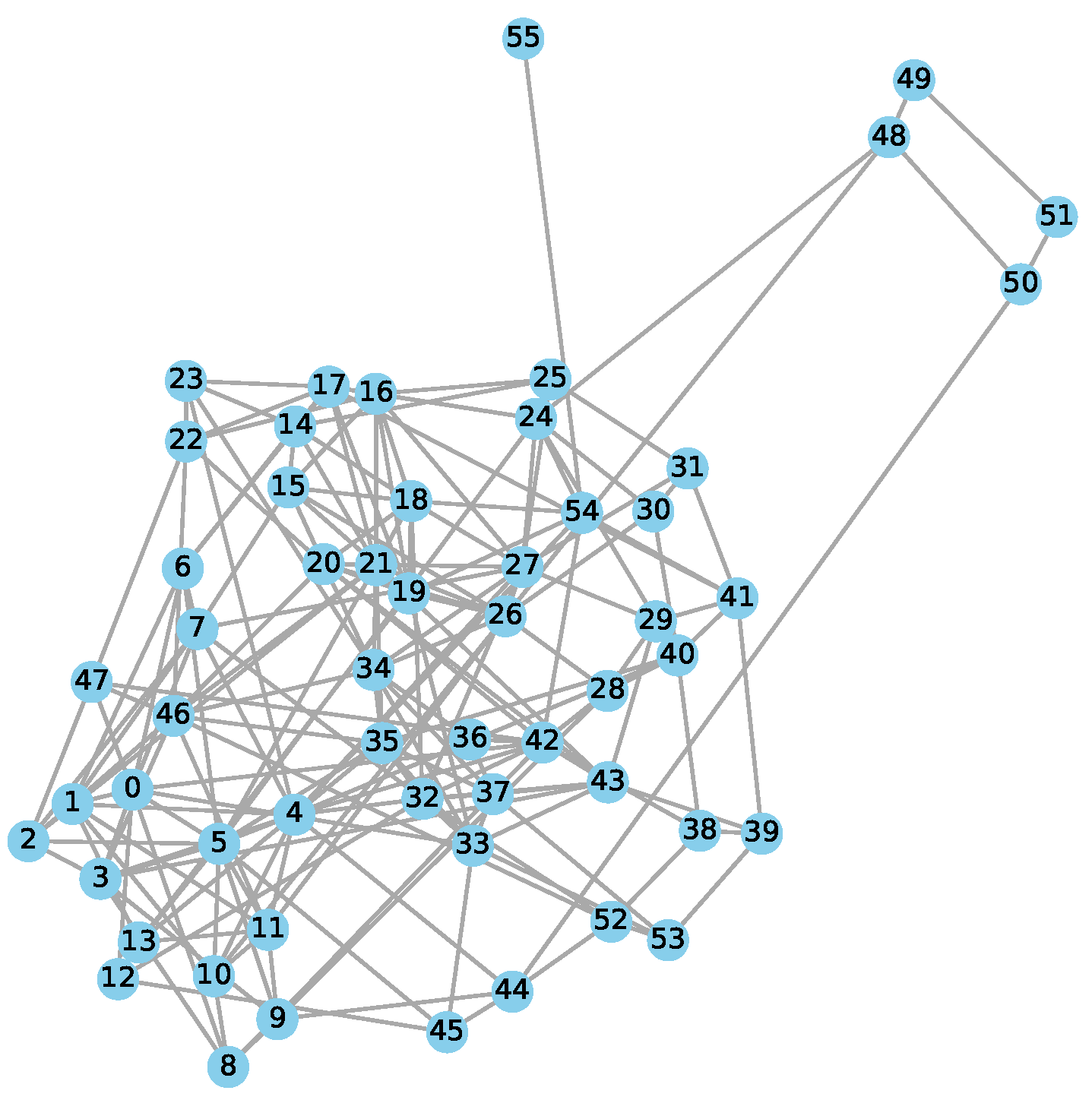
2.3. Construction of Anatomical Network
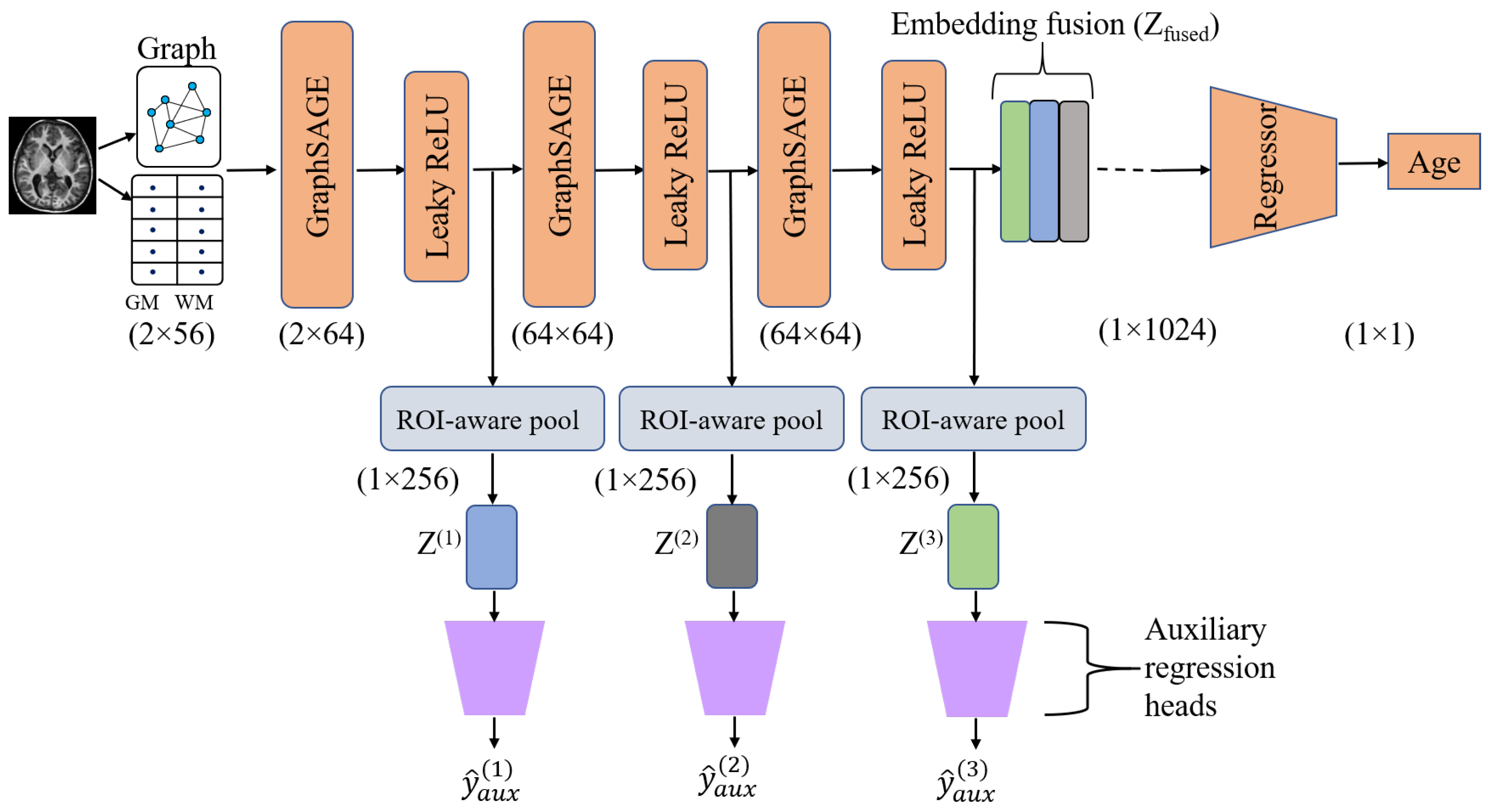
2.4. Model Description
ROI-Aware Pooling
| Algorithm 1 SAGEFusionNet model algorithm |
