Factors Influencing Virtual Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Sample
2.2. Assessment and Therapy
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRPS | Pittsburgh Rehabilitation Participation Scale |
| BI | Barthel Index |
| MMT | Manual Muscle Test |
| AS | Ashworth Scale |
| VR | Virtual reality |
| VAT | Virtual art therapy |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
References
- Fancourt, D.; Finn, S. What Is the Evidence on the Role of the Arts in Improving Health and Well-Being? A Scoping Review; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, J.H.; Kelly, C.; Joice, S.; Kroll, T.; Mead, G.; Donnan, P.; Toma, M.; Williams, B. Art participation for psychosocial wellbeing during stroke rehabilitation: A feasibility randomised controlled trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkasuwan, R.; Voraakhom, K.; Pisolayabutra, P.; Maneechai, P.; Boonin, J.; Kuptniratsaikul, V. Creative art therapy to enhance rehabilitation for stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salera, C.; Capua, C.; De Angelis, D.; Coiro, P.; Venturiero, V.; Savo, A.; Marinozzi, F.; Bini, F.; Paolucci, S.; Antonucci, G.; et al. Michelangelo Effect in Cognitive Rehabilitation: Using Art in a Digital Visuospatial Memory Task. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosa, M.; Aydin, M.; Candelise, C.; Coda, N.; Morone, G.; Antonucci, G.; Marinozzi, F.; Bini, F.; Paolucci, S.; Tieri, G. The Michelangelo Effect: Art Improves the Performance in a Virtual Reality Task Developed for Upper Limb Neurorehabilitation. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 611956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giorgi, R.; Fortini, A.; Aghilarre, F.; Gentili, F.; Morone, G.; Antonucci, G.; Vetrano, M.; Tieri, G.; Iosa, M. Virtual Art Therapy: Application of Michelangelo Effect to Neurorehabilitation of Patients with Stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieri, G.; Iosa, M.; Fortini, A.; Aghilarre, F.; Gentili, F.; Rubeca, C.; Mastropietro, T.; Antonucci, G.; De Giorgi, R. Efficacy of a Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Protocol Based on Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.L.; Monin, J.; Ovchinnikova, P.; Levi, A.; McCall, T. Psychedelic Art and Implications for Mental Health: Randomized Pilot Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2024, 