Pain Hypersensitivity and Increased Urinary Tetrahydrobiopterin Levels in Mice Submitted to High-Fat Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Strategy
- -
- The minimum difference between the groups’ means will be set at least at 54.4%;
- -
- Biological experiments inherently have a 10–15% error margin;
- -
- Differences less than 20% in each group’s mean can increase the probability of type I or type II errors;
- -
- The standard deviation is typically 35% of the mean value.
2.3. Calorie Intake Measurement
2.4. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test
2.5. Physical Exercise
2.5.1. Incremental Test to Determine the Maximal Capacity for Exercise
2.5.2. Physical Exercise Protocol
Caudal Blood Collection
Lactate Measurement
2.6. Behavioral Tests
2.6.1. Locomotor Activity
2.6.2. Motivational Behavior
2.6.3. Mechanical Hypersensitivity
2.6.4. Thermal Hypersensitivity
2.6.5. Chemical Hypersensitivity
2.7. Urine Sample Collection
2.8. Adipose Tissue Dissection
2.9. BH4 Quantification
Quantification of Creatinine
2.10. Gene Promoter DNA Methylation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
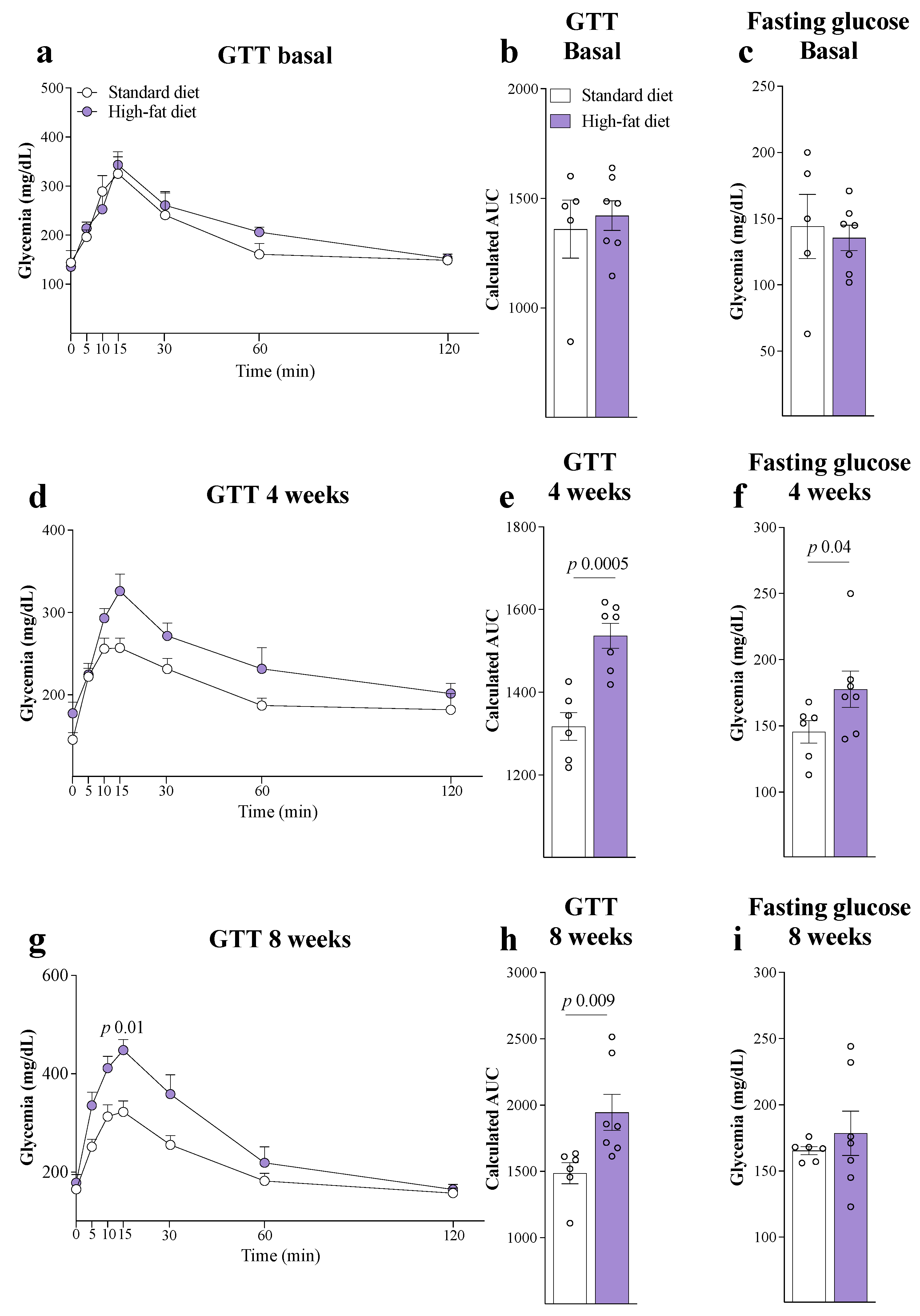
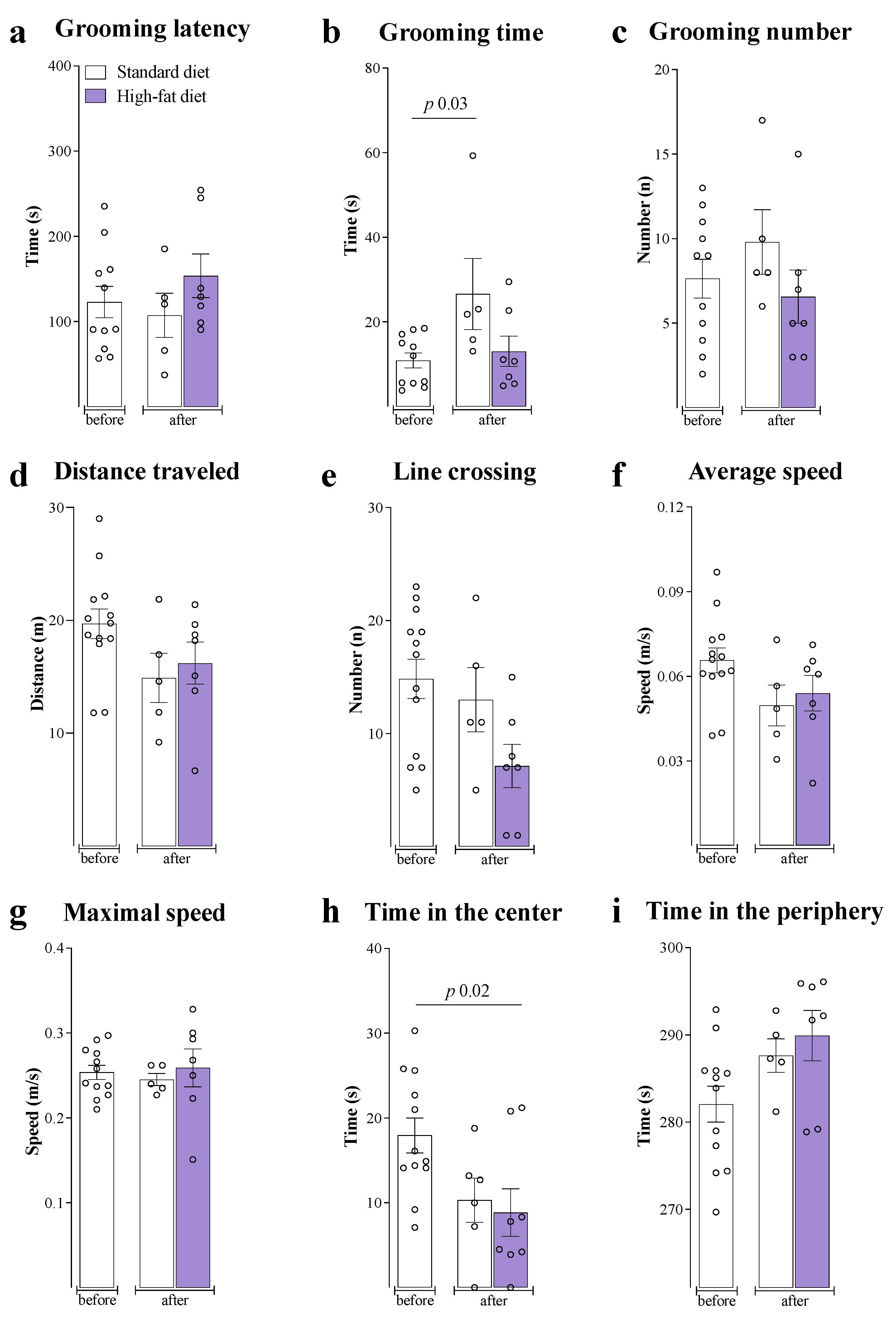
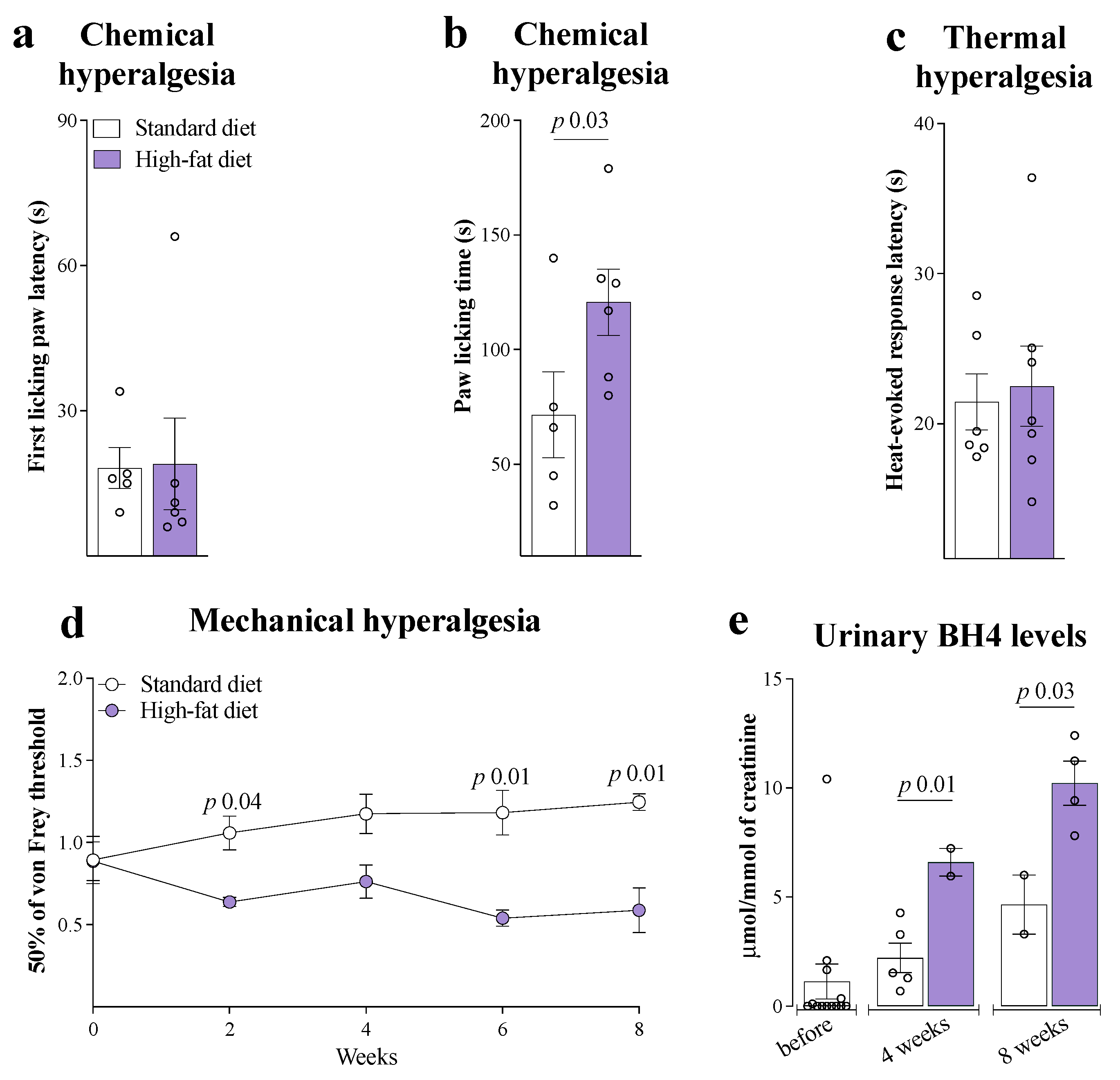
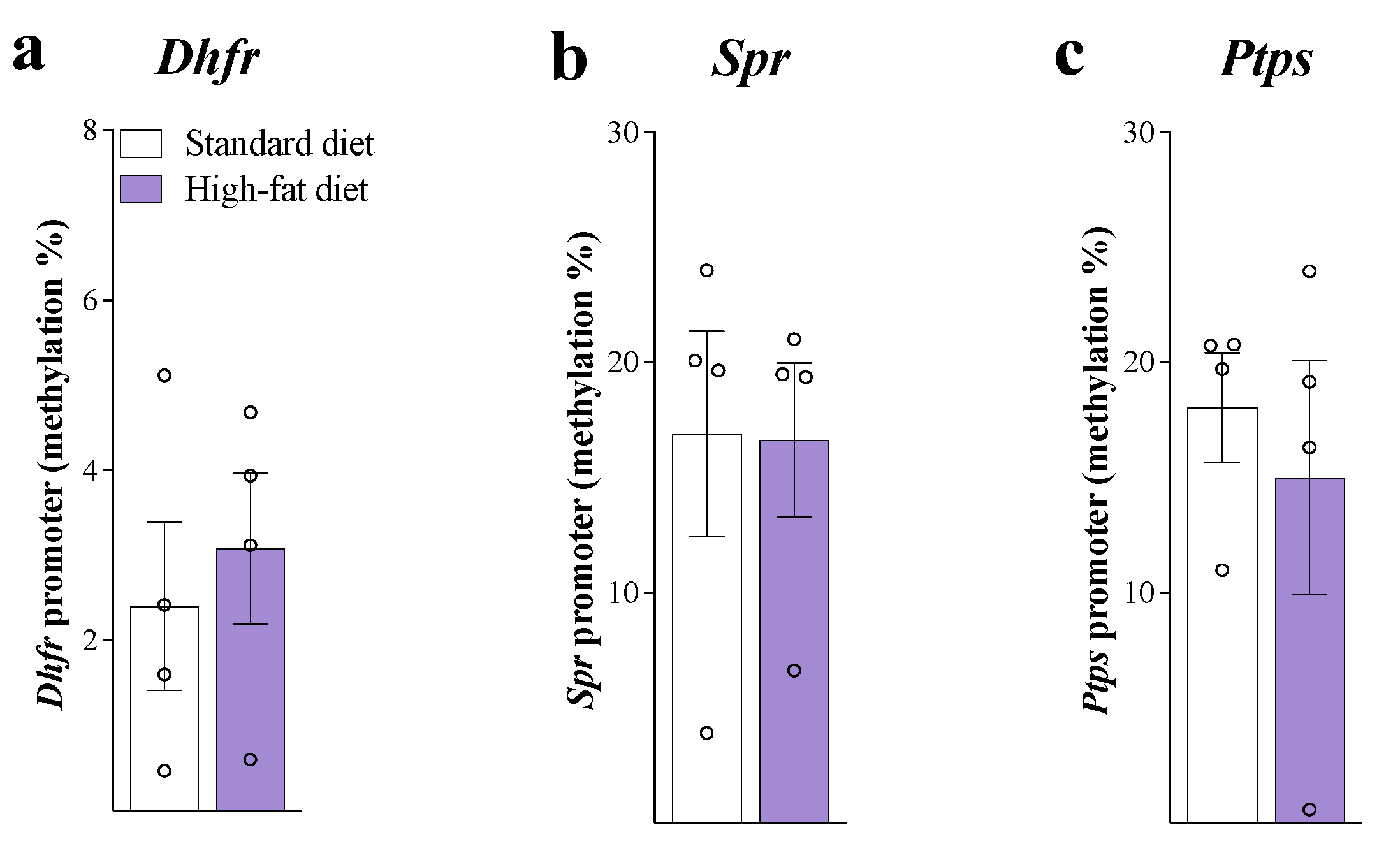
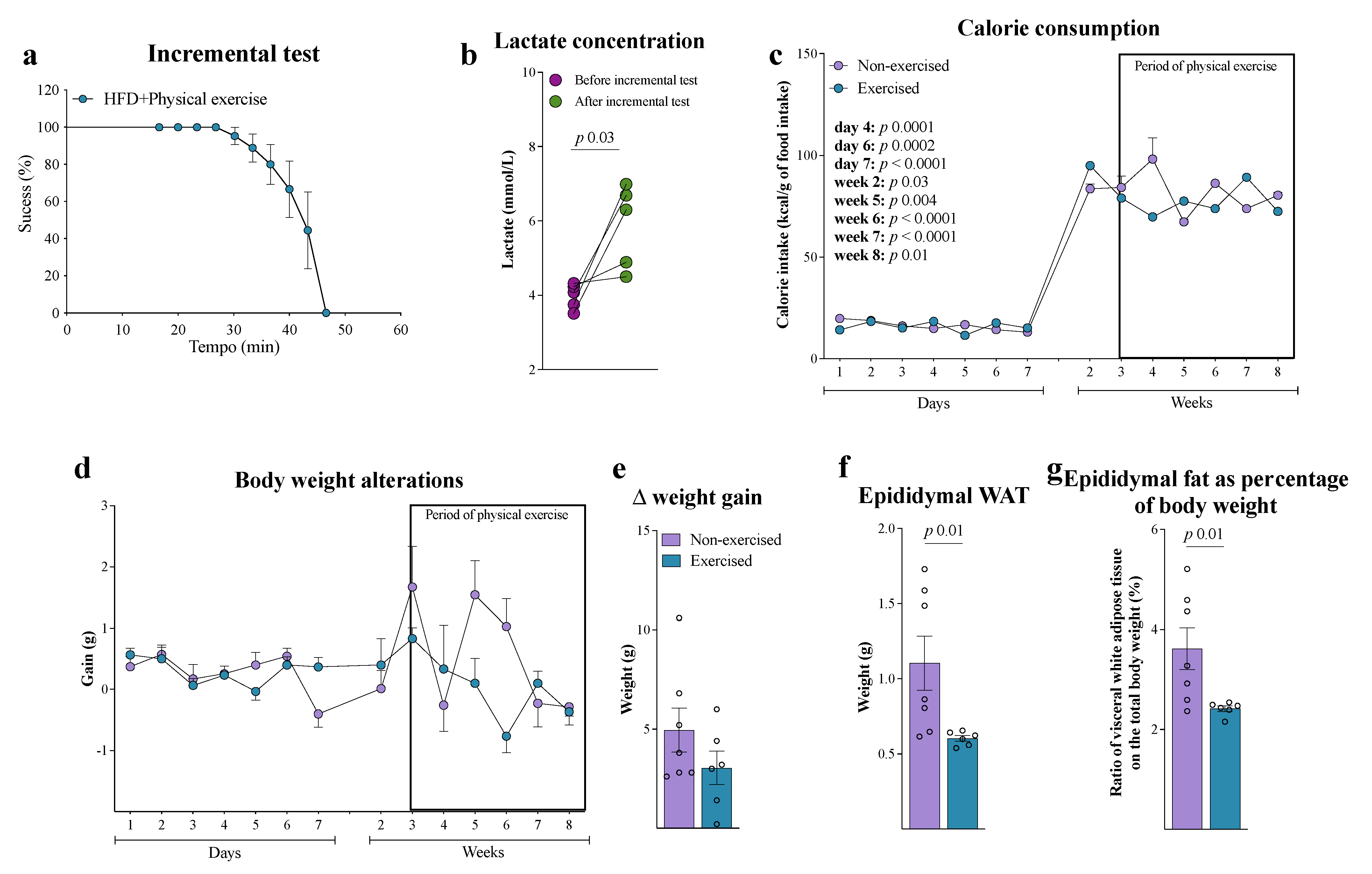
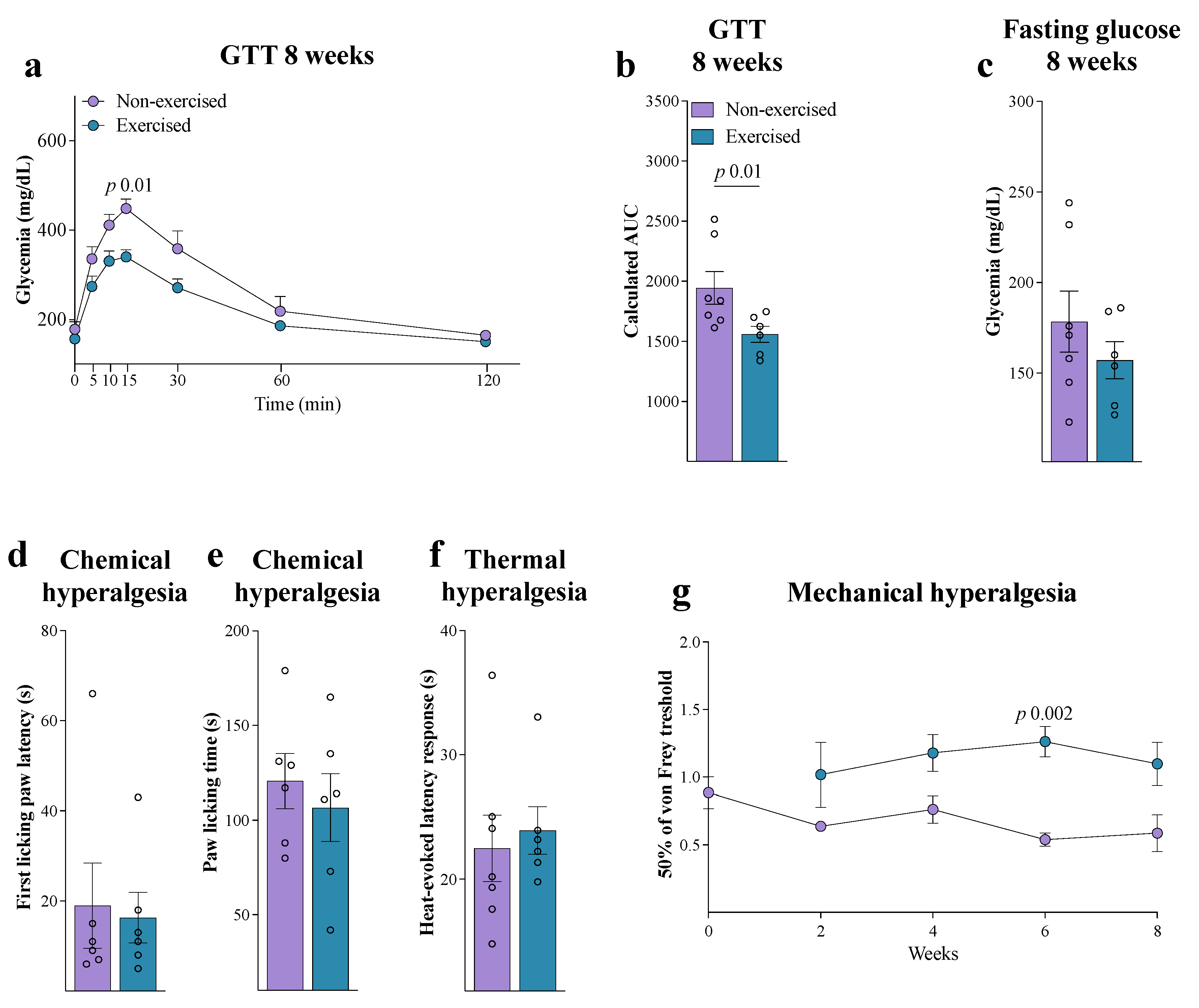
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Ministério da Saúde. Cenário da Obesidade no Brasil. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/epidemiologicos/edicoes/2024/boletim-epidemiologico-volume-55-no-07.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Thomazeau, J.; Perin, J.; Nizard, R.; Bouhassira, D.; Collin, E.; Nguyen, E.; Perrot, S.; Bergmann, J.-F.; Lloret-Linares, C. Pain Management and Pain Characteristics in Obese and Normal Weight Patients before Joint Replacement. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2014, 20, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Hay, P.; Campbell, L.; Trollor, J.N. A Review of the Association between Obesity and Cognitive Function across the Lifespan: Implications for Novel Approaches to Prevention and Treatment. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, X.E.C.; Lamarca, E.A.; Monari, X.P.K.; Olson, L.B.; Martinez, S.; Zych, A.D.; Katchur, X.N.J.; Gould, X.E. Microglia Play an Active Role in Obesity-Associated Cognitive Decline. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 8889–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; Castilho, Á.; Baptista, F.I.; Liberal, J.; Ambrósio, A.F. Long-Term Exposure to High Glucose Induces Changes in the Content and Distribution of Some Exocytotic Proteins in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, Metaflammation and Immunometabolic Disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichwald, T.; Talbot, S. Neuro-Immunity Controls Obesity-Induced Pain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Exercise: Mechanisms and Implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedell-Neergaard, A.-S.; Lang Lehrskov, L.; Christensen, R.H.; Legaard, G.E.; Dorph, E.; Larsen, M.K.; Launbo, N.; Fagerlind, S.R.; Seide, S.K.; Nymand, S.; et al. Exercise-Induced Changes in Visceral Adipose Tissue Mass Are Regulated by IL-6 Signaling: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 844–855.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, E.; Koutsikos, K.; Pigatto, M.; Rampudda, M.E.; Doria, A.; Masiero, S. Medium-/Long-Term Effects of a Specific Exercise Protocol Combined with Patient Education on Spine Mobility, Chronic Fatigue, Pain, Aerobic Fitness and Level of Disability in Fibromyalgia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 474029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.R.; Werner-Felmayer, G.; Fuchs, D.; Hausen, A.; Reibnegger, G.; Yim, J.J.; Pfleiderer, W.; Wachter, H. Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthetic Activities in Human Macrophages, Fibroblasts, THP-1, and T 24 Cells. GTP-Cyclohydrolase I Is Stimulated by Interferon-Gamma, and 6-Pyruvoyl Tetrahydropterin Synthase and Sepiapterin Reductase Are Constitutively Present. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 3189–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.R.; Blau, N.; Thöny, B. Tetrahydrobiopterin: Biochemistry and Pathophysiology. Biochem. J. 2013, 438, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichwald, T.; da Silva, L.D.B.; Staats Pires, A.C.; Niero, L.; Schnorrenberger, E.; Filho, C.C.; Espíndola, G.; Huang, W.-L.; Guillemin, G.J.; Abdenur, J.E.; et al. Tetrahydrobiopterin: Beyond Its Traditional Role as a Cofactor. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, J.K.; Douglas, G.; McNeill, E.; Channon, K.M.; Crabtree, M.J. Tetrahydrobiopterin in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 3040–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, S.J.F.; Seehus, C.; Weidinger, A.; Talbot, S.; Reissig, S.; Seifert, M.; Pierson, Y.; McNeill, E.; Longhi, M.S.; Turnes, B.L.; et al. The Metabolite BH4 Controls T Cell Proliferation in Autoimmunity and Cancer. Nature 2018, 563, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegeder, I.; Costigan, M.; Griffin, R.S.; Abele, A.; Belfer, I.; Schmidt, H.; Ehnert, C.; Nejim, J.; Marian, C.; Scholz, J.; et al. GTP Cyclohydrolase and Tetrahydrobiopterin Regulate Pain Sensitivity and Persistence. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latremoliere, A.; Latini, A.; Andrews, N.; Cronin, S.J.; Fujita, M.; Gorska, K.; Hovius, R.; Romero, C.; Chuaiphichai, S.; Painter, M.; et al. Reduction of Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain through Inhibition of the Tetrahydrobiopterin Pathway. Neuron 2015, 86, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisoni, K.; Latini, A.; Kuehne, L.K.; Reiber, H.; Bechter, K.; Hagberg, L.; Fuchs, D. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Is Brain-Derived and Not Associated with Blood-CSF Barrier Dysfunction in Non-Inflammatory Affective and Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Martins, R.; Glaser, V.; Aguiar, A.S., Jr.; de Paula Ferreira, P.M.; Ghisoni, K.; da Luz Scheffer, D.; Lanfumey, L.