|
2.5. Training and Testing
- Loss Function
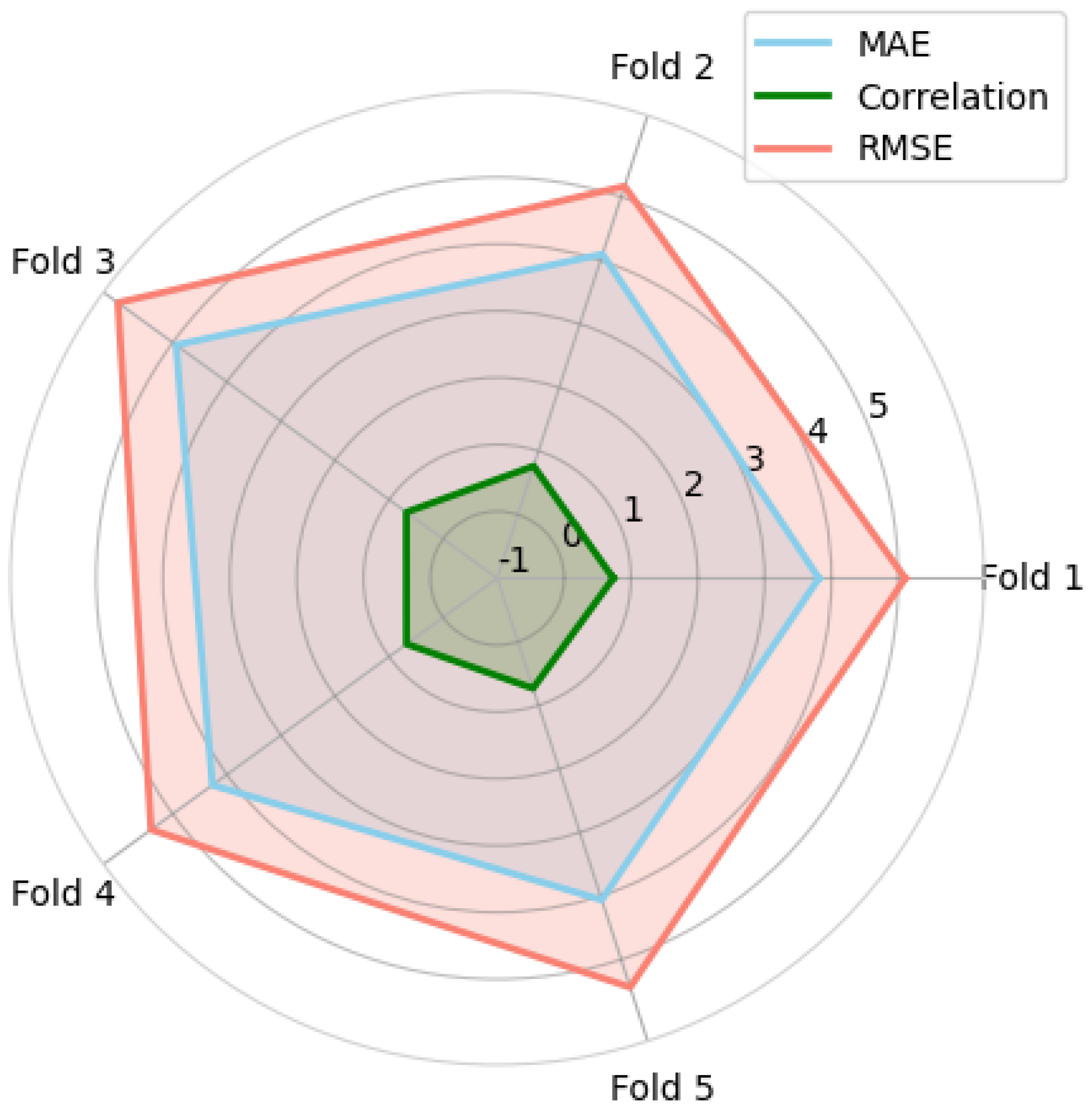
Performance Metrics
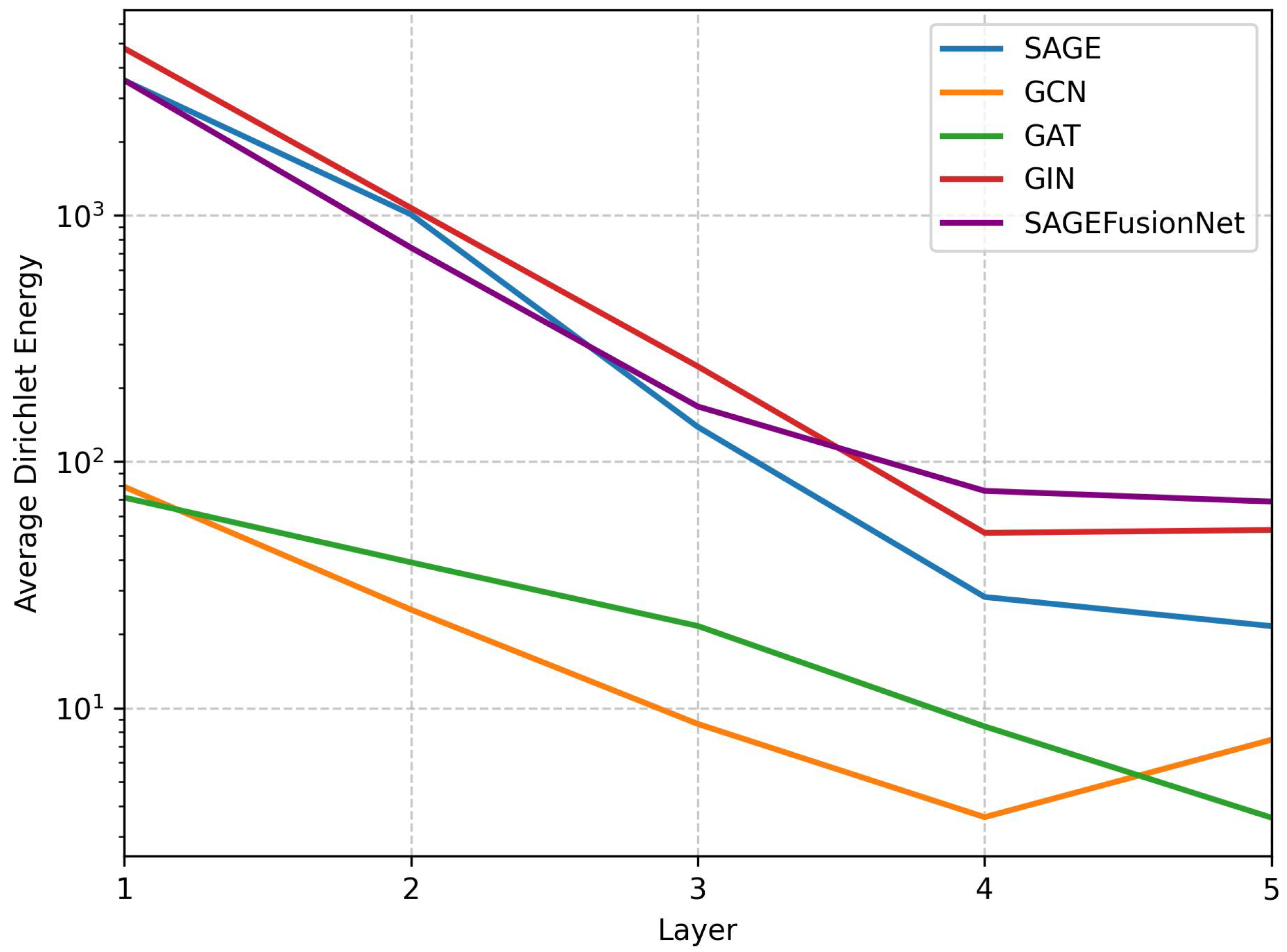
- Dirichlet energy:It is one of the metrics to measure the oversmoothing in deep GNN on graph-structured data [36,53]. The normalised version of the Dirichlet energy at the GNN layer is given in the following Equation (11):where is the set of all nodes and is the set of neighbours of node i. The terms and represent the features of nodes i and j at the layer, respectively. The terms and denote the degrees of nodes i and j, respectively. Finally, denotes the squared -norm.