8, e66430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yin, H.; Hua, X.; Bi, S.; Zhou, D. Effects of artificial intelligence and virtual reality interventions in art therapy among older people with mild cognitive impairment. Australas. J. Ageing 2025, 44, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, C.; Roche, D.; Hegarty, F.; McCann, S. “Open Window”: A randomized trial of the effect of new media art using a virtual window on quality of life in patients’ experiencing stem cell transplantation. Psychooncology 2013, 22, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitere, Ē.; Duhovska, J.; Karkou, V.; Mārtinsone, K. Telehealth in arts therapies for neurodevelopmental and neurological disorders: A scoping review. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1484726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Iosa, M.; Antonucci, G.; De Bartolo, D. Are neuroaesthetic principles applied in art therapy protocols for neurorehabilitation? A systematic mini-review. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1158304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, D.T.; Hewer, R.L.; Wood, V.A. Stroke: Influence of patient’s sex and side of weakness on outcome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1984, 65, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Vanclay, F.; Cooper, B. Predicting discharge status at commencement of stroke rehabilitation. Stroke 1989, 20, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, S.; Antonucci, G.; Grasso, M.G.; Bragoni, M.; Coiro, P.; De Angelis, D.; Fusco, F.R.; Morelli, D.; Venturiero, V.; Troisi, E.; et al. Functional outcome of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke patients after inpatient rehabilitation: A matched comparison. Stroke 2003, 34, 2861–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S.; Antonucci, G.; Troisi, E.; Bragoni, M.; Coiro, P.; De Angelis, D.; Pratesi, L.; Venturiero, V.; Grasso, M.G. Aging and stroke rehabilitation. a case-comparison study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 15, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S.; Antonucci, G.; Grasso, M.G.; Morelli, D.; Troisi, E.; Coiro, P.; Bragoni, M. Early versus delayed inpatient stroke rehabilitation: A matched comparison conducted in Italy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S.; Antonucci, G.; Pratesi, L.; Traballesi, M.; Lubich, S.; Grasso, M.G. Functional outcome in stroke inpatient rehabilitation: Predicting no, low and high response patients. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1998, 8, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosa, M.; Morone, G.; Antonucci, G.; Paolucci, S. Prognostic Factors in Neurorehabilitation of Stroke: A Comparison among Regression, Neural Network, and Cluster Analyses. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenze, E.J.; Munin, M.C.; Quear, T.; Dew, M.A.; Rogers, J.C.; Begley, A.E.; Reynolds, C.F. 3rd The Pittsburgh Rehabilitation Participation Scale: Reliability and validity of a clinician-rated measure of participation in acute rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosa, M.; Galeoto, G.; De Bartolo, D.; Russo, V.; Ruotolo, I.; Spitoni, G.F.; Ciancarelli, I.; Tramontano, M.; Antonucci, G.; Paolucci, S.; et al. Italian Version of the Pittsburgh Rehabilitation Participation Scale: Psychometric Analysis of Validity and Reliability. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojić, T.; Spang, R.; Vergari, M.; Meier, L.; Möller, S.; Voigt-Antons, J.N. Effects of user factors on user experience in virtual reality: Age, gender, and VR experience as influencing factors for VR exergames. Qual. User Exp. 2023, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, S.E. Effects of age on the subjective presence experience in virtual reality. In Challenging Presence, Proceedings of the International Society for Presence Research 15th International Conference on Presence, Wien, Austria, 1 March 2014; Felnhofer, A., Kothgassner, O.D., Eds.; facultas.wuv Universitaets: Wien, Austria, 2014; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, G.E.; Wissel, J.; Platz, T.; Li, S. Clinical Pathways in Stroke Rehabilitation: Evidence-based Clinical Practice Recommendations. In Post-Stroke Spasticity; Platz, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 149–173. [Google Scholar]
- Iosa, M.; Bini, F.; Marinozzi, F.; Antonucci, G.; Pascucci, S.; Baghini, G.; Guarino, V.; Paolucci, S.; Morone, G.; Tieri, G. Inside the Michelangelo effect: The role of art and aesthetic attractiveness on perceived fatigue and hand kinematics in virtual painting. PsyCh J. 2022, 11, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhimani, R.; Chappuis, D.; Mathiason, M.A.; Anderson, L.C. Spasticity, Pain, and Fatigue: Are They Associated With Functional Outcomes in People With Stroke? Rehabil. Nurs. Off. J. Assoc. Rehabil. Nurses 2022, 47, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrichsen, K.M.; Alnaes, D.; Kolskår, K.K.; Richard, G.; Sanders, A.M.; Dørum, E.S.