Prognostic Value of the Goutallier Scale for Paravertebral Muscle Atrophy in Predicting Disability and Pain Outcomes in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 100 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria
2.2. Clinical Parameters
2.3. Radiological Parameters
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Preoperative Muscle Assessment as a Tool for Risk Stratification
4.2. Impact of Paraspinal Degeneration on Disability and Pain Outcomes
4.3. Comparison with Existing Literature and Pathophysiological Considerations
4.4. Advantages and Limits of a Semiquantitative MRI-Based Approach
4.5. Study Limitations and Interpretative Boundaries
4.6. Future Perspectives and Clinical Integration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSS | Lumbar Spinal Stenosis |
| GS | Goutallier Classification System |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CSA | Cross-Sectional Area |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| CD | Clavien-Dindo Classification |
| ΔODI | Change in Oswestry Disability Index |
| ΔVAS | Change in Visual Analog Scale |
References
- Steurer, J.; Nydegger, A.; Held, U.; Brunner, F.; Hodler, J.; Porchet, F.; Min, K.; Mannion, A.F.; Michel, B. LumbSten: The lumbar spinal stenosis outcome study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelli, F.; Nüesch, C.; Zhang, Y.; Halbeisen, F.; Schären, S.; Mündermann, A.; Netzer, C. Assessing fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscles in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: Goutallier classification and quantitative MRI measurements. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 656487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schizas, C.; Theumann, N.; Burn, A.; Tansey, R.; Wardlaw, D.; Smith, F.W.; Kulik, G. Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine 2010, 35, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slabaugh, M.A.; Friel, N.A.; Karas, V.; Romeo, A.A.; Verma, N.N.; Cole, B.J. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the Goutallier classification using magnetic resonance imaging: Proposal of a simplified classification system to increase reliability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, L.B.; Teefey, S.A.; Middleton, W.D.; Dahiya, N.; Steger-May, K.; Kim, H.M.; Wessell, D.; Yamaguchi, K. Diagnostic performance and reliability of ultrasonography for fatty degeneration of the rotator cuff muscles. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2012, 94, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazzelli, G.; Meglio, V.; Corvino, S.; Leonetti, S.; Ricciardi, F.; D’Elia, A.; Pizzuti, V.; Santilli, M.; Innocenzi, G. The Goutallier Classification System: How does Paravertebral Adipose Degeneration Change in Patients with Symptomatic Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? Spine 2024, 49, E174–E182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, K.; Chen, J.; Stone, M.; Arakelyan, A.; Paholpak, P.; Nakamura, H.; Buser, Z.; Wang, J.C. The evaluation of lumbar paraspinal muscle quantity and quality using the Goutallier classification and lumbar indentation value. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banitalebi, H.; Aaen, J.; Storheim, K.; Negård, A.; Myklebust, T.Å.; Grotle, M.; Hellum, C.; Espeland, A.; Anvar, M.; Indrekvam, K. A novel MRI index for paraspinal muscle fatty infiltration: Reliability and relation to pain and disability in lumbar spinal stenosis: Results from a multicentre study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.J.; Maeda, Y.; Welk, A.; Hough, B.; Kettner, N. Reliability of the Goutallier classification in quantifying muscle fatty degeneration in the lumbar multifidus using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2014, 37, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazzelli, G.; Capece, M.; Meglio, V.; Leonetti, S.; Pizzuti, V.; Ricciardi, F.; D’Elia, A.; Santilli, M.; Innocenzi, G. Multiple univariate analysis of radiologic and clinical features on 168 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: What is the role of the erector spinae in the development of a patient’s disability? Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 3947–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Baker, D.; Disney, S.; Pynsent, P. Oswestry Disability Index scoring made easy. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2008, 90, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.-Z.; Kong, C.; Li, X.-Y.; Sun, X.-Y.; Lu, S.-B.; Zhao, G.-G. Different degeneration patterns of paraspinal muscles in degenerative lumbar diseases: A MRI analysis of 154 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzelli, G.; Corvino, S.; Ricciardi, F.; Pizzuti, V.; Leonetti, S.; D’Elia, A.; Santilli, M.; Aloj, F.; Innocenzi, G. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy in elderly patients undergoing lumbar discectomy: A retrospective study on 163 patients. Neurosurg. Rev. 2024, 47, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korovessis, P.G.; Stamatakis, M.V. Prediction of scoliotic Cobb angle with the use of the scoliometer. Spine 1996, 21, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumann, H.; Nüesch, C.; Loske, S.; Byrnes, S.K.; Kovacs, B.; Janssen, R.; Schären, S.; Mündermann, A.; Netzer, C. Severity of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis affects pelvic rigidity during walking. Spine J. 2020, 20, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, K.; Widbom-Kolhanen, S.; Pernaa, K.; Arokoski, J.; Saltychev, M. Reliability and validity of Oswestry Disability Index among patients undergoing lumbar spinal surgery. BMC Surg. 2024, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.; Keating, J.L. A comparison of five low back disability questionnaires: Reliability and responsiveness. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, P.; Bendix, T.; Sorensen, J.S.; Korsholm, L.; Leboeuf-Yde, C. Are MRI-defined fat infiltrations in the multifidus muscles associated with low back pain? BMC Med. 2007, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, K.C.; O’Brien, L.C.; Gorgey, A.S. Quantification of trunk and android lean mass using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry compared to magnetic resonance imaging after spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2019, 42, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abilmona, S.M.; Gorgey, A.S. Associations of the trunk skeletal musculature and dietary intake to biomarkers of cardiometabolic health after spinal cord injury. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mandelli, F.; Mündermann, A.; Nüesch, C.; Kovacs, B.; Schären, S.; Netzer, C. Association between fatty infiltration of paraspinal muscle, sagittal spinopelvic alignment and stenosis grade in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2021, 5, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzelli, G.; Capece, M.; Pizzuti, V.; Leonetti, S.; D’Elia, A.; Santilli, M.; Aloj, F.; Innocenzi, G. Antithrombotic therapy and spinal surgery: A retrospective cohort study of 289 consecutive elderly patients with degenerative lumbar stenosis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2023, 40, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannil, M.; Burgstaller, J.M.; Thanabalasingam, A.; Winklhofer, S.; Betz, M.; Held, U.; Guggenberger, R. Texture analysis of paraspinal musculature in MRI of the lumbar spine: Analysis of the lumbar stenosis outcome study (LSOS) data. Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzmann, J.M.; Ashouri, H.; Burgstaller, J.M.; Valeri, F.; Winklhofer, S.; Ulrich, N.H.; Guggenberger, R. The effect of paraspinal fatty muscle infiltration and cumulative lumbar spine degeneration on the outcome of patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis: Analysis of the Lumbar Stenosis Outcome Study (LSOS) data. Spine 2023, 48, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, S.; Sandhu, M.; Wright-Chisem, J.; Vaishnav, A.; Albert, T.; Qureshi, S.A. The association between spondylolisthesis and decreased muscle health throughout the lumbar spine for patients with operative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capece, M.; Corazzelli, G.; Pizzuti, V.; Leonetti, S.; Innocenzi, G. A challenging recurrent thoracic disc herniation. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2023, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariniello, G.; Corvino, S.; Corazzelli, G.; Maiuri, F. Cervical epidural abscess complicated by a pharyngoesophageal perforation after anterior cervical spine surgery for subaxial spondylodiscitis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2023, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekşi, M.Ş.; Öztaş, U.O.; Topaloğlu, F.; Yeşilyurt, S.C.; Duymaz, U.C.; Osama, M.; Özcan-Ekşi, E.E. Erector spinae could be the game changer in surgical decision-making in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis: A cross-sectional analysis of an age-, sex-, subtype-, level-matched patients with similar spinopelvic parameters received surgical or conservative management. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, Y. Fatty infiltration in paraspinal muscles: Predicting the outcome of lumbar surgery and postoperative complications. World Neurosurg. 2024, 190, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Head, J.; Mouchtouris, N.; Hines, K.; Shea, P.; Schmidt, R.; Hoelscher, C.; Stricsek, G.; Harrop, J.; Sharan, A. The implications of paraspinal muscle atrophy in low back pain, thoracolumbar pathology, and clinical outcomes after spine surgery: A review of the literature. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libda, N.; Fahmy, H.; Al Smmak, A.A.E.; Tantawy, H.F. Correlation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Changes of Multifidus Muscle with Other Degenerative Changes at Lumbosacral Spine in Patients with Low Back Pain. Zagazig Univ. Med. J. 2024, 30, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Ramadan, B.; Karam, M.; Rouyer, J.; Mitulescu, A.; Campana, S. Muscle fat infiltration: A narrative review of the magnetic resonance (MR)-based evaluation methods and their clinical applications. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.H.; Koh, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi, S.-S.; Shin, J.-W.; Kim, D.-H. Association between fatty infiltration in the cervical multifidus and treatment response following cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injection. Korean J. Pain 2023, 36, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felippe, V.G.; Amaral, C.A.B.d.; Labronici, P.J. Correlation between low back pain due to fatty degeneration and sex and age: Study by MRI. Coluna/Columna 2022, 20, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, M.; Fankhauser, G.; Meichtry, A.; Luomajoki, H. Correlation between lumbar dysfunction and fat infiltration in lumbar multifidus muscles in patients with low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, J.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Galbusera, F. Cross-sectional area and fat infiltration of the lumbar spine muscles in patients with back disorders: A deep learning-based big data analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
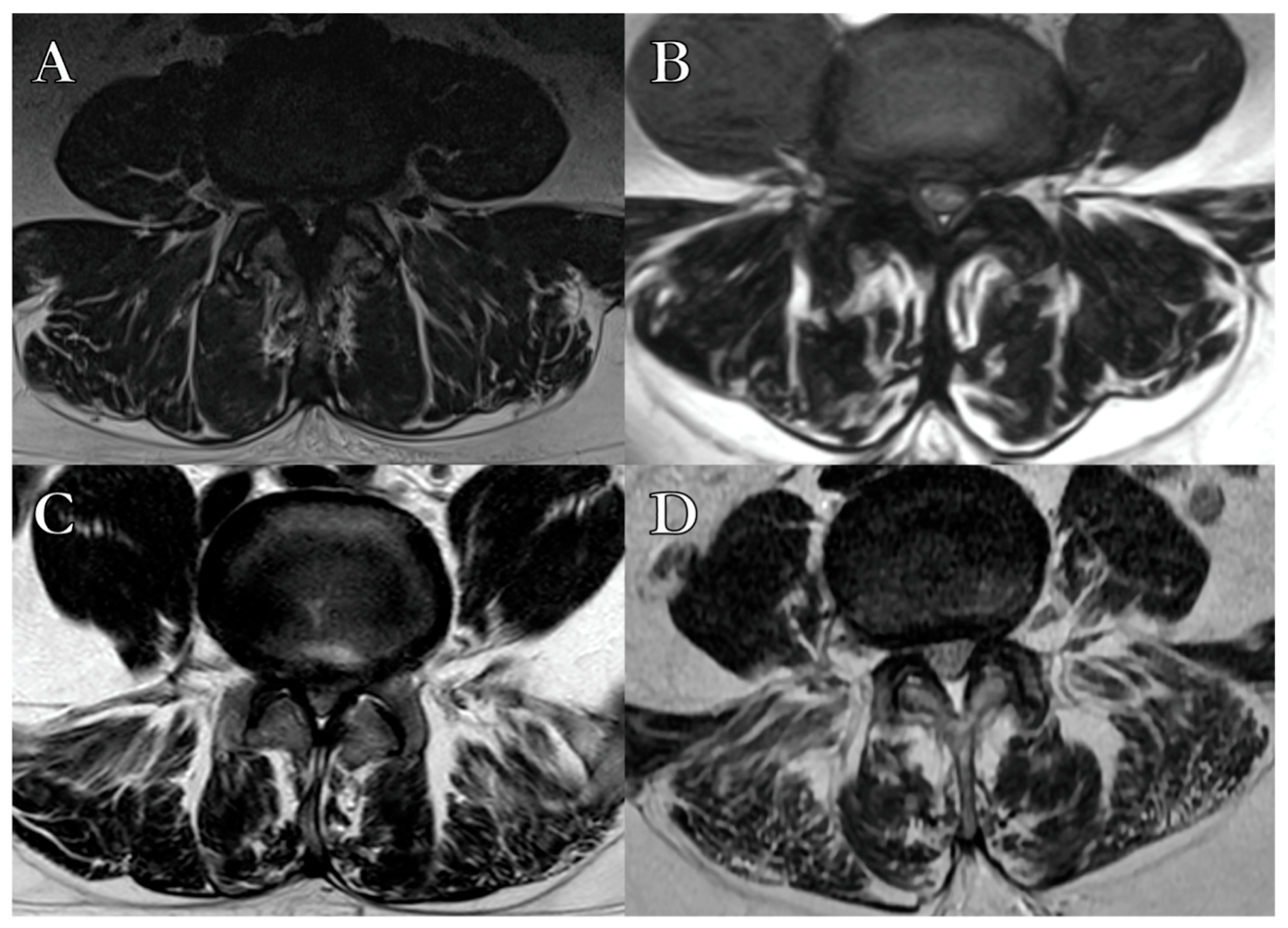


| Goutallier Classification System Grade | Percentage of Muscular Fatty Degeneration |
|---|---|
| 0 | No fatty infiltration |
| 1 | Few fatty streaks within the muscle |
| 2 | Less than 50% fat within the muscle |
| 3 | 50% fat within the muscle |
| 4 | More than 50% fat within the muscle |