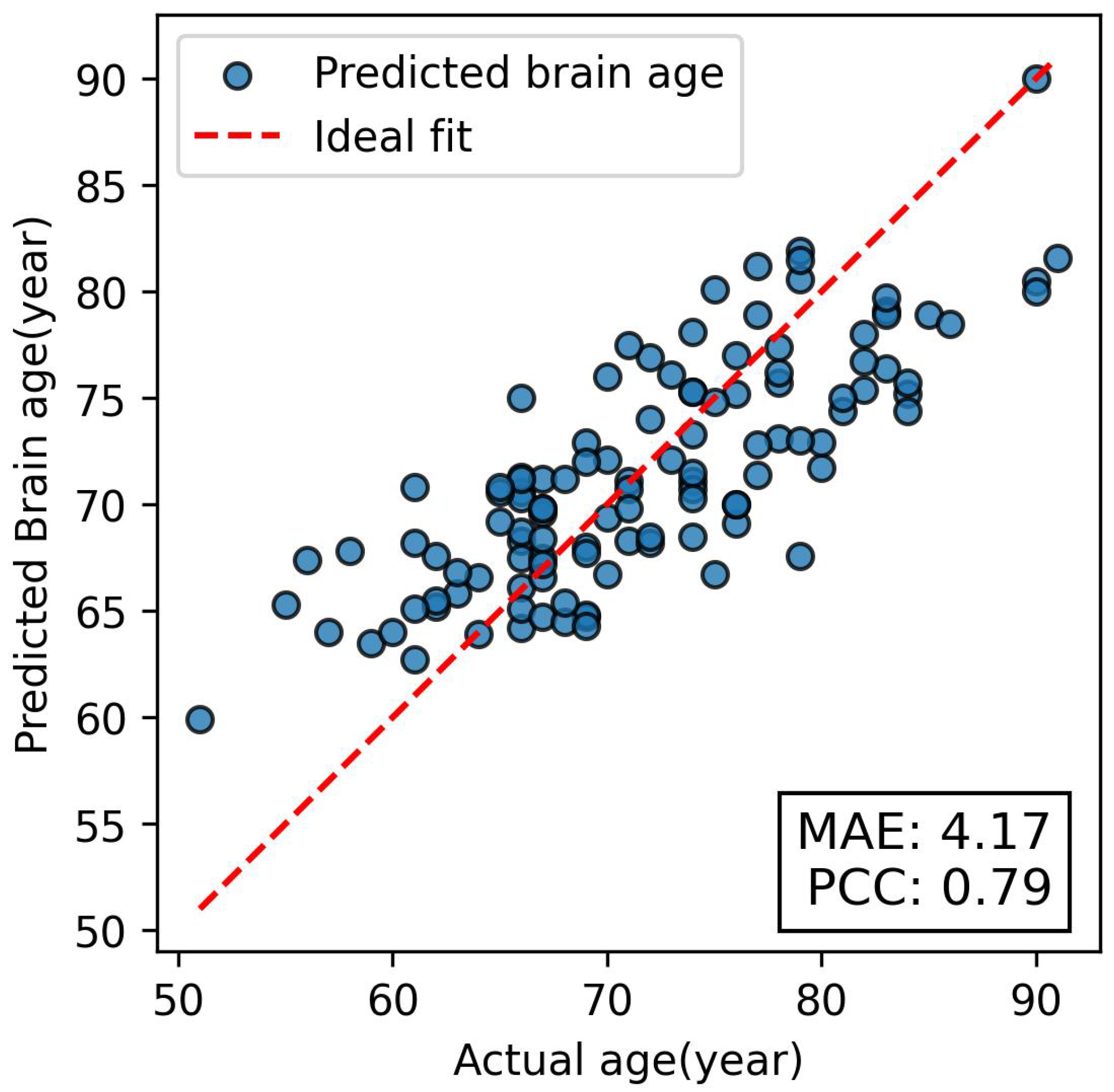
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fjell, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B. Structural brain changes in aging: Courses, causes and cognitive consequences. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 21, 187–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.J. Normal aging induces changes in the brain and neurodegeneration progress: Review of the structural, biochemical, metabolic, cellular, and molecular changes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 931536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A. Dementia: A problem for our age. Nature 2011, 475, S2–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaser, C.; Franke, K.; Klöppel, S.; Koutsouleris, N.; Sauer, H.; Initiative, A.D.N. BrainAGE in mild cognitive impaired patients: Predicting the conversion to Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lu, C.H.; Wang, Y.W.; Chou, K.H.; Lin, W.C. Multiscale brain age prediction reveals region-specific accelerated brain aging in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2024, 140, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.D.; Wu, Y.F.; Tsai, S.J.; Lin, C.P.; Yang, A.C. Investigating brain aging trajectory deviations in different brain regions of individuals with schizophrenia using multimodal magnetic resonance imaging and brain-age prediction: A multicenter study. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.H.; Poudel, R.P.; Tsagkrasoulis, D.; Caan, M.W.; Steves, C.; Spector, T.D.; Montana, G. Predicting brain age with deep learning from raw imaging data results in a reliable and heritable biomarker. NeuroImage 2017, 163, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Gaser, C. Ten years of BrainAGE as a neuroimaging biomarker of brain aging: What insights have we gained? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, K.; Gaser, C. Longitudinal changes in individual BrainAGE in healthy aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. GeroPsych 2012, 25, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, K.; Ziegler, G.; Klöppel, S.; Gaser, C.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Estimating the age of healthy subjects from T1-weighted MRI scans using kernel methods: Exploring the influence of various parameters. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeighami, Y.; Fereshtehnejad, S.M.; Dadar, M.; Collins, D.L.; Postuma, R.B.; Mišić, B.; Dagher, A. A clinical-anatomical signature of Parkinson’s disease identified with partial least squares and magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2019, 190, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beheshti, I.; Mishra, S.; Sone, D.; Khanna, P.; Matsuda, H. T1-weighted MRI-driven brain age estimation in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Aging Dis. 2019, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, C.R.; Hoffstaedter, F.; Caspers, J.; Reetz, K.; Mathys, C.; Dogan, I.; Amunts, K.; Schnitzler, A.; Eickhoff, S.B. Advanced brain ageing in Parkinson’s disease is related to disease duration and individual impairment. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Voxel-based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage 2000, 11, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Qin, R.; Ye, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Biomarkers of Punding in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafflon, J.; Pinaya, W.H.; Turkheimer, F.; Cole, J.H.; Leech, R.; Harris, M.A.; Cox, S.R.; Whalley, H.C.; McIntosh, A.M.; Hellyer, P.J. An automated machine learning approach to predict brain age from cortical anatomical measures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 3555–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xia, Z.; Gao, X. Predicting brain age using Tri-UNet and various MRI scale features. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, S.; Antonopoulos, G.; Hoffstaedter, F.; Caspers, J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Patil, K.R.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Brain-age prediction: A systematic comparison of machine learning workflows. NeuroImage 2023, 270, 119947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, M.M.; Bruna, J.; Cohen, T.; Veličković, P. Geometric deep learning: Grids, groups, graphs, geodesics, and gauges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, P.; Parrish, T.; Katsaggelos, A.K.; Bandt, S.K. Geometric deep learning on brain shape predicts sex and age. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 91, 101939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, C.N. Multi-Volumetric Feature-Based Brain Age Prediction Using sMRI and Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Kuching, Malaysia, 6–10 October 2024; pp. 3300–3304. [Google Scholar]
- Parisot, S.; Ktena, S.I.; Ferrante, E.; Lee, M.; Moreno, R.G.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Spectral graph convolutions for population-based disease prediction. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Proceedings, Part III 20. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, O.; Cumplido-Mayoral, I.; Cacciaglia, R.; González-de Echávarri, J.M.; Gispert, J.D.; Vilaplana, V. Structural networks for brain age prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning. PMLR, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 944–960. [Google Scholar]
- Gama, F.; Isufi, E.; Leus, G.; Ribeiro, A. Graphs, convolutions, and neural networks: From graph filters to graph neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.; Ying, Z.; Leskovec, J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Hu, W.; Leskovec, J.; Jegelka, S. How powerful are graph neural networks? arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.00826. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Graphsmote: Imbalanced node classification on graphs with graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Jerusalem, Israel, 8–12 March 2021; pp. 833–841. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, H.; Fujii, M.; Sakaji, H.; Masuyama, S. Enhancing risk analysis with GNN: Edge classification in risk causality from securities reports. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2024, 4, 100217. [Google Scholar]