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Pedersen, M.L.; Tornås, S.; Nordvik, J.E.; et al. Dissecting the cognitive phenotype of post-stroke fatigue using computerized assessment and computational modeling of sustained attention. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 3828–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudarham, J.; Roche, N.; Teixeira, M.; Hameau, S.; Robertson, J.; Bensmail, D.; Zory, R. Relationship between neuromuscular fatigue and spasticity in chronic stroke patients: A pilot study. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Electrophysiol. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedberg, D.; Gallese, V. Motion, emotion and empathy in esthetic experience. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2007, 11, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dio, C.; Ardizzi, M.; Massaro, D.; Di Cesare, G.; Gilli, G.; Marchetti, A.; Gallese, V. Human, Nature, Dynamism: The Effects of Content and Movement Perception on Brain Activations during the Aesthetic Judgment of Representational Paintings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblich, G.; Seigerschmidt, E.; Flach, R.; Prinz, W. Authorship effects in the prediction of handwriting strokes: Evidence for action simulation during action perception. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2022, 55, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishkhani, M.K.; Dalvandi, A.; Ebadi, A.; Hosseini, M.A. Adherence to a Rehabilitation Regimen in Stroke Patients: A Concept Analysis. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery Res. 2020, 25, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, E.; Smits, A.; Terént, A.; Borg, J. Time-course and determinants of spasticity during the first six months following first-ever stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 42, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, M.J.; Alarcón, R.; Arnau, J.; Bono, R.; Bendayan, R. Non-normal data: Is ANOVA still a valid option? Psicothema 2017, 29, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umilta’, M.A.; Berchio, C.; Sestito, M.; Freedberg, D.; Gallese, V. Abstract art and cortical motor activation: An EEG study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chung, Y.J. A single case study of digital art therapy for a child with ADHD using the metaverse platform. Arts Psychother. 