| Goutallier Grade | Sample (n = 100) | Grade I (n = 9) | Grade II (n = 33) | Grade III (n = 36) | Grade IV (n = 22) | Statistical Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender † | ||||||
| Male | 48 | 9 (100) | 21 (64) | 14 (39) | 4 (18) | |
| Female | 52 | 0 | 12 (36) | 22 (61) | 18 (82) | p < 0.05 |
| Age at surgery (yrs) ‡ | 66.1 (±7.3) | 64.39 (±6.42) | 67.80 (±5.51) | 67.47 (±7.97) | 69.11 (±8.32) | p = 0.39 |
| Schizas grade † | ||||||
| A4 | 16 | 1 (11) | 10 (30) | 2 (6) | 3 (14) | |
| B | 31 | 5 (56) | 13 (39) | 8 (22) | 5 (23) | |
| C | 40 | 2 (22) | 9 (27) | 21 (58) | 8 (36) | |
| D | 13 | 1 (11) | 1 (3) | 5 (14) | 6 (27) | p = 0.13 |
| Levels of stenosis † | ||||||
| Single-level | 54 | 6 (67) | 21 (64) | 18 (50) | 12 (41) | |
| Two-level | 34 | 3 (33) | 10 (30) | 14 (39) | 7 (32) | |
| Three-level | 12 | 0 (0) | 2 (6) | 4 (11) | 6 (27) | p = 0.12 |
| Preop CCI | 3.93 (±1.06) | 4.1 (±0.96) | 3.96 (±1.42) | 3.7 (±1.35) | 3.96 (±1.07) | p = 0.74 |
| Oswestry Disability Index ‡ | ||||||
| Preoperative | 41.0 (±17.5) | 35.0 (±17.7) | 42.0 (±16.4) | 44.8 (±18.1) | 45.0 (±19) | |
| Follow-up | 16.9 (±8.2) | 4.33 (±2.35) | 14.4 (±8.82) | 22.1 (±7.39) | 25.1 (±6.56) | |
| Wilcoxon matched test | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | ||
| ΔODI | 30.67 (±16.65) | 27.60 (±14.22) | 22.70 (±15.76) | 19.90 (±16.72) | Friedman test | |
| R = 0.39; p < 0.01 | ||||||
| Visual Analog Scale ‡ | ||||||
| Preoperative | 6.23 (±2.52) | 4.75 (±2.89) | 6.64 (±1.99) | 6.55 (±1.77) | 6.95 (±2.48) | |
| Follow-up | 3.75 (±2.38) | 1.83 (±1.76) | 3.21 (±1.87) | 4.26 (±2.32) | 4.50 (±2.74) | |
| Wilcoxon matched test | p = 0.01 | p = 0.02 | p < 0.01 | p = 0.01 | ||
| ΔVAS | 2.92 (±2.52) | 3.43 (±1.93) | 2.29 (±2.10) | 2.45 (±2.62) | Friedman test | |
| R = 0.06; p = 0.01 | ||||||
| CD Score | 1.88 (±0.92) | 1.66 (±0.64) | 2.17 (±1.13) | 1.79 (±0.94) | 1.98 (±1.2) | p = 0.36 |
| Mean follow-up (yrs) ‡ | 3.36 (±0.68) | 3.46 (±0.77) | 3.48 (±0.69) | 3.31 (±0.59) | 3.13 (±0.49) | p = 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corazzelli, G.; Corvino, S.; Di Domenico, C.; Russo, F.; Meglio, V.; Leonetti, S.; Pizzuti, V.; Santilli, M.; D’Elia, A.; Ricciardi, F.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Goutallier Scale for Paravertebral Muscle Atrophy in Predicting Disability and Pain Outcomes in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 100 Patients. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070674
Corazzelli G, Corvino S, Di Domenico C, Russo F, Meglio V, Leonetti S, Pizzuti V, Santilli M, D’Elia A, Ricciardi F, et al. Prognostic Value of the Goutallier Scale for Paravertebral Muscle Atrophy in Predicting Disability and Pain Outcomes in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 100 Patients. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(7):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070674
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorazzelli, Giuseppe, Sergio Corvino, Chiara Di Domenico, Federico Russo, Vincenzo Meglio, Settimio Leonetti, Valentina Pizzuti, Marco Santilli, Alessandro D’Elia, Francesco Ricciardi, and et al. 2025. "Prognostic Value of the Goutallier Scale for Paravertebral Muscle Atrophy in Predicting Disability and Pain Outcomes in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 100 Patients" Brain Sciences 15, no. 7: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070674
APA StyleCorazzelli, G., Corvino, S., Di Domenico, C., Russo, F., Meglio, V., Leonetti, S., Pizzuti, V., Santilli, M., D’Elia, A., Ricciardi, F., Paolini, S., de Falco, R., de Divitiis, O., Esposito, V., & Innocenzi, G. (2025). Prognostic Value of the Goutallier Scale for Paravertebral Muscle Atrophy in Predicting Disability and Pain Outcomes in Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of 100 Patients. Brain Sciences, 15(7), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070674







