The Differential and Interactive Effects of Aging and Mental Fatigue on Alpha Oscillations: A Resting-State Electroencephalography Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
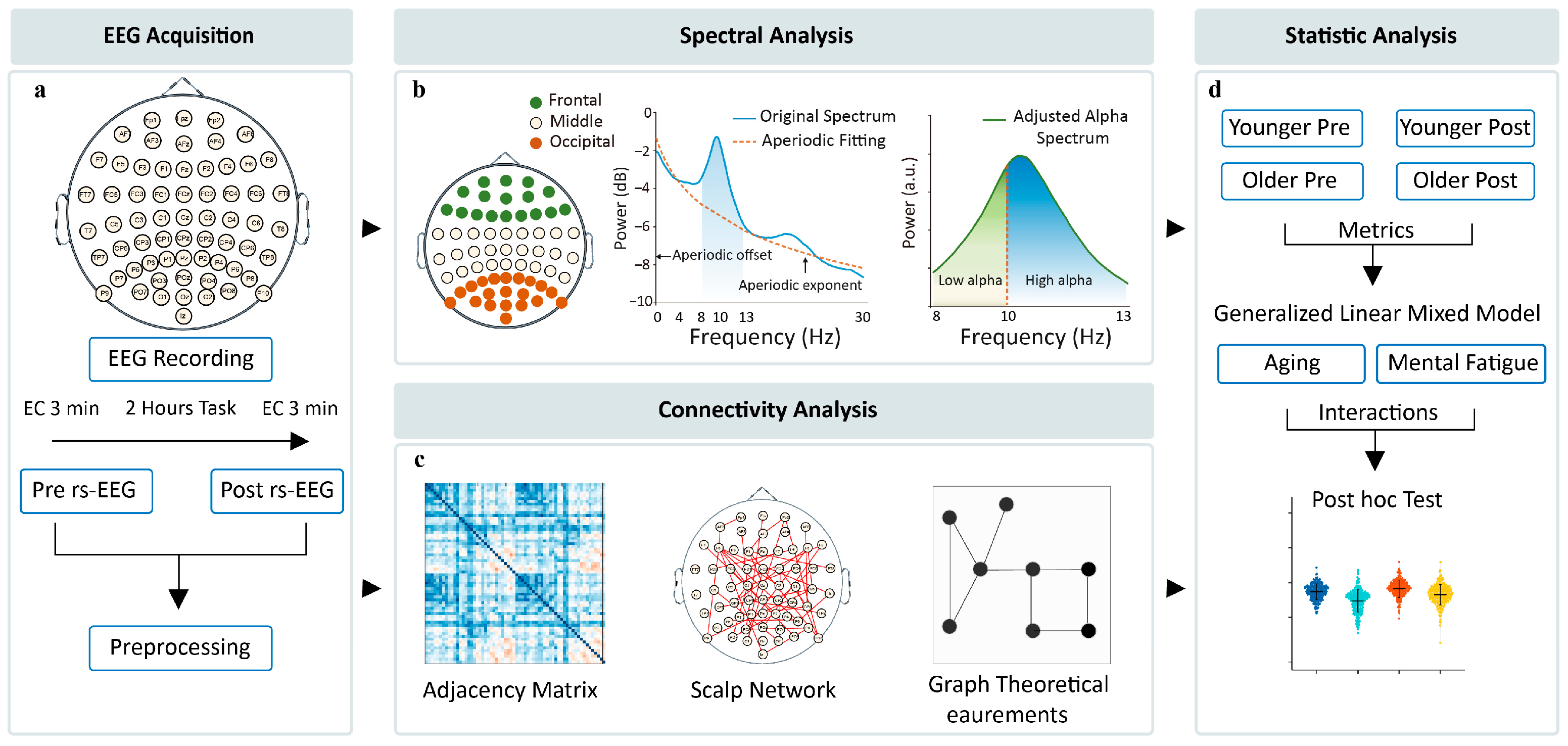
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sourcing and Description
2.2. EEG Preprocessing
2.3. Spectral Analysis
2.4. Functional Connectivity
2.5. Graph Theory Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
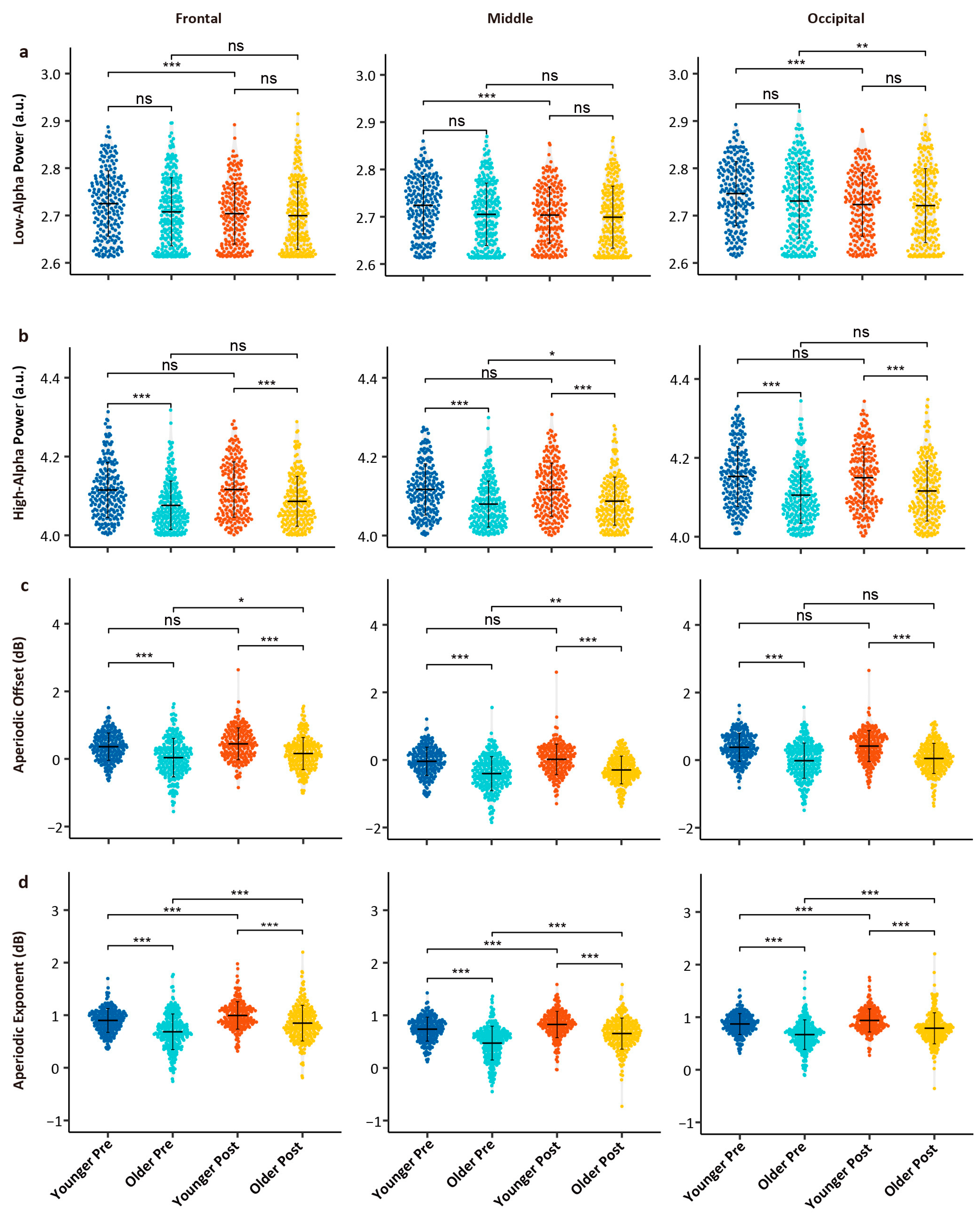
3.1. Age- and Task-Related Differences in Spectral Metrics
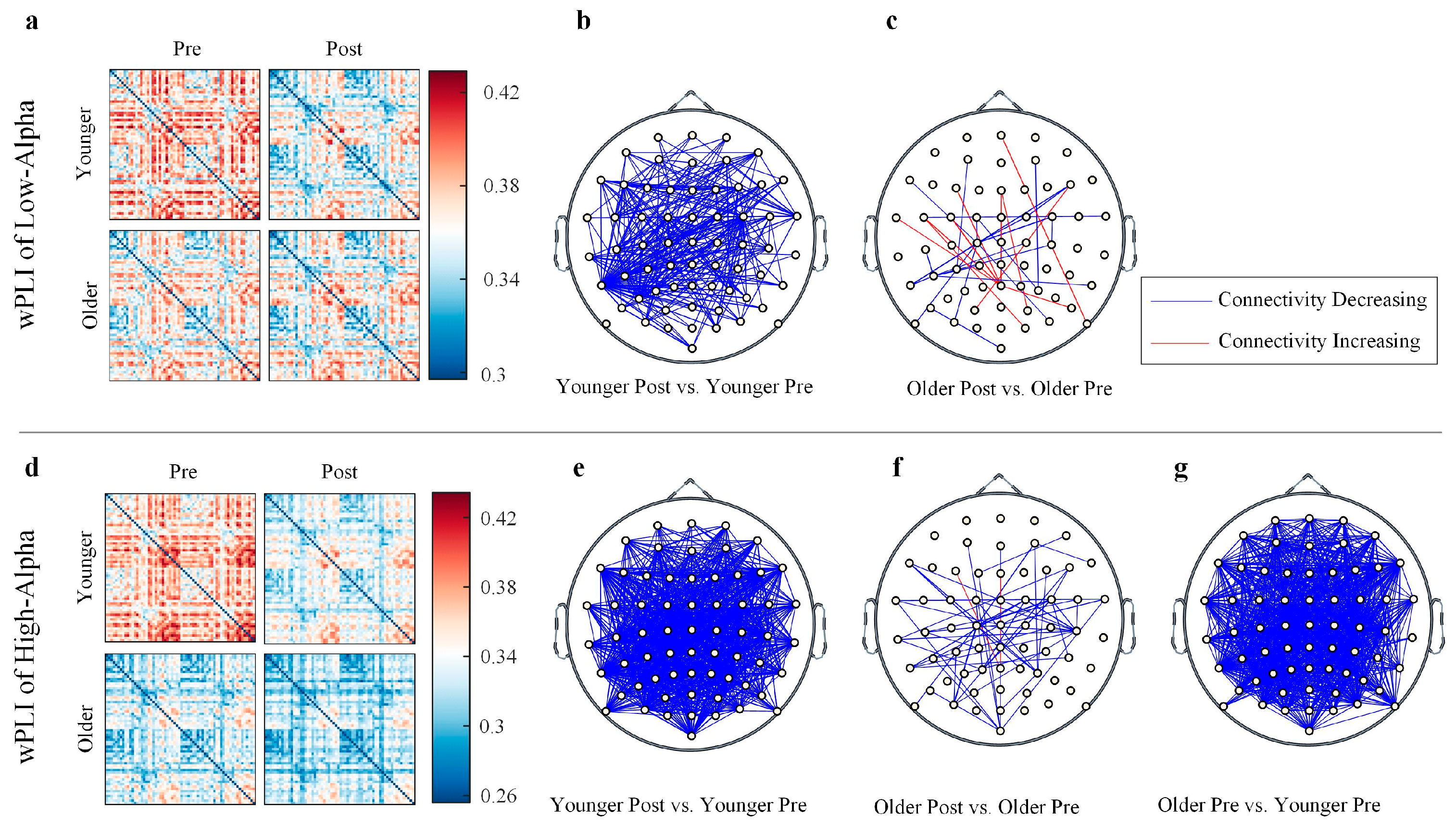
3.2. Age- and Task-Related Differences in Functional Connectivity
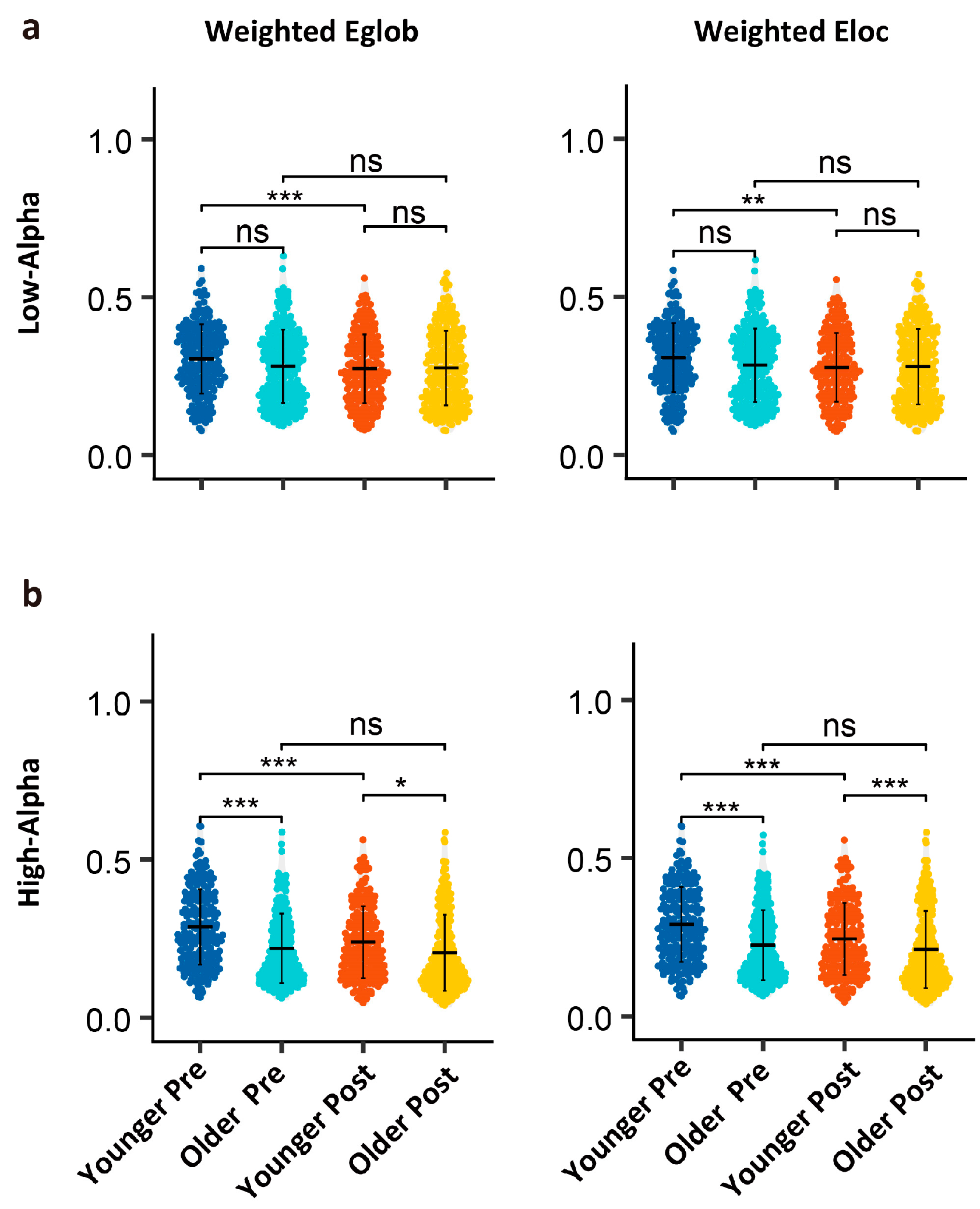
3.3. Age- and Task-Related Differences in Graph Theory Metrics
4. Discussion
4.1. Power Changes in Alpha Sub-Bands: Aging Drives and Fatigue–Aging Interplay
4.2. Decomposing Aperiodic Components in Aging and Cognitive Fatigue
4.3. Functional Connectivity and Network Efficiency
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boksem, M.A.S.; Meijman, T.F.; Lorist, M.M. Effects of mental fatigue on attention: An ERP study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2005, 25, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boksem, M.A.S.; Tops, M. Mental fatigue: Costs and benefits. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borragán, G.; Slama, H.; Bartolomei, M.; Peigneux, P. Cognitive fatigue: A Time-based Resource-sharing account. Cortex 2017, 89, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sghirripa, S.; Graetz, L.; Merkin, A.; Rogasch, N.C.; Semmler, J.G.; Goldsworthy, M.R. Load-dependent modulation of alpha oscillations during working memory encoding and retention in young and older adults. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wascher, E.; Getzmann, S. Rapid mental fatigue amplifies age-related attentional deficits. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 28, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.A.; Schroeder, D.H.; Ferrer, E. Estimating retest effects in longitudinal assessments of cognitive functioning in adults between 18 and 60 years of age. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. α-band oscillations, attention, and controlled access to stored information. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazanova, O.M.; Vernon, D. Interpreting EEG alpha activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Binetti, G.; Cassetta, E.; Dal Forno, G.; Del Percio, C.; Ferreri, F.; Ferri, R.; Frisoni, G.; Hirata, K.; Lanuzza, B.; et al. Sources of cortical rhythms change as a function of cognitive impairment in pathological aging: A multicenter study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaden, R.J.; Hutcheson, N.L.; McCollum, L.A.; Kentros, J.; Visscher, K.M. Older adults, unlike younger adults, do not modulate alpha power to suppress irrelevant information. NeuroImage 2012, 63, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scally, B.; Burke, M.R.; Bunce, D.; Delvenne, J.-F. Resting-state EEG power and connectivity are associated with alpha peak frequency slowing in healthy aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Linden, D.; Frese, M.; Meijman, T.F. Mental fatigue and the control of cognitive processes: Effects on perseveration and planning. Acta Psychol. 2003, 113, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, T.; Goldthorpe, R.; Peach, R.; Hebron, H.; Violante, I.R. Functionally annotated electrophysiological neuromarkers of healthy ageing and memory function. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2024, 45, e26687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Huang, S.; Xu, W.; Jiao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J. The impact of mental fatigue on brain activity: A comparative study both in resting state and task state using EEG. BMC Neurosci. 2020, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkenkaer-Hansen, K.; Nikulin, V.V.; Palva, S.; Ilmoniemi, R.J.; Palva, J.M. Prestimulus Oscillations Enhance Psychophysical Performance in Humans. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10186–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Bressler, S.L.; Chen, Y.; Ding, M. Prestimulus cortical activity is correlated with speed of visuomotor processing. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2008, 20, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel-Oliveros, C.; Medel, V.; Whitaker, G.A.; Astudillo, A.; Gallagher, D.; Z-Rivera, L.; Prado, P.; El-Deredy, W.; Orio, P.; Weinstein, A. Elevating understanding: Linking high-altitude hypoxia to brain aging through EEG functional connectivity and spectral analyses. Netw. Neurosci. 2024, 8, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Shao, S.; Xiao, Y. Decreased resting-state alpha-band activation and functional connectivity after sleep deprivation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Q. Dissociating the roles of alpha oscillation sub-bands in visual working memory. NeuroImage 2025, 307, 121028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lim, J.; Kwok, K.; Bezerianos, A. Functional cortical connectivity analysis of mental fatigue unmasks hemispheric asymmetry and changes in small-world networks. Brain Cogn. 2014, 85, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voytek, B.; Knight, R.T. Dynamic Network Communication as a Unifying Neural Basis for Cognition, Development, Aging, and Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, T.; Dominguez, J.; Voytek, B. Electrophysiological Frequency Band Ratio Measures Conflate Periodic and Aperiodic Neural Activity. eNeuro 2020, 7, ENEURO.0192-20.2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voytek, B.; Kramer, M.A.; Case, J.; Lepage, K.Q.; Tempesta, Z.R.; Knight, R.T.; Gazzaley, A. Age-Related Changes in 1/f Neural Electrophysiological Noise. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13257–13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkin, A.; Sghirripa, S.; Graetz, L.; Smith, A.E.; Hordacre, B.; Harris, R.; Pitcher, J.; Semmler, J.; Rogasch, N.C.; Goldsworthy, M. Do age-related differences in aperiodic neural activity explain differences in resting EEG alpha? Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.S.; Sporns, O. Network neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghernezhad, S.; Daliri, M.R. Age-related changes in human brain functional connectivity using graph theory and machine learning techniques in resting-state fMRI data. GeroScience 2024, 46, 5303–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Trongnetrpunya, A.; Samuel, I.B.H.; Ding, M.; Kluger, B.M. Compensatory Neural Activity in Response to Cognitive Fatigue. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3919–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, L.J.; Knuth, K.; Prado, R.; Rosipal, R.; Kubitz, K.; Kochavi, R.; Matthews, B.; Zhang, Y. EEG-Based Estimation of Mental Fatigue: Convergent Evidence for a Three-State Model. In Foundations of Augmented Cognition; Schmorrow, D.D., Reeves, L.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunasegaran, K.; Ismail, A.M.H.; Ramasamy, S.; Gnanou, J.V.; Caszo, B.A.; Chen, P.L. Understanding mental fatigue and its detection: A comparative analysis of assessments and tools. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.P.J.; Collins, B.; Shorter, K.; Moreland, A.T.; Papic, C.; Hamlin, A.S.; Kassman, B.; Marino, F.E. Approaches to inducing mental fatigue: A systematic review and meta-analysis of (neuro)physiologic indices. Behav. Res. Methods 2025, 57, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.J.; Anijärv, T.E.; Pace, T.; Treacy, C.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hermens, D.F.; Levenstein, J.M.; Andrews, S.C. Resting-state EEG correlates of sustained attention in healthy ageing: Cross-sectional findings from the LEISURE study. Neurobiol. Aging 2024, 144, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Holliday, E.; Okhio, C.; Newman, A.; LaTella, L.; Mcginnis, M.; Požar, R.; Giordani, B.; Kavcic, V. States, traits, and the resting state EEG task aftereffect. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2025, 210, 112523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getzmann, S.; Gajewski, P.D.; Schneider, D.; Wascher, E. Resting-state EEG data before and after cognitive activity across the adult lifespan and a 5-year follow-up. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzen, D.; Genç, E.; Getzmann, S.; Larra, M.F.; Wascher, E.; Ocklenburg, S. Frontal and parietal EEG alpha asymmetry: A large-scale investigation of short-term reliability on distinct EEG systems. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinert, T.; Koenig, T.; Nash, K.; Wascher, E. On the Reliability of the EEG Microstate Approach. Brain Topogr. 2024, 37, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open-source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.P.; Makeig, S.; Westerfield, M.; Townsend, J.; Courchesne, E.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, T.; Haller, M.; Peterson, E.J.; Varma, P.; Sebastian, P.; Gao, R.; Noto, T.; Lara, A.H.; Wallis, J.D.; Knight, R.T.; et al. Parameterizing neural power spectra into periodic and aperiodic components. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinck, M.; Oostenveld, R.; van Wingerden, M.; Battaglia, F.; Pennartz, C.M.A. An improved index of phase-synchronization for electrophysiological data in the presence of volume-conduction, noise and sample-size bias. NeuroImage 2011, 55, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel, M.P.; de Lange, S.C.; Zalesky, A.; Seguin, C.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Schmidt, R. Proportional thresholding in resting-state fMRI functional connectivity networks and consequences for patient-control connectome studies: Issues and recommendations. NeuroImage 2017, 152, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, L.E.; Karwowski, W. A Graph Theory-Based Modeling of Functional Brain Connectivity Based on EEG: A Systematic Review in the Context of Neuroergonomics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155103–155135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C.E.; Nichols, T.E.; Bullmore, E.T.; Simmons, A. Brain network analysis: Separating cost from topology using cost-integration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palva, S.; Palva, J.M. Functional roles of alpha-band phase synchronization in local and large-scale cortical networks. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knyazeva, M.G.; Barzegaran, E.; Vildavski, V.Y.; Demonet, J.-F. Aging of human alpha rhythm. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 69, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Bramanti, P.; Rossini, P.M. Human brain networks in physiological aging: A graph theoretical analysis of cortical connectivity from EEG data. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 41, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artola, G.; Isusquiza, E.; Errarte, A.; Barrenechea, M.; Alberdi, A.; Hernández-Lorca, M.; Solesio-Jofre, E. Aging Modulates the Resting Brain after a Memory Task: A Validation Study from Multivariate Models. Entropy 2019, 21, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Mazaheri, A. Shaping Functional Architecture by Oscillatory Alpha Activity: Gating by Inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, A.; Gross, J. Normal and pathological oscillatory communication in the brain. Nat. Reviews. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesnaite, E.; Steinfath, P.; Jamshidi Idaji, M.; Stephani, T.; Kumral, D.; Haufe, S.; Sander, C.; Hensch, T.; Hegerl, U.; Riedel-Heller, S.; et al. Alterations in rhythmic and non-rhythmic resting-state EEG activity and their link to cognition in older age. NeuroImage 2023, 268, 119810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Lizio, R.; Marzano, N.; Capotosto, P.; Soricelli, A.; Triggiani, A.I.; Cordone, S.; Gesualdo, L.; Del Percio, C. Brain neural synchronization and functional coupling in Alzheimer’s disease as revealed by resting state EEG rhythms. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 103, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, S.; Brothers, T.A.; Swaab, T.Y. 1/f neural noise and electrophysiological indices of contextual prediction in aging. Brain Res. 2018, 1691, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuwal, K.; Banerjee, A.; Roy, D. Aperiodic and Periodic Components of Ongoing Oscillatory Brain Dynamics Link Distinct Functional Aspects of Cognition across Adult Lifespan. eNeuro 2021, 8, ENEURO.0224-21.2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendner, J.D.; Helfrich, R.F.; Mander, B.A.; Romundstad, L.; Lin, J.J.; Walker, M.P.; Larsson, P.G.; Knight, R.T. An electrophysiological marker of arousal level in humans. eLife 2020, 9, e55092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnau, S.; Möckel, T.; Rinkenauer, G.; Wascher, E. The interconnection of mental fatigue and aging: An EEG study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 117, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barulli, D.; Stern, Y. Efficiency, capacity, compensation, maintenance, plasticity: Emerging concepts in cognitive reserve. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu Henry Samuel, I.; Wang, C.; Burke, S.E.; Kluger, B.; Ding, M. Compensatory Neural Responses to Cognitive Fatigue in Young and Older Adults. Front. Neural Circuits 2019, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffener, J.; Brickman, A.M.; Rakitin, B.C.; Gazes, Y.; Stern, Y. The impact of age-related changes on working memory functional activity. Brain Imaging Behav. 2009, 3, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeza, R.; Anderson, N.D.; Locantore, J.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Aging gracefully: Compensatory brain activity in high-performing older adults. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter-Lorenz, P.A.; Cappell, K.A. Neurocognitive Aging and the Compensation Hypothesis. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 17, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, L.; Zullo, J.; Yankner, B.A. The adaptive aging brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 72, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, S.; Bullmore, E. Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Task | Age | Interaction | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z Value | Pr (>|z|) | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | |||||
| Low-alpha power | F | −7.685 | <0.001 | *** | −2.570 | 0.010 | * | 3.513 | <0.001 | *** |
| M | −8.555 | <0.001 | *** | −3.112 | 0.002 | ** | 4.425 | <0.001 | *** | |
| O | −8.551 | <0.001 | *** | −2.170 | 0.030 | * | 3.662 | <0.001 | *** | |
| High-alpha power | F | −0.089 | 0.929 | −6.141 | <0.001 | *** | 1.367 | 0.172 | ||
| M | −0.343 | 0.732 | −6.434 | <0.001 | *** | 1.894 | 0.058 | # | ||
| O | −1.203 | 0.229 | −6.172 | <0.001 | *** | 2.344 | 0.019 | * | ||
| Aperiodic offset | F | 2.303 | 0.021 | * | −7.123 | <0.001 | *** | 1.089 | 0.276 | |