2024, 89, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.J. The potential of rehabilitative computer art therapy for the quadriplegic, cerebral vascular accident and brain trauma patient. Art Ther. 1985, 3, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, N.W. Application of virtual reality technology and its impact on digital health in healthcare industry. J. Commer. Biotechnol. 2023, 27, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubala, A.; Kennell, N.; Hackett, S. Art therapy in the digital world: An integrative review of current practice and future directions. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 595536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleba, B. The Integration of Computerized Art-Making as a Medium in Art Therapy Theory and Practice. Master’s Thesis, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, May 2008. [Google Scholar]
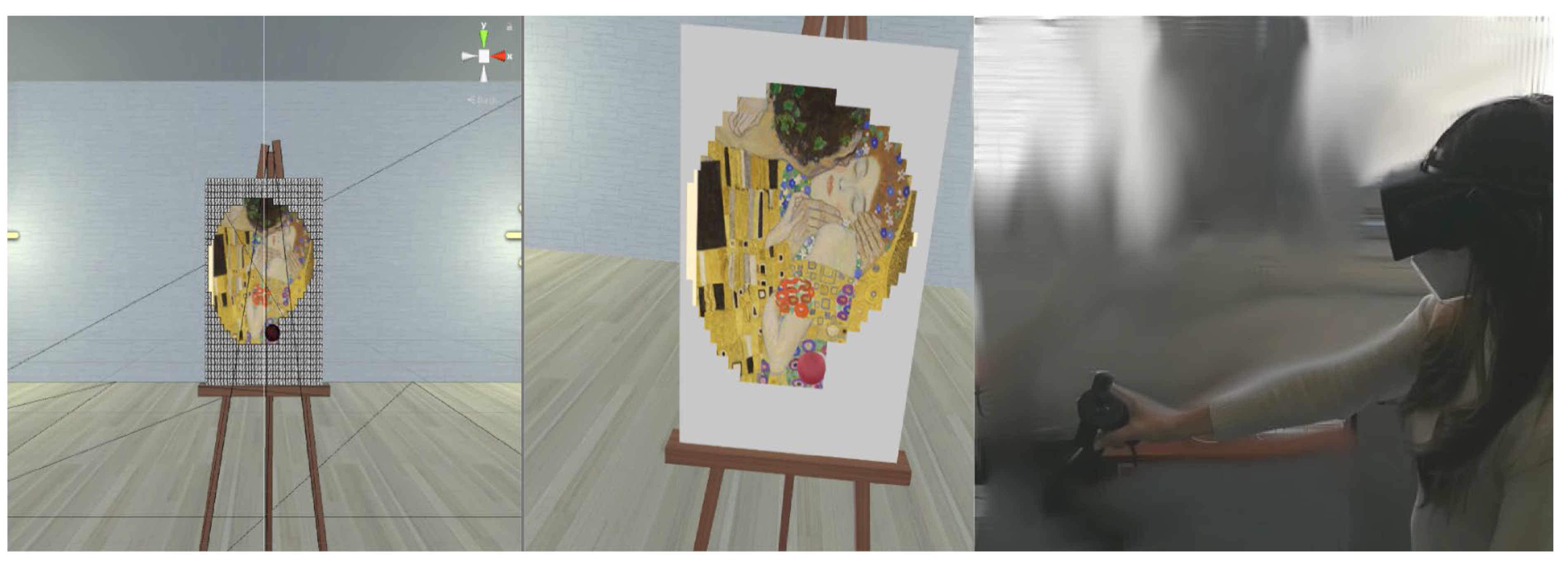

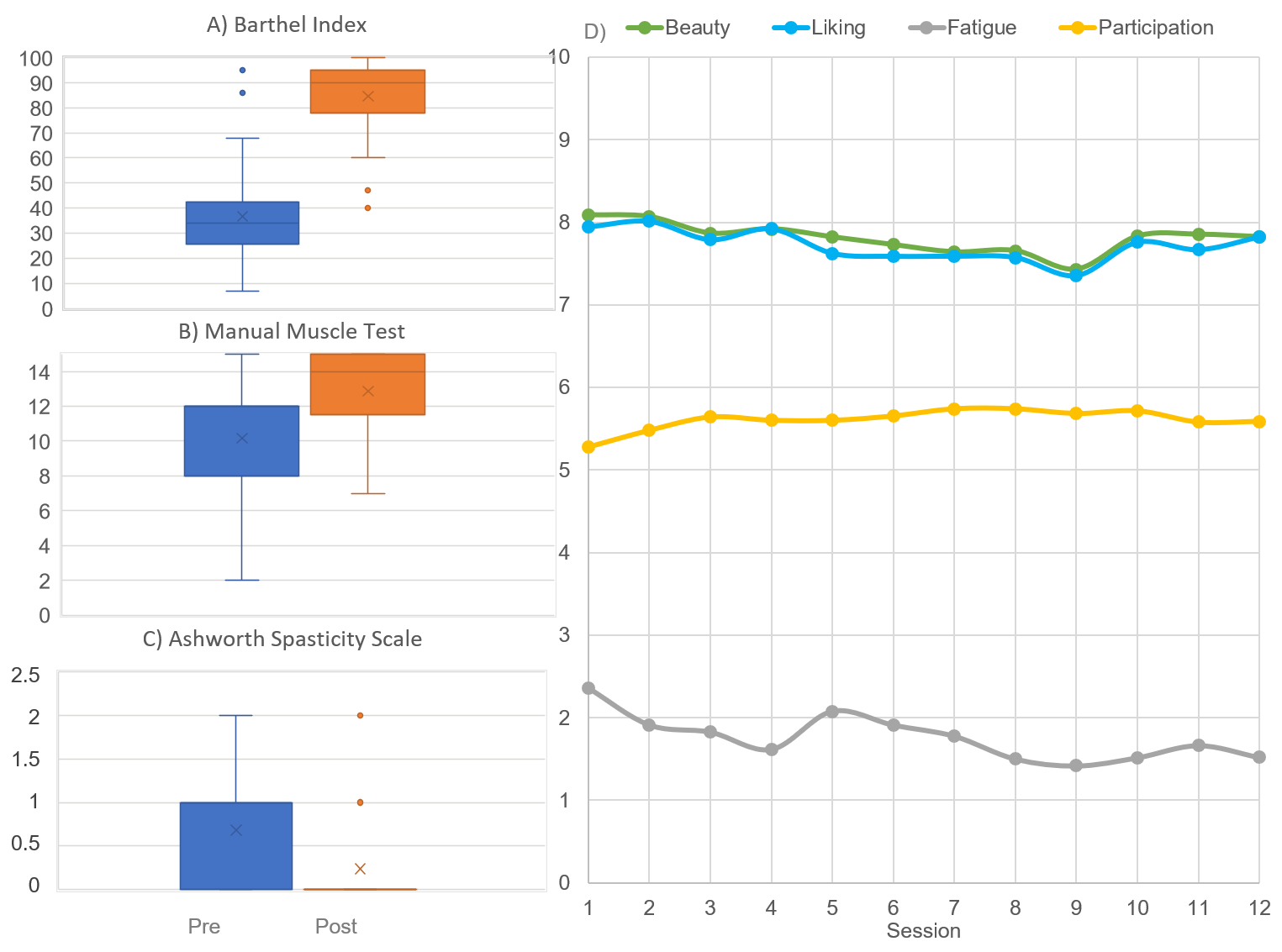
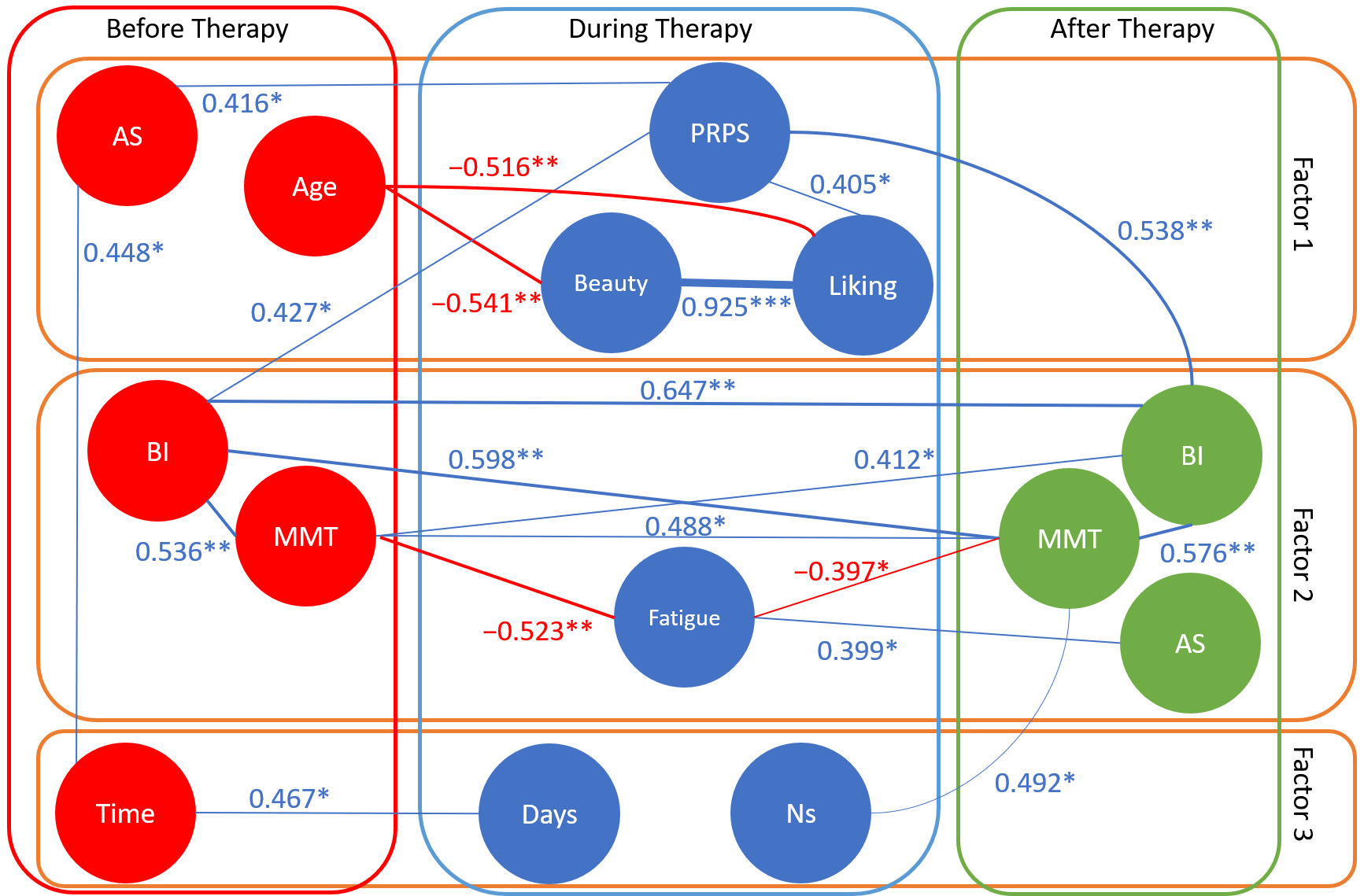
| Timing | Variables | Mean ± SD or Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Before Therapy | Age (years) | 68.1 ± 9.6 |
| Time from stroke (days) | 19.2 ± 8.9 | |
| Gender (F: female; M: male) | F: 40% M: 60% | |
| Type of Stroke (I: ischemic; H: hemorrhagic) | I: 76% H: 24% | |
| Affected body side (L: left; R: right) | L: 48% R: 52% | |
| Barthel Index (BI) | 36.7 ± 20.3 | |
| Manual Muscle Test (MMT) | 10.2 ± 3.1 | |
| Ashworth Scale (AS) | 0.68 ± 0.69 | |
| During Therapy | Number of sessions | 11.0 ± 2.1 |
| Length of therapy (days) | 25.9 ± 6.5 | |
| PRPS (mean) | 5.6 ± 0.4 | |
| VAS perceived fatigue | 2.1 ± 1.8 | |
| VAS beauty | 7.7 ± 0.8 | |
| VAS liking | 7.7 ± 0.8 | |
| After Therapy | Barthel Index | 84.6 ± 15.9 |
| MMT | 12.9 ± 2.4 | |
| Ashworth Scale | 0.2 ± 0.5 |
| Timing | Variable | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Therapy | Age | −0.774 | −0.053 | −0.188 |
| Time | 0.220 | 0.127 | 0.715 | |
| BI | 0.316 | 0.494 | 0.020 | |
| MMT | 0.156 | 0.808 | −0.180 | |
| AS | 0.487 | −0.071 | 0.474 | |
| During Therapy | N° sessions | −0.161 | 0.125 | 0.752 |