- Errica, F.; Podda, M.; Bacciu, D.; Micheli, A. A fair comparison of graph neural networks for graph classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.09893. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y. Link prediction based on graph neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 5165–5175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, L.; Ling, M.; Peng, Y. A survey of graph neural network based recommendation in social networks. Neurocomputing 2023, 549, 126441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, T.K.; Bronstein, M.M.; Mishra, S. A survey on oversmoothing in graph neural networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Wu, X.M. Deeper insights into graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Keriven, N. Not too little, not too much: A theoretical analysis of graph (over) smoothing. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 2268–2281. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Rong, Y.; Xu, T.; Sun, F.; Huang, J. Tackling over-smoothing for general graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.09864. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wei, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ding, B.; Li, Y. Simple and deep graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1725–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Measuring and relieving the over-smoothing problem for graph neural networks from the topological view. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 3438–3445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Akoglu, L. Pairnorm: Tackling oversmoothing in gnns. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.12223. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Villar, S.; Priebe, C.E.; Zheng, D.; Huang, C.; Yang, L.; Braverman, V. From local to global: Spectral-inspired graph neural networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; You, J.; Morris, C.; Ren, X.; Hamilton, W.; Leskovec, J. Hierarchical graph representation learning with differentiable pooling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 4800–4810. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Muller, M.; Thabet, A.; Ghanem, B. DeepGCNs: Can GCNs go as deep as CNNs? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9267–9276. [Google Scholar]
- Rorden, C. From MRIcro to MRIcron: The Evolution of Neuroimaging Visualization Tools. Neuropsychologia 2025, 207, 109067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaser, C.; Dahnke, R.; Thompson, P.M.; Kurth, F.; Luders, E.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. CAT: A computational anatomy toolbox for the analysis of structural MRI data. Gigascience 2024, 13, giae049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The MathWorks, Inc. MATLAB2022a, Version 9.12; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022.