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Corti, O.; De Paul, A.L.; et al. De Novo Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthesis Is Impaired in the Inflammed Striatum of Parkin(−/−) Mice. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Ma, Q. Nociceptors—Noxious Stimulus Detectors. Neuron 2007, 55, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, M.; Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Neuropathic Pain: A Maladaptive Response of the Nervous System to Damage. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 32, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbæk, M.S.; Ditzel, N.; Hejbøl, E.K.; Præstholm, S.M.; Markussen, L.K.; Avolio, F.; Li, L.; Lehtonen, L.; Hansen, A.K.; Schrøder, H.D.; et al. C57BL/6J Substrain Differences in Response to High-Fat Diet Intervention. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Togo, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; et al. Dietary Fat, but Not Protein or Carbohydrate, Regulates Energy Intake and Causes Adiposity in Mice. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 415–431.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machin, D.; Campbell, M.J.; Tan, S.B.; Tan, S.H. Sample Size Tables for Clinical Studies; BMJ Books: London, UK, 2008; ISBN 9781405146500. [Google Scholar]
- Rafacho, A.; Ribeiro, D.L.; Boschero, A.C.; Bosqueiro, R. Increased Pancreatic Islet Mass Is Accompanied by Activation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate-2/Serine-Threonine Kinase Pathway and Augmented Cyclin D2 Protein Levels in Insulin-Resistant Rats. Int. J. Exp. Path. 2008, 89, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.S.; Duzzioni, M.; Remor, A.P.; Tristão, F.S.M.; Matheus, F.C.