| N° days | −0.107 | −0.089 | 0.890 | |
| PPRS | 0.699 | 0.082 | 0.105 | |
| Beauty | 0.857 | −0.052 | −0.173 | |
| Liking | 0.848 | 0.052 | −0.163 | |
| Fatigue | −0.099 | −0.483 | 0.302 | |
| After Therapy | BI | 0.068 | 0.866 | 0.082 |
| MMT | −0.090 | 0.889 | 0.129 | |
| AS | 0.417 | −0.628 | 0.034 |
| Assessment Timing | Variable | High Participation PRPS > 5.75 (N = 13) | Medium Participation PRPS ≤ 5.75 (N = 12) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Therapy | Age (years) | 66.1 ± 10.3 | 70.3 ± 8.8 | 0.288 |
| Days from stroke | 19.3 ± 10.8 | 19.0 ± 6.1 | 0.937 | |
| Ashworth score | 0.9 ± 0.8 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.066 | |
| MMT score | 11.2 ± 2.1 | 9.1 ± 3.8 | 0.099 | |
| BI score | 44.3 ± 25.2 | 28.4 ± 8.1 | 0.048 | |
| During Therapy | Participation PRPS | 5.9 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| N° sessions | 11.1 ± 2.0 | 10.9 ± 2.2 | 0.851 | |
| N° days | 25.3 ± 5.6 | 26.6 ± 7.5 | 0.634 | |
| Fatigue | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 2.6 ± 2.2 | 0.182 | |
| Beauty | 8.0 ± 0.8 | 7.4 ± 0.7 | 0.070 | |
| Liking | 8.0 ± 0.7 | 7.3 ± 0.6 | 0.011 | |
| After Therapy | Ashworth score | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.6 | 0.929 |
| MMT score | 13.5 ± 2.0 | 12.2 ± 2.7 | 0.161 | |
| BI score | 93.1 ± 7.0 | 75.3 ± 17.9 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iosa, M.; De Giorgi, R.; Gentili, F.; Ciotti, A.; Rubeca, C.; Casolani, S.; Salera, C.; Tieri, G. Factors Influencing Virtual Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070736
Iosa M, De Giorgi R, Gentili F, Ciotti A, Rubeca C, Casolani S, Salera C, Tieri G. Factors Influencing Virtual Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(7):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070736
Chicago/Turabian StyleIosa, Marco, Roberto De Giorgi, Federico Gentili, Alberto Ciotti, Cristiano Rubeca, Silvia Casolani, Claudia Salera, and Gaetano Tieri. 2025. "Factors Influencing Virtual Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke" Brain Sciences 15, no. 7: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070736
APA StyleIosa, M., De Giorgi, R., Gentili, F., Ciotti, A., Rubeca, C., Casolani, S., Salera, C., & Tieri, G. (2025). Factors Influencing Virtual Art Therapy in Patients with Stroke. Brain Sciences, 15(7), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070736