| M | 1.877 | 0.061 | # | −8.448 | <0.001 | *** | 1.575 | 0.115 | ||
| O | 1.083 | 0.279 | −8.895 | <0.001 | *** | 1.264 | 0.206 | |||
| Aperiodic exponent | F | 4.378 | <0.001 | *** | −7.123 | <0.001 | *** | 2.310 | 0.021 | * |
| M | 4.886 | <0.001 | *** | −8.448 | <0.001 | *** | 3.876 | <0.001 | *** | |
| O | 4.028 | <0.001 | *** | −8.895 | <0.001 | *** | 2.270 | 0.023 | * | |
| Task | Age | Interaction | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z Value | Pr (>|z|) | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | |||||
| Low-alpha | Eglob | −4.739 | <0.001 | *** | −2.165 | 0.030 | * | 2.784 | 0.005 | ** |
| Eloc | −4.587 | <0.001 | *** | −2.216 | 0.027 | * | 2.845 | 0.004 | ** | |
| High-alpha | Eglob | −6.912 | <0.001 | *** | −6.049 | <0.001 | *** | 3.158 | 0.002 | ** |
| Eloc | −6.432 | <0.001 | *** | −5.786 | <0.001 | *** | 2.893 | 0.004 | ** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Du, Y.; Yu, H.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, C. The Differential and Interactive Effects of Aging and Mental Fatigue on Alpha Oscillations: A Resting-State Electroencephalography Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060546
Yang X, Liu K, Liu L, Du Y, Yu H, Yao Y, Sun Y, Li C. The Differential and Interactive Effects of Aging and Mental Fatigue on Alpha Oscillations: A Resting-State Electroencephalography Study. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(6):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060546
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaodong, Kaixin Liu, Lei Liu, Yanan Du, Hao Yu, Yongjie Yao, Yu Sun, and Chuantao Li. 2025. "The Differential and Interactive Effects of Aging and Mental Fatigue on Alpha Oscillations: A Resting-State Electroencephalography Study" Brain Sciences 15, no. 6: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060546
APA StyleYang, X., Liu, K., Liu, L., Du, Y., Yu, H., Yao, Y., Sun, Y., & Li, C. (2025). The Differential and Interactive Effects of Aging and Mental Fatigue on Alpha Oscillations: A Resting-State Electroencephalography Study. Brain Sciences, 15(6), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15060546