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Latini, A.; Prediger, R.D. Moderate-Intensity Physical Exercise Protects against Experimental 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Hemiparkinsonism through Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Element Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Luz Scheffer, D.; Ghisoni, K.; Aguiar, A.S.; Latini, A. Moderate Running Exercise Prevents Excessive Immune System Activation. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 204, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoden, E.L.; Rhoden, C.R. Princípios e Técnicas Em Expertimentação Animal, 1st ed.; Editora da UFRGS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sigwalt, A.R.; Budde, H.; Helmich, I.; Glaser, V.; Ghisoni, K.; Lanza, S.; Cadore, E.L.; Lhullier, F.L.R.; de Bem, A.F.; Hohl, A.; et al. Molecular Aspects Involved in Swimming Exercise Training Reducing Anhedonia in a Rat Model of Depression. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.S.; Moreira, E.L.G.; Hoeller, A.A.; Oliveira, P.A.; Córdova, F.M.; Glaser, V.; Walz, R.; Cunha, R.A.; Leal, R.B.; Latini, A.; et al. Exercise Attenuates Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Mice. Neuroscience 2013, 243, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Luz Scheffer, D.; Freitas, F.C.; Aguiar Jr, A.S.; Ward, C.; Guglielmo, L.G.A.; Prediger, R.D.; Cronin, S.J.F.; Walz, R.; Andrews, N.A.; Latini, A. Impaired Dopamine Metabolism Is Linked to Fatigability in Mice and Fatigue in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Cano, R.; Boivin, B.; Bullock, D.; Cornelissen, L.; Andrews, N.; Costigan, M. Up—Down Reader: An Open Source Program for Efficiently Processing 50% von Frey Thresholds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, G.; Macdonald, A.D. The evaluation of the analgesic action of pethidine hydrochloride (demerol). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1944, 80, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, T.; Katsumata, K.; Tan-No, K.; Sakurada, S.; Kisara, K. The Capsaicin Test in Mice for Evaluating Tachykinin Antagonists in the Spinal Cord. Neuropharmacology 1992, 31, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; da Luz Scheffer, D.; Turnes, B.L.; Cronin, S.J.F.; Latrémolière, A.; Costigan, M.; Woolf, C.J.; Latini, A.; Andrews, N.A. Sepiapterin Reductase Inhibition Leading to Selective Reduction of Inflammatory Joint Pain in Mice and Increased Urinary Sepiapterin Levels in Humans and Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.A.; Feltran, G.d.S.; Fernandes, C.J.d.C.; Zambuzzi, W.F. Osteogenic Gene Markers Are Epigenetically Reprogrammed during Contractile-to-Calcifying Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Transition. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66, 109458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, D.B.; York, B. Dietary Fat, Genetic Predisposition, and Obesity: Lessons from Animal Models. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 505S–512S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, K.L.; Lorenzi, M.M.; Widmaier, E.P. High-Fat Diet-Induced Changes in Body Mass and Hypothalamic Gene Expression in Wild-Type and Leptin-Deficient Mice. Endocrine 2008, 33, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atshaves, B.P.; McIntosh, A.L.; Storey, S.M.; Landrock, K.K.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. High Dietary Fat Exacerbates Weight Gain and Obesity in Female Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein Gene-Ablated Mice. Lipids 2010, 45, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity Induces a Phenotypic Switch in Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; DeYoung, S.M.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Increased Inflammatory Properties of Adipose Tissue Macrophages Recruited During Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binshtok, A.M.; Wang, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Amaya, F.; Vardeh, D.; Shi, L.; Brenner, G.J.; Ji, R.-R.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J.; et al. Nociceptors Are Interleukin-1 Sensors. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14062–14073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, R.B.; Dark, J. Sensory Innervation of White Adipose Tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1987, 253, R942–R944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartness, T.J.; Liu, Y.; Shrestha, Y.B.; Ryu, V. Neural Innervation of White Adipose Tissue and the Control of Lipolysis. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Luz Scheffer, D.; Latini, A. Exercise-Induced Immune System Response: Anti-Inflammatory Status on Peripheral and Central Organs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidley, C.; Haruki, H.; Pedersen, M.G.; Muller, E.; Johnsson, K. A Yeast-Based Screen Reveals That Sulfasalazine Inhibits Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir da Silva, T.; Muller Linhares, R.M.; Pertile Remor, A.; Ghisoni, K.; de Paula Martins, R.; Poli, A.; Aguiar, A., Jr.; Fernando Ronsoni, M.; Hohl, A.; Walz, R.; et al. Blood Advanced Glycation End Products and Biomarkers of Inflammation in Class III Obese Brazilian Subjects. Integr. Obes. Diabetes 2017, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Kaufman, S.; Milstein, S. Tetrahydrobiopterin Is Required for Cytokine-Induced Nitric Oxide Production in a Murine Macrophage Cell Line (RAW 264). Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 43, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd ed.; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Nieman, D.C.; Wentz, L.M. The Compelling Link between Physical Activity and the Body’s Defense System. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.; Batchelor, J.R.; Fuchs, D.; Hausen, A.; Lang, A.; Niederwieser, D.; Reibnegger, G.; Swetly, P.; Troppmair, J.; Wachter, H. Immune Response-Associated Production of Neopterin. Release from Macrophages Primarily under Control of Interferon-Gamma. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remor, A.P.; da Silva, R.A.; de Matos, F.J.; Glaser, V.; de Paula Martins, R.; Ghisoni, K.; da Luz Scheffer, D.; Andia, D.C.; Portinho, D.; de Souza, A.P.; et al. Chronic Metabolic Derangement-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Neurotoxicity Are Associated with REST Inactivation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 1539–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Training Weeks | Session Duration (min) | Treadmill Inclination (%) | Activity Intensity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | 2 | 60 |
| 2 | 40 | 2 | 60 |
| 3 | 45 | 2 | 60 |
| Effort test to equalize intensities | |||
| 5 | 35 | 2 | 60 |
| 6 | 40 | 2 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eichwald, T.; Scheffer, D.d.L.; Barros, L.; Solano, A.; Menegassi, V.D.S.; Staats Pires, A.C.; Spivakoski, C.S.; Da Silva, R.A.; Gaspar, J.M.; Ronsoni, M.F.; et al. Pain Hypersensitivity and Increased Urinary Tetrahydrobiopterin Levels in Mice Submitted to High-Fat Diet. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060646
Eichwald T, Scheffer DdL, Barros L, Solano A, Menegassi VDS, Staats Pires AC, Spivakoski CS, Da Silva RA, Gaspar JM, Ronsoni MF, et al. Pain Hypersensitivity and Increased Urinary Tetrahydrobiopterin Levels in Mice Submitted to High-Fat Diet. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060646
Chicago/Turabian StyleEichwald, Tuany, Débora da Luz Scheffer, Leonardo Barros, Alexandre Solano, Vivian De Souza Menegassi, Ananda Christina Staats Pires, Camila Sartor Spivakoski, Rodrigo A. Da Silva, Joana M. Gaspar, Marcelo Fernando Ronsoni, and et al. 2025. "Pain Hypersensitivity and Increased Urinary Tetrahydrobiopterin Levels in Mice Submitted to High-Fat Diet" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060646
APA StyleEichwald, T., Scheffer, D. d. L., Barros, L., Solano, A., Menegassi, V. D. S., Staats Pires, A. C., Spivakoski, C. S., Da Silva, R. A., Gaspar, J. M., Ronsoni, M. F., & Latini, A. (2025). Pain Hypersensitivity and Increased Urinary Tetrahydrobiopterin Levels in Mice Submitted to High-Fat Diet. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060646