- Shattuck, D.W.; Mirza, M.; Adisetiyo, V.; Hojatkashani, C.; Salamon, G.; Narr, K.L.; Poldrack, R.A.; Bilder, R.M.; Toga, A.W. Construction of a 3D probabilistic atlas of human cortical structures. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, L.; Sejdić, E. Vertex-Frequency Analysis of Graph Signals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Dai, W.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, X.; Gu, A.A.C.; Lukemire, J.; Zhan, L.; He, L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, C. Braingb: A benchmark for brain network analysis with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Y. A note on over-smoothing for graph neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bu, J.; Ester, M.; Zhang, J.; Yao, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C. Hierarchical graph pooling with structure learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.05954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Sonobe, T.; Kawarabayashi, K.i.; Jegelka, S. Representation learning on graphs with jumping knowledge networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 5453–5462. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, H.; Karwowski, W. Graph Neural Networks in Brain Connectivity Studies: Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions. Brain Sci. 2024, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, S.; Malloni, W.M.; Tomé, A.M.; Frank, S.M.; Henze, G.I.; Wüst, S.; Greenlee, M.W.; Lang, E.W. A graph neural network framework for causal inference in brain networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, X.; Yang, C. Comprehensive review of Transformer-based models in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry. Brain-X 2024, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levakov, G.; Rosenthal, G.; Shelef, I.; Raviv, T.R.; Avidan, G. From a deep learning model back to the brain—Identifying regional predictors and their relation to aging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 3235–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Abdelmegeed, M.; Modl, J.; Kim, M. Edge-boosted graph learning for functional brain connectivity analysis. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, M.; Rieck, J.R.; Golafshan, S.; Grady, C.L.; Misic, B.; Dunkley, B.T.; Khatibi, A. The brain selectively allocates energy to functional brain networks under cognitive control. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Guo, Z.; Long, Z. Energy landscape analysis of brain network dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1375091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardella, G.; Franchini, S.; Pan, L.; Balzan, R.; Ramawat, S.; Brunamonti, E.; Pani, P.; Ferraina, S. Neural activity in quarks language: Lattice Field Theory for a network of real neurons. Entropy 2024, 26, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, M.J.; Brubaker, J.K.; Katzgraber, H.G. Combinatorial optimization with physics-inspired graph neural networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabian, M.; Babaee, H.; Laksari, K. Physics-informed neural networks for brain hemodynamic predictions using medical imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 2285–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, T.; Palmarini, N.; Corner, L.; Barzilai, N.; Maier, A.B.; Sagner, M.; Bensz, J.; Strygin, A.; Yadala, N.; Kern, C.; et al. Cities, communities and clinics can be testbeds for human exposome and aging research. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1066–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Model | Sparsity Parameter | MAE | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAGEFusionNet | 0.02 | ||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.04 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.07 | |||
| 0.08 |
| Model | MAE | PCC |
|---|---|---|
| FCNN | ||
| GCN | ||
| GraphSAGE | ||
| GAT | ||
| GIN | ||
| SAGEFusionNet |
| Model | Fusion Method | Mean | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAGEFusionNet | Mean | ||
| Max | |||
| Sum | |||
| Weighted Sum | |||
| Attention | |||
| Concatenation |
| Model | Layers | MAE | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAGEFusionNet | 2 | ||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Hazarika, S.; Gupta, C.N. SAGEFusionNet: An Auxiliary Supervised Graph Neural Network for Brain Age Prediction as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070752
Kumar S, Hazarika S, Gupta CN. SAGEFusionNet: An Auxiliary Supervised Graph Neural Network for Brain Age Prediction as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(7):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070752
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Suraj, Suman Hazarika, and Cota Navin Gupta. 2025. "SAGEFusionNet: An Auxiliary Supervised Graph Neural Network for Brain Age Prediction as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker" Brain Sciences 15, no. 7: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070752
APA StyleKumar, S., Hazarika, S., & Gupta, C. N. (2025). SAGEFusionNet: An Auxiliary Supervised Graph Neural Network for Brain Age Prediction as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker. Brain Sciences, 15(7), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